1 Department of Thoracic Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital, Bengbu Medical College, 233000 Bengbu, Anhui, China
2 Anhui Province Key Laboratory of Clinical and Preclinical Research in Respiratory Disease Bengbu Medical College, 233000 Bengbu, Anhui, China
3 Molecular Diagnosis Center, First Affiliated Hospital, Bengbu Medical College, 233000 Bengbu, Anhui, China
4 Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, First Affiliated Hospital, Bengbu Medical College, 233000 Bengbu, Anhui, China
†These authors contributed equally.
Abstract
Background: Lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) is one of the leading causes of cancer-related mortality. Lysophosphatidylglycerol acyltransferase (LPGAT1) regulates the biosynthesis of triacylglycerol, which is essential for maintaining phospholipid homeostasis and modulating the structural integrity of mitochondrial membranes. LPGAT1 has been demonstrated to be differentially expressed in normal lung tissue and LUAD tissues, and can serve as a metabolically relevant gene with potential prognostic value. However, the potential role of LPGAT1 in LUAD is still unknown. This study sought to determine the role of LPGAT1 in LUAD progression. Methods: LPGAT1 expression was examined in LUAD cells and tumor tissues from LUAD patients. The effect of LPGAT1 was then assessed in both cell and animal models after LPGAT1 was knocked down by RNA interference. Results: LPGAT1 was upregulated in LUAD tissues. Overexpression of LPGAT1 was associated with an unfavorable prognosis in LUAD patients, as revealed by univariate and multivariate Cox analyses. Knockdown of LPGAT1 abrogated tumor growth and proliferation in both cell and animal models. Conclusions: This study demonstrates that LPGAT1 promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis in LUAD. Hence, LPGAT1 may provide new treatment strategies for LUAD.
Keywords
- lung adenocarcinoma
- LPGAT1
- phosphatidylglycerol metabolic process
- lung cancer
Lung cancer (LC) has become one of the most deadly malignancies worldwide [1, 2]. The predominant histopathologic subtype of LC is non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), which accounts for over 80% of all LCs [3, 4]. Lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) is the most common subtype of NSCLC, with a 5-year survival rate of approximately 15% [5, 6]. Recently, much progress has been achieved in the study of driver oncogenes, including mesenchymal lymphoma kinase and epidermal growth factor receptor [7, 8]. However, resistance to targeted therapies against these genes is a significant limitation for patients. Therefore, it is of utmost importance to explore new therapeutic mechanisms for LUAD in clinical practice [9].
Lysophosphatidylglycerol acyltransferase (LPGAT1) is encoded by a gene on chromosome 1q32.2, which was originally cloned in 2004 [10]. It has been reported that LPGAT1 regulates the biosynthesis of triacylglycerol, which is essential for maintaining phospholipid homeostasis and modulating the structural integrity of mitochondrial membranes [11]. LPGAT1 has also been shown to be primarily involved in lipid metabolism, and its effects on body mass index and body fat have been confirmed [12]. These effects of LPGAT1 on the organism occur when it is in its regular expression profile. However, at levels beyond normal expression, it may lead to the development of certain diseases. Previous studies have shown that LPGAT1 gene expression is upregulated in tumor tissue compared to normal tissue, suggesting that LPGAT1 may be a potential target for the diagnosis of LUAD [13, 14, 15]. Therefore, LPGAT1 is a metabolically relevant gene with prognostic significance, and may be a new therapeutic and diagnostic target for LUAD.
In this study, by analyzing the results of the LUAD-TCGA database, LPGAT1 was found to be upregulated in LUAD tissue compared to normal tumor-adjacent lung tissue. Univariate and multivariate Cox analyses revealed that LPGAT1 was related to an unfavorable prognosis in LUAD patients. LPGAT1 expression was analyzed in LUAD cells and lung tumor tissues from patients. It was found that LPGAT1 was overexpressed in LC tissues. Subsequently, the functional roles of LPGAT1 were examined in both cell and animal models. On a cellular level, LPGAT1 promoted cell proliferation and inhibited apoptosis in LUAD. In mouse models, knockdown of LPGAT1 reduced the growth of the LUAD xenograft. The transcriptome analysis of the H1299 cell line indicated that LPGAT1 knockdown upregulated the phosphatidylglycerol metabolism pathway. However, validation of the associated mechanisms requires more extensive investigation. In summary, the findings in the present study indicate that up-regulation of LPGAT1 facilitates the oncogenesis of LUAD.
Between October 2018 and December 2019, 60 pairs of LUAD and neighboring lung tissues were obtained from LUAD patients in the First Affiliated Hospital of Bengbu Medical College (Anhui Province, China). All subjects underwent surgery after obtaining informed consent. This research was approved by the Ethics Committee of the same institute, and was in compliance with the standards established by the Declaration of Helsinki. After snap-freezing in liquid nitrogen, the samples were kept at –80 ℃ until further analysis.
The tissue specimens were fixed in 4% formalin, embedded in paraffin, and
sectioned at 4
Human LUAD cell lines (PC9, H1299, A549 and H23) and HEK-293T cell line were
supplied by the Institute of Cell Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences
(Shanghai, China). All cell lines were tested for mycoplasma and no mycoplasma
