1. Introduction
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory disease
with a high rate of disability and is accompanied by a variety of complications
[1, 2]. The pathogenesis of RA is complex, with multiple targets and links, and
has not been fully elucidated [3, 4]. The main pathological feature of RA is
synovial pannus formation caused by angiogenesis associated with inflammation,
leading to cartilage and bone destruction [5]. The inflammatory state in RA is
maintained by enhanced angiogenesis that delivers inflammatory cells and oxygen
to the synovium [6]. Therefore, inhibition of angiogenesis and inflammation may
be important targets for RA therapy [7].
The nuclear factor kappa B (NF-B) is an important transcription factor
in the inflammatory response, immune regulation, and cell apoptosis. It has been
found that the NF-B pathway is associated with the occurrence and
progression of RA [8]. NF-B p65 gene silencing can inhibit the
proliferation of synovial cells in RA [9]. In addition, blocking the
NF-B pathway is an effective strategy to control the inflammatory
response of RA [10]. For example, a serine/threonine kinase inhibitor (fasudil)
inhibited interleukin-1beta (IL-1)-induced NF-B activation,
which mitigated RA to some extent [11].
NF-B-inducing kinase (NIK), as an important factor in the
NF-B pathway, is highly expressed in synovial endothelial cells of RA
patients. It also promotes the generation of pathogenic blood vessels and
synovial inflammation by inducing C-X-C motif chemokine ligand
12 (CXCL12) [12, 13]. Studies have reported
that NIK mice are resistant to antigen-induced arthritis caused by T-cell
responses [14, 15]. NIK knockdown has significantly reduced the activation of
synovia-induced endothelial inflammation in RA patients [16]. In RA patients, the
IB kinase (IKK) is highly expressed in fibroblast-like synovial cells
(FLSs) [17]. It has been found that the CXCL12/C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 4
(CXCR4) axis participates in vascular remodeling and formation in the joints of
RA patients [18]. After the use of the CXCL12 blocker (AMD3100), vascular
remodeling was impaired, the morphology of new endothelial cells was abnormal,
and the growth of capillaries was inhibited [19]. However, the role of the
NIK/IKK/CXCL12 pathway in the treatment of RA has not been reported.
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has many advantages, such as being
multi-component, multi-target, multi-pathway, and having less toxic side effects,
so it has become one of the hotspots in the development of new RA drugs [20, 21].
Several plants from the Cleome genus have been found to have strong
anti-arthritis activity. The presence of secondary bioactive metabolites such as
flavonoids, glycoside triterpenes and tannins may be responsible for the
antiarthritic activity. The antiarthritic mechanism of action of these active
ingredients mainly involves preventing the release and destruction of lysosomes
to inhibit the spread of inflammatory responses [22]. Studies have shown that
diterpenoids extracted from the fruits of Rhododendron molle G. Don can
inhibit the abnormal proliferation of T lymphocytes and B lymphocytes, and reduce
the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6, IL-1, and tumor
necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-), which has the potential to be used in RA
therapy [23]. In addition, Rhodojaponin II has been found to inhibit
TNF--induced inflammatory responses in FLSs by blocking the protein
kinase B (Akt), NF-B, and toll-like receptor 4/myeloid differentiation
factor 88 (TLR4/MyD88) pathways [24]. Rhodojaponin III, as one of
the diterpenoids, has many pharmacological activities, such as anti-inflammatory
[25] and analgesic [26], and has been widely studied. However, the specific
mechanism of Rhodojaponin III on RA remains unclear.
Therefore, the aim of this study was to
investigate the therapeutic effect and mechanism of Rhodojaponin III on RA. To
achieve this, a bovine type II collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) rat model and a
TNF--induced human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) model were
constructed. The NIK/IKK/CXCL12 pathway was selected as the focus of
investigation. This study will provide a theoretical basis for the prevention and
treatment of RA by analyzing the effects of Rhodojaponin III on this pathway.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1 Construction of CIA Rat Model and
Intervention
A total of 48 male Wistar rats (6 weeks, 170–200 g) were bought from Changsha
Tianqin Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Changsha, China). Rats were housed under standard
laboratory conditions, with a temperature of 25 2 °C, humidity
of 50 5%, and a 12-hour light/dark cycle. They were raised in separate
cages with 4 in each one, and had free access to food and water for one week of
adaptive feeding before experiments. 2.0 mg/mL bovine type II collagen (20022,
Chondrex, Woodinville, WA, USA) that dissolved in acetic acid solution was mixed
with complete Freund’s adjuvant (7001, Chondrex, Woodinville,
WA, USA) in the ice bath at the volume of 1:1, repeated suction by syringe, fully
emulsified, to make bovine type II collagen emulsion. The emulsion was injected
subcutaneously into the tail (300 µL) of rats. 7 days later, the rats were
inoculated with bovine type II collagen emulsion (300 µL) for a second time
[27]. Normal rats were injected with normal saline. Groups
included Sham, CIA, TWG, Rhodojaponin III Lo, Rhodojaponin III Mi, and Rhodojaponin III
Hi, with 8 rats in each group. Rats in the TWG group were given intragastric
administration with Tripterygium wilfordii
Glycosides (TWG, 50 mg/kg) (Z33020422, Dnd Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Shaoxing,
China) once a day. Rats in the Rhodojaponin III Lo, Rhodojaponin III Mi, and
Rhodojaponin III Hi groups were separately given intragastric administration with
Rhodojaponin III (0.06 mg/kg, 0.12 mg/kg, 0.24 mg/kg) (26342-66-5, yuanye
Bio-Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) once a day [23]. Rats in Sham and CIA
groups were intragastrically given normal saline. After 4 weeks, all rats were
anesthetized to obtain the whole blood by abdominal aorta puncture. The rats were
sacrificed by the cervical dislocation method to obtain knee joints and synovium
for subsequent experiments. All animal experiments followed the ARRIVE
guidelines. This study has been approved by the Experimental Animal Ethics
Committee of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine (No. LL2022061401).
2.2 Arthritis Index (AI) Score
The arthritis index (AI) was evaluated according to the swelling degree of
joints every 4 days during the experiment [28]. AI was utilized as the criterion
to judge the successful construction of the CIA rat model. When AI 4, the
CIA rat model was successfully constructed. AI scoring rule: 0, no swelling; 1,
slight swelling of toe joints; 2, swelling of
phalangeal joints and toe joints; 3, Paw swelling below the ankle joint; 4,
Swelling of all feet, including the ankle joints. Since the incidence of forepaw
inflammation was very low, and the joints of the hind feet were more prone to
severe swelling, we calculated the AI score of the two hind feet of rats (total
scores: 8).
2.3 Cell Culture
HUVECs (AW-CNH488, Abiowell, Changsha, China) were cultured in
Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS)
(10099141, Gibco, Carlsbad, CA, USA) and 1% Penicillin/Streptomycin (SV30010,
Beyotime, Shanghai, China) with 5% CO at 37 °C. HUVECs can be used in
experiments when the confluence reached 70–80%. The oe-NC plasmids or oe-NIK
plasmids (HonorGene, Changsha, China) were transfected separately into HUVECs
with Lipofectamine 2000 (11668019, Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA). The cells used
in the experiment were validated and were free from bacteria, fungi, and
mycoplasma infections. In addition, the expression of von Willebrand factor (VWF)
in HUVECs was evaluated using immunofluorescence (IF) staining, as shown in the
Supplementary Figure.
2.4 Cell Grouping and Treatment
Experiment 1 was divided into the following groups: Control, TNF-,
Rhodojaponin III Lo, Rhodojaponin III Mi, and Rhodojaponin III Hi. The cells in the
Control group were not treated. Cells in the TNF- group were induced
with 10 ng/mL TNF- (ab259410, Abcam, Cambridge, UK) for 24 h [24, 29, 30, 31]. Cells in Rhodojaponin III Lo, Rhodojaponin III Mi, and Rhodojaponin III Hi
groups were induced with 10 ng/mL TNF- for 24 h and treated with 9
µg/mL, 18 µg/mL, and 36 µg/mL Rhodojaponin III for 24 h [32].
