1 The Second Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian Medical University, 116027 Dalian, Liaoning, China
2 Department of Anatomy, College of Basic Medicine, Dalian Medical University, 116044 Dalian, Liaoning, China
3 The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian Medical University, 116011 Dalian, Liaoning, China
4 Department of Surgery, the Affiliated Zhongshan Hospital of Dalian University, 116001 Dalian, Liaoning, China
Abstract
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a common neurodegenerative disease that tends to occur in the elderly. The main symptom is hypomnesia. More and more older people are suffering from this disease worldwide. By 2050, 152 million people worldwide are expected to have AD. It is thought that the aggregation of amyloid-beta peptides and hyper-phosphorylated tau tangles contribute to AD. The microbiota-gut-brain (MGB) axis appears as a new concept. The MGB axis is a collection of microbial molecules produced in the gastrointestinal tract that influence the physiological function of the brain. In this review, we discuss how the gut microbiota (GM) and its metabolites affect AD in different ways. Dysregulation of the GM has been shown to be involved in various mechanisms involved in memory and learning functions. We review the current literature on the role of the entero-brain axis in the pathogenesis of AD and its potential role as a future therapeutic target in the treatment and/or prevention of AD.
Keywords
- Alzheimer's disease
- human gut microbiota
- neurodegenerative disease
- neurotransmitters
- neuroinflammation
The microbes that live in the human gut include bacteria, eukaryotes, and viruses. These microbes modulate human health by regulating the function and development of the immune system [1]. Gut microbiota (GM) affect nutrient absorption/metabolism, and influence brain development and neurogenesis. The pathway connecting the GM to the brain is called the “microbiota-gut-brain (MGB) axis” [2]. The MGB axis is mediated by various microbial molecules produced in the gastrointestinal tract, which can then infiltrate many organs, even the brain [3]. In recent