- Academic Editor
-
-
-
Background: Breast cancer-related depression (BCRD) is strongly
associated with BC and increases recurrence and mortality. This study
investigated the role of kaempferol in the pathogenesis of BCRD and its
underlying mechanism. Methods: 4T1 mouse BC cells were treated with
corticosterone (Cort) in vitro to develop a neuronal injury model, and a
BCRD mouse model was established by injecting 4T1 cells and Cort. The effects of
kaempferol on 4T1 cells and BCRD models were measured by behavioral tests, Cell
Counting Kit-8 assay, wound healing assay, colony formation assay, Western blot
analysis, quantitative real-time PCR, hematoxylin and eosin staining,
enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, and immunofluorescence. BCRD cells were
transfected with the cyclo-oxygenase-2 (COX-2) overexpression plasmid to study
the role of the COX-2/prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) axis in the anti-BCRD activity of
kaempferol. The connection between kaempferol and COX-2 was analyzed by molecular
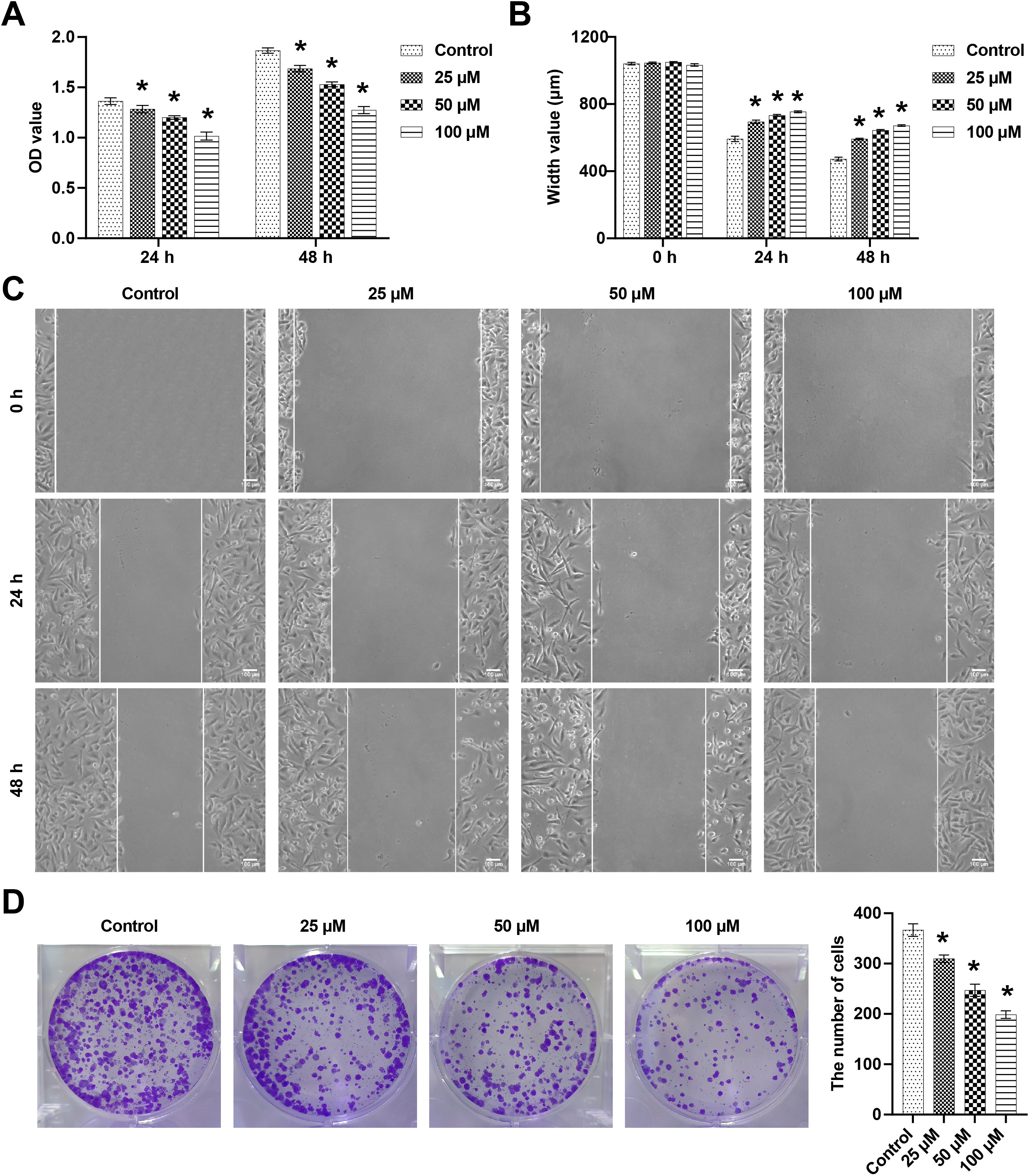
docking. Results: Kaempferol reduced the viability, migration, and
clones of 4T1 cells and inhibited BC growth and depression-like behavior in mice.
Kaempferol alleviated inflammation in BCRD, decreased interleukin 1 beta
(IL-1