1 Department of Analytical and Food Chemistry, Faculty of Pharmacy, Al-Andalus University for Medical Sciences, 35XQ+C2F Tartous, Syria
2 Facultad de Ciencias de la Salud, Universidad Arturo Prat, Avda. Arturo Prat 2120, 1110939 Iquique, Chile
3 Facultad de Medicina, Universidad del Azuay, 14-008 Cuenca, Ecuador
4 Department of Plant Production, Faculty of Agronomy, Universidad de Concepción, Avenida Vicente Mendez, 595, 3812120 Chillán, Chile
5 Departamento de Suelos y Recursos Naturales, Facultad de Agronomía, Universidad de Concepción, 4070386 Concepción, Chile
6 Department of Nutrition and Dietetics, Faculty of Pharmacy, and Centre for Healthy Living, University of Concepción, 4070386 Concepción, Chile
7 Research Institution “Chinese-Tajik Innovation Center for Natural Products” of the National Academy of Sciences of Tajikistan, Ayni str. 299/2, 734063 Dushanbe, Tajikistan
8 Faculty of Science, University of Bamenda, 39 Bamenda-Bambili, Cameroon
9 Department of Pharmacology, University of Free State, 9300 Bloemfontein, South Africa
10 Department of Veterinary Sciences and Animal Husbandry, Amrita School of Agricultural Sciences, Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham University, Coimbatore, 642109 Tamil Nadu, India
11 Chemical and Biochemical Processing Division, ICAR – Central Institute for Research on Cotton Technology, 400019 Mumbai, India
12 Department of Life Sciences, National University of Kaohsiung, 811 Kaohsiung, Taiwan
13 Phytotherapy Lab (PhT-Lab), Endocrinology Unit, Department of Medicine (DIMED), University of Padova, via Ospedale 105, 35128 Padova, Italy
14 AIROB, Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca Oncologica di Base, 35046 Padova, Italy
Academic Editor: Gustavo Caetano-Anollés
Abstract
Melissa officinalis L. is a plant of the Lamiaceae family known in numerous countries for its medicinal activities. This plant has been used since ancient times to treat different disorders, including gastrointestinal, cardiovascular, neurological, psychological conditions. M. officinalis contains several phytochemicals such as phenolic acids, flavonoids, terpenoids, and many others at the basis of its pharmacological activities. Indeed, the plant can have antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antispasmodic, antimicrobial, neuroprotective, nephroprotective, antinociceptive effects. Given its consolidated use, M. officinalis has also been experimented with clinical settings, demonstrating interesting properties against different human diseases, such as anxiety, sleeping difficulties, palpitation, hypertension, depression, dementia, infantile colic, bruxism, metabolic problems, Alzheimer’s disease, and sexual disorders. As for any natural compound, drug, or plant extract, also M. officinalis can have adverse effects, even though the reported events are very rare and the plant can be considered substantially safe. This review has been prepared with a specific research strategy, interrogating different databases with the keyword M. officinalis. Moreover, this work analyzes the properties of this plant updating currently available literature, with a special emphasis on human studies.
Keywords
- Melissa officinalis L.
- lemon balm
- phytotherapy
- phytochemicals
- health properties
- clinical trials
In today’s world, the prevalence of anxiety disorders has skyrocketed. Anxiolytics can be used to treat these illnesses, although they can have some negative side effects despite their effectiveness. Because of the lack of understanding about drug interactions and possible harmful effects, traditional medicine poses a serious risk to public health. Plants’ clinical efficacy must be evaluated in research investigations. Melissa officinalis L., popularly known as lemon balm, is utilized in traditional medicine for its effects on CNS processes such as sedation and memory improvement and additionally possess various health benefits if consumed in optimum concentration but unfortunately, no comprehensive compilation has been done so far [1]. The majority of beneficial effects of the Therefore, it is important to present complete information of Melissa officinalis L. are due to volatile oils, triterpenes, and phenolic compounds.
An increasing body of evidence suggests that this plant may have therapeutic potential in the management of disorders such as diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease. It also contains antioxidant, antibacterial, and anti-inflammatory properties [2, 3]. The low toxicity and lack of side effects of this plant have been proven in several investigations utilizing different experimental models [4]. But if the plant extracts are not used optimally, they may exert toxicity both in cell and animal models. In the clinical trials, the effect of M. officinalis extracts has been proved evaluated on a variety of diseases, mainly related to neurological disorders, i.e., anxiety and sleeping difficulties, but also metabolic problems and infantile colic and shown to have positive effects. The present review was aimed to compile information on botany and phytochemistry, traditional medicinal, and ethnopharmacological uses of M. officinalis, and also various clinical aspects and biomedical properties of this well-known plant are discussed.
This review has been prepared through an interrogation of different databases, such as Chrocane library, Embase-Elsevier, Google Scholar, Ovid, PubMed, Science Direct, SciFinder, Scopus, Web of Science. Both articles, papers, and books have been considered, while the search strategy was based on the keyword Melissa officinalis, in addition to its English translation or common names as “common balm”, “honey balm”, “lemon balm”, “melissa balm”, “sweet balm”.
Melissa officinalis can be taxonomically classified as follows: Kingdom: Plantae; Division: Tracheophyta; Subdivision: Speramtophyta; Class: Magnoliopsida; Superorder: Asteranae; Order: Lamiales; Family: Lamiaceae; Genus: Melissa; Species: Melissa officinalis L. [5].
From a botanical point of view, Melissa officinalis L. (Greek word “Melissa”—honeybee) is the only acceptable name for the plant and possesses different accepted varieties, i.e., M. officinalis var. altissima (Sm.) K.Koch, M. officinalis var. cordifolia (Pers.) K.Koch, M. officinalis var. foliosa Briq., M. officinalis var. graveolens (Host) Nyman, M. officinalis var. hirsuta K. Koch, M. officinalis var. romana (Mill.) Woodv. and M. officinalis var. villosa Benth [6, 7]. M. officinalis L. is also known as lemon balm, bee balm, sweet balm, common balm, honey balm [5, 6].
There is also an infraspecific taxon of the species M. officinalis which are naturally expended in our wild flora: M. officinalis ssp. altissima (Sm.) Arcang., M. officinalis ssp. officinalis, M. officinalis subsp. inodora Bornm [8, 9]. M. officinalis shows economic significance because there is an increase in growth terrain and novel varieties exploration [9].
A haploid base number of M. officinalis of x =
16 chromosomes is likely, diploid genotypes with
2n = 2
M. officinalis is a cross-pollinating species and has complete flowers with petals. Two stamens and four-lobed ovaries can give rise to 1–4 nutlets. The seeds are very small about 1–1.5 mm long, with ovate dark brown or black color. The weight of seeds is 0.5 to 0.7 g and they can be considered fragile as a long storage period (5 years) can induce a decrease in germination vigor [6, 8]. The plant possesses a highly branched root system, which guarantees the plant excellent adaptive capabilities; the upper parts of the plant perish at the beginning of the winter, while in spring new saplings re-emerge from the roots [7]. M. officinalis is cultivated all over the world, with the Mediterranean basin or Western Asia are considered as the area of origin [9]. There is a different opinion that suggests this plant is originated from a more wide area comprising South and Central Europe, Northern Africa, the Caucasus, and Northern Iran [11, 12]. M. officinalis occurs naturally in sandy and loamy fertile soils but sometimes can grow on moist wasteland from sea level to the mountains [5, 8, 12]. The plant prefers well-drained soils with a pH range from 5 to 7, it can grow in full sun, but also partial shade. When the plant grows in semi-shade, it produces bigger leaves compared to the sunny situation. This means that M. officinalis can promptly develop in a temperate environment (15 to 35 °C) necessitating at least 500 to 600 mm precipitation during all growing seasons. It suffers from drought, particularly in the establishment year, however after the root system is developed, requires a reduced amount of water [8]. The plant can be considered for easy cultivation and this reason can be suggested for beginners. In addition, given its adaptive capacities and strength, some gardeners consider it a weed [5].
