1 Department of Advanced Medical and Surgical Sciences, University of Campania “Luigi Vanvitelli'', 80138 Naples, Italy
2 Internal Medicine and Hepatology Unit, Ospedale Evangelico Betania, 80147 Naples, Italy
3 Department of Translational Medical Sciences, University of Campania ‘Luigi Vanvitelli', 80138 Naples, Italy
†These authors contributed equally.
Abstract
Sodium-glucose co-transporters (SGLTs) family members are involved in several vital biological functions. Except for SGLT3, they are involved in the mechanisms of active transport of sodium and glucose and several micromolecules. The discovery of functions and mechanisms of SGLT1 inhibition and, in particular, of SGLT2 has radically changed the natural history of some pathologies. SGLT2 inhibitors have revolutionized the therapeutic approach not only of type 2 diabetes mellitus but also of heart failure and chronic kidney failure. Considering the role played by the other SGLTs and the functions still unknown to date, clinical implications of the inhibition of SGLT2 could represent the prelude for a wider modulation of these cotransporters. A better understanding of the role and function of SGLTs could represent a revolution in the therapeutic approach in the hepatological, metabolic, neurological and oncological fields. The purpose of this review is to illustrate the knowledge currently available on SGLTs, its clinical implications and future perspectives.
Keywords
- SGLTs
- SLC5
- Sodium Glucose Transporters
- SGLT2 inhibitors
- heart failure
- chronic kidney failure
- diabetes mellitus
Glucose is the main form of cellular energy support. Because of its hydrophilic nature, it cannot pass through the cell membrane by simple diffusion. Its transport through the lipid double layer, in fact, is provided by glucose transporters that are generally divided into two large groups: the GLUcose Transporters (GLUT), which through glucose spread within the cell by facilitated transport and according to gradient concentration, and the Sodium Glucose Transporters (SGLTs), by which glucose enters the cell with secondary active transport mechanism and against gradient concentration [1, 2, 3, 4]. Recently, it has been identified in plants a third group of glucose transporters, the SWEET, transport mechanisms of which are not clear yet [5].
SGLTs belong to a larger family of solute carriers called SLC5 (solute carrier 5 family) which includes 12 different members [1]. In fact, along with SGLT 1-6 playing the role of glucose transporters, it includes also myo-inositol (SLC5A3 and SLC5A11), iodide (SLC5A5), vitamin (SLC5A6), choline (SLC5A7) and monocarboxylate (SLC5A8 and SLC5A12) transporters. Among SGLTs, with the exception of SGLT3, these proteins are all involved in the active transport of sodium and glucose and other micromolecules (mannose, inositol, choline, iodine, galactose, fructose, biotin, short chain fatty acids) and are expressed variably in human tissues [1, 2, 4].
To date, the most consistent data available concern SGLT2 and its mechanism of inhibition that is currently one of the main cornerstones of the medical therapy of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and its micro and macrovascular complications. In particular, in addition to their anti-hyperglycemic effect, SGLT2 inhibitors have demonstrated such a surprisingly cardiorenal protective effect that have been recommended also in non diabetic patients suffering from heart failure (HF) (or at high cardio-vascular risk) and/or chronic kidney disease [6]. Although still little known, growing evidences are available also for other SGLTs. Their regulation has shown potential clinical applications in metabolic as well as in oncological, haematological, neurological fields and in diagnostic imaging. An adequate knowledge of all SGLTs pathophysiological mechanisms in order to modulate their effects could have unexpected implications, as it was for the inhibition of SGLT2.
For these reasons, in this review we summarize the currently available data on the family of co-transporters sodium-glucose, from the biochemical characteristics to the clinical implications, with the purpose of hypothesize future perspectives and application fields, focusing on the role of pioneers that SGLT1 and SGLT2 play in the current scientific landscape. For this purpose, an electronic search of the MEDLINE, Scopus, and Embase databases was conducted up to November 4, 2022 using the following keywords and their MeSH terms: sodium-glucose co-transporter inhibitor or SGLT or solute carrier 5 family or SLC5 (and each subclass). A total of 740 articles were evaluated, of which 105 were included in this review.