Experiment 2 was divided into the following groups: TNF-, Rhodojaponin
III, Rhodojaponin III+oe-NC, and Rhodojaponin III+oe-NIK. Cells in the
TNF- group were treated as above. Cells in the Rhodojaponin III group
were induced with 10 ng/mL TNF- for 24 h and then treated with 36
µg/mL Rhodojaponin III for 24 h. Cells in the Rhodojaponin III+oe-NC group
were treated with oe-NC plasmids, induced with 10 ng/mL TNF- for 24 h,
and then treated with 36 µg/mL Rhodojaponin III for 24 h. Cells in the
Rhodojaponin III+oe-NIK group were transfected with oe-NIK plasmids, induced with
10 ng/mL TNF- for 24 h, and then treated with 36 µg/mL
Rhodojaponin III for 24 h.
2.5 Hematoxylin-Eosin (HE) Staining
The knee joint and synovium were firstly fixed with 4%
paraformaldehyde (N1012, NCM Biotech, Suzhou, China), then sliced after paraffin
embedding. They were dewaxed in xylene followed by dehydration with gradient
ethanol (75–100%). Slices were stained with hematoxylin (AWI0001a, Abiowell,
Changsha, China) and returned to blue with
phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). After being
stained with eosin (AWI0029a, Abiowell, Changsha, China), the slices were rinsed
with distilled water, followed by dehydration with gradient ethanol (95–100%).
The slices were placed in xylene for 10 min for transparency and observed by a
microscope after being sealed with neutral gum (AWI0238a, Abiowell, Changsha,
China).
2.6 Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Staining
Platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 (CD31) and vascular endothelial
cell growth factor (VEGF) expressions in the synovium were detected by IHC
staining. The slices were dewaxed in xylene followed by dehydration with gradient
ethanol (75–100%). Subsequently, antigen retrieval and inactivation of
endogenous enzymes were performed. Slices were incubated with primary antibodies
of CD31 (1:300, ab182981, Abcam, Cambridge, UK) and VEGF (1:200, 19003-1-AP,
Proteintech, Chicago, IL, USA) at 4 °C overnight followed by 100 µL of
horseradish peroxidase (HRP) goat anti-rabbit
IgG (1:100, AWS0005, Abiowell, China) at 37 °C for 30 min. Then 100 µL of
DAB (ZLI-9017, ZSBG-Bio, Beijing, China) was added for color
development. Slices were re-stained with hematoxylin and returned to blue with
PBS. The slices were placed in xylene for 10 min for transparency and observed by
a microscope after being sealed with neutral gum.
2.7 Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
The whole blood, the synovial samples, and cell cultures were pretreated to
obtain the supernatant for detection. IL-6 (CSB-E04638h, CUSABIO, Wuhan, China),
IL-1 (CB-E08053h, CUSABIO, Wuhan, China), and TNF-
(CB-E04740h, CUSABIO, Wuhan, China) ELISA kits were utilized to detect the levels
of cytokines (IL-6, IL-1, and TNF-).
2.8 Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) Assay
Logarithmic growth of HUVECs was digested by trypsin (AWC0232, Abiowell,
Changsha, China). 1 10 cells were inoculated in 96-well plates,
100 µL per well. After cell adhesion, each group was treated with the
corresponding drug for 24 h and 48 h, respectively. Then, 10 µL of CCK-8
reagent (NU679, Dojindo, Kumamoto, Japan) was added and incubated at 37 °C for 4
h. Optical density (OD) at 450 nm was analyzed with a multifunctional microplate
reader (MB-530, HEALES, Shenzhen, China).
2.9 Scratch Assay
The scratch assay was applied to detect the migration ability of HUVECs. HUVECs
from different treatment groups were digested to make cell suspension. 5
10 cells were uniformly inoculated in 6-well plates. When the
cells had filled the plates, lines were drawn and viewed under a microscope to
measure the initial scratch width. After 24 h and 48 h, the scratch widths were
measured and photographed.
2.10 Transwell Invasion Assay
All reagents and equipment were pre-chilled one day in advance. 100 µL of
Matrigel (354262, Corning Inc. Corning, NY, USA) was added to
the upper transwell chamber (3428, Corning Inc. Corning, NY,
USA) and incubated at 37 °C for 30 min for solidification. HUVECs from different
treatment groups were digested to make cell suspension. DMEM without FBS was used
to suspend the cells to 2 10 cells/mL. 100 µL of cell
suspension was added to the upper chamber, and 500 µL of DMEM with 10% FBS
was added to the lower chamber followed by incubation at 37 °C for 48 h. The upper
chamber was washed with PBS, and the cells not penetrating the membrane were
gently wiped off with sterile cotton balls. After fixation with 4%
paraformaldehyde and staining with 0.1% crystal violet (G1062, Solarbio,
Beijing, China), cells on the outer surface of the upper chamber were observed
and counted.
2.11 Tube Formation Assay
All reagents and equipment were pre-chilled one day in advance. 70 µL of
Matrigel was evenly spread in the 96-well plates at 37 °C for 30 min for
solidification. HUVECs from different treatment groups were digested to make cell
suspension. 1 10 cells were inoculated in 96-well plates for 24
h. The formation of blood vessels was evaluated by observing and counting
closed-loop or pro-angiogenic structures with an inverted microscope.
2.12 Molecular Docking Verification of Rhodojaponin III and NIK
The three-dimensional structure diagram of NIK was searched from the PDB
database (https://www.rcsb.org/), and imported into PyMOL (ver.2.3.1, Schrödinger, LLC., New York, NY, USA) to remove
water molecules. Then, it was imported into Autodock tools (ver.1.5.6, The Scripps Research Institute, La Jolla,CA, USA) to add
hydrogen atoms and then saved in PDBQT format after calculation of the total
charge and set of the atomic type. The Chemical Abstracts Service (CAS) number
was searched from the PubChem database (https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/), and
the 3D structure diagram of Rhodojaponin III was downloaded. Its energy was
minimized with Chem3D pro and was saved in mol2 format. VINA software
(Ver. 1.1.2, The Scripps Research Institute, La Jolla, CA, USA) was used for docking, and the
results were visualized with Discovery Studio software (ver. 18.0, BIOVIA, San Diego, CA, USA). Finally, the 3D molecular
docking model was output.
2.13 Western Blot
Different samples were treated with RIPA lysate (AWB0136, Abiowell, Changsha,
China) to extract total proteins. The proteins were transferred to nitrocellulose
(NC) membranes after sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
(SDS-PAGE). After blocking in 5% bovine serum albumin (BSA) or 5% skimmed milk
(AWB0004, Abiowell, Changsha, China), the membranes were incubated with the
primary antibodies at 4 °C overnight, including NIK (15 µg/mL, ab203568,
Abcam, Cambridge, UK), IKK (1:1000, ab32041, Abcam, Cambridge, UK),
p-IKK (1:1000, ab38515, Abcam, Cambridge, UK), p52 (1:5000,
10655-1-AP, Proteintech, Chicago, IL, USA), CXCL12 (1:20,000, ab155090, Abcam,
Cambridge, UK), and -actin (1:5000, 66009-1-Ig,
Proteintech, Chicago, IL, USA). The membranes were incubated with HRP-labled
secondary antibodies for 1.5 h. Finally, the membranes were incubated with ECL
reagent (AWB0005, Abiowell, Changsha, China) and followed by imaging. The protein
expressions were analyzed by Quantity One 4.6.6 (Bio-Rad Inc., Hercules, CA, USA)
with -actin as the reference protein.
2.14 Data Analysis
All data were analyzed by GraphPad Prism 8.0 (GraphPad Software Inc., San Diego,
CA, USA) and presented as mean standard deviation (SD). One-way analysis
of variance (ANOVA) and Tukey’s post-hoc test were conducted in comparison
between groups. Two-way ANOVA was performed in groups at different time points.
The difference was significant as p 0.05. All the experiments
followed randomization and blind analysis to avoid experimental bias.
