- Academic Editor
-
-
-
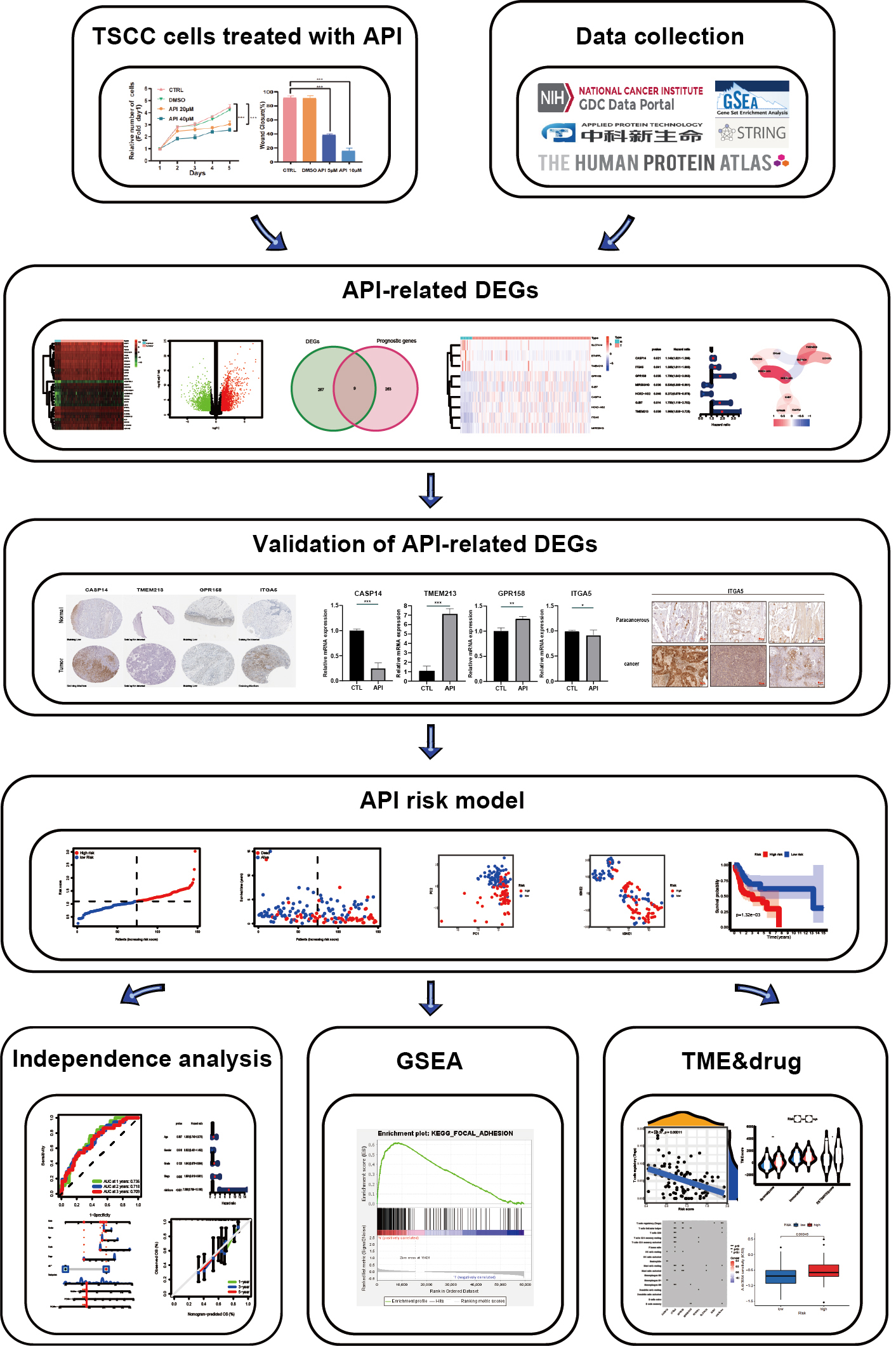
Background: Clinical indexes are often selected as relevant factors for constructing prognostic models of tongue squamous cell carcinoma (TSCC) patients, while factors related to therapeutic targets are less frequently included. As Apigenin (API) shows anti-tumor properties in many tumors, in this study, we construct a novel prognostic model for TSCC patients based on Apigenin-associated genes through transcriptomic analysis. Methods: The effect of Apigenin (API) on the cell characteristics of TSCC cells was measured by several phenotype experiments. RNA-seq was executed to ensure differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in squamous cell carcinoma-9 (SCC-9) cells after API treatment. Furthermore, reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) and immunohistochemistry were performed to verify the expression of API-related genes. Then, combined with the gene expression data and relevant individual information of TSCC samples acquired from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), an API-related model was built through Lasso regression and multivariate Cox regression. A receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve and a nomogram and calibration curve were created to forecast patient outcomes to improve the clinical suitability of the API-related signature. The relationships between the two risk groups and function enrichment, immune infiltration characteristics, and drug susceptibility were analyzed. Results: We demonstrated that API could inhibit the malignant behavior of TSCC cells. Among API-related genes, TSCC cells treated with API, compared to the control group, have higher levels of transmembrane protein 213 (TMEM213) and G protein-coupled receptor 158 (GPR158), and lower levels of caspase 14 (CASP14) and integrin subunit alpha 5 (ITGA5). An 7 API-associated gene model was built through Lasso regression and multivariate Cox regression that could direct TSCC prognostic status and tumor immune cell infiltration. In addition, we acquired 6 potential therapeutic agents for TSCC based on the prognostic model. Conclusions: Our research suggested the inhibition effect of API on TSCC cells and provided a novel prognostic model combined with therapeutic factors that can guide the prognosis of TSCC and clinical decision-making in TSCC.