contamination was observed. All cell lines were detected by short tandem repeat
(STR) and all were detected correctly. All cells were cultured in DMEM containing
10% fetal bovine serum (FBS, A3160802, Gibco, Grand Island, NY, USA), and 10
mg/mL penicillin-streptomycin (PS, 15140122, Gibco, Grand Island, NY, USA). Cells
were grown at 37 ℃ in an appropriate incubator with 5% CO
LPGAT1 knockdown was performed by siRNA and shRNA viruses. siLPGAT1 and siCtrl
were the experimental and control groups, respectively. H1299 and A549 cells were
transfected with siLPGAT1 and siCtrl. The target sequences of siLPGAT1 and siCtrl
are displayed in Supplementary Table 1. shLPGAT1 and shCtrl were cloned
into pLKO.1 plasmid, followed by sequencing. The shRNA-pLKO.1 and helper plasmids
(delta8.9 and VSVG) were transfected into HEK293T cells for 3 days. Lentiviruses
were generated, collected, and purified via ultracentrifugation. The viral titer
was determined by evaluating the infectious capacity of HEK293T cells. Stable,
transfected cells were screened with 2
The lentivirus-infected H1299 and A549 cells (1000 cells/well) were grown in a
96-well plate, followed by incubation at 37 °C. At 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
days, 10
To evaluate the impact of LPGAT1 on apoptosis, the treated H1299 and A549 cells
(5
To assess the effect of LPGAT1 on the cell cycle, A549 and H1299 cells (1
H1299 (or A549) cells were exposed to sh-LPGAT1 or sh-Ctrl lentivirus and
cultured for 2 days. The cells were then dissociated and grown in a 6-well plate
for colony formation at six hundred viable cells per well. Three replicate wells
were set up for each experimental group. After 14 days, most clones contained
more than 50 cells (medium was exchanged every three days). Crystal violet
staining (1000
After being interfered by siLPGAT1 and siCtrl, the H1299 cell lines were
extracted for RNA, and transcriptome sequencing was performed. We selected
differentially expressed genes (DEGs) with
Total RNA was extracted from the H1299 cells treated with lentivirus using the
TRIzol® Plus RNA Purification Kit (12183-555, Invitrogen,
Carlsbad, CA, USA). RNA was reverse-transcribed by SuperScript™
III First-Strand Synthesis SuperMix (11752-050, Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA),
and qPCR was performed by Power SYBR Green PCR Master Mix (4367659, Applied
Biosystems, Waltham, MA, USA). The primer sequences are displayed in
Supplementary Table 1. The CFX384 multiplex RT-PCR instrument (Bio-Rad,
Berkeley, CA, USA) was employed for mRNA expression analysis. The fold-change was
measured using the 2
A total protein extraction kit containing protease inhibitor cocktail (BC3710,
Solarbio, Beijing, China) was utilized for total protein isolation. A
bicinchoninic acid (BCA) quantification kit (B0010, Beyotime, Shanghai, China)
was utilized for total protein quantification. After separation through 10%
SDS-PAGE, the proteins were subsequently transferred onto PVDF membranes
(IPVH00010, Millipore, St. Louis, MO, USA). The membranes were incubated with the
primary antibodies at 4 °C overnight, followed by the secondary
antibodies (Goat anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L), 31210, Thermo Pierce, Waltham, MA, USA)
at RT for 1 h. The following primary antibodies were employed: anti-LPGAT1
(bs-18347r, Bioss, Woburn, MA, USA), anti-GPAM (bs-5063r, Bioss, Woburn, MA,
USA), anti-LCLAT1 (bs-18190r, Bioss, Woburn, MA, USA), anti-LPCAT1(16112-1-AP,
Proteintech, Wuhan, China) anti-LPCAT4 (17905-1-AP, Proteintech, Wuhan, China),
anti-CRLS1 (14845-1-AP, Proteintech, Wuhan, China), and anti-
All the experimental protocols were conducted in accordance with the
institutional ethics and safety guidelines of the same institute. Twenty-two
BALB/c nude mice (female, 6 weeks old, 16–18 g) were supplied by Shanghai
Lingchang Biotechnology (Shanghai, China), and were maintained at the
Experimental Animal Center, and underwent a 10/14-h light-dark cycle (55
The mRNA level of LPGAT1 was detected using the TCGA-LUAD cohort. After merging with LPGAT1 expression data, the samples with complete information on patient survival, age, gender, N stage, T stage and tumor stage were used to construct the Kaplan-Meier curve and perform univariate and multivariate Cox analyses.
All values are shown as mean
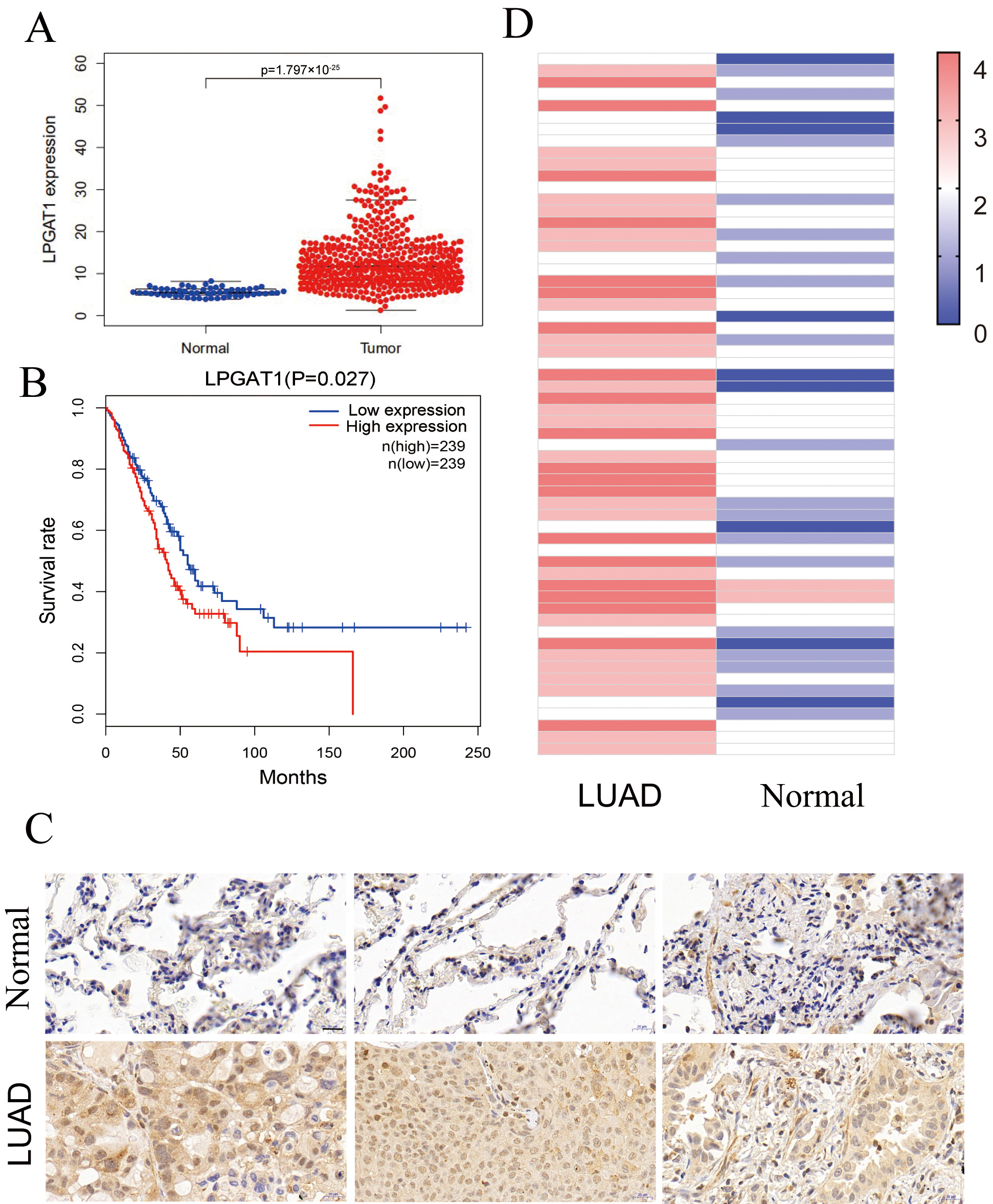
This study assessed the role of LPGAT1 in LUAD. Expression data from the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA-LUAD), comprising 497 LUAD tissues and 54 non-tumor tissues, were analyzed. Our results indicated that LPGAT1 was significantly increased in LUAD tissue compared to non-tumor tissue (Fig. 1A). All LUAD patients were classified into LPGAT1 high-expression and low-expression groups based on the median value of LPGAT1 expression. However, Kaplan-Meier analysis revealed that the survival rate of the LPGAT1 low-expression group was not better than that of the LPGAT1 high-expression group (Fig. 1B). In addition, after combining LPGAT1 expression data and survival data from these samples, univariate and multivariate Cox analyses were performed. The results demonstrated that LPGAT1 was an independent poor prognostic factor (Supplementary Tables 2, 3). 60 pairs of LUAD and neighboring normal tissues were acquired, and the following steps were performed: immunohistochemical staining, photography, interpretation, and pathological analysis. The findings were highly consistent with the above data, in which the expression of LPGAT1 was higher in LUAD tissues than in paracancer tissues (Fig. 1C). The immunohistochemical scores of the 60 clinical samples are shown in Fig. 1D.
