- Academic Editor
-
-
-
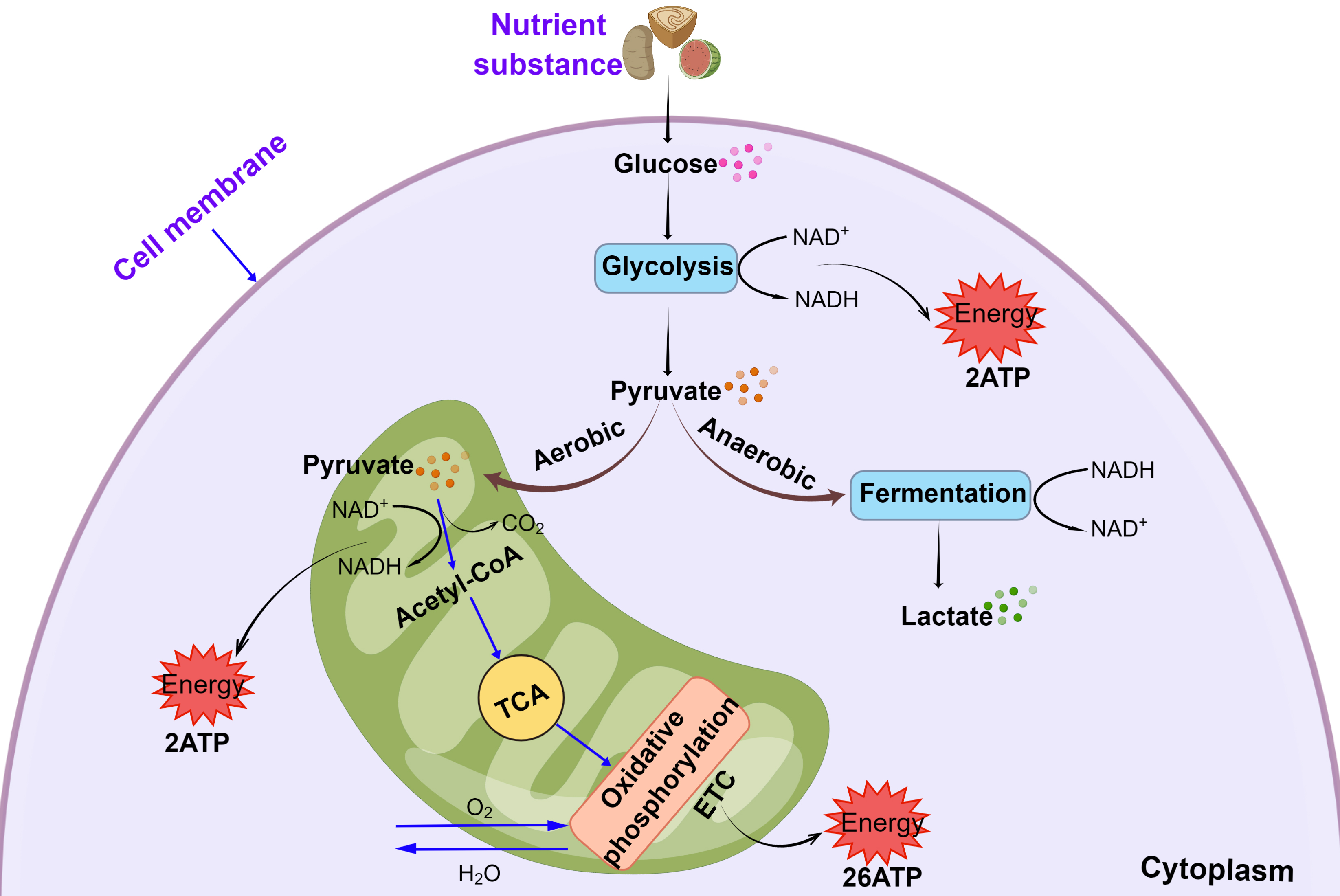
Vascular diseases are amongst the most serious diseases affecting human life and health globally. Energy metabolism plays a crucial role in multiple vascular diseases, and the imbalance of energy metabolism in cells from the blood vessel wall can cause various vascular diseases. Energy metabolism studies have often focused on atherosclerosis (AS) and pulmonary hypertension (PH). However, the roles of energy metabolism in the development of other vascular diseases is becoming increasingly appreciated as both dynamic and essential. This review summarizes the role of energy metabolism in various vascular diseases, including AS, hemangioma, aortic dissection, PH, vascular aging, and arterial embolism. It also discusses how energy metabolism participates in the pathophysiological processes of vascular diseases and potential drugs that may interfere with energy metabolism. This review presents suggestions for the clinical prevention and treatment of vascular diseases from the perspective of energy metabolism.