Background: Mitochondrial dysfunction plays a crucial role in Parkinson’s disease (PD) pathogenesis. The present study was undertaken to investigate the effects of Telmisartan (TEL), an angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1R) blocker, on the mitochondria-specific genes expression in a mouse model of Parkinsonism.
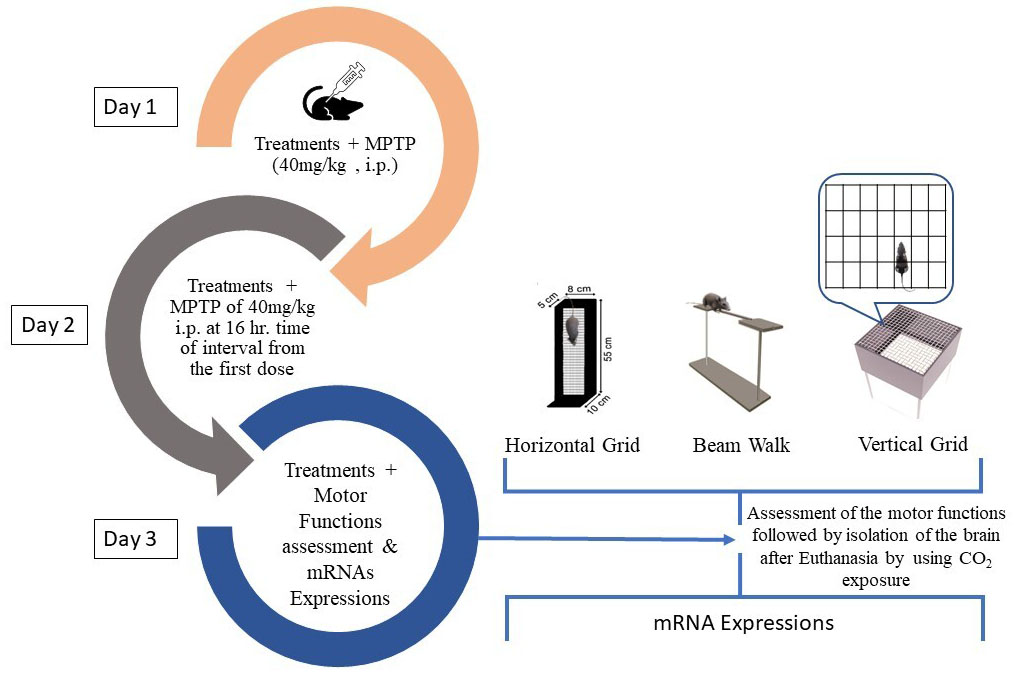
Materials and methods: Mice were divided into 5 groups with 6 in each; Group I received 0.5% CMC (control) + saline, Group II received 0.5% CMC + 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) (positive control), Group III & IV received MPTP + TEL 3 and 10 mg/kg, p.o. respectively, Group V received TEL 10 mg/kg, p.o. (drug control). MPTP was given 80 mg/kg intraperitoneal in two divided doses (40 mg/kg