†These authors contributed equally.
Academic Editor: Kuei-Sen Hsu
Background: Epilepsy is a disease caused by paroxysmal abnormal
supersynchronous electrical activity of brain neurons, and it is also one of the
most common illnesses in neurology. Among the causes, hippocampal sclerosis may
be one of the main causes of temporal lobe epilepsy. However, the pathogenesis of
hippocampal sclerosis in epilepsy remains unclear. Methods: We
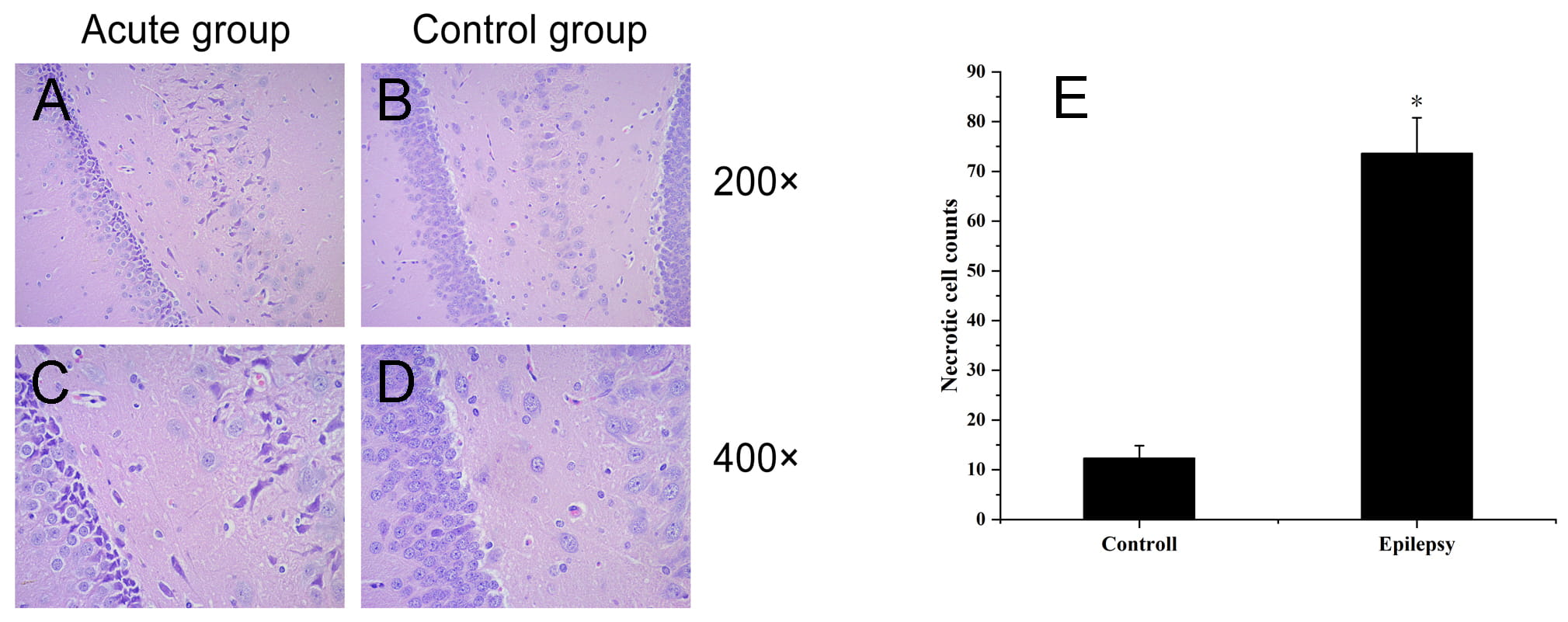
established an epilepsy model by intraperitoneal injection of pentetrazol (PTZ)
into Sprague-Dawley rats, and applied isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantitation (iTRAQ) technology to identify differentially
expressed proteins (DEPs) in the hippocampus. We quantified a total of 3782
proteins. DEPs were defined as proteins with a fold change