years, more and more attention has been paid to the influence of the MGB axis on the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s disease (AD), Parkinson’s disease (PD), and Huntington’s disease (HD). Recent preclinical and clinical studies have reported the latest advances in the study of the brain-enteric axis and neurodegenerative diseases [4, 5, 6]. Approximately 70–80% of immune cells are found in the gut. Mediators derived from the gut microbiome, including short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) and other metabolites, lipopolysaccharides (LPS), and neurotransmitters, can affect neuro-immune interactions and the pathways by which these interactions may occur [7]. There is a complex bidirectional interaction between the intestinal microbiome and AD [8]. More than 80% of PD patients have various severe gastrointestinal symptoms [9]. The genetic susceptibility to PD may be related to the ecological imbalance in the intestinal microbiome [10]. The MGB axis can influence motor, mental, and cognitive symptoms as well as weight loss in HD [11].
In this review, we focus on the close association between AD and the MGB axis.
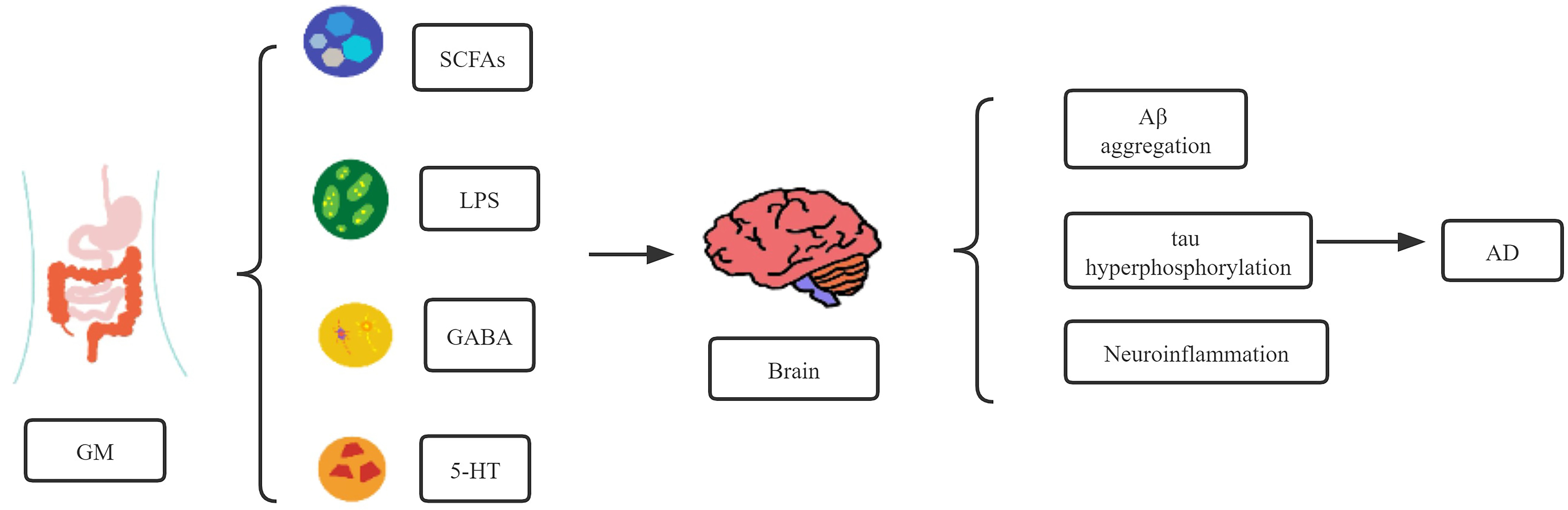
In addition, we provide a figure to show the possible mechanism between the GM
and AD (Fig. 1). By 2050, 152 million people worldwide are expected to have AD
[12]. The main characteristics of AD are
amyloid-beta (A
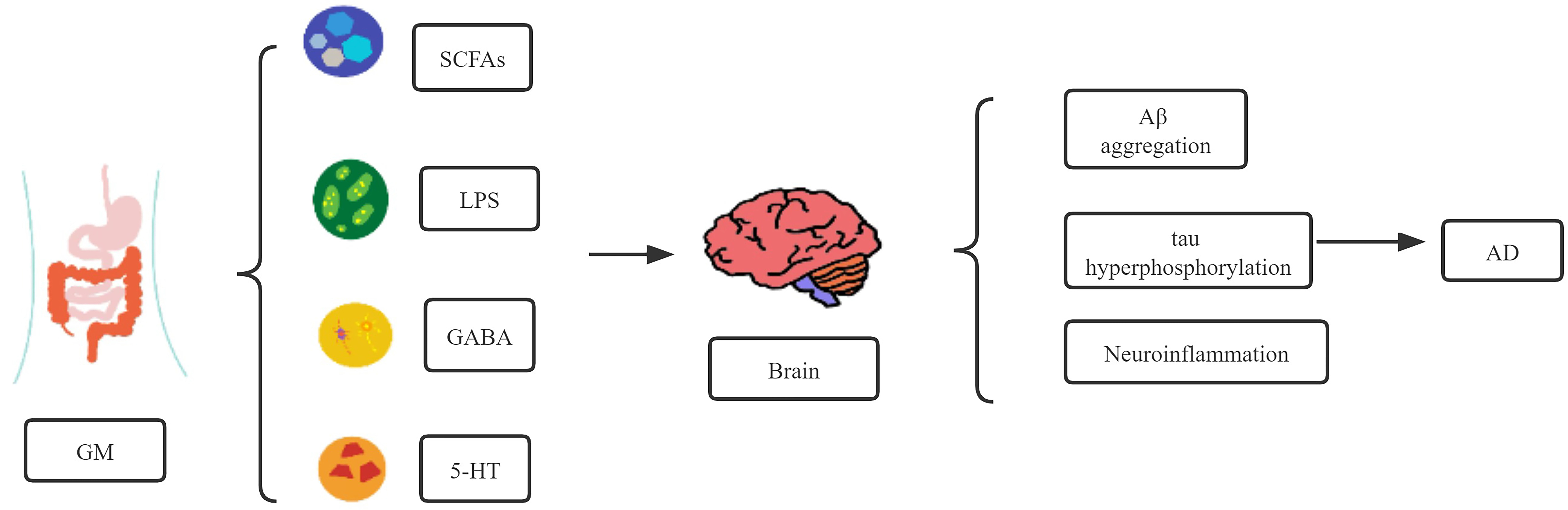 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.GM affects the mechanism of AD. The imbalance of GM affects the
lack of GM diversity. GM release metabolic substances that can be transferred to
the brain through the MGB axis. These substances can directly or indirectly cause
A
| Name of Microorganisms | Role in AD | Research | Year | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacteroides fragilis | Inflammation | Human 16S rRNA gene sequencing | 2016 | [16, 17] |
| The release of proinflammatory cytokines | 2021 | |||
| Actinobacteria | Inflammation | Human 16S rRNA gene sequencing | 2017 | [18, 19] |
| Firmicutes | Anti-inflammatory effects | Human 16S rRNA gene sequencing | 2012 | [18, 20] |