SGLT1 is a low-capacity, high affinity sodium-glucose co-transporter with 2:1
stoichiometry expressed by the SLC5A gene, located on chromosome 22
(22q13.1) and consisting of 664 amino acids [2]. It has 14 alpha-helix
transmembrane domains and the NH2 and COOH ends are located, respectively, on the
extra-cellular and intracellular membrane [2]. SGLT1 is a high affinity
transporter for glucose (Michaelis-Menten constant [Km] = 0.4 mmol/L) and
galactose, but not for fructose. SGLT1 is expressed mainly at the apical membrane
of enterocytes in small intestine, especially in duodenum, where it is
responsible for the absorption of d-glucose and d-galactose across the intestinal
brush border membrane (Table 1, Fig. 1) [1, 2]. It is also expressed in the
proximal convoluted tubule of the cortical zone of the kidney (segment S3) where
it is responsible, in conditions of euglycemia, for the absorption of about 5%
of glucose filtered daily [1]. In addition to the main activity of glucidic
transport, SGLT1 appears to be involved in the transport of sodium through a
uniport mechanism and to act as a urea and water channel [7]. Numerous evidences
suggest the expression of SGLT1 also in the pancreas both in
| SGLTs | Main localizations | Action | Other localizations | Related diseases | Clinical implications | Inhibitors |
| SGLT1 | - Small intestine | Absorption of d-glucose, d-galactose, urea and water | Proximal convoluted tubule (segment S3); Myocardium; Brain; Liver; Lungs; Pancreas; T cells; Endometrial cells | - Glucose-galactose malabsorption syndrome | - Oral rehydration therapy | - KGA2727 (experimental models) |
| - Obesity | - Hyperglycemia | - Phlorizin (severe side effects) | ||||
| - Cholestasis | - Sotagliflozin, Canaglifozin | |||||
| - Cancer | ||||||
| SGLT2 | - Proximal convoluted tubule (segment S1–S2) | Reabsorption of sodium and glucose | Brain; Liver; Pancreas; Thyroid; Salivary glands; Cancer cells | - Renal familial glycosuria | - T2DM | Gliflozins |
| - Diabetic nephropathy | - CKD | |||||
| - HF | ||||||
| - NAFLD | ||||||
| - Cancer (?) | ||||||
| SGLT3 | - Cholinergic neurons of enteric nervous system | Glucose sensor | Skeletal muscle tissue; Testis; Kidney; Brain | - ADHD | Unknown | Not available |
| SGLT4 | - Small intestine | Mannose, glucose and fructose transporter | Liver; Brain | - Diabetic proliferative retinopathy | Unknown | Not available |
| - Kidney | ||||||
| SGLT5 | - Kidney cortex | Mannose, fructose, galactose and glucose transporter | Skeletal muscle tissue | - Monitoring hyperglycemia (1,5-anhydroglucitol) | Not available | |
| - Neutropenia G6PC3 deficiency-related | ||||||
| - NAFLD (?) | ||||||
| SGLT6 | - Proximal twisted tubule | Myo-inositol and glucose transporter | Small intestine; Brain | - Rheumatological diseases | Not available | |
| - ICCA syndrome and BFIC | ||||||
| - Schizophrenia/bipolar disorder | ||||||
| - Ischemic stroke | ||||||
| ADHD, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder; BFIC, benign familial infantile convulsions; CKD, chronic kidney disease; HF, heart failure; ICCA, syndrome of infantile convulsions and paroxysmal dyskinesia; NAFLD, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus. | ||||||
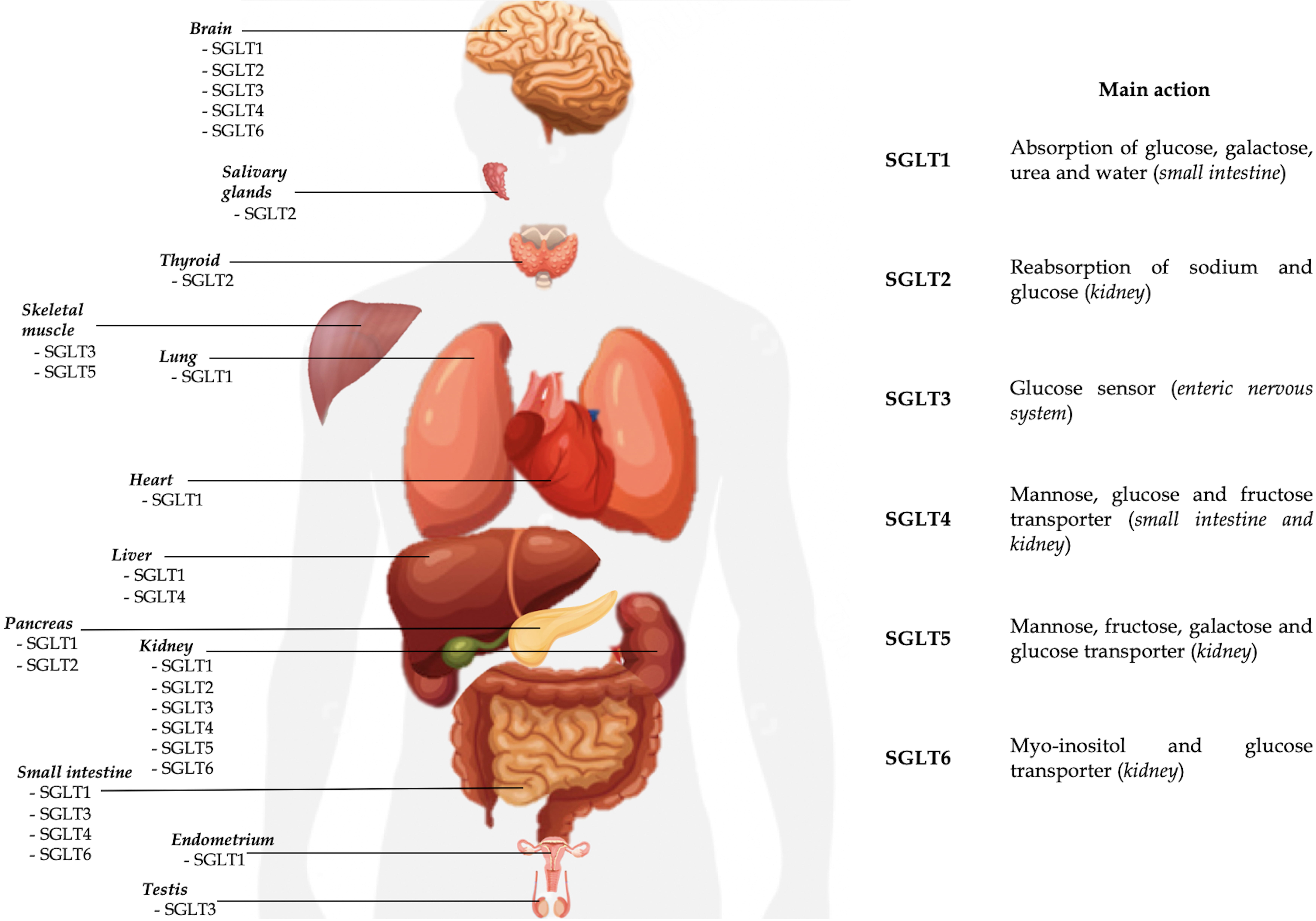 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.Currently known localizations and main activities of SGLTs.
