1 Department of Anesthesiology, First Affiliated Hospital of USTC, Division of Life Sciences and Medicine, University of Science and Technology of China, 230001 Hefei, Anhui, China
2 School of Medicine, Xiamen University, 361000 Xiamen, Fujian, China
3 Department of Neurology, The 904th Hospital of PLA, Medical School of Anhui Medical University, 214000 Wuxi, Jiangsu, China
4 Department of Neurosurgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xiamen University, School of Medicine, Xiamen University, 361000 Xiamen, Fujian, China
†These authors contributed equally.
Abstract
Background: The inflammation and immune response contribute to ischemic stroke pathology. Damaged brain cells release inflammatory substances to activate the immune system in the acute phase of stroke, including altering the interferon signaling pathway. However, the involvement of histone deacetylation in stroke remains unclear. Methods: To investigate whether histone deacetylation modulation could regulate the interferon signaling pathway and mediate the pathogenic changes after stroke, the middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) mouse model was treated with histone deacetylase 3 (HDAC3) inhibitor and RGFP966. Additionally, a series of approaches, including middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO), real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR), western blot, 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride (TTC) staining, behavioral experiments, and confocal imaging were utilized. Results: It is observed that RGFP966 pretreatment could lead to better outcomes in the MCAO mouse model, including the decrease of infarction volumes, the amelioration of post-stroke anxiety-like behavior, and the relief of inflammatory responses. Furthermore, we found that RGFP966 could counteract the hyperactivation of the interferon signaling pathway and the excessive expression of Z-DNA Binding Protein 1 (ZBP1) in microglia. Conclusions: We demonstrated a novel mechanism that HDAC3 inhibition could ameliorate the pathological injury after ischemic stroke by downregulating the ZBP1/phosphorylated Interferon Regulatory Factor 3 (p-IRF3) pathway. Thus, these data provide a new promising target for therapies for ischemic stroke.
Keywords
- ischemic stroke
- histone deacetylase 3
- Z-DNA binding protein 1
- phosphorylated Interferon Regulatory Factor 3
Stroke is a devastating cerebrovascular disease with high mortality and morbidity [1, 2]. Ischemic stroke is commonly observed when arteries supplying blood to the brain become stenosed or occluded, resulting in local brain tissue hypoxia and ischemia, neuronal cell death, neuroinflammation, and secondary brain injury in hypoperfusion and ischemia/reperfusion [3, 4, 5]. Notably, epigenetic modifications, especially histone deacetylation, were found to be involved in the etiology of ischemia-related neuroinflammation.
HDACs, also known as histone deacetylases, are a class of essential epigenetic
regulator enzymes. HDACs can remove the acetyl group from the target protein’s
lysine-amino group, thereby changing the activity of the protein or affecting
gene transcription. Eighteen different HDACs have been discovered in eukaryotes,
categorized into two groups based on their active mechanisms: classical HDACs and
non-classical HDACs. Notably, the deacetylation activity of classical HDACs
(classes I, II, and IV) depends on the metal ion Zn
Z-DNA Binding Protein 1 (ZBP1), one of the interferon-inducible nucleic acid sensors, plays a vital role in inflammatory cell death and innate immune responses [11]. A previous study has revealed that ZBP1 could recruit Interferon Regulatory Factor 3 (IRF3) in inflammatory lung disease in response to double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) [12]. Thus, the mechanism of ZBP1 recruiting IRF3 might provide novel insight for treating multiple myeloma [13]. Additionally, interferon regulatory factors are a family of transcription factors [14] involved in developing and differentiating distinct immune cells and responding to pathogen infection [15]. The IRF family includes 9 homogeneous isotypes with a common helix-turn-helix DNA binding motif. Notably, IRF-3 is a vital member of the IRF family, whose transcriptional activity is only influenced by post-translational alterations [14]. However, the role of the ZBP1/IRF3 pathway in ischemic stroke has not been investigated yet.
Here, we proposed that HDAC3 could regulate the expression/activity of ZBP1 and that the HDAC3-ZBP1-pIRF3 signaling pathway plays a vital role in ischemic brain injury. RGFP966, a specific suppressor of HDAC3, can decrease p-IRF3 and ZBP1 levels, inhibit proinflammatory cytokines expression, and relieve post-stroke anxious-like behavior. These effects indicate that targeting the HDAC3-ZBP1-pIRF3 signaling pathway might be a candidate therapeutic approach for ischemic stroke.
The Charles River Laboratory in Beijing provided the experimental mice. Age-matched male C57BL/6 wild-type mice were housed in an adaptive habitat with a 12-hour light/dark cycle and food and water accessibility. All animal procedures were carried out strictly per the National Institutes of Health’s guidelines for the care and use of Laboratory Animals. They were followed by the Care Committee of the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC). RGFP966 (CSN17747, CSNpharm, Chicago, IL, USA) powder was dissolved in corn oil with 10% dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO), then RGFP966 solution (8 mg/kg) or Oil was delivered intraperitoneally twice before the ischemia-reperfusion injury according to our previous study [16].