| Neuroprotective effects | 2017 | |||
| Helicobacter pylori | A |
Human CSF and serum anti-Helicobacter pylori IgG concentrations measurement | 2009 | [13, 21] |
| Inflammation | 2019 | |||
| Escherichia coli | Deposit amyloid | Human DNA sequencing, Immunohistochemical staining | 2005 | [22, 23] |
| tau phosphorylation | 2016 | |||
| Porphyromonas gingivalis | Neuroinflammation | Animal qRT-PCR, immunohistochemistry | 2018 | [24] |
| Akkermansia muciniphila | 5-HT levels in the hippocampus | Animal Serotonin measurement | 2020 | [25] |
| Bifidobacterium | Reduce the expression of inflammatory cytokines | Feeding animal model | 2017 | [26] |
| Lactobacillus | Reduce neuroinflammation | Reduce neuroinflammation | 2018 | [27, 28] |
| 2020 |
Immune system dysregulation is a major
feature of AD [29, 30]. GM have been found to play a role in influencing amyloid
plaque deposition [31]. Neuronal injury is a common pathological manifestation of
AD. The occurrence of innate immune responses in the central nervous system (CNS)
usually results in neuronal damage [32]. The capillary
endothelium, astrocyte terminal foot and basement membranes are the morphological
basis of the blood-brain barrier (BBB). LPS can be found in a
large proportion of the human gastrointestinal tract [33]. Many amyloid and
immunogenic mediators are also produced by the GM [34]. GM and its products
travel to the blood circulation of the brain via a cytokine cascade
[35]. The permeability of the gastrointestinal mucosa and the BBB is greater
among older people, which contributes to the deposition of A
GM play a role in the metabolism of nutrients and support
immunity. The intestinal mucosa plays a vital role in resisting pathogens [37].
More and more evidence suggests a complex relationship between the gut and the
CNS. Visceral signals from the gut affect the CNS via the vagus nerve;
in turn, the brain directs signals to regulate the function of the gut. This
two-way communication is termed the MGB axis [38]. GM
significantly affect the physiological function and behavior of the brain through
three pathways of the MGB axis (immune, neuroendocrine and vagal pathways) [15].