In the enterocytes, the activity of SGLT1 is coupled to another glucose transporter, GLUT2, expressed in the basal membrane of the enterocyte, by which glucose, once absorbed, reaches the blood stream [1, 2]. The symport of SGLT1 works against gradient concentration, with 2:1 stoichiometry, with a secondary active transport mechanism. In fact, a Na+/K+ pump placed on the baso-lateral membrane of the cell is responsible for the energy support in this molecular flow: to maintain electroneutrality, chlorine moves with sodium [4, 10]. The osmolar force produced by glucose across the membrane also promotes the absorption of water through the brush edge. Probably, the physiopathological mechanism behind the reabsorption of water acts by paracellular way through the GAP junction via solvent drag and by transcellular way. The rationale for oral rehydration therapy used in the treatment and prevention of complications of secretive diarrhea, especially in cholera, is based on this mechanism [4].
Hereditary disorder caused by homozygous mutation of SCL5A in humans configures the intestinal glucose-galactose malabsorption syndrome (GGM), first described in 1962 as a severe form of osmotic diarrhea in the newborn caused by ingestion of glucose and galactose [11]. It is an autosomal, life-threatening, recessive disorder with manifestations at birth, often complicated by dehydration and metabolic acidosis. Mutations involved are mostly missense, nonsense and frame-shift mutations: the transcription of the defective gene determines the synthesis of a protein inserted into the cell membrane but not working [12]. A glucose-galactose free diet ensures the resolution of symptoms [2, 3, 12].
A high content of glucose and/or sodium in the diet promotes the expression of SGLT1 in the small intestine [13, 14]. In diabetic and obese patients this phenomenon is responsible for the rapid postprandial hyperglycemia, typical of these patients [15, 16]. Studies by Osswald et al. [17] suggest a causative role of SGLT1 in obesity: knock-out mice for the RS1 regulating protein have increased intestinal expression of SGLT1, resulting in increased glucose absorption and the development of non-leptin-mediated obesity compared to the wild type.
In the kidney, SGLT1 is responsible, in the euglycemic patient, for a small share of reabsorption of glucose filtered daily from the lumen to the proximal convoluted tubule cells [1, 2]. Overall, SGLT1 is able to guarantee, under physiological conditions, that about 5% of glucose is filtered daily, whereas SGLT2 is, instead, responsible for the reabsorption, in the S1 and S2 segments of the proximal twisted tubule, of almost all filtered monosaccharide (180 g/day) [18]. Subsequently, GLUT1, localized on the basal membrane of tubular cells, is responsible for glucose moving to the the blood. However, SGLT1 activity can be upregulated by SGLT2 inhibition [1, 2]. In fact, in patients receiving SGLT2 inhibitors (also called gliflozins) and in mice and humans with homozygous deletion of the SGLT2 coding gene, the few hypoglycemic events would be justified by increased renal SGLT1 activity able to reabsorb up to 50% of the glucose that comes to tract S3 due to the lack of resorption produced by SGLT2 in this setting [19, 20].
Conversely, hereditary defects in the SCL5A gene causing GGM show minimal effects on glycosuria, confirming the negligible contribution of SGLT1 in the kidney in presence of a performing SGLT2 [2, 3].
In recent literature the expression of SGLT1 has been also detected in cardiomyocytes and capillary endothelium, unlike SGLT2, not expressed [1]. The role of the cotransporter in the myocardium is not completely clarified to date. In this regard the expression of SGLT1 seems to be increased in hypertrophic or ischemic cardiomiopathy [21]. Its inhibition might play a role in the cardioprotection of diabetic patients, probably counteracting the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the myocardium and consequent tissue damage, hypertrophy and disarray, as demonstrated in animal models after the use of phlorizin [19, 22, 23]. In addition to atherosclerotic macrovascular complications, free radicals induced by ROS damage the proteins and DNA of cardiomyocytes. In vitro, ROS production is significantly reduced by phlorizin administration, which acts by inhibiting cardiac SGLT1. However, the role of cotransporter inhibition in cardiomyopathies has not been yet demonstrated in vivo [19].
Expression of SGLT1 is also described in the brain of humans, pigs, and rodents, especially in glucosensing neurons of the hypothalamus, midbrain, and brainstem [24]. The co-transporter also seems to be located on the luminal side of the endothelial cell membrane of the blood-encephalic barrier, thus playing a key role in the reserve energy support for neurons in conditions of increased glucose demand, such as hypoxia and hypoglycemia [2, 25].