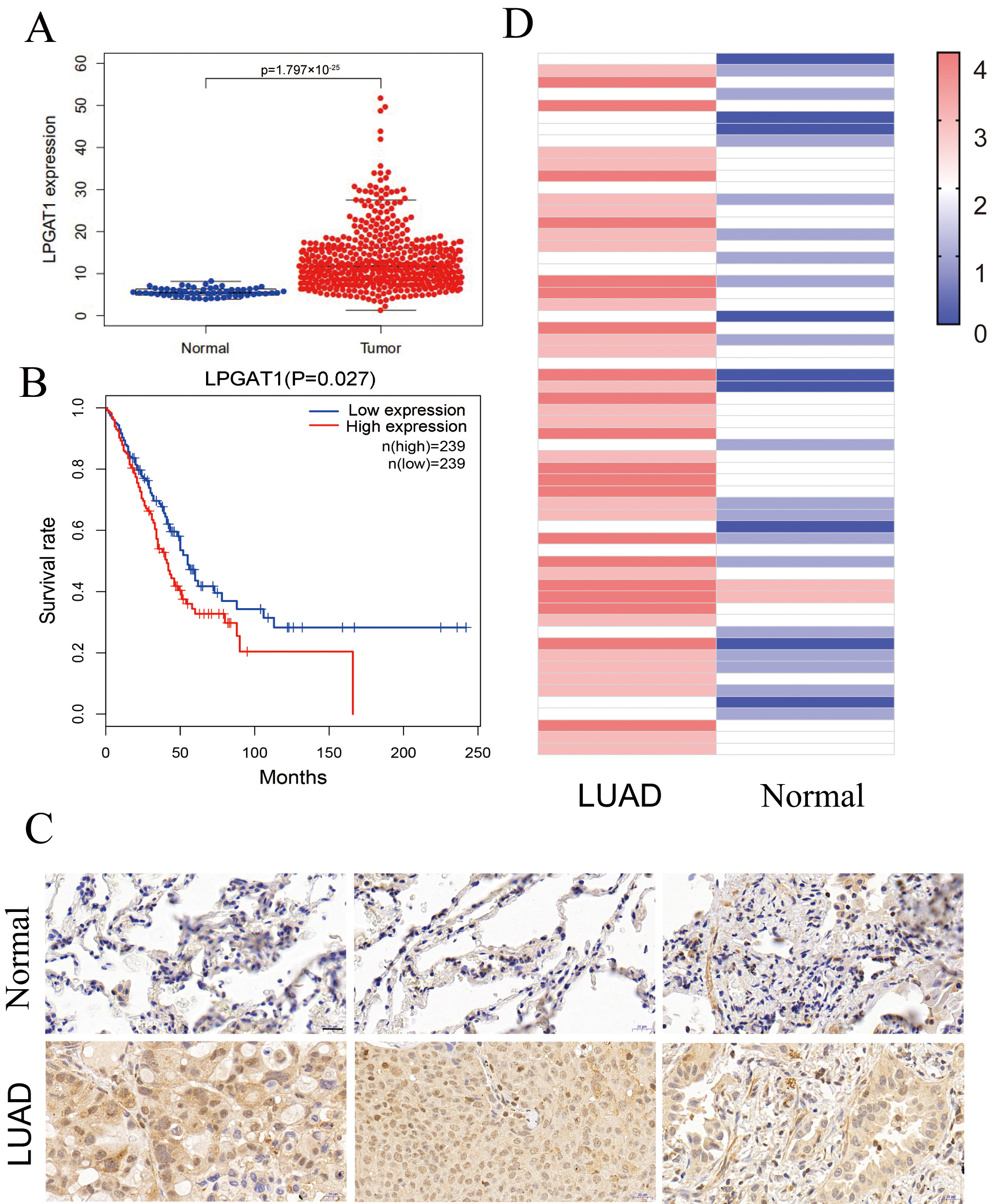 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.LPGAT1 is highly expressed in lung adenocarcinoma tissues. (A)
Statistical results of LPGAT1 expression data from TCGA-LUAD. (B) Kaplan-Meier
analysis of LUAD patients’ prognosis with high and low expression of LPGAT1. (C)
LPGAT1 expression in tumor tissues and normal tissues via IHC staining. Scale
bars: 20
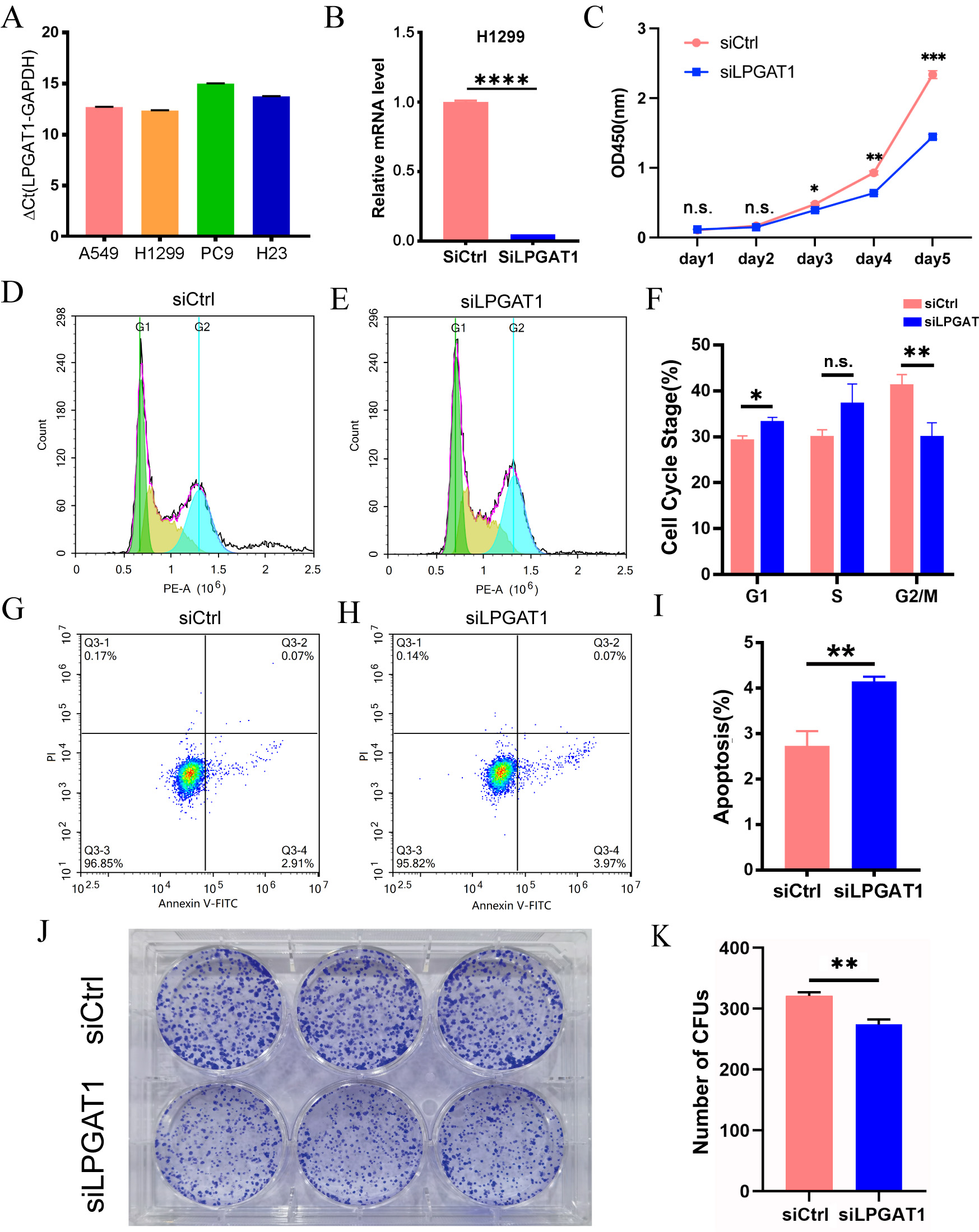
To explore the role of LPGAT1 in LUAD, a series of functional assays were performed in LUAD cells. H1299 and A549 cells with the highest LPGAT1 expression were selected for the subsequent analyses (Fig. 2A and Supplementary Fig. 1A,B). These LUAD cell lines were transfected with siLPGAT1 and siCtrl, and qPCR assays were then conducted to detect the endogenous LPGAT1 expression. It was observed that the expression of LPGAT1 was downregulated by 95% in H1299 cells (Fig. 2B) and 88% in A549 cells (Supplementary Fig. 1C). Next, CCK-8, FC