The enteric nervous system (ENS) is made up of various types of
neurons. The brain receives information from neurons near the spine and intestine
that is transferred by spinal and vagal afferent nerves [39]. As the ENS is the
communication channel between the GM and the CNS, there is a vital connection
between the GM and the physiological activity of the brain [40]. GM develop and
regulate the body’s immune system; at the same time, the immune system also
affects the composition of the GM. Normal physiological functions in the brain,
such as the development of the nervous system, the transmission of signals
between nerves, and the activation of the CNS immune system, are affected by the
GM through changes in microglia and astrocytes. The integrity and permeability of
the BBB are also related to the GM [41]. The immune system plays a role in the
formation of the brain’s physical structure and its response to inflammation
[32]. Intestinal inflammation and leakage of the intestinal barrier may be caused
by the imbalance of the GM. The efflux of incompletely digested food,
microorganisms, endotoxins, and immune factors may be the cause of chronic
systemic inflammation. The intestinal barrier is permeated mainly by incompletely
digested food molecules [42]. The development of a majority of chronic diseases
is accompanied by an overactive immune system, which is often associated with
immune system overload. The overloading of the immune system can be caused by a
chronic inflammatory reaction of the intestinal mucosa, such as neurodegenerative
diseases [43]. However, the effect of probiotics on A
Microglia are non-neuronal cells. The maturation and function
of microglia are influenced by host intestinal microbes [46]. When the GM
decrease, microglia develop defects and cannot mature [47]. Acetate is an
important GM metabolite that stimulates microglia to mature [48]. Microglia
activation increased after SCFAs supplementation in germ-free (GF) mice [49]. LPS
produced by the GM increased the inflammatory response of microglia and promoted
the activation of microglia [50]. The increase of Clostridium and Bacillus in the
intestinal tract decreased the expression of IB4 binding and
The production of pro-inflammatory cytokine/chemokine microglia
is the main manifestation of advanced AD-related chronic
neuroinflammatory pathology. In humans and animal models of AD-like pathology,
enhanced levels of associated inflammatory cytokines are detected in the early
stages of AD [52]. Microglia are the main source of Complement component 1q in
the brain [53]. The innate immune response mediated by CNS-resident microglia
plays an important role in neuroinflammation in AD. Therefore, microglia may play
an important role in regulating neurodegeneration [54]. In the presence of aging
or genetic predisposing factors, tau pathologically induces abnormal activation
of microglia, resulting in the accumulation of toxic amyloid proteins; in turn,
the activated microglia promote the spread of tau pathology by phagocytic
synapses and secreting neurotoxic cytokines [55]. Bacterial products or
metabolites from the GM modulate microglia maturation, morphology and function,
such as SCFAs [47, 56]. Microglia have an active role in synaptic formation
[57]. In addition to plaques, microglia and immune-related
pathways are also the focus of interest in AD. They may be early mediators of
synaptic loss and dysfunction in AD [58]. GM dominate the
development, maturation and activation of microglia. Activated microglia are
involved in brain development and homeostasis [59]. However, activated microglia
can serve as a source of inflammatory mediators, as well as phagocytosis of
regulating synapses that contribute to AD [55]. The number of microglia in
cortical gray and white matter was increased in postmortem AD cases. Furthermore,
microglial proliferation was increased in AD and correlated with the severity of
AD [60]. Microglia also degraded some of the tau species
released from the brains of AD patients [61]. Microglia participated in the
process of AD. Studies have shown that the decrease of microglia inhibited the
proliferation of tau cells. In addition, neuronal death might be related to
astrocytes regulated by microglia. In the pathogenesis of AD, activated microglia
play a role in the activation of acute microglia that enhanced phagocytosis and
clearance, thereby reducing A
Using single-nucleus RNA-seq, a group of disease-associated astrocytes was found in a mouse model of AD [68]. The A1 neurotoxic phenotype describes mouse astrocytes after exposure to a specific cytokine secreted by microglia of LPS [69]. The formation of A1 neurotoxic reactive astrocytes is a fundamental pathological response of the CNS, which is associated with LPS-induced neuroinflammation, acute CNS injury, and all neurodegenerative diseases. A1 reactive astrocytes are induced by classical activated neuroinflammatory microglia. A1 reactive astrocytes have many normal astrocyte functions that are decreased, such as synaptic functions, phagocytic capacity and neurovirulence. A1-activated astrocytes account for a large proportion of AD in central neurodegenerative regions [70]. In AD mouse models, microglia-mediated reactive astrocyte transformation was blocked by repeated subcutaneous administration of NLY01, a long-acting glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist. Neuronal activity was maintained, and spatial learning and memory were improved [71]. Following CNS injury, astrocytes and microglia produced a large number of mutually regulated signaling molecules. More research is needed to understand how microglia and astrocytes act on neurons in AD environments [72].