SGLT1 has been detected in several other tissues (lungs, liver, pancreas, immune
system), although its role is still unclear. In particular, SGLT1 was found in
the trachea, bronchi and lungs tissues. In alveolar type 2 cells and cells of
Clara it would be involved in fluid absorption and production of surfactant and
mucin [26]. In the pancreas, the administration of SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin
results in an increased SGLT1 and glucagone expression suggesting the SGLT1
contribute to the SGLT2 inhibition-mediated effect on glucagon release from
Considering the central role that the cotransporter has in the intestinal and renal absorption of glucose, it is clear that SGLT1 could represent an ideal pharmacological target in the control of hyperglycemia. Although the inhibition of SGLT1 could reduce the intestinal and renal re-uptake of glucose, lowering serum glucose levels and contributing to the cardioprotection by reducing ROS production and glycogen storage, this strategy could have serious consequences on gastrointestinal tract, such as diarrhea and volume depletion [30]. For these reasons, specific and safe SGLT1 inhibitors are not commercially available to date. In experimental models on diabetic rodents, a selective SGLT1 inhibitor (KGA2727) has been shown to be able to inhibit the intestinal absorption of glucose, optimizing the post meal glycemia and reducing glycosylated hemoglobin [31]. Moreover, the higher intraluminal concentration of glucose in the colon would favor fermentation by the intestinal microbiota producing short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs). This induces the late release of glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) and gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP) by incretino-like effect, improving blood glucose levels control through an insular-centric mechanism. The selective inhibition of SGLT1 through KGA2727 in mice has demonstrated to have a protective role against myocardial infarction-induced ventricular remodeling and heart failure [32]. Moreover, in SGLT1 knock out mice has been demonstrated that chronic pressure overload-induced cardiomyopathy improved [33].
If selective SGLT1 inhibitors are not available to date, there are instead a series of molecules able to inhibit the cotransporter in a non-selective way. In this regard, phlorizin was the first recognized molecule with a non-selective inhibiting activity both on SGLT1 and SGLT2 [30]. Although its use has shown to normalize blood glucose levels in animal models suffering from post-pancreatectomy diabetes, the lack of selectivity of the molecule determines serious intestinal effects, acting mainly on SGLT1, which make it in clinical practice [34].
Among the SGLT2 inhibitors currently available, Canagliflozin and Sotagliflozin are the less selective, with mild SGLT1 inhibitory effects. A recent study recognizes to Canagliflozin, when taken at full dose, a functional role in hindering intestinal reabsorption of glucose with promising results on post-prandial blood glucose without significant worsening of the side effects (malabsorption, diarrhea) [15, 16, 31, 35]. The activity of Canagliflozin on SGLT1 is also responsible for significative anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects in the human myocardium through the suppression of the myocardial NADPH oxidase activity and improvement of the nitric oxide synthase (NOS) coupling [36]. This effect could contribute to the cardioprotective role shown by Canagliflozin.
Finally, as already described, the activity of SGLT1 is the heart of the pharmacodynamic mechanisms of oral rehydration therapy (ORT) [37]. Defined as the most important medical advance of the twentieth century, ORT has led to a significant reduction in infantile mortality for secretive diarrhea. In severe forms, in fact, the amount of liquids lost can cause serious complications, especially in children. The balance of losses can be recovered through the administration of glucose plus sodium solution (75 mm of glucose and 75 mm of NaCl, with potassium and citrate to obtain an osmolarity of 245 milliosmols), promoting the reabsorption, for each mole of glucose, of about 4–6 liters of water. Probably, SGLT1 plays a role as a channel for water reabsorption, while the osmotic force of glucose pumped against concentration gradient ensures water flow [10, 37, 38, 39].
SGLT2 is the most known sodium-glucose cotransporter to date. In recent years the development of SGLT2 inhibitors (also called glifozins) has completely revolutionized the approach to 3 of the most prevalent diseases in the world: diabetes mellitus, heart failure and chronic kidney failure [6].
SGLT2 is the product of SLC5A2 gene expression, localized on human chromosome 16p11.2. The co-transporter is a low-affinity (Km 6 mm), high-capacity glucose symporter of about 73 kDa [1, 2]. The protein consists of 672 amino acids with a structure similar to SGLT1 for about 60% and expressed mainly in the S1 and S2 segments of the proximal twisted tubule where it is responsible for sodium and glucose reabsorption (Table 1, Fig. 1). Similar to SGLT1, the mechanism of action is characterized by secondary active transport, but with a stoichiometric ratio 1:1: of the approximately 180 g of glucose filtered daily in an euglycemic individual. Located at the apical membrane of the S1 and S2 segments, SGLT2 is responsible for reabsorption of about 90–95% of filtered glucose [40]. Once inside the renal tubular cell, glucose reaches the blood stream through the facilitated transport of GLUT2, located on the basal membrane. Unlike SGLT1, SGLT2 cannot carry D-galactose [3]. Recent evidence suggests that the activity of SGLT2 is partly regulated by a small auxiliary protein, called MAP17, which intensifies its transport over a hundred-fold [40, 41]. In the literature SGLT2 expression has been detected in the pancreas, brain, liver, thyroid, muscle but also in prostate tumors and glioblastoma. Unlike SGLT1, no expression of the protein is recorded in the intestinal or cardiac tissue [1].
