1 College of Pediatrics, Hainan Medical University, 571199 Haikou, Hainan, China
2 Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine, The First Affiliated Hospital of Hainan Medical University, 570100 Haikou, Hainan, China
3 Department of Interventional Vascular Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Hainan Medical University, 570100 Haikou, Hainan, China
4 Hainan Provincial Key Laboratory of Tropical Brain Research and Transformation, Hainan Medical University, 571199 Haikou, Hainan, China
5 Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, The First Affiliated Hospital of Hainan Medical University, 570100 Haikou, Hainan, China
†These authors contributed equally.
Abstract
Background: Huang Qi (HQ, Astragalus) and Hong Hua (HH, Safflower), two
Chinese herbal remedies, are widely used to treat coronary heart disease (CHD).
However, the underlying mechanisms of this herb pair remain unclear. The aim of
this study was to determine the potential synergistic effects and mechanisms of
Astragalus-Safflower in the treatment of CHD. Methods: Network
pharamcology was performed to identify the core components, targets, and key
genes of Astragalus-Safflower herbal pair (ASHP) for the treatment of CHD.
Enrichment analysis was performed to identify overlapping genes.
Ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography coupled with Q-Exactive MS/MS
(UHPLC-QE-MS) was used to detect the blood component of rat ASHP drug-containing
serum, which is also considered to be the core components of the ASHP. Molecular
docking of ASHP core compounds with core proteins of the pyroptosis pathway
mediated by the NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3)
inflammasomes. In vivo experiments were conducted to verify the effect
and mechanism of ASHP in the CHD mice model. Results: 54 active
compounds and 404 target genes were identified from ASHP, and 1576 targets for
CHD with 90 overlapping genes for both. IL6, AKT1, IL1B, TP53, VEGFA,
PTGS2, MMP9, CCL2, CXCL8 and EGF were the key hub target genes.
Enrichment analysis of Kyoto Encyclopedia of Gene and Genome (KEGG) revealed that
the NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated signaling pathway was one of the more critical
signaling pathways. The UHPLC-QE-MS was used to identify the rat ASHP containing
serum enrollment compound as calycosin and isorhamnetin. Molecular docking showed
that quercetin, kaempferol, apigenin, calycosin and isorhamnetin possessed good
binding sites with NLRP3 and Caspase-1. Animal experiments showed that the
expression of NLRP3, Caspase-1, GSDMD, IL-1
Keywords
- coronary heart disease
- Astragalus-Safflower herb pair
- network pharmacology
- NLRP3 inflammasome
- pyroptosis
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) accounts for about one-third of all deaths
worldwide each year. The number of CVD cases worldwide reached 523 million in
2019 and 18.6 million CVD deaths by 2019 [1]. According to a recent report
released by the National Center for CVD, the number of people with CVD in China
is about 330 million, including 11 million with coronary heart disease (CHD) [2].
Myocardial ischemia, hypoxia, or necrosis is caused by stenosis of the coronary
arteries or obstruction by atherosclerosis (AS), resulting in CHD. Drug therapy
is one of the most basic treatments for CHD, and commonly used drugs include
anti-thrombotic drugs, lipid-lowering drugs,
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has long been used in China for the treatment of CHD due to multi-target and multi-component advantages [6]. According to the TCM theory, the primary cause of CHD is qi deficiency and blood stasis, and therefore reviving qi and fostering blood circulation are the primary principles in the treatment of CHD [7]. Astragalus and Safflower are representative herbal medicines for reviving qi and fostering blood circulation [8]. Astragalus is the root of the leguminous plant Astragalus membranaceus, family legume, which has the effects of invigorating qi, eliminating toxins, draining diuresis, regenerating muscles, and strengthening body resistance. Astragalus has been shown to play a protective role in ischemic stroke, improvement of myocardial fibrosis and myocardial remodeling, lung injury and other diseases [9]. The primary active ingredient of the plant Astragalus membranaceus is Astragaloside IV (AGIV). A study reported that astragaloside IV enhanced the vasodilatation function in rat aorta endothelial cells (ECs) by controlling the PI3K/Akt/eNOS signaling pathway [10]. Formononetin is an isoflavone extracted from Astragalus membranaceus. It can substantially attenuate the development of atherosclerosis by regulating the interplay between krüppel-like factor 4(KLF4) and Scavenger receptor A (SRA), suggesting that formononetin might be a novel therapeutic approach for inhibiting atherosclerosis [11]. By triggering ROS/NLRP3-mediated suppression of the inflammatory response, AS-IV prevented pyroptosis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) that had been triggered by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) [12]. Safflower is the flower of the Carthamus tinctorius L., family Asteraceae, which has the properties of activating blood circulation, dispersing blood stasis, and relieving pain. Our previous study showed that Safflower could exert anti-apoptotic effects by regulating the expression of proteins related to Bax, Bcl-2 and SIRT1/FoxO1 signaling pathways for the treatment of CAD [13]. Hydroxy saffron yellow A (HSYA) is one of the main components of Safflower. A study by Qiang Xu et al. [14] showed that through inflammation, Bcl-2/Bax and the PPAR signaling pathway, HSYA could attenuate the symptoms of CAD. In recent years, more and more studies have shown that Safflower has shown effective protective effects in diseases such as atherosclerosis and myocardial ischemia-reperfusion(I/R) injury [13, 15]. The main active components of Safflower has been shown to suppress foam cell formation, vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration, and platelet activation [16]. In summary, Astragalus and Safflower can promote blood flow, prevent thrombosis, and removing congestion. The use of ASHP has been studied in ischemic stroke and cerebral I/R injury [8, 17]. Chen et al. [18] have demonstrated the preventive benefits of combination use of their two active ingredients calycosin and hydroxysafflor yellow A against cerebral I/R injury in a rat model. However, the effects and mechanisms of ASHP in the prevention and treatment of CHD are unclear.
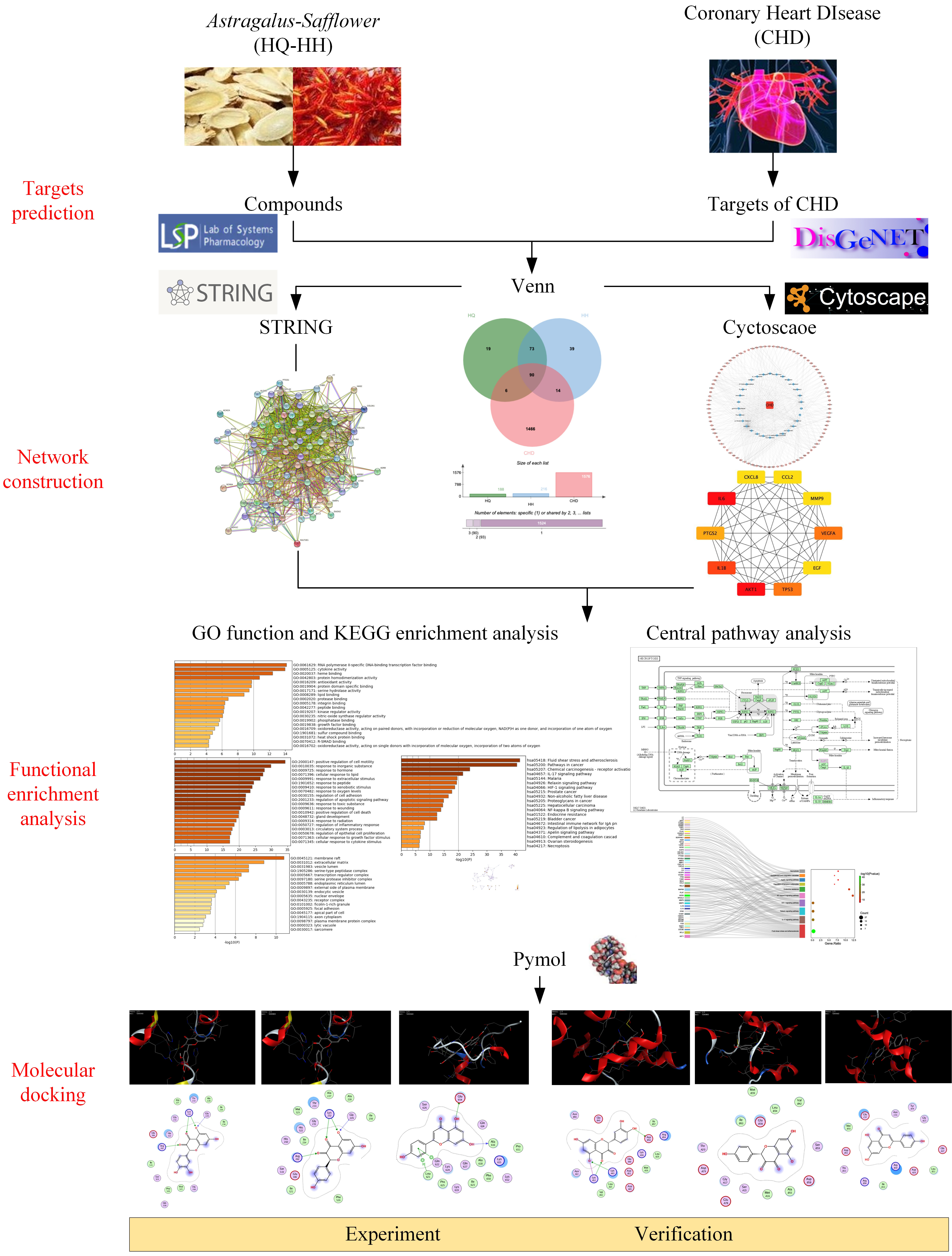
Network pharmacology can rigorously assess the relationships between illnesses and medications and pinpoint the precise processes by which each drug acts on the genes it is designed to target [19]. This study was intended to clarify the specific components and targets of the action of ASHP, explore its underlying mechanism in CHD through network pharmacology and molecular docking, envisage the clinical application of ASHP in CHD. The general flowchart of the study is shown in Fig. 1.
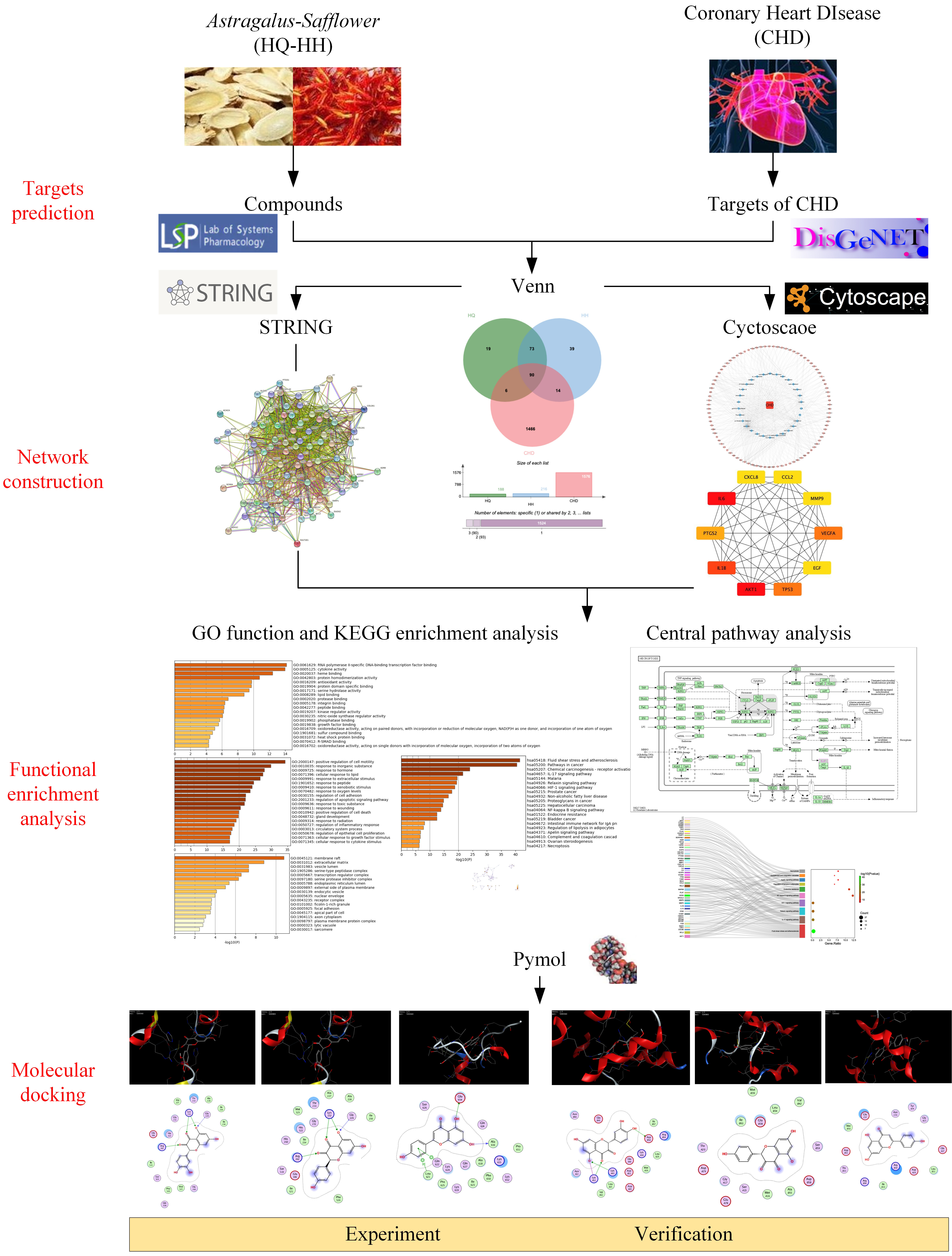 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.The overall process of the study.
The traditional chinese medicine systems pharmacology database and analysis
platform (TCMSP) database (https://old.tcmsp-e.com/tcmsp.php) was searched using
the keywords “Astragalus and Safflower”, and the active compounds were screened
based on the oral bioavailability (OB)
Using the keyword “coronary heart disease” as a search term, we used the disease database (DisGeNET, http://www.disgenet.org) to find disease targets [21].
The main pharmacological targets of ASHP and the corresponding target genes of CHD were introduced into the online website bioinformatics (http://www.bioinformatics.com.cn) [22]. The overlap targets were the potential therapeutic target genes of ASHP for CHD.
The obtained overlapping genes were imported into the STRING database, and the species “homo sapiens” was selected with the lowest interaction score of 0.40 at the highest confidence level to obtain the PPI network map of overlapping genes, which was then imported into Cytoscape (Version 3.8.0, Oracle, Austin, TX, USA) to obtain the most significant top 10 hub genes using the degree algorithm in the cytoHubba plug-in.
The active compounds of ASHP, CHD-related targets and overlapping genes were imported into Cytoscape to construct a network diagram to understand the correlation of the three more visually. The “Compound-Target-Disease” network was created using Cytoscape [23].
GO and KEGG enrichment analysis were performed on the key target genes screened by the Metascape database (https://metascape/org/gp) [24]. The search species was limited to homo sapiens, minimum overlap was set to 3, p-value cutoff was set to 0.01, and minimum enrichment was set to 0.01. The GO and KEGG signaling pathways involved in the therapeutic effect of ASHP were obtained. Sankey dot plots were plotted by the online platform bioinformatics (https://www.bioinformatics.com.cn).
