†These authors contributed equally.
Academic Editor: Graham Pawelec
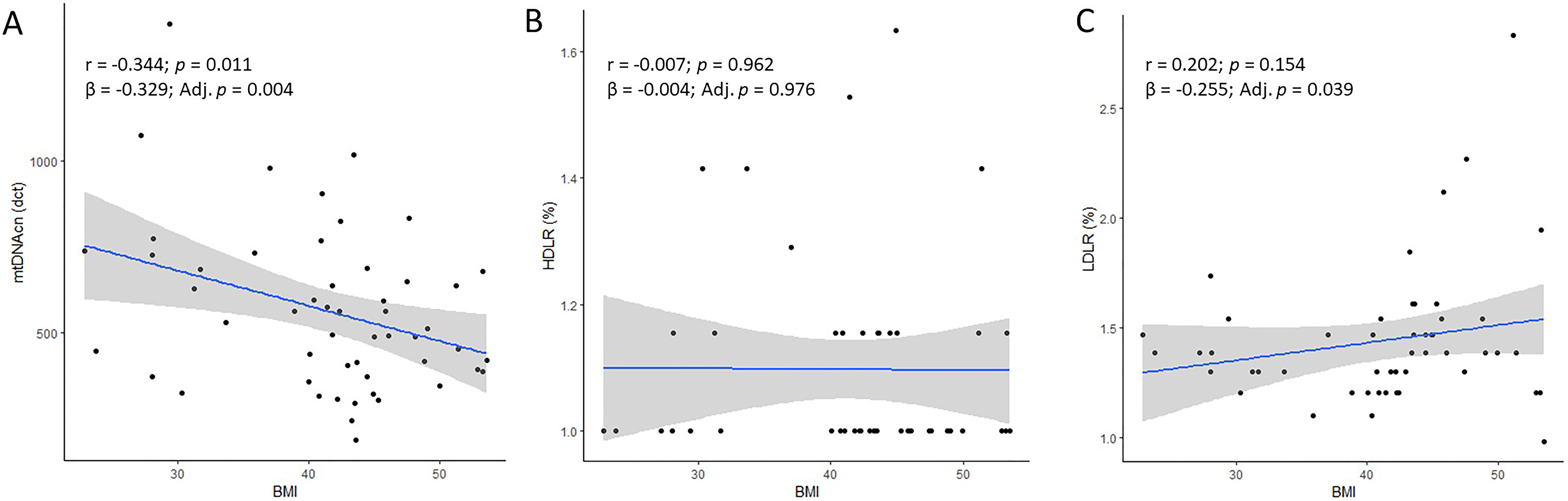
Background: Peripheral alterations of mitochondrial DNA copy number (mtDNAcn) in obesity and associated co-morbidities have been previously shown. Furthermore, the possibility that methylation could occur in the mtDNA (in particular in the displacement loop, D-Loop) and regulate its functions has been raised. However, limited data about mtDNA methylation in adipose tissue are currently available. Since a strict crosstalk between the nucleus and mitochondria exists, especially in terms of the one-carbon cycle (that supports methylation reactions in the cell), we investigated methylation in selected areas of the mitochondrial and nuclear DNA and their expression in visceral adipose tissue (VAT) samples of patients with severe obesity. Methods: VAT biopsies were collected from surgery patients to isolate DNA and RNA. Gene expression and mtDNAcn were assessed through qPCR. DNA methylation in both nuclear and mitochondrial areas were determined through bisulfite pyrosequencing. Results: Methylation levels of the mtDNA were only marginally associated with the obesity degree (higher D-Loop methylation in severe obesity) and were not correlated with mtDNAcn. A significant correlation between D-Loop methylation and LINE-1 methylation was observed in VAT samples, and this was independent from the obesity degree. A progressive reduction of mtDNAcn and increase in NRF1 expression levels were measured in VAT in severe obesity. NRF1 expression was directly correlated with PPARG and MTHFR expression levels, while mtDNAcn was associated to TFAM expression. The correlation between mtDNAcn and TFAM expression was affected by the obesity status. Conclusions: This evidence supports the hypothesis that mtDNA alterations occur in obesity and a complex dynamic correlation between mitochondrial and nuclear DNA methylation exists, highlighting the need for further investigations.