1 School of Medicine, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, 19839-63113 Tehran, Iran
2 Department of Food Science and Technology, University of Tehran, 14155-6619 Tehran, Iran
3 Student Research Committee, University of Social Welfare and Rehabilitation Sciences, 1985713871 Tehran, Iran
4 Student Research Committee, Vita-Salute San Raffaele University, 20132 Milan, Italy
5 Student Research Committee, Shahroud University of Medical Sciences, 3614773955 Shahroud, Iran
6 Student Research Committee, Mashhad University of Medical Sciences, 91778 99191 Mashhad, Iran
7 School of Medicine, Zanjan University of Medical Sciences, 4513956111 Zanjan, Iran
8 Student Research Committee, Arak University of Medical Sciences, 3818146851 Arak, Iran
9 Student Research Committee, Azerbaijan Medical University, AZ1022 Baku, Azerbaijan
10 Student Research Committee, Faculty of Medicine, Mashhad University of Medical Sciences, 91778 99191 Mashhad, Iran
†These authors contributed equally.
Abstract
Due to the growth of the elderly population, age-related neurological disorders are an increasing problem. Aging begins very gradually and later leads to several neurological issues such as lower neurotransmitter levels, oxidative stress, neuronal inflammation, and continual neuronal loss. These changes might contribute to brain disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD), dementia or mild cognitive impairment, and epilepsy and glioma, and can also aggravate these disorders if they were previously present. Momordica charantia (bitter gourd), a member of the Cucurbitaceae family, is a good source of carbohydrates, proteins, vitamins, and minerals. It is used for diabetes and known for its hypoglycemic and antioxidant effects. In this review, we discuss the pharmaceutical effects of M. charantia on age-related neurological disorders. We searched several databases, including PubMed and Google Scholar, using MeSH terms. We searched articles published up until 2022 regardless of publication language. M. charantia is rich in luteolin, which increases acetylcholine in neurons by binding to enzymes in acetylcholine metabolism pathways, including butyrylcholinesterase and acetylcholinesterase. This binding inhibits the hyperphosphorylation of tau protein by restraining its kinase enzyme. Furthermore, this substance can lower serum cholesterol and has multi-target activity in AD and memory loss. M. charantia can also improve memory by decreasing tau protein and it also has potent antioxidant activity and anti-inflammatory effects. This review highlights that M. charantia has effects on many age-related neurological disorders, and can be a cost-effective supplement with minimal side effects.
Keywords
- bitter gourd
- M. charantia
- age-related neurological diseases
- Alzheimer's disease
- Parkinson's disease
Aging has a considerable impact on the central nervous system (CNS). Due to the recognition of diseases related to the CNS, recent estimates show that the neurological diseases included in the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) Study, such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD), multiple sclerosis (MS), epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease (PD), as well as migraine, medication-overuse headache (MOH), and tension-type headache (TTH), account for 3% of the universal burden of illness. Nevertheless, this accounts for a considerable amount overall. Dementia, especially AD, migraine, epilepsy, and stroke are among the 50 most important agents of disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) [1]. Despite characteristic etiologies, interestingly, aging is the principal risk factor for all the afore mentioned diseases [2, 3, 4]. Based on the significant impacts of aging on neurological diseases, to make real progress in terms of medicines, treatment, and control of these diseases, the molecular causes must be accurately characterized. The molecular mechanisms comprise genome instability through mutations, telomere friction, and epigenetic changes. The connections and collaborations between these mechanisms induce the functional decrease in aging organisms [5]. Appropriate therapies and medicines for the diseases mentioned above have not yet been developed [6]. Considering the previous data and the importance of treating and controlling these diseases that affect health and quality of life, alternative and preventive treatment methods should be sought. Many medicinal plants have been investigated for the prevention and treatment of these diseases [7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17]. One of these plants is Momordica charantia, otherwise known as bitter gourd or bitter melon. Fig. 1 outlines current knowledge regarding the potential pharmacotherapeutic effects and mechanisms of M. charantia in age-related neurological diseases (ANDs).
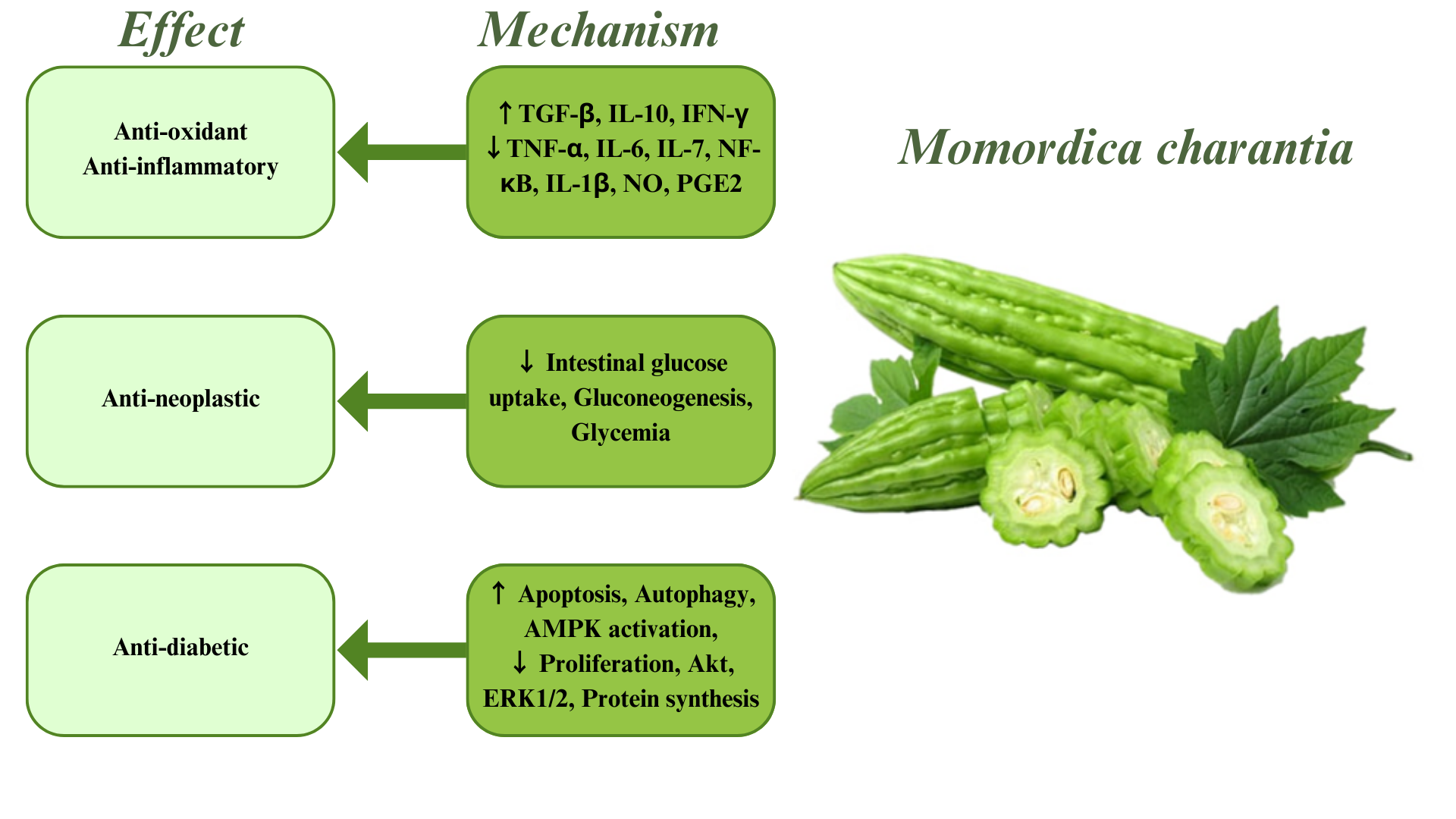 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.Effects and related mechanisms of Momordica charantia.