The pubchem database (https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/) was searched for InChIKey numbers of drug small molecules and download 3D structures of drug small molecules [25]. The crystal structure of the core target protein was downloaded using the RCSB PDB database (http://www.rcsb.org/), and the water molecules and ligand small molecules were removed with PyMol software (Version 2.5, Schrodinger Inc., New York, NY, USA) to obtain the 3D structure of the receptor protein. MOE software (Version 2019.0102, Chemical Computing Group Inc., Montreal, Canada) was used to perform the fractionation of ligand small molecules and protein receptors. The docking of ligand small molecules and protein receptors was performed using MOE software. It is generally believed that either the conformation with a lower binding energy between molecules or the conformation with the lowest energy is more stable. In this study, the optimal conformation with the lowest energy was selected and the docking results were visualized by PyMol software.
Ten SPF grade healthy male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats (180
400
Using a Waters UPLC BEH C18 column (1.7
Raw mass spectrometry data were imported using XCMS software (Version 1.41.0, La Jolla, CA, USA). Retention time correction, peak identification, peak extraction, peak integration, peak alignment, etc., and the self-built secondary mass spectrometry database and the corresponding cleavage law matching method were used to identify the peaks containing MSMS data. Positive and negative ion modes were used to collect data on samples such as Astragalus-Safflower granules, rat drug-containing serum and rat blank serum, and the total ion chromatogram (TIC) was created.
After one-week acclimatization, healthy male ApoE
Thirty mice were equally randomized into three groups: control group, model group, and ASHP (Huangqi-Honghua, HQ-HH) group. Animals in the control group were given normal chow, and those in model and ASHP groups were given high-fat chow for 12 weeks [26]. The high-fat feed was purchased from Changzhou Rat One Rat Two Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Changzhou, China; No. D12108C). Astragalus-Safflower was converted into a gavage dose for mice according to the dose commonly used in humans. A combination dose of Astragalus and Safflower was given at 4.5 g/kg/day and 1.5 g/kg/day. Mice were gavaged 0.2 mL each time, once a day for four weeks, and the experimental protocol was reviewed and approved by the ethics committee of Hainan Medical University. Animals in the control group received an equal amount of distilled water through intragastric administration. Under pentobarbital anesthesia, blood was taken through the abdominal aorta after the experiment. For biochemical analysis, serum was centrifuged at 4 °C and 3000 rpm for 15 min and then kept at –20 °C. For use in later investigations, the heart tissue was extracted during an autopsy and either promptly frozen in liquid nitrogen or preserved in 10% paraformaldehyde.
The heart tissue was dried, embedded in paraffin, fixed in 4% recent
paraformaldehyde solution overnight, hematoxylin/eosin (H&E) stained, and sliced
into (4
Mouse heart tissue RNA was extracted using the Eastep super total RNA extraction
kit (Promega, Shanghai, China) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. A
total of 2
| Gene Name | Forward | Reverse |
|---|---|---|
| 5′-CGTGACATTAAGGAGAAGCTG-3′ | 5′-CTAGAAGCATTTGCGGTGAC-3′ | |
| NLRP3 | 5′-ACAGCCACCTCACTTCCAG-3′ | 5′-CCAACCACAATCTCCGAATG-3′ |
| Caspase-1 | 5′-AGAGGATTTCTTAAGGATGCA-3′ | 5′-TCACAAGACCAGGCATATTCTT-3′ |
| GSDMD | 5′-GGCCCTACTGCCTTCTG-3′ | 5′-AAAACACTCCGGTTCTGGT-3′ |
| IL-1 |
5′-AGTTGACGGACCCCAAA-3′ | 5′-TCTTGTTGATGTGCTGCTG-3′ |
The mouse heart tissue was cut into small pieces, and the myocardial tissue was
lysed by adding RIPA lysis solution to extract the total protein. The protein
concentration was determined according to the instructions of the BCA Protein
Assay Kit. An equal amount of protein (20
Data are presented as the mean
The chemical composition of ASHP was searched through the TCMSP database. The
major components of ASHP were screened by OB
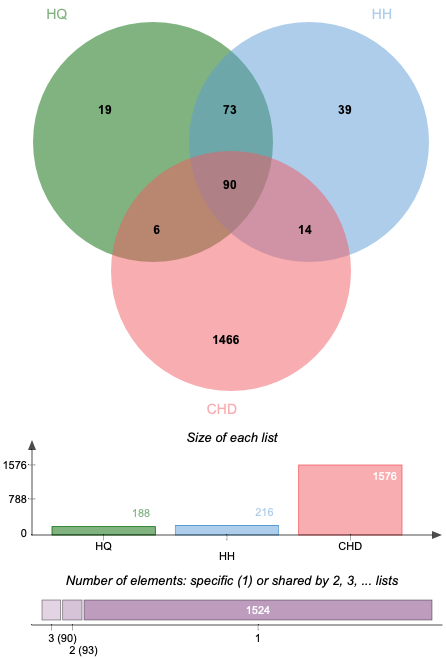
Altogether 1576 CHD-related targets were discovered by searching the databases of DisGeNET. Some of the CHD-related targets and the predictive targets of ASHP are overlapping. After removing any duplicate targets, 90 potential ASHP targets for CHD were identified (Fig. 2), which are detailed in Supplementary Table 2.
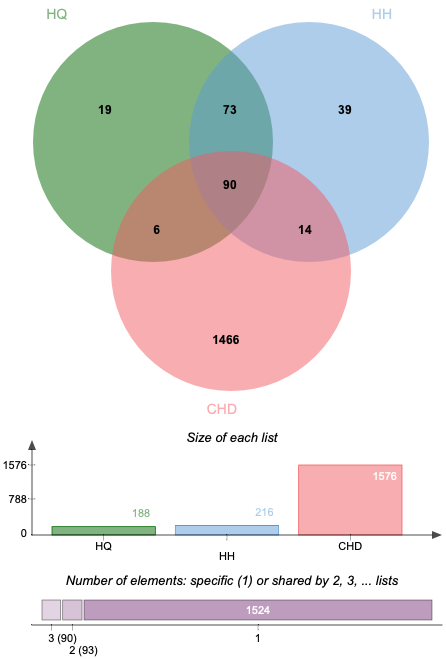 Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.Venn diagram of overlapping genes associated with CHD in ASHP.
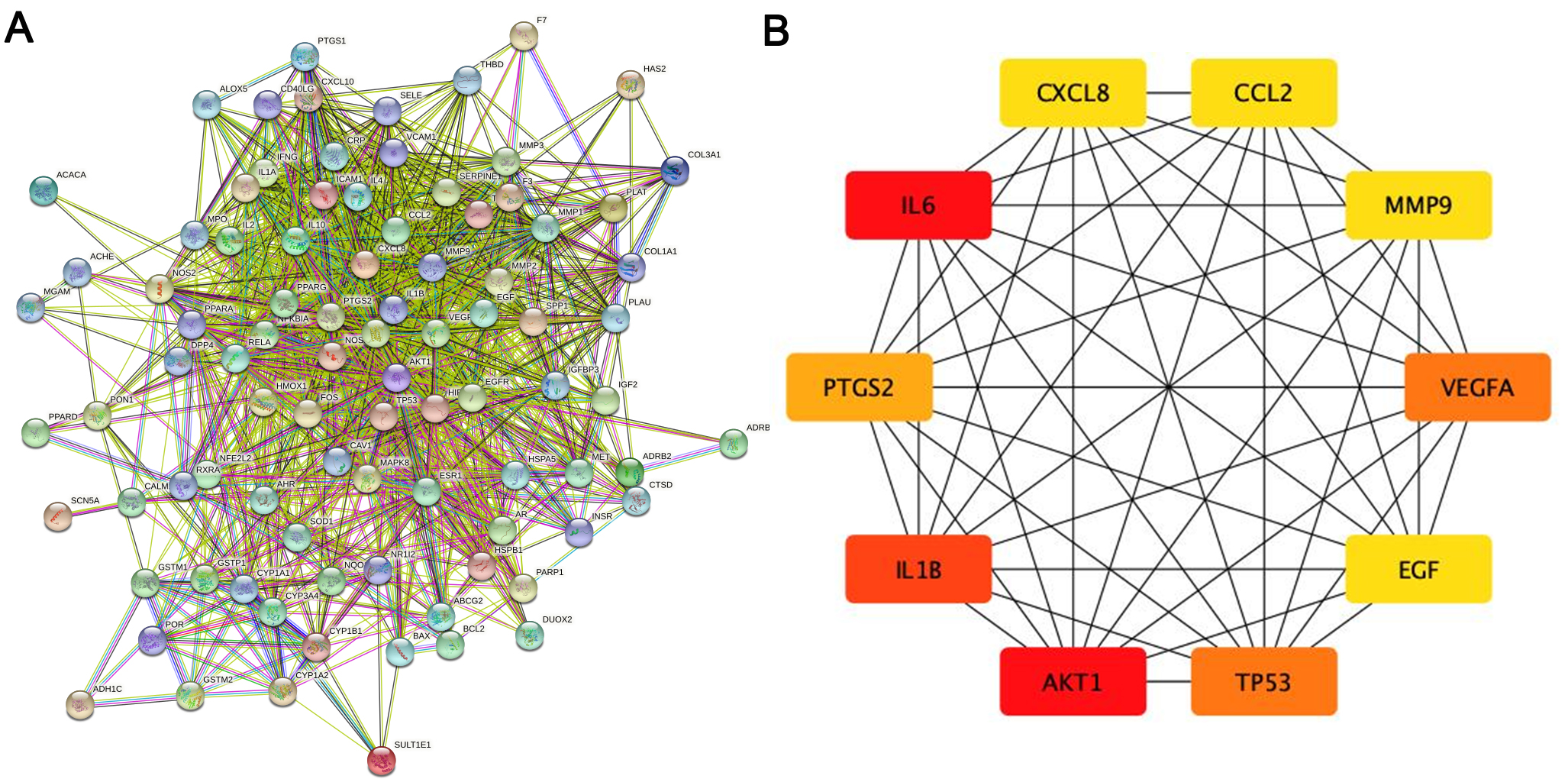
The PPI network of the herb compound-disease target interactions for the 90 over-lapping targets was constructed using the STRING database. From the analysis, we chose a score greater than 0.7. The PPI network had 90 nodes and 1379 edges, with a mean node degree of 30.6 and a local clustering coefficient on the order of 0.699 (as shown in Fig. 3A). After analysis using the cytohub plugin in Cytoscape software, the top 10 key genes were ranked according to the degree of display integrity. The 10 hub genes were IL6, AKT1, IL1B, TP53, VEGFA, PTGS2, MMP9, CCL2, CXCL8 and EGF (Fig. 3B). Topologically, the most important node in the network has betweenness centrality, the highest degree, and closeness centrality. The quantity of edges that are connected to a node determines its “degree”. The quantity of shortest paths passing through a certain node is known as “betweenness” . The quantity of average diastance from a certain node is known as “closeness”. The features of hub genes are displayed in Table 2 [27].
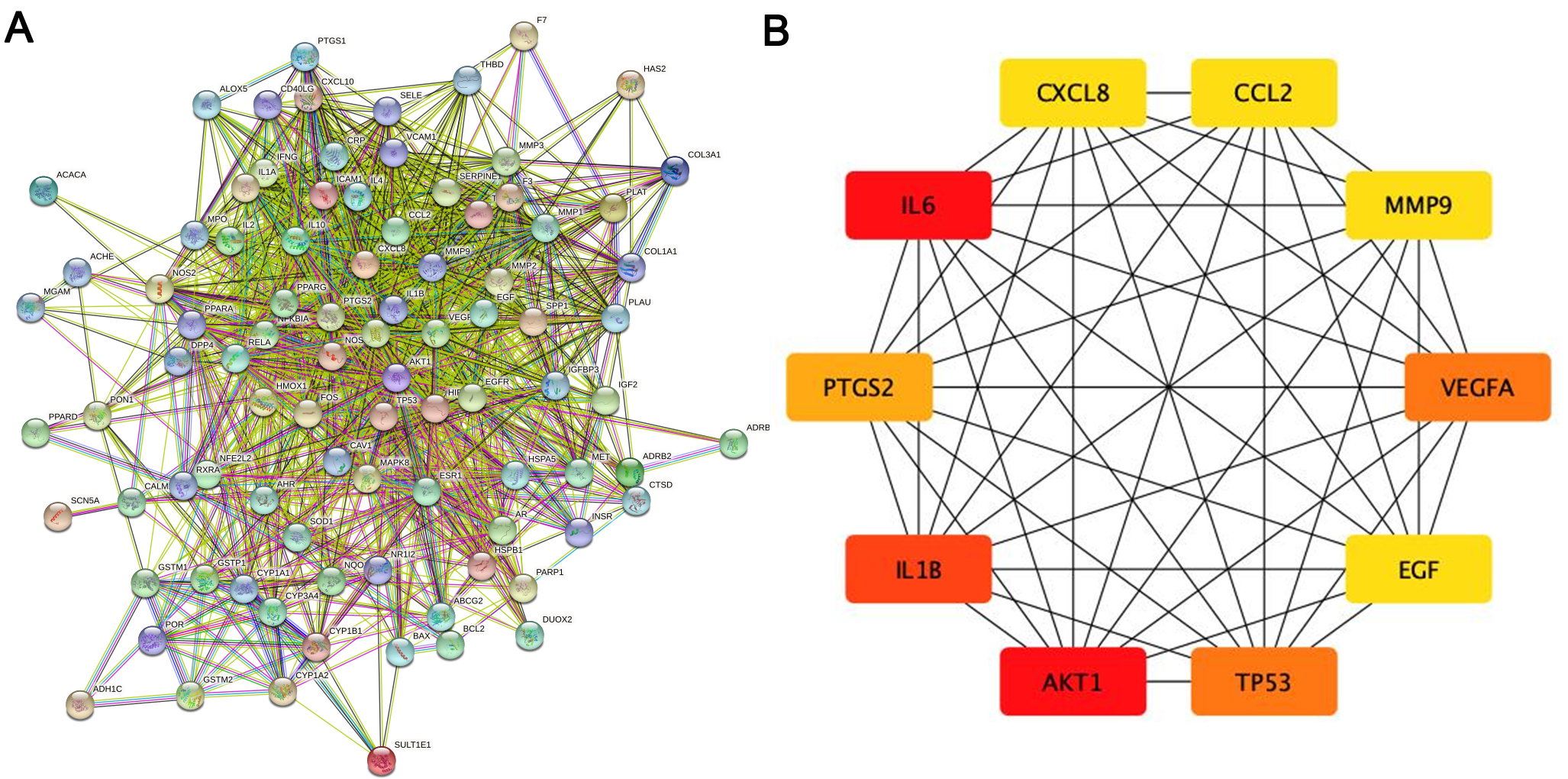 Fig. 3.