Animals were intravenously anesthetized with 1% sodium pentobarbital at a 45 mg/kg dose. After the right common carotid artery and downstream external carotid artery (ECA) were exposed, a cut was made on the ECA, and a silicone-coated 6-0 monofilament suture (MSMC21B120PK50, RWD Life Science Corporation, Shenzhen, Guangdong, China) was inserted into the ECA and advanced into the internal carotid artery (ICA) about 10 to 11 mm to block the initial segment of the middle cerebral artery (MCA). The artery was reperfused by pulling out the suture after an occlusion over 90 minutes. The mice were kept warm through the operation with a heating pad with a consistent temperature of 37 °C for recovery. Additionally, sham control mice had undergone the same procedure as the MCAO group without the insertion of filament to occlude the MCA. Neurological function assessments from animals in each group were performed 24 h after reperfusion. A five-point scale was utilized for value: A score of 0 indicated no neurological deficit. Mouse with a score of 1 indicated mild focal neurological deficit, accompanied by failing to fully extend their forepaw. A score of 2 indicated moderate focal neurological deficit, with circling. A score of 3 indicated severe focal deficit, with slumping when walking. Mice with a score of 4 failed to walk independently and exhibited a depressed level of consciousness.
The brain tissues were lysed in Radio-immunoprecipitation assay (RIPA) buffer with protease and phosphatase inhibitors. The lysate was homogenized using ultrasound and centrifuged at 13,000 g for 30 min. BCA Protein Assay (#23227, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Cambridge, UK) was applied to validate the protein concentration. After that, protein samples were dissolved in sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) buffer and divided into equal aliquots before being electrophoresed on an 8% to 10% sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) gel. The protein stripe was then transferred to polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membranes, which were then incubated with primary antibodies cGAS (1:3000; #31659, Cell Signaling Technology, Danfoss, MA, USA), ZBP1 (1:3000; sc-271483, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Dallas, TX, USA), p-IRF3 (1:3000; #79945, Cell Signaling Technology, Danfoss, MA, USA), glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) (1:10,000; ab8245, Abcam, Cambridge, UK) overnight at 4 °C after being blocked with 5% nonfat milk in 0.05% Tween TBS buffer for an hour. After 3 washes with PBS, PVDF membranes were incubated with Goat anti-Mouse HRP (1:10,000; Pierce, 1858413, Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA, USA) or Goat anti-Rabbit Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP) (1:10,000; Pierce, 1858415) secondary antibodies for 1 hour at room temperature. Furthermore, the ChemiDoc imaging system (#1708195, Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) was employed to detect the signals of the protein bands, and ImageJ (java8, LOCI, University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI, USA) was used to quantify the band intensity.
Total RNA from brain tissues was isolated using the TRIzol reagent according to the manufacturer’s instructions (#15596018, Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, USA) and reverse transcribed into complementary DNA (cDNA) by a cDNA Synthesis Kit (A5001, Promega, Madison, WI, USA). Then, SYBR qPCR Master Mix (4344463, Thermo Fisher, Danfoss, MA, USA) was adopted for Quantitative Real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) analysis from different groups (see Table 1). The expression of the gene was compared to either Actin or glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH).
| Gene name | Primer (5′-3′) |
| IL-1 |
F 5′-CCTTCCAGGATGAGGACATGA -3′. |
| R 5′-TGAGTCACAGAGGATGGGCTC -3′. | |
| IL-6 (mouse) | F 5′-GAGGATACCACTCCCAACAGACC -3′. |
| R 5′-AAGTGCATCATCGTTGTTCATACA -3′. | |
| GAPDH (mouse) | F 5′-CCCATCACCATCTTCCAGGAGC -3′. |
| R 5′-CCAGTGAGCTTCCCGTTCAGC -3′. | |
| Myd88 (mouse) | F 5′-CACTCGCAGTTTGTTGGATG -3′. |
| R 5′-TCTGGAAGTCACATTCCTTGC -3′. | |
| IL33 (mouse) | F 5′-TCCAACTCCAAGATTTCCCCG -3′. |
| R 5′-CATGCAGTAGACATGGCAGAA -3′. | |
| ZBP1 (mouse) | F 5′-TTGAGCACAGGAGACAATCTG -3′. |
| R 5′-TTCAGGCGGTAAAGGACTTG -3′. | |
| ISG-15 (mouse) | F 5′-GGTGTCCGTGACTAACTCCAT -3′. |
| R 5′-TGGAAAGGGTAAGACCGTCCT -3′. | |