TGF-
We used the online databases Scopus, Google Scholar, and PubMed to retrieve all articles related to the connection between M. charantia and neurological diseases, such as AD, dementia, PD, brain tumors (glioma and glioblastoma), neuroinflammation and neurotoxicity, oxidative stress, epilepsy, and seizure among the elderly, without regard for article date. The search was carried out on March 7th, 2022. For each of the databases we used momordica charantia (MeSH) terms with a specific strategy, e.g.,
([bitter gourd] or [momordica charantia]) and ([Alzheimer disease] or [Alzheimer dementia])
([bitter gourd] or [momordica charantia]) and ([glioma] or [glial cell tumor])
([bitter gourd] or [momordica charantia]) and ([Parkinson disease] or [idiopathic Parkinson’s disease])
([bitter gourd] or [momordica charantia]) and ([neurotoxicity syndrome] or [neurotoxin disorder])
#1 Bitter Gourd
#2 Momordica charantia
#3 Momordica charantias
#3 #1 or #2
#4 Alzheimer’s disease
#5 Alzheimer’s dementia
#6 Memory
#7 dementia
#8 glioma
#9 glial cell tumor
#10 glioblastoma
#11 Parkinson’s disease
#12 Idiopathic Parkinson’s disease
#13 neurotoxicity syndrome
#14 neurotoxin disorder
#15 neuroinflammation
#16 Neuroinflammatory diseases
#17 neuroprotective
#18 neuroprotection
#19 seizure
#20 epilepsy
#21 #4 or #5 or #6 or #7 or #8 or #9 or #10 or #11 or #12 or #13 or #14 or #15 or #16 or #17 or #18 or #19 or #20
#22 #21 and #3
(((bitter gourd [Title/Abstract]) OR (Momordica charantia [Mesh]) OR (Momordica charantia [Title/Abstract]) OR (Momordica charantias [Title/Abstract]) OR (charantias, Momordica [Title/Abstract]) OR (Bitter Melon [Title/Abstract]) OR (Bitter Melons [Title/Abstract]) OR (Melon, Bitter [Title/Abstract]) OR (Melons, Bitter [Title/Abstract]) OR (Gourd, Bitter [Title/Abstract]) OR (Bitter Gourd [Title/Abstract]) OR (Bitter Gourds [Title/Abstract]) OR (Gourds, Bitter [Title/Abstract]) OR (Karela [Title/Abstract]))) AND (((Alzheimer Disease [Mesh]) OR (Alzheimer Disease [Title/Abstract]) OR (Alzheimer [Title/Abstract]) OR (Alzheimer dementia [Title/Abstract]) OR (memory [Title/Abstract]) OR (dementia [Title/Abstract]) OR (Glioma [Mesh]) OR (Glioma [Title/Abstract]) OR (glial cell tumor [Title/Abstract]) OR (Glioblastoma [Title/Abstract) OR (Parkinson Disease [Mesh]) OR (Parkinson [Title/Abstract]) OR (idiopathic Parkinson’s disease [Title/Abstract]) OR (Neurotoxicity Syndromes [Mesh]) OR (Neurotoxicity [Title/Abstract]) OR (neuroinflammation [Title/Abstract]) OR (Neuroinflammatory Diseases [Mesh]) OR (Neuroprotective [Title/Abstract]) OR (“ALS” [Title/Abstract]) OR (“MS” [Title/Abstract]) OR (“Multiple Sclerosis” [Mesh]) OR (“Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis” [Mesh]) OR (Neuroprotection [Title/Abstract]) OR (seizure [Title/Abstract]) OR (epilepsy [Title/Abstract])))
In total, 119 articles were retrieved and 106 articles remained after removing duplicates. We then reviewed the titles and abstracts of these articles, and 64 articles were eligible for assessment of the full text. After full text assessment, 30 articles did not meet the criteria as being an original article or review presenting data on the effectiveness of M. charantia on the listed conditions and were excluded. Thirty-four studies remained and were included in this review (Fig. 2).