3. Results
3.1 Rhodojaponin III Alleviated Arthritis Progression and Disease
Severity in CIA Rats
To explore the effect of Rhodojaponin III on RA, rats were induced by bovine type
II collagen and then given intragastric administration with different
concentrations of Rhodojaponin III with TWG as a positive control drug. High AI
score in the CIA group indicated that the CIA rat model was successfully
constructed. The AI scores in the TWG group and different concentrations of
Rhodojaponin III groups were decreased compared with the CIA group (Fig. 1A). HE
staining in knee joints showed that inflammatory infiltration and cartilage
damage were significant in the CIA group. However, these lesions were
significantly alleviated in the TWG group or different concentrations of
Rhodojaponin III groups (Fig. 1B). It was further found by ELISA that IL-6,
IL-1, and TNF- levels in serum and synovium of rats in the TWG
group or different concentrations of Rhodojaponin III groups were decreased
compared with the CIA group (Fig. 1C). Together, the above results proved that
Rhodojaponin III alleviated arthritis progression and disease severity in CIA rats.
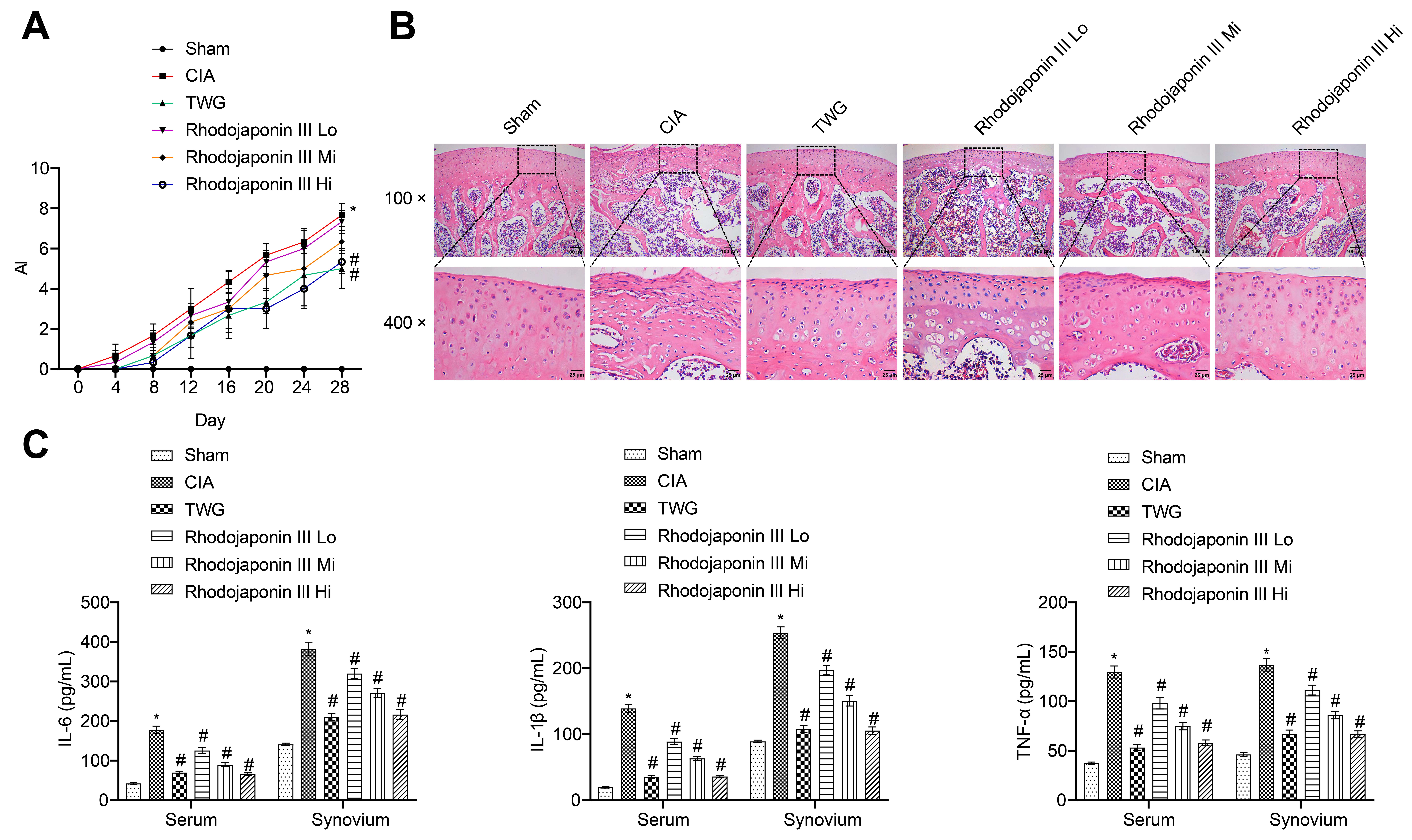 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.
Rhodojaponin III alleviated rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) rats. (A) Arthritis index (AI) score. (B) Hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining analyzed the pathological changes in the knee joints (n = 8). (C) Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) detected cytokine levels in serum and synovium (n = 8). * p 0.05 vs.
Sham, # p 0.05 vs. CIA. TWG, Tripterygium
wilfordii Glycosides.
3.2 Rhodojaponin III Decreased Vascular Density in the Synovium of
Inflammatory Joints of CIA Rats
Then, we studied the effect of Rhodojaponin III on the vascular density in the
synovium of inflammatory joints. HE staining showed a large number of synovial
hyperplasia and pannus formation in the synovium. However, these were
significantly reduced after intervention with TWG or different concentrations of
Rhodojaponin III (Fig. 2A). In addition, IHC staining analysis displayed that CD31
and VEGF were highly expressed in the synovium. After intervention with different
concentrations of Rhodojaponin III, CD31 and VEGF expressions in the synovium
significantly decreased, and the expression level in the Rhodojaponin III Hi group
reached in the TWG group (Fig. 2B). These results proved that Rhodojaponin III
decreased vascular density in the synovium of inflammatory joints in CIA rats.
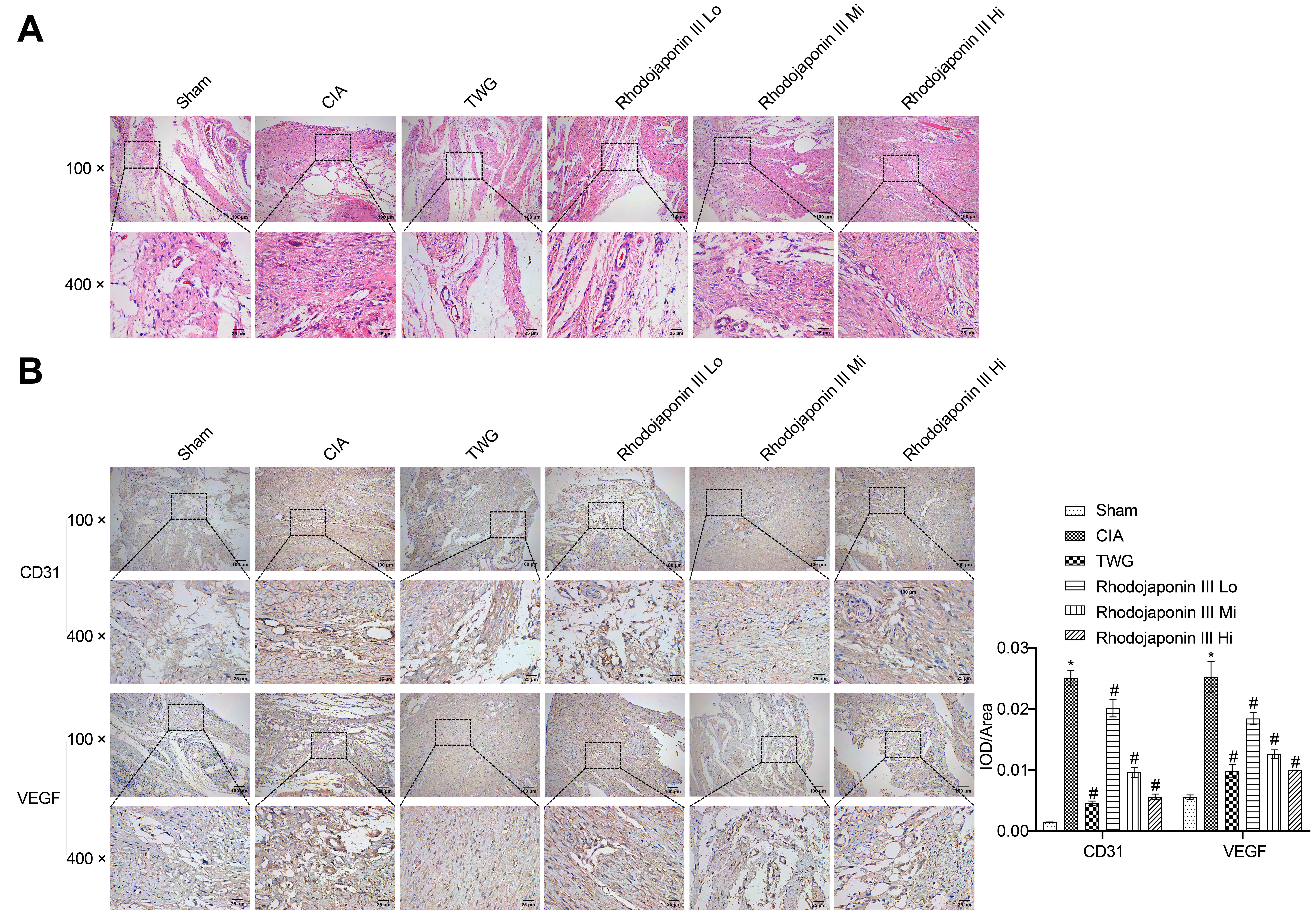 Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.