and CFA were conducted on the stable transfected LUAD cells to assess cell proliferation and apoptosis. The findings of CCK-8 assays demonstrated that the proliferation of H1299 cell line (Fig. 2C) and A549 cell line (Supplementary Fig. 1D,E) was attenuated by LPGAT1 knockdown. FC analysis revealed that, compared to the control group, the LPGAT1-knockdown group inhibited the cell cycle progression, G2/M cells were decreased, and G1 cells were increased in H1299 cell lines (Fig. 2D–F and Supplementary Fig. 1F), while only G1 cells were increased in A549 cell lines (Supplementary Fig. 1G,H). The green-, yellow-, and blue-emitting populations in the latter corresponded to G1, G1/S and S/G2-M cells, respectively. In addition, the data of FC indicated that the apoptotic rate of LUAD cells was dramatically elevated after LPGAT1 knockdown (Fig. 2G–I, Supplementary Fig. 1I,J and Supplementary Fig. 2A). Furthermore, the findings of CFA showed that the number of colonies was decreased in H1299 cells with LPGAT1 knockdown (Fig. 2J,K).
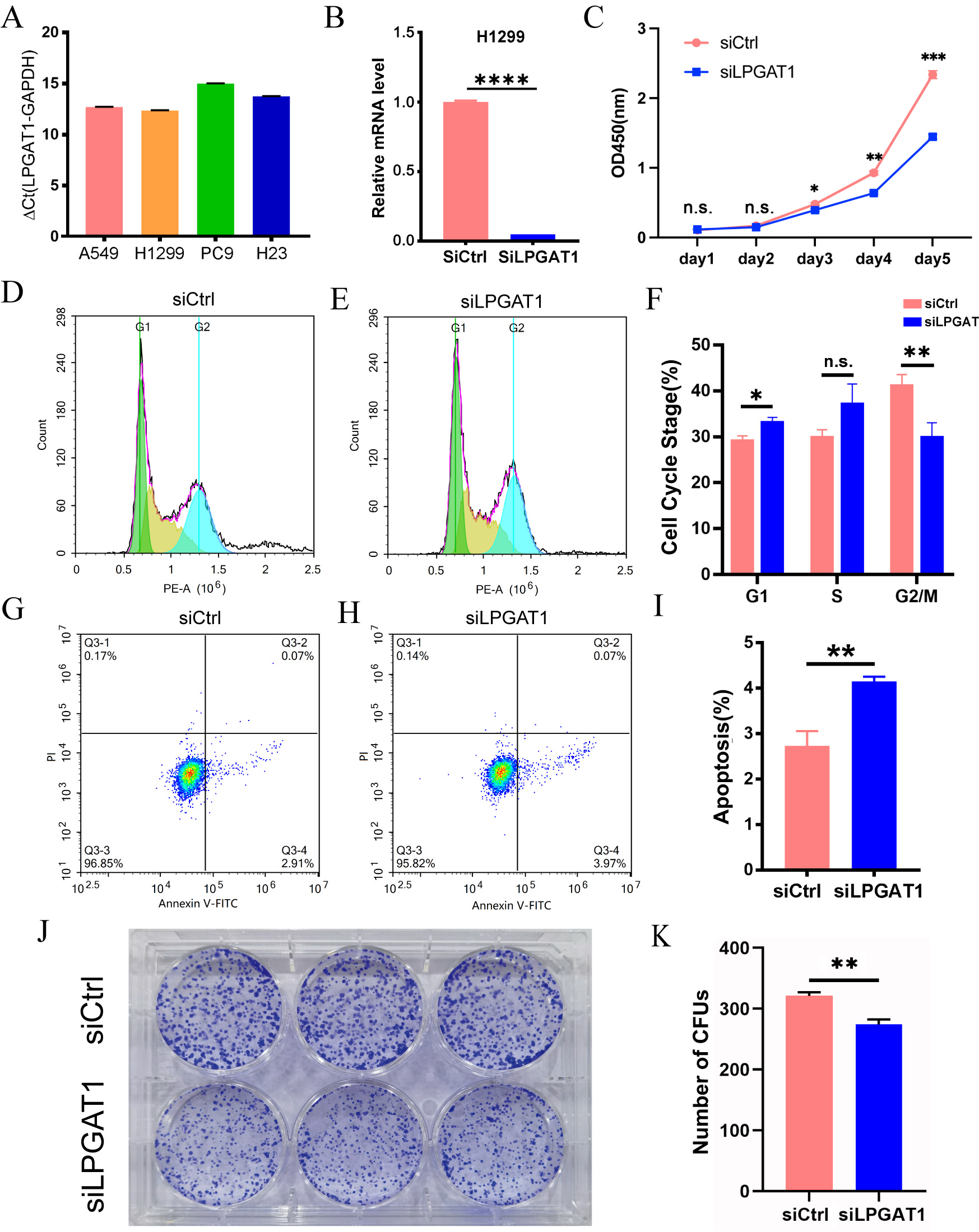 Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.Knockdown of LPGAT1 inhibits cell proliferation and promotes
cell apoptosis in H1299 cell lines. (A,B) The expression levels of LPGAT1 in
four NSCLC cell lines (A549, H1299, PC9, and H23), and the knockdown efficiency
of siLPGAT1 in H1299, were detected by qRT-PCR. Unpaired
two-tailed t-test;
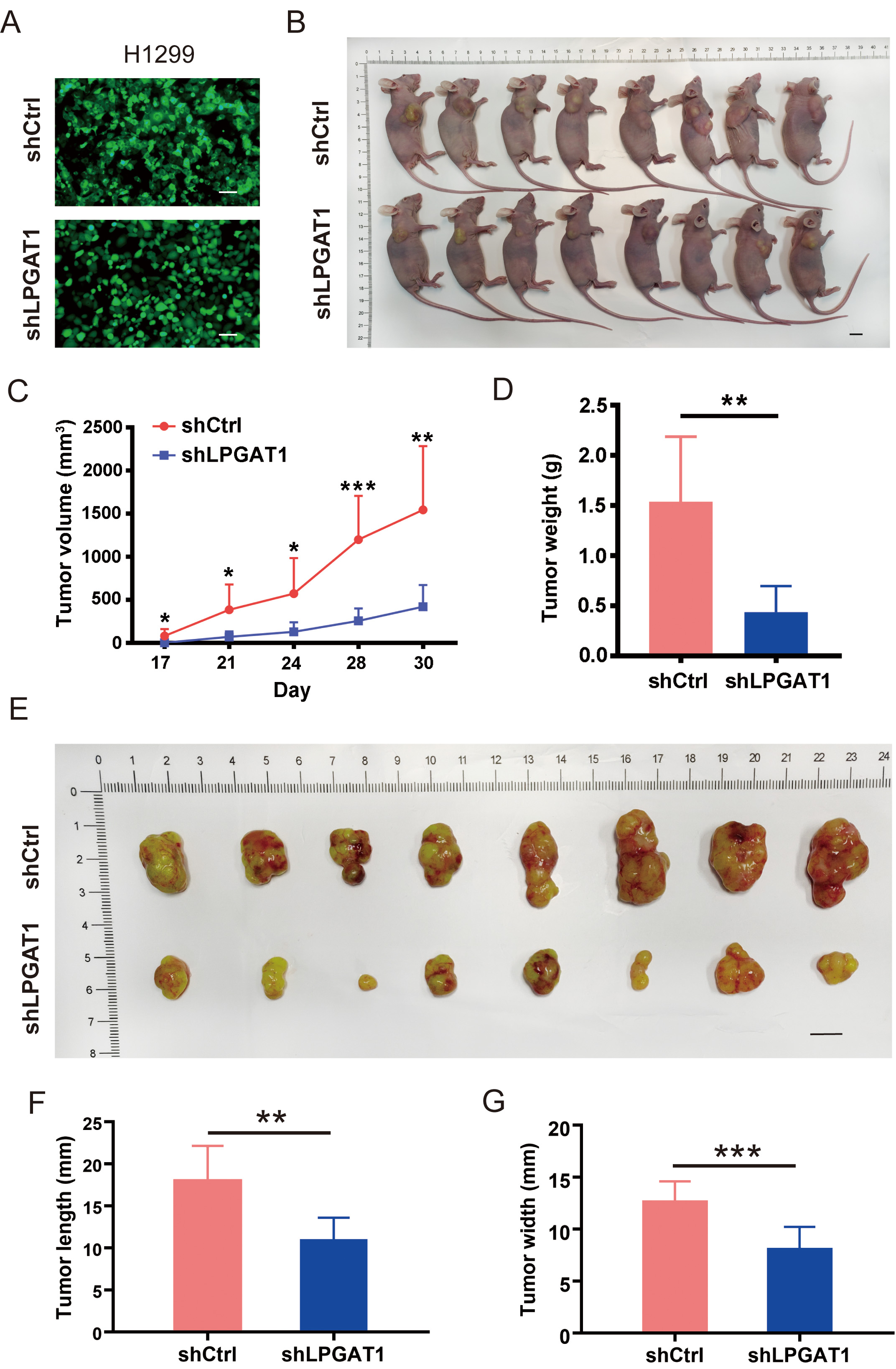
A BALB/cnu/nu nude mouse xenograft model was constructed by subcutaneously
injecting H1299 cells to investigate whether LPGAT1 knockdown can suppress LUAD
progression in vivo. H1299 cells were transfected with lentiviruses
(shCtrl and shLPGAT1) for 48 h (Fig. 3A). The infection efficiency of the
lentivirus was 93.6% and 94.1%, respectively (Supplementary Fig. 2B).
Eight mice were subcutaneously injected with shCtrl-infected H1299 cells (4
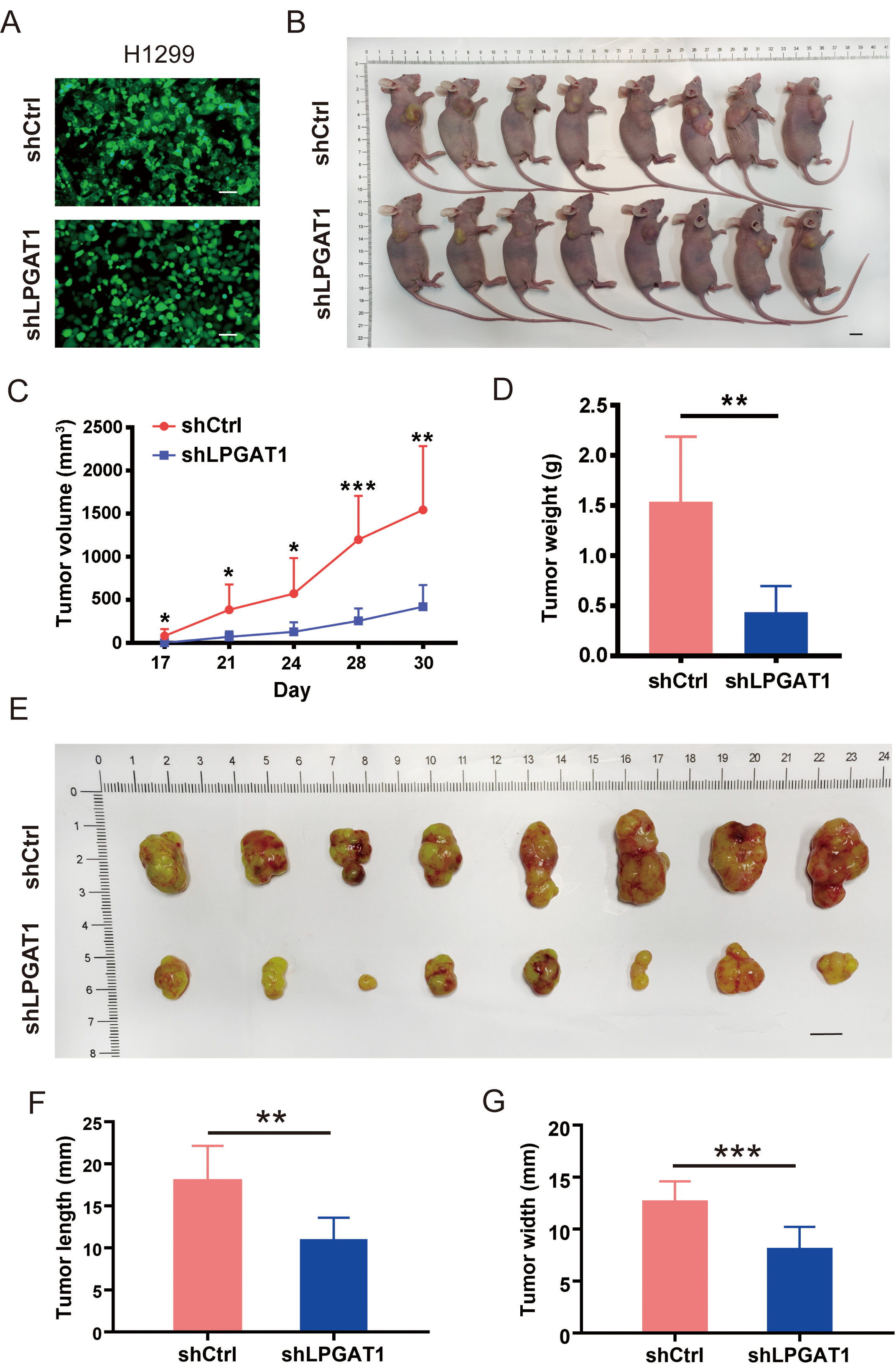 Fig. 3.
