1 Department of Psychiatry, the First Hospital of Hebei Medical University, 050031 Shijiazhuang, Hebei, China
2 Mental Health Center, Hebei Medical University and Hebei Technical Innovation Center for Mental Health Assessment and Intervention, 050031 Shijiazhuang, Hebei, China
3 Hebei Clinical Research Center for Mental Disorders and Institute of Mental Health, 050031 Shijiazhuang, Hebei, China
4 Hebei Key Laboratory of Brain Science and Psychiatric-Psychologic Disease, 050031 Shijiazhuang, Hebei, China
5 Hebei Brain Ageing and Cognitive Neuroscience Laboratory, 050031 Shijiazhuang, Hebei, China
†These authors contributed equally.
Abstract
Background: Salvianolic acids possess anti-inflammatory properties. This study investigated the therapeutic effect of salvianolic acids on chronic mild stress (CMS)-induced depressive-like behaviors in rats and the involvement of toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and myeloid differentiation factor 88 (MyD88). Methods: Eighty male Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly subjected to CMS or non-CMS protocol for 6 weeks. Starting 3 weeks after CMS exposure, the rats in each group were administered saline, fluoxetine (positive control), salvianolic acids, or salvianolic acids + fluoxetine daily for 3 weeks. The body weight change, sucrose preference, and immobility duration in forced swimming were examined before and after drug treatment. The rats were sacrificed at 3 weeks after drug treatment. Quantitative real-time PCR was performed to measure the mRNA levels of TLR4 and MyD88 in the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus of rats. Results: Compared with non-CMS rats, CMS rats had significantly reduced weight gains and sucrose preference, along with significantly increased immobility durations and elevated mRNA levels of TLR4 and MyD88 in both the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus. Treatment with fluoxetine and salvianolic acids, alone or in combination, facilitated weight gains, alleviated depressive-like behaviors, and reduced cerebral TLR4/MyD88 mRNA levels in CMS rats. Besides, fluoxetine and salvianolic acids additively suppressed TLR4/MyD88 mRNA expression in the prefrontal cortex of rats. Furthermore, TLR4 mRNA levels in both hippocampus and prefrontal cortex positively correlated with MyD88 mRNA expression, inflammatory cytokine secretion, and immobility duration but negatively correlated with sucrose preference. Conclusions: Thus, salvianolic acids alleviate depressive-like behaviors, possibly by suppressing TLR4/MyD88-mediated inflammatory signaling in the brain.
Keywords
- chronic mild stress
- depression
- Salvia miltiorrhiza
- salvianolic acids
- toll-like receptor 4
- myeloid differentiation factor 88
Depression is a mood disorder characterized by a persistent feeling of sadness and loss of interest, representing one of the leading causes of disability worldwide [1]. Major depressive disorder (MDD) is a highly prevalent type of depression that has been projected by WHO as the first cause of the burden of disease globally by 2030 [2]. Approximately 30% of patients with MDD are resistant to conventional treatment for depression [3]. Therefore, it is urgently needed to better understand the development of depression to identify a more effective treatment.
Accumulating evidence has suggested that inflammation contributes to the pathogenesis of depression [4, 5, 6]. Numerous studies have shown that microglia mediate inflammatory signaling that regulates mood and that microglial activation is responsible for depression symptoms [7, 8, 9]. The innate immune receptor Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) is highly expressed on the surface of microglia, serving as a first-line defense against invading microbes [10]. Together with its signaling adaptor myeloid differentiation factor 88 (MyD88), TLR4 plays a critical role in microglial activation [11]. Hines et al. [12] have reported that inflammatory stimulus lipopolysaccharide (LPS) activates TLR4/MyD88 signaling and triggers cytokine production in mouse microglia, resulting in depressive behaviors in mice. Blocking TLR4/MyD88 interaction may prevent LPS-induced microglial activation, cytokine production, and depressive behaviors. Besides, TLR4 signaling is upregulated in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of untreated patients with MDD. Psychotherapy reduces the expression of TLR4 and inflammatory markers, displaying a positive correlation with the improvement of depressive symptoms [13]. Thus, targeting TLR4/MyD88 signaling represents a promising therapeutic strategy in depression treatment.
Salvia miltiorrhiza (Danshen) is a traditional Chinese medicine that is widely used in patients with cardiovascular diseases and acute ischemic stroke due to its function in promoting blood circulation. Salvianolic acids are the most abundant water-soluble components in S. miltiorrhiza, including salvianolic acid A and salvianolic acid B [14]. Salvianolic acid B can cross the blood-brain barrier and alleviate chronic mild stress (CMS)-induced depressive behaviors in animal models [15, 16, 17, 18]. However, the underlying mechanism remains unclear. Recent studies have shown that salvianolic acid B suppresses TLR4/MyD88 signaling in primary cortical neurons and white adipose tissue in rodents [19, 20]. Thus, we hypothesized that the suppression of TLR4/MyD88 signaling is involved in the antidepressant effect of salvianolic acids.
To test our hypothesis, we examined the antidepressant effect of salvianolic acids and the involvement of TLR4/MyD88 signaling in a CMS rat model that is widely used in depression research [21]. FDA-approved antidepressant drug fluoxetine was used as a positive control [22]. Our results suggest that the antidepressant effect of salvianolic acids is associated with the disturbance of TLR4/MyD88-mediated inflammatory signaling in the brain.
