- Academic Editor
-
-
-
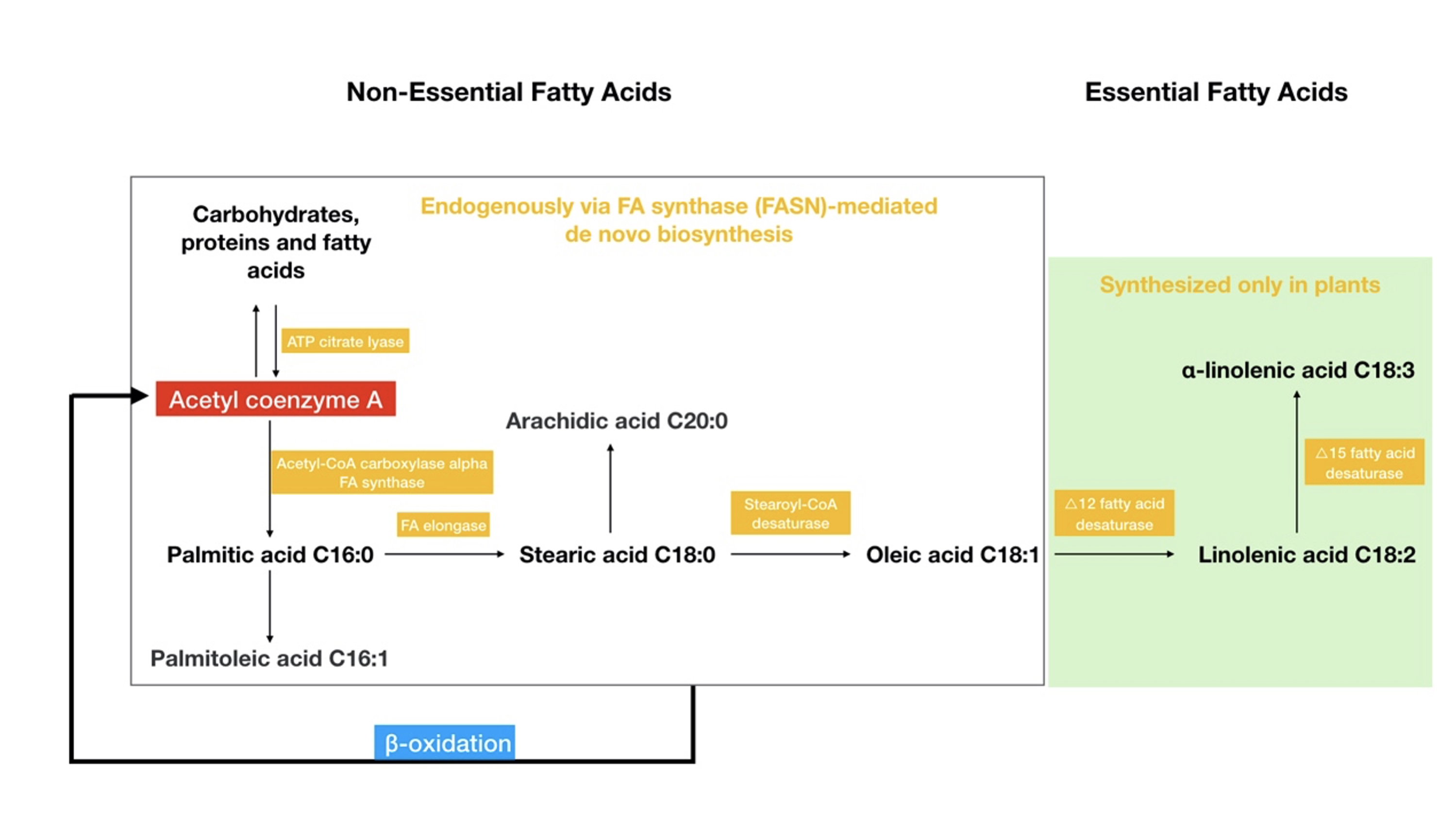
Breast cancer has a special tumor microenvironment compared to other solid tumors, which is usually surrounded by a large number of adipocytes that can produce and secrete fatty acids and adipokines. Adipocytes have a remodeling effect on breast cancer lipid metabolism, while fatty acids and lipid droplets can make breast cancer cells more aggressive. Lipid metabolism, especially the synthesis of fatty acids, is an important cellular process for membrane biosynthesis, energy storage, and signal molecule production. Therefore, blocking the lipid supply to cancer cells or changing the lipid composition has an important impact on the signal transmission and cell proliferation of cancer cells. Alterations in lipid availability can also affect cancer cell migration, induction of angiogenesis, metabolic symbiosis, evasion of immune surveillance, and cancer drug resistance. Fatty acid synthesis and metabolism have received extensive attention as potential targets for cancer therapy, and studies on modulating the tumor lipid microenvironment to improve the sensitivity of antitumor drugs have also been discussed; however, strategies to target these processes have not been translated into clinical practice.