Rhodojaponin III decreased vascular density in the
synovium of inflammatory joints in CIA rats. (A) HE staining in the synovium (n
= 8). (B) Platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 (CD31) and vascular endothelial cell growth factor (VEGF) expressions in the synovium were assessed by immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining
(n = 8). * p 0.05 vs. Sham, # p 0.05 vs. CIA.
3.3 Rhodojaponin III Inhibited Migration, Invasion, Angiogenesis, and
Inflammation of TNF--Induced HUVECs
To determine the specific therapeutic effect of Rhodojaponin III on RA, a cell
model of HUVECs was constructed by TNF- induction. The proliferation
ability of HUVECs increased after TNF- induction and decreased in a
concentration-dependent manner after intervention with different concentrations
of Rhodojaponin III (Fig. 3A). The migration ability of HUVECs enhanced after
TNF- induction. However, after intervention with different
concentrations of Rhodojaponin III, the migration ability of HUVECs markedly
decreased (Fig. 3B). The number of HUVECs passing through the membrane increased
after TNF- induction. After intervention with different concentrations
of Rhodojaponin III, the number of cells passing through the membrane considerably
decreased (Fig. 3C). In addition, TNF- induced the formation of
numerous tubes from HUVECs. After intervention with different concentrations of
Rhodojaponin III, the number of tubes decreased significantly (Fig. 3D). Next,
ELISA illustrated that IL-6, IL-1, and TNF- levels in the
supernatant of HUVECs increased after TNF- induction, while they were
significantly reduced after intervention with different concentrations of
Rhodojaponin III (Fig. 3E). These results showed that Rhodojaponin III inhibited
migration, invasion, angiogenesis, and inflammation of TNF--induced
HUVECs.
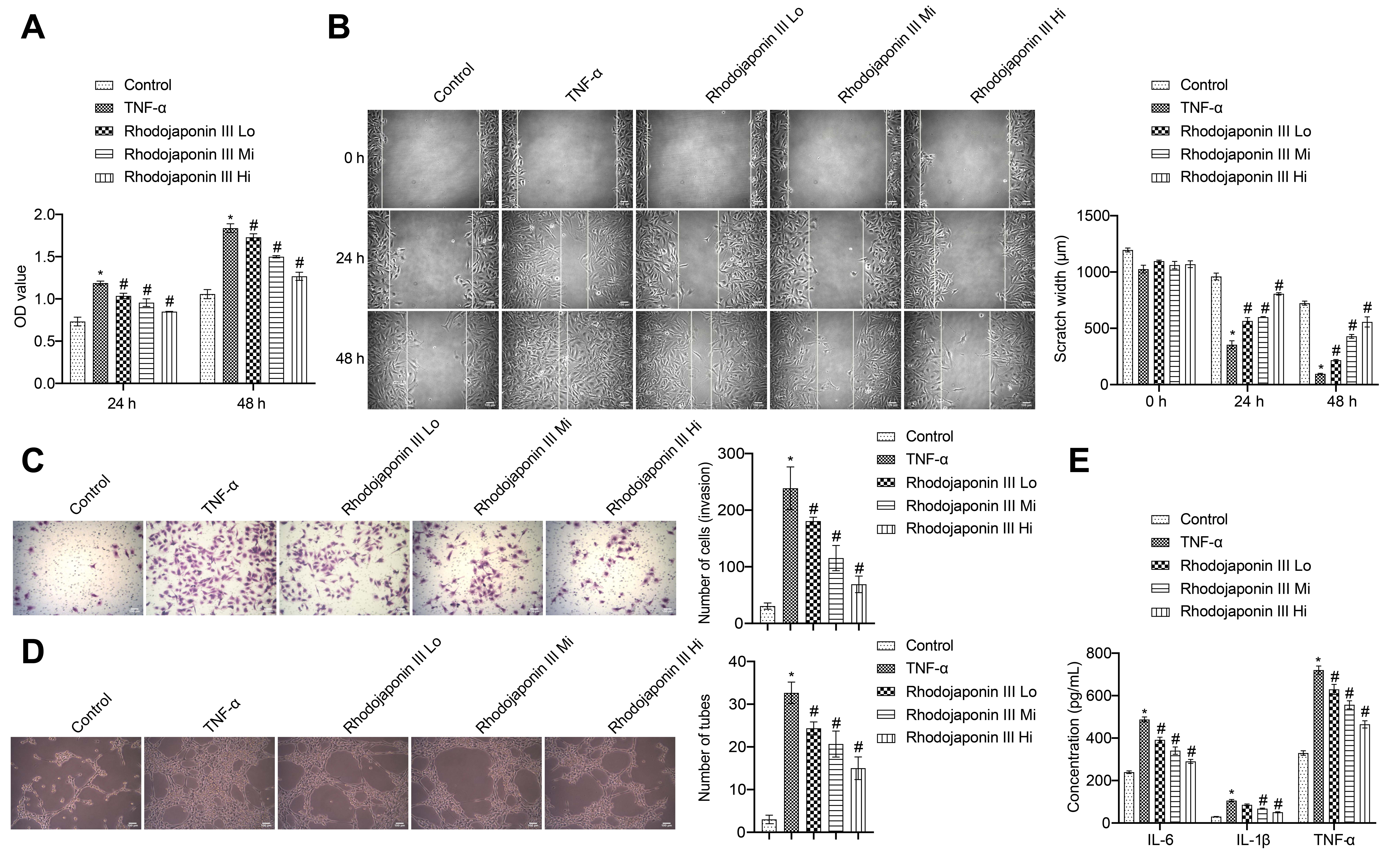 Fig. 3.
Fig. 3.
Rhodojaponin III inhibited migration, invasion, angiogenesis, and
inflammation of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-)-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs).(A) Cell proliferation was assessed by CCK-8
(n = 3). (B) Cell migration was detected by scratch assay (n = 3). (C) Cell
invasion was detected by Transwell invasion assay (n = 3). (D) Tube formation
assay (n = 3). (E) Cytokine levels in the cell supernatant were determined by
ELISA (n = 3). * p 0.05 vs. Control, # p 0.05 vs. TNF-.
3.4 Rhodojaponin III Interacted with NIK
The binding of Rhodojaponin III and NIK was simulated by molecular docking. In
Fig. 4, the binding energy of Rhodojaponin III to NIK was –7.2 kcal/mol,
indicating that Rhodojaponin III could spontaneously bind to NIK. The optimal
docking conformation between Rhodojaponin III and NIK was shown on the left.