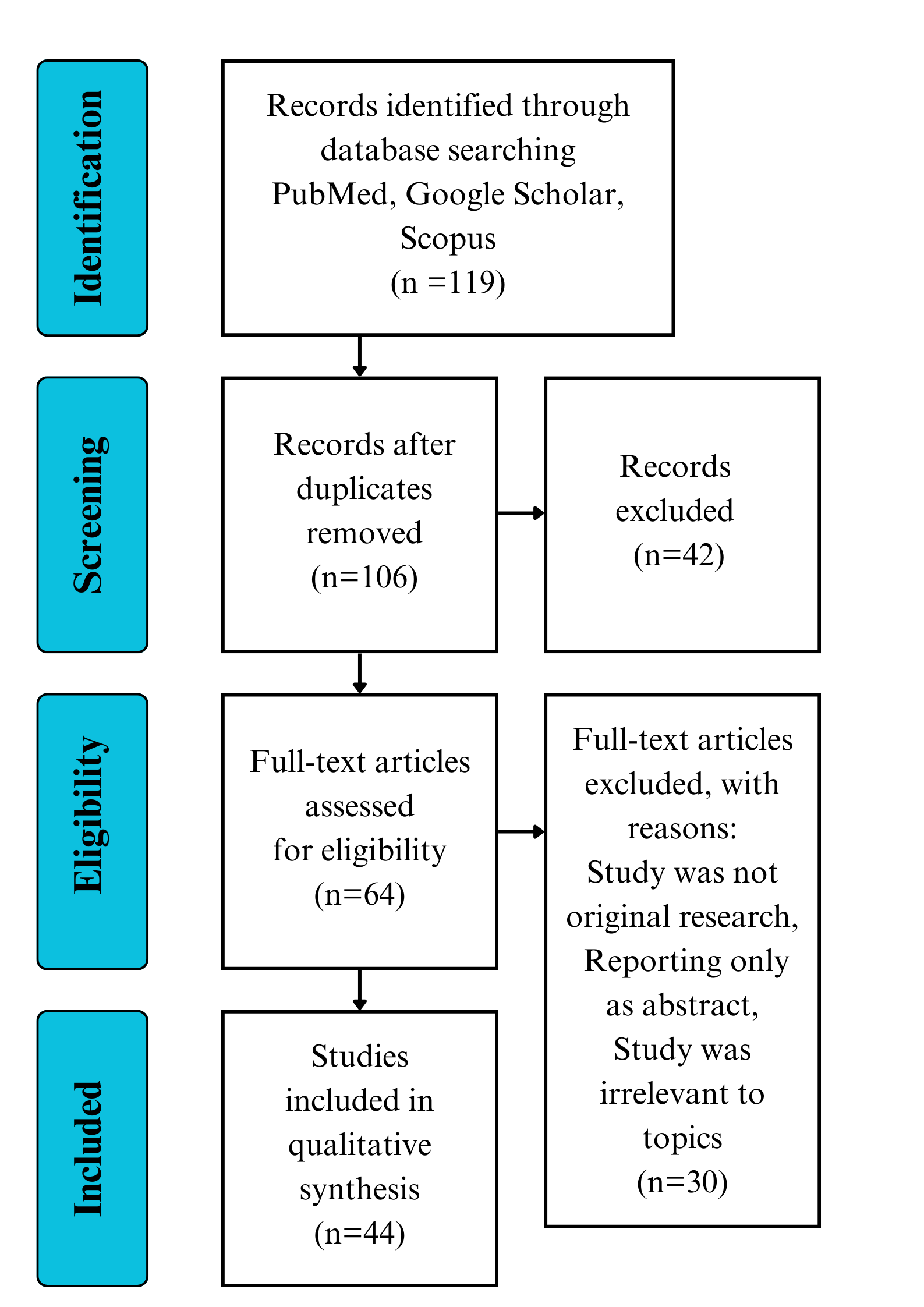 Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.Outline of the review process.
M. charantia belongs to the genus Momordica and the family Cucurbitaceae. M. charantia can grow at high temperatures and is used as an edible vegetable in Asia. This plant grows in a tropical and warm climate; its tree is found in parts of Asia, the Americas, Africa, and the Caribbean. This plant may have therapeutic effects on diabetes, cancer, obesity, and bacterial and viral infections [18].
For centuries, people have used medicinal plants to make products that have been used to prevent and treat diseases. M. charantia is widely distributed in tropical and subtropical regions of the world. It is used in folk medicine to treat diabetes, and its fruit has been used as a vegetable for thousands of years [19].
M. charantia contains many substances, including various biological molecules such as proteins and carbohydrates. It also contains minerals such as different vitamins, essential oils, and alkaloids. Other substances found in M. charantia include phenolic acids, quinines, and triterpenoids. Fig. 3 shows the structure of some of the small molecules in this plant [20].
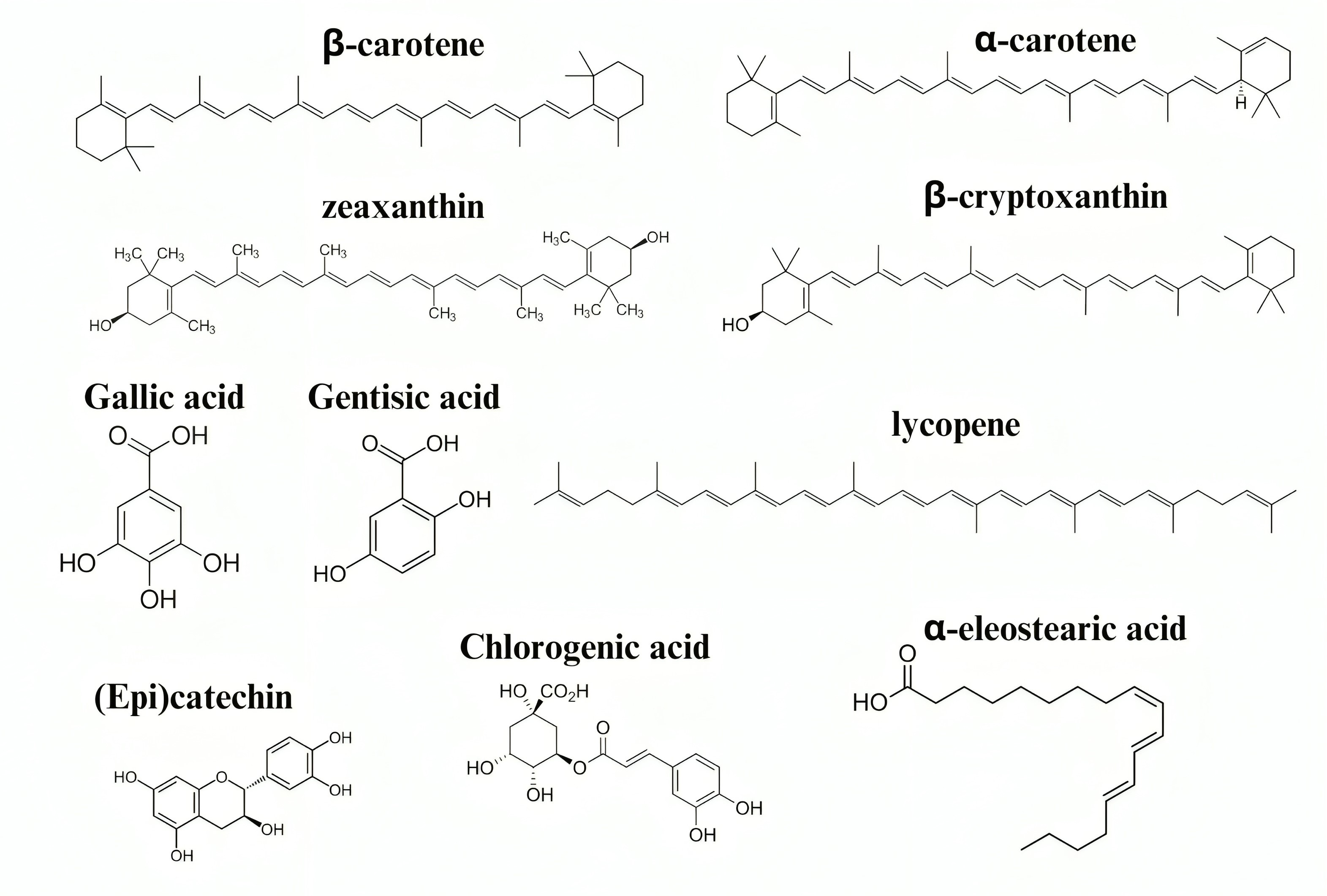 Fig. 3.