Fig. 3.The main targets and network of ASHP in the treatment of CHD. (A) Protein-protein interaction network of ASHP in the treatment of CHD. (B) The top 10 hub gene of ASHP in the treatment of CHD.
| Gene | Degree | Betweenness | Closeness |
|---|---|---|---|
| IL6 | 71 | 409.44446 | 0.8240741 |
| AKT1 | 71 | 522.7065 | 0.8317757 |
| IL1B | 65 | 220.52296 | 0.78070176 |
| TP53 | 64 | 233.48093 | 0.78070176 |
| VEGFA | 64 | 181.15057 | 0.773913 |
| PTGS2 | 60 | 245.07791 | 0.7542373 |
| MMP9 | 55 | 85.41447 | 0.7177419 |
| CCL2 | 55 | 96.76832 | 0.7177419 |
| CXCL8 | 55 | 94.17428 | 0.7177419 |
| EGF | 55 | 156.39207 | 0.7177419 |
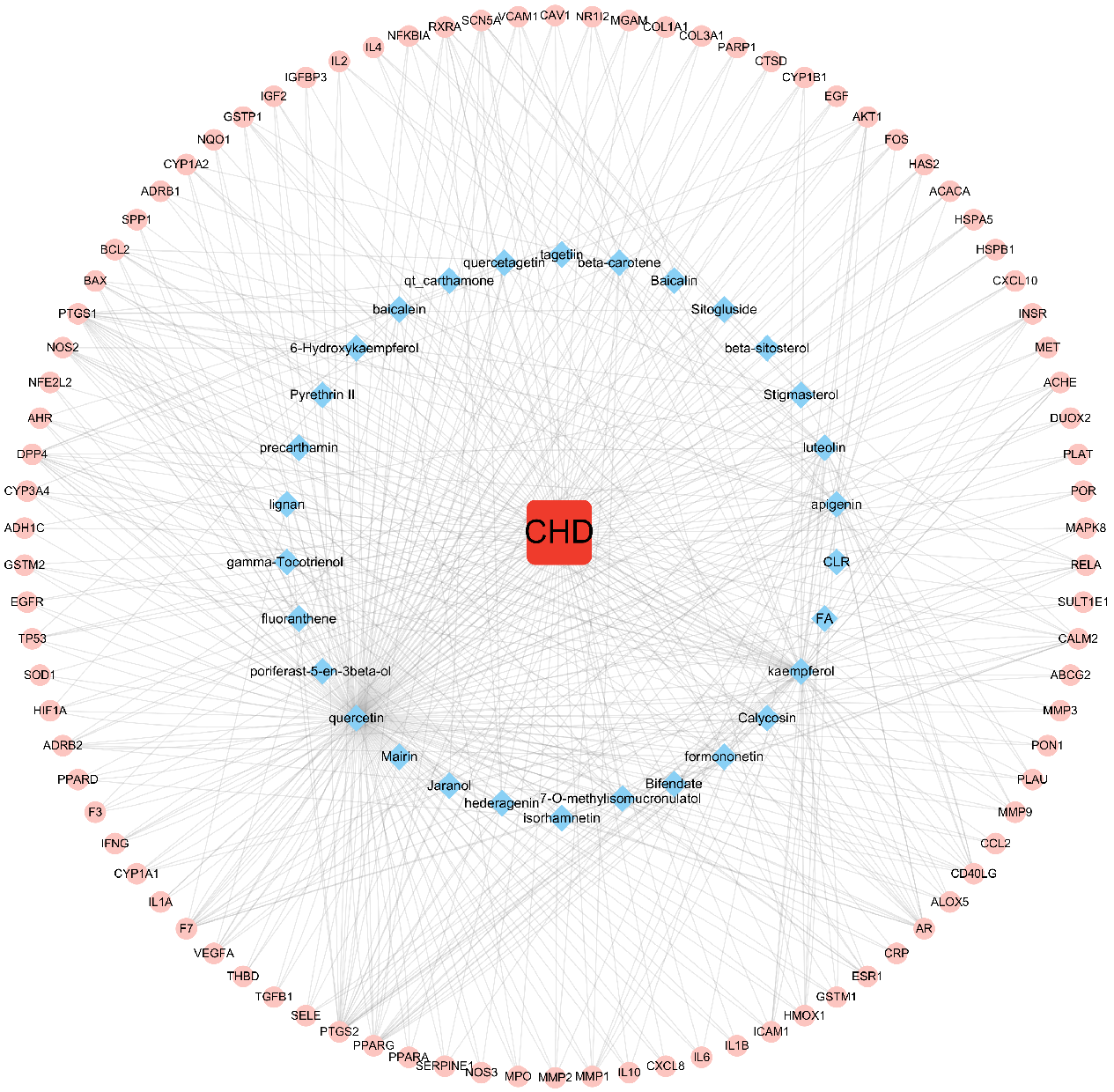
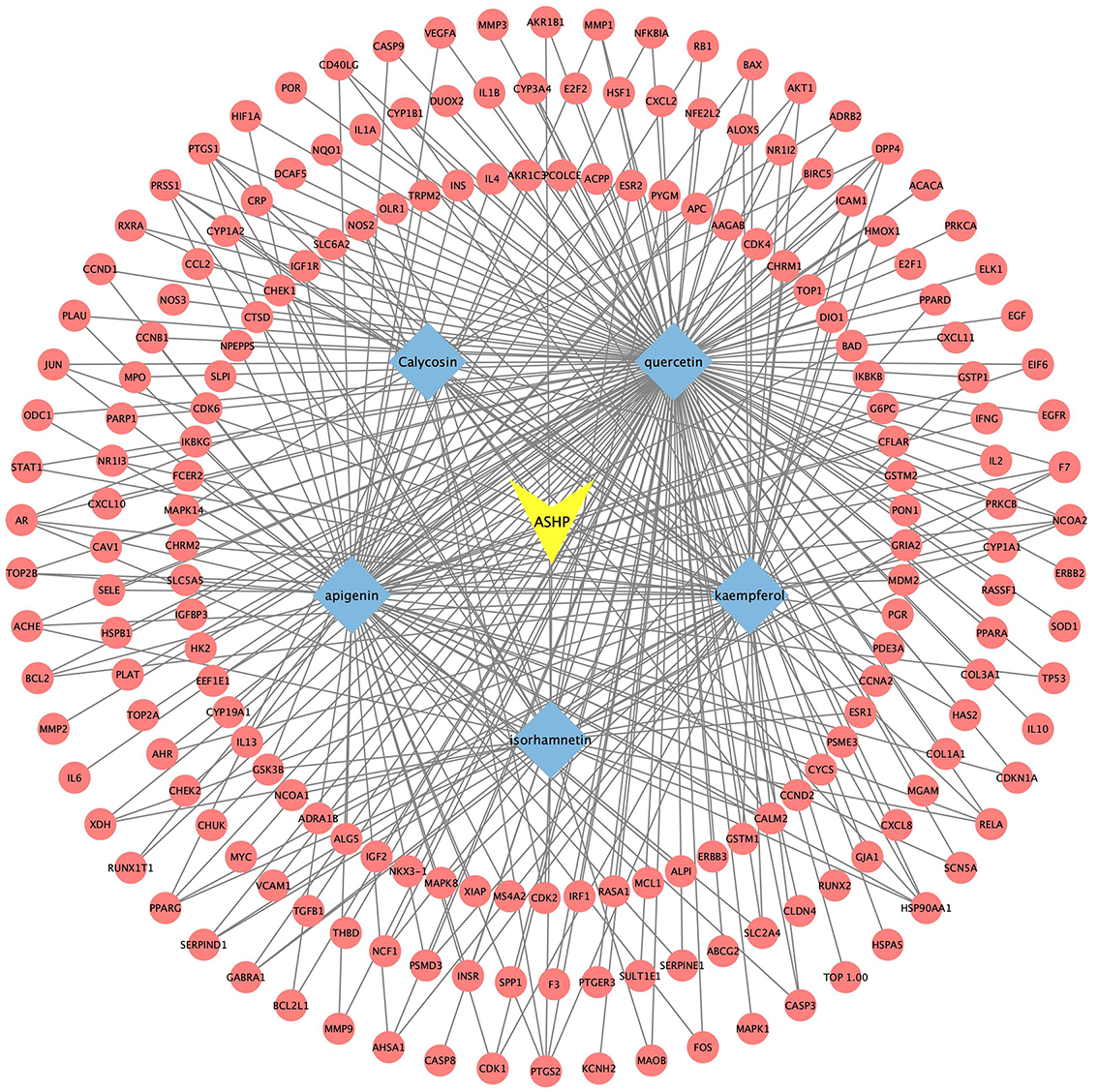
The disease, compounds and overlapping genes were imported into Cytoscape software to map a “compound-target-disease” network graph, which showed 121 nodes and 508 edges, containing 1 disease name, 30 compounds, and 90 targets (Fig. 4).
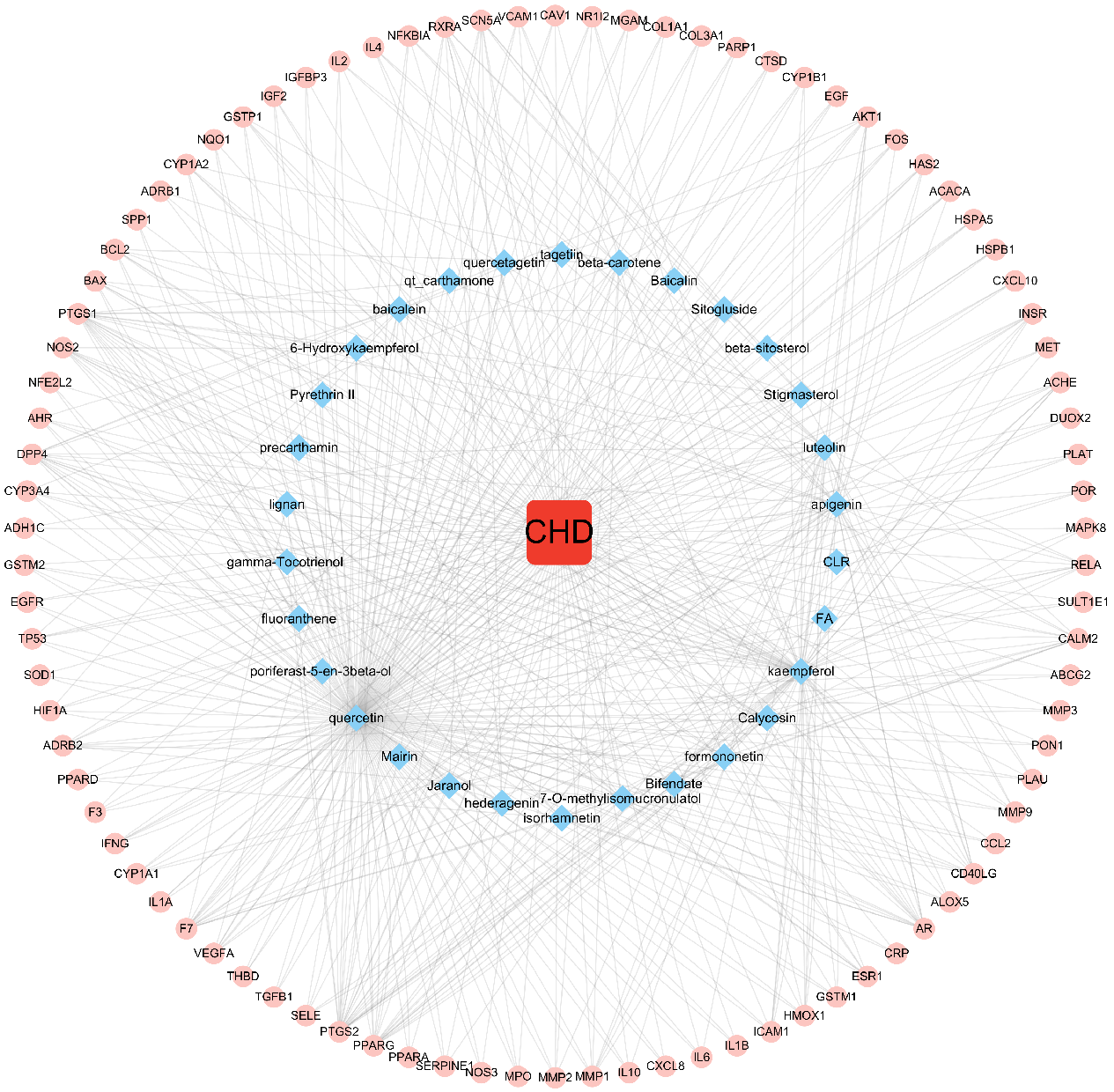 Fig. 4.
Fig. 4.C-T-D Network Construction of ASHP in the treatment of CHD.