| DDX58 (mouse) | F 5′-AGCCAAGGATGTCTCCGAGGAA -3′. |
| R 5′-ACACTGAGCACGCTTTGTGGAC -3′. | |
| cGAS (mouse) | F 5′-TTCCACGAGGAAATCCGCTGAG -3′. |
| R 5′-CAGCAGGGCTTCCTGGTTTTTC -3′. | |
| MAVS (mouse) | F 5′-CTGCCAACACAATACCACCTGAG -3′. |
| R 5′-TCTCTGGTCCAGAGTGCAAGCT -3′. | |
| MX1 (mouse) | F 5′-TCTGAGGAGAGCCAGACGAT -3′. |
| R 5′-CTCAGGGTGTCGATGAGGTC -3′. | |
| MDA5 (mouse) | F 5′-TGA TGC ACT ATT CCA AGA ACT AAC A -3′. |
| R 5′- TCTGTGAGACGAGTTAGC CAA G -3′. | |
| TMEM173 (mouse) | F 5′-TGTGGCTGCTGATGCCATAC -3′. |
| R 5′-CCAGCACGGTCGATGTTTTG -3′. |
Brain tissues were dehydrated with 20% sucrose and 30% sucrose successively
after cardio-perfusion and fixation with 4% paraformaldehyde solution (PFA) for
8 hours. Using a cryostat, the optimal cutting temperature (OCT)-embedded brain tissue was cut into 16 µm
thick coronal sections (CM1950, Leica, Wetzlar, Germany). Subsequently, slides were
permeabilized and blocked with 0.5% Triton X-100 (T8787, Sigma, St. Louis, MI, USA) and 3%
Bovine Serum Albumin (A2153, Sigma, St. Louis, MIM, USA). Slides were incubated overnight at 4
°C with diluted primary antibodies against glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) (1:2000; ab4674, Abcam,
Cambridge, UK), Iba-1 (1:1000; PA5-27436, Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA), ZBP1 (1:500;
sc-271483, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Dallas, TX, USA), NeuN (1:500; ABN91, Sigma, St. Louis, MI,
USA) in 1% BSA. Brain samples were then stained with Alexa Fluo-conjugated
secondary antibodies (including CY2 Goat anti-Chicken (A11039, Invitrogen, Waltham, MA,
USA), CY3 Goat anti-Rabbit (A21429, Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA), CY5 Goat anti-Mouse
(Z25008, Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA) for two hours at room temperature following three
times washes with PBS, and the cell nucleus was stained with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) (Vector labs
H-1000, Burlingame, CA, USA) for 10 min. Images were captured with a Zeiss LSM880 microscope to
visualize the fluorescence signals and qualified with Image J software (National
Institutes of Health, https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/). For the analysis of microglia
activation, unit about AnalyzeSkeleton was used for analyzing dendrite length. To
analyze microglia soma size, a three-dimensional reconstruction of microglia was
performed according to the 3D Script unit. The volume of microglia was then
calculated. For the analysis of ZBP1 colocalization with other cells (Neuron
(stained with NeuN), Astrocyte (stained with GFAP) and microglia/macrophage
(stained with Iba-1)), Coloc 2 unit in Image J was utilized. Respective
colocalized signals in each cell were marked as an effective value to divide by
the number of all cells per high power field (HPF). The percentage of ZBP1
An open-field test was conducted to assess the anxiety-like behavior of the
mice. It was carried out using smooth wooden equipment (50 cm width
Shortly after the compounds or their corresponding vehicle were supplied, each
mouse was placed individually in the open container after a two-hour acclimation
phase. Fresh sawdust of 3 cm thickness was paved in a polycarbonate cage (26.5 cm
length
The elevated plus maze was used to assess the anxiety-like behavior of the mice. The maze comprises two open and two closed arms with a 50 cm wall and a central zone. After a two-hour adaptation phase in the test room, the mice were placed in the maze’s center facing the closed arm. The mice were allowed to explore the maze freely for five minutes. The video-tracking system (Video camera system, Smart 3.0 , Panlab, Spain) recorded their motion traces. The duration and entries into the open arms and closed arms were reported. Every mouse in the group was summarized according to open arm entry (counts), open arm time (s), and open arm time (%) for further statistics.
To evaluate the change in the size of the ischemic zones, 2,3,5-Triphenyltetrazolium Chloride (TTC) staining (1% 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride, Sigma-Aldrich Co., St. Louis, MO, USA) was applied. Brain tissues were cut into 1-mm thick coronal slices and moved slightly into a dish containing TTC dye for 30 minutes at 37 °C. TTC labels non-injured tissue, leaving the infarct area white. The stained slices were scanned and photographed for further Image J software analysis after being fixed in a 4% formaldehyde solution for two hours, as previously reported [17].