The homozygous mutation of SGLT2 results in renal familial glycosuria, which is characterized by the pathological excretion of urinary glucose (1 to 170 gr/day) with normal plasma glucose levels [42]. Insulin levels and glucose tolerance test response are also normal in these patients [4, 42]. Clinically it is a benign condition with glycosuria, sometimes associated with polyuria and enuresis [3]. It is likely that SGLT1 is responsible for a glucose reabsorption in the kidney as to avoid hypoglycemia. Interestingly, patients with familial renal glycosuria do not have intestinal involvement. Confirming the role of MAP17, some of the renal familial glycosuria are attributable to the mutation of this protein, without direct gene involvement of the co-transporter [41].
Currently available evidence seems to consider SGLT2 to have a key role in diabetic nephropathy. Nephropathy is one of the most scary and widespread microvascular complications of diabetes [43]. In fact, up to 40% of diabetic patients show renal involvement, with possible evolution towards end-stage disease and increase in mortality and cardiovascular morbidity. Hyperglycemia/hyperinsulinemia-induced SGLT2 overexpression would contribute to renal hyperfiltration, typically described in the early phase of diabetic kidney disease [3, 4]. In particular, SGLT2 would be responsible for a tubular glucidic overload. The resulting glucotoxicity, through mechanisms mediated by ROS [1, 44], would lead to progressive loss of nephrons favoring a compensatory hyperfiltration and tubular hypertrophy, with associated glomerular sclerosis and reduced kidney function [3]. According to Gyimesi et al. [1], another consequence of SGLT2 overexpression in diabetic patients would be a marked absorption of sodium, resulting in tubular overload and misreading on the macula dense, with renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system (RAAs) hyperactivation. This determines vasoconstriction of the efferent arteriole and vasodilation of the afferent arteriole, which could increase intraglomerular pressure with consequent glomerular damage, fueling a deleterious vicious circle.
Inhibition of the SGLT2 cotransporter has been shown to effectively reduce
hyperglycemia in diabetic patients [45]. In fact, pharmacological class of SGLT2
inhibitors (gliflozins) is able to induce glycosuria by hindering reabsorption of
glucose in the proximal convoluted tubule. Canagliflozin, Dapagliflozin and
Empagliflozin are the three main approved SGLT2 inhibitors. Among these,
Canagliflozin is the less selective, being able to act partially on SGLT1. The
main societies of diabetology suggest their use in monotherapy or in combination
with other antidiabetic drugs, including insulin. In fact, gliflozins demonstrate
stability of long-term control of blood sugar, reducing glycosylated hemoglobin,
with an absolutely negligible risk of hypoglycemia. During SGLT2 inhibitors
treatment, renal glucose resorption is partially vicariated at the S3 segment by
SGLT1, able to reabsorb up to 50% of filtered glucose. In the pancreas, SGLT2
would favor the suppression of glucagon secretion by pancreatic
Beyond their anti-hyperglycemic effect, SGLT2 inhibitors have shown a surprising cardio- and nephroprotective role [49, 50, 51, 52, 53, 54, 55]. In fact, this class of drugs has shown to be able to reduce overall cardiovascular mortality, as well as incidence of major cardiovascular events, rate of hospitalization for heart failure, progression of chronic kidney disease and albuminuria, regardless of glycemic control. For these reasons, SGLT2 inhibitors, together with glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RA), are responsible for an epochal breakthrough in the treatment of T2DM, shifting the therapeutic goal from glycemic control to cardiovascular risk control [6, 56].
As concern the cardiovascular protective role, SGLT2 inhibitors have demonstrated a significative impact on mortality from cardiovascular causes, regardless glycemic control. The greatest benefit has been shown hospitalization rate for HF [6]. For this reason, dapagliflozin and empagliflozin are recommended by leading global cardiological guidelines in patients with HF even in absence of T2DM [57]. Even though data on ischemic stroke and myocardial infarction reduction are controversial, SGLT2 inhibitors are also indicated in diabetic patients with high cardiovascular risk and/or with renal insufficiency and/or proteinuria. The mechanisms of their cardio- and nephroprotective activity are complex and still not fully understood. They can be divided in hemodynamic and metabolic mechanisms and effects on the cardiovascular risk factors control [6]. Among the first mechanisms, SGLT2 inhibitors are able to reduce both pre- and post-overload by increasing natriuresis, reducing blood volume and arterial pressure and stiffness. Among the metabolic effects SGLT2 inhibition determines an increase in cardiac efficiency, reduction of oxidative stress and myocardial inflammation, inhibition of pro-hypertrophic transcription pathways and potential reduction of pro-arrhythmic factors. In this regard, it is hypothesized a protective role of gliflozins for the early stage complications of acute myocardial infarction (HF and malignant arrhythmias), probably due to a neuro-hormonal effect contrasting sympathetic and metabolic hyperactivation through acting on myocardial necrosis and reperfusion damage. Three clinical trials are ongoing to validate this hypothesis (EMMY; EMPACT-MI; DAPA-MI) [58]. Recently it has been shown that the use of SGLT2 inhibitors in diabetic patients with acute myocardial infarction is associated to a significantly reduced inflammatory response and smaller infarct size compared to patients receiving other hypoglycemic drugs, regardless of glycemic and metabolic control [59]. In addition, SGLT2 inhibitors may have an antiarrhythmic and protective action towards sudden cardiac death, ventricular arrhythmias and atrial arrhythmias [60]. Within the limits of data obtained from retrospective studies or small numbers of events, it is not known whether the potential antiarrhythmic action is due to a direct action of gliflozines or to mechanisms mediated by improvement in cardiac performance. Several ongoing clinical trials (EMPA-ICD, ERASE trial) are trying to clarify the role of gliflozins in this setting [61]. Moreover, SGLT2 inhibitors are able to improve the overall cardiovascular risk profile. In addition to favoring glycemic control, they also reduce low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and triglycerides blood levels, promote weight loss and, as already mentioned, lower systemic arterial pressure. The weight loss would be favored not only by a diuretic osmotic effect of glycosuria (with reduction in extracellular volume), but also by reduction in fat mass with negative energy balance and increased lipolysis, oxidation of fatty acids, inhibition of lipogenesis and increased production of ketone bodies [1]. Among pleiotropic effects is also noted an antioxidant activity through direct mechanism of strengthening the scavenger endogenous systems, and indirect mechanism promoting the state of euglycemia, since hyperglycemia is directly associated with oxidative stress [61]. Finally, recent implications of the cardiovascular protective role of SGLT2 inhibitors have also been highlighted in the endocrinological field. Due to the high prevalence of obesity, insulin resistance, hypertension in polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), the efficacy of SGLT2 inhibitors in improving cardiometabolic complications has been hypothesized. In hyperandrogenemic PCOS murine models, empagliflozin indeed proved significant beneficial in adiposity and BP reduction [62].