Fig. 3.Structure of some of the active compounds found in M. charantia that act against age-related neurological diseases.
M. charantia can inhibit cell death via phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B (PI3K/Akt) pathway blockade in
glioma and glioblastoma. In addition, in AD, it suppresses amyloid-beta
(A
M. charantia has an anti-cancer effect through the modulation of
M. charantia has neuroprotective roles through the enhancement of
soluble guanylate cyclase. In PD, it inhibits
1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MTPT), which produces inflammatory
cytokines, and also affects toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), inhibiting the
Myeloid differentiation primary response 88 (MyD88)/NF-
M. charantia has therefore been used for many different neurological disorders, as shown in Table 1 [21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29].
| Author | Year | Type of study | Neurological disorder | Outcome |
| Qiaoli Li et al. [21] | 2018 | In vitro | Epilepsy | Momordica charantia polysaccharide (MCP) treatment significantly reduced malondialdehyde levels, increased superoxide dismutase and catalase activities, and mitigated Kainic acid (KA)-induced neuronal loss in the Cornu Ammonis 1 (CA1) and CA3 regions of hypocampus. |
| Pratibha V Nerurkar et al. [22] | 2011 | In vivo mouse | Neuroinflammation | Blue mussel treatment improved blood–brain barrier permeability, normalized neuroinflammatory markers, reduced oxidative stress, and normalized plasma antioxidant enzymes and pro-inflammatory cytokines in mice fed a high-fat diet, reducing glial cell activation, forkhead box O (FoxO), sirtuin 1 (Sirt1) protein expression, and up-regulation of Sirt3 mRNA expression. |
| Seung Mi Sin et al. [23] | 2021 | In vivo mouse model | Alzheimer’s disease (AD) | M. charantia’s butanol (BuOH) fraction improved learning and memory by reducing time in the Morris water maze test. It also reduced lipid peroxidation and nitric oxide levels, thus reducing cognitive impairment caused by A25-35. |
| Hei-Jen Huang et al. [24] | 2018 | In vivo mouse | AD | The neuroprotective effect of momordica charantia (MC5), MC3, MC2, and MC5523 is mediated by hyperglycemia or tau hyperphosphorylation. A combination of MC5523 and lithium chloride (LiCl) was administered to ovariectomized mice, boosting survival, increasing neuroprotection, and preventing memory deficits. This suggests that MC5523 and LiCl could be a potential treatment for AD. |
| Dengjun Guo et al. [25] | 2021 | In vitro mouse | Parkinson’s disease | 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6 tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) treatment can cause brain damage, alter neurotransmitter metabolism, cause inflammation, and induce apoptosis. However, M. charantia polysaccharide treatment can reverse these changes, regulating Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)/Myeloid differentiation primary response 88 (MyD88)/Nuclear factor
kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF- |
| Gunasekar Manoharan [26] | 2019 | In vivo | Glioma | M. charantia’s anti-carcinogenic properties were tested on five cancer cell lines. The extract, combined with paclitaxel, significantly decreased cell viability, a significant decrease compared with paclitaxel alone, suggesting its potential for xenobiotic metabolism and oxidative stress. |
| Zafar Ahmad Malik et al. [27] | 2011 | In vivo mouse | Cerebral ischemia | M. charantia juice significantly reduced oxidative stress, damage, and neurological impairments in brains, and exhibited dose-dependent antihyperglycemic action in diabetic mice. |
| Ankur Joshi et al. [28] | 2017 | In vivo rat | Memory enhancing activity | M. charantia significantly corrected scopolamine-induced amnesia and decreased cholinesterase (ChE) activity in rat brain after 7 and 14 days of administration. |
| Tamilanban Thamaraikani et al. [29] | 2020 | In silico | AD | The study found that MC5523 and LiCl, when combined with streptozotocin, increased neuroprotection and anti-gliosis in ovariectomized (OVX) 3Tg-AD mice. This treatment also prevented memory deficits and enhanced synaptic-related protein expression. Luteolin, a compound responsible for AD, showed high affinity for its target protein, indicating its potential as a potential treatment. The study suggests that MC5523 and LiCl could be a potential treatment for AD. |
Neuroprotection is defined as the ability of a therapy to prevent neuronal cell death by intervening in and inhibiting the pathogenetic cascade that results in cell dysfunction and eventual death [30].
Ghanta et al. [31] analyzed the docking of the phytoconstituents of M. charantia with the catalytic domain of guanylate cyclase. A lyase enzyme known as soluble guanylate cyclase is vital in treating cardiovascular and neurodegenerative disorders. Reduced glutamate excitotoxicity caused by modulating soluble guanylate cyclase activity benefits PD [32]. The soluble guanylate cyclase is required for cyclic guanosine monophosphate (GMP) synthesis from guanosine triphosphate (GTP) [33, 34]. A heme-containing heterodimer with alpha and beta subunits is also essential [35]. Several subunit isoforms exist: alpha 1, alpha 2, beta 1, and beta 2 [36]. Alpha 1 and beta 1 are the two most common subunits in the human brain [37]. In humans, the heme part of the beta 1 subunit acts as the active site [32].
Numerous studies have been performed to identify the allosteric binding sites of the enzyme that regulates soluble guanylate cyclase activity. The search for binding sites for allosteric enzymes is limited to their catalytic domain. Defects or inhibitions in this region can lead to enzyme dysfunction. 1H-[1,2,4]oxadiazolo-[4,3-a]quinoxalin-1-one (ODQ), a specific inhibitor targeting the catalytic domain of soluble guanylate cyclase, was proven to show antiparkinsonian activity [38].
A water extraction alcohol precipitation process used to process unripe fruit extract from M. charantia showed complete inhibition of soluble guanylate cyclase [39]. Several subsequent studies have confirmed M. charantia’s ability to inhibit soluble guanylate cyclase [40, 41]. M. charantia extracts showed neuroprotective effects mainly because of their D-galacturonic acid content [42].
Antioxidants scavenge free radicals from the body’s cells and prevent or reduce the damage caused by oxidation. The protective effect of antioxidants continues to be studied around the world. Oxidative stress is caused by the mass production of ROS, primarily because of an imbalance of oxidative and neutralizing processes [43]. Excessive ROS increases age-related disease, triggering inflammation and proatherogenic activities. One of the mechanisms by which antioxidant agents show their effects is reducing the ROS levels in cells. Antioxidants prevent the aging process and age-related and degenerative diseases by helping to balance the production cycle and neutralize free radicals [44, 45, 46, 47].