The BBB is a barrier that separates the CNS from the
peripheral blood circulation [73]. The BBB is composed of cerebral vascular
endothelial cells, astrocytes of the perivascular foot, basement membrane and
perivascular cells [74]. Tight junctions are expressed in the vascular
endothelial cells, preventing polar molecules from passing freely between the
blood and the brain [75]. The BBB breakdown is thought to be an
early biomarker of cognitive dysfunction in humans [76]. It
separates nerve cells from immune system cells. BBB dysfunction during AD
influences A
There is evidence that deterioration of the BBB morphology and function occurs
in many neurodegenerative diseases and is considered a marker of cognitive
decline [83]. One study confirmed greater BBB permeability in GF mice than in GM
normal disease-free mice. In addition, SCFAs or metabolites produced by the GM
reduced BBB permeability [80]. The basement membranes cover the brain capillary
endothelial cells of the BBB, and the pericytes and astrocytes end foot surround
the BBB neurovascular unit. The ability of the BBB to regulate the exchange of
molecules between blood flow and the brain parenchyma, determines homeostasis of
the CNS. Therefore, BBB dysfunction may be involved in the pathogenesis of
several neurological diseases, including AD [84]. Researchers observed an
approximately 4.2-fold increase in A
These studies provide evidence that the human GM influence the development of
the immune system through primary immune cells. Brain microglial activation,
neuro-inflammation, neuronal apoptosis and A
The two-way communication between the CNS and GM plays a vital role in human health. There is growing evidence that a variety of metabolites secreted by the GM affect the human brain and behavior, and can even affect the cognitive performance of patients with neurodegenerative diseases [93]. Metabolites such as LPS and SCFAs have the ability to regulate hormone release produced by the GM and can therefore influence cerebral function [94].
Endotoxins can cause or contribute to neurodegenerative changes.
Neurodegenerative diseases can be triggered by the interaction
of endotoxins with different aggregators, which is related to the promotion of
the aggregation of A
The loss of connections between synapses could lead to
cognitive deficits. During neuroinflammation, synaptic proteins can be altered by
co-activated pro-inflammatory markers and associated cytotoxic products. Altered
synaptic proteins are harmful to neurons [104]. Peripheral injection of LPS could
induce learning and memory impairments in mice, which is attributed to the
microglia-induced synapse damage [105]. When hippocampal
dysfunction occurs, such as a reduction in the number of contact zones and the
size of postsynaptic densities, it results in a decrease in hippocampal-dependent
learning and memory performance [106]. LPS could act directly
within brain tissue to disrupt synapses in hippocampal slice cultures, which were
dependent on microglia and IL1
SCFAs are the main metabolite of mammalian intestinal dietary
fiber by microbial anaerobic fermentation. They have important physiological
functions for the human body, and are sources of energy and act as signaling
molecules. SCFAs are absorbed effectively by the intestinal mucosa and recognized
by specific receptors [108]. SCFAs are not digested and absorbed in the small
intestine [109]. Acetate, propionate, and butyrate are the most abundant SCFAs in
humans [56]. Butyrate is produced mainly by the gram-positive
anaerobes Roseburia and Faecalibacterium (previously Fusobacterium)
[110]. SCFAs affect the function of the peripheral nervous
system and CNS in different ways [111]. In radiation-induced cognitive impairment
models, hippocampal phosphorylated cAMP-responsive element binding protein and
brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression were reduced by butyrate, and
cognitive impairment was subsequently improved [112]. The GM that produced select
SCFAs could reduce the formation of toxic soluble A
Butyrate plays an important role in the human gut. It is the
primary source of energy for the colonic epithelial cells and maintains the
intestinal barrier and regulates intestinal immunity. Haran et al. [115]
demonstrated that butyrate producing species were decreased and taxa was
increased in elderly individuals with AD compared to those without dementia. Sun
et al. [116] found that cognitive impairment in APPswe/PS1dE9 transgenic
mice could be improved by fecal microflora transplantation therapy. The brain
deposition of A
Functional amyloid peptides and immunogenic mediators, such as LPS, can be produced by the GM. The physiological processes of the bacterial cell surface are closely related to the amyloid peptide in bacteria. The structure and biophysical properties of this amyloid peptide were similar to those of human pathological amyloid [118]. SCFAs can also influence the CNS by modulating microglia [119]. SCFAs are important metabolites secreted by the human GM. SCFAs levels in feces of AD were lower than normal values. The presence of SCFAs has a positive effect on reducing the occurrence of AD.