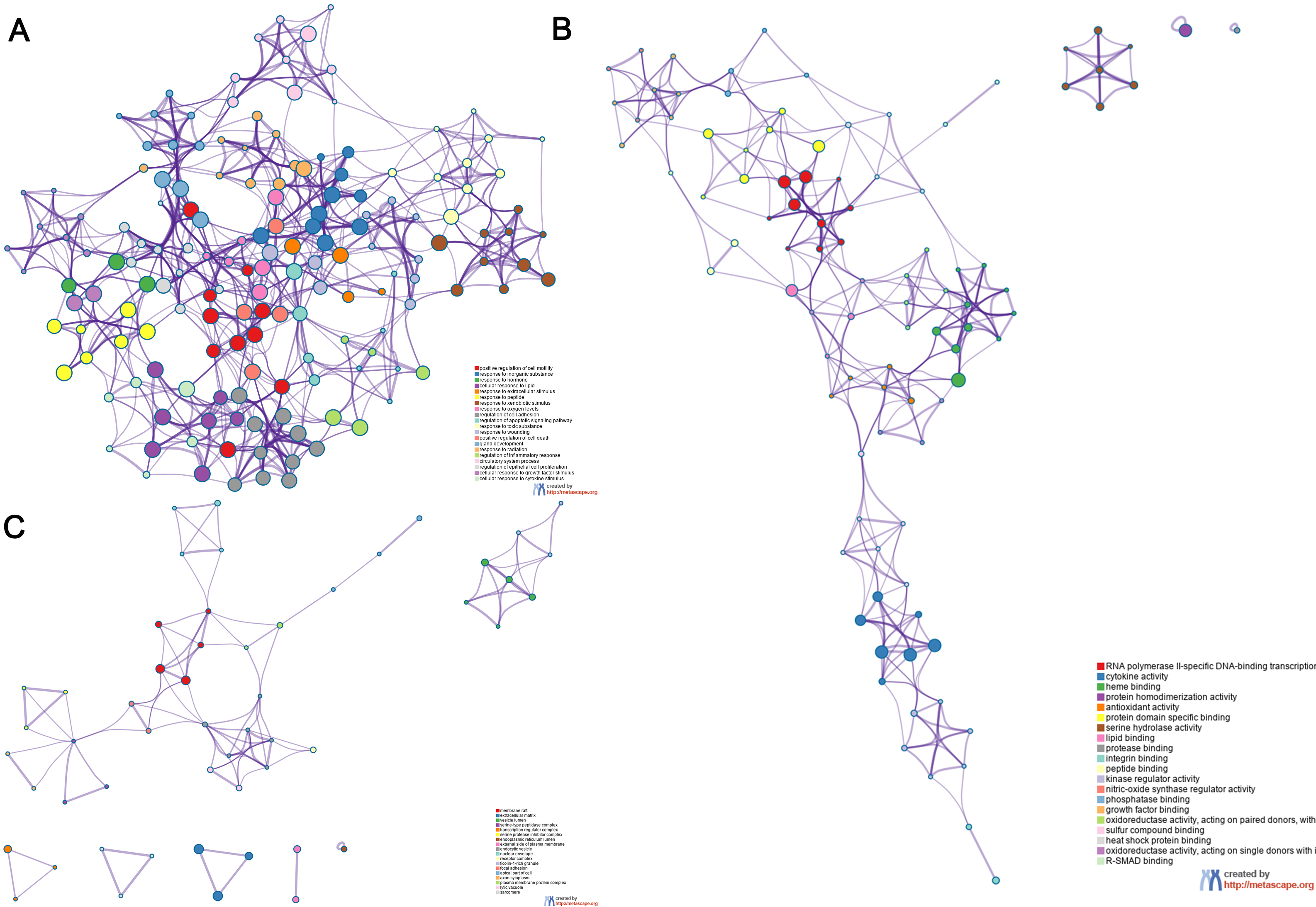
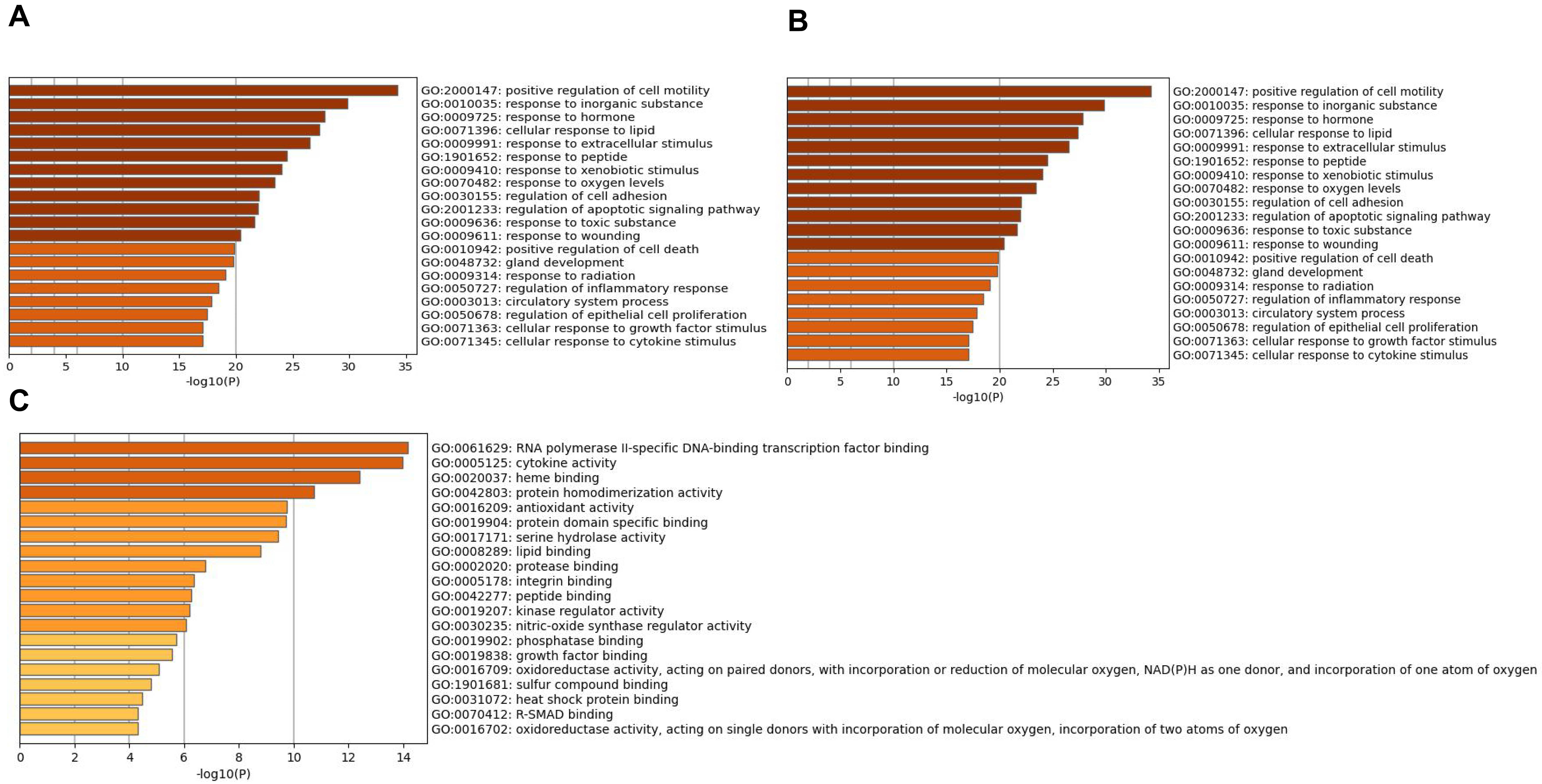
The overlapping genes were analyzed by the Metascape database for GO enrichment analysis, including the biological process (BP), cell composition (CC), and molecular function (MF) (Figs. 5 and 6). The top 20 BP are presented, mainly including the following: positive regulation of cell motility, response to an inorganic substance, and response to the hormone (Table 3). The top 20 MF are presented, mainly including RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding and cytokine activity (Table 4); The top 20 CC are presented, mainly including the membrane raft, extracellular matrix, vesicle lumen and heme binding (Table 5).
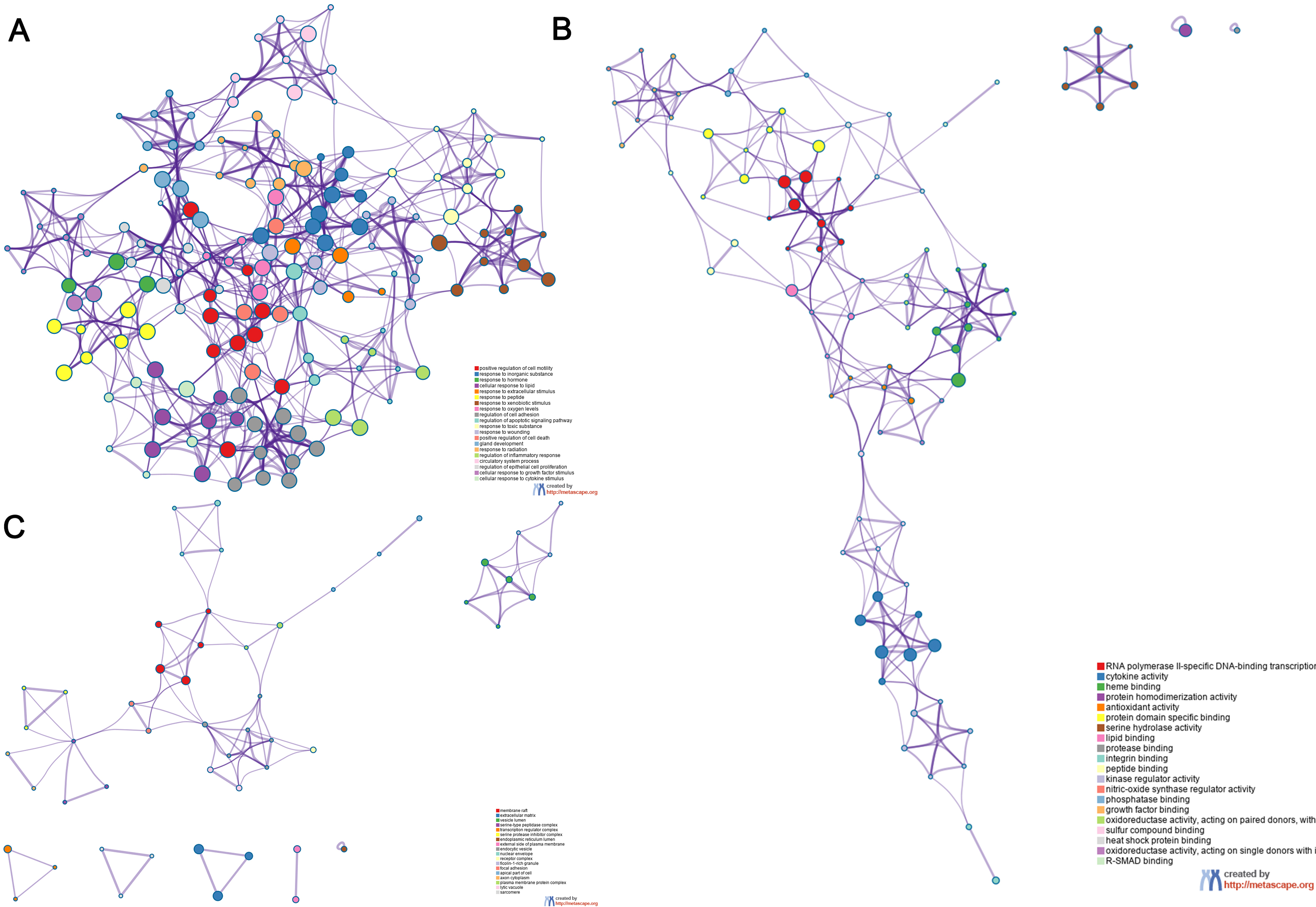 Fig. 5.
Fig. 5.Go functional enrichment analysis of the top 20 results from enrichment analysis of overlapping genes. GO analysis of terms for (A) BP, (B) MF, and (C) CC. Each cluster ID is indicated with a specific color. Each term is represented by a circular node, whose size corresponds to the term’s number of input genes, and whose color indicates membership in the same cluster.
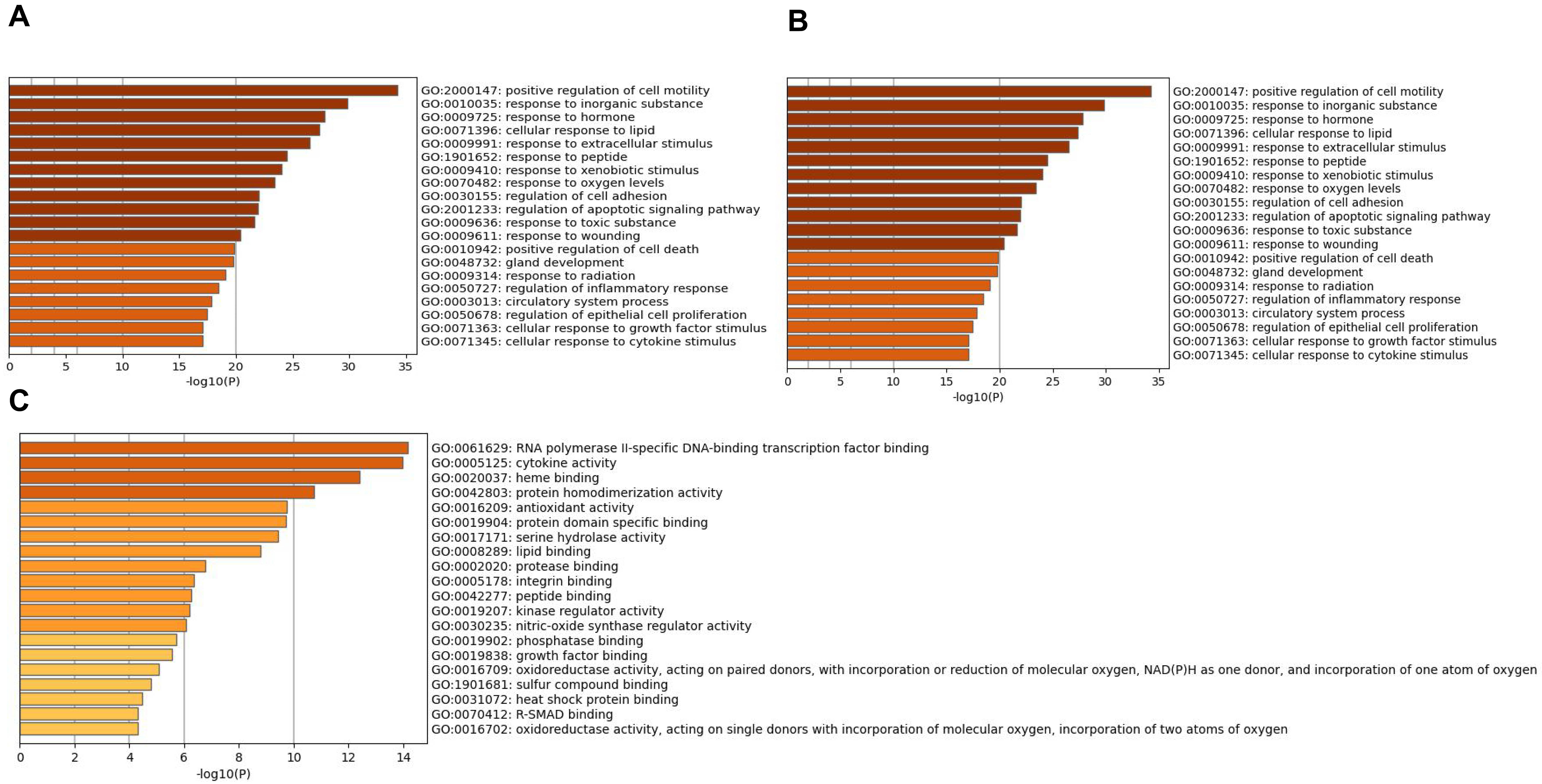 Fig. 6.