The polysaccharides in M. charantia are found to be antioxidants. According to an in vivo study, M. charantia polysaccharide could play a role in detoxification, improving immunity, and decreasing blood sugars [48]. Furthermore, the polysaccharide may increase chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) in mouse serum, liver, and spleen. It can also reduce malondialdehyde (MDA) in these tissues [49]. MDA is considered one of the most vital products in the process of membrane lipid peroxidation. The polysaccharides found in M. charantia might therefore possess antioxidant properties [21]. Another study showed that using the polysaccharides found in M. charantia for treating kainic acid-induced epileptic mice could decrease MDA levels and increase the function of SOD and CAT in the rat hippocampus. As a result, the antioxidant and free radical scavenging activities of M. charantia polysaccharides can significantly reduce neuronal damage in the brain and central nervous system [50].
In addition, Chen et al. [50] found that phosphorylated polysaccharides and sulfated polysaccharides of M. charantia have different sugar levels. Introducing phosphate and sulfate can therefore enhance the anti-lipid peroxidation capability and scavenging capacity of superoxide anions in the M. charantia polysaccharides [51].
M. charantia is also rich in phenolic compounds. Gallic acid is the
main phenolic acid found in M. charantia. Several studies support that
the phenolic compounds of M. charantia have antimutagen and antioxidant
effects [52, 53]. The antioxidant effect signified by the Half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC
The antioxidant effect of aqueous extract and phenolic extract of M.
charantia in protecting against damage from hydrogen peroxide (H
Neurotoxicity occurs when exposure to natural or manufactured toxic substances (neurotoxicants) alters the normal activity of the nervous system. This can eventually disrupt or even kill neurons, key cells that transmit and process signals in the brain and other parts of the nervous system [56]. Neurotoxicity can result from exposure to substances used in chemotherapy, radiation treatment, drug therapies, and organ transplants, as well as exposure to heavy metals such as lead and mercury, certain foods and food additives, pesticides, industrial or cleaning solvents, cosmetics, and some naturally occurring substances. Symptoms may appear immediately after exposure or after a delay [57]. They may include limb weakness or numbness, memory loss, vision. Individuals with certain disorders may be especially vulnerable to neurotoxicants [58].
In 2021, Kumar et al. [58] experimented with the anticholinesterase and antioxidant activity of M. charantia in Danio rerio (zebrafish). They used trimethyltin chloride (TMT) to induce neuronal death. Six groups were used in this in vivo study as follows: control, TMT (day1), TMT (day2), TMT + food and drug administration (FDA)-approved drug for AD (donepezil), TMT + M. charantia, and TMT + (M. charantia + mesoporous silica nanoparticle) [59, 60, 61]. Their results showed that M. charantia causes no adverse changes in behavior and mortality during treatment. Furthermore, no pathological changes were seen in the brain histopathological analysis of M. charantia-treated fish. The results of the acetylcholinesterase activity assay indicated that M. charantia at the concentration of 50 g/mL caused significant inhibitory activity of acetylcholinesterase compared with the positive control group (donepezil-treated group). In addition, the aqueous M. charantia showed significant antioxidant activity compared with ascorbic acid, the standard antioxidant in the positive control, according to 2, 2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical scavenging activity, a method for evaluating antioxidant potential. The results of the total antioxidant assay indicated a significant total antioxidant activity of M. charantia compared with the positive control (ascorbic acid). In addition, the lipid peroxidation assay showed that M. charantia had significant lipid peroxidation activity compared with MDA (as a standard antioxidant, positive control) [62].
Neuroinflammation is a crucial part of the general pathology of several chronic and severe problems in the CNS [63]. The occurrence of neurologic diseases in people over 65 years is 1.8 and 2.6 for people aged 85 to 90 years, per 100 population [64]. The aggregation of damaging products caused by oxidative stress, such as glycated products, oxidized proteins, and lipid peroxidation, results in the destruction of neurons, which is more noticeable in brain disorders. Cerebrovascular diseases are characterized by vascular lesions that cause cognitive decline and dementia in old age [65].
Signaling molecules generated throughout the process of neuroinflammation
meditate a number of pro-apoptotic pathways. In operating microglial cells, a
transcription factor named NF-
Kim et al. [66] found that protocatechuic acid (PA), an active phenolic
compound of M. charantia, reduced the increased levels of
NF-
M. charantia supplementation significantly reduced high-fat
diet-induced brain oxidative stress in C57BL/6 mice, reducing blood–brain
barrier (BBB) leakage, neuroinflammatory cytokines, NF-
Obesity increases the development of T-helper (Th) 17 cell genealogy, leading to
inflammation [68]. IFN-
Horax et al. [76] reported that M. charantia contains various flavonoids, bitter triterpene aglycones, non-bitter cucurbitane, and glycosides that transmit antioxidants. Horax et al. [76] also showed that catechin is a major polyphenol in the seeds of BM and pericarp.
Deng et al. [77] used the chronic social defeat stress (CSDS) mouse model to assess the efficacy of Momordica charantia polysaccharide (MCP). MCP prohibits depressive-like behaviors brought on by CSDS. Moreover, MCP diminishes the amount of pro-inflammatory cytokines and restrains The c-Jun-NH(2)-terminal kinase (JNK3) and c-Jun production in the hippocampus. Furthermore, MCP protects against depressive-like behaviors in mice. Consequently, the protective efficacy of MCP in CSDS mice against depressive-like behaviors could be because of reduced neuroinflammation and down-regulation of the JNK3/PI3K/Akt pathway in the hippocampus [78].
In 2020, Kung et al. [78] studied the effects of wild bitter melon
(WBM) on mouse models with spinal cord injuries (SCI), which induced secondary
neuroinflammation. The investigators also used astrocyte-like cells stimulated by
LPS for in vitro studies of astrocyte inflammation. They found that WBM
reduces spinal cord injury. Furthermore, WBM, which contains alpha-eleostearic
acid (
Mitochondrial malfunction and inflammation can lead to irreparable neuronal
deficits. Chitosan/gelatin/sodium hyaluronate (CGSH) iron-sulfur domain 2 is a
protein located on the outer membrane of mitochondria and is involved in
maintaining the integrity of mitochondria and inhibiting apoptosis [79, 80].
Furthermore, CGSH iron-sulfur domain 2 reduces inflammatory responses caused by
CNS injuries. Aging downregulates the expression of CGSH iron-sulfur domain 2,
which aggravates mitochondrial malfunction and increases inflammatory responses
[81, 82]. Spinal cord injury-induced downregulation of IL-4 is reduced by WBM
because losing IL-4 increases microglial polarization from M2 to M1 [83]. WBM can
increase the volume of M2 microglia, which are anti-inflammatory. The
anti-inflammatory effects of WBM are therefore facilitated through the increase
of CGSH iron-sulfur domain 2 in mice with spinal cord injuries and astrocyte-like
cells stimulated with LPS. In addition, its protective effects in mice are shown
by the deactivation of astrocytes and the downregulation of NF-
There have been reports of headaches following the consumption of M. Charantia seeds; however, there is no information regarding amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and headache severity or duration, or effectiveness as a treatment [84].