Eighty Sprague-Dawley male rats weighing 180–220 g were obtained from the
Experimental Animal Center of Hebei Medical University (Shijiazhuang, Hebei,
China; Certificate No. 1411040). The rats were housed at 23
The rats were randomly divided into CMS and non-CMS groups (n = 40/group). Rats in the CMS group were exposed to mild stressors daily for 6 weeks, as previously described [23]. The mild stressors included cage shaking for 1 h, water deprivation for 24 h, soiled cage for 24 h, reverse of light/dark cycle, food deprivation for 24 h, cage tilting for 24 h, swimming in 45 °C water for 5 min, wrap restraint at 4 °C for 1 h, tail clamping for 1 min, and wrap restraint for 1 h (Table 1). Rats in the non-CMS group were housed in a separate room under identical conditions without stress.
| Stressor | Details |
|---|---|
| Cage shaking | Rats were subjected to cage shaking for 1 h |
| Water deprivation | Rats were subjected to water deprivation for 24 h |
| Reversed day/night cycle | Rats were under a 12:12 h light: dark cycle |
| Food deprivation | Rats were subjected to food deprivation for 24 h |
| Tilted cage | Rats were subjected to cage tilting (about 45°) along the vertical axis for 24 h |
| Hot water swimming | Rats were forced to swim in 45 °C water for 5 min |
| Wet bedding | Rats were subjected to wet bedding for 24 h |
| Wrap restraint | Rats were individually restrained for 1 h at 4 °C |
| Tail clamping | Rat’s tail was clamped for 1 min |