Data were presented as the mean
We assessed the mice’s infarct size and neurobehavioral prognosis from different
groups using TTC staining and the neurological function score. As demonstrated,
the average infarct size of mice with MCAO was about twice as large as that of
mice pretreated with RGFP966 (Fig. 1C). In addition, RGFP966 significantly
reduced motor impairment in mice following ischemia (Fig. 1D, * p
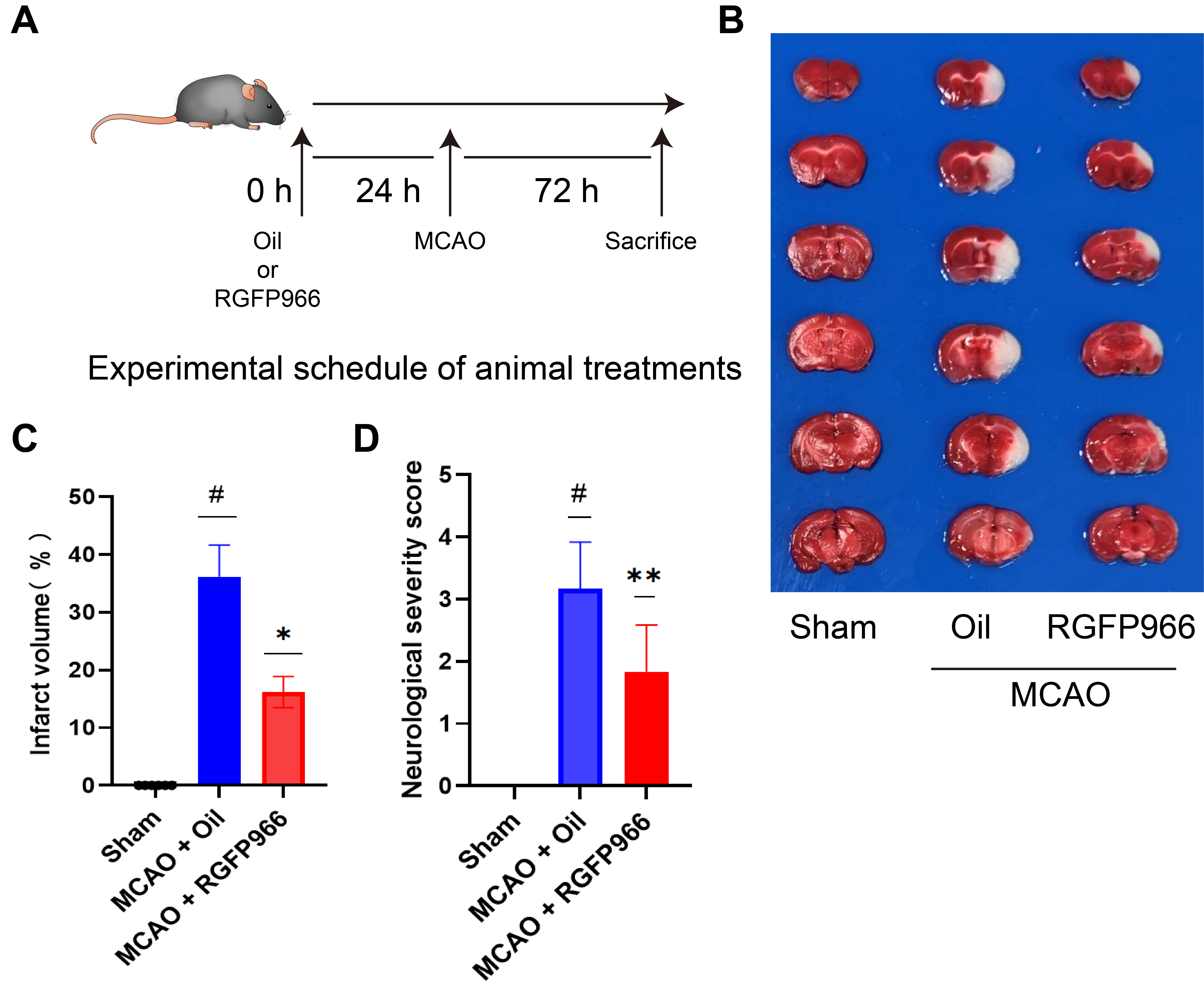 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.HDAC3 inhibition can significantly attenuate ischemic brain
injury. (A) Systematic scheme of the experiment. (B) An overall observation and
TTC staining of the brains of the three groups: Sham, MCAO + Oil, and MCAO +
RGFP966. (C) Statistical analysis of infarct volume of Sham, MCAO + Oil, and MCAO
+ RGFP966 (N = 6 per group). (D) Statistical analysis of neurological severity
score of three groups (N = 6 per group). The above data were presented as the
means
To assess the anxiety-like behavior of mice following infarction, a variety of behavioral tests were performed on three groups of mice. In the open field test, as shown in Fig. 2A–C, the anxiety-like behavior of the mice suffering from cerebral infarction is greatly reduced after RGFP966 treatment, as indicated by increased time spent in the central area. Similarly, administration of RGFP966 prior to MCAO significantly increased the number of entries and percentage of time spent in the open arm in the elevated plus maze test compared to the MCAO-Oil group, as demonstrated in Fig. 2D–F. Furthermore, the burying behavior in the RGFP966 group was greatly decreased compared to the vehicle group (Fig. 2G,H), suggesting that RGFP966 pretreatment can alleviate anxiety-like behavior in mice after an ischemic stroke attack.