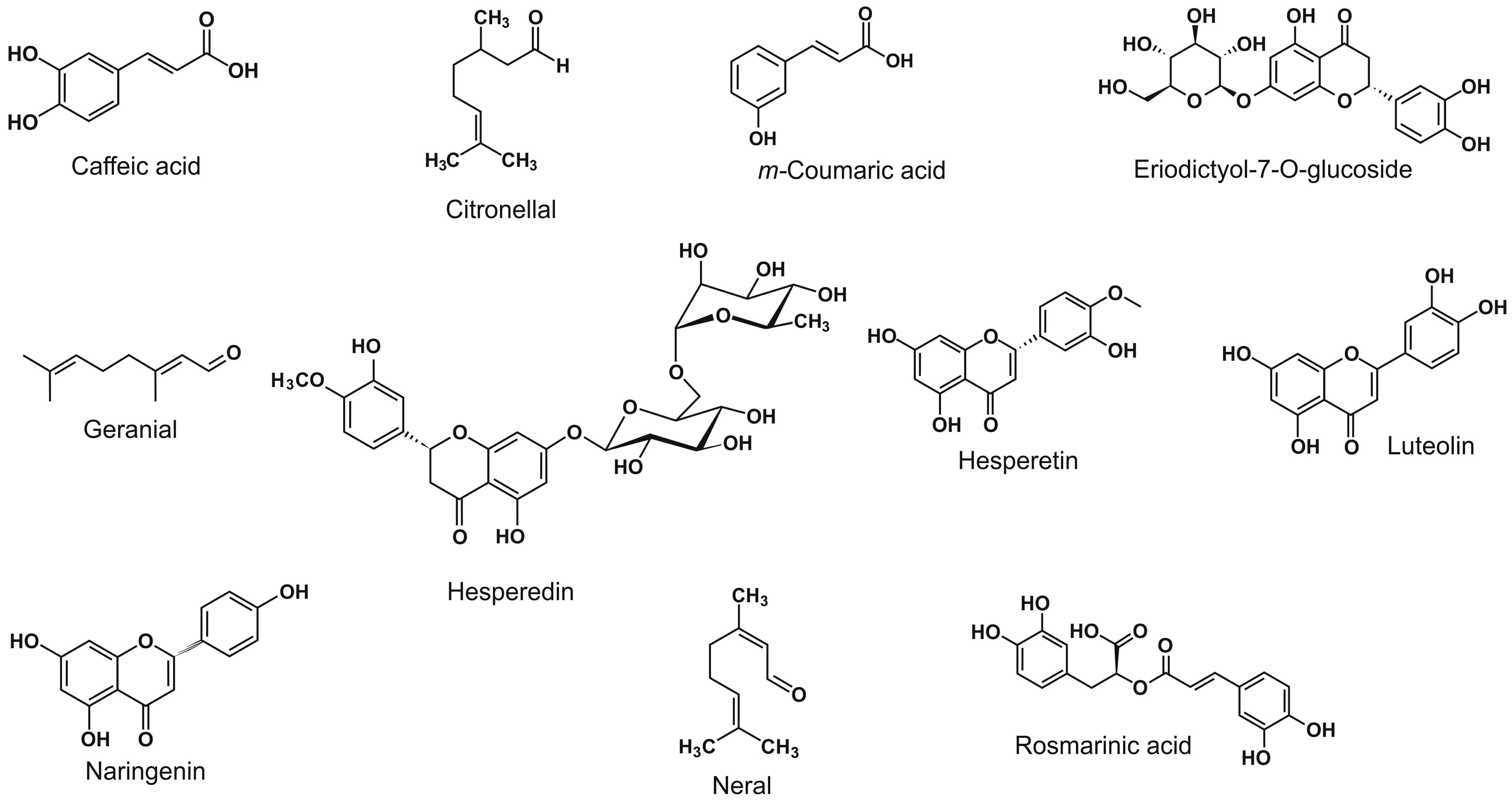
M. officinalis is widely used in food, medicine, and cosmetics. Its application is particularly related to the presence of valuable phytochemicals such as pleasant volatile compounds (e.g., Neral, geranial, citronellal), phenolic acids (e.g., rosmarinic acid), flavonoids (e.g., luteolin) and many others (Fig. 1). In 1998, Carnat and co-authors have reported that M. officinalis leaves contained 0.32% essential oil, 11.8% polyphenol compounds (hydroxycinnamic compounds 11.3%, RA 4.1%, and total flavonoid compounds 0.5%) [13]. Later, Shakeri and co-workers described that M. officinalis contained volatile compounds, triterpenoids, phenolic acids, and flavonoids [6].
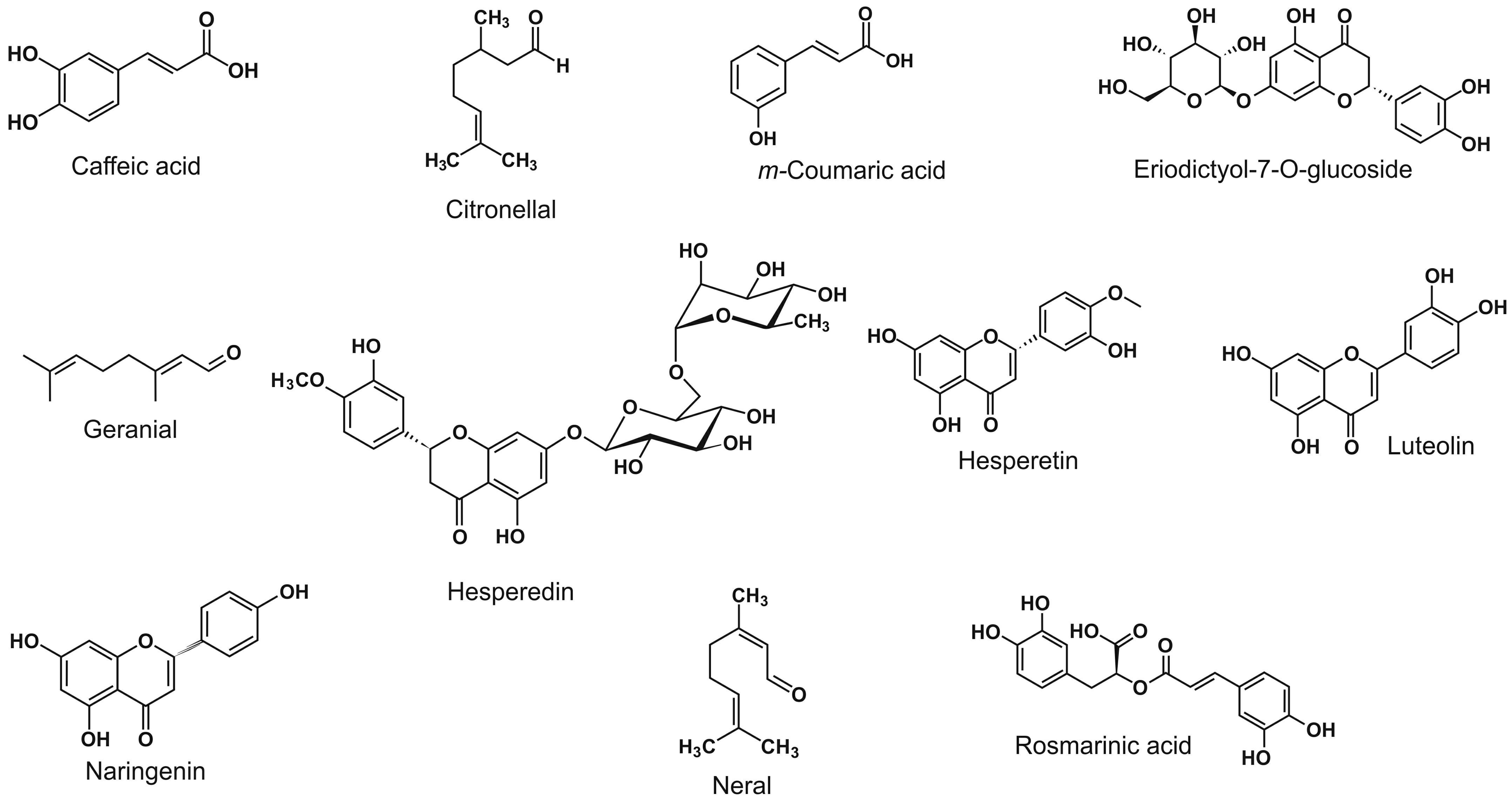 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.Chemical structure of the main phytochemicals of M. officinalis L.
The volatile compounds of M. officinalis have been intensively studied
in many countries. The chemical composition of volatile oils of M.
officinalis from different origins is represented in Table 1 (Ref. [2, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25]).
According to the literature reports, the major components of the M.