Fluoxetine was purchased from Tokyo Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. (BODF0-DQ, Tokyo
Chemical Industry Co., Ltd, Tokyo, Japan). Salvianolic acids were obtained from
Tasly Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. (Z20110011, Tasly Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd,
Tianjin, China). The drugs were dissolved in 0.9% saline solution on the day of
treatment. At 3 weeks after CMS exposure, both CMS and non-CMS rats were
randomized into 4 subgroups (n = 10 rats/subgroup), respectively, and treated
with 0.9% saline solution (10 mL/kg), fluoxetine (20 mg/kg) [24], salvianolic
acids (40 mg/kg) [25], or fluoxetine + salvianolic acids daily for 3 weeks via
intraperitoneal injection. The body weights were measured before CMS exposure
(baseline), 3 weeks post-stress (before drug treatment), and 3 weeks
post-treatment. The weight gain rate post-stress was calculated as [(body weight
post-stress – baseline body weight)/body weight post-stress]
The sucrose preference test was carried out in the animal’s home cage as
previously described [26, 27]. The rats were given 1% sucrose (13-201-00107,
Tianjin Baishi Chemical Co. Ltd, Tianjin, China) solution for acclimation for 1
day, and the sucrose water was replaced with pure water on the second day. On the
day of the test, the rats were fasted with no water for 10 h, provided with 1%
sucrose solution and pure water bottles, and the consumption of sucrose was
measured after 2 h. Preference % = [consumption of sucrose water/(consumption of