The microbiota can synthetize the neurotransmitters and neuromodulators. However, it is unknown whether it can produce the neuropeptide-like compounds [120]. Microbiota homeostasis can influence complex neurodegenerative disorders through neurotransmitters [121]. Studies have shown that the GM influences neurotransmitter, synaptic, neurotrophic signaling systems and neurogenesis in GF mice [122]. GM affect the MGB through immune, neuroendocrine and direct nerve mechanisms. The central, peripheral, hormonal and immune systems have bidirectional communications due to the MGB axis. GM alter the activity of neurons by producing neuromodulators and neurotransmitters, as well as amino acid metabolites. Studies have demonstrated that variations in the composition of the GM could result in behavioral abnormalities, but surprisingly, few results were found about direct cause-and-effect relationships between the GM and behavioral abnormalities. Another plausible hypothesis is that the GM can lead to the generation of neurotoxic substances in the brain. Increasing evidence has demonstrated that intestinal dysbiosis may participate in the development of AD [123].
Neurotransmitters transmit signals throughout the brain and regulate some of
physiological functions of the brain. The synthesis and release of
5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) and
GABA is the main inhibitory neurotransmitter. Studies have shown that GABA can
be produced by the human GM, such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium [125].
Lactobacillus brevis and Bifidobacterium dentium are the most efficient GABA
producers among the strains that have been tested [125]. Both lactobacillus
inoculation and lactic acid treatment significantly increase the GABA level in
the hippocampus of mice [126]. Commensal Bifidobacterium dentium produces GABA
through glutamate decarboxylase catalyzed by the decarboxylation of glutamate
[127]. GABA is a non-protein amino acid synthesized by dependent glutamic acid
decarboxylase (GAD) through irreversible
Studies have shown that GABA is not only present in neurons, but also in
astrocytes. GABA in astrocytes can release and activate GABA receptors in
neighboring neurons [131]. However, GABA is not present in normal astrocytes.
Diseased astrocytes become reactive and produce GABA around amyloid plaques
[132]. The mode of GABAergic glial cell delivery is altered in the AD mouse
model. The upregulation of GABA released by astrocytes can bind to extra-synaptic
associated GABA receptors and strongly inhibit synaptic function, ultimately
leading to memory and cognitive impairments in AD [133]. Recent
evidence indicates that the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA in the
brains of AD patients was different from that of a group of non-AD patients, and
was mainly distributed in the frontal, parietal, temporal cortex and hippocampus
regions [134]. High GABA levels of reactive astrocytes in the dentate gyrus were
associated with the development of AD in mouse models (5xFAD), and increased the
incidence of tension suppression and memory deficits [135].
Early neuropathological changes from AD were mostly confined to
the loss of excitatory glutamatergic pyramidal neurons and synaptic connections
in the hippocampus and temporal cortex. The balance between excitatory and
inhibitory signals was important for normal cognitive function and memory
formation within the hippocampus and cortex, and was needed to be carefully
maintained [136]. Part of the risk of cognitive and memory loss came from loss of
excitatory glutamate pyramidal neurons and synaptic connections. The GABA levels
of CSF decreased significantly, and synaptic loss correlated with memory loss in
AD patients [137]. Both GABA and 5-HT can be
synthesized and released by the GM. These molecules have important physiological
roles in the brain. They act as neurotransmitters or precursors of
neurotransmitters and control neuron activity [124]. Glutamate, acting at
N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors primarily in peri-synaptic astrocytes, can impair
function in AD. The downregulation of vesicular glutamate transporters is related
to the abnormal APP expression in AD patients. Glutamate uptake/recycling
mechanisms are disrupted by toxic A