officinalis essential oils are mono-, sesquiterpenes, and aliphatic
aldehydes, alcohols such as geranial, neral, and citronellal, geranyl acetate,
(E)-caryophyllene, caryophyllene oxide, geraniol, pinene, sabinene,
thymol, carvacrol and muurolene, decadienal and trans-carveol [2, 6, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25]. The numerical cluster analysis has been carried out based on 15 major
essential oil components from thirty M. officinalis samples published in
the literature. Geranial/neral (I); geraniol/caryophyllene oxide (II);
citronellal (III);
| Origin | Plant’s part | Composition | References |
| Algeria | leaves | geranial (44.20%), neral (30.20%) and citronellal (6.30%) | [15] |
| Bulgaria | aerial parts | citronellal (18.5%), geraniol (15.2%), citronellol (9.5%), geranyl acetate (7.2%) and geranial (5.9%) | [16] |
| Egypt | aerial parts | geranial and neral (54.82%) | [17] |
| Greece | leaves | [18] | |
| Iran | flowers | trans-carveol (28.89%), citronellol (25.24%), δ-3-carene (5.26%), citronellal (4.9%), geraniol (2.2%), 1-octene-3-ol (2.03%) and spathulenol (2.06%) | [19] |
| Iran | aerial parts | geranyl acetate (27.9%), citral (24.2%), citronellal (8.4%), and citronellol (7.6%) | [2] |
| Iran | leaves | before flowering stage: decadienal (29.38%), geraniol (25.3%), caryophyllene oxide (8.75%), geranyl acetate (5.41%); in the flowering stage: decadienal (28.04%), geraniol (24.97%), caryophyllene oxide (7.55%), caryophyllene E (4.65%); and after flowering stage: carvacrol (37.62%), methyl citronellate (32.34%), geranyl acetate (5.82%), caryophyllene (5.50%) | [20] |
| Jordan | leaves | caryophyllene oxide (43.6%), muurolene (28.8%) | [21] |
| Poland | aerial parts | camphene, citronellal, neral, methyl citronellate, geranial, |
[22] |
| Romania | aerial parts | citral (neral and geranial) (16.10%), citronellal (3.76%) and trans-caryophyllene (3.57%) | [23] |
| Russia | aerial parts | citronellоl (36.71%), geraniol (27.20%) | [24] |
| Tajikistan | aerial parts | geranial (43.2%), neral (31.5%), (E)-anethole (12.3%), (E)-caryophyllene (4.0%) and citronellal (2.8%) | [14] |
| Turkey | aerial parts | citronellal (36.62–43.78%), citral (10.10–17.43%), thymol (0.40–11.94%), and |
[25] |
Several new triterpenes were discovered from M. officinalis. Mencherini
and others have been isolated six new ursane-type triterpenes from the leaves and
leaves of M. officinalis [26]. Recently, three new ursene triterpene
glycosides (melissiosides A–C) with promising antimicrobial actions have been
isolated from the aerial parts of M. officinalis [27]. In 2015, Ji and
co-authors isolated serratagenic acid,
2
Hanganu and co-authors (2008) have reported that M. officinalis leaves
contain 0.64% flavonoids expressed in rutoside and 8.962% phenyl-propane
derivatives expressed in caffeic acid [30]. Six polyphenolic compounds, i.e.,
caftaric acid, caffeic acid, p-cumaric acid, ferulic acid, luteolin, and apigenin
were identified from ethyl-ether, ethyl acetate, and 1-buthanol extracts of
M. officinalis leaves [30]. Toth and co-authors have reported that an
important phenolic active compound of M. officinalis was RA [31]. In
2002, Patora and Klimek isolated for the first time a new glycoside compound,
7-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside-3’-O-beta-D-glucuronopyranoside from the leaves of
M. officinalis [32]. In 2015, Ji and co-authors isolated thirteen
compounds, including protocatechuyl aldehyde, vanillin, luteolin, rosmarinic
acid, luteolin-7-O-
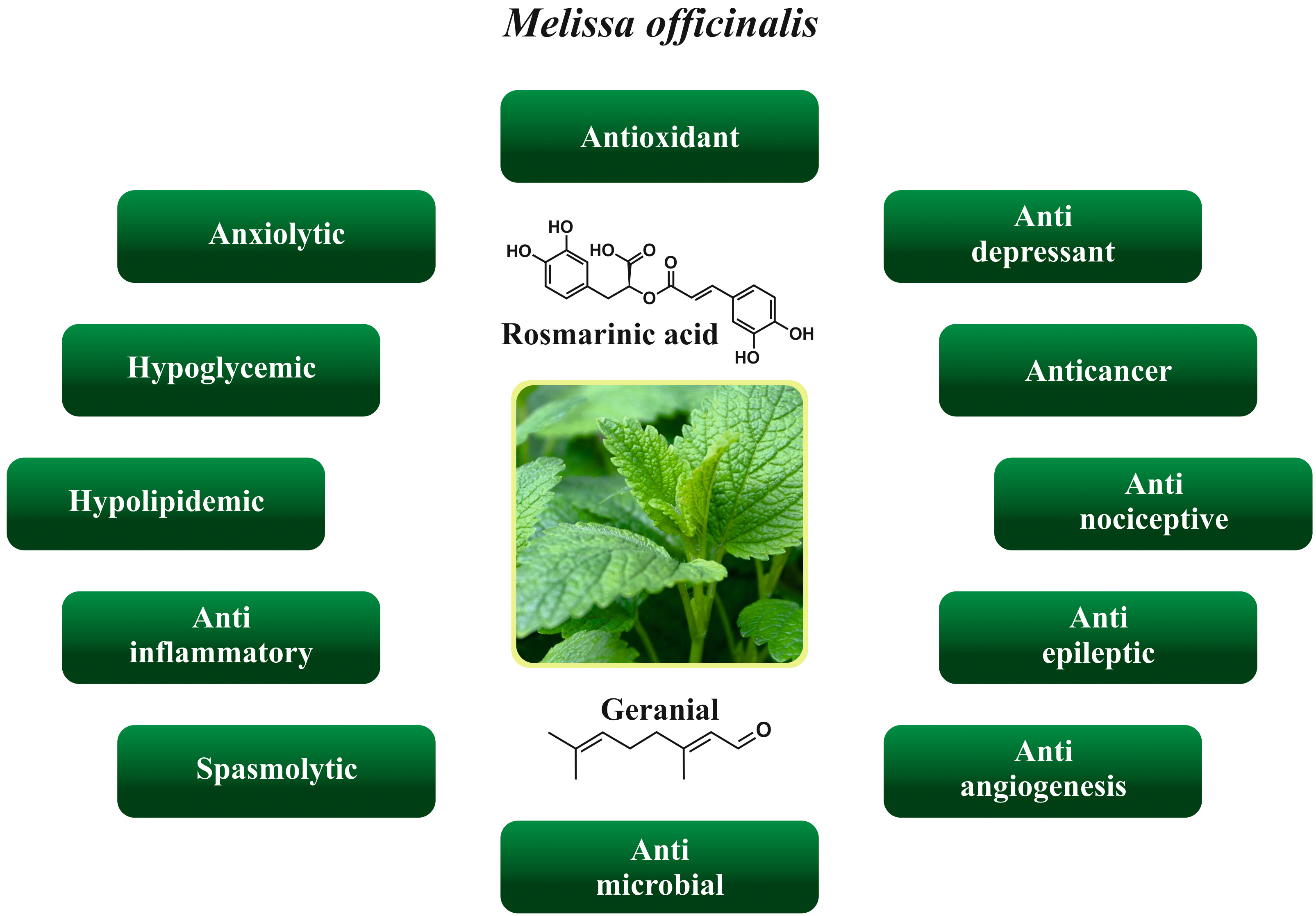
The Melissa officinalis possess diverse biological and health properties such as anxiolytic, antioxidant, antidepressant, anticancer, antinociceptive, anti-epileptic, anti-angiogenesis, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, hypolipidemic, and hypoglycemic. Various health properties of the Melissa officinalis are depicted in Fig. 2.
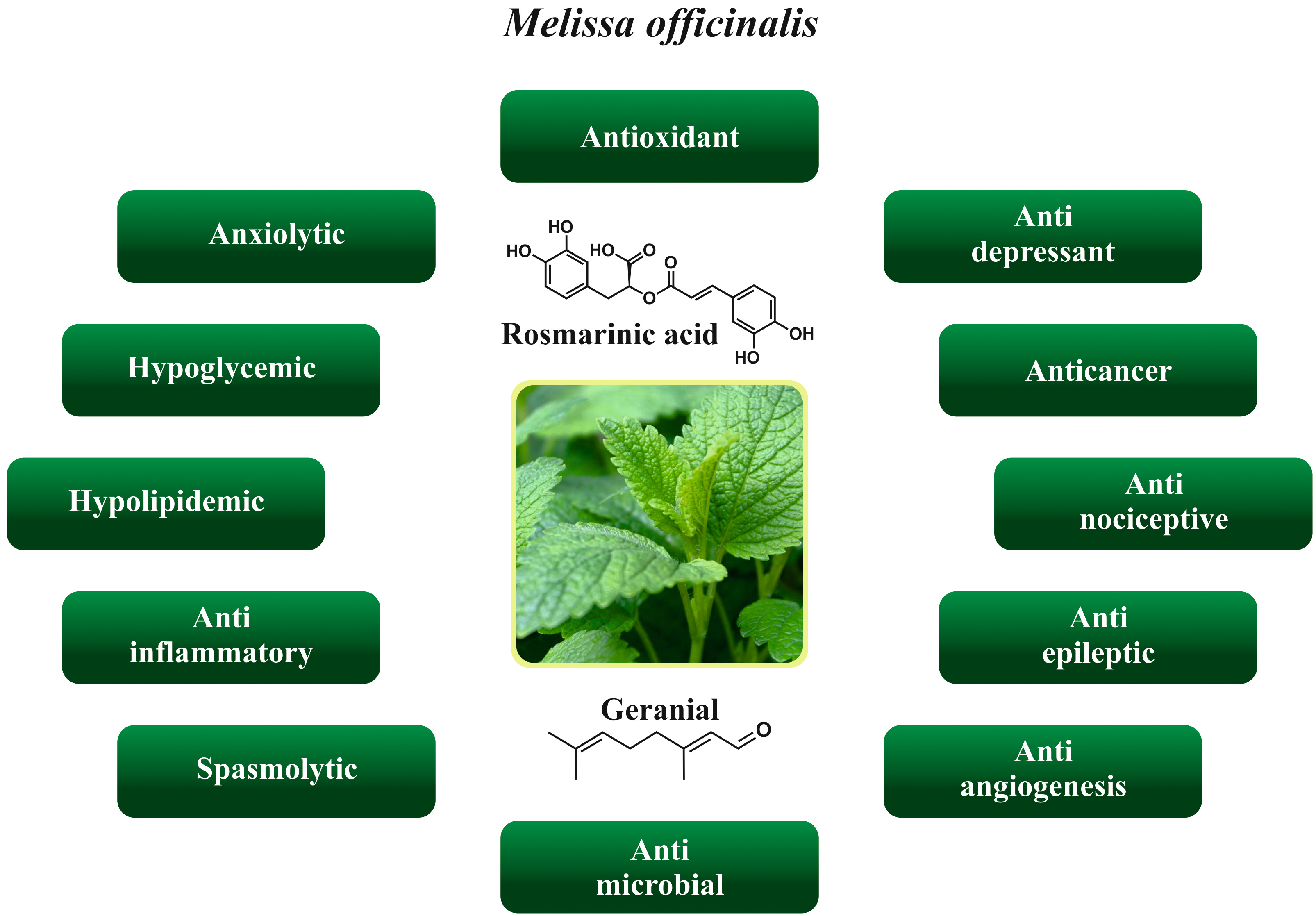 Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.Various health properties of the Melissa officinalis.