Macrophages are part of the first line of defense against injury, mediating the
innate non-specific immune response via inflammation, and playing an important
role not only in host defense but also in tissue homeostasis, repair, and
pathology development, including MS. RAW 264.7 mouse derived macrophages have
been widely used as an in vitro model to study the modulatory effects of
various compounds using LPS for activation. It has been observed that treatment
with Bitter Gourd (BG)-4 peptide extracted from M. Charantia has anti-inflammatory
effects. In the investigation conducted by Nieto-Veloza et al. [84],
BG-4 doses up to 375 g/mL had no effect on macrophage viability. It is known that
LPS can activate NF-
AD is among the most prevalent of neurological diseases. Oxidative stress and
the abnormal increases in A
According to an in vivo study by Sin et al. [23], 100 and 200
mg/kg/day of butanol (BuOH) fraction derived from M. charantia can
improve memory and learning in the A
In an in-silico study [89], luteolin, extracted from M. charantia, increased ACh in neuronal cells by attaching to acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase. The authors suggested luteolin as a multi-target molecule against AD. Luteolin can therefore effectively act as a multi-target molecule against AD. The summarized effects of M. charantia on age-related neurological disorders is shown in Figs. 4,5.
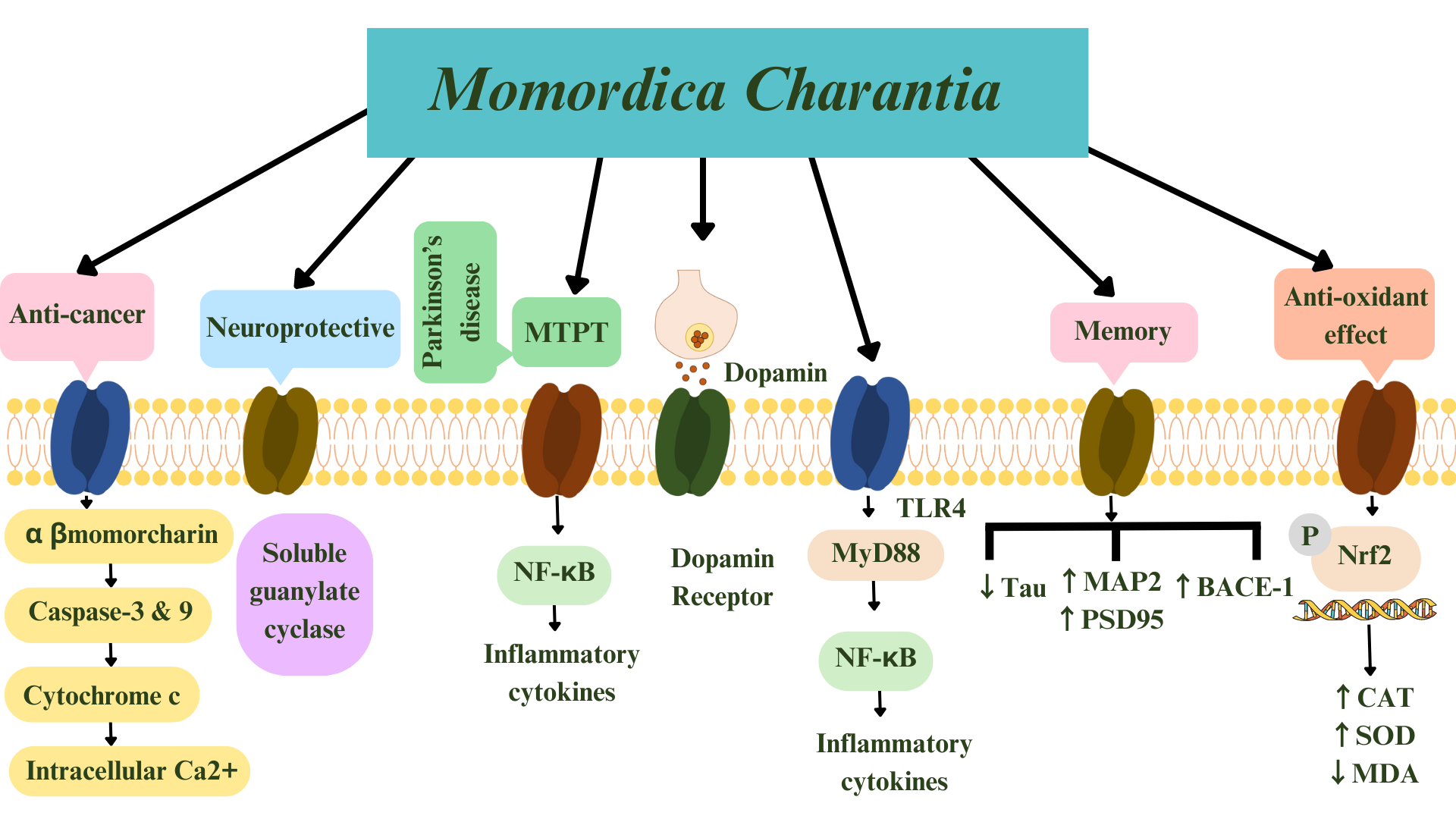 Fig. 4.
Fig. 4.Summary of Momordica charantia’s effects
including anti-oxidant, anti-cancer, anti-glioma, anti-Alzheimer’s disease, and
anti-Parkinson’s disease. Arrows indicate mechanism of actions of M.