The human GM can determine the production of 5-HT through its metabolites. Entero-endocrine cells are found throughout the intestinal mucosal epithelium. They are specialized hormone-secreting cells, consisting of an array of different cell types that receive stimulation from the luminal and the basolateral surfaces and secrete a combination of more than 20 hormones [139]. Chemical messengers involved in messaging, such as 5-HT, and serotonin, interact with the GM [140]. The rate-limiting enzyme tryptophan hydroxylase 1 (TPH1) found in entero-chromaffin cells of the gut produces more than 90% of the 5-HT in humans [141]. Studies in GF mice have shown that GM is necessary for the development of the central serotonergic system [142]. SCFAs enhance the expression of the enzyme TPH1 mRNA by interacting with EC cells. EC cells use TPH1 to synthesize 5-HT [143]. In human EC cell models, butyrate enhanced Tph1 transcription in mice by inducing ZBP-89, a zinc finger transcription factor [141]. Tryptophan is a central precursor in the synthesis of 5-HT. Tryptophan is produced by the GM. The peripheral tryptophan is able to cross the BBB, where it is involved in 5-HT synthesis [144]. It was found that gut Firmicutes Clostridium sporogenes could decarboxylate tryptophan to tryptamine. Tryptamine enhances the inhibitory response of cells to serotonin [145]. Kynurenine and its metabolites are an important pathway in tryptophan metabolism. Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase is a rate-limiting enzyme responsible for the initiation of the Kyn metabolic pathway [146]. L. plantarum treatment can increase 5-HT in the human gut [147]. GM play a key role in enhancing colon and serum 5-HT levels by inducing and reversibly promoting 5-HT in colonic entero-chromaffin cells. Gastrointestinal motility and platelet function are significantly affected by the microbiota-dependent effects on 5-HT [148].
5-HT can affect dopaminergic neurons in several ways, which is vital to the ENS [149]. Studies have found that the occurrence of AD in humans could be delayed and alleviated by most selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors [150]. Serotonin content significantly decreased in the temporal and frontal cortex and was altered in the CSF [151]. A connection between 5-HT and AD showed that citalopram acted as a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) that increased serotonin levels in AD neurons. Citalopram-treated APP mice exhibited improved cognitive behavior [152].
Memory retention and the ability to learn depend on the
serotonergic system. 5-HT-related receptors, such as 5-HT1, 5-HT4, 5-HT6 and
5-HT7 receptor classes, have unique abilities to enhance cognition [150].
In patients with severe AD, the density of the 5-HT2A receptors
in the brain was lower than that in the control group, specifically in the
frontal and temporal cortex. Despite the effects of choline acetyltransferase
activity and the presence of behavioral symptoms, there was an association
between the loss of the 5-HT2A receptor and cognitive decline [153]. Burke
et al. [154] reinforced the relationship between depression, APOE
In addition to AD, there is a strong association between the gut-brain axis and neurodegenerative diseases, such as PD and HD.
PD is the second most common neurodegenerative disease. It is estimated that the prevalence of PD will reach nearly 1,238,000 cases by 2030 in the United States alone [156]. PD is characterized by the absence of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra and the presence of misfolded alpha-synaptic nucleoproteins (Lewy bodies) [157]. Motor symptoms of PD include tremor, tetanus, bradykinesia, and postural abnormalities [158]. The gut microbiome interacts with the autonomic and CNS through a variety of pathways including ENS and the vagus nerve [159]. The metabolites of the GM may induce intestinal inflammation and even PD [160]. One study demonstrated that motor function was impaired in mice treated with the SCFA mixture [161]. Fecal SCFAs concentrations were significantly reduced in PD patients [162], and Bifidobacteriaceae, Christensenellaceae, Tissierellaceae, Lachnospiraceae, Lactobacillaceae, Pasteurellaceae and Verrucomicrobiaceae families were all significantly decreased [163]. Intestinal microbiota can exacerbate motor deficits in Parkinson disease (PD) [164]. GM are also related to the Linchuan phenotype of PD. Compared to healthy controls, the prevalence of the Prevotellaceae bacteria family in PD decreased. Compared to patients with tremor-dominant PD, patients with postural instability and gait difficulty phenotypes had a higher abundance of the Enterobacteriaceae family of bacteria [165]. However, several studies demonstrated that dietary intake of polyphenols might inhibit neurodegeneration and PD progression [166].