sucrose water + consumption of pure water)
The forced swimming test was performed as previously described using a glass
cylinder (20 cm in diameter and 50 cm high) (XR-XQ202, Shanghai Xinruan
Information Technology Co. Ltd, Shanghai, China) filled with tap water (20 cm
deep) at 25
Rats were sacrificed at 3 weeks after drug treatment (24 h after the final
stressor exposure). The whole prefrontal cortex and hippocampus of each rat were
immediately harvested and snapped frozen in liquid nitrogen. Quantitative
real-time PCR was performed to measure the mRNA levels of TLR-4 and
MyD88 in the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus tissue samples. Total RNA
was isolated using TRIzol (DP405-02, Tiangen Biotech Co. Ltd., Beijing, China),
followed by cDNA synthesis (RR047B, TaKaRa, Tokyo, Japan). PCR was performed
using SYBR green (RR82LR, TaKaRa, Tokyo, Japan) and the primers (Table 2).
| Gene | Sense Primer (5ʹ-3ʹ) | Antisense Primer (5ʹ-3ʹ) |
|---|---|---|
| TLR4 | TCCACAAGAGCCGGAAAGTT | TGAAGATGATGCCAGAGCGG |
| MyD88 | AGTTTGGCTTCACCCCACAA | GCAAAGAGGCCTCCATTCCT |
| GGAGATTACTGCCCTGGCTCCTA | GACTCATCGTACTCCTGCTTGCTG | |
| TLR4, toll-like receptor 4; MyD88, myeloid differentiation factor 88. | ||
Data were expressed as the mean
Because body weight changes reflect the overall impact of a chronic stressful
situation [29], we examined the effect of salvianolic acids treatment on body
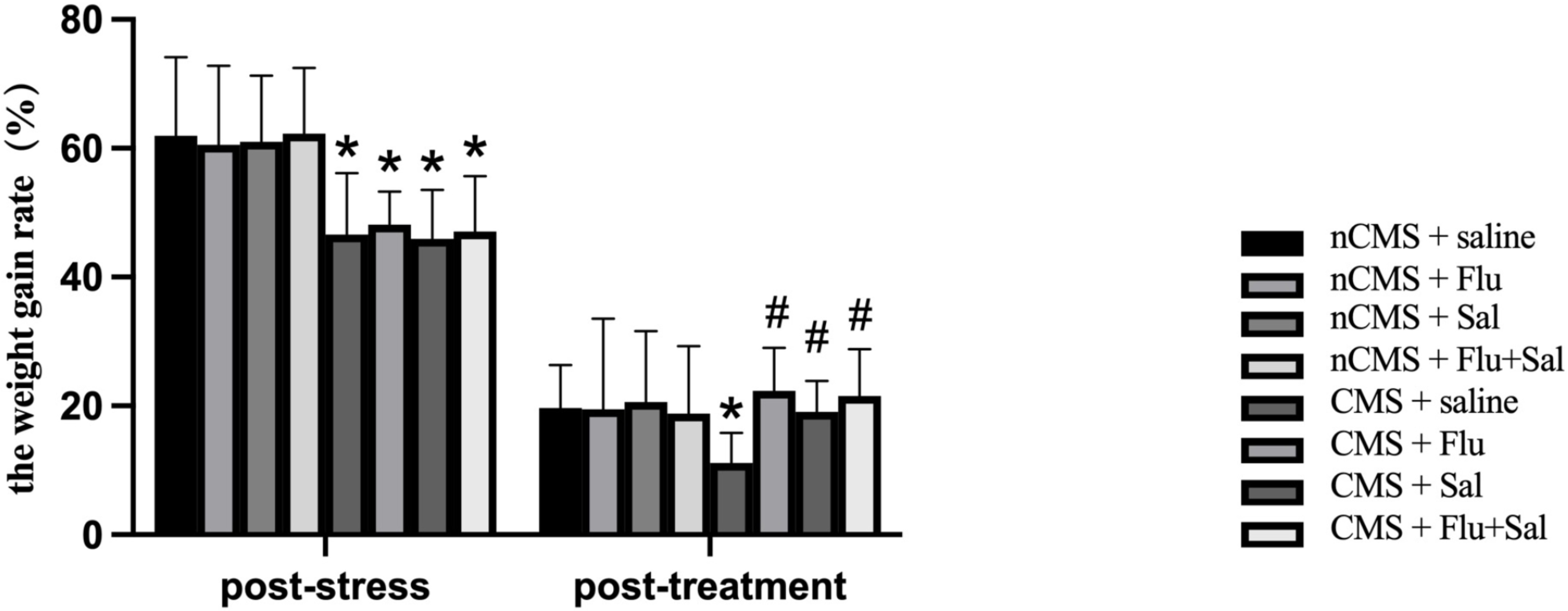