Fig. 6.Go enrichment analysis of overlapping genes Bar graph
showing the top 20 results of targets for Astragalus-Safflower drug pairs against
CHD. (A) BP terms (B) MF terms and (C) CC terms. The x-axis values correspond to
–log
| GO | Description | Count | % | Log |
Log |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO:2000147 | positive regulation of cell motility | 34 | 37.78 | –34.26 | –30.18 |
| GO:0010035 | response to inorganic substance | 30 | 33.33 | –29.84 | –26.35 |
| GO:0009725 | response to hormone | 32 | 35.56 | –27.80 | –24.39 |
| GO:0071396 | cellular response to lipid | 28 | 31.11 | –27.35 | –24.00 |
| GO:0009991 | response to extracellular stimulus | 27 | 30.00 | –26.47 | –23.28 |
| GO:1901652 | response to peptide | 25 | 27.78 | –24.50 | –21.46 |
| GO:0009410 | response to xenobiotic stimulus | 24 | 26.67 | –24.05 | –21.04 |
| GO:0070482 | response to oxygen levels | 22 | 24.44 | –23.44 | –20.48 |
| GO:0030155 | regulation of cell adhesion | 28 | 31.11 | –22.04 | –19.17 |
| GO:2001233 | regulation of apoptotic signaling pathway | 22 | 24.44 | –21.93 | –19.09 |
| GO:0009636 | response to toxic substance | 19 | 21.11 | –21.66 | –18.85 |
| GO:0009611 | response to wounding | 22 | 24.44 | –20.41 | –17.67 |
| GO:0010942 | positive regulation of cell death | 24 | 26.67 | –19.85 | –17.16 |
| GO:0048732 | gland development | 21 | 23.33 | –19.75 | –17.08 |
| GO:0009314 | response to radiation | 21 | 23.33 | –19.05 | –16.43 |
| GO:0050727 | regulation of inflammatory response | 20 | 22.22 | –18.42 | –15.84 |
| GO:0003013 | circulatory system process | 21 | 23.33 | –17.86 | –15.33 |
| GO:0050678 | regulation of epithelial cell proliferation | 19 | 21.11 | –17.45 | –14.96 |
| GO:0071363 | cellular response to growth factor stimulus | 20 | 22.22 | –17.10 | –14.62 |
| GO:0071345 | cellular response to cytokine stimulus | 23 | 25.56 | –17.06 | –14.60 |
| GO | Description | Count | % | Log |
Log |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO:0061629 | RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding | 16 | 17.78 | –14.17 | –10.58 |
| GO:0005125 | cytokine activity | 14 | 15.56 | –13.97 | –10.58 |
| GO:0020037 | heme binding | 11 | 12.22 | –12.40 | –9.56 |
| GO:0042803 | protein homodimerization activity | 17 | 18.89 | –10.73 | –8.22 |
| GO:0016209 | antioxidant activity | 8 | 8.89 | –9.74 | –7.31 |
| GO:0019904 | protein domain specific binding | 16 | 17.78 | –9.71 | –7.30 |
| GO:0017171 | serine hydrolase activity | 10 | 11.11 | –9.42 | –7.03 |
| GO:0008289 | lipid binding | 16 | 17.78 | –8.78 | –6.42 |
| GO:0002020 | protease binding | 7 | 7.78 | –6.75 | –4.57 |
| GO:0005178 | integrin binding | 7 | 7.78 | –6.35 | –4.20 |
| GO:0042277 | peptide binding | 9 | 10.00 | –6.27 | –4.15 |
| GO:0019207 | kinase regulator activity | 8 | 8.89 | –6.20 | –4.10 |
| GO:0030235 | nitric-oxide synthase regulator activity | 3 | 3.33 | –6.05 | –4.01 |
| GO:0019902 | phosphatase binding | 7 | 7.78 | –5.73 | –3.71 |
| GO:0019838 | growth factor binding | 6 | 6.67 | –5.54 | –3.53 |
| GO:0016709 | oxidoreductase activity, acting on paired donors, with incorporation or reduction of molecular oxygen, NAD(P)H as one donor, and incorporation of one atom of oxygen | 4 | 4.44 | –5.08 | –3.13 |
| GO:1901681 | sulfur compound binding | 7 | 7.78 | –4.79 | –2.89 |
| GO:0031072 | heat shock protein binding | 5 | 5.56 | –4.46 | –2.60 |
| GO:0016702 | oxidoreductase activity, acting on single donors with incorporation of molecular oxygen, incorporation of two atoms of oxygen | 3 | 3.33 | –4.31 | –2.47 |
| GO:0070412 | R-SMAD binding | 3 | 3.33 | –4.31 | –2.47 |
| GO | Description | Count | % | Log |
Log |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO:0045121 | membrane raft | 13 | 14.44 | –10.78 | –7.77 |
| GO:0031012 | extracellular matrix | 14 | 15.56 | –8.81 | –6.16 |
| GO:0031983 | vesicle lumen | 10 | 11.11 | –7.29 | –4.90 |
| GO:1905286 | serine-type peptidase complex | 4 | 4.44 | –7.29 | –4.90 |
| GO:0005667 | transcription regulator complex | 11 | 12.22 | –6.57 | –4.28 |
| GO:0097180 | serine protease inhibitor complex | 3 | 3.33 | –6.29 | –4.07 |
| GO:0005788 | endoplasmic reticulum lumen | 8 | 8.89 | –5.37 | –3.31 |
| GO:0009897 | external side of plasma membrane | 9 | 10.00 | –5.01 | –3.00 |
| GO:0030139 | endocytic vesicle | 7 | 7.78 | –4.12 | –2.18 |
| GO:0005635 | nuclear envelope | 8 | 8.89 | –3.99 | –2.06 |
| GO:0043235 | receptor complex | 8 | 8.89 | –3.65 | –1.74 |
| GO:0101002 | ficolin-1-rich granule | 5 | 5.56 | –3.63 | –1.74 |
| GO:0005925 | focal adhesion | 7 | 7.78 | –3.57 | –1.70 |
| GO:0045177 | apical part of cell | 7 | 7.78 | –3.53 | –1.70 |
| GO:1904115 | axon cytoplasm | 3 | 3.33 | –3.07 | –1.30 |
| GO:0098797 | plasma membrane protein complex | 8 | 8.89 | –2.89 | –1.14 |
| GO:0000323 | lytic vacuole | 8 | 8.89 | –2.78 | –1.07 |
| GO:0030017 | sarcomere | 4 | 4.44 | –2.44 | –0.78 |
| GO:0045121 | membrane raft | 13 | 14.44 | –10.78 | –7.77 |
| GO:0031012 | extracellular matrix | 14 | 15.56 | –8.81 | –6.16 |
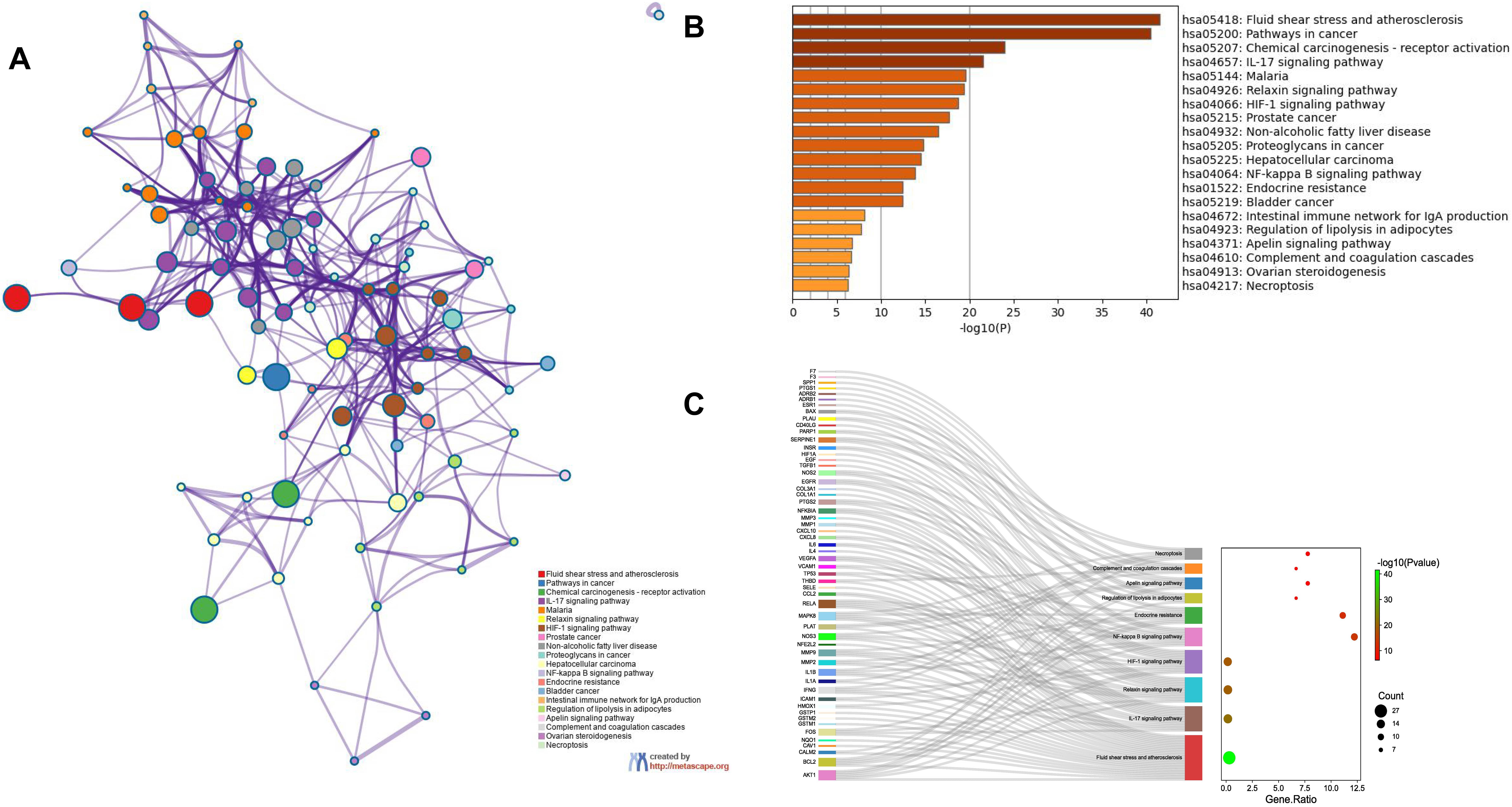
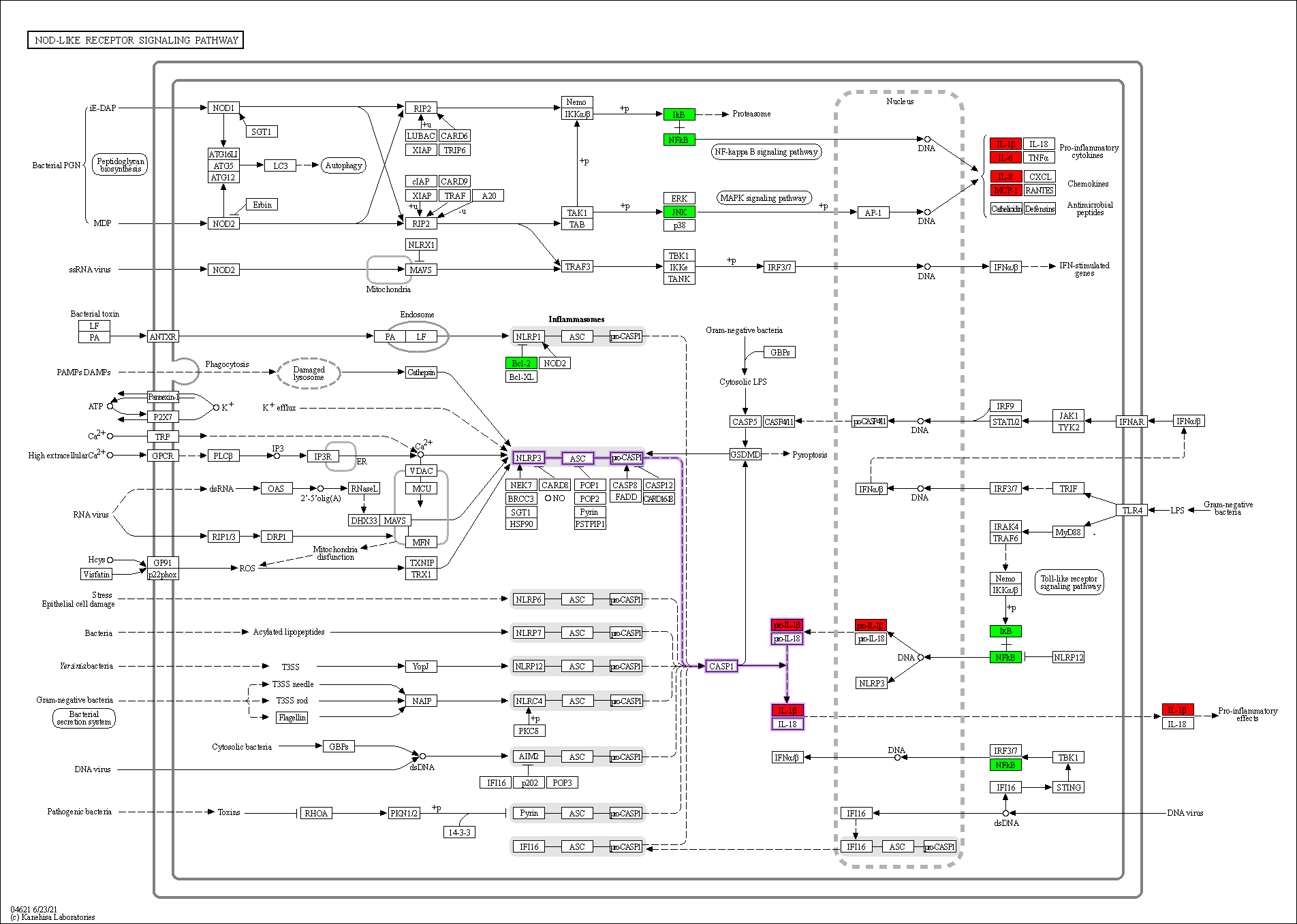
Enrichment analysis of the overlapping genes for the KEGG signaling pathway was performed through the Metascape database. The top 20 ranked KEGG pathways are presented, mainly including fluid shear stress, atherosclerosis, cancer-related pathways, activation of chemical carcinogenesis-receptors, interleukin (IL)-17 signaling pathway, malaria, and relaxin signaling pathway (Fig. 7A,B; Table 6). We selected 10 pathways with high relevance to CHD for KEGG signaling pathway using Sankey bubble plots. The left side of this figure is a Sankey diagram, representing the genes contained in each pathway, and the right side is a regular bubble diagram, with the bubble size indicating the number of genes belonging to the pathway and the bubble color indicating the p-value (Fig. 7C). Using the KEGG mapping color, we selected the Nod-like receptor signaling pathway for display (Fig. 8). The NLRP3-mediated proptosis pathway was seen in this pathway, which was confirmed by subsequent molecular docking and experimental verification.
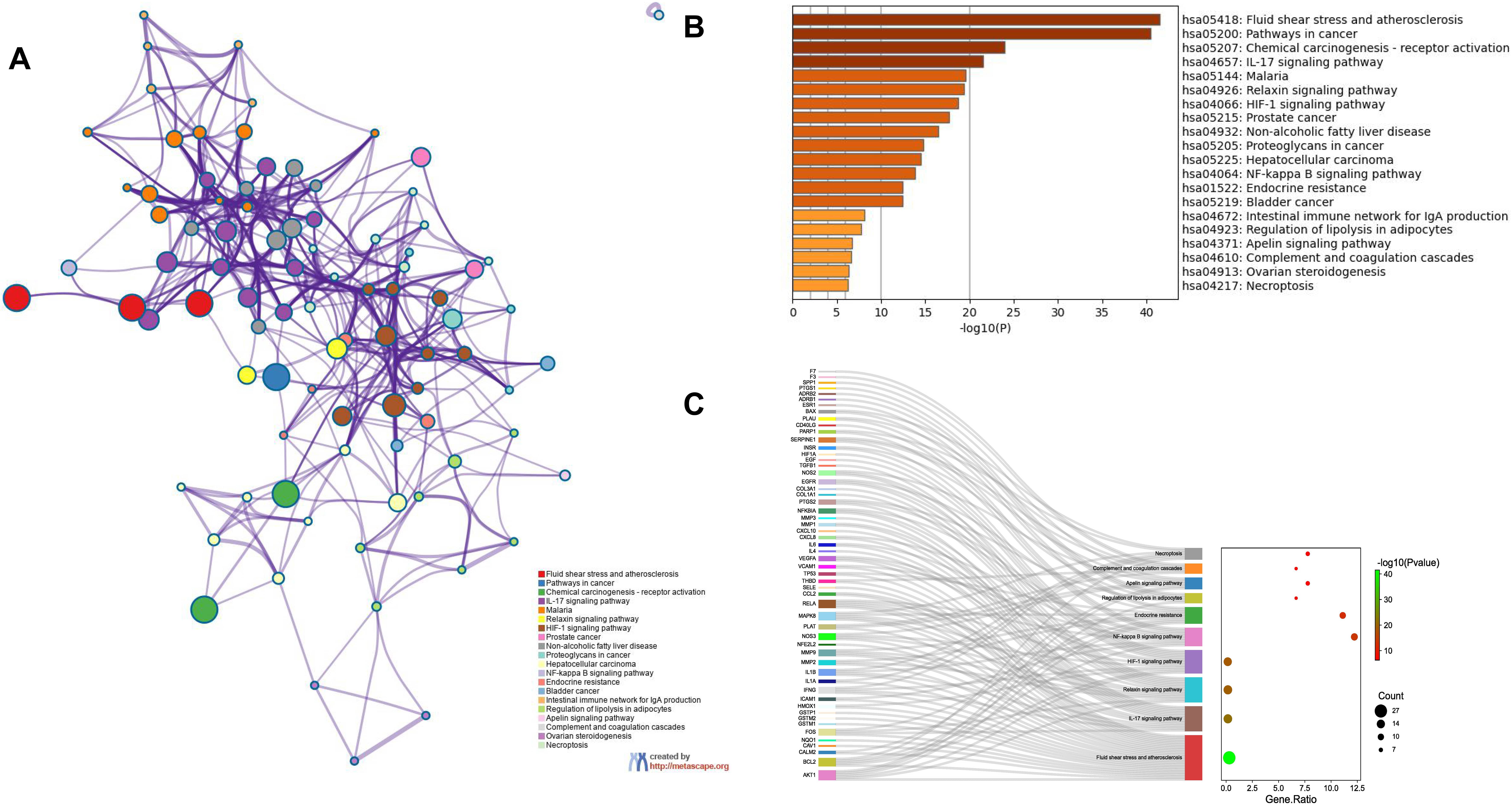 Fig. 7.