HD is an inherited neurodegenerative disorder that can cause progressive movement disorders, psychiatric symptoms, and cognitive impairment. In most cases, it occurs in mid-adulthood [167]. The atrophy of the striatum and cerebral cortex is the main cause of motor symptoms of HD. HD is caused by expansion of CAG repeats in the Huntingtin gene. Intestinal flora can affect the occurrence of HD. HD patients develop intestinal disorders [168]. Changes in the composition of the GM were observed in men with HD. In addition, plasma acetate levels were elevated in male Huntington’s mice in the early and late stages of the disease [169]. In the R6/2 mouse model of HD, the relative abundance of Bacteroidetes increased and that of Firmicutes decreased. In addition, R6/2 mice showed increased intestinal permeability [170]. The 16S V3-V4 rRNA sequencing results of fecal samples were used to express the intestinal microbiome. The HD gene expansion carrier groups significantly reduced the intestinal microbiome richness. In obvious HD gene expansion carriers, low abundance of E. hallii was strongly associated with the severity of motor symptoms and the proximity time of disease onset [171]. A comparison of longitudinal fecal microbiome data from early 4 weeks to 12 weeks of wild-type and HD mice confirmed the presence of intestinal ecological disorders in HD mice. Reductions in plasma concentrations of propionate and butyrate were also observed in HD mice, but were not significant [172].
With more and more research, we found that the GM may be a new breakthrough in the treatment or prevention of AD. The positive intervention effect of probiotics and prebiotics on AD has been gradually discovered.
Probiotics and prebiotics can regulate neuroinflammation and improve cognitive
function via the brain-gut axis [12]. Accumulating clinical evidence
suggests that the therapeutic potential of probiotics in AD is generated through
a variety of mechanisms [173]. One study found improved cognitive function in AD
patients treated with probiotics [174]. Probiotic-4 (a probiotic preparation)
significantly improved memory deficits in the brains of older
senescence-accelerated prone 8 (SAMP8) mice and significantly reduced intestinal
barrier damage and inflammation in older SAMP8 mice [175]. SLAB51 (a novel
formulation of lactic acid bacteria and bifidobacteria) was treated in 3xTg-AD
mice at the early stages of AD. This study demonstrated the beneficial effect of
probiotics in AD subjects. Probiotics could improve the loss of middle brain
weight and the reduction of cortical areas in AD mice [176]. This study
demonstrated that the nonviable Bifidobacterium breve strain A1 and acetate could
partially improve the behavioral defect of AD model mice [177].
Tryptophan-related dipeptides can prevent cognitive decline, inhibit the
inflammatory response of microglia and enhance the phagocytosis of A
Prebiotic is the name given to substrates selectively used by host microorganisms to confer health benefits. Several different food components are considered to be prebiotics, including resistant starch (RS), insulin, fructooligosaccharides (FOS), galactooligosaccharides, and xylo-oligosaccharides [179]. FOS have been found to improve memory in AD animals. FOS not only improve oxidative stress and inflammatory disorders, but also regulate the synthesis and secretion of neurotransmitters [26].
This review describes the importance of bidirectional communication between the
gut and brain for AD. There is increasing evidence that the GM
have an important role in the pathogenesis of nervous system
diseases. The human gut has a complex bacterial composition. Changes in the
species and number of the GM have a huge impact on the brain through the MGB
axis, leading to neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration through different
pathways, and even promoting the possibility of AD. The MGB axis is the bridge
between the human gut and the brain, involving neural, endocrine, and
inflammatory mechanisms. The immune system, brain development and behavior are
influenced by the GM. Their metabolites and neurotransmitters have different
effects on the body. These studies suggest that gut dysbiosis may be related to
A
Inflammatory infections have the potential to act as the triggers for
neurodegenerative processes, primarily by disrupting the function of the immune
system, causing excessive synthesis and accumulation of
A
J-TY, X-YY and X-GW planned and conducted the review. J-TY, X-WX and C-YJ collected the data and drafted the manuscript.
Not applicable.
Thanks to all the peer reviewers for their opinions and suggestions.
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [grant NSFC32100928], and Liaoning Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China [grant No.2020-BS-201].
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Publisher’s Note: IMR Press stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.