1 Institute of Applied Physics “Nello Carrara”, National Research Council, 50019 Sesto Fiorentino, Italy
Academic Editors: Fabio Moda and Giorgio Giaccone
Abstract
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common neurodegenerative disorder, resulting in memory loss, cognitive decline, bodily function impairment, and finally death. The growing number of people suffering from AD increasingly urges the development of effective early diagnosis and monitoring techniques. Here, we review the most recent developments in the field of Raman-based techniques, which have shown a significant potential in identifying AD by detecting specific biomarkers in biological fluids, as well as in providing fundamental insights into key molecules involved in the disease progression or in the analysis of histological specimens of patients with AD. These techniques comprise spontaneous and resonant Raman spectroscopies, exploit plasmon- or fiber- enhanced effects, such as surface-, tip- or fiber- enhanced Raman spectroscopies, or involve non-linear techniques like coherent Raman scattering. The scientific efforts employed up to now as well as the rapid technological advancements in optical detection instruments (spectrometers, lasers, substrates for analysis, etc.) and the diffusion of advanced data processing methods suggest a leading role of Raman techniques in the perspective of a preclinical or clinical detection of AD.
Keywords
- Raman spectroscopy
- optical detection
- Alzheimer's disease
- biomarkers
- biological fluids
- early diagnosis
- label-free methods
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) affects tens of millions of patients worldwide,
representing the most common neurodegenerative disease [1]. Due to the increment
of life expectancy, the number of people affected by AD and other forms of
dementia is likely to reach about 152 million by 2050 [2]. AD occurs in most
cases in subjects over 65, causing memory loss, cognitive decline, progressive
impairment of physiological functions and death, usually within 5–12 years from
the onset of the symptoms [3]. Despite the fact that the pathogenic mechanism is
not completely understood, AD is characterized by the aggregation in the brain of
two different proteins: (i) the amyloid-
AD is commonly detected when irreversible damages in the brain have occurred, and the definitive diagnosis can only be made post-mortem, upon the identification of the aforementioned aggregates. Therefore, a sensitive and affordable method for the diagnosis of AD, which would allow an early therapeutic intervention, represents one of the main challenges in the field.
Raman-based detection techniques have shown a significant potential for the early diagnosis of AD [1, 7]. Raman spectroscopy provides the molecular fingerprint of biosamples in a non-invasive, non-destructive and label-free manner. Weak Raman signals of biomolecules, as well as frequent fluorescence interferences, have fuelled recent technological breakthroughs aimed at overcoming these constraints through signal enhancement techniques, which were then proposed as investigation and diagnostic tools for AD. Previous reviews extensively discussed Raman-based techniques employed in the study and the diagnosis of AD [7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12]. Consequently, here we will focus on the latest advancements in the field.