weight changes. As shown in Fig. 1, at 3 weeks post-stress, CMS rats had reduced
weight gain rates compared with non-CMS rats (all p
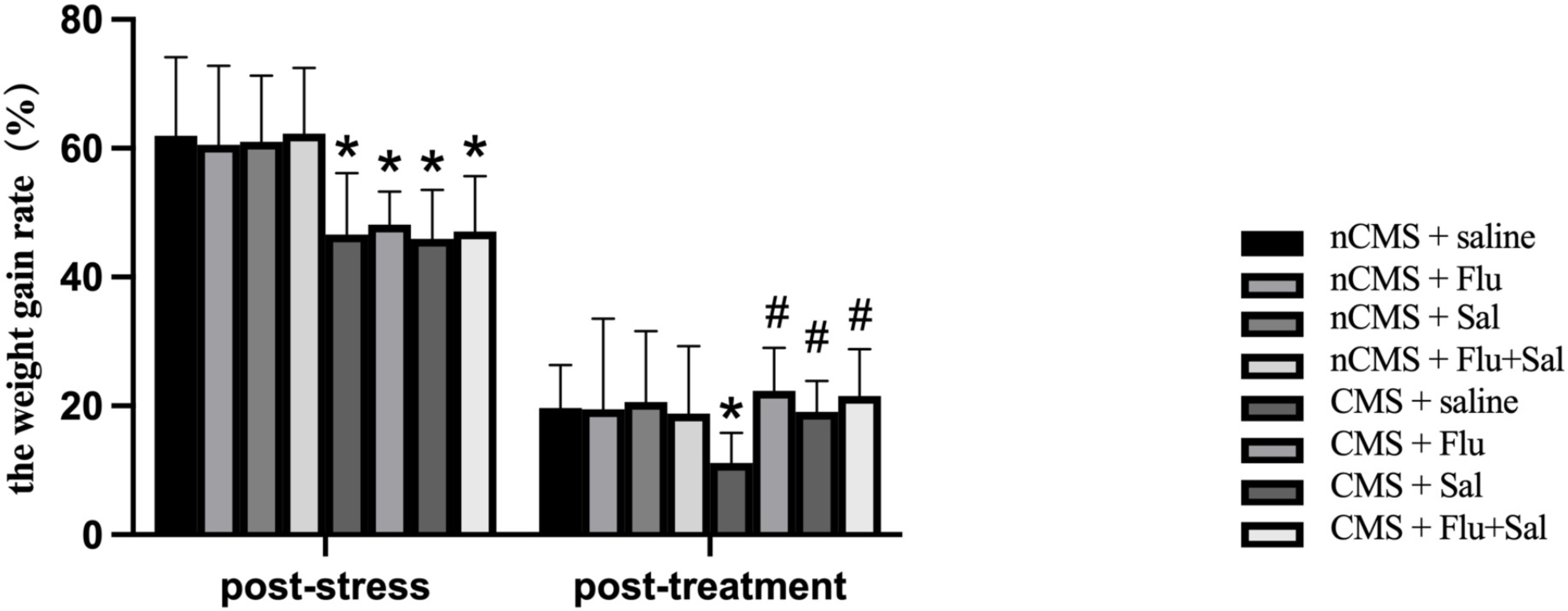 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.Salvianolic acids increased body weight gain rates in rats
exposed to chronic mild stress (CMS). The body weights were measured before CMS
exposure (baseline), 3 weeks post-stress (before drug treatment), and 3 weeks
post-treatment. The weight gain rate post-stress was calculated as [(body weight
post-stress – baseline body weight)/body weight post-stress]
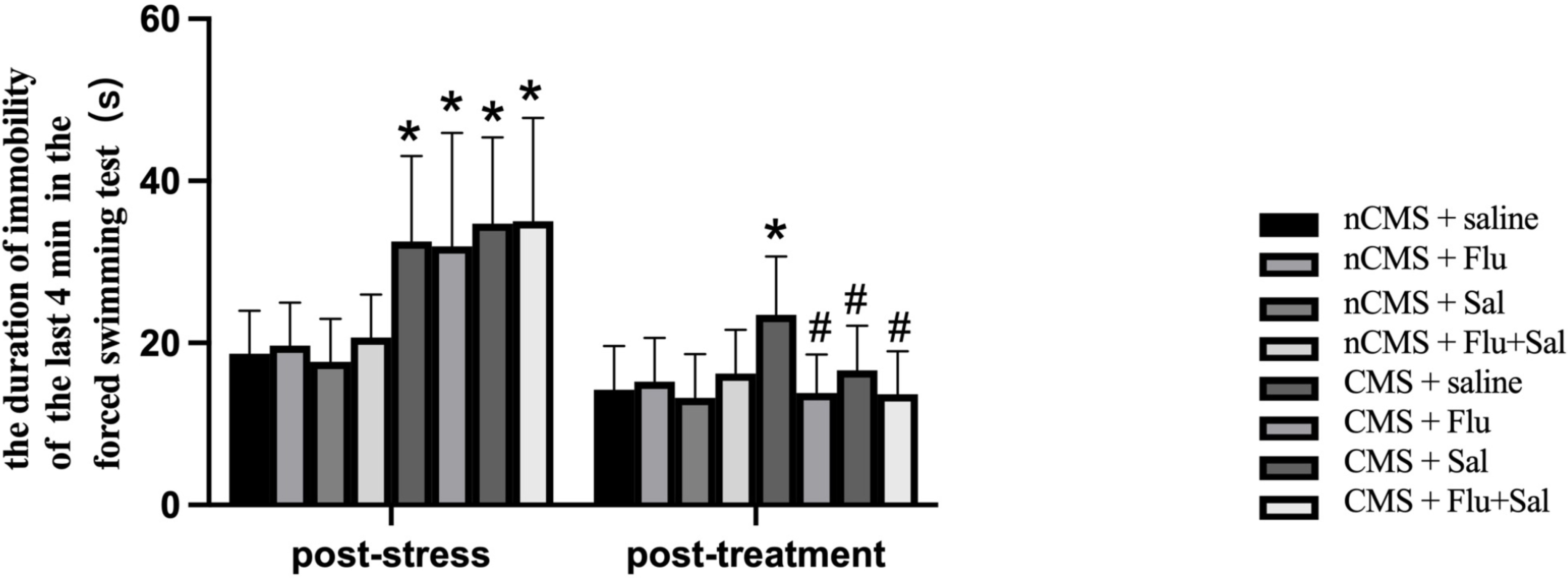
The forced swimming test is commonly used to evaluate behavioral despair in
animal models [30]. As shown in Fig. 2, before treatment, CMS rats showed
significantly increased immobility durations compared with non-CMS rats (all
p
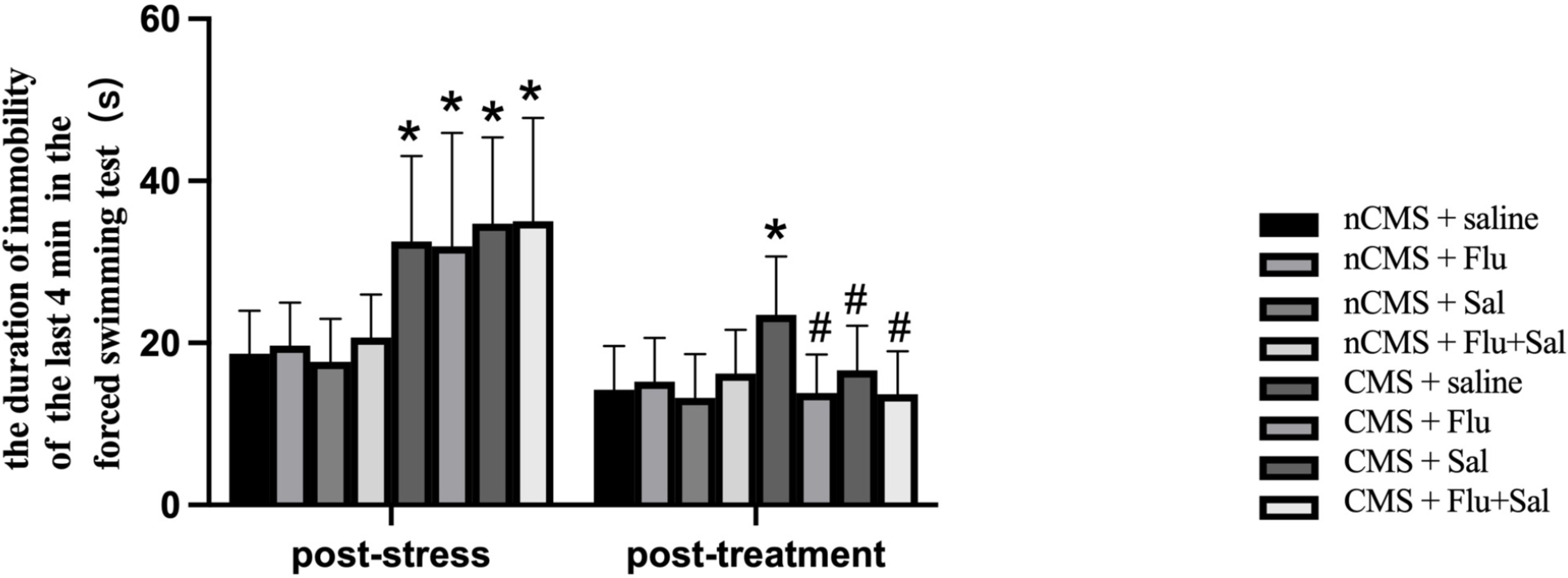 Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.Salvianolic acids alleviated immobility in CMS rats. The forced
swimming test was performed before and after drug treatment. The duration of
immobility was recorded during the last 4 min of the test. Data are expressed as
the mean
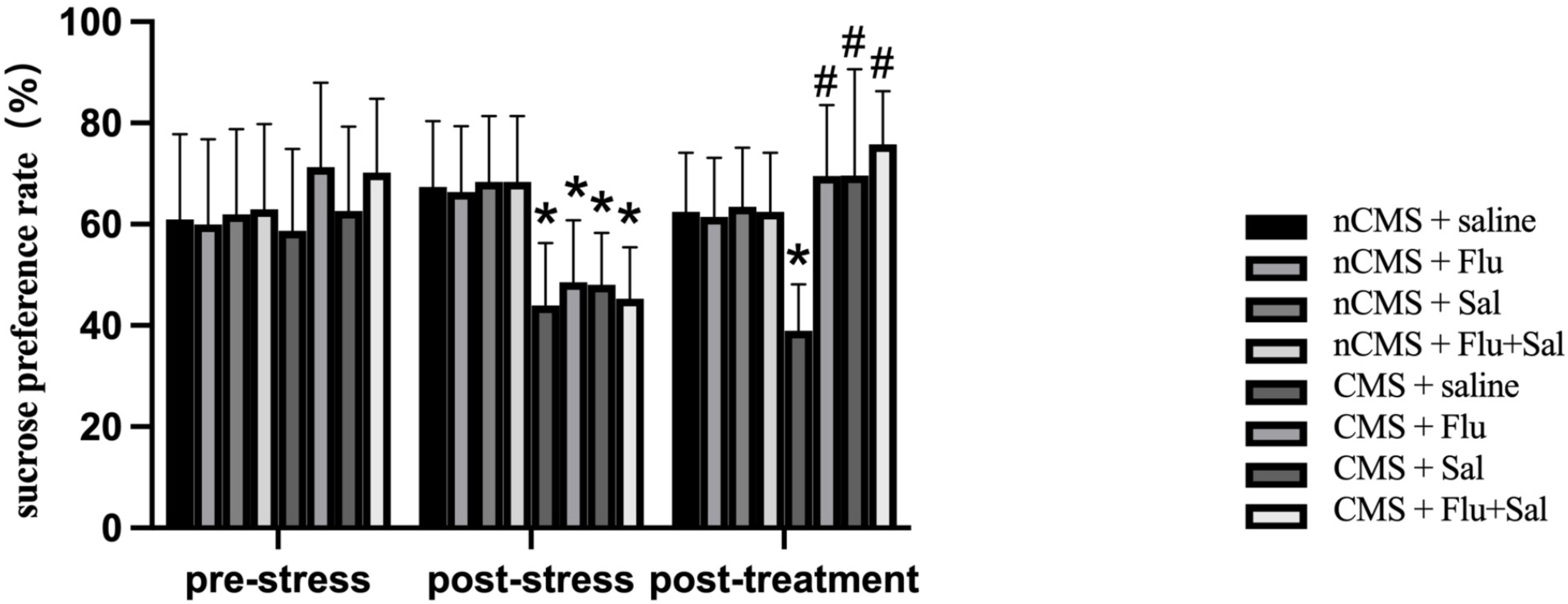
To examine the effect of salvianolic acids on anhedonia, we performed the
sucrose preference test [26]. As shown in Fig. 3, sucrose preference was reduced
in CMS rats compared with that in non-CMS rats before drug treatment (all
p
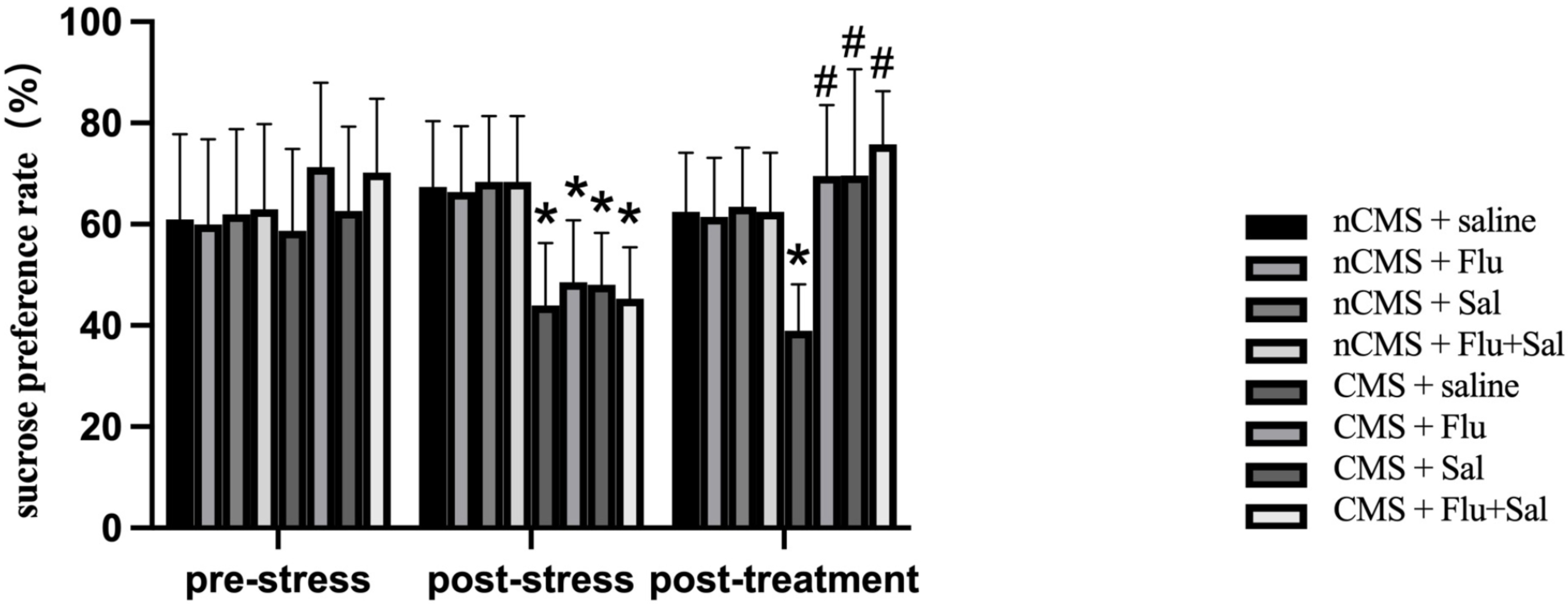 Fig. 3.