charantia. Keap1 is the factor accommodating Nrf2. MTPT,
1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine; NF-
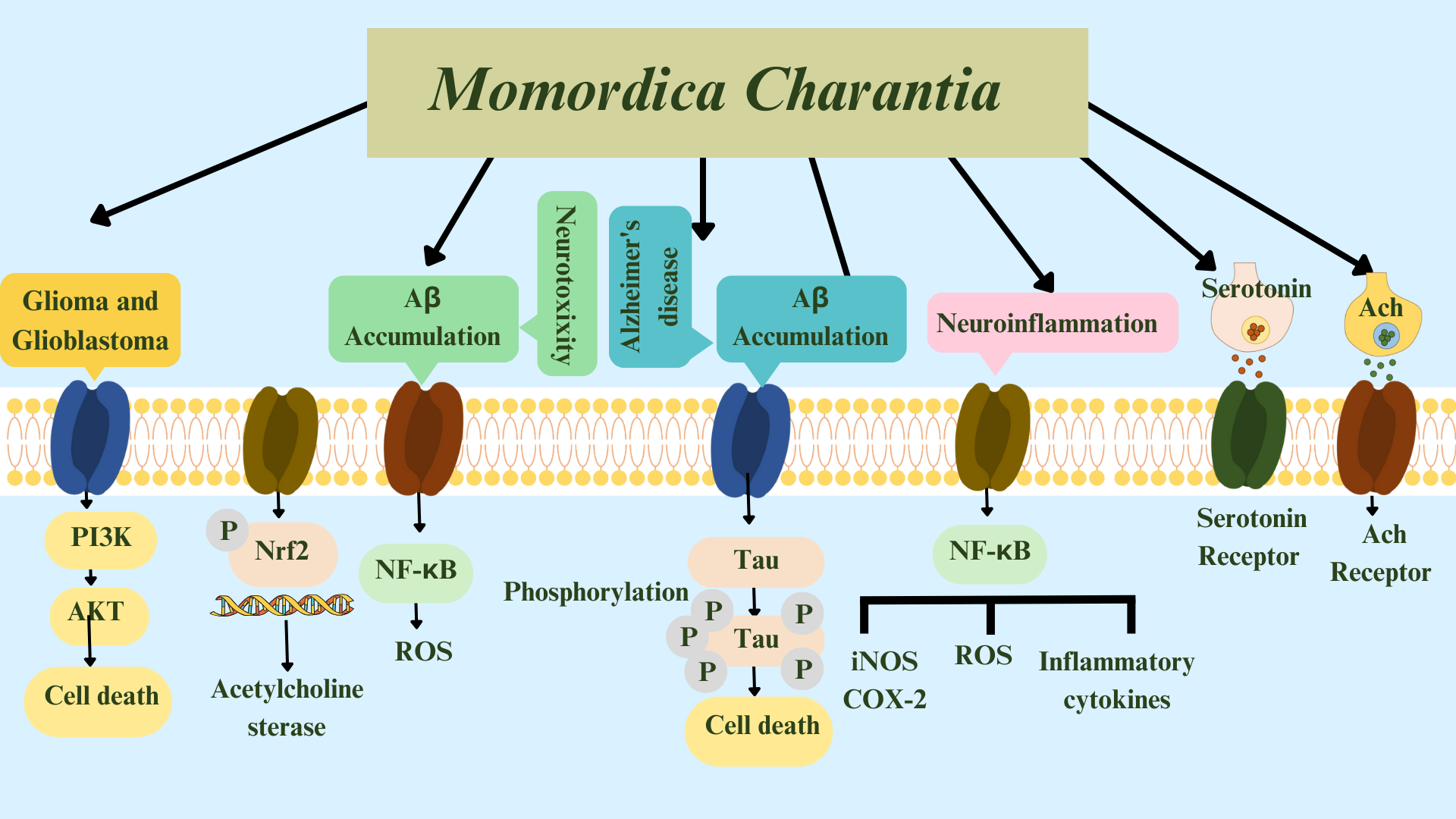 Fig. 5.
Fig. 5.Summary of pathways: Momordica charantia acts in
Gliomas, Glioblastomas, neurotoxicity, and Alzheimer’s disease, and on
neuroinflammation, serotonin, and acetylcholine. Glutamate-activated AMPA and
NMDA receptors mediate A
A study [90] reviewed the therapeutic role of
A study [90] investigated the neuroprotective benefits of sulforaphane (SFN) on
cognitive illnesses such as AD, PD, Huntington’s disease, amyotrophic lateral
sclerosis, MS, autistic spectrum disorder, and schizophrenia in a separate
review. they described the anti-AD-like action of SFN and how it reduced levels
of AD biomarkers, including A
Yoshinori Okada and Mizue Okada [90] evaluated the protective effects of plant seeds against
A
Katsouri et al. [91] showed promising results regarding a lithium chloride (LiCl) compound, including increased cognition and short-term memory, as well as decreased amounts of oligomer, tau protein phosphorylation, and BACE-1 expression, and improved expression of synaptic plasticity-related proteins. Other neuroprotective results have been reported by synthesizing LiCl with L-dopa or other histone deacetylase inhibitors [67, 92, 93, 94, 95, 96, 97, 98, 99, 100, 101]. Many studies showed that synthesizing therapies with multifold drugs has better therapeutic potential for AD [102, 103, 104, 105].
Epilepsy is a common condition that affects the brain and causes frequent seizures. Seizures are bursts of electrical activity in the brain that temporarily affect how it works, causing many symptoms. Epilepsy can start at any age but usually it starts in childhood or in people over 60 years [106]. The drugs that are currently available to treat epilepsy might adversely affect human health. The herbal medicines that have been used in the past and traditional medicines have fewer side effects [107].
Soliman et al. [107] investigated the anticonvulsant potential of M. charantia in rats. Thirty minutes after treatment, ear electrodes were used to give rats a 150 mA shock. According to the reported results, M. charantia might have tremendous anticonvulsant effects against maximal electroshock-induced seizures and reduce the duration and delay the onset of seizures [108].
PD is the second most common neurodegenerative disease after AD [109, 110]. The
cause of PD is not yet well understood, but genetic and environmental factors,
including poisons, are proven to contribute to its development [111]. In PD,
dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra compact area are lost, and Lewy
bodies accumulate in the brain [112]. The active metabolite of
1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6 tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) is N-methyl
4-phenylpyridinium (MPP
Natural ingredients such as polysaccharides in plants delay aging and protect the brain. Momordica charantia polysaccharides (MCPs) have been studied for their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor, hypoglycemic, and anti-diabetic effects [19]. Little is known about their role in the regulation of neurogenesis [114]. However, MCPs reduce nerve damage after stroke by scavenging free radicals [42].
MCPs showed neuroprotective effects in MPTP- and MPP
Increasing the average life expectancy is one of the most significant achievements of the past century [118, 119]. However, a healthy lifestyle and life expectancy free of disease have not increased as much [118, 120]. In addition to disability and reduced physical strength, aging is a risk factor for chronic diseases and cancer, and it has become a pervasive challenge [118, 121, 122]. Research to identify the causes of these destructive changes in the body that occur with the aging process and find a solution to reduce these changes will therefore help to increase quality of life and personal productivity. Cancer and tumors are a group of age-related diseases that we are facing more often due to increases in the average age of society. Prolonged exposure to endogenous and exogenous factors contributing to oxidative stress can eventually lead to gene mutations and inflammatory processes [123]. Antioxidant therapy is therefore accepted as one of the main methods to limit cell damage caused by oxidative stress [124, 125]. Many studies have been conducted to find effective natural and artificial antioxidants for fighting excess free radicals. Currently, people older than 65 years comprise around 60% of all patients with malignant tumors, and they make up 69% of whole cancer deaths [126]. Based on etiology, some highlighted common causes of aging and cancers include oxidative damage and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) damage [127, 128, 129, 130], cellular senescence [131], and insulin/insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) signaling [132].