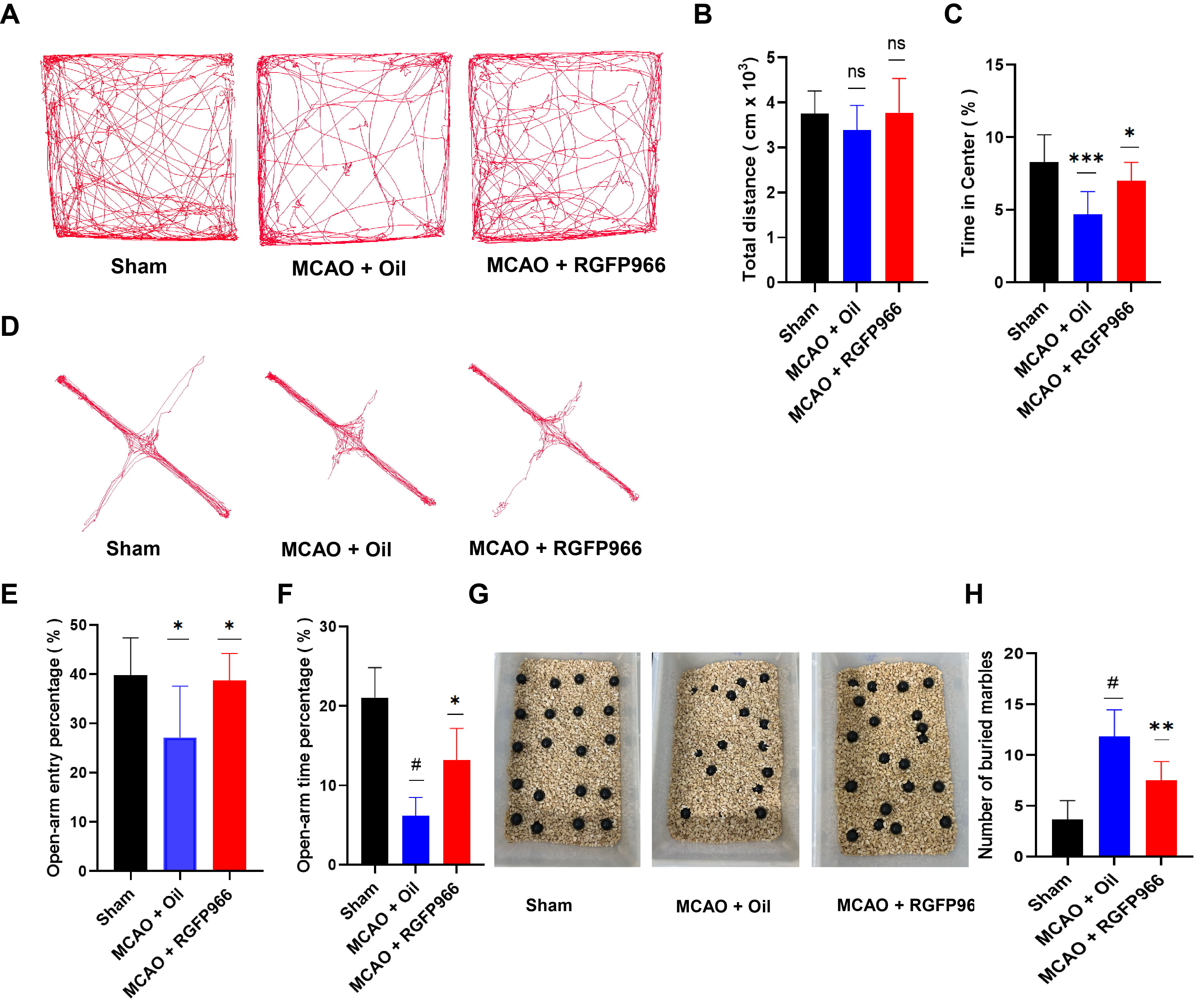 Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.HDAC3 inhibition can significantly reduce anxiety-like behavior
in mice after stroke. (A) Typical tracks in the Open-Field Test (OFT) following
model induction in mice with Sham, MCAO + Oil, and MCAO + RGFP966. (B)
Statistical analysis of total distance traveled (N = 6 per group). (C)
Statistical analysis of time in the center (%) (N = 6 per group). (D) Elevated
plus-maze (EPM) represented in three groups of mice tracks. (E) Statistical
analysis of the percentage of distance traveled in open-arm entry percentage (N =
6 per group). (F) Statistical analysis of the percentage of time spent in the
center area (N = 6 per group). (G) Marbles buried test outcomes in Sham, MCAO +
Oil, MCAO + RGFP966 group. (H) Statistical analysis of the number of buried
marbles among three groups (N = 6 per group). The above data are presented as the
means
To investigate the mechanism of HDAC3 inhibition in alleviating ischemic brain
damage, we obtained brain tissue from each group 3 days after surgery for quantitative PCR (qPCR)
