- Academic Editor
-
-
-
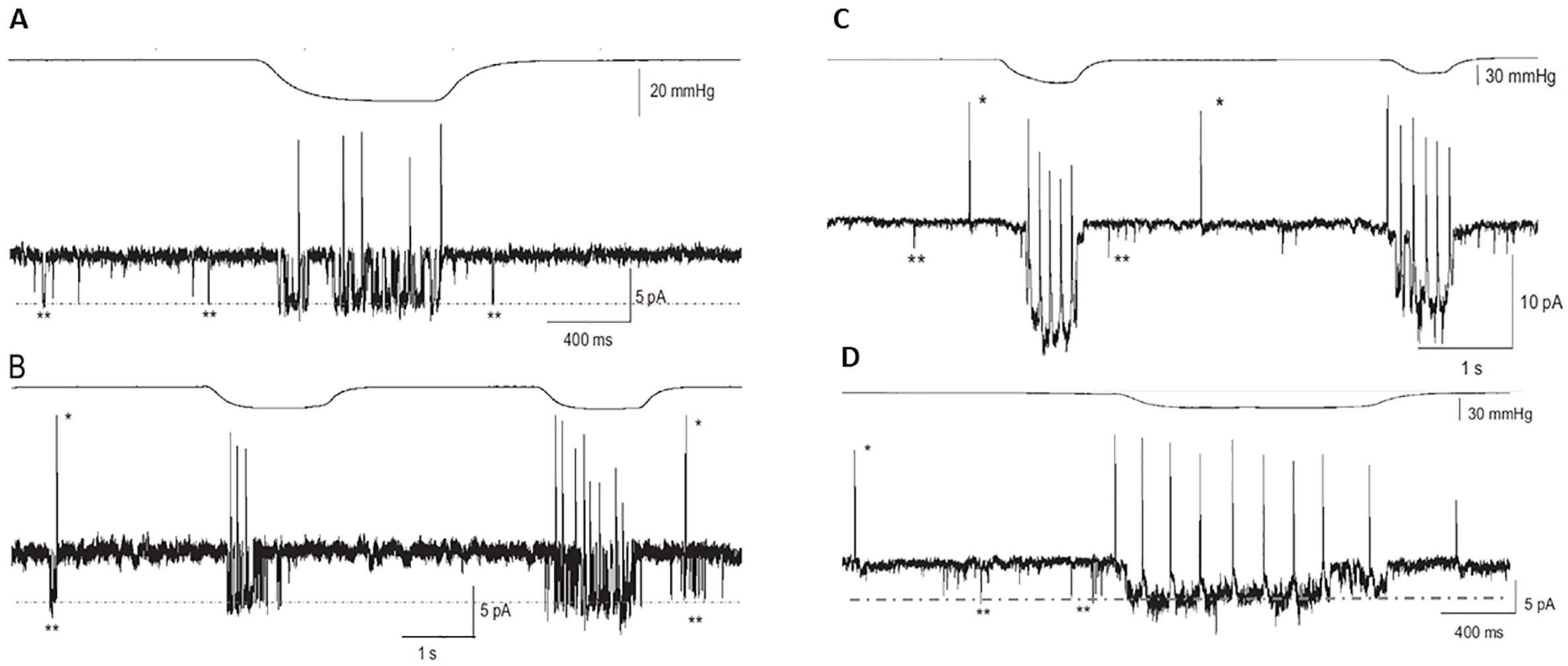
This article presents evidence indicating that intracranial pressure (ICP) pulsatility, associated with the heartbeat and breathing, is not just a source of mechanical artefact in electrical recordings, but is “sensed” and plays a role in the brain’s information processing. Patch-clamp recording of pressure-activated channels, and detection of Piezo2-protein channel expression in brain neurons, suggest that these channels provide neurons with an intrinsic resonance to ICP pulsatility, which acts to synchronize remote neural networks. Direct measurements in human patients indicate that heartbeat and breathing rhythms generate intracranial forces of tens of millinewtons, exceeding by orders of magnitude the localized forces shown by atomic force microscopy and optical tweezers to activate Piezo channels in isolated neocortical and hippocampal neurons. Additionally, many human touch and proprioceptors, which are also transduced by Piezo channels, show spiking that is phase-locked to heartbeat- and breathing-induced extracranial pressure pulsations. Finally, based on the observation that low-frequency oscillations modulate the phase and amplitude of high-frequency oscillations, body and brain oscillations are proposed to form a single hierarchical system in which the heartbeat is the basic frequency and scaling factor for all other oscillations. Together, these results support the idea that ICP pulsatility may be elemental in modulating the brain’s electrical rhythmicity.