The role of SGLT2 inhibitors in slowing down chronic kidney failure (CKD) progression is also remarkable [51, 52, 53, 63, 64]. In fact, gliflozins have demonstrated to improve albuminuria and reduce the risk of kidney failure, dialysis, or kidney transplant slowing the long-term glomerular filtration rate (GFR) decline [51]. In particular, the effect on GFR appears bi-phasic, first with a reduction in the short-term, followed by a substantial preservation on the long-term [51, 64]. In the EMPAREG OUTCOME trial, treatment with Empaglifozin was associated with –39% of incident nephropathy or worsening of a pre-existing nephropathy, –38% of progression of albuminuria and –55% of risk of renal replacement therapy [64]. Recently this effect has been shown to be the same regardless the diabetic status [63]. Similar effects have been reported also for dapagliflozin and canagliflozin [51, 52, 53]. As for cardioprotection, also the nephroprotection mechanisms of SGLT2 inhibitors have not been clarified yet. It could be possible that their activity involves multifactorial mechanisms including reduced intraglomerular pressure and renal hyperfiltration, lower arterial blood pressure, lower uricemia and increased natriuresis in addition to the anti-inflammatory effects [6].
Research about the role of SGLT2 inhibition is also achieving significant
results in the hepatological field [65]. In particular, non-alcoholic fatty liver
disease (NAFLD) shares with T2DM several pathophysiological mechanisms, as
insulin resistance and visceral obesity [66]. Similarly to GLP-1 RA [67], several
clinical trials have shown a promising role of SGLT2 inhibitors in improving the
associated liver fibrosis [68, 69]. Some pilot studies have already demonstrated
a significative improvement of both hepatic cytolysis and steatosis in patients
with NAFLD and T2DM under SGLT2 inhibitors treatment [70, 71, 72]. As concern the
impact on liver fibrosis, crucial data are expected from the NCT03723252 (DEAN)
trial, an ongoing phase 3 study that aims to evaluate the effect of Dapagliflozin
on NASH histology in patients suffering from T2DM [73]. Recently, some promising
evidences have been produced on the role of SGLT2 cotransporter inhibition in
oncology. In fact, neoplastic cells of pancreatic and prostatic neoplasms and
glioblastoma seem to overexpress SGLT2 [74]. In the diagnostic field, the use of
a specific positron emission tomography (PET) tracer, the
Despite it was identified 25 years ago, little is known about the localization and the role of SGLT3. SGLT3 is a glucosensor mainly expressed in the cholinergic neurons of the enteric nervous system and is encoded by the SLC5A4 gene located on chromosome 22q12.3. [3, 79]. It seems to be expressed also in the neuromuscular junctions of skeletal muscle tissue, brain and testis (Table 1, Fig. 1) [79, 80]. Some studies have shown the expression of SGLT3 also in the kidney, probably with a role in sodium transport, although it is not yet clear and needs further investigation [81]. In this regard data are conflicting [82]. Unlike other proteins of the SCLA family, it is not a glucose transporter but seems to act as a glucose sensor able to depolarize the plasmatic membrane through an electrochemical flow of sodium once bound the glucose molecule [79]. Given its localization prevalent in the small intestine (duodenum, jejunum and ileum), the role of SGLT3 would be linked to the regulation of intestinal motility in response to glucose. Its expression in duodenum and jejunum seems to be reduced in obesity. Soták et al. [82] demonstrated in obese mice that intestinal mRNA SGLT3a/3b expression was significantly reduced. Furthermore, jejunal SGLT3 expression in obese human patients were lower than in lean patients, but substantially upregulated 6 months after gastric bypass surgery. In contrast to what was highlighted by Soták et al. [82], recently Ren et al. [83] instead demonstrated that mRNA expression of SGLT3a (and SGLT1) decreased after sleeve gastrectomy, together with body weight reduction. Therefore, the real role of SGLT3 in obesity, the metabolic pathways and the potential implications of SGLT3 stimulation or inhibition in the treatment of obesity and metabolic syndrome are not known to date. Beyond the role of glucose sensor, other potential functions have been hypothesized for SGLT3 (as regulator of gastric emptying and GLP-1 release modulator), but currently no reliable data are available [79]. In the central nervous system, SGLT3 could act as a neuronal and astrocytic glucose sensor, controlling cerebral glycemic metabolism [84]. In fact, of the 5 SGLTs expressed in the brain (all except SGLT5), SGLT3 is the only present in the hypothalamus, where it is probably responsible for glucosensing [38]. In SGLT3 glucosensing, the entry of glucose into the cell mediated by SGLTs can lead to hyperpolarization of the neuronal membrane (with an inhibitory effect) or a depolarization (with an excitatory effect) [84].