quantitative analysis of inflammation-related cytokines. Fig. 3A illustrates a
member of the Toll-like receptor family in mice related to ischemia damage, the
myeloid differentiation factor 88 (MYD88), and the inflammatory cytokines like
interleukin-1
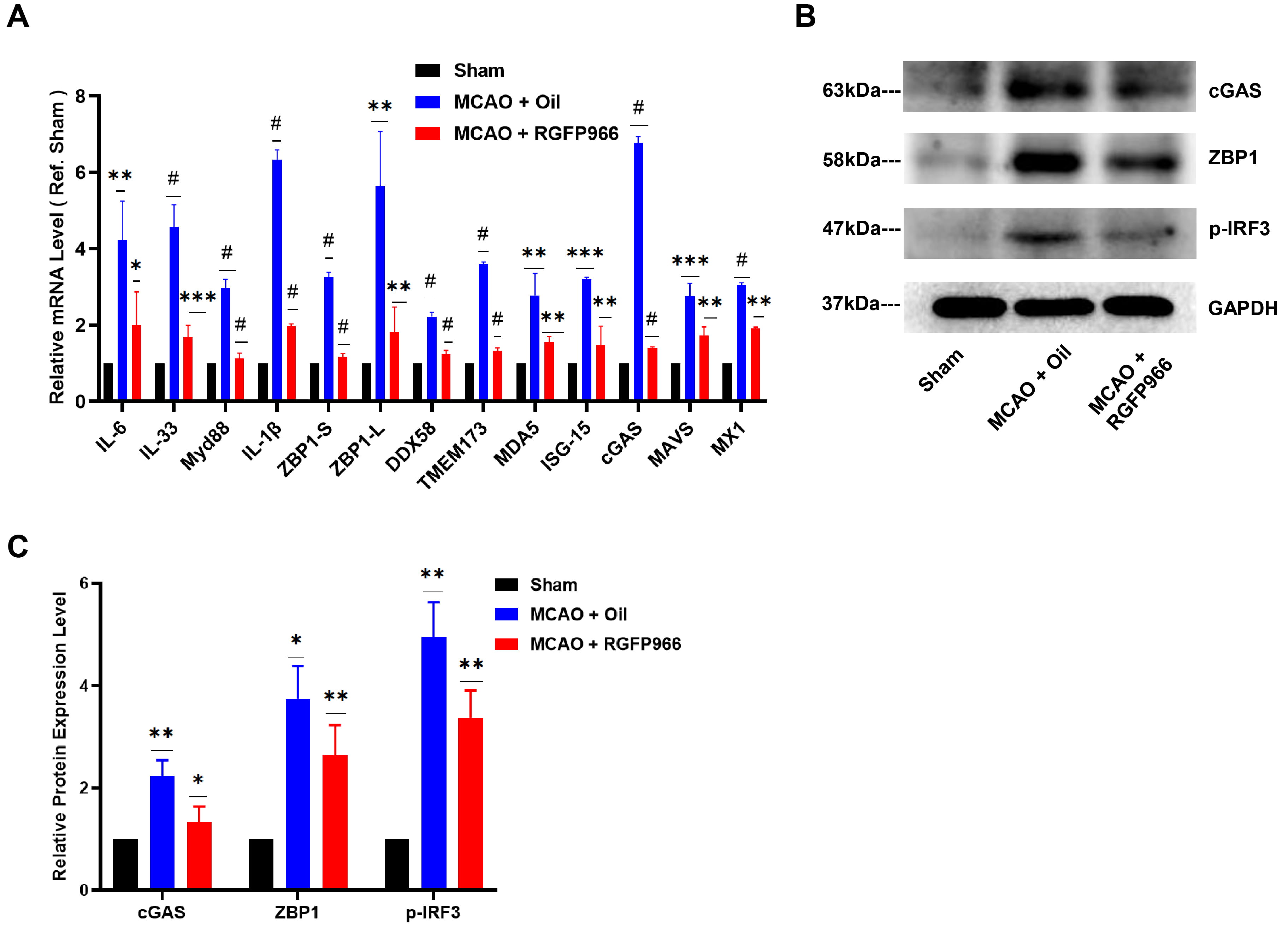 Fig. 3.
Fig. 3.ZBP1/p-IRF3 was downregulated after HDAC3 inhibition in MCAO.
(A) RGFP966 pretreatment decreases the relative mRNA level of IL-6, IL-33, Myd88,
IL-1
Our results showed that ZBP1 was considerably upregulated in the infarct periphery in the MCAO-Oil group compared to the Sham group (Fig. 4A), which aligned with the elevated ZBP1 mRNA expression in Fig. 3A. At the same time, pre-treatment of RGFP966 substantially suppressed the expression of ZBP1 in the ischemic penumbra. Since activated ZBP1 has been shown to recruit TANK Binding Kinase 1 (TBK1) and IRF3 [18], we also detected the expression of IRF3. Notably, the level of p-IRF3 in mouse brain tissue was increased significantly after ischemia, while HDAC3 inhibition significantly decreased the p-IRF3 expression, as shown in Fig. 3B,C.