COVID-19 has been defined as a pandemic on 11 March 2020 and entered the fifth
position of the most important and documented pandemics since the 1918 influenza
outbreak [34]. Worldwide researchers and clinicians hardly worked to find
effective therapies and develop vaccines to reduce and prevent infectivity.
Plants’ bioactive compounds represent a major field of research for the
development of safe and effective treatments potentially useful to fight against
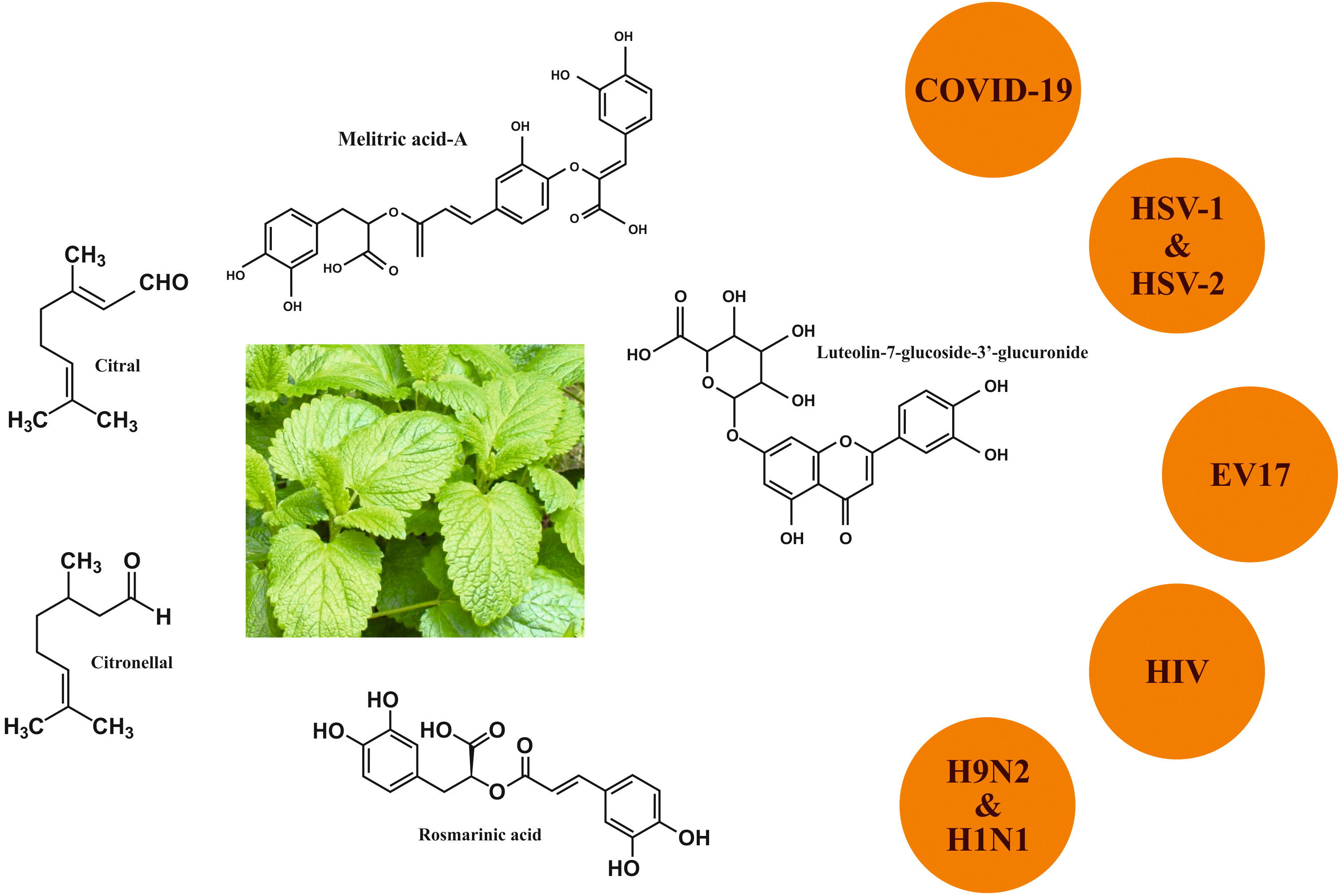
COVID-19. Several studies showed that M. officinalis possessed antiviral
activity against a wide number of viruses (Fig. 3) [35]. Today’s research aims to
recognize its antiviral bioactive compounds against the main protease and spike
protein of COVID-19. Docking experiments conducted by Prasanth and his colleagues
showed that three phytoconstituents from M. officinalis, namely,
luteolin-7-glucoside-3
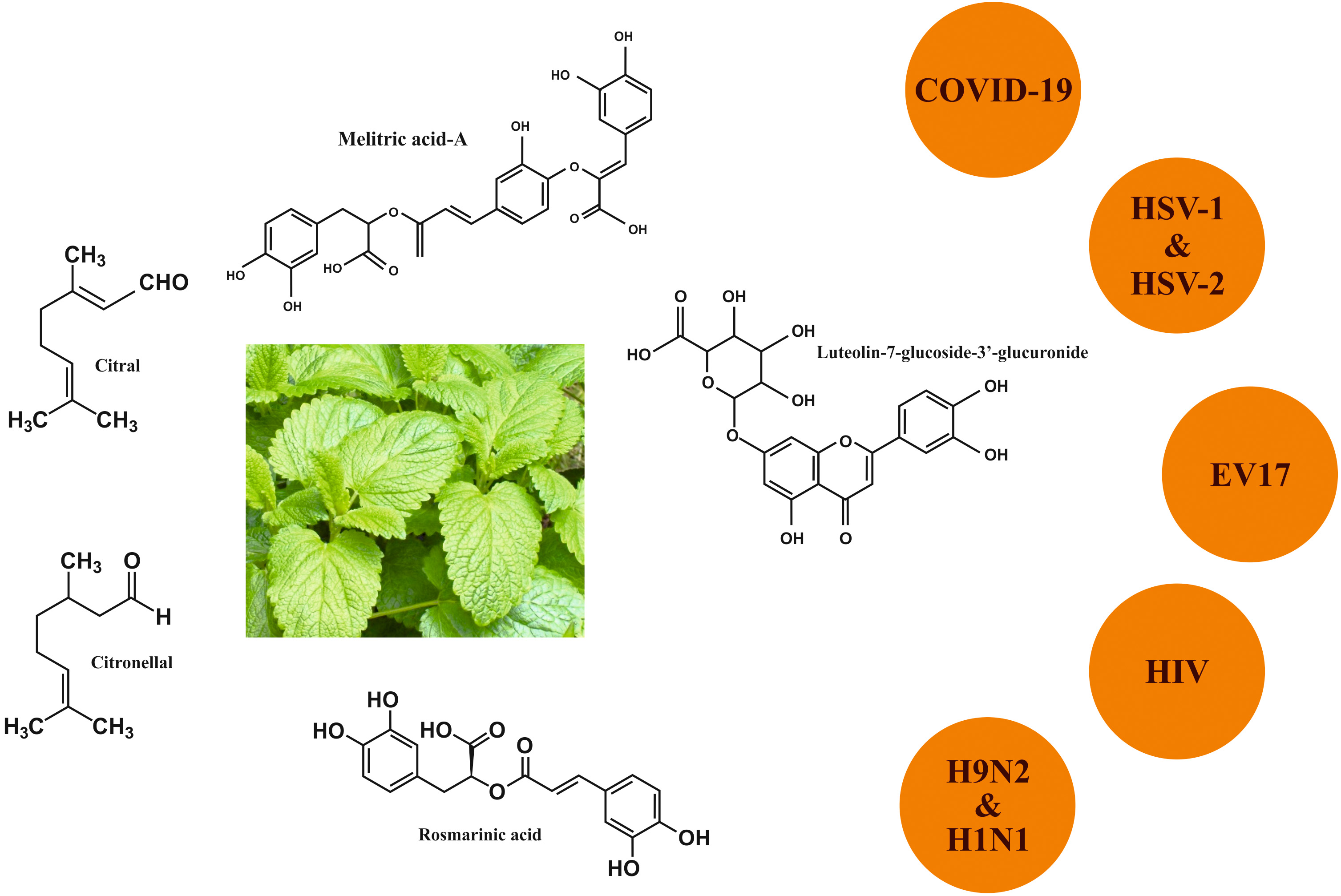 Fig. 3.