Rhodojaponin III bound to the hydrophobic cavity of NIK and interacted with
surrounding amino acid residues. Amino acid residues around Rhodojaponin III were
shown in the truncated part on the right, including 13 amino acid residues: ASP
A:519, SER A410, LYS A:517, ARG A:408, GLY A:409, ARG A:405, GLY A:407, GLU
B:396, GLU B:395, GLU B:461, VAL B:397, ARG B:394, and GLU B:375. Rhodojaponin III
was bound to ASP A:519, ARG A:408, ARG A:405, and GLU B:375 by conventional
hydrogen bonds. Rhodojaponin III was bound to SER A410, LYS A:517, GLY A:409, GLY
A:407, GLU B:396, GLU B:395, GLU B:461, VAL B:397, and ARG B:394 by van der Waals
force. These results proved that Rhodojaponin III interacted with NIK.
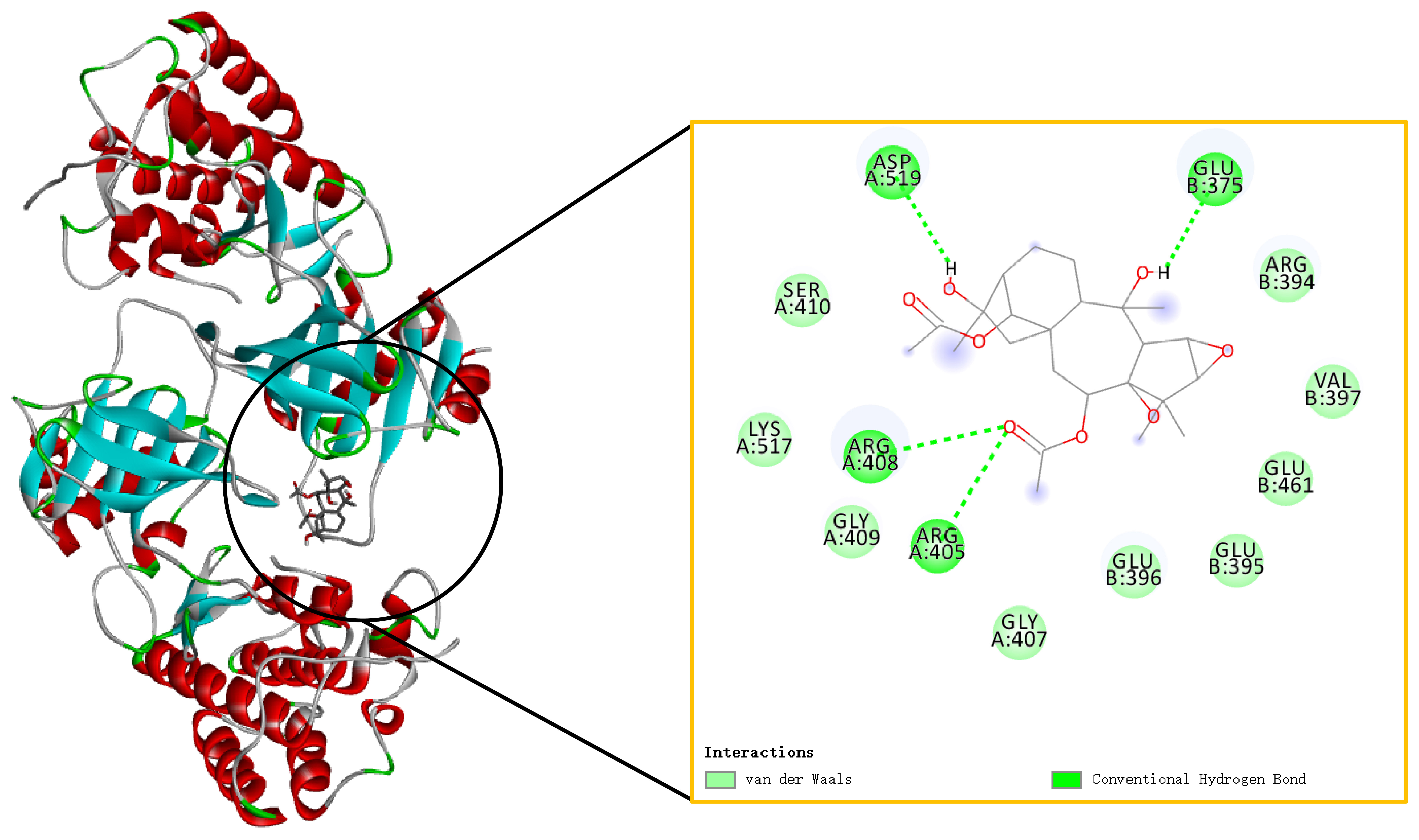 Fig. 4.
Fig. 4.
Rhodojaponin III interacted with NF-κB-inducing kinase (NIK). Molecular docking model of
Rhodojaponin III and NIK (Binding energy: –7.2 kcal/mol).
3.5 Rhodojaponin III Inhibited the Activation of the NIK Pathway in
CIA Rats and TNF--Induced HUVECs
To elucidate the specific molecular mechanism of Rhodojaponin III on RA, Western
blot was applied to detect the expressions of NIK pathway-associated proteins in
CIA rats and TNF--induced HUVECs. Compared with the Sham group, NIK,
p52, and CXCL12 expressions in the synovium of rats in the CIA group were
up-regulated, and the phosphorylation level of IKK was increased.
Compared with the CIA group, NIK, p52, and CXCL12 expressions in the synovium of
rats in the TWG group or different concentrations of Rhodojaponin III groups were
significantly down-regulated, and the phosphorylation level of IKK was
decreased (Fig. 5A). NIK, p52, and CXCL12 expressions were up-regulated, and the
phosphorylation level of IKK was increased in HUVECs after
TNF- induction. Compared with the TNF- group, NIK, p52, and
CXCL12 expressions in HUVECs intervened with different concentrations of
Rhodojaponin III was significantly down-regulated, and IKK
phosphorylation was decreased (Fig. 5B). These results displayed that
Rhodojaponin III inhibited the NIK pathway activation in CIA rats and
TNF--induced HUVECs.
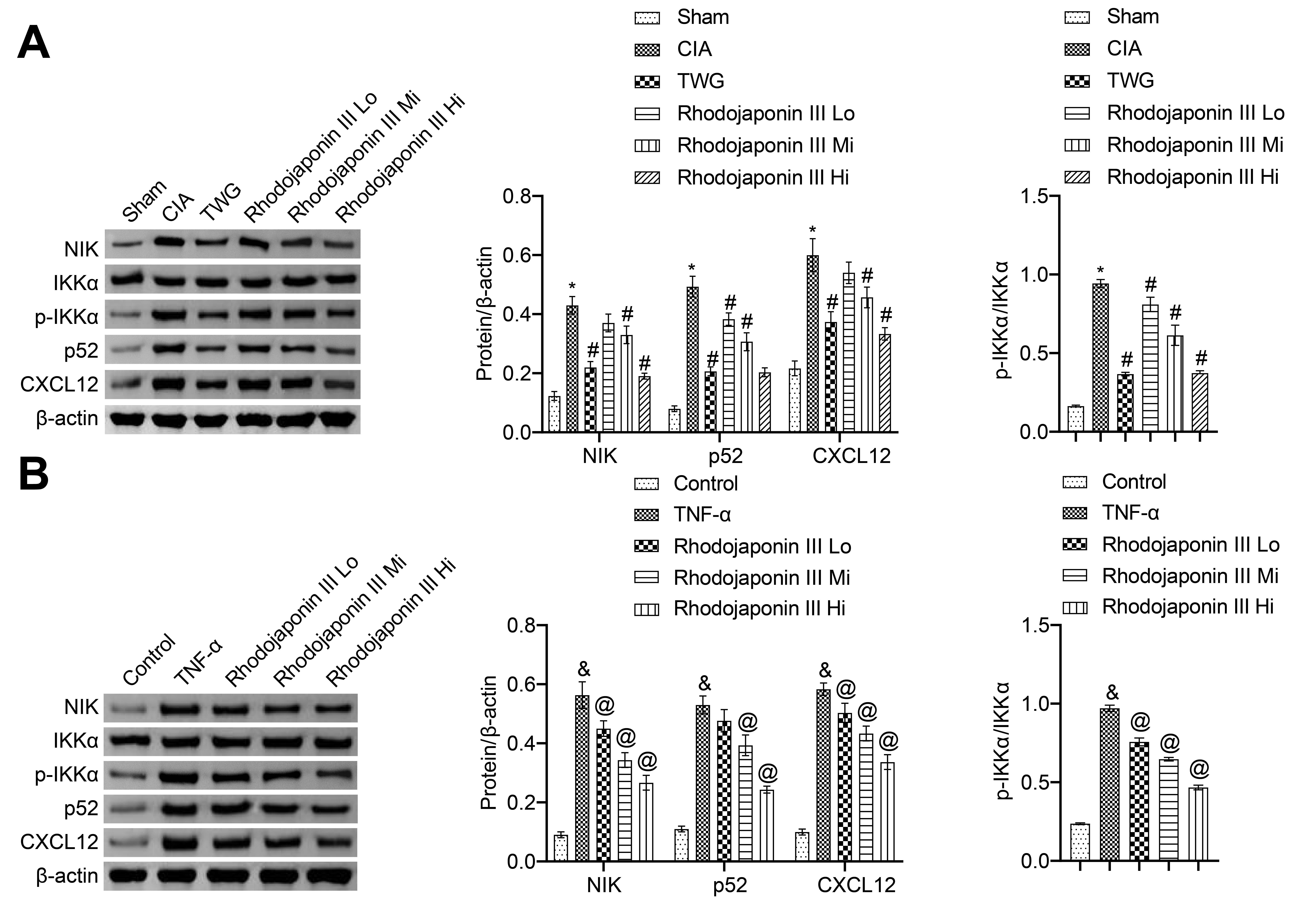 Fig. 5.