RS, described by V.C. Raman in 1928, provides information on the molecular
vibrations of a sample, by collecting its inelastic scattering signal under a
monochromatic excitation wavelength in the UV, visible or near-infrared (NIR)
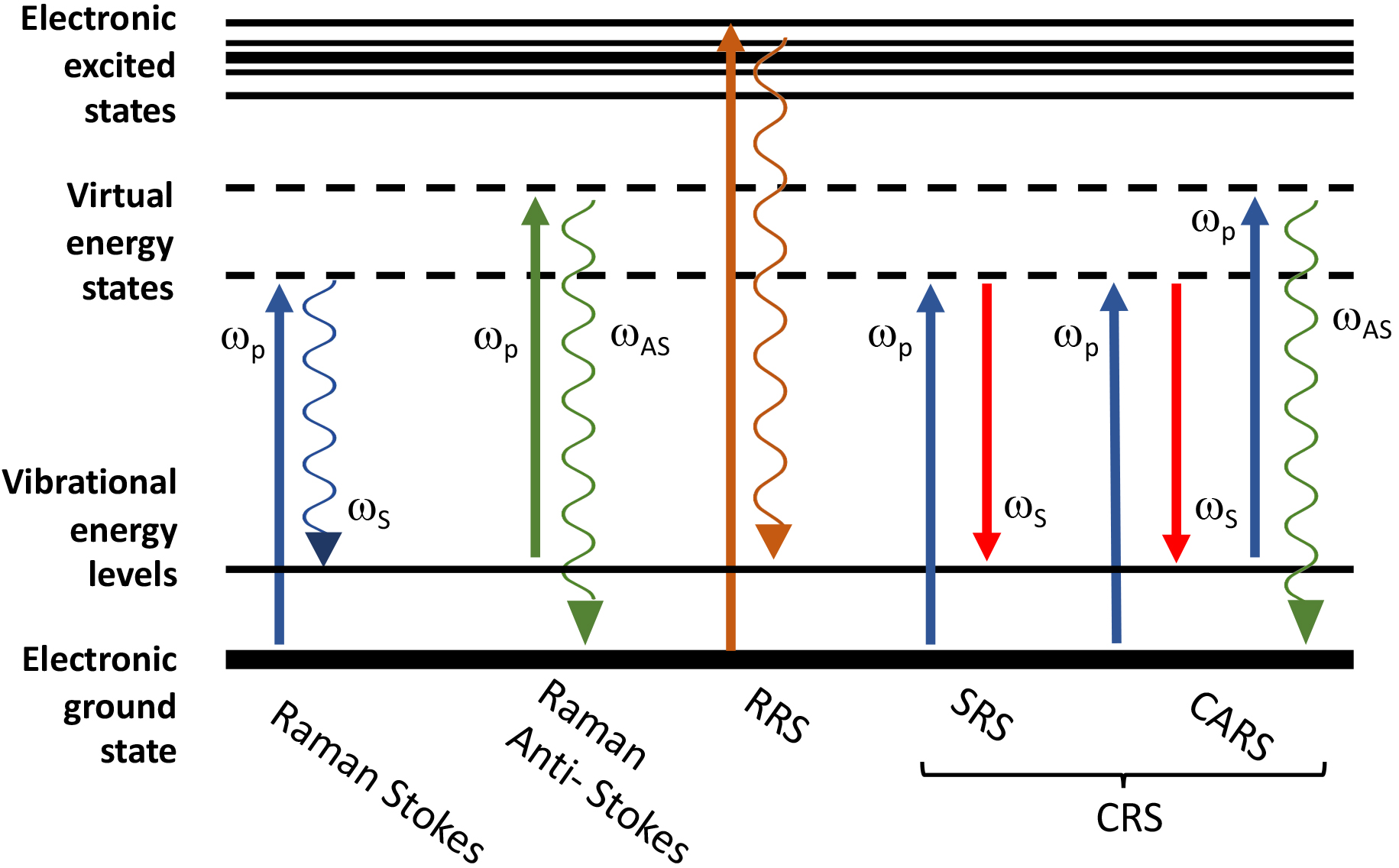
range (Fig. 1) [13]. The interaction of incident light with the vibrational modes
of molecules gives rise to an energy loss (Raman Stokes,
 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.Schematic representation of the energy level diagram of Raman
scattering processes. From left to right: spontaneous Raman Stokes
(
Specifically, information on the chemistry and structure of biomolecules, such as protein secondary or tertiary arrangements, folding states, aggregation, or pH dependent conformations, can be obtained from the analysis of Raman spectra [14, 15, 16, 17]. Exploiting these peculiarities, RS demonstrated great potential for the analysis of AD biosamples, such as histologic specimens and biological fluids. Several studies have shown that Raman experiments can allow detection of amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles in unlabelled samples as derived from human brain tissue of AD patients or in animal models, as well as distinguish them from the surrounding areas [18, 19, 20, 21, 22]. For example, a Raman study in mice demonstrated the ability to differentiate AD from healthy subjects with an accuracy of 85.9%, identifying distinctive disease-related biochemical alterations in retina samples [23].
RS has also shown a high potential in the identification of early-stage AD and
its discrimination from late forms of AD and other types of dementia, like
dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB), by screening of biological fluids, such as CSF,
blood serum and saliva, and analysis of spectral data by machine learning
techniques [5, 6, 24, 25]. Exosomes are small extracellular vesicles (sEVs)
released from cells into surrounding body fluids. They have been detected in
different biological fluids and are now subject of extensive investigation
because of their rich protein content involved in a variety of pathological
processes. RS has recently been proven as an effective tool for the
characterization of sEVs isolated from MC65 cells, and associated with the toxic
A
In RRS the energy of the incident photons or, in other words, the wavelength of
the excitation laser, is tuned to match the electronic transition of the sample
under examination. Such frequency coincidence (or resonance) leads to increased
Raman scattering signals, allowing the analysis of molecules that are scarcely or
not detected in non-resonance conditions. In essence, selecting the appropriate
laser illumination, RRS can highlight signals from desired molecules of the
sample, excluding interference from other components or from the background [11].