Fig. 3.Anti-viral activity of Melissa officinalis L.
Influenza viruses that belong to a virus family known as Orthomyxoviridae are also a target of the active ingredients of M. officinalis. The H9N2 subtype virus, a member of the influenza family that has been classified as a low pathogenic virus, had unfortunately developed viral resistance to all the conventional drugs approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) [38, 39]. Recent findings showed that M. officinalis essential oil (monoterpenaldehydes citral a, citral b) could inhibit influenza virus replication by different mechanisms of action such as masking the host cellular surface protein, intracellular steps, and direct virucidal effect by structural damage [40]. It was also demonstrated that the combination of M. officinalis essential oil with oseltamivir augmented the inhibitory effect of the antiviral drug particularly at very low concentration (0.005 mg/mL) [40]. Similar results on the effect of the hydroalcoholic extract of M. officinalis on the growth of influenza virus subtype H1N1 in the MDCK cell culture were demonstrated by Jalali et al. [41].
Antiviral activity of extracts from M. officinalis has also been
described for herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) and type 2 (HSV-2) [42, 43].
Astani et al. [44] evaluated the antiviral activity of M.
officinalis extract by choosing active phenolic compounds against HSV-1 and
investigating their mechanism of action. They found that both the aqueous
M. officinalis extract and the phenolic molecules significantly
decreased the infectivity of HSV-1 at the early stage of virus replication. This
action was mainly due to the inhibition of herpes viral attachment caused by the
predominant phenolic compound in M. officinalis extract RA at a
concentration of 9.75
Worldwide HIV in 2019 affected approximately 38 million people, mainly adults
(36.2 million) and 1.8 million children (
Enterovirus 71 (EV71) is one of the major pathogens causing Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) in infants and children aged under 5 [49]. A small proportion of EV71-infected patients develop severe complications that can lead to death which urge the progress toward novel drugs affecting patients’ medical history [50]. It has been reported that M. officinalis extract (due to its high RA content) could block plaque formation and viral protein synthesis in EV71-infected cells, suggesting a cytopathic effect of this methanolic extract [51].
Generally, aromatic plants are rich in essential oils with significant
antimicrobial properties. GC-MS analysis revealed that the chemical composition
of the essential oils extracted from M. officinalis was citronellal
(37.33%), thymol (11.96%), citral (10.10%), and
E. coli ATCC 25922 and the multiresistant strain of Shigella
sonei IPH-MR exhibited high sensitivity to the essential oil of M.
officinalis [52]. The petroleum ether extract of M. officinalis
demonstrated varying inhibitory potencies against Gram-positive bacteria in
particular Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas
aeruginosa with MICs ranging between 1.65 and 191.40
Notably, essential oils revealed significant antifungal activity, even if not in
all cases. Prominent was the low MIC and MFC of the essential oil of M.
officinalis against Trichophyton tonsurans if compared to the reference
drug bifonazole (antimycotic) [52]. Also, the crude petroleum ether extract and
its derived fractions demonstrated remarkable antifungal activities
against Candida albicans, Candida krusei, and Candida
glabrata with MICs of 0.30–345.10
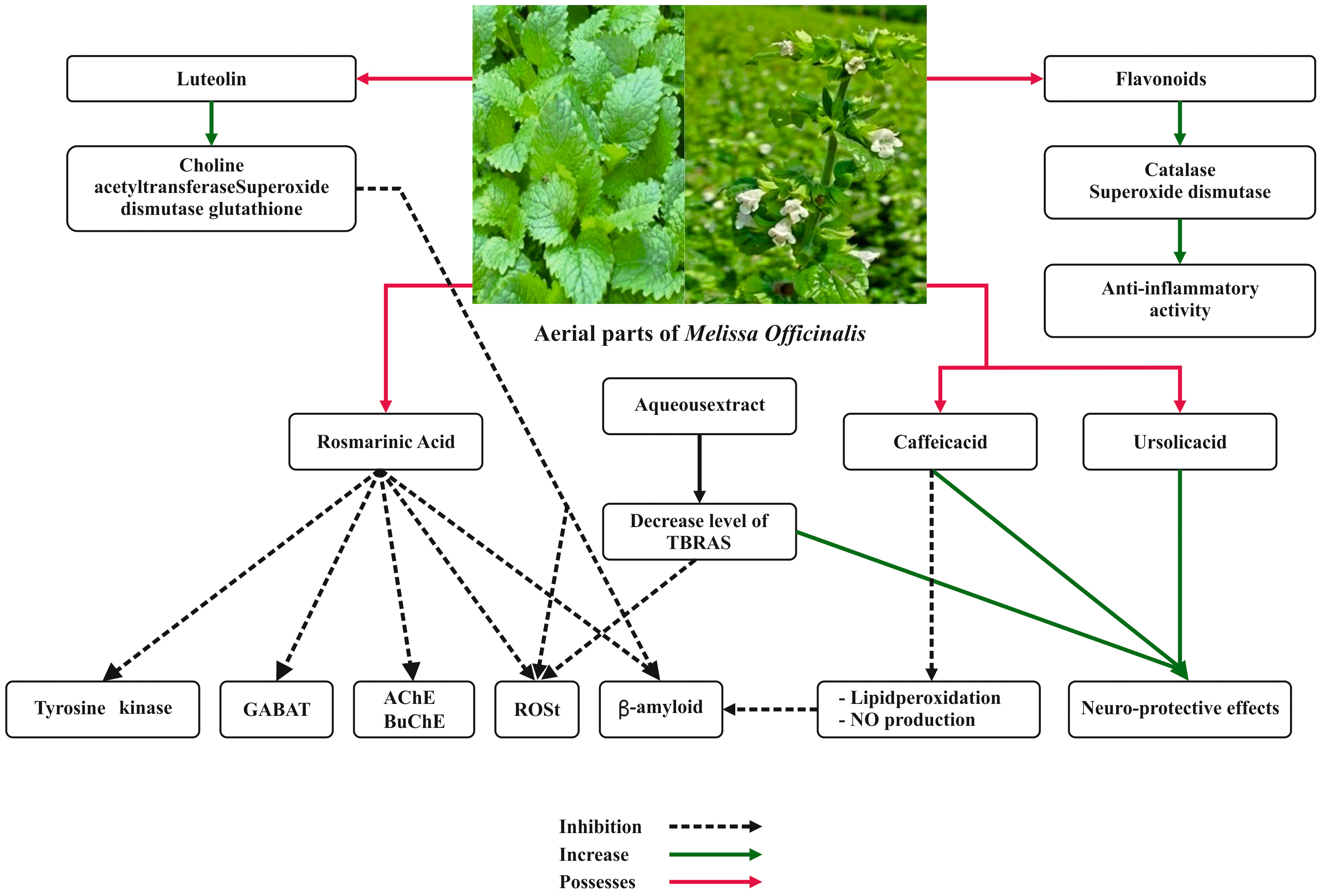
The anti-inflammatory activities of M. officinalis leaves were widely examined. Results showed that its essential oil possessed anti-inflammatory activities, supporting its traditional use in different diseases related to inflammation and pain [55]. Recent works proved that the extract of M. officinalis exerted anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive effects by interacting with muscarinic and nicotinic receptors and the L-arginine-nitric oxide pathway which were ascribable to RA, terpenoids, and flavonoids [56]. RA and flavonoids are known to block different enzymes involved in the inflammatory process, such as cyclooxygenase, lipooxygenase, and monooxygenase [57].
