†These authors contributed equally.
‡These authors contributed equally.
Background: The infection and negative effects of the SARS-CoV-2
(severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus) virus are mitigated by vaccines.
It is unknown whether vaccination has worked by eliciting robust protective
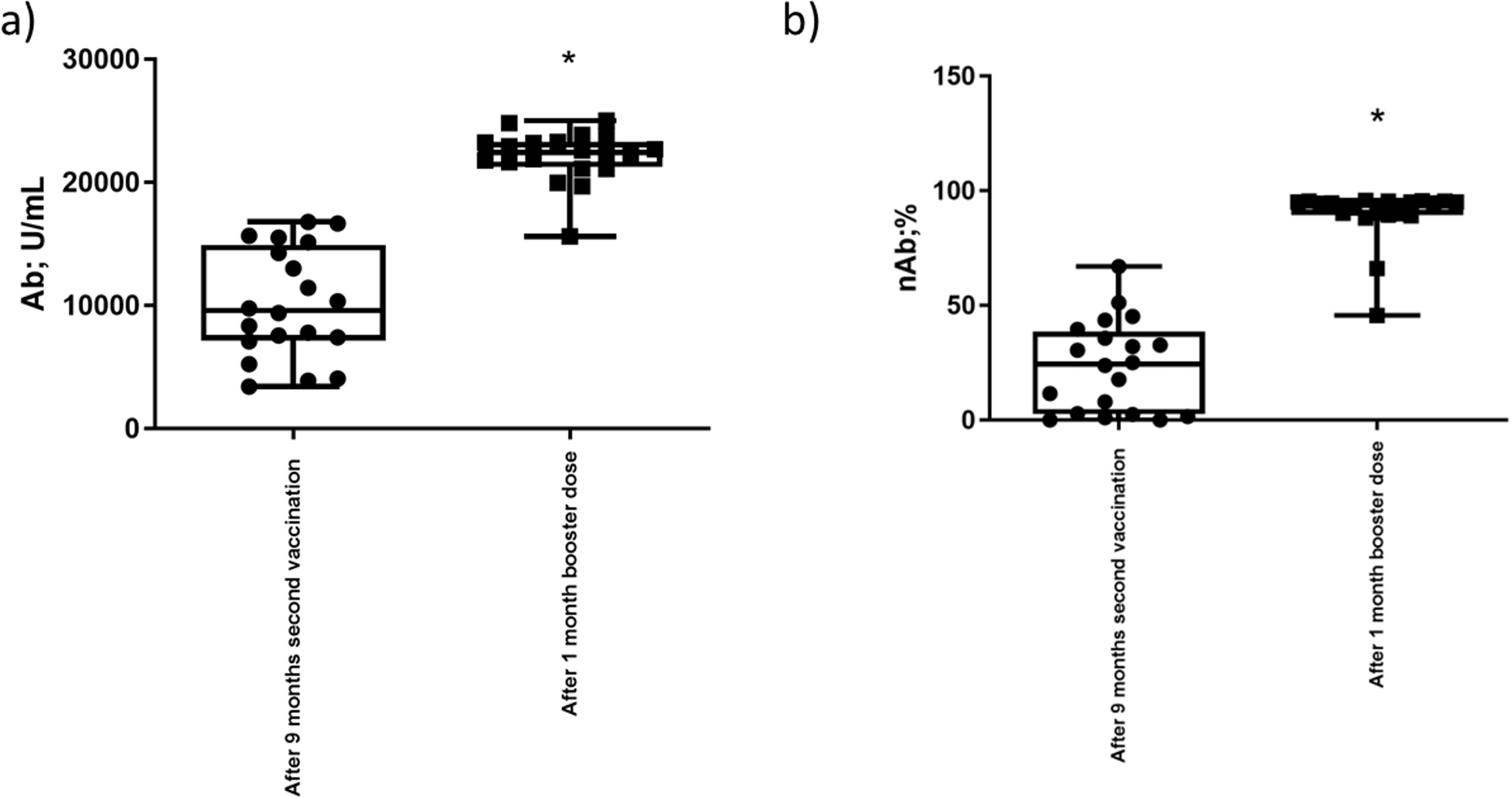
innate immune responses with high affinity. Methods: Twenty healthy
volunteers received three doses of Comirnaty (Pfizer Australia Pty Ltd.) and were
evaluated 9 months after the second vaccination and 1 month after the booster
dose. The exclusion criteria were the presence of adverse effects following the
vaccination, a history of smoking, and heterologous immunization. The inclusion
criteria were the absence of prior Coronavirus Disease (COVID)-19 history, the
absence of adverse effects, and the absence of comorbidities. Specific phenotype
and levels of CD107a and granzyme production by blood NK (natural killer) cells
were analyzed after exposure to SARS-CoV-2 spike antigen (Wuhan, Alpha B.1.1.7,
Delta B.1.617.2, and Omicron B1.1.529 variants), and related with anti-SARS-CoV-2
antibody production. Results: The booster dose caused early NK CD56