Fig. 5.
Rhodojaponin III inhibited the NIK pathway activation in CIA rats
and TNF--induced HUVECs. (A,B) NIK, IκB
kinase-alpha (IKK), p-IKK,
p52, and C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 12 (CXCL12) expressions in the synovium of rats (n = 8) and HUVECs (n = 3)
were detected by Western blot. * p 0.05 vs. Sham, # p
0.05 vs. CIA, & p 0.05 vs. Control, @ p 0.05 vs. TNF-.
3.6 Rhodojaponin III Inhibited the Migration, Invasion, Angiogenesis,
and Inflammation of HUVECs by Inhibiting the NIK/NF-B Pathway
To verify the role of the NIK/NF-B pathway in RA, HUVECs were
transfected with oe-NIK plasmids, induced by TNF-, and then intervened
with Rhodojaponin III. Compared with the TNF- group, NIK, p52, and CXCL12
expressions in HUVECs in the Rhodojaponin III group were down-regulated, and the
phosphorylation level of IKK was decreased. Compared with the
Rhodojaponin III+oe-NC group, NIK, p52, and CXCL12 expressions in HUVECs in the
Rhodojaponin III+oe-NIK group were significantly up-regulated, and the
phosphorylation level of IKK was increased (Fig. 6A). The migration
ability of HUVECs in the Rhodojaponin III group was decreased compared with the
TNF- group. The migration ability of HUVECs in the Rhodojaponin
III+oe-NIK group was increased compared with the Rhodojaponin III+oe-NC group (Fig. 6B). The proliferation ability of HUVECs in the Rhodojaponin III group decreased
compared with the TNF- group. The proliferation ability of HUVECs in
the Rhodojaponin III+oe-NIK group was increased compared with the Rhodojaponin
III+oe-NC group (Fig. 6C). The number of HUVECs passing through the membrane in the
Rhodojaponin III group decreased compared with the TNF- group. The number
of HUVECs passing through the membrane in the Rhodojaponin III+oe-NIK group was
increased compared with the Rhodojaponin III+oe-NC group (Fig. 6D). The number of
tubes in HUVECs in the Rhodojaponin III group decreased compared with the
TNF- group. The number of tubes in HUVECs in the Rhodojaponin III+oe-NIK
group increased compared with the Rhodojaponin III+oe-NC group (Fig. 6E). It was
found by ELISA that compared with the TNF- group, IL-6, IL-1and, TNF- levels in the supernatant of HUVECs in the Rhodojaponin III
group were decreased. Compared with the Rhodojaponin III+oe-NC group, IL-6,
IL-1, and TNF- levels in the supernatant of HUVECs in the
Rhodojaponin III+oe-NIK group were increased (Fig. 6F). These results indicated
that Rhodojaponin III inhibited the migration, invasion, angiogenesis, and
inflammation of HUVECs by inhibiting the NIK/NF-B pathway.
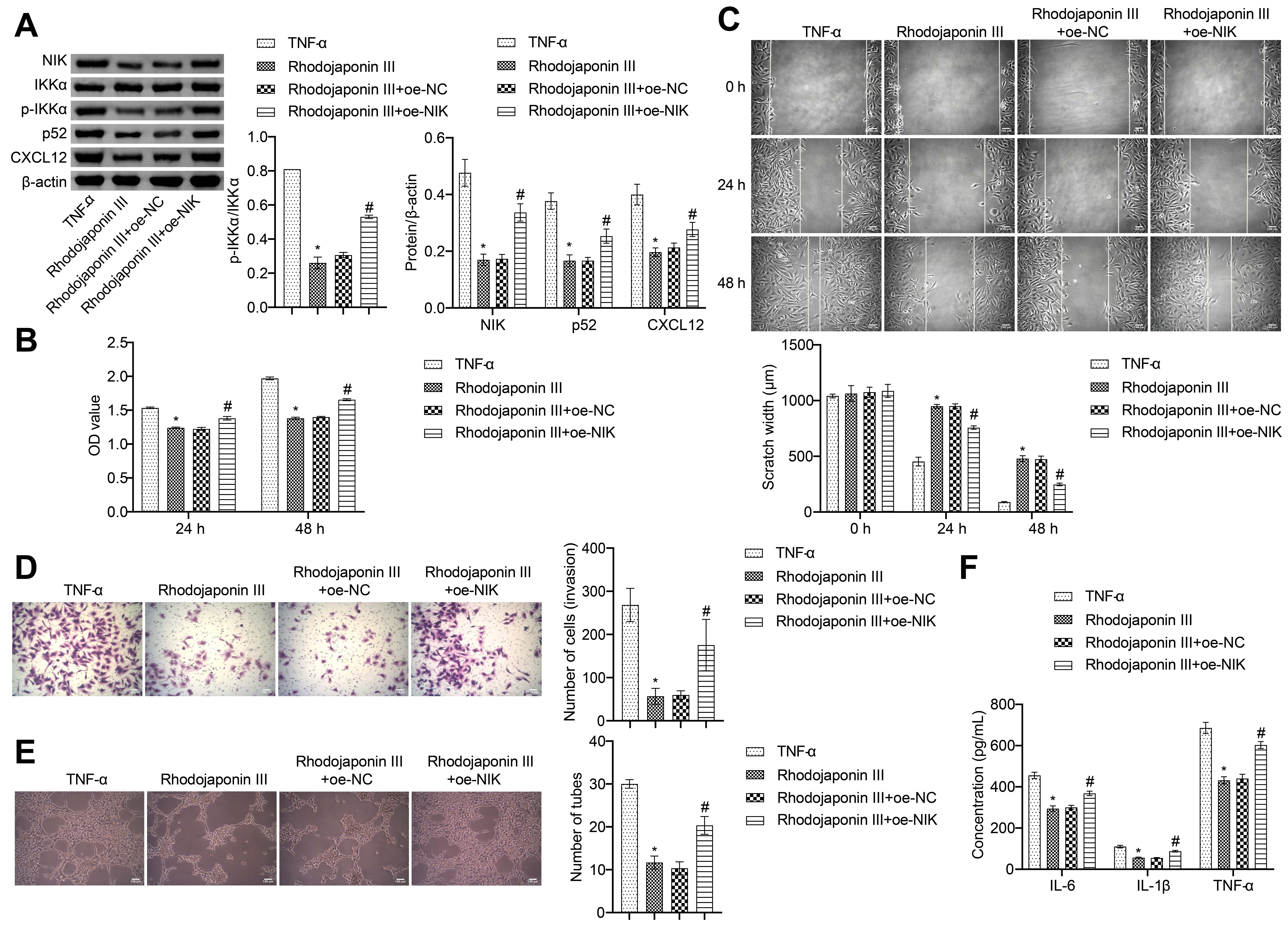 Fig. 6.