Fig. 3.Salvianolic acids improvedsucrose preference in CMS
rats. Sucrose preference test was performed before and after drug treatment. The
sucrose preference was calculated as the percentage of the sucrose solution
intake of the total fluid intake. Data were expressed as the mean
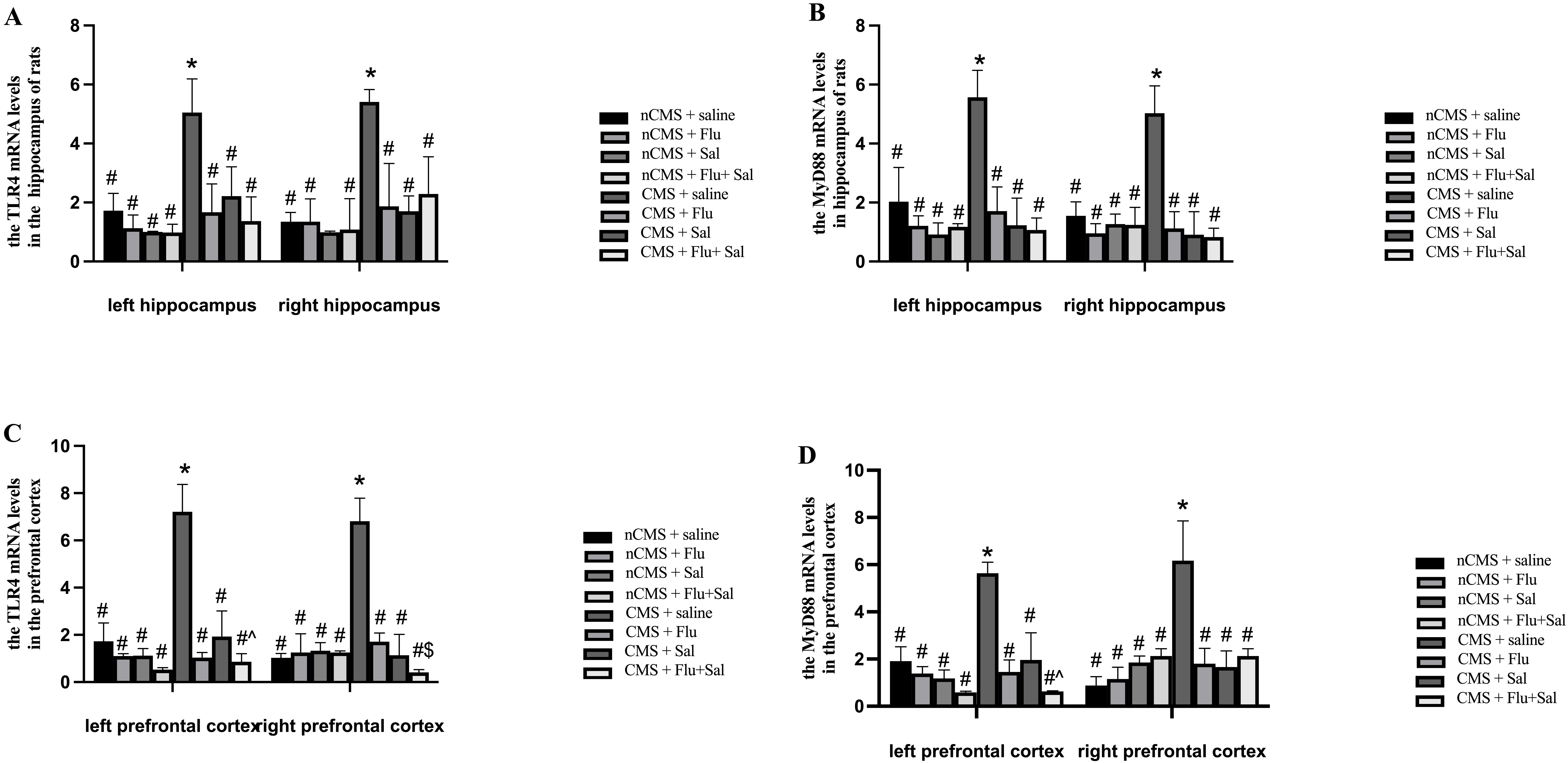
Considering the involvement of TLR4 and MyD88 in the
development of depression [12], we determined the mRNA levels of TLR4
and MyD88 in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex of rats. As shown in