Due to these anti-inflammatory properties, the extract of M.
officinalis proved to have good effects in relieving symptoms of atopic
dermatitis [57]. The anti-inflammatory property of M. officinalis is
depicted in Fig. 4. Ramanauskien et al. [58] investigated the effect of
M. officinalis extract and its RA content on skin cells in normal
conditions and under oxidative stress. The work on human keratinocyte cells
showed that, in oxidative stress conditions, RA decreased intracellular ROS by
about 28%, while enhancing cell viability by 10–24% (at a concentration of
0.25–0.5 mg/mL) and protecting cells from H
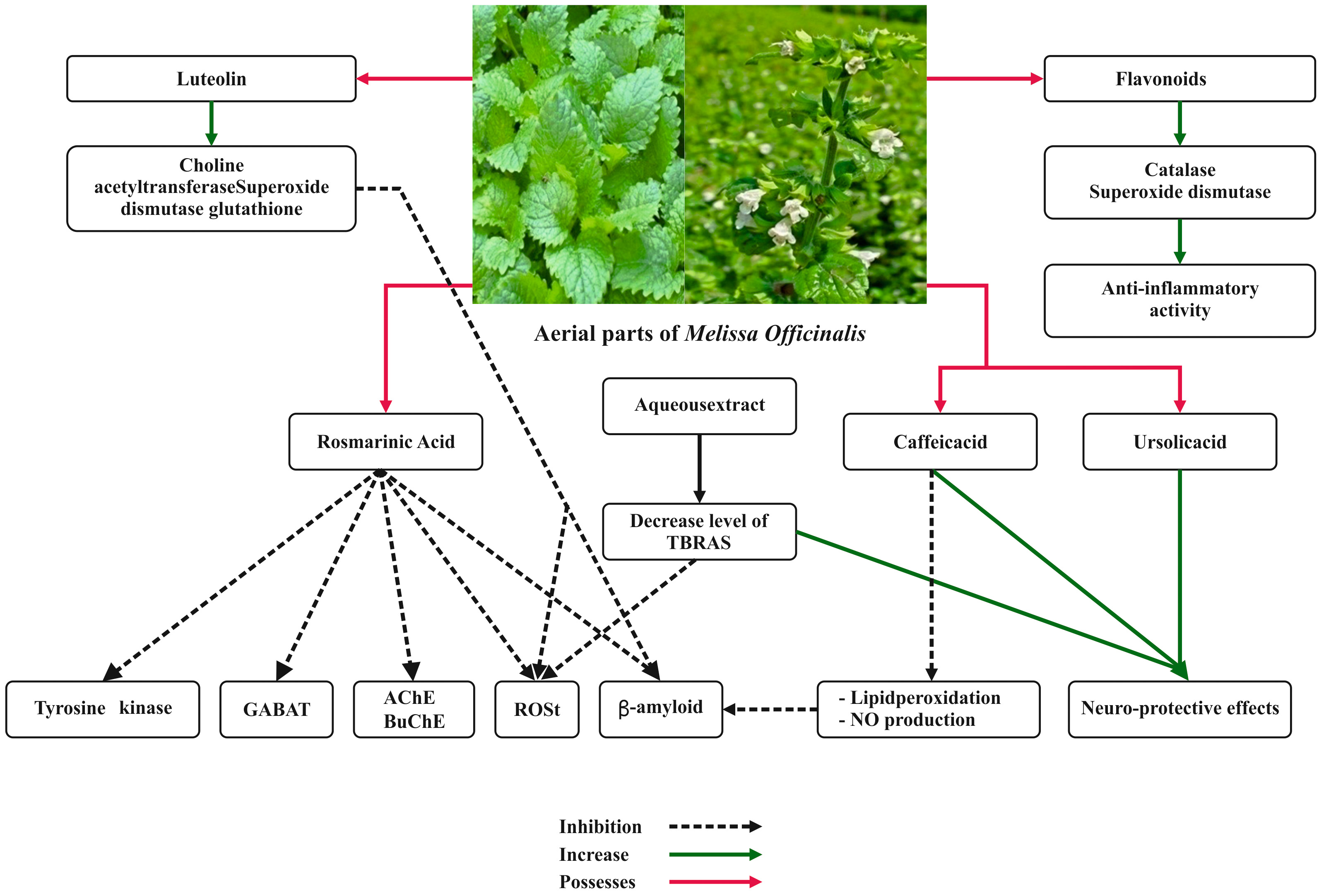 Fig. 4.
Fig. 4.Anti-inflammatory property and neuroprotective effects of Melissa officinalis L.
Anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive effects of M. officinalis were investigated with the histamine- and carrageenan-induced paw edema tests in rats and mice. It was found that pretreatment with the aqueous extract of M. officinalis considerably lessened inflammagen-induced paw edema in rats and diminished the nociceptive response in mice [59].
Müzell and his colleagues assessed the anti-inflammatory activity of an aqueous extract of M. officinalis in hepatic and renal lesions caused by acetaminophen in animal models [60]. Even if not hepatoprotective, the extract demonstrated a nephroprotective activity against acetaminophen lesions and exhibited an anti-inflammatory effect on carrageenan-induced pleurisy [60].
M. officinalis was also found to be a good source of chemopreventive
agents. Its extracts demonstrated cytotoxicity in breast cancer cells (MDAMB-
231) even at low concentrations (100
The number of people suffering from neurological disorders such as
neurodegenerative diseases as well as psychiatric ones has lately increased
worldwide [62]. M. officinalis has traditionally been used for its
impact on the nervous system owing to elevated contents of phenolic compounds and
tocopherols [52]. Both crude ethanol extract of M. officinalis and its
fractions blocked acetylcholinesterase in vitro and in vivo [63, 64, 65]. Similarly, methanol and aqueous extracts of M. officinalis
possessed a significant protective effect on hydrogen peroxide-induced toxicity
in PC12 cells mainly due to monoamine oxidase inhibition [66]. In addition, the
effects of an ethanol extract of M. officinalis were tested in the
hippocampus of pilocarpine treated rats, as a potential model of epilepsy [67].
In particular, the antioxidative and anti-inflammatory activity of the extract
orally administered at 250 mg/kg impacted positively on Nrf2/HO-1 signaling
pathway, Na
Hassanzadeh et al. [68] reported that aqueous extract of M. officinalis could support neuroprotective effects against ecstasy-induced neurotoxicity in hippocampal primary culture. In addition, Yoo and his colleagues proved that oral administration of M. officinalis could augment differentiation and cell growth by lessening serum corticosterone while boosting GABA levels in the mouse dentate gyrus [69].
The effect of M. officinalis on hypoxia-induced neuronal death in a
cortical neuronal culture system was tested both in vitro and
in transient hippocampal ischemia in vivo models [70]. Cytotoxicity
assays showed significant protection of M. officinalis against hypoxia
in cultured neurons by decreasing caspase3 activity and TUNEL-positive cells
significantly. M. officinalis oil was found to inhibit malondialdehyde
levels and attenuate the decrease of the antioxidant capacity in the hippocampus.
Pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-
M. officinalis extracts have been proved in clinical trials focused on
a variety of diseases, mainly related to neurological disorders, i.e., anxiety
and sleeping difficulties, but also metabolic problems and infantile colic.
M. officinalis has been used as a cure for memory, cognition, anxiety,
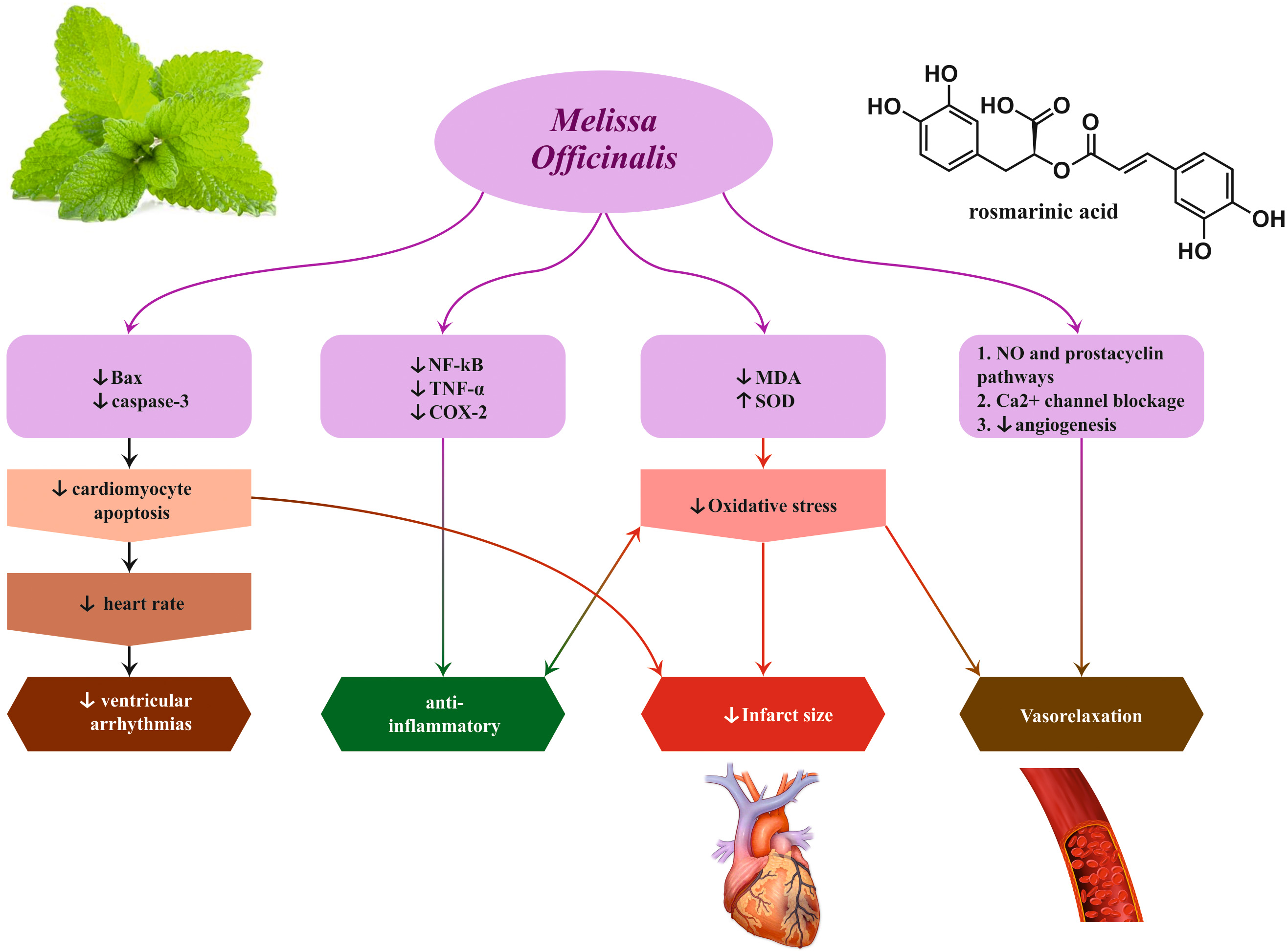
depression, and heart palpitations for many centuries. Preclinical animal studies
on this plant confirmed its evocative cardiovascular effects including anti
arrhythmogenic, negative chronotropic and dromotropic, hypotensive, vasorelaxant,
and infarct size–reducing, by the use of different extracts (aqueous, alcoholic,
and hydroalcoholic), essential oil, or isolated compounds. Nonetheless, only the