Fig. 3.Knockdown of LPGAT1 inhibits tumor growth in tumor-bearing
mice. (A) Infection efficiency of lentiviruses (shCtrl and shLPGAT1) in H1299
cells. Scale bars: 25
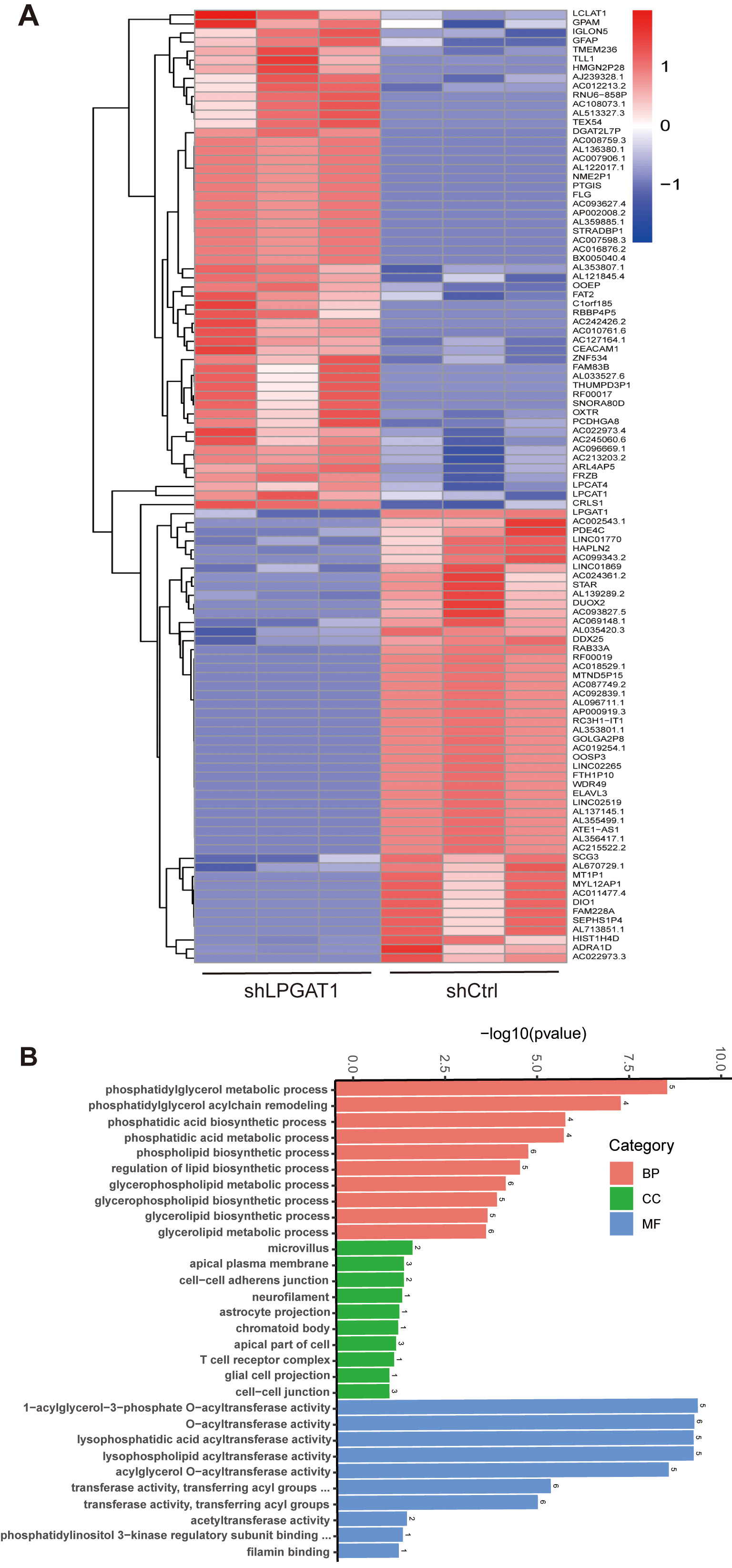
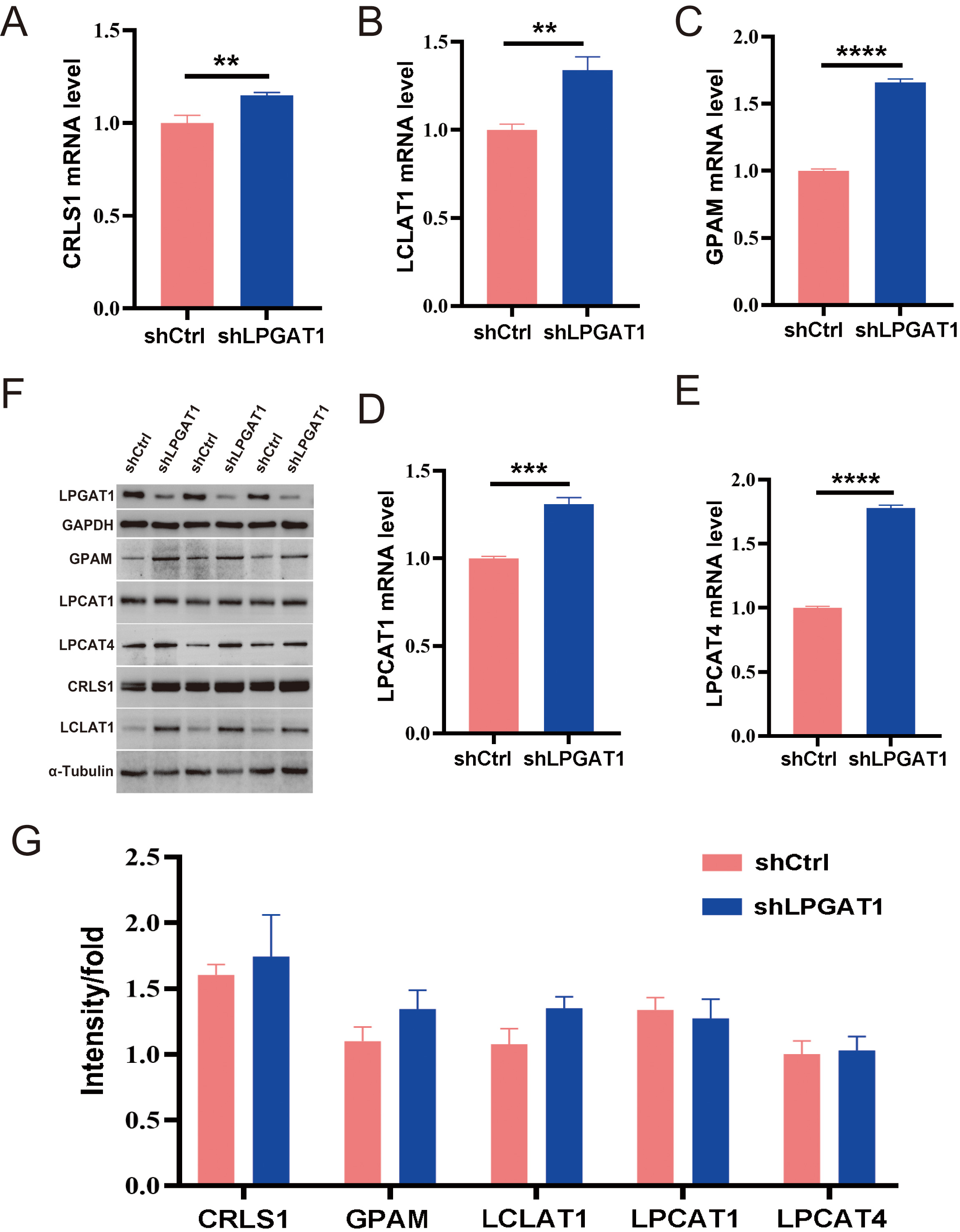
After the knockdown of LPGAT1, H1299 cells were collected for RNA-Seq. 106 DEGs are shown in the heatmap (Fig. 4A). These genes were detected by GO enrichment analysis; the top 10 results in BPs, CCs, and MFs are shown in Fig. 4B and Supplementary Table 4. We found the most prominent regulation involved the phosphatidylglycerol metabolic pathway, phosphatidylglycerol acyl-chain remodeling, the phosphatidic acid biosynthetic process, the phosphatidic acid metabolic processes, and the phospholipid biosynthetic process in BPs. There were five common genes in the five most prominent pathways, namely LPCAT4, LPCAT1, Lyso-CL acyltransferase 1 (LCLAT1), Glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase mitochondrial (GPAM), and cardiolipin synthase 1 (CRLS1). In order to verify the effect of target gene LPGAT1 knockdown on these pathways, we performed qRT-PCR and WB analyses. Based on the qRT-PCR data, these genes were up-regulated in H1299 cells with LPGAT1 knockdown compared to the control group (Fig. 5A–E). However, WB analysis demonstrated that the levels of CRLS1, GPAM and LPLAT1 proteins had an upward trend in H1299 cells with LPGAT1 knockdown, but no statistical significance was observed. Similarly, there was no marked difference in the expression of LPCAT1 and LPCAT4 between the two groups (Fig. 5F,G).