Fig. 7.Functional enrichment analysis of overlapping genes. (A) The network of enriched terms of overlapping genes; colors represent the same cluster ID. (B) Bar graph of KEGG analysis of overlapping genes. p value is shown in color. (C) Sankey plots show 10 pathways involved in KEGG enrichment pathways associated with CHD. The Sankey diagram on the left represents the genes contained in each pathway, and the regular bubble diagram on the right, with bubble size indicating the number of genes belonging to the pathway and bubble color indicating the p-value.
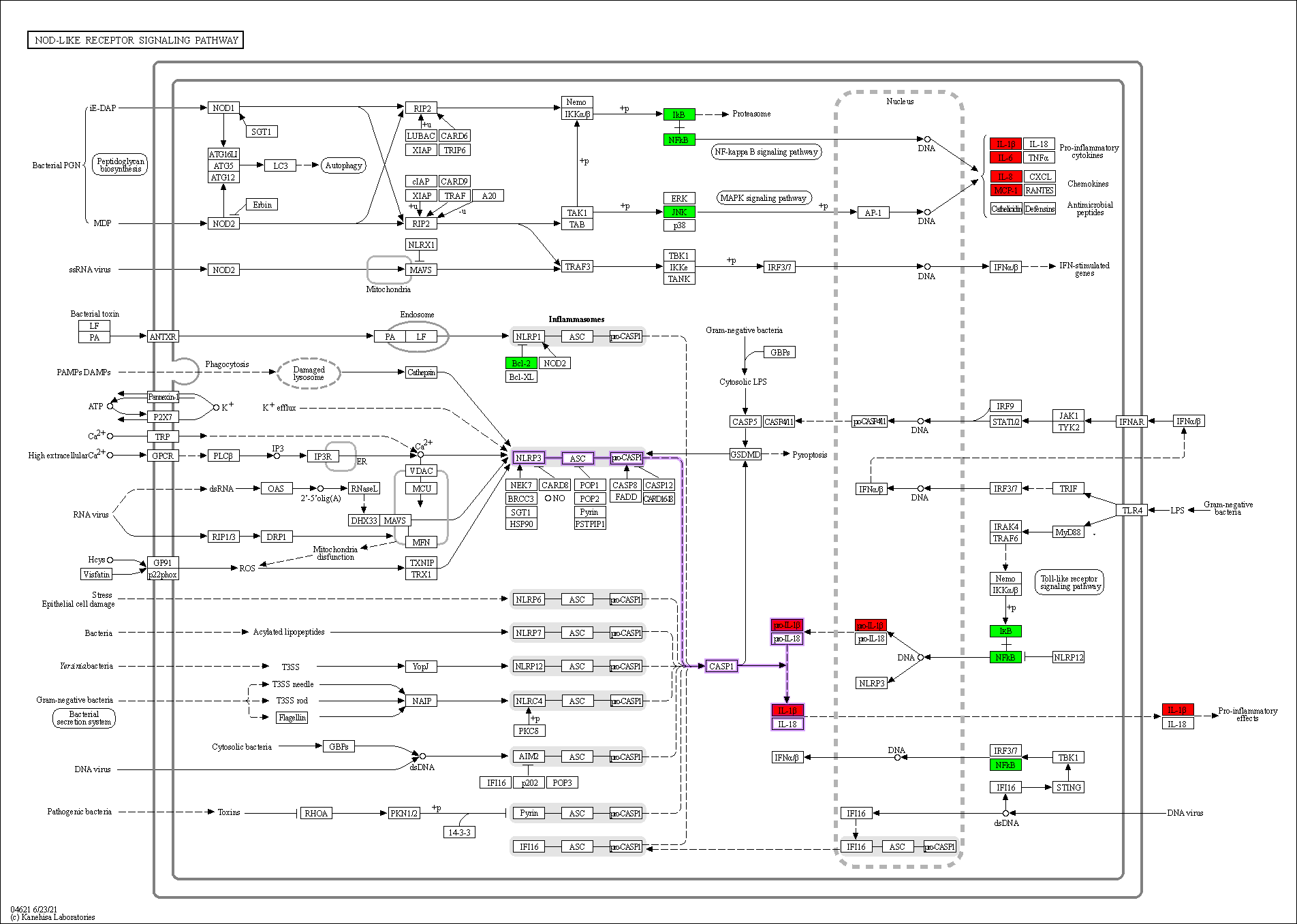 Fig. 8.
Fig. 8.Nod-like receptor signaling pathway. Overlapping genes in green, hub genes in red, and NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis pathway are shown in purple.
| GO | Description | Count | % | Log |
Log |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hsa05418 | Fluid shear stress and atherosclerosis | 27 | 30 | –41.53 | –38.99 |
| hsa05200 | Pathways in cancer | 37 | 41.11 | –40.45 | –38.21 |
| hsa05207 | Chemical carcinogenesis- receptor activation | 20 | 22.22 | –23.95 | –22.11 |
| hsa04657 | IL-17 signaling pathway | 15 | 16.67 | –21.53 | –19.84 |
| hsa05144 | Malaria | 12 | 13.33 | –19.60 | –18.06 |
| hsa04926 | Relaxin signaling pathway | 15 | 16.67 | –19.36 | –17.86 |
| hsa04066 | HIF-1 signaling pathway | 14 | 15.56 | –18.71 | –17.25 |
| hsa05215 | Prostate cancer | 13 | 14.44 | –17.65 | –16.22 |
| hsa04932 | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease | 14 | 15.56 | –16.50 | –15.14 |
| hsa05205 | Proteoglycans in cancer | 14 | 15.56 | –14.79 | –13.59 |
| hsa05225 | Hepatocellular carcinoma | 13 | 14.44 | –14.46 | –13.28 |
| hsa04064 | NF-kappa B signaling pathway | 11 | 12.22 | –13.81 | –12.7 |
| hsa01522 | Endocrine resistance | 10 | 11.11 | –12.43 | –11.46 |
| hsa05219 | Bladder cancer | 8 | 8.89 | –12.40 | –11.44 |
| hsa04672 | Intestinal immune network for IgA production | 6 | 6.67 | –8.13 | –7.44 |
| hsa04923 | Regulation of lipolysis in adipocytes | 6 | 6.67 | –7.77 | –7.09 |
| hsa04371 | Apelin signaling pathway | 7 | 7.78 | –6.69 | –6.10 |
| hsa04610 | Complement and coagulation cascades | 6 | 6.67 | –6.67 | –6.08 |
| hsa04913 | Ovarian steroidogenesis | 5 | 5.56 | –6.35 | –5.79 |
| hsa04217 | Necroptosis | 7 | 7.78 | –6.29 | –5.74 |
The data were collected in positive and negative ion mode for Astragalus-Safflower granule, Astragalus-Safflower drug-containing serum and blank serum. The total ion flow chromatograms (TIC) are shown in Supplementary Figs. 1 and 2. A total of 489 positive ion serum drug compounds and 379 negative ion serum drug compounds were identified, and after comparison with the database, 2 negative ion mode blood compounds were finally obtained, which were calycosin and isorhamnetin (marked with 1.2 in Supplementary Fig. 2, Supplementary Table 3). Two serum compounds were compared with the Astragalus-Safflower that we retrieved in the TCMSP database, the results show that calycosin and isorhamnetin were in the core compound table obtained from this database.
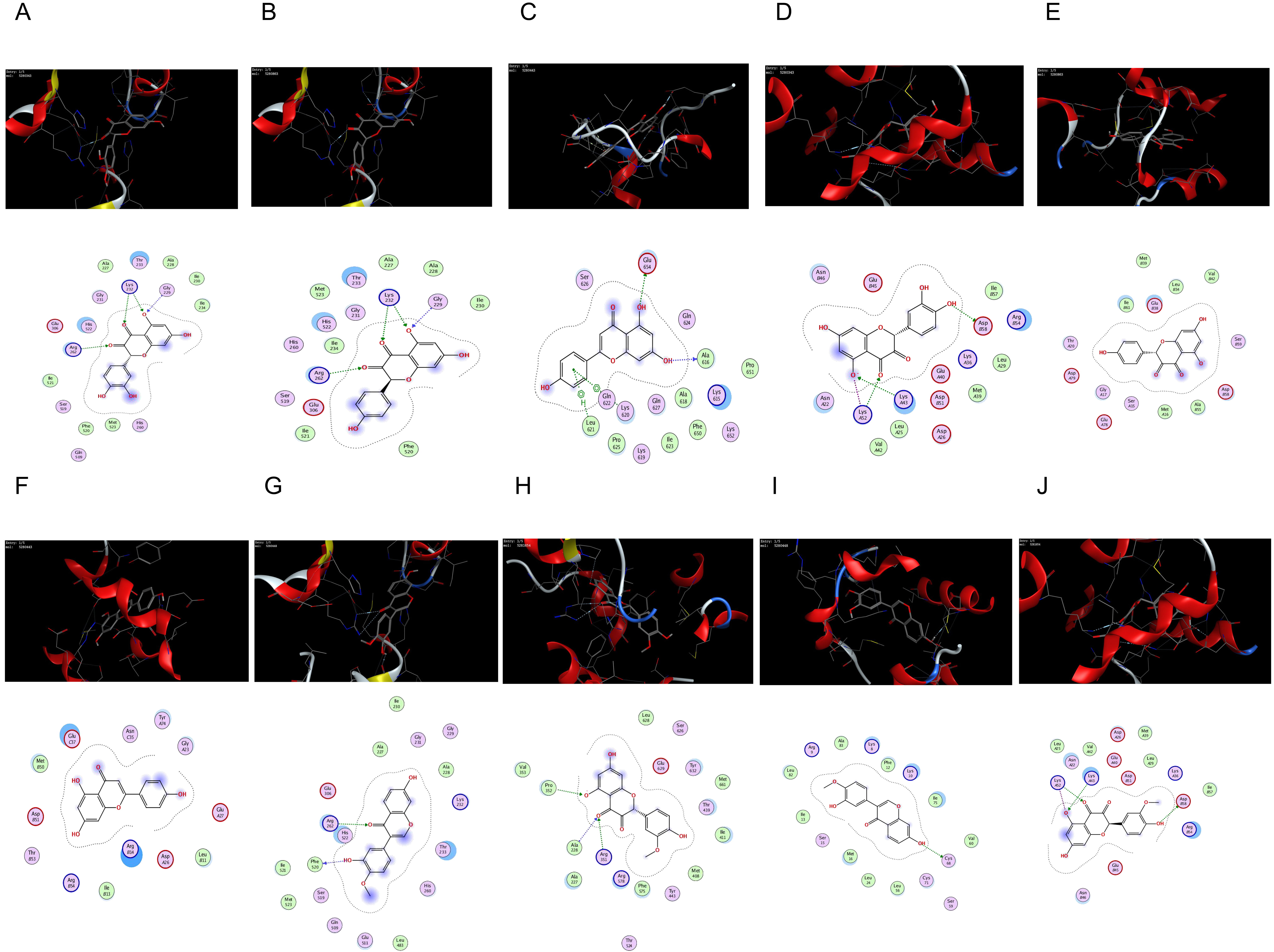
The core targets of the NLRP3-mediated proptosis pathway, NLRP3 (PDB: 7ALV)
[28], Caspase-1 (PDB: 5FNA) [29], and Astragalus-Safflower were selected for
molecular docking analysis of the screened active ingredient quercetin,
kaempferol and apigenin. Meanwhile, Molecular docking of the two entry compounds
calycosin and isorhamnetin identified from Astragalus-Safflower rat serum with
NLRP3 and Caspase-1 proteins. The docking results are shown in Table 7 and Fig. 9. It was found that the molecular docking binding energy was
| Compounds | Targets | PDB ID | Score, kJ/mol |
|---|---|---|---|
| quercetin | NLRP3 | 7ALV | –6.2744 |
| kaempferol | NLRP3 | 7ALV | –6.1576 |
| apigenin | NLRP3 | 7ALV | –5.8945 |
| calycosin | NLRP3 | 7ALV | –6.1122 |
| isorhamnetin | NLRP3 | 7ALV | –6.1980 |
| quercetin | Caspase-1 | 5FNA | –6.0698 |
| kaempferol | Caspase-1 | 5FNA | –6.1021 |
| apigenin | Caspase-1 | 5FNA | –6.0009 |
| calycosin | Caspase-1 | 5FNA | –6.3561 |
| isorhamnetin | Caspase-1 | 5FNA | –6.4310 |
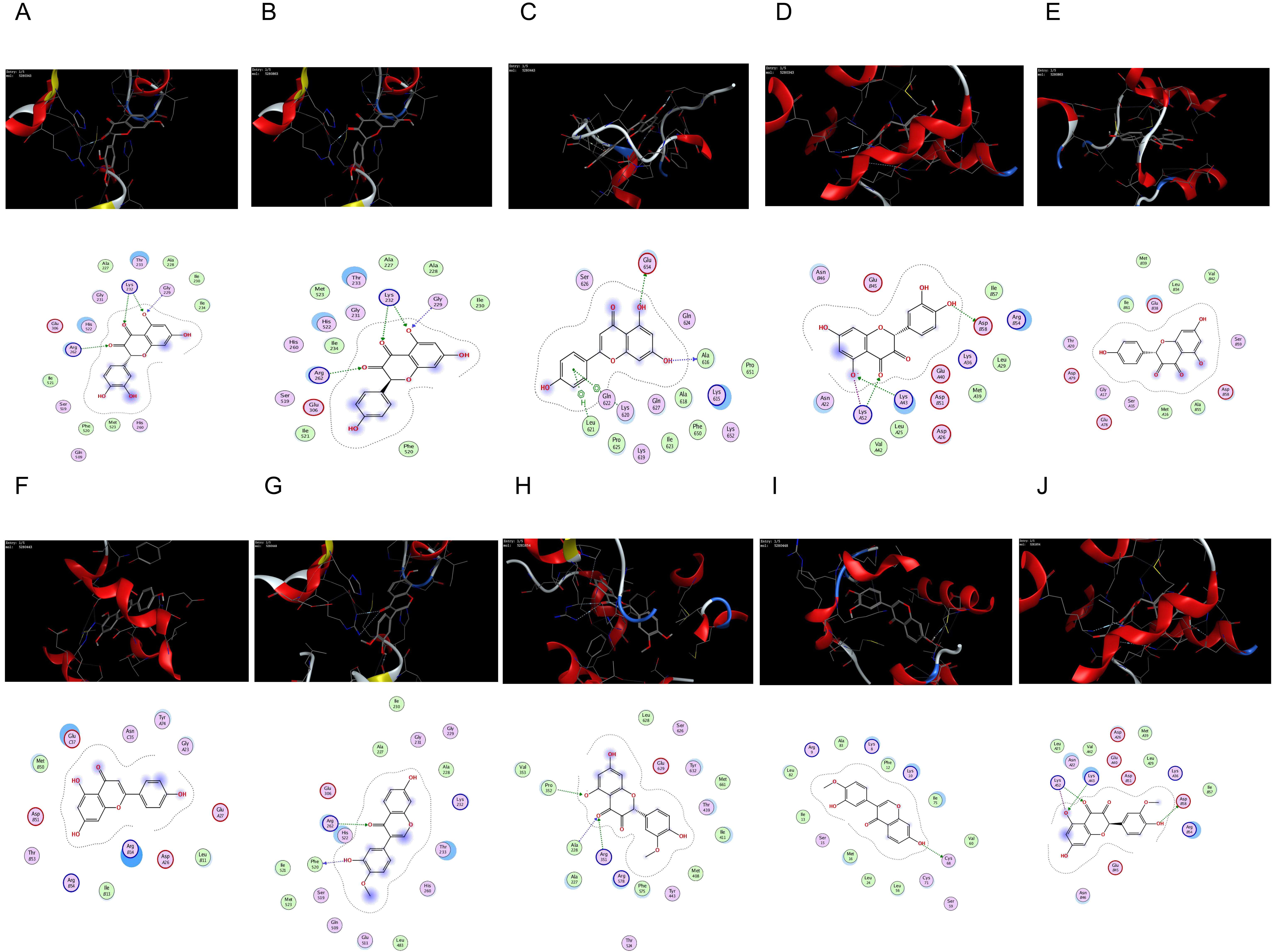 Fig. 9.
