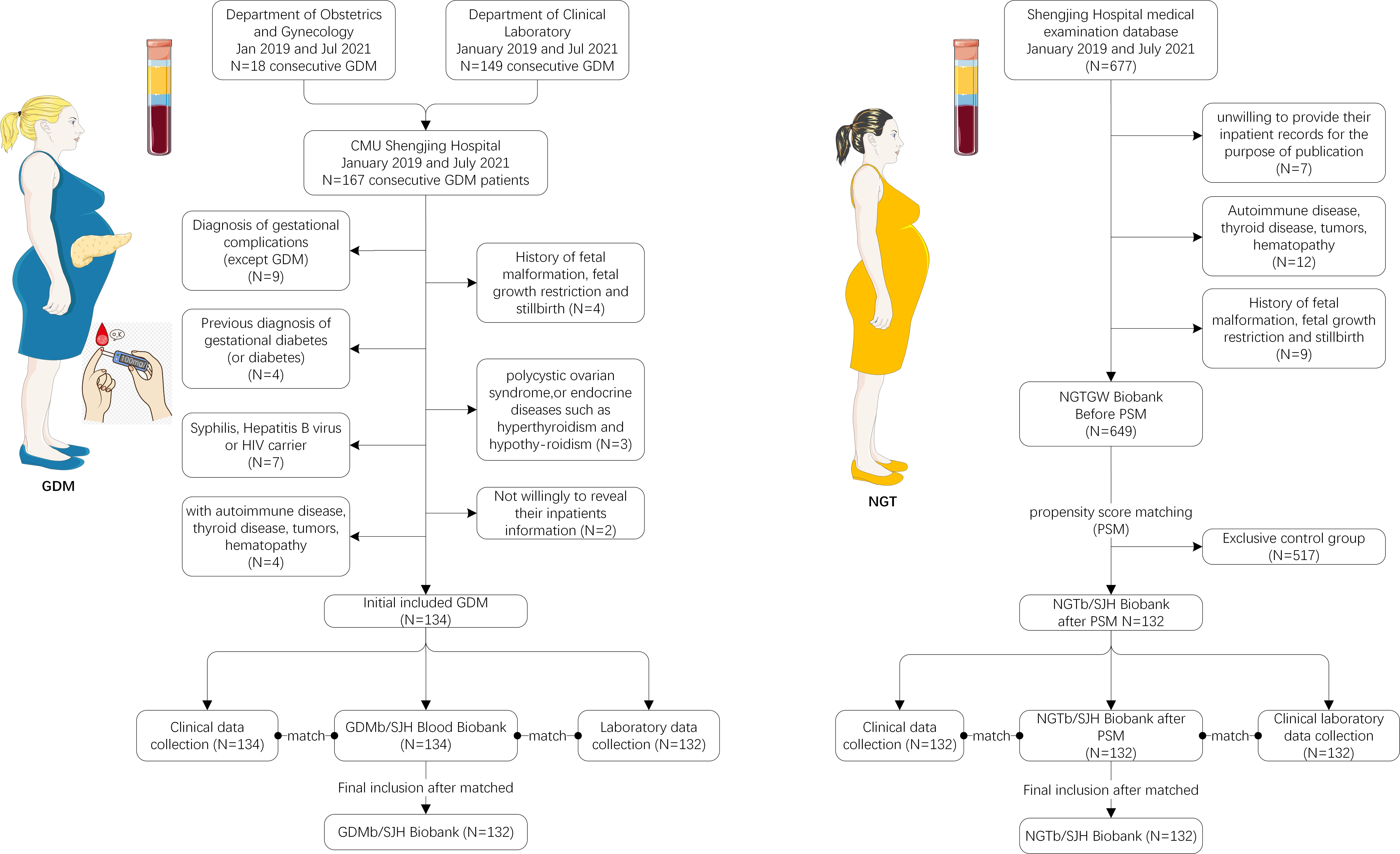
Purpose: This study investigated the association of
serum lipid peroxidation (LPO) and glutathione peroxidase 4
(GPx4) with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) and metabolic abnormalities in
Chinese pregnant women. Methods: The present case-control study was
matched at a ratio of 1:1, and it recruited 132 pairs of participants at 24–28
gestational weeks. The serum LPO and GPx4 level were determined in each subject
by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The associations of LPO and GPx4 with
metabolic parameters were analyzed. Thereafter, this study classified all
subjects based on metabolic abnormality frequency (including body mass index,
blood pressure, triglycerides, and fasting plasma glucose), and explored the
association of the serum LPO and GPx4 levels in relation to metabolic
abnormalities and clinical outcomes. Simultaneously, logistic regression analysis
was used to estimate the odds radio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (CI)
expressing the association between LPO/GPx4 and metabolic abnormalities.
Results: Women with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) in second
trimester displayed an increased LPO concentration, whereas the GPx4
concentration was decreased compared with normal subjects (174.58 22.01
ng/mL vs. 119.54 8.93 ng/mL, p 0.001 and 27.31 16.88
vs. 33.84 19.55 ng/mL, p 0.001, respectively). In addition,
the GPx4 concentration was negatively associated with the plasma fasting 2 h
plasma glucose level (2h-PG) and percentage glycated albumin (GA%) in the second
trimester. Bivariate correlation analysis revealed that in GDM patients the serum
GPx4 concentration displayed a significant linear correlation with glucose
metabolism indexes, including fasting plasma glucose, glycated
albumin, and 2h-PG (all p 0.05). By contrast, there was no
relationship between the serum LPO concentration and glucose metabolism
(p 0.05) in GDM patients. Nevertheless, the LPO and GPx4
concentrations in the second trimester were not significantly related to the
pregnancy/neonatal outcomes. Moreover, after the GDM subjects were grouped based
on metabolic abnormality component, the metabolic abnormality risk was elevated
with the increase in the LPO concentration (elevated diastolic blood pressure, OR
= 1.04, p = 0.048; and high triglycerides, OR = 2.19, p
0.001), together with a greater incidence of multiple metabolic abnormalities.
Additionally, the serum LPO concentration increased with the increased metabolic
abnormality frequency (OR = 1.93, 95% CI: 1.62–2.29, p 0.001).
Conclusions: In women with GDM, the serum GPx4 concentration was lower,
which was strongly associated with second trimester glucose metabolism among the
Chinese pregnant population. According to our findings, women with GDM had an
increased LPO concentration, which was strongly associated with metabolic
abnormalities among the pregnant women; this might be adopted as a predictor
factor for metabolic abnormalities. The results of the present study suggest that
a higher lipid oxidative stress and lower lipid antioxidant associated with an
increased risk of GDM.