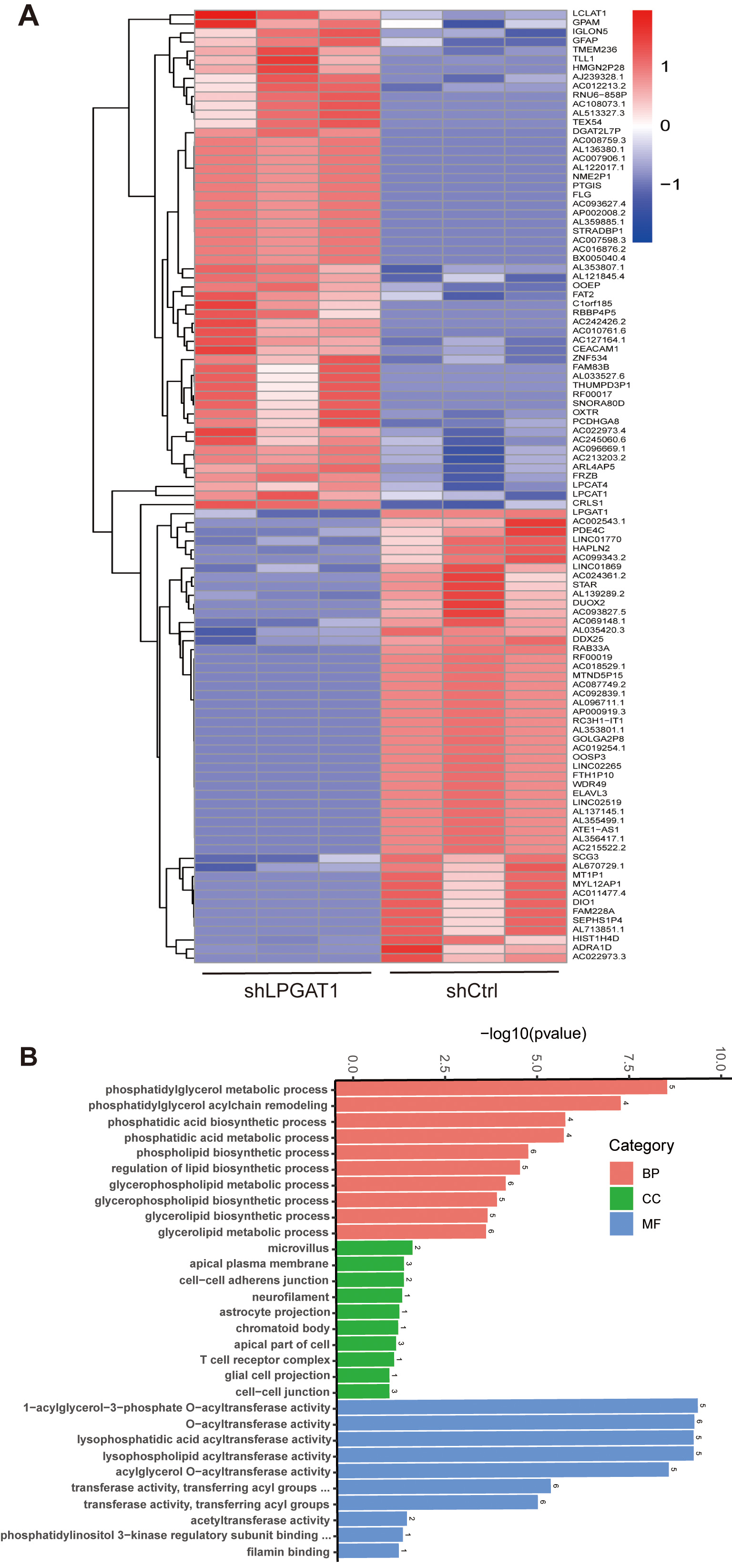 Fig. 4.
Fig. 4.Heatmap of DEGs and GO functional enrichment analysis after LPGAT1 knockdown in H1299 cell lines. (A) Heatmap of differentially expressed genes between the control group (on the right) and the shLPGAT1 group (on the left). (B) Top 30 GO terms, including biological processes (BPs), cellular components (CCs) and molecular functions (MFs).
