- Academic Editor
-
-
-
†These authors contributed equally.
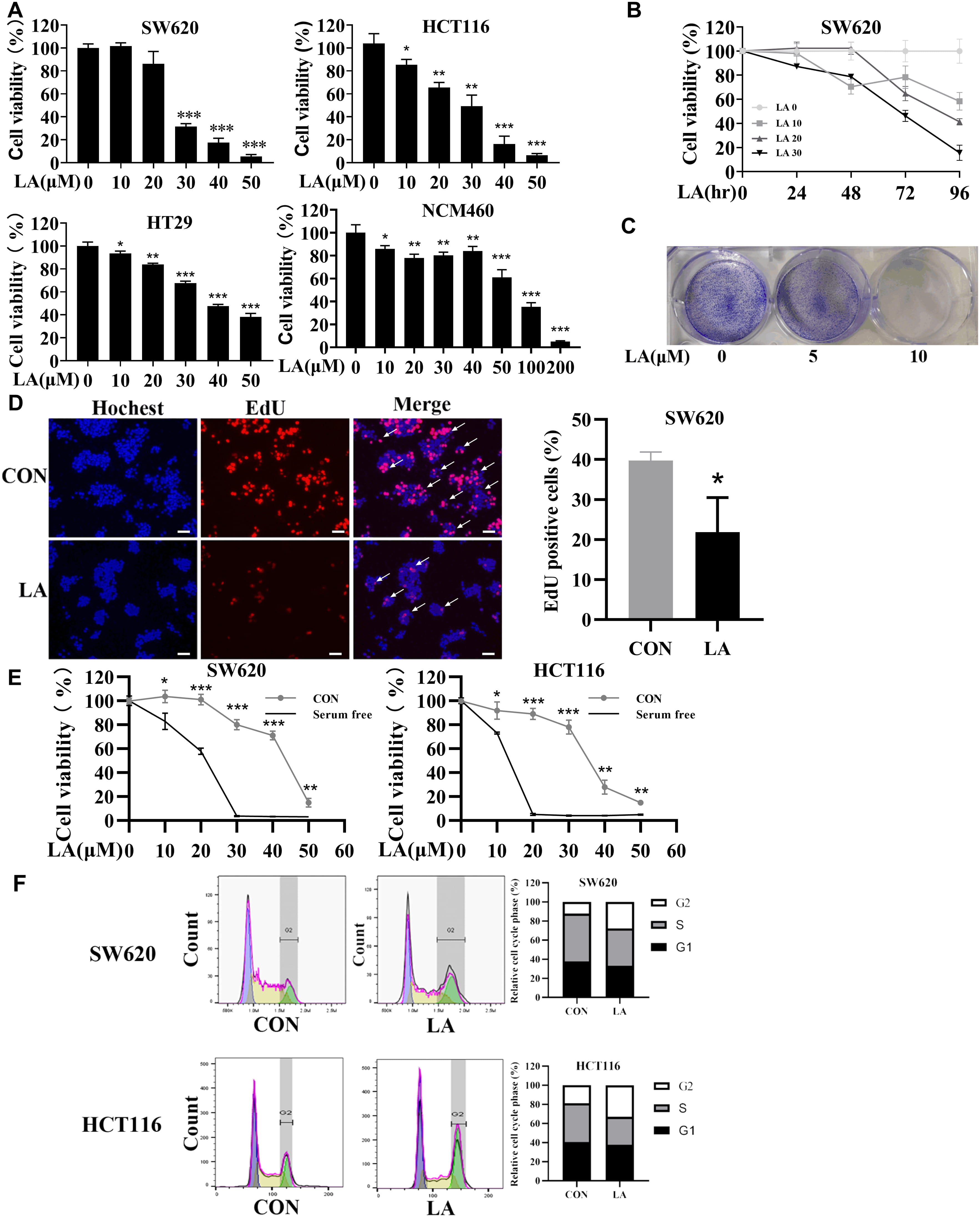
Background: The mortality rate of colorectal cancer (CRC) ranks second
worldwide. Previous research had indicated that licochalcone A (LA) was a
flavonoid in licorice with diverse anticancer effects. We explored the underlying
mechanisms of LA-triggered anticancer activity in CRC. Methods: Thiazolyl Blue (MTT)
experiment and EdU staining were utilized to evaluate cell proliferation.
Meanwhile, cells were stained by Annexin V/PI to investigate apoptosis through
flow cytometry assay. Moreover, expressions of proteins were detected by
immunoblotting, and the level of related mRNA was investigated using real-time
quantitative PCR. Results: LA selectively suppressed the proliferation
and triggered apoptosis of CRC cells. Strikingly, LA induced cytoprotective
autophagic activities since the suppression of autophagy significantly
strengthened LA-induced cytotoxicity and FLICE inhibitory protein (c-FLIP