effectiveness of M. officinalis on heart palpitations has been verified
in humans. Antioxidant free radical–scavenging properties, oxidative stress
modulation, anti-inflammatory effects, activation of M2 receptors and antagonism
of
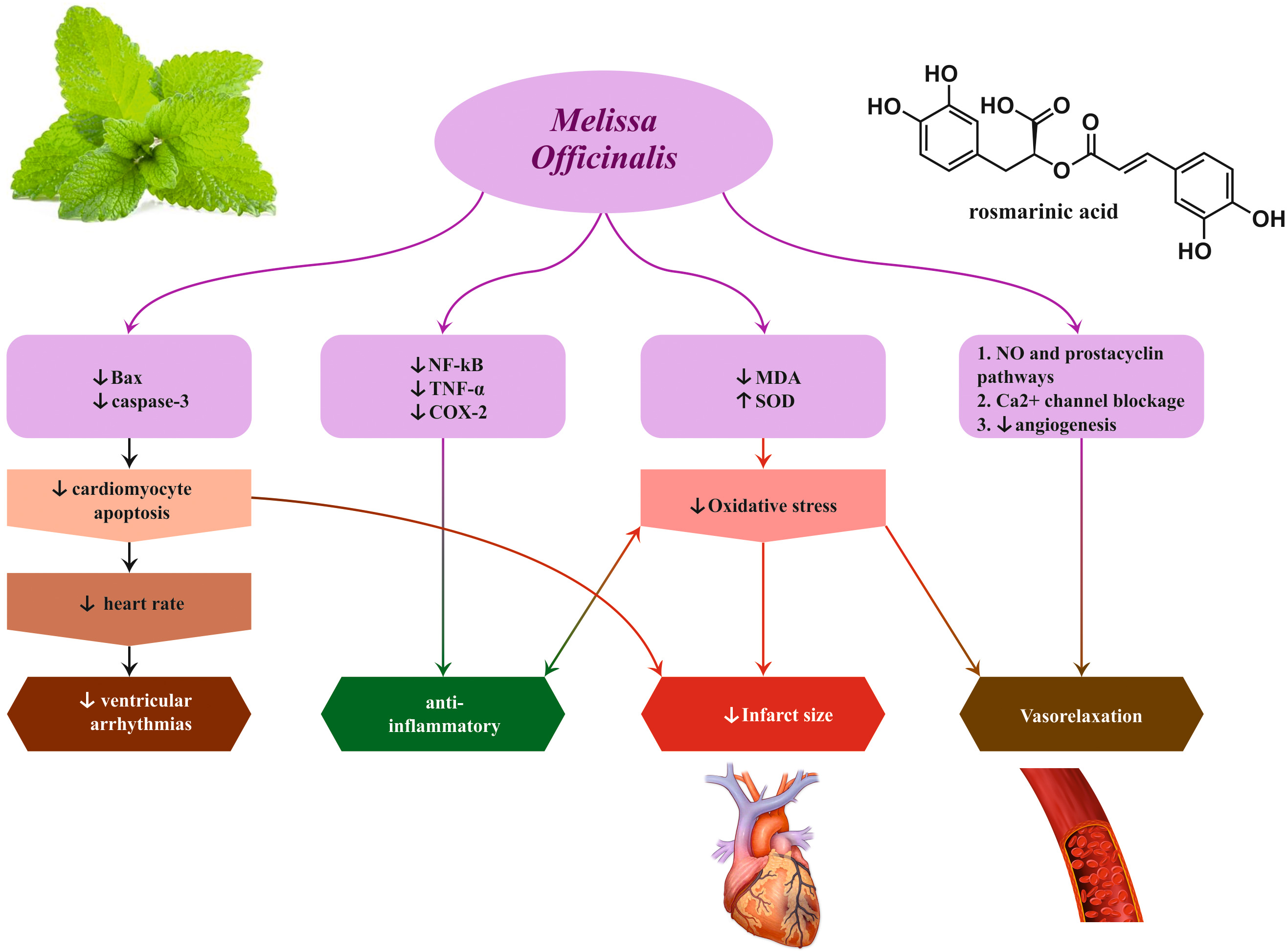 Fig. 5.
Fig. 5.Cardio-protective effects induced by Melissa officinalis L.
For the neurological effects, some authors investigated in the UK addressed the improvement of memory and brain function in healthy people by applying a combination of Salvia officinalis L., Rosmarinus officinalis L., and M. officinalis (SRM) [78]. The work showed that an oral administration of M. officinalis combination at a dose of 5 mL twice a day for 2 weeks was more effective compared to placebo. Araj-Khodaei et al. [79] with a study on neurological disorders used M. officinalis to treat 45 adult outpatients who met the diagnosis (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders) for major depression, and were randomly assigned to 3 groups to daily receive either 2 g of M. officinalis or 2 g of Lavandula angustifolia Mill. or also fluoxetine (20 mg) and were assessed until 8 weeks [79]. Although the results were promising (usefulness of the extracts in moderate depression), the absence of a placebo group was relevant for the conclusion of the study, suggesting that more work is necessary to support the use of these plants to treat depression.
Other authors, researched neurological disorders [80]. An M. officinalis extract enriched in RA was tested in a randomized placebo-controlled double-blind 24-week trial by evaluating the safety and tolerability (primary endpoint) of RA (500 mg daily) and its clinical effects and disease-related biomarker changes (secondary endpoints). The group of patients (n = 23) was affected by mild dementia as a result of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). The outcomes demonstrated that no difference in vital signs or physical and neurologic examination was perceived between the placebo and M. officinalis groups. In addition, no severe adverse effects were found while the cognitive function was not modified in both groups. The authors concluded that M. officinalis extract (500 mg of RA taken daily) was safe and well-tolerated for AD patients. Therefore, these data suggested that RA can impact AD neuropsychiatric symptoms and can stop the deterioration of AD patients’ conditions. Even though these investigations have been recent, it should be noted that several studies on the effect of M. officinalis to treat neurological disorders were reported more than a decade ago. Burns et al. [81] carried out a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial to study the effect of M. officinalis oil against agitation in AD. However, aromatherapy with M. officinalis oil was not effective. Also, years before, Kennedy et al. [82] conducted a similar study. In this case, the authors analyzed the effects of M. officinalis on the modulation of mood and cognitive performance [82]. High doses of M. officinalis (1600 mg) could improve cognitive performance. Other researchers conducted a similar study focusing on the efficacy and safety of M. officinalis extract in mild to moderate AD patients [83]. The use of 60 drops per day demonstrated an improvement in cognitive function after 4 months of treatment.
Other researchers have reported that M. officinalis could impact anxiety or sleep disorders. Indeed M. officinalis leaves (Melissa capsule) were evaluated on anxiety and sleep quality in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass surgery [84]. Eighty patients were administered three times a day with an herbal drug (500 mg of M. officinalis leaves) or a placebo (500 mg of wheat starch). Forty-nine % of the patients reduced their anxiety levels at seven days and 54% improved their sleep quality [84]. Other authors showed that M. officinalis essential oil was effective in reducing agitated behavior in the elderly affected or not by dementia [85]. The study was conducted in a nursing home recruiting 39 patients affected by dementia and 10 control patients (no dementia). Treatment was given for two weeks followed by a two-week washout period before starting subsequent treatment. The results of the study suggested that M. officinalis essential oil could effectively decrease anxiety, however in patients without dementia.