This technique has been employed in the study of the aggregation and deposition
processes of amyloid-
Although spontaneous RS provides excellent chemical specificity, it is an
intrinsically weak scattering technique that does not allow the detection of
analytes at low concentrations (typically below mM). This is a key constraint
when it comes to biosample analysis. SERS relies on the enhanced electromagnetic
field arising from the collective oscillation of conduction band electrons, under
visible or NIR laser excitation of the surface of noble metal nanoparticles [29].
Thanks to this phenomenon, known as localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR),
the Raman signal of an analyte placed nearby or adsorbed on a nanostructured
metal surface (the so-called “hot-spot”) can be enhanced by a factor
of up to 10
SERS has been also proposed to study key species associated with AD, their
structure and aggregation process, in order to shed light on their role in the
neurodegenerative mechanism of AD. The secondary structure of different
amyloid-
So far, several SERS nanostructured substrates have been proposed to improve the
signal quality and reproducibility or to increase the affinity toward a
particular target analyte. They span from colloidal solutions of spherical or
quasi-spherical gold and silver nanoparticles, to more complex, assembled or
hybrid substrates. For example, dot arrays of silver nanowires were deposited on
a hydrophobic substrate of polytetrafluoroethylene for the rapid and sensitive
detection of A
Metal nanostructures can be further conjugated with different functional
molecules in order to confer affinity toward specific analytes and improve the
detection limit. Nanogap silver cells, conjugated with antibodies specific for
A
TERS combines the chemical specificity of Raman spectroscopy with the high
spatial resolution of scanning probe microscopy (SPM), providing a
non-destructive, direct and label-free chemo-structural characterization at the
nanoscale [50, 51, 52]. In a typical TERS experiment a laser excitation wavelength
generates a hot-spot on to the apex of a nanometric tip, that is
equipped and driven by a scanning probe microscope (including scanning tunnelling
microscopy, STM, or atomic force microscopy, AFM). The interaction of the tip
with the sample surface reconstructs the morphological image and, upon
amplification of the Raman signal, provides a chemo-structural map of the sample
with a spatial resolution comparable to the size of the tip’s apex. TERS allowed
to study the relationship between structure and neurotoxicity of protein
oligomers, such as those formed by the HypF-N model protein [53], providing a
direct characterization of the specific amino acid residues that are exposed on
the surface of toxic and nontoxic species [54]. Such evaluation provides
important information about how the amyloid aggregates can affect cell membrane
integrity and signalling pathways. Natural A
The intensity of the Raman signal is directly proportional to the power of the
excitation laser and the concentration of the analyte molecules. However, the
laser power cannot be increased beyond certain thresholds for technical reasons
and without incurring uncontrolled temperature increases, which can damage the
sample. FERS can overcome this problem by expanding the interaction between the
excitation laser and the analyte molecules. In particular, the use of hollow core
fibres (HCFs) permits to confine the excitation and the Raman scattered light in
a transmission channel, matching the channel where the sample flows. As a result,
the interaction volume is increased through multiple internal reflections, thus
raising the Raman scattering events and improving signal collection [59]. For
example, an HCF was successfully integrated with a conventional Raman
spectroscopic system, and the signal of A
CRS, that typically includes coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering (CARS) and
stimulated Raman scattering (SRS) effects, is based on nonlinear optical
processes that employ multiple photon excitations to stimulate characteristic
molecular vibrations of the target molecule. In this way a coherent signal is
produced, which is orders of magnitude stronger than the spontaneous Raman
scattering [11, 30, 61]. Both of these nonlinear technologically advanced
techniques use a first laser beam (
The main features of RS techniques described in this review, are summarized in Table 1 (Ref. [5, 6, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 24, 25, 27, 28, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 52, 54, 55, 56, 57, 60, 61, 62, 63, 64]).
