-
- Academic Editor
-
-
-
†These authors contributed equally.
Background: Osteogenesis imperfecta (OI) is a rare genetic disorder
characterized by recurring bone fractures. Some OI patients have other clinical
manifestations such as growth retardation, dental abnormalities, blue sclera, and
hearing loss. The relationship between the phenotype and genotype of OI is
indistinct, and there is no cure for OI. Therefore, an appropriate disease model
is urgently needed to understand the pathophysiology of OI. Induced pluripotent
stem cells (iPSCs) are capable of developing into three germ layers and have the
same genetic background as the donor cells they were derived from; thus, they are
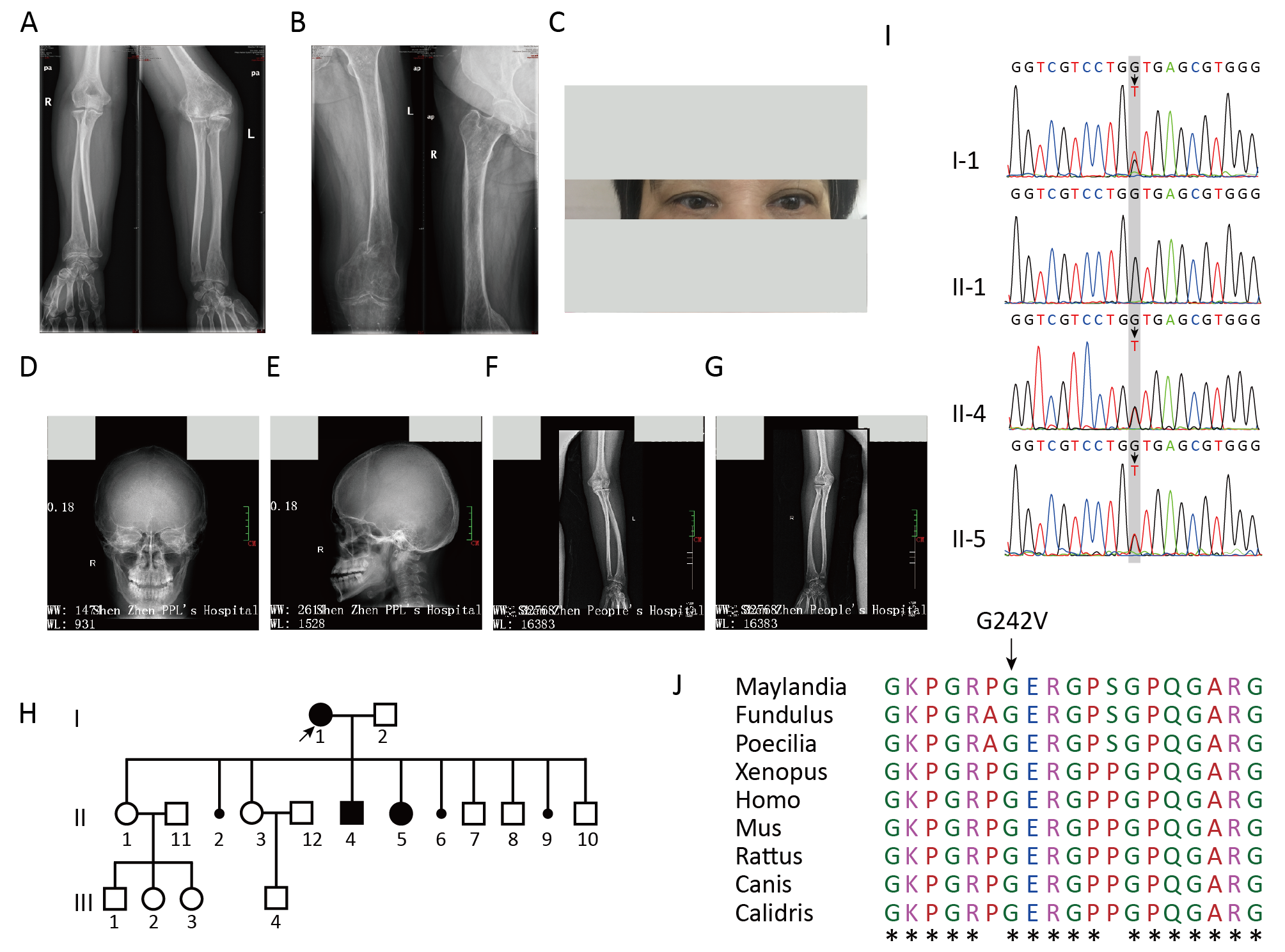
an appropriate disease model. Methods: Blood
samples collected from the proband and her affected children and one unaffected
child were used forgenotyping by whole genome
sequencing. A patient-specific iPSC line and a healthy donor iPSC line were
generated by reprogramming peripheral blood mononuclear
cells with episomal plasmids containing seven
transcription factors, namely, OCT4, SOX2, NANOG,
LIN28, cMYC, KLF4, and SV40LT.
Results: The proband and her two affected children were homozygous for
a mutation in collagen type I alpha 1 exon 10,
c.725G