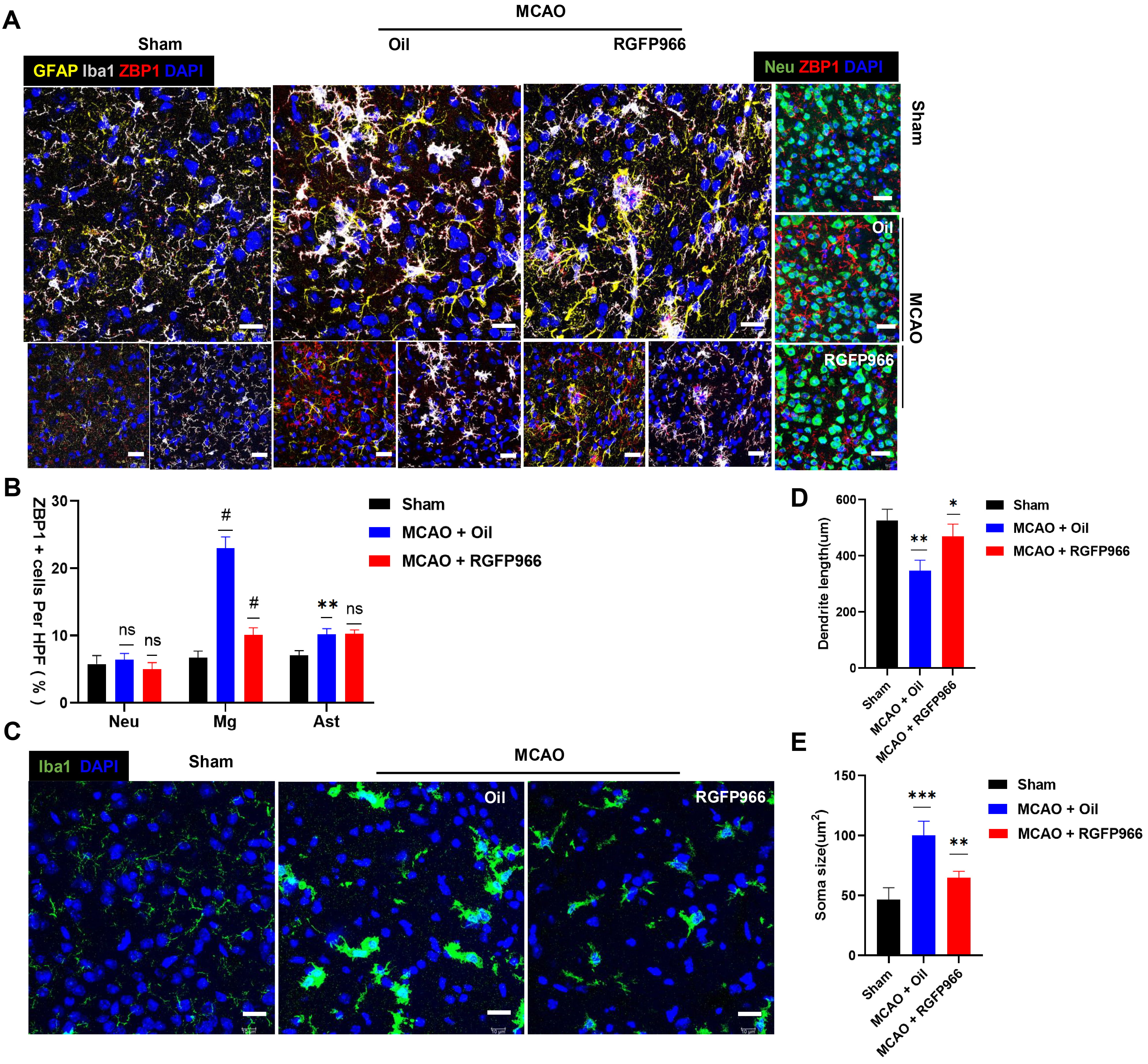 Fig. 4.
Fig. 4.RGFP966 treatment relieved over activation of ZBP1 in microglia
in the ischemic penumbra. (A) Representative immunofluorescence images showing
the morphological changes of microglia labeled with Iba-1 (white) and astrocyte
labeled with GFAP (yellow), and neurons labeled with Neu (green), and
colocalization of Iba-1 (white) and ZBP1 (red), and GFAP (yellow) and ZBP1 (red)
in the ischemic penumbra 72 h after reperfusion, respectively. Scale bar = 10
µm. (B) Percentages of ZBP1-positive cells in NeuN-positive,
Iba-1-positive, GFAP-positive cells in the ischemic penumbra (Slices = 4 per
group). (C) Histological analysis of microglia from Sham, MCAO + Oil, and MCAO +
RGFP966 mice were performed by staining for Iba-1 (green) and DAPI (blue). Scale
bar = 10 µm. (D,E) Statistical analysis of microglial morphology
(soma size and dendrite length) from three groups, respectively. ns, no
significance; *p
There was obvious gliosis in the ischemic penumbra following ischemic brain
injury (Fig. 4). As shown in Fig. 4C, microglia labeled with Iba-1 exhibited a
more rounded morphology, and a decrease in both the length of their branches
after 72 hours of ischemia-reperfusion damage and reactive astrogliosis was also
observed. Interestingly, the ZBP1-positive signal was also augmented, and ZBP1
was found predominantly colocalized with microglia. The percentage of
ZBP1-positive microglia in the MCAO + Oil group was higher than in the Sham group
(p
Ischemic stroke is closely linked to inflammation and immune reaction. Epigenetic modifications were recently found to play a significant role in the pathological damage caused by stroke, which was involved in regulating cellular damage, neuron inflammation, cognitive ability, and motor function [19].