In a study by Manoharan et al. [132], the impacts of
M. charantia is a plant with medical effects, such as anti-inflammatory
[138, 139, 140, 141, 142, 143, 144, 145] and anti-cancer effects, as well as anti-diabetic and antiviral
activities [146, 147]. Its evaluation is therefore valuable for discovering its
influential factors. Previous studies identified some of its beneficial
components, including the ribosome-inactivating proteins
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), also referred to as a grade four astrocytoma, is a fast-growing and aggressive brain tumor. It invades the nearby brain tissue but does not spread to distant organs. Gliomas are tumors that have a peak incidence in middle-aged humans [160]. Gliomas account for over half of all intracranial tumors [161]. The average annual age-adjusted incidence rate of glioma is estimated at 6 per 100,000 population [162]. These tumors are the most common primary tumors in the brain, originating from different glial cells, including oligodendrocytes, astrocytes, and ependymal cells [163]. Standard of care includes surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. However, due to the exceedingly invasive capability of glioblastoma cells, tumors develop over time and integrate into surrounding brain tissue [164].
Wang et al. [161] found that M. charantia impedes viability
and reduces the multiplication of U251 glioma cells, repressing their influx,
which has an anti-glioma effect. However, it had no considerable efficacy in the
apoptosis of these cells. Moreover, M. charantia-derived extracellular
vesicle-like nanovesicles exert anti-glioma effects by adjusting the
PI3K/Akt signaling route [165]. In
an in vitro study the effects of the anti-tumor activity of M.
charantia (MAP30) on proliferation, migration, and invasion of the U87 and U251
cell lines were assessed [166, 167]. MAP30 inhibited U87 and U251 cell viability
in a dose‑ and time‑dependent manner and decreased colony formation of these cell
lines. It also induced apoptosis and S-phase cell cycle arrest by breaking the
bonds of the adenine‑ribose glycoside. The invading proportions of the cells
treated with MAP30 were significantly lower than their control counterparts.
Western blot analysis indicated decreased leucine rich repeat containing G
protein-coupled receptor 5 (LGR5) expression and increased Smac (activator of
intrinsic apoptosis) expression in cells treated with MAP30. The
Wnt/
Furthermore, 800 µg of the crude water-soluble M. charantia extraction in combination with 250 µg of paclitaxel showed a significant decline in cell viability of five cell lines mentioned earlier [173]. Another study on the U87G Glioblastoma cell line showed that M. charantia extraction displays a cytotoxic and anti-proliferative role and might be helpful as a therapeutic agent against GBM [174]. According to these studies, M. charantia can be considered a plant with pharmacological and nutritional properties. Its compounds make this plant a potential anti-carcinogenic agent and therapeutic aid for the treatment of glioma.
Stroke is the second leading cause of disability and death worldwide, and has the most concerning and excessive burden in countries with revenue deficiency. The universal number of incidents was 13.7 million in 2016, and it is estimated that 87% of those were ischemic stroke [27]. Furthermore, stroke is one of the world’s most prevalent vascular ailments and remains the fifth leading cause of death in the United States [175]. Brain ischemia could be focal or multifocal and is caused by an abrupt cessation or diameter reduction of the artery supply of a region in the brain. The decreased brain blood supply leads to hemodynamic dysfunction, which contributes to damage to the brain tissue [28]. There are some uncommon causative agents of ischemia. Rarely, dissection of cervical blood vessels causes brain ischemia and may cause stroke in younger patients. Another rare cause of brain ischemia is vasospasm. An infection can also lead to stroke.
It should be noted that an increased stroke incidence has occurred with the COVID-19 pandemic [174]. Aging and related conditions, including diabetes, could be important factors in ischemia manifestation. Special attention must therefore be paid to ischemia as an age-related disorder.
The potential neuroprotective effect of the freeze-dried juice of fresh M. charantia in cerebral injury caused by ischemia-reperfusion was studied by Malik et al. [27] using cerebral infarct size, measuring thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) and immediate memory and motor activity. Cerebral oxidative stress and damage with a shortfall in neurological functions were observed related to the dosage. The authors reported that the manifestations were extenuated by lyophilized M. charantia juice pre-treatment. M. charantia might therefore be an efficient option with neuroprotective activity in treating patients with stroke [27].
The aging process begins with molecular changes, such as epigenetic changes, telomere weakening, and the buildup of mutations, which causes genomic instability. These defects increase rapidly over time, with a “snowball effect”, and finally lead to a functional and morphological worsening of the brain, which includes excessive inflammation, reduced amounts of neurotransmitters, progressive neuronal damage, and damaged integrity of vessels, leading to microbleeds and infarction. Furthermore, the reduced effectiveness of the DNA repair systems makes us more vulnerable to spontaneous mutagenesis and ROS, leading to age-related neoplasia. In addition, the malabsorption and malnutrition usually seen in older people may lead to a deficiency in folic acid and vitamin B12, leading to vascular damage. These factors cause brain injuries in the elderly and increase the risk of CNS diseases such as epilepsy, dementia, PD, stroke, and AD [175].
M. charantia is used for diabetes, AD, glioma, neuro-inflammation,
seizure, and PD. Its antioxidant compounds, including luteolin, increase
acetylcholine in neurons, reduce cholesterol, and treat memory loss [28, 29].
It seems that M. charantia can also improve memory by decreasing tau
protein and increasing MAP2, postsynaptic density protein 95 (PSD95), and beta-site amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzyme 1 (BACE-1) [166]. The neurotoxin MPTP targets
dopaminergic neurons and causes PD [61]. MCPs reduce exercise instability and
coordination loss caused by MPTP, inhibit inflammatory factors and oxidative
stress products in the brain, and increase dopamine levels. MCPs also inhibit
apoptosis and oxidative stress caused by MPP
M. charantia liposomes are specific for brain tumor cell lines such as U87-MG, GOS-3, and astrocytoma cell line1321N1 and not human astroglial cells (SVGP12), the standard glial cell line. When compared with paclitaxel (an anti-cancer medicine), the side effects of M. charantia were far less, and whereas paclitaxel could inhibit 44–66% of glioma cells without affecting normal glial cells, the M. charantia liposomes inhibited 60–80% of them [176]. Extracts of the seeds of M. charantia contain ethanolic, which can be used for treating maximal electroshock and pentylenetetrazole seizures. These anticonvulsant effects are due to their phytochemical constituents [108].
This review has highlighted that M. charantia has effects on many ANDs, and it can be a cost-effective drug with minimal side effects. We recommend further in vitro and in vivo studies to fully understand its mechanisms, in addition to clinical trials to investigate the effects of this plant on patients.
Study concept and design: ND. Acquisition of data: SMHHA, OJKA, AA, RT, SB, MF, MR, MSS, SH, SP, DA, MP, HA, SAM, RK. Drafting of the Manuscript: SMHHA, OJKA, AA, RT, SB, MF, MR, MSS, SH, SP, DA, MP, HA. Critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content: SAM, MF, RK. Study supervision: ND. All authors contributed to editorial changes in the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. All authors have participated sufficiently in the work and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
This research received no external funding.
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Publisher’s Note: IMR Press stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.





