Background: Alcohol abuse leads to alcoholic liver disease (ALD), for
which no effective treatment is yet known. Gentiana Scabra Bge is a
traditional Chinese medicine; its extract has a significant liver protection
effect, but its effects on the mechanism of improving alcohol-induced toxicity
remain unclear. Therefore, this study used cell and mouse models to investigate
how Gentiana Scabra Bge extract (GSE) might affect the
TLT4/NF-B inflammation pathway in ALD. Methods: In mice, we
induced the alcoholic liver injury model by applying alcohol and induced the
inflammatory cell model by lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced macrophages. Using an
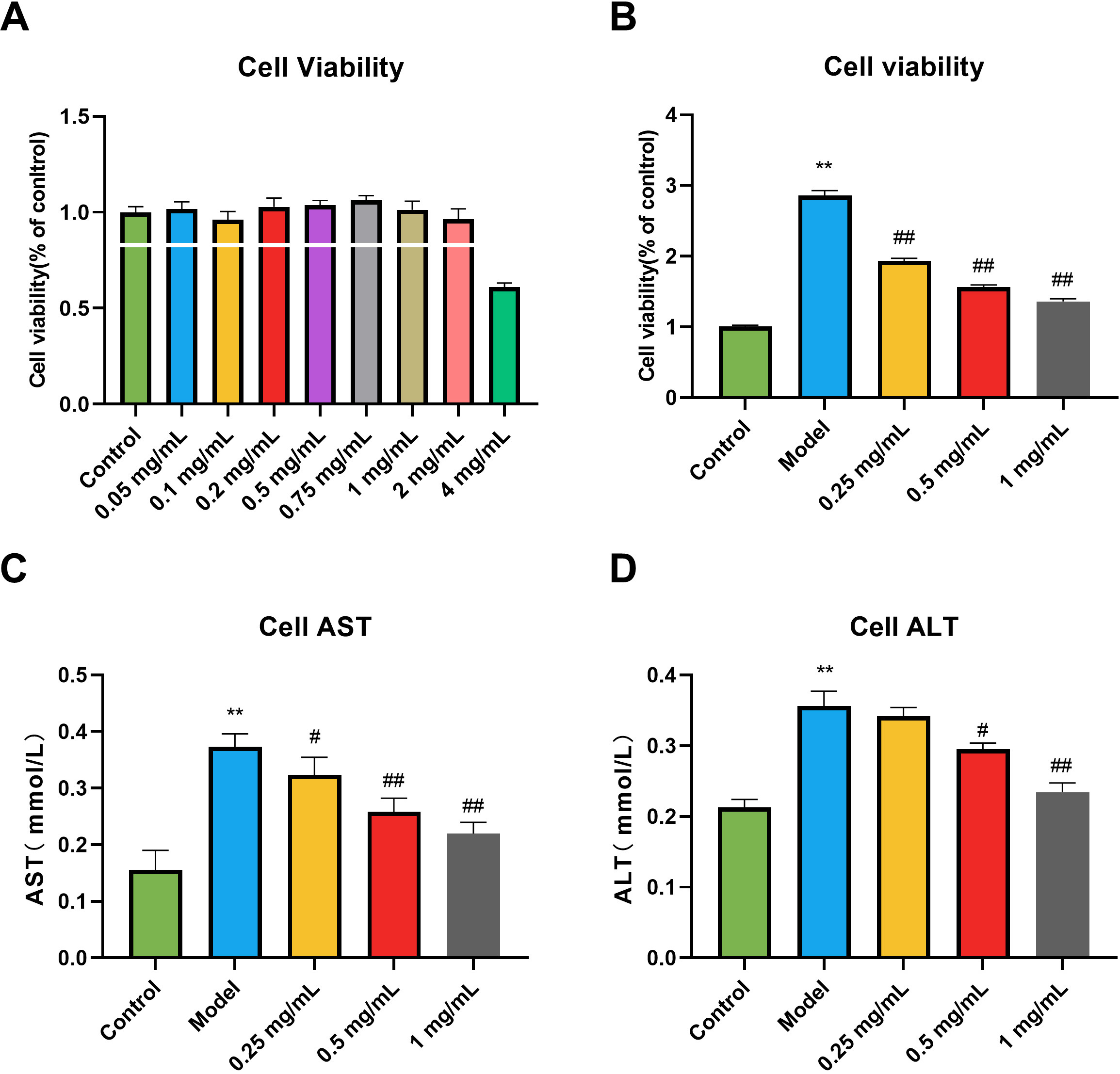
enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit, aspartate aminotransferase (AST)
and alanine aminotransferase (ALT), and interleukin 1 (IL-1),
interleukin 6 (IL-6), and tumor necrosis factor- (TNF-)
levels were measured in liver tissue; we also performed histological analysis of
liver tissue sections to assess the hepatoprotective effect of GSE on alcohol.
Using real-time fluorescence quantification, we determined the expression of
toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and nuclear factor B (NF-B) mRNA
levels; we used Western blotting to detect the expression of TLR4/NF-B
signaling pathway-related proteins. Results: We demonstrate that GSE
decreased AST and ALT activity, ameliorated liver dysfunction, decreased cytokine
levels, and reduced LPS-induced cellular inflammation. In addition, GSE protected
mouse liver cells from the inflammatory response by reducing alcohol-induced
liver pathological damage and downregulating genes and proteins such as nuclear
factors. Conclusions: GSE can attenuate liver injury in mice through the
TLR4/NF-B pathway by inhibiting the activation of nuclear factors.