HDACs are a set of contributing epigenetic enzymes that possess an essential function in regulating inflammation. Notably, previous studies have demonstrated that HDAC inhibitors have strong anti-inflammatory effects [8, 20]. HDAC inhibitors manipulate the expression patterns of downstream genes, protecting against ischemic stroke. Valproic acid, a non-selective HDAC inhibitor, has been demonstrated to drastically decrease cerebral infarction volume and enhance neurological behavioral scores in ischemic stroke [21]. Additionally, an investigation found that Trichostatin A enhanced behavioral score and decreased infarct volume in the MCAO model via the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/serine-threonine kinase (PI3K/AKT) pathway [22]. However, there are certain restrictions on the practical use of non-selective HDACs inhibition due to the adverse effects of activating other targets, such as the general toxicity of HDAC6 [23]. HDAC3 has tremendous potential for treating illness of the central nervous system due to its high expression in the brain and regulation of cerebral biological processes, notably learning and memorizing. This suggests that inhibiting HDAC3 activity might be a way to reduce ischemia damage. It has also recently been established that selective inhibition of HDAC3 aids in managing type 1 and type 2 diabetes [24] and Huntington’s disease in mice [25]. In our study, we discovered that RGFP966, a selective HDAC3 inhibitor, considerably reduced the extent of cerebral infarction and alleviated anxious behavior in MCAO mice, in line with the previous findings that HDAC3 inhibition enhances cognitive memory performance [26].
In recent years, innate immune receptors, cGAS and ZBP1, have become pivotal in activating the interferon pathway and releasing pro-inflammatory factors. Pathological changes were found in acute brain ischemia-reperfusion injury, including cell death, oxidative stress, and mitochondrial dysfunction. Due to their structural resemblance to viral DNA, these released dsDNA molecules (nuDNA, mtDNA) accumulate in the cytoplasm [27]. Additionally, these dsDNA molecules can be recognized by cGAS or ZBP1. The expression of cGAS and ZBP1 was found to be upregulated in the MCAO model. The cGAS enzyme catalyzes the production of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGAMP) [28, 29]. Subsequently, the protein STING is recruited and continues to recruit the downstream TANK Binding Kinase 1 (TBK1) in the forms of dimers [30], and IRF3 is subsequently recruited and phosphorylated, leading to the activation of cGAS-cGAMP-STING-IRF3 interferon signal pathway.
Besides acting as an interferon-stimulated gene (ISG), ZBP1 can also boost the
gene expression of interferon (IFN) type I. ZBP1, also known as DAI or DLM-1, has two
Z
Microglia is one of the most significant immune cells in the central nervous system, participating in poststroke inflammation and neuronal injury regulation [40]. Microglia represents a hyperactivated state after an ischemic stroke. A previous study has shown that HDAC3 is mainly expressed in activated microglia in an ischemia mouse model [8]. Additionally, our finding indicated that the expression of ZBP1 is highly synchronized with the morphological changes of microglia. Notably, the microglial ZBP1 was significantly upregulated compared with neurons and astrocytes. Pre-administration of RGFP966 inhibited microglia activation and markedly decreased ZBP1 expression in microglia. Therefore, we speculated that lower ZBP1 expression in microglia induced by HDAC3 inhibitor might indicate a substantial protective effect.
The mechanism of HDAC3 is not thoroughly examined in this paper, for which we did not detect the enzyme activity or expression after utilizing an HDAC3 inhibitor. Additionally, it is unclear how HDAC3 may affect the long-term prognosis of stroke. Furthermore, we did not explore the direct roles of ZBP1 between HDAC3-mediated pathways. Theoretically, ZBP1 KO mice should be used because of non-candidates of ZBP1 specific inhibitors and non-reliable viruses to effectively knock down microglial ZBP1 in the brain. Thus, testing Z-RNA/Z-DNA and using ZBP1 gene knockout mice will provide more persuasive proof. Here, we provided evidence regarding the mechanism of inhibition of the ZBP1/p-IRF3 pathway involving HDAC3 to provide a more theoretical framework for the clinical transformation of HDAC3 inhibitors. However, we intend to further analyze the mechanism of HDAC3 and investigate the pertinent pathways.
We demonstrated HDAC3 inhibition could ameliorate the pathological changes after ischemic stroke by downregulating the hyperactivation of the ZBP1/p-IRF3 pathway, especially in microglia. Importantly, these findings provide a candidate therapeutic target for ischemia-reperfusion injury.
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
HZhu and SW designed the research study. JW, MY, and YC performed the research. YL provided help and advice on the experiments, such like instructing animal behavior experiments and helping immunofluorescence. HZhang, RT and WZ analyzed the data. All authors contributed to editorial changes in the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. All authors have participated sufficiently in the work and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
The protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of First Affiliated Hospital of University of Science and Technology of China (approval number: 2022-N(A)-365).
This work was supported by Department of Anesthesiology, First Affiliated Hospital of USTC, Division of Life Sciences and Medicine, University of Science and Technology of China. The authors thank AiMi Academic Services (https://www.aimieditor.com/) for English language editing and review services.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant numbers: 82272225, 81860249).
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Publisher’s Note: IMR Press stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.