Tavares-Silva and collaborators proved the usefulness of M. officinalis and Phytolacca americana L. (syn. Phytolacca decandra L.) alone or in combination, in children affected by sleep bruxism [86]. Fifty-two children participated in this trial, where M. officinalis reduced sleep bruxism up to 30 days after treatment. Another research group also discovered the combination of M. officinalis and Nepeta menthoides Boiss. & Buhse in sleep disorder [87]. The trial evaluated 80 patients treated with the 1000 mg dose of M. officinalis plus 400 mg of N. menthoides or a placebo for four weeks. The study established that a combined regimen possessed a substantial activity against insomnia.
In other studies carried out in Iran and UK through randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials, high response to the use of M. officinalis to treat anxiety was observed. In the study conducted by Alijaniha et al. [88] M. officinalis extract was tested against heart palpitation. Leaf extract of M. officinalis (500 mg two times per day up to 14 days) considerably lessened the incidence of anxiety and palpitation, while no side effect was reported. Similarly, in the UK, two studies were carried out on the use of M. officinalis for anxiety problems. In the first one, the effects of M. officinalis on laboratory-induced psychological stress were examined using a 600 mg dose of herbal extract. This dose decreased the negative mood effects of the defined intensity stressor simulation while augmenting the self-ratings of calmness [89]. In the other work, the anxiolytic effect of the herbal combination was assessed during laboratory-induced stress [90]. In this case doses of 80 mg of M. officinalis and 120 mg of Valeriana officinalis L. improved the negative effects of the defined intensity stressor simulation on ratings of anxiety. It is worth noting that another study tested the effects of “cyracos” (standardized extract of M. officinalis) in anxiety disorders and sleep disturbance [91]. Long-lasting administration of this extract cyracos (600 mg per day up to 15 days) diminished the stress-related effects, such as insomnia (42%), anxiety (18%), and anxiety-associated symptoms (15%).
However, the use of M. officinalis has not only been studied for neurological disorders or patients suffering from anxiety and stress. Some other studies were redirected to other problems. Darvish-Mofrad-Kashani and collaborators studied the response of M. officinalis in behavior modifications [92]. In this work, the efficacy and safety of M. officinalis in improving hypoactive sexual desire disorder in 89 women were evaluated. The treatment doses were 500 mg per day of aqueous extract of M. officinalis or placebo. Results demonstrated that M. officinalis extract at 4 weeks significantly increased desire, arousal, lubrication, orgasm, satisfaction, and pain scores compared to placebo in hypoactive sexual desire disorder in women. Other investigations were conducted on the use of M. officinalis by diabetic patients or for the treatment of metabolic disorders. Nayebi et al. [93] described the potential effect of M. officinalis in diabetic patients (type 2). The work analyzed 37 dyslipidemic diabetic patients treated or not with 500 mg capsules per day for up to 3 months. M. officinalis could significantly reduce only serum triglyceride level, while no other metabolic alteration was noted if compared to the control group. Another group of researchers also tested the hydroalcoholic extract of M. officinalis in type 2 diabetic patients. The clinical trial was conducted with 62 patients treated with M. officinalis or placebo of 700 mg per day twice for 12 weeks. M. officinalis caused a substantial modulation in fasting blood sugar, glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), and systolic blood pressure [94]. On the same line, M. officinalis were suggested to modify biomarkers of oxidative stress, inflammation, and lipid profile in patients with stable chronic angina [95]. Indeed, 80 patients participated in this clinical trial and were challenged with a dose of 3 g per day for 8 weeks. M. officinalis capsules significantly ameliorated the lipid profile, malondialdehyde (MDA), highly sensitive c-reactive protein (hs-CRP) and PNO1 in patients with stable chronic angina. More recently, M. officinalis was studied in systolic and diastolic blood pressures of 49 hypertensive patients, receiving 400 mg/d capsules of the extract for 4 weeks [96]. The plant was able to significantly reduce blood pressure (systolic and diastolic) up to the follow-up period of 10 weeks in this double-blind, controlled, randomized crossover study. Furthermore, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial with supplementation of M. officinalis evaluated borderline hyperlipidemia patients [97]. Herbal capsules of M. officinalis exhibited interesting results in hyper-lipidemic patients, reducing low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and aspartate transaminase (AST) in patients treated with 500 mg of M. officinalis.
Finally, we must highlight the studies carried out with this plant to treat infantile colic. Martinelli et al. [98] demonstrated the effectiveness of Matricaria chamomilla L., M. officinalis, and Lactobacillus acidophilus tyndallized (HA122) in infantile colic. The children (n = 176) were treated for up to 28 days. Crying time was significantly shorter in the group that received M. chamomilla, M. officinalis, and L. acidophilus tyndallized than the group that received only Lactobacillus reuteri or simethicone. Similar to the previous work, another study investigated the effectiveness and side effects of M. officinalis associated or not with Matricariae recutita and Foeniculum vulgare in infantile colic during one-week treatment. Again crying time was lessened in 85.4% of subjects compared to control (48.9%) while no side effects were reported [99].
The use of M. officinalis for various diseases, from neurological, metabolic disorders to infantile colic opens a new insight into scientifically supported treatments.
As for numerous plants, also M. officinalis can exert toxicity if not optimally used.
An aqueous extract of M. officinalis exhibits showed low toxicity on
RC-37 cells a cultured line derived from African green monkey kidneys, with a
50% cytotoxic concentration of 350
M. officinalis leaves essential oil extract showed no acute toxicity in rats treated with 2000 mg/kg [30]. The oral administration of aerial parts essential oil of M. officinalis presents the oral LD50 in BALB/c mice (2.57 g/kg). This oil altered animal behavior and liver and kidney biochemical parameters at doses higher than 1 g/kg in BALB/c mice. Besides, an increased rate of lipid peroxidation and a depletion of antioxidant capacity of the liver and kidney suggest moderate toxicity [106]. M. officinalis whole methanolic and aqueous extracts were found to be safe or non-toxic to rats up to 2000 (mg/kg b.wt.) with no mortality in swiss albino mice [107]. This suggests that the organic extracts of M. officinalis are less toxic through the oral route than the essential oil extracts irrespective of the plant parts. In addition, M. officinalis aqueous extract showed to cause genotoxic and histopathologic damage to the liver, kidneys, heart, and spleen if consumed by Oncorhynchus mykiss fish at doses greater than 450 mg/kg [108], while ethanolic extract showed no antigenotoxic/antimutagenic properties in Swiss albinos mice at 100–250 mg/kg [109]. However, the European Commission, the Panel on Additives and Products or Substances used in Animal Feed could not conclude on the safety of the use of a dried aqueous ethanol extract of M. officinalis leaves as a sensory feed additive for all animal species [110]. On the other hand, a randomized controlled trial using a single dose of M. officinalis extract comprising 500 mg rosmarinic acid, showed to be harmless and well tolerable in healthy humans [111]. This is confirmed by randomized clinical trials where different treatment regimens of M. officinalis extracts also showed no adverse effects in humans [83, 93, 94, 112]. Overall, though M. officinalis toxicity data are scarce and have been poorly investigated despite the variety of practical applications in medical science, available data point out its putative safety in human beings.
M. officinalis is a medicinal plant with numerous health properties and is a curative tool for fighting cardiovascular, neurological, and psychological disorders. Nonetheless, M. officinalis is commonly known and prevalently used for anti-anxiety and anti-depression properties, particularly in the acute setting (among the general population M. officinalis is used to calm and relax). As reported in this work, this plant can be useful also in other human conditions, such as palpitation, hypertension, dementia, infantile colic, bruxism, metabolic problems, Alzheimer’s disease, and sexual disorders. Even if the therapeutic effects of M. officinalis are well documented and studied, its current use in clinical settings is scarce and anecdotic. Thus this work wants to fill in this gap and suggest clinicians, general practitioners, physiotherapists, and interested people expand the rational use of this recognized curative plant. From a pharmacological point of view, M. officinalis possesses a wide number of remarkable properties, i.e., antiviral, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, neuroprotective among the most common. In particular, antiviral activity is of current interest, because COVID-19 pandemia is still taking its toll and in the future, we will need new therapeutic tools to fight this disease, even in the perspective to co-exist with the SARS-CoV-2 virus. Moreover, given its safety — it is generally well tolerated having no relevant side effects, only occasionally headache, vomiting, abdominal pain, nausea have been reported — M. officinalis should be considered in general medicine to increase its use. Medicinal plants should be considered a powerful means to cure human conditions: this review sheds new light on the potential of M. officinalis and encourages researchers to increase the therapeutic possibilities of this medicinal plant.
WZ, CQ, JSR, MDL, MS, MM, FS, PVTF, APM, DC, MK, JTC, RP contributed to the manuscript. WZ, CQ, JSR, MDL, MS, MM, FS, PVTF, APM, DC, MK, JTC, RP collected resources and were responsible for data curation and writing. Literature review analysis was performed by WZ, CQ, JSR, MDL, MS, MM, FS, PVTF, APM, DC, MK, JTC, RP. Reviewing and editing were carried out by JSR and RP. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
This research received no external funding.
The authors declare no conflict of interest. JTC is serving as one of the Guest Editor of this journal. We declare that JTC had no involvement in the peer review of this article and has no access to information regarding its peer review. Full responsibility for the editorial process for this article was delegated to GCA.