Fig. 9.The network of molecular docking results. (A) quercetin interacting with NLRP3. (B) kaempferol interacting with NLRP3. (C) apigenin interacting with NLRP3. (D) quercetin interacting with Caspase-1. (E) kaempferol interacting with Caspase-1. (F) apigenin interacting with Caspase-1. (G) calycosin interacting with NLRP3. (H) isorhamnetin interacting with NLRP3. (I) calycosin interacting with Caspase-1. (J) isorhamnetin interacting with Caspase-1.
According to the aforementioned study, the core active compounds of ASHP were quercetin, kaempferol, apigenin, calycosin and isorhamnetin. The core active compounds and targets were imported into Cytoscape software to map a “core active compound-target-disease” network graph, which showed 198 nodes and 328 edges, containing 1herb pair, 5 core active compounds, and 192 targets (Fig. 10).
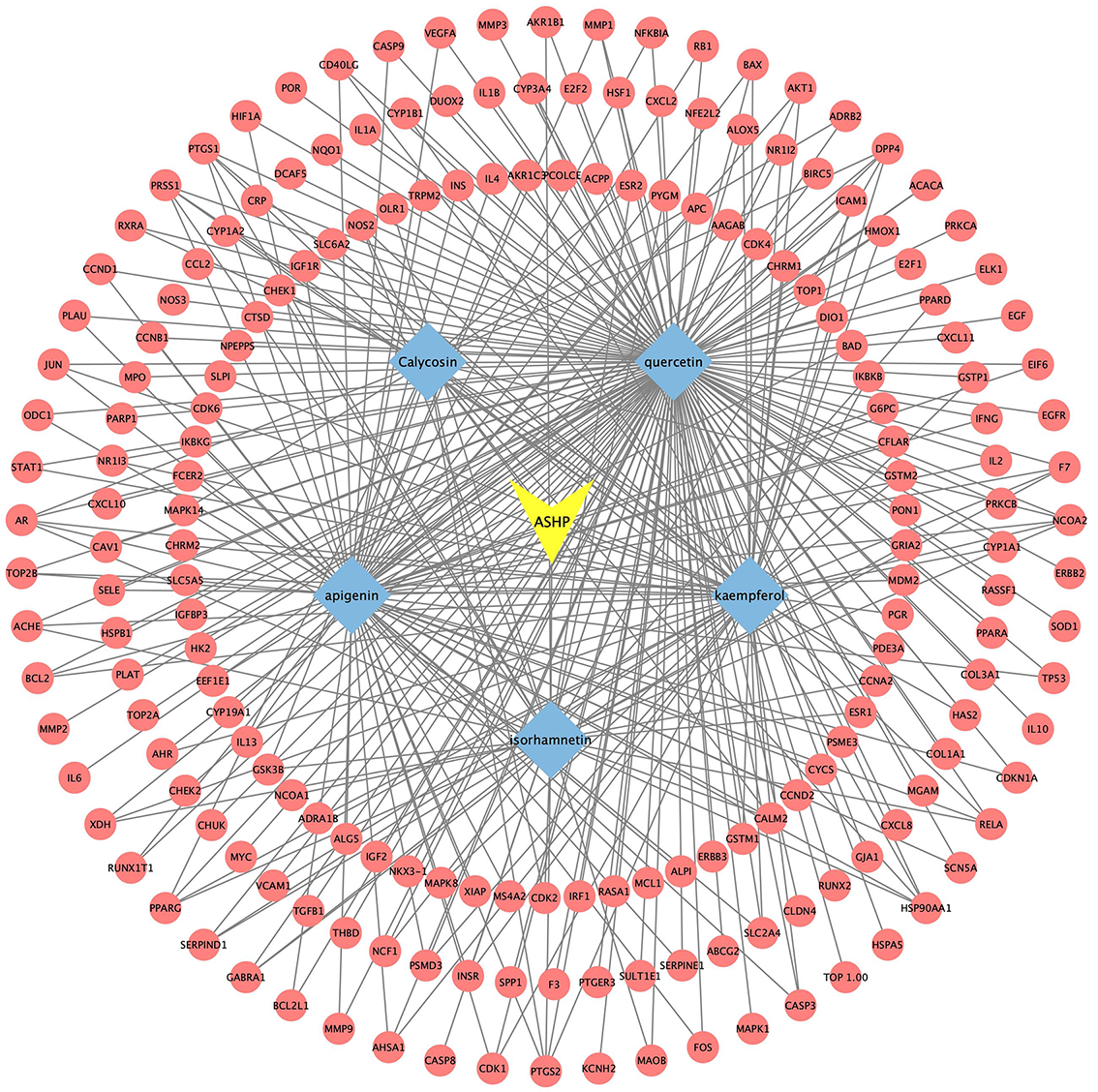 Fig. 10.
Fig. 10.Core Active Compound-Target Network Construction of ASHP.
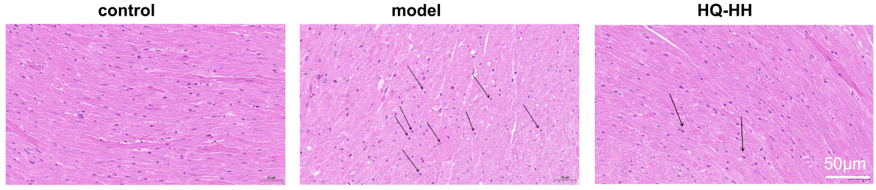
In the normal group, the myocardium was evenly stained; the cell shape was intact and closely arranged; the nucleus was centered with no break or defect; and no inflammatory cell infiltration was seen. In the CHD model group, myocardial cells were changed in shape and disordered in arrangement with widened myocardial gaps; the nuclei were fixed, some of which were edematous and deformed; and a small amount of inflammatory cell infiltration was seen. In ASHP group (HQ-HH), the cell shape and arrangement of the myocardial tissue improved significantly; the myocardial gap was narrowed; and the inflammatory cell infiltration and nuclear consolidation were significantly reduced (Fig. 11).
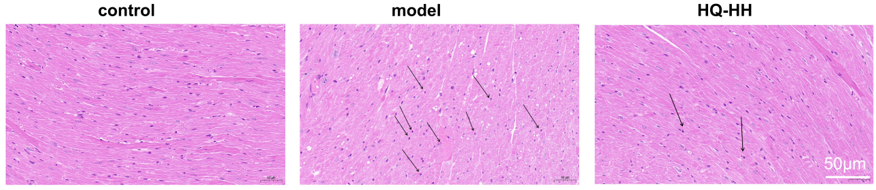 Fig. 11.
Fig. 11.
HE staining of myocardial pathology in groups of mice
(
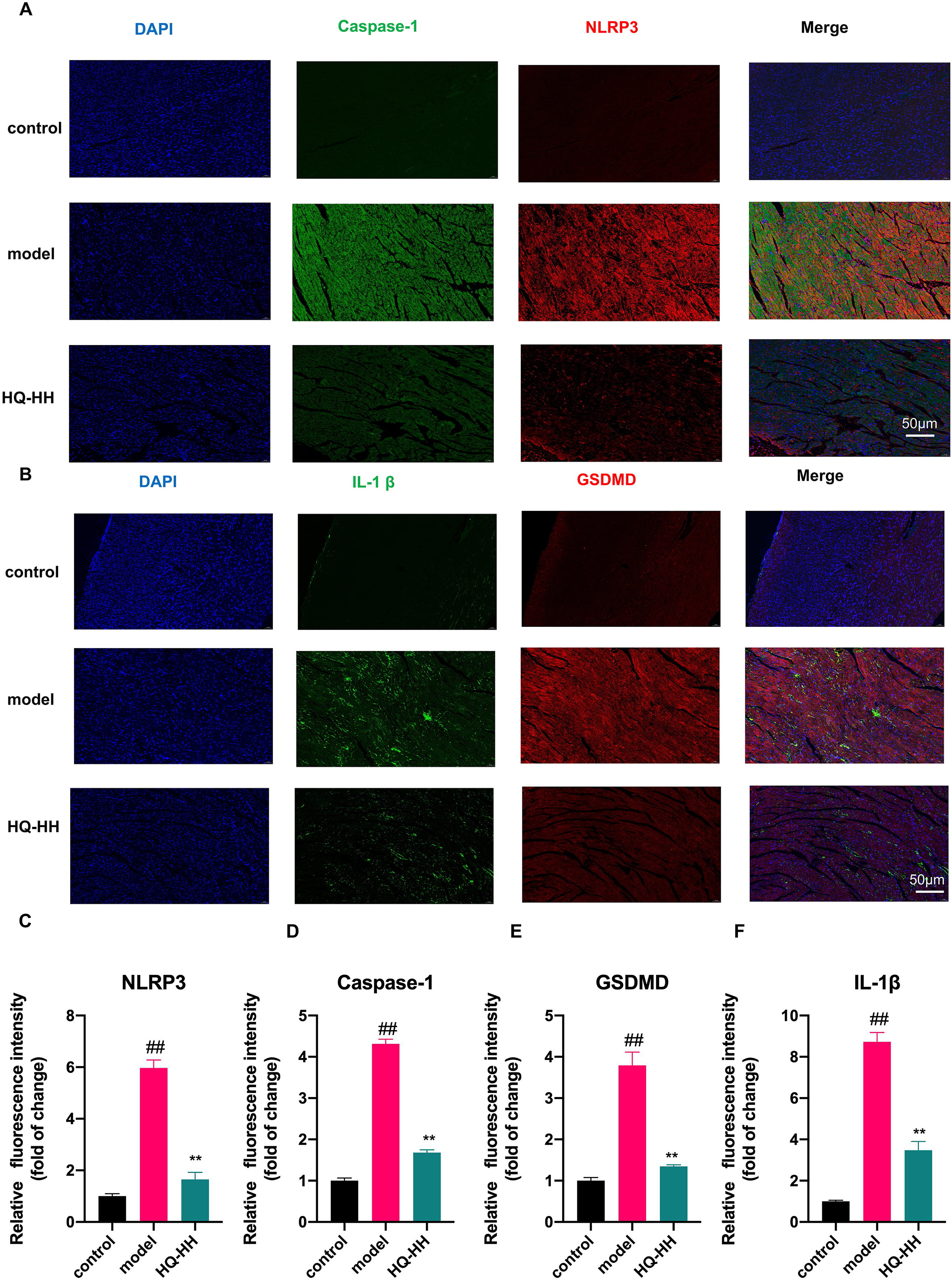
To confirm the findings from the KEGG pathway, we selected the four highly
linked targets (NLRP3, Caspase-1, GSDMD, IL-1
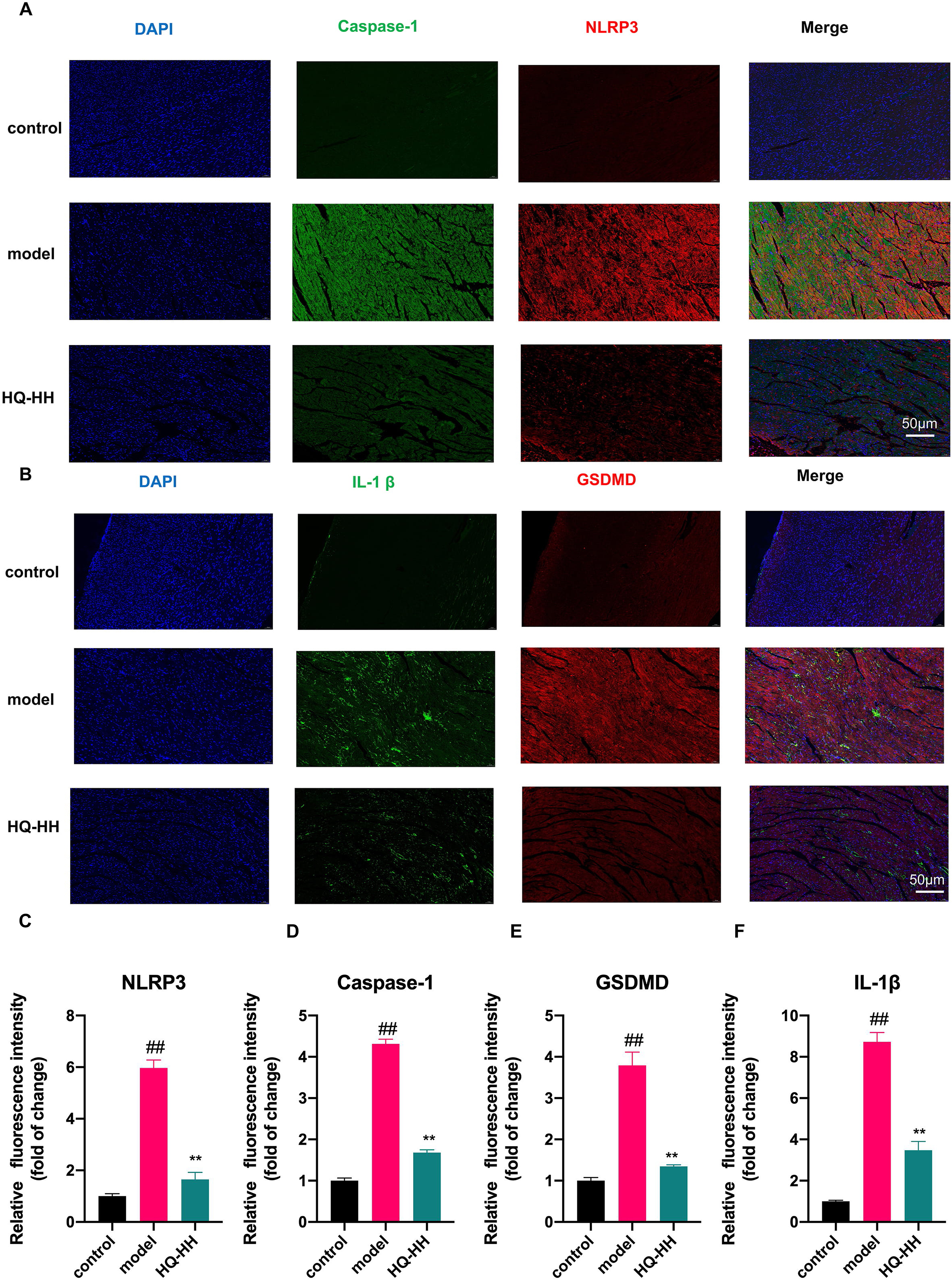 Fig. 12.