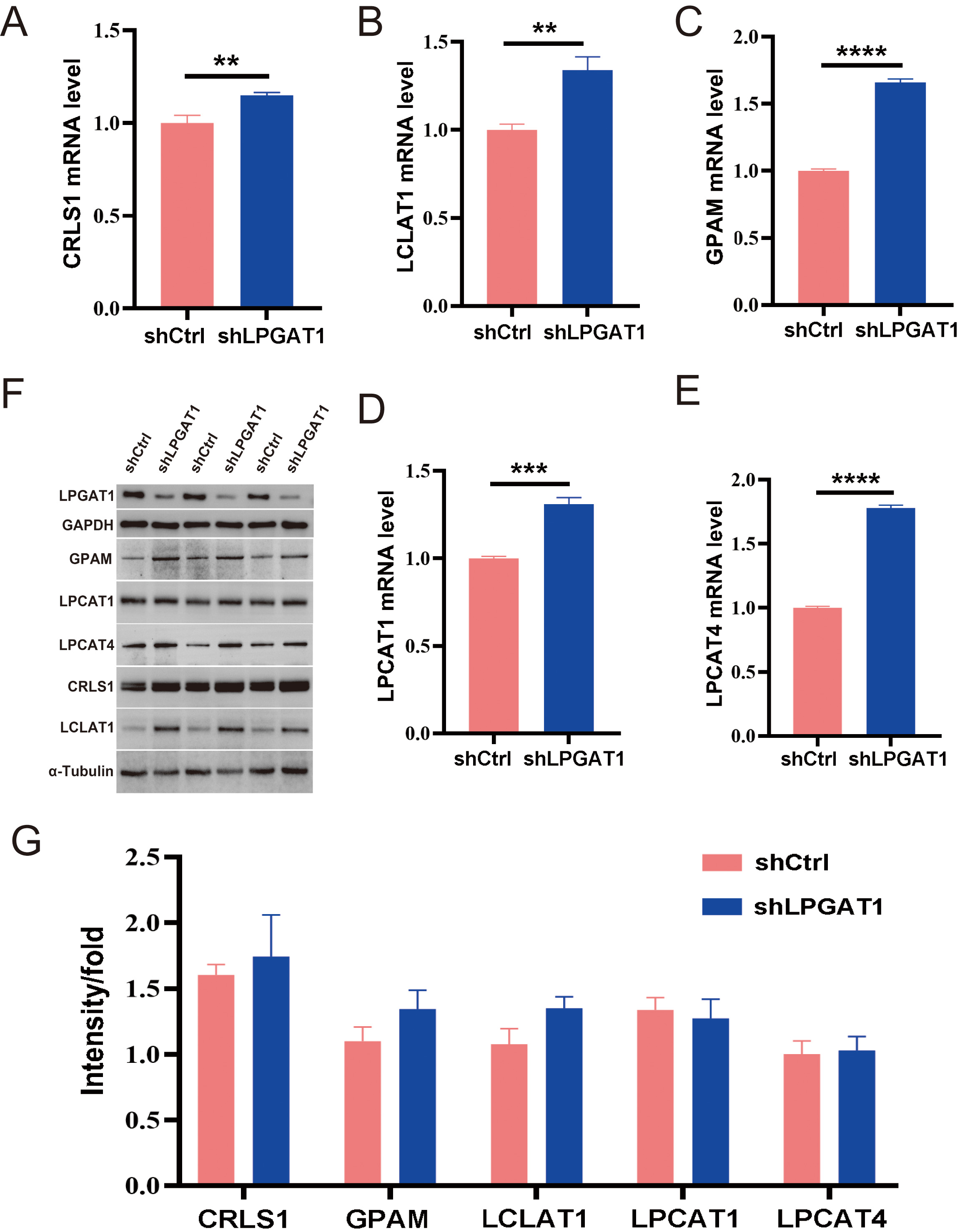 Fig. 5.
Fig. 5.Expression of the related proteins after LPGAT1 knockdown in
H1299 cell lines. (A–E) The mRNA levels of CRLS1, LCLAT1, GPAM, LPCAT1 and
LPCAT4 in the shCtrl and shLPGAT1 groups. Unpaired two-tailed t-test;
LC is a leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide, with around 1.76 million deaths and 2 million new cases annually [16]. Existing studies [17, 18] have shown that the development and progression of LC is closely associated with lipid metabolism.
LPGAT1 regulates triacylglycerol biosynthesis and is essential for maintaining phospholipid homeostasis and modulating the structural integrity of the mitochondrial membrane [11]. It has been reported that LPGAT1 is differentially expressed in normal and tumor tissues [14]. It is a target gene for upregulated expression of miRNAs in LUAD and may be involved in lipid metabolic processes. A previous study has proposed that LPGAT1 can remodel phosphatidylglycerol, an intermediate of the cardiolipin (CL) pathway. LPGAT1 is of central importance for the regulation of lipid metabolism [19, 20].
In this study, we confirmed that the expression of LPGAT1 in LUAD tissues was higher than that in adjacent tissues by IHC in 60 pairs of clinical samples. This study is the first to demonstrate that LPGAT1 knockdown could inhibit the progression of NSCLC in both human cell lines and mouse models. In the cell lines, after knockdown of LPGAT1, cell proliferation was inhibited as shown by the CCK-8 assay, apoptosis was increased, and the cell cycle was arrested as shown by FC. In in vivo experiments in mice, tumor growth was also inhibited in the knockdown group compared to the controls. Thus, in addition to previous reports [19, 20], we further clarified the role of LPGAT1 in LUAD progression, and hypothesized that the inhibition of tumor growth after LPGAT1 knockdown was related to lipid metabolism. We performed transcriptome sequencing to further explore this concept.
After the transcriptome sequencing of H1299 cell lines in the LPGAT1 knockdown and control groups, GO enrichment analysis was performed to screen the up-regulated pathways and pathway-related genes (CRLS1, GPAM, LCLAT1, LPCAT1, LPCAT4). The functions of these genes have also been reported. LPCAT catalyzes the conversion of Lys phosphatidylcholine to phosphatidylcholine, thereby remodeling the biosynthesis pathway [21]. GPAM has been reported to play a vital role in lipid biosynthesis; especially phospholipid synthesis [22]. Human CRLS1 is critical for CL synthesis and phosphatidylglycerol remodeling [23, 24]. CLs are specific phospholipids of the mitochondria [25, 26, 27]. LCLAT1 localizes in the mitochondria-associated membrane [28], and its overexpression elevates the levels of polyunsaturated fatty acids containing CL [28, 29, 30], all of which are related to lipid metabolism. Therefore, we speculate that the downregulation of LPGAT1 affects lipid metabolism and the expression of these genes. Subsequently, we verified the genes by qPCR, and the knockdown group showed significant up-regulation compared to the control group. However, WB results showed no significant difference in protein-level expression of these genes between the two groups. Thus, further exploration of the interaction between LPGAT1 and these pathway related genes is still needed, and will be examined in future studies.
In conclusion, our study revealed that LPGAT1 plays a critical role in the tumorigenesis of NSCLC. These experimental results demonstrated that knockdown of LPGAT1 inhibited tumor growth, which was characterized by inhibited cell proliferation and the induction of cell apoptosis. Nevertheless, the mechanism by which LPGAT1 promotes LUAD needs to be further investigated. In conclusion, LPGAT1 may serve as a new therapeutic target for treatment of LUAD.
The original contributions presented in the study are included inthe article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can bedirected to the corresponding authors.
HG, XW, CM and NW conceived the experiments. XW and NW designed the experiments. HG, CM, XL, YH, PC, XZ and LZ conducted the experiment. TH and WW performed bioinformatics analyses. All the authors analyzed and discussed the results. HG, XW, NW guided the work. HG, CM wrote the first draft. NW, XW revised the first draft. All authors contributed to editorial changes in the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. All authors have participated sufficiently in the work to take public responsibility for appropriate portions of the content and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to its accuracy or integrity.
The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by the Ethics Review Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Bengbu Medical College (approval no. 2021KY092). The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. The animal study was reviewed and approved by the Ethics Review Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Bengbu Medical College (approval no. 2021-268).
Thanks to the First Affiliated Hospital of Bengbu Medical College for his permission to publish this article. We would also like to extend special thanks to the technical staff of Anhui Clinical and Preclinical Key Laboratory of Respiratory Disease for their excellent laboratory assistance. Moreover, we thank all the clinicians of Thoracic Surgery Department who participated in the patient’s management.
This work was supported by the Key Program of Natural Science Research of Higher Education of Anhui Province (grant KJ2020A0575); National Natural Science Foundation of China (82072585); Anhui Provincial Major Science and Technology Project (202003a07020024).
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Supplementary material associated with this article can be found, in the online version, at https://doi.org/10.31083/j.fbl2805089.
References
Publisher’s Note: IMR Press stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.