A genetic variant of SGLT3 has been identified in some patients with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), but its pathogenetic role requires further characterization [1, 85]. No drugs acting on SGLT3 are commercially available to date. However, it has recently been demonstrated that some SGLT2 inhibitors (dapagliflozin, ertugliflozin, sergliflozin etabonate) are able to influence the brain expression of SGLT3 [80]. The clinical significance of this effect is unknown. However, pharmacological targeting of central glucosensors (as SGLT3) could be used to yield new lines of treatment for metabolic diseases that affect the central nervous system.
SGLT4 is the expression of the gene SLC5A9, localized on the chromosome 1p33 [3]. SGLT4 is mainly a mannose transporter, but with less affinity it can carry also the glucose, fructose and 1,5-anhydro-D-glucitol (1,5-AG) [86]. SGLT4 is expressed in the small intestine, kidney, brain and liver (Table 1, Fig. 1). Similarly to other SGLTs, the transport mechanism is a symporto with sodium. The role of SGLT4 in carrying these sugars is not clear yet. If SGLT1 and SGLT2 regulate the renal glucose reabsorption, probably SGLT4 (and SGLT5) are involved in apical fructose uptake [87]. In particular, SGLT4 and SGLT5 would be responsible for the transport of fructose in the luminal side of the cell membrane, whereas GLUT2 would be responsible for the transport in the baso-lateral membrane [88].
Recent studies have shown a potential role of SGLT4 in the pathogenesis of diabetic proliferative retinopathy [89]. In fact, SGLT4 could be expressed in the retinal endothelial cells: three rare variants have been identified in patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy. In addition, expression of this molecule is described in the kidney, pancreas and colon-rectal tumor [1, 90]. Therapeutical implications of its modulation are not being evaluated to date.
SGLT5 is the expression of the SCL5A10 gene, localized on chromosome 17p11.2 [3]. SGLT5 is expressed mainly in the renal cortex, in particular in the proximal straight tubules, and in scheletric muscle (Table 1, Fig. 1) [3, 91]. It is a transporter with high capacity and affinity for fructose and mannose and with less affinity also for galactose, glucose and 1,5-AG. Although its physiological role is not clear yet, SGLT5 would contribute to the tubular reabsorption of the filtered fructose (together with SGLT4), glucose and mannose [1, 88].
An association between renal fructose reabsorption mediated by SGLT5 and hepatic lipid metabolism has been put in evidence [92]. In particular has been hypothesized, through mice models, that SGLT5 inhibition could favor the urinary excretion of fructose thus affecting fructose-induced hepatic steatosis. Currently no specific or safe inhibitors of SGLT5 are available. Furthermore, a protective role of some SGLT5 mutations has been found in cases of neutropenia due to G6PC3 deficiency [93]. In these forms, neutropenia results from an accumulation of of 1,5-anhydroglucitol-6-phosphate (1,5-AG6P), an inhibitor of hexokinase coming from 1,5-AG. Some rare heterozygous missense mutations in SGLT5 have been associated with more benign forms of neutropenia, due to higher urinary clearance of 1,5-AG. If these observations are confirmed, selective inhibition of SGLT5 could be a valid therapeutic option in cases of neutropenia in G6PC3-deficient children.
Although SGLT5 inhibition does not have a therapeutic role to date, its mechanism of action (together with that of SGLT4) is crucial in some diagnostic techniques aimed at monitoring diabetes mellitus therapy. In this regard, 1,5-AG is a monosaccharide contained in almost all foodstuffs and appears to be a substrate of SGLT4 and SGLT5, which is responsible for its renal reabsorption [94]. During hyperglycemia, this mechanism is impaired since glucose is able to compete with the molecule, resulting in greater urine loss and in lower blood concentration. However, the return to the state of euglycemia results in restoration of the normal concentration values of 1,5-AG within about two weeks. For this reason, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved 1,5-AG measurement test “in diabetic patients” blood with the aim of monitoring therapy adherence and controlling episodes of hyperglycemia, similarly to glycosylated hemoglobin test [94]. It should be noted that therapy with SGLT2 inhibitors nullifies the diagnostic role of 1,5-AG since, in addition to inhibiting the renal reabsorption of glucose, the reabsorption of 1,5-AG by SGLT4 and SGLT5 is simultaneously suppressed [95].