| Technique | Physical principles/adaption | Benefits | Drawbacks | Target samples and concentration/dimensional range |
| Raman spectroscopy (RS) | Inelastic scattering of UV-Vis-NIR light | - Non destructive | - Weak signals | - Brain tissue: resolution at cellular level [18, 19, 20, 21, 22] |
| - Label free | - Resolution limited by diffraction | - Biological fluids: CSF, blood, serum, saliva [5, 6, 24, 25] | ||
| - Fluorescence background | ||||
| Resonant RS (RRS) | Excitation of electronic transitions of the sample | - Signal enhancement due to the “resonance effect” | - Fluorescence signal enhancement | - ab initio simulations of amyloid- |
| Surface-enhanced RS (SERS) | Plasmon resonance effects on metal nanoparticles | - Huge signal enhancement (up to 10 |
- Metal nanostructures required | - Biological fluids: CSF, blood, serum, saliva, tears [31, 32, 33, 34, 44, 46, 47], down to tens fM [31] |
| - Low detection limit | - Signal variability due to nanostructured substrate | - Aβ monomers or aggregates, mM-µM [35, 36, 37, 38], down to pM* [43, 45] | ||
| - Quenching of fluorescence | - Tau protein, µM-pM [42, 43, 46, 47, 48], down to fM * [46] | |||
| Tip-enhanced RS (TERS) | Plasmon resonance effects on a metal SPM tip | - Huge signal enhancement (up to 10 |
- Experimental complexity and expensive setup | - Single structure analysis: oligomer, fibril [54, 55, 56, 57], down to µM [52, 54, 57] |
| - Nanometric spatial resolution | - Signal variability due to tip response | |||
| - Low detection limit | - Sample heating at the apex of the tip | |||
| - Quenching of fluorescence | ||||
| Fiber-enhanced RS | Confinement of light-sample interaction within an optical fiber | - Enhanced signal due to increased light-sample scattering events | - Requires fine alignment between the spectrometer and the fiber | - nL-µL volumes of sample solution, down to µM [60] |
| - Integrable with handheld Raman systems | - Requires coupling with a microfluidic system | |||
| - Small samples volumes | ||||
| - Can be coupled with SERS | ||||
| Coherent RS | Non-linear optical effects that use multiple photons excitations, tuned at defined vibrational frequencies, to generate coherent signals | - Increased coherent signals | - Single wavelength selection | - Brain tissues: resolution at cellular level [61, 62, 63, 64] |
| - Fast imaging | - Expensive setups due high-rate pulsed laser excitation | |||
| * calculated values. | ||||
Together with the increase in life expectancy, an increase in the number of people with AD is expected in the near future and this will subsequently lead to an increase in the cost of medical care, as well as in the social cost of supporting the families of people with AD. To date, AD can be diagnosed when irreversible brain damage has already occurred. Therefore, the implementation of efficient methods for early diagnosis could facilitate the adoption of adequate healthcare strategies and the design of more effective therapies.
Herein, we reviewed the most recent advancements in Raman spectroscopies in the investigation and diagnosis of AD, highlighting their potential in revealing the fingerprint of AD biomarkers from biological samples and in discriminating between healthy and diseased specimens. Small amounts of sample required, label-free detection, versatility, sensitivity, and cost convenience of Raman-based techniques, make them very promising in AD research. In this context, AD has recently been linked to neurovascular alterations [65, 66], which could represent a promising target for future Raman investigations of brain tissue [62, 67].
The continuous advancements in the technology and physics of instruments, such
as fibers, lasers, confocal systems, microscopes and spectrometers or in the
efficacy of the substrates and of the tools for analysis will further contribute
to increase the quality of the spectroscopic information. In addition, RS can be
coupled with other techniques, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed
tomography (CT), positron emission tomography (PET), immunohistochemistry and
micro-Fourier transform infrared (
PP wrote the original draft. MB, CD’A, MdeA and PM reviewed and edited the original draft. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Not applicable.
We acknowledge our hospital colleagues for their help and discussion.
We thank the funding support from the European Community and the Italian Ministry of Education University and Research within the EuroNanoMed3 ERANET SPEEDY project (ID 221).
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Publisher’s Note: IMR Press stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.