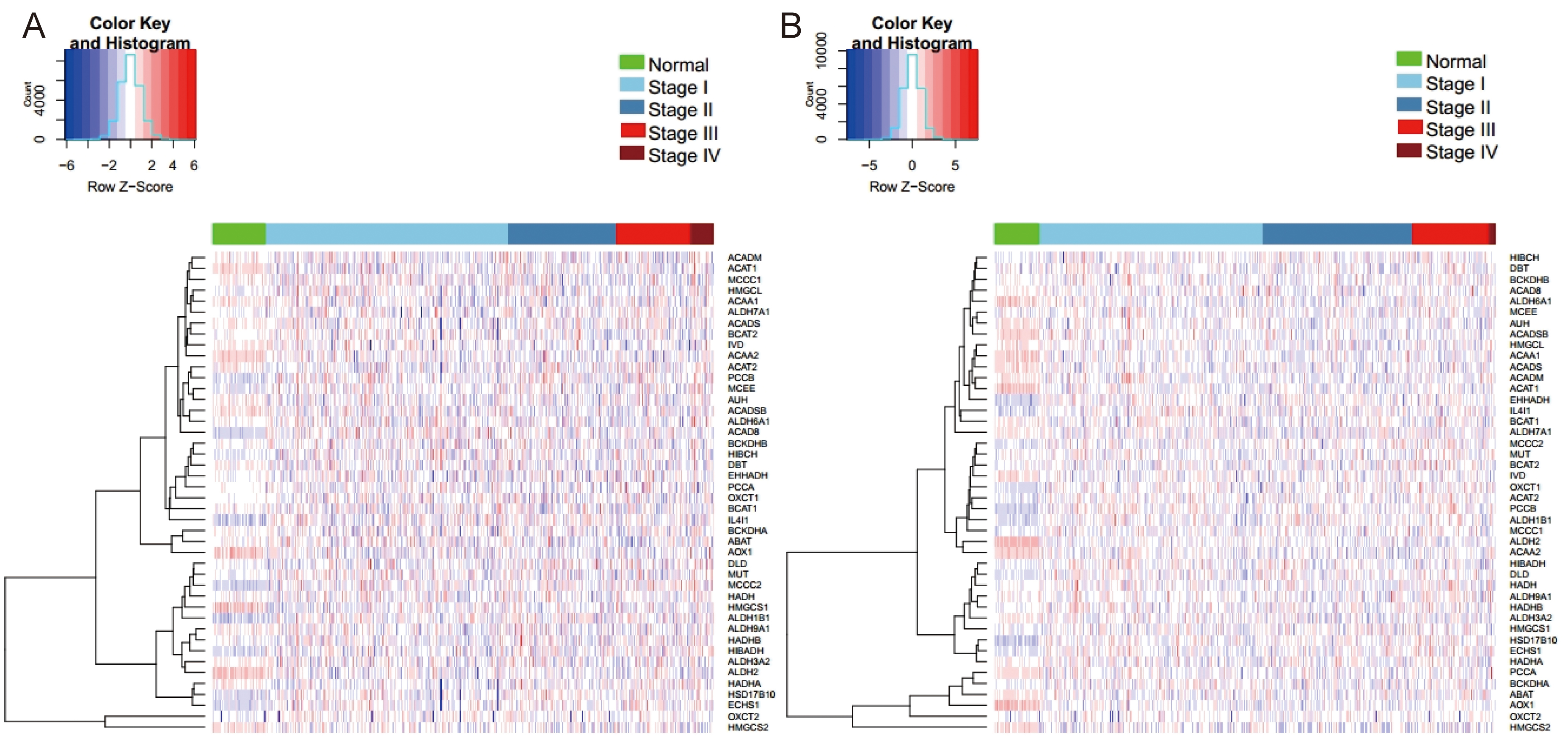
Background: The purpose of our study is to analyze the expression pattern and prognostic value of catabolism-related enzymes of branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Methods: Differential expression analysis, mutation, copy number variation (CNV), methylation analysis, and survival analysis of BCAAs catabolism-related enzymes in NSCLC were performed using the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database. Results: Six and seven differentially expressed genes were obtained in lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) and lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC), respectively. IL4I1 was located at the core regulatory nodes in the gene co-expression networks of both LUAD and LUSC. The AOX1 mutation rate was the highest in both LUAD and LUSC. For CNV, IL4I1 was up-regulated in both LUAD and LUSC with an increase in copy number, whereas AOX1 and ALDH2 were differentially regulated in the two subtypes of lung cancer. In patients with NSCLC, high expression of IL4I1 was associated with lower overall survival (OS), and low expression of ALDH2 predicted shorter disease-free survival (DFS). ALDH2 expression was related with LUSC survival. Conclusions: This study explored the biomarkers of BCAAs catabolism related to the prognosis of NSCLC, which provided a theoretical foundation to guide the clinical diagnosis and treatment of NSCLC.