MicroRNAs (miRNAs) have been regarded as modulators in vascular pathologies,
including hypertension. Dysregulated proliferation and migration of VSMCs
(vascular smooth muscle cells) contributes to vascular remodeling during
hypertension. miR-634 was reported to be dysregulated in hypertensive patients.
The involvement of miR-634 in hypertension and the role of miR-634 on VSMCs
proliferation and migration were then evaluated. Firstly, HASMCs (human aortic
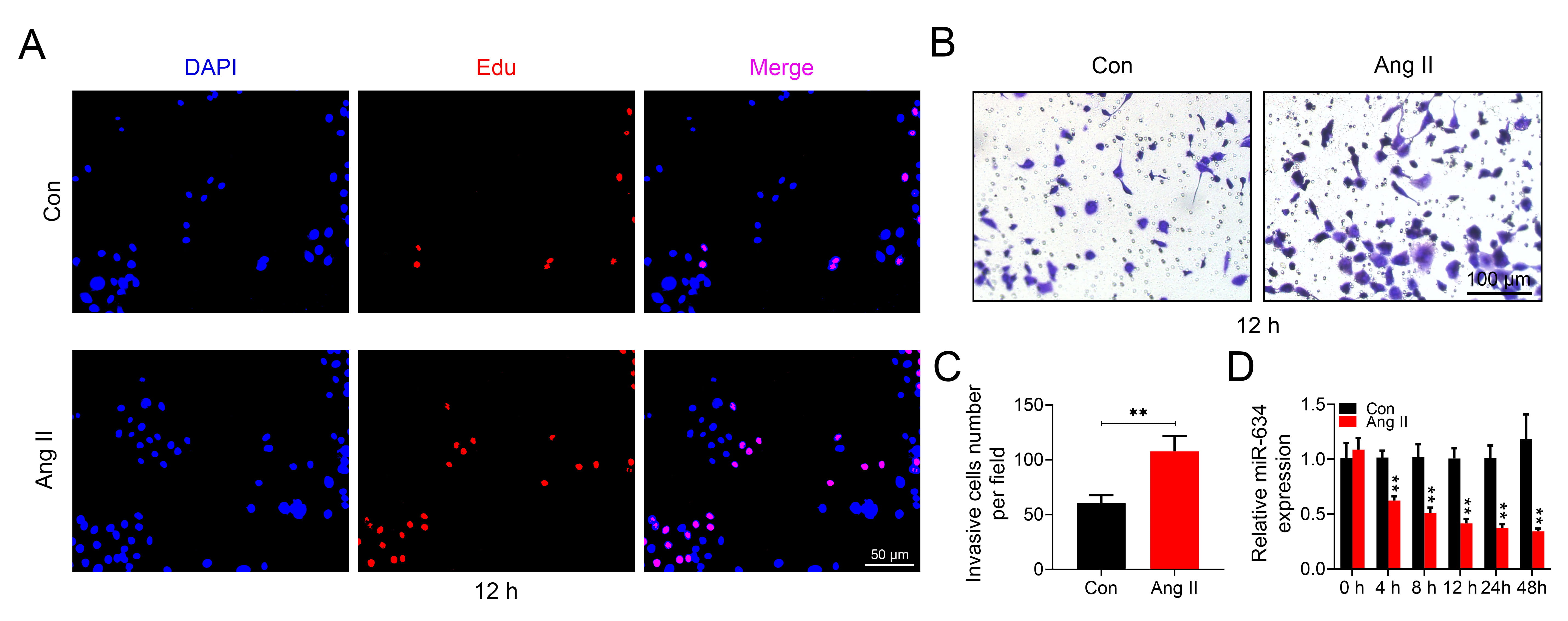
smooth muscle cells) were incubated with 2 M angiotensin (Ang) II for 12
hours to establish the cell model of Ang II-induced hypertension. Results showed
that Ang II treatment promoted proliferation and migration of HASMCs. Secondly,
miR-634 was down-regulated in the hypertensive patients, and reduced in Ang
II-induced HASMCs in a time dependent manner. Functional assays revealed that Ang
II promoted proliferation and migration of HASMCs were suppressed by miR-634
mimic. Lastly, miR-634 targeted 3 untranslated region (UTR) of Wnt4, and reduced
Wnt4 expression in HASMCs. miR-634 inhibited -catenin nuclear
translocation. Over-expression of Wnt4 counteracted the suppressive effects of
miR-634 on Ang II-induced proliferation and migration of HASMCs. In conclusion,
miR-634 inhibited HASMCs proliferation and migration through inactivation of
Wnt4/-catenin pathway.