SGLT6, also known as sodium/myo-inositol transporter 2 (SMIT2), is expressed by the SCL5A11 gene located on chromosome 16p12 [3]. SGLT6 is a myo-inositol and D-glucose transporter located on the luminal cell membrane in the proximal twisted tubule level (Table 1, Fig. 1). Recently its expression has been found also in the small intestine and brain [80, 96].
SGLT6 could act as an autoimmune gene modifier in rheumatological diseases, especially in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), able to influence some phenotypes of the disease [97]. It has also been identified as a major gene responsible for the infantile convulsions and paroxysmal dyskinesia syndrome (ICCA syndrome), as well as for benign familial infantile convulsions (BFIC) [98]. Finally, impaired brain expression of SMIT1 and SMIT2 has been shown to close correlate with some psychiatric diseases (schizophrenia and bipolar disorder) [99]. SGLT6 modulation could guarantee a greater transition of myo-inositol to hypoperfused brain tissues in case of ischemic stroke, potentially resulting in neuroprotection [100]. Similar to SGLT3, brain expression of SGLT6 is also affected by some SGLT2 inhibitors, although the clinical significance of this is unknown [80].
In addition to the SGLTs, the SLC5 family includes other solute carriers (SMIT1, NIS, SMVT, CHT1, SMCT1, SMCT2), counting altogether 12 different members. As already mentioned, they have a role in the transport of sugars, vitamins, amino acids, or ions.
SMIT1 (also called SLC5A3) is a sodium-myo-inositol cotranscarrier, with less affinity also for glucose. In SMIT1 knock-out mice the phenotype is characterized by a severe deficit of inositol, associated with early death due to abnormalities of respiratory and bone development. Probably, SMIT1 has a role in the osteogenesis process, bone formation and maintenance of bone mineral density [101]. Similarly to SMIT2 (SGLT6), mutations of SMIT1 have been associated to some psychiatric diseases (schizophrenia and bipolar disorder) [99].
NIS (alse called SLC5A5) is a sodium-iodine cotranscarrier expressed in the thyroid tissue where it promotes the accumulation of iodine, thus contributing to hormonal synthesis. Its expression is also described in the intestine, where it is involved in the absorption of iodine introduced with diet [102]. NIS expression is increased by Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH). Gene mutations are associated with forms of hypothyroidism [1]. The co-transporter plays a central role not only in the diagnostic characterization of malignant thyroid neoplasms, but also in the therapeutic phase representing a target in the treatment with radioisotopes.
SMVT (also called SLC5A6) is the product of the expression of SCL5A6, located on 2p13. It is a co-transporter sodium-vitamins (pantothenic acid, biotin and alpha-lipoic acid) and its expression is almost ubiquitous [103]. SMVT might be involved in iodine transport mechanisms and in the absorption of biotin in the gut.
CHT1 (also called SLC5A7) is a co-transporter sodium-choline chlorine-dependent expressed in the central nervous system. In CHT1 knock-out mice, there is evidence of a defect in the cholinergic synaptic activity, which is incompatible with life [104]. An incomplete expression results in motor neuropathies instead.
SMCT1 (also called SLC5A8) and SMCT2 (also called SLC5A12) are sodium-monocarboxylated transporters (lactate, pyruvate and nicotinate) with 2:1 stechiometry, both expressed in the gut. Compared to SMCT2, in humans SMCT1 has a higher affinity for lactate [50]. Their defective mutations lead to an increase in the excretion of lactates lowering their serum level. In the colon SMCT1 is involved in the absorption of SCFAs produced by bacterial fermentation. It is hypothesized a role as an oncosuppressor gene in the brain, gastro-intestinal, thyroid and renal cancers [105].
Sodium-glucose co-transporters family members are involved in several biological functions crucial for life. The discovery of the acting mechanisms and the role of SGLT2 inhibition has strongly influenced the natural history of diabetes mellitus, heart failure and chronic kidney failure. These clinical applications represent only the prelude to a greater modulation of these cotransporters. The modulation of SGLTs could in fact allow therapeutic progress in the treatment of diabetes mellitus and childhood secretory diarrhea (SGLT1), obesity, metabolic syndrome and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (SGLT3), diabetic proliferative retinopathy (SGLT4), disorders related to fructose metabolism (SGLT4, SGLT5), neutropenia due to G6PC3 deficiency (SGLT5) and rheumatological and psychiatric diseases (SGLT6). Furthermore, many fields of application may still be unknown today. Nevertheless, better knowledge of their acting mechanisms could allow to open new therapeutic scenarios in several fields of medical sciences including liver, metabolic, neurological and oncological diseases.
RN and AV contributed to the study conception and design. AV, SI, MA, LC, DB, RR, ADF and RN made substantial contributions to the acquisition, analysis, and interpretation of data for the work. The first draft of the manuscript was written by AV and RN. FG, DC, RM, LEA, LR and FCS edited the draft and revised the manuscript for important intellectual content. All authors contributed to editorial changes in the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript to be published.
Not applicable.
We thank all the residents of the School of Internal Medicine of the University of Campania “Luigi Vanvitelli” for their exceptional dedication and extraordinary skills.
This research received no external funding.
Given his role as Guest Editor, Riccardo Nevola had no involvement in the peer-review of this article and has no access to information regarding its peer-review. Full responsibility for the editorial process for this article was delegated to Graham Pawelec. The authors declare no conflict of interest
References
Publisher’s Note: IMR Press stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.