Fig. 6.
Rhodojaponin III inhibited the migration, invasion, angiogenesis,
and inflammation of HUVECs by inhibiting the NIK/nuclear factor kappa B (NF-B) pathway. (A)
NIK, IKK, p-IKK, p52, and CXCL12 expressions in HUVECs were
detected by Western blot (n = 3). (B) Cell proliferation was detected by CCK-8.
(C) Cell migration was detected by scratch assay (n = 3). (D) Cell invasion was
detected by Transwell invasion assay (n = 3). (E) Tube formation assay (n = 3).
(F) Cytokine levels in the cell supernatant were determined by ELISA (n = 3). *
p 0.05 vs. TNF-, # p 0.05 vs. Rhodojaponin
III+oe-NC.
4. Discussion
Currently, the therapeutic drugs of RA can be divided into three categories:
chemical drugs, biological products, and TCM [33]. Chemical drugs and biological
products mainly treat RA by inhibiting the activity of target enzymes, the
release of cytokines, and the activation of inflammatory pathways, but these
drugs have certain toxic side effects and limitations [34, 35]. TCM can regulate
the immune system, induce the apoptosis of inflammatory cells and reduce
angiogenesis in the treatment of RA [36, 37, 38]. TCM has many advantages in the
treatment of RA, and many effective ingredients and their mechanisms of action
have been confirmed in clinical and experimental studies. Here, the effect and
mechanism of Rhodojaponin III on CIA rats and TNF- induced HUVECs were
investigated, which provided a theoretical foundation for the further application
of Rhodojaponin III in the clinical treatment of RA (Fig. 7).
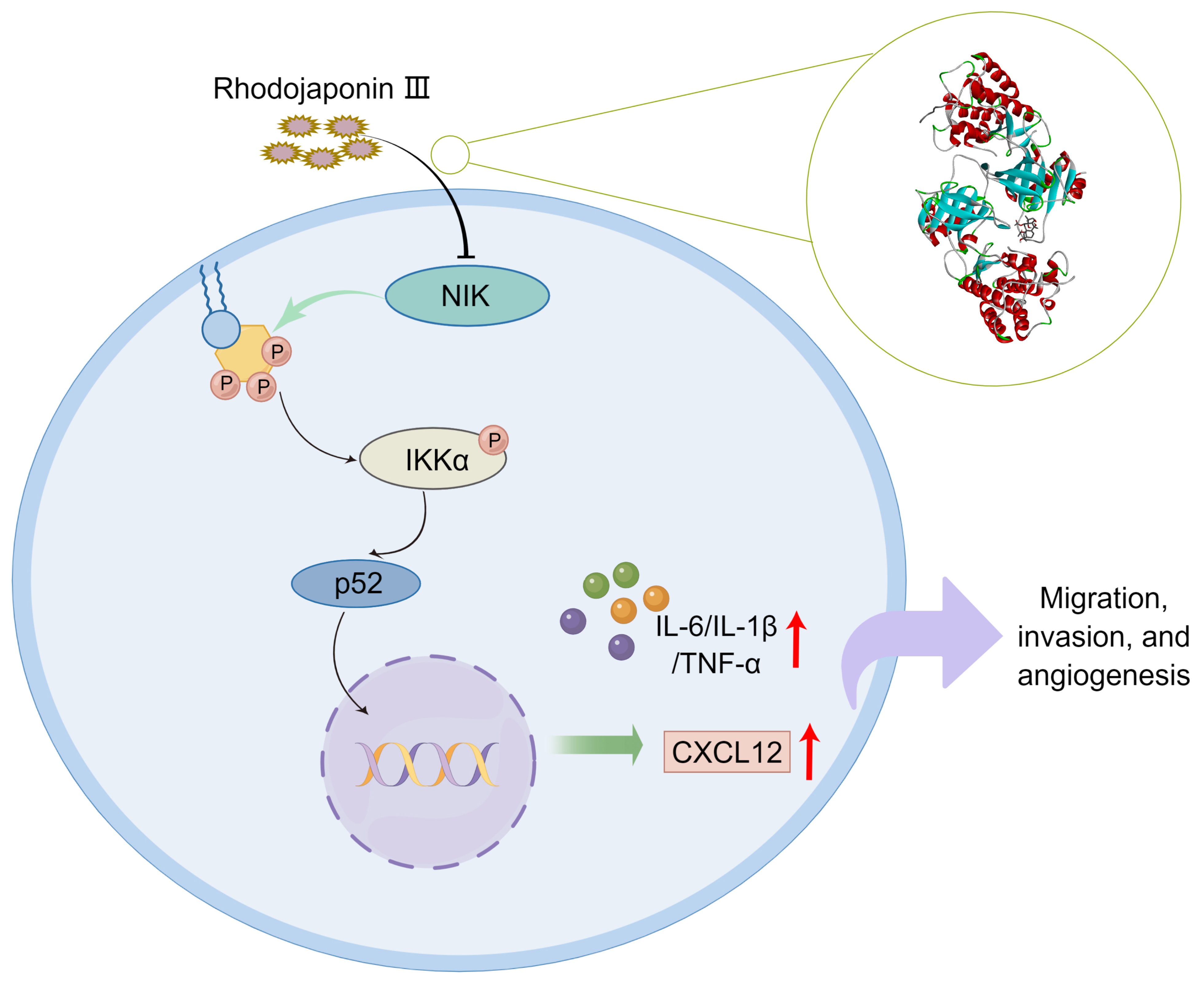 Fig. 7.
Fig. 7.
Rhodojaponin III inhibited
migration, invasion, angiogenesis and inflammation of endothelial cells in
rheumatoid arthritis through inhibiting the NIK/NF-B pathway by
targeted binding to NIK.
Oxidative stress in RA patients can induce inflammation in the body and produce
many inflammatory cytokines, which have an important impact on
the occurrence and development of RA [39]. Pathologically, inflammatory cytokines
are the main mediators of the inflammatory response of RA and the initial factors
to regulate inflammation. In RA, IL-6, IL-1, and TNF- can
activate and prolong the lifespan of osteoclasts and promote bone resorption
[40]. IL-6 plays a key role in the immune activation and inflammatory response of
RA. Therefore, inhibition of IL-6 can effectively control the progression of RA
[41]. Excessive secretion of IL-1 can lead to synovial inflammation,
breakdown of cartilage matrix, aggregation of inflammatory cells, and aggravation
of joint inflammation [42]. TNF- is one of the earliest cytokines
produced during the course of RA. TNF- and its receptors widely exist
in the synovial fluid of RA patients to promote inflammation. In addition,
TNF- inhibitors are also used clinically to block the binding of
TNF- and receptors to treat RA [43]. Here, the knee joint of CIA rats
suffered serious cartilage injury, inflammatory infiltration, and bone erosion,
which were significantly improved after intervention with TWG and different
concentrations of Rhodojaponin III. In addition, high concentrations of IL-6,
IL-1, and TNF- were detected in the serum and synovium of CIA
rats, but the concentrations decreased significantly after intervention with TWG
and different concentrations of Rhodojaponin III. These results indicated that
Rhodojaponin III could affect other cells in joints by regulating the secretion of
pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as inhibiting the activation of osteoclasts and
reducing the aggregation of inflammatory cells, to delay the development of RA
disease.