Fig. 4A,B, before treatment, the mRNA levels of TLR4 and
MyD88 in both the left and right hippocampus of saline-treated CMS rats
were higher than those of saline-treated non-CMS rats, suggesting that CMS
induces upregulation of TLR4/MyD88 expression in the brain. Compared
with saline treatment, 3 weeks of treatment with fluoxetine and salvianolic
acids, alone or in combination, reduced TLR4 and MyD88 mRNA in
CMS rats (all p
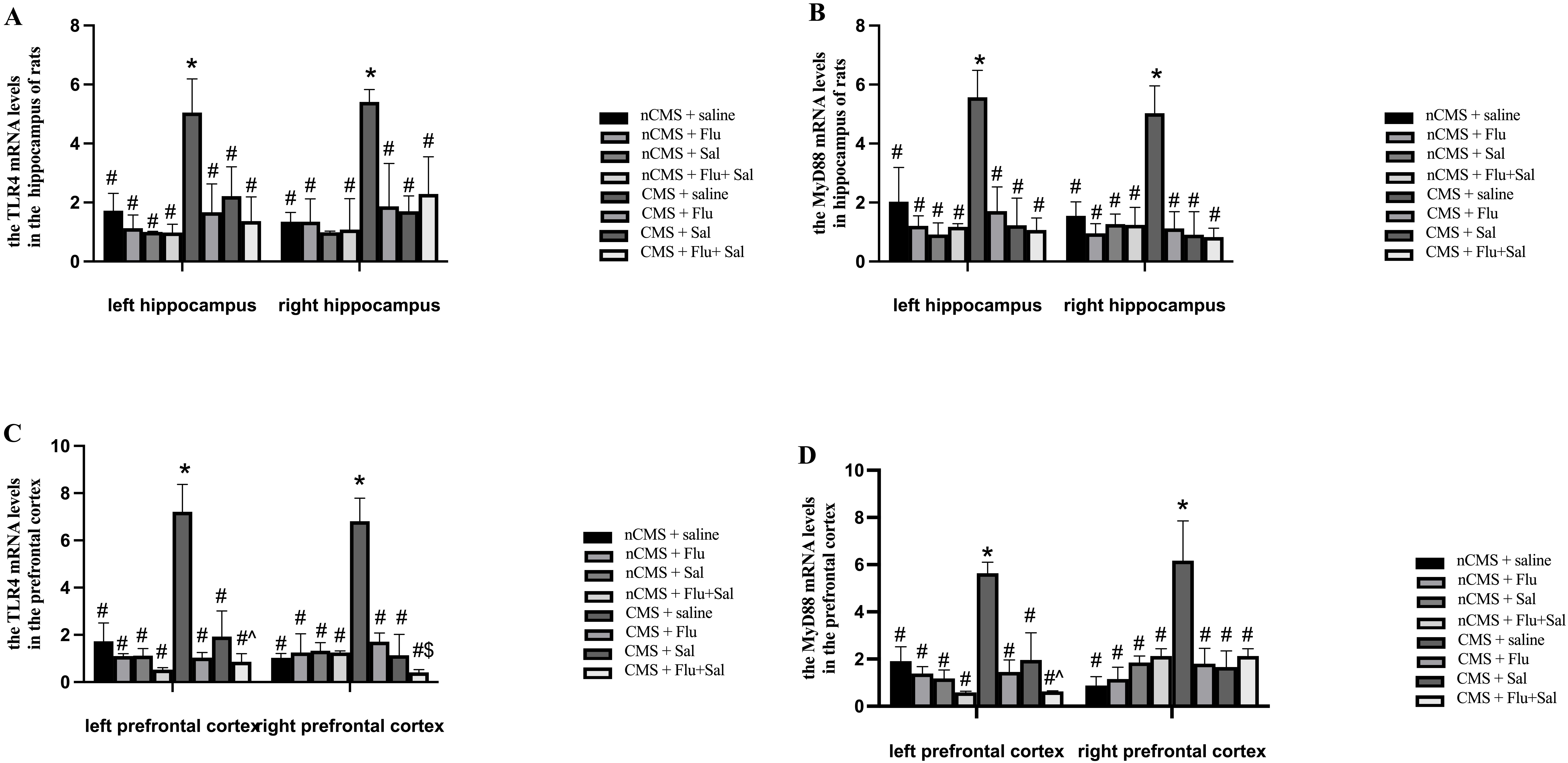 Fig. 4.