Studies have shown that the activated synovium in RA further expands into the
pannus and invades bone to destroy cartilage. Synovial angiogenesis often
contributes to the formation and maintenance of RA pannus [44]. CD31 is
frequently expressed in HUVECs and RA synovium, suggesting that CD31 may be an
important marker of synovium inflammation and pannus formation [45]. VEGF
contributes to promoting the growth of vascular endothelial cells, enhancing
vascular permeability, and promoting angiogenesis [46]. VEGF, which is mainly
secreted by fibroblasts and neutrophils, is essential in the destruction of
articular cartilage and joint deformity. Studies have shown that VEGF is highly
expressed in the synovium of joints in RA patients, and its content increases
gradually with the development of the disease [47]. Blocking VEGF and its
regulatory pathways and inhibiting angiogenesis can play an effective role in
treating RA [48]. Here, synovial hyperplasia, increased pannus formation, and
high expressions of CD31 and VEGF in synovium were found in CIA rats. However,
these lesions were improved by different concentrations of Rhodojaponin III.
Vascular endothelial cells are the main effector cells of angiogenesis, and their
proliferation, migration and invasion and tube formation play an important role
in promoting angiogenesis [49]. Here, Rhodojaponin III significantly decreased the
abilities of proliferation, migration, invasion, and tube formation of
TNF--induced HUVECs. These results indicated that Rhodojaponin III could
reduce pannus formation by regulating different stages of angiogenesis to reduce
the degree of joint damage.
The IKK/NF-B pathway consists of NF-B, IB, and
IKK. NF-B is a transcription factor that regulates the transcription of
multiple genes and is involved in cell inflammation, immunity and proliferation.
NF-B signaling is one of the key transcriptional pathways in RA [50].
Activation of the NF-B pathway leads to the release of many cytokines,
chemokines, and other pro-inflammatory mediators. Therefore, blocking the
NF-B pathway is considered an important strategy to control the
inflammatory response in RA [51]. The role of the IKK/NF-B pathway in
RA has already been studied. For example, an inhibitor of IKK prevented
NF-B activation and bone destruction, thus effectively treating RA
[52]. NIK is a kinase that controls the expressions of some cytokines and
chemokines by activating the nonclassical NF-B pathway [13]. NIK and
IKK are activated and phosphorylated to p100, which is then
ubiquitinated to p52 [53]. High expression of NIK can induce NF-B
activation, and NIK can also act as the upstream regulatory kinase of IKK [54].
The expression of CXCL12 is regulated by the nonclassical NF-B pathway
[55]. It was significantly highly expressed in vascular and lymphatic endothelial
cells [56]. Here, NIK, p52, and CXCL12 expressions were up-regulated, and the
phosphorylation level of IKK was increased in the synovium of CIA rats
and TNF--induced HUVECs. After intervention with different
concentrations of Rhodojaponin III, the expressions of these proteins were observed
to be down-regulated. Studies have shown that NIK-specific inhibitor Cpd33
inhibits p52 production and bone resorption activity of mature osteoclasts [57].
In the mechanism study, Rhodojaponin III and NIK were found to be combined by
conventional hydrogen bonds and van der Waals force. In addition, oe-NIK
transfection reversed the inhibitory effects of Rhodojaponin III on the expressions
of NIK/NF-B pathway-related proteins, proliferation, migration,
invasion, and angiogenesis in TNF--induced HUVECs. All these proved
that Rhodojaponin III inhibited the progression of RA by inhibiting the activation
of the NIK/IKK/CXCL12 pathway.
This study has the advantages of establishing
in vivo and in vitro models, multiple indexs evaluation and
practical significance, and elucidates the possible mechanism of Rhodojaponin III
on RA, providing strong support for the application of Rhodojaponin III in the
treatment of RA. However, there are certain limitations to this study. It mainly
focuses on animal experiments and in vitro cell culture, which may not
fully reflect the complex pathological processes and therapeutic responses in
human RA patients. Moreover, the study does not investigate the long-term effects
and safety profile of Rhodojaponin III, especially considering its potential use as
a therapeutic agent in clinical cases. In terms of future research directions,
this study suggests several areas that can be further investigated. Firstly,
further research involving larger sample sizes and long-term follow-up can be
conducted to evaluate the safety and efficacy of Rhodojaponin III in human subjects
with RA. Clinical trials can be designed to assess its therapeutic effects,
optimal dosage, and potential side effects. Secondly, the underlying molecular
mechanisms of Rhodojaponin III in regulating the NIK/IKK/CXCL12 pathway
can be further elucidated. Thirdly, the combination of Rhodojaponin III with other
therapeutic agents or treatment approaches can be explored to enhance its
therapeutic effects and broaden its clinical applications. Lastly, the
non-targeted site distribution of RA therapeutic drugs has inspired a
comprehensive study of nanomedicine for the treatment of RA [58]. Based on
nanomedicine, the development of Rhodojaponin III-loaded nanodrugs for targeted
therapy of RA has a bright prospect.
5. Conclusions
In summary, this study highlighted the
potential therapeutic effects of Rhodojaponin III in the treatment of RA.
Rhodojaponin III effectively suppressed cartilage damage, bone erosion, and
angiogenesis in the joints of CIA rats. Additionally, Rhodojaponin III inhibited
the proliferation, migration, invasion, and angiogenesis of
TNF--induced HUVECs. Mechanically, these therapeutic effects were
mediated by the regulation of the NIK/IKK/CXCL12 pathway, leading to
the suppression of inflammation and angiogenesis. The results of this study
provide a foundation for future investigations into the clinical application of
Rhodojaponin III as a treatment option for RA patients.
Abbreviations
RA, rheumatoid arthritis; CIA, collagen-induced arthritis; AI, arthritis index;
NF-B, nuclear factor kappa B; NIK, NF-B-inducing kinase;
IL-1, interleukin-1beta; HUVECs, human umbilical vein endothelial cells;
FLSs, fibroblast-like synovial cells; TNF-, tumor necrosis
factor-alpha; CXCL12, C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 12; IKK, IB kinase;
CXCR4, C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 4; Akt, protein kinase B; TLR4, toll-like
receptor 4; MyD88, myeloid differentiation factor 88; TWG, Tripterygium wilfordii
Glycosides; DMEM, Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium; FBS, fetal bovine serum;
HE, hematoxylin-eosin; IHC, immunohistochemistry; CD31, platelet endothelial cell
adhesion molecule-1; VEGF, vascular endothelial cell growth factor;
HRP, horseradish peroxidase; ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent
assay; CCK-8, cell counting kit-8; CAS, Chemical Abstracts Service; NC,
nitrocellulose; SDS-PAGE, sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel
electrophoresis; SD, standard deviation; ANOVE, analysis of variance; TCM,
traditional Chinese medicine; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; BSA, bovine serum
albumin.
Availability of Data and Materials
The datasets used during the current study available from the corresponding
author on reasonable request.
Author Contributions
XL contributed to conceptualization, data curation, investigation, methodology,
funding acquisition, and writing of the original draft. SL, YX and WM,
contributed to conceptualization, formal analysis, validation, investigation,
software, and validation. RZ contributed to conceptualization, project
administration, supervision, and review. All authors contributed to editorial
changes in the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. All authors have participated sufficiently in the work and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
This study was approved by the animal experiment ethics committee of Hunan
University of Chinese Medicine and conducted in strict accordance with the
national institutes of health guidelines for the care and use of experimental
animals (LL2022061401).
Acknowledgment
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (No.
2022JJ80086 and 2023JJ60342), the Project of Hunan Provincial Health and Health
Commission (No. D202302078705), the Project of Hunan Provincial Student
Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program (No. 2022-5313), the Scientific
research project of Hunan Provincial Education Department (No. 19C1384), the
Hunan Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine Scientific
Research Program (No. 2021161), the Hunan University of Traditional Chinese
Medicine Primary Discipline Open Fund Project in Chinese Medicine (No.
2020ZYX01), the Hunan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine Youth Program
(No. [2017]25), the Key Discipline Project on Chinese Pharmacology of Hunan
University of Chinese Medicine (No. 202302), the construction point of
first-class specialty in Hunan Province in 2020: Chinese medicine resources and
development (No. [2020]248), the National first-class undergraduate major
construction in 2020 (No. [2021]7), and the Scientific Research Project of Hunan
Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine (No. B2023150).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1. Fig. 2.
Fig. 2. Fig. 3.
Fig. 3. Fig. 4.
Fig. 4. Fig. 5.
Fig. 5. Fig. 6.
Fig. 6. Fig. 7.
Fig. 7.