Fig. 4.Salvianolic acids reversed CMS-induced upregulation of toll-like
receptor 4 (TLR4) and of myeloid differentiation factor 88
(MyD88) mRNA expression in rat brain. Rats were sacrificed at
3 weeks after drug treatment. Quantitative real-time PCR was performed to measure
the mRNA expression of TLR4 in the hippocampus (A) and the mRNA
expression of TLR4 in the prefrontal cortex (C). Quantitative real-time
PCR was performed to measure the mRNA expression of MyD88 in the
hippocampus (B) and the mRNA expression of MyD88 in the prefrontal
cortex (D). *p
Of note, fluoxetine and salvianolic acids cotreatment outperformed fluoxetine
alone in suppressing TLR4 mRNA expression in the right prefrontal cortex
of rats (p
Our previous data have shown that CMS enhances interleukin-1
| TLR4 mRNA level | Sucrose preference | Forced swimming test | Interleukin-1 |
Interleukin-2 (IL-2) | Interferon- |
Tumor necrosis factor- |
MyD88 mRNA level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TLR4 mRNA level in the hippocampus | −0.153 |
0.011 |
0.001 | 0.061 | 0.274 | 0.070 |
0.810 |
| TLR4 mRNA level in the prefrontal cortex | −0.178 |
0.027 |
0.028 |
0.033 | 0.194 | 0.041 |
0.915 |
Depression is characterized by persistent sadness and loss of interest, along with cognitive and physical symptoms such as feelings of worthlessness, sleep disturbances, and lack of energy [1]. In this study, we used a well-established CMS protocol to induce depressive symptoms in rats [21]. By monitoring the body weight changes and assessing the results of forced swimming and sucrose preference tests that are common behavioral tests in depression-like behavior in rodents [32], we found that three weeks of CMS exposure significantly reduced weight gains and sucrose preference while increasing immobility duration in rats. This is consistent with the results of previous studies [33, 34], suggesting that the CMS rat model is successfully generated. We further found that treatment with fluoxetine and salvianolic acids, alone or in combination, effectively facilitated weight gains and alleviated depressive-like behaviors in CMS rats. Importantly, treatment with fluoxetine and salvianolic acids, alone or in combination, significantly reduced the mRNA levels of TLR4 and MyD88 in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex of CMS rats. Moreover, TLR4 mRNA expression in the brain positively correlated with MyD88 expression, inflammatory cytokine production, and behavioral performance in CMS rats. These results suggest that salvianolic acids exhibited a comparable antidepressant effect to fluoxetine possibly by suppressing TLR4/MyD88 signaling in the brain.
Microglial activation is involved in the development of depression. Significant
changes are noted in the number, morphology, and activity of microglia in
depression [35, 36, 37]. Kreisel et al. [38] have demonstrated
that in a chronic unpredictable stress mouse model, following an initial 2–3
days of stress-induced microglial proliferation and activation, some microglia
underwent apoptosis, dystrophy, and decline in numbers within the hippocampus,
but not in other brain regions. Pharmaceutical blockade of the initial
stress-induced microglial activation rescued the microglial disturbance as well
as the depressive-like behavior, suggesting that the dynamic microglial
alteration has an etiological role in chronic stress-induced depression.
TLR4 expressed in the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus plays an
important role in stress-induced depression [39]. Upon recognizing specific
pathogen-associated molecular patterns, TLR4 initiates innate immune
responses through MyD88 or TRIF to activate the transcription factor
nuclear factor
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, alone or in combination with other antidepressants, are promising therapeutic agents for depression [42, 43]. Studies have shown that salvianolic acids attenuate inflammation in different organs and tissues, including the brain [19, 44]. A recent study has shown that salvianolic acid B ameliorates CMS-induced depressive-like behaviors and inhibits CMS-induced neural apoptosis and microglial activation in the hippocampus and cortex of mice [18]. Consistent with these reports, our results showed that salvianolic acids alleviated depressive-like behaviors in CMS rats, comparable to antidepressant fluoxetine. No additive or synergistic effect was observed in depressive-like behavior alleviation when fluoxetine and salvianolic acids were administered in combination. Furthermore, salvianolic acids reversed CMS-induced upregulation of TLR4 and MyD88 mRNA expression in the hippocampus and front cortex of rats, consistent with a previous study [19]. Interestingly, fluoxetine and salvianolic acids cotreatment outperformed fluoxetine alone in suppressing TLR4 mRNA expression in the right prefrontal cortex of rats and outperformed salvianolic acids alone in suppressing TLR4 and MyD88 mRNA expression in the left prefrontal cortex of rats, suggesting that fluoxetine and salvianolic acids have an additive effect on disturbing cerebral TLR4/MyD88 signaling. However, the underlying mechanism remains unknown and needs further investigation.
This study has several limitations. First, we only examined the mRNA levels of TLR4 and MyD88 in rat brains. The protein expression of these two genes and other components of TLR4 signaling will be investigated in future studies. Second, we did not examine the cerebral production of inflammatory cytokines in this study. The correlation assay was based on the results of our previous study. Third, further investigation is required to establish a causal link between salvianolic acid treatment and the suppression of TLR4 signaling in microglia.
In conclusion, we demonstrated that salvianolic acids were comparable to fluoxetine in alleviating CMS-induced depressive-like behaviors in rats while suppressing mRNA expression of TLR4 and MyD88 in the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus of rats. Salvianolic acids and fluoxetine showed an additive effect on suppressing TLR4/MyD88 signaling in the prefrontal cortex of rats. Our results suggest that salvianolic acids are promising antidepressants targeting TLR4/MyD88 signaling in the brain.
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
CMS, chronic mild stress; TLR4, toll-like receptor 4; MyD88, myeloid differentiation factor 88; MDD, Major depressive disorder; LPS, lipopolysaccharide.
FZ and LY conceived and coordinated the study, designed, performed and analyzed the experiments, wrote the paper. LW, WL, SW, XW and CA carried out the data collection, data analysis, and revised the paper. All authors contributed to editorial changes in the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. All authors have participated sufficiently in the work and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
All experimental protocols were carried out in accordance with the guidelines of the Animal Care and Use Committee of The First Hospital of Hebei Medical University (#2014116).
The authors thank Dr. Shuang Chen who significantly assisted us during different stages of the research.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [grant number 81271489], the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province [grant number H2022206544], Hebei Medical University “14th Five-Year” Clinical Medicine Innovation Research Team Support Program [grant number 2022LCTD-A1], The Hebei Province Government-funded Clinical Medicine Outstanding Talent Training Project [grant number LS202009].
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Publisher’s Note: IMR Press stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.