Fig. 12.Immunofluorescence double-staining of myocardial pathology in
groups of mice (
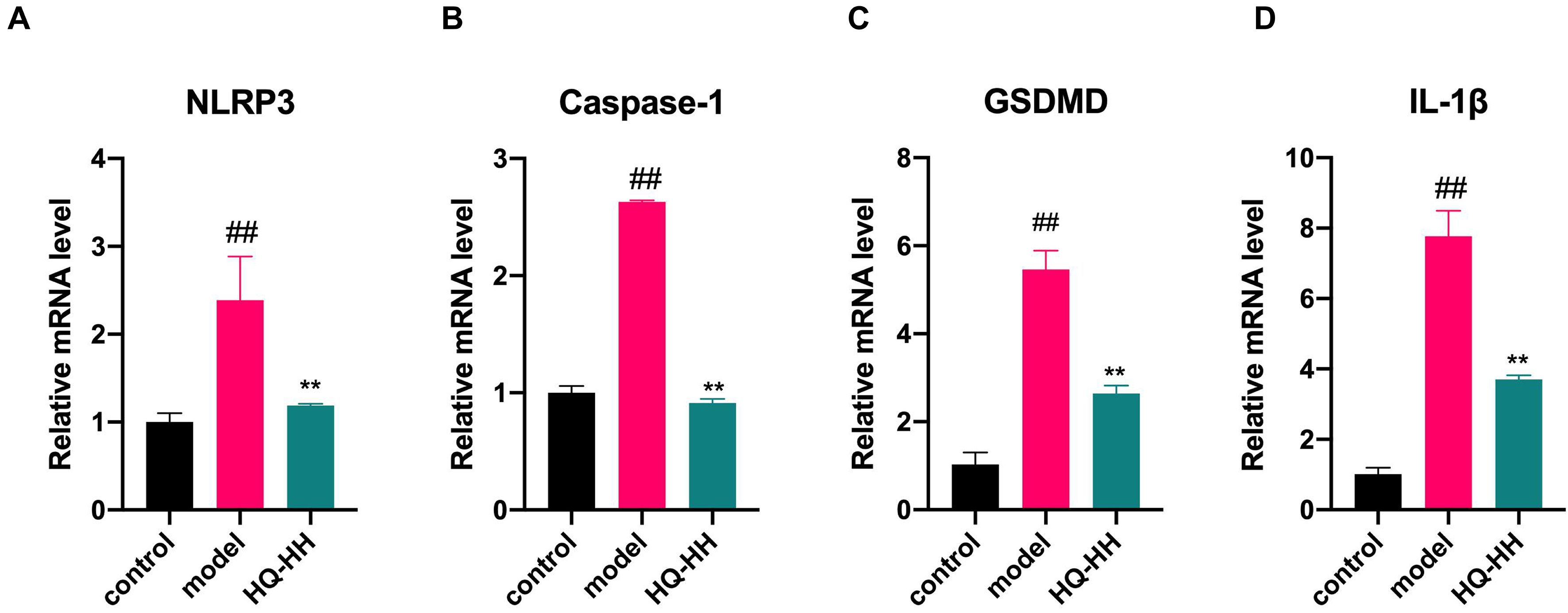 Fig. 13.
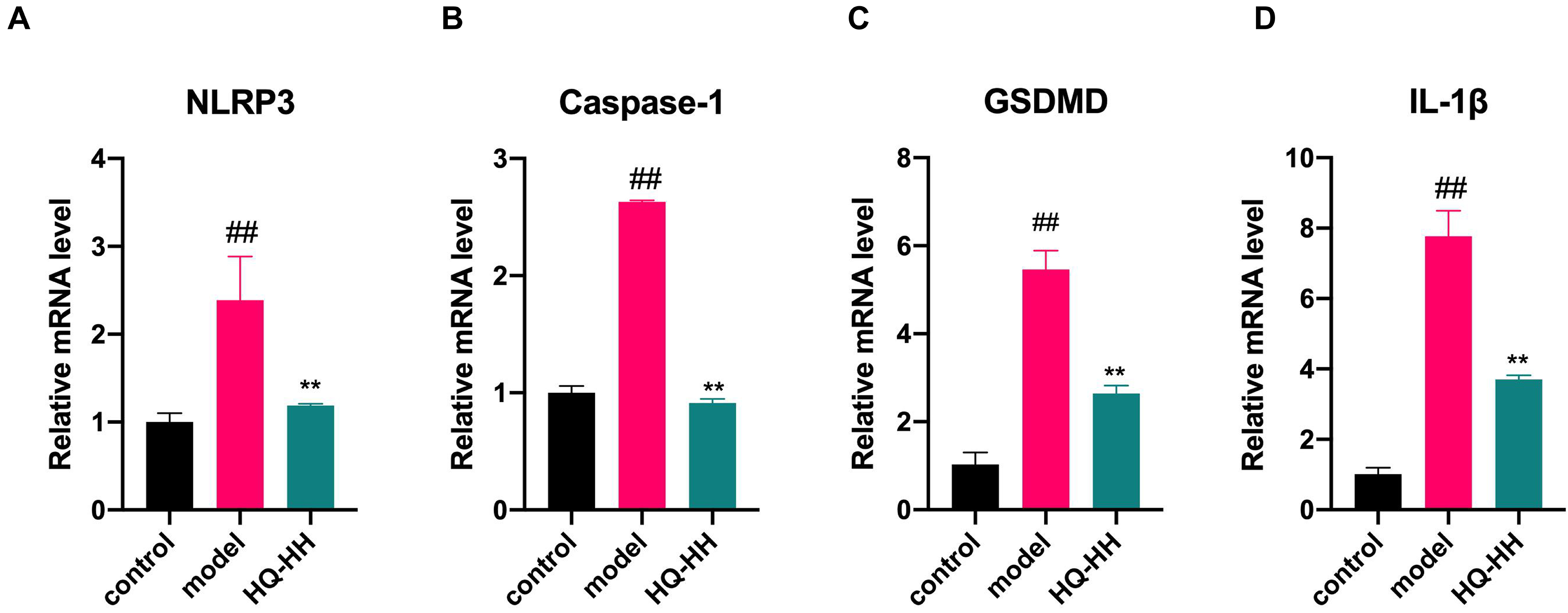
Fig. 13.Effects of Astragalus-Safflower drug pair on the mRNA
expression of NLRP3, Caspase-1, GSDMD and IL-1
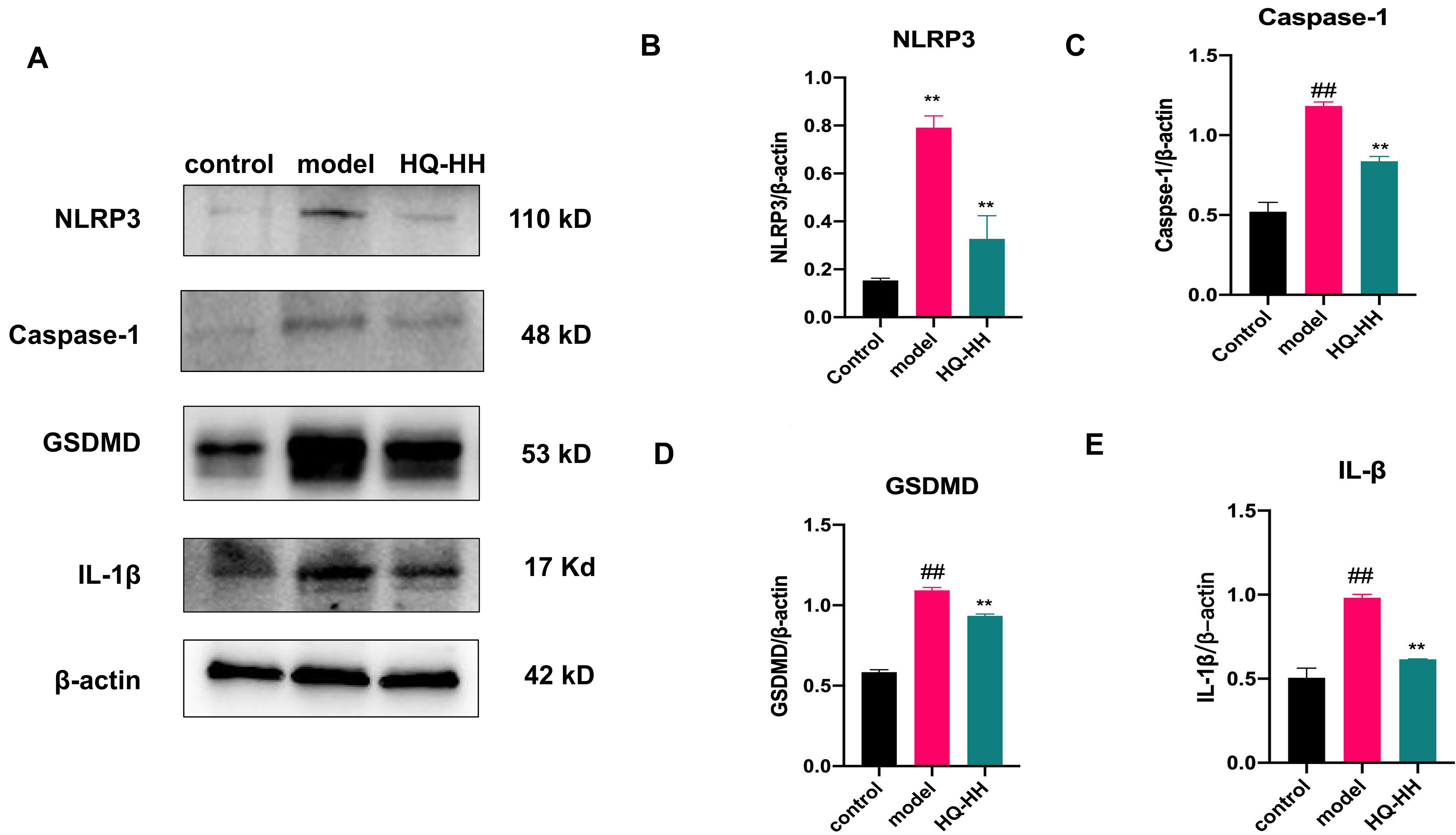
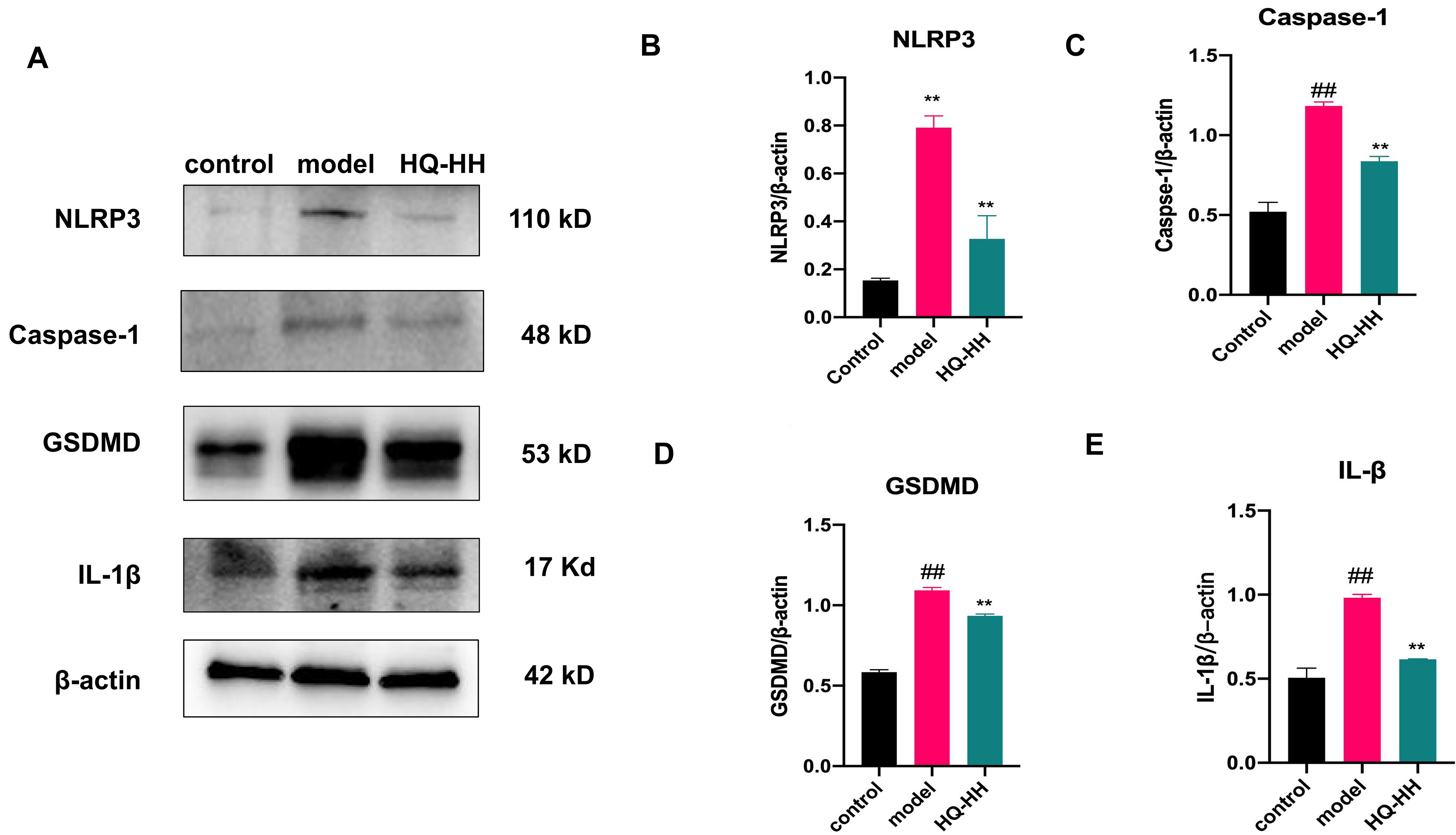 Fig. 14.
Fig. 14.Expression of NLRP3, Caspase-1, GSDMD and
IL-1
CVD is a common disease in people over 50 years of age. About 330 million people are affected by various cardiovascular diseases in China, of which CHD is one of the main causes of morbidity [2]. CHD is a multifactorial and complex disease. Secondary prevention of CHD is still the basic principle of western medicine for the treatment of coronary artery disease (CAD). Antiplatelet and statin drugs are the cornerstone of CAD treatment, but their adverse effects include gastrointestinal adverse effects, bleeding events, antiplatelet drug resistance, and liver function impairment and rhabdomyolysis. Most of these drugs are single-targeting, and most of these studies have focused on the single pathway related to the disease.
TCM have the advantages of multi-targets and multi-pathways. According to the TCM theory, the most common type of CHD is qi stagnation and blood deficiency, and Astragalus and Safflower are the representative drugs of relieving qi stagnation and blood deficiency, respectively. In addition, Astragalus is used to tonify qi and promote the operation of qi, while Safflower is representative of invigorating blood circulation and removing blood stasis. When these two herbal drugs are combined, one plays an eliminating role and the other plays a tonifying role; one treats deficiency and the other treats actual symptoms to achieve the ultimate therapeutic effect of tonifying qi and removing blood stasis. The studies have shown that the primary ingredients of Huangqi-Honghua combination and their antioxidant function alleviate cerebral infarction with qi deficit and blood stasis syndrome. The primary active components of Astragalus-Safflower are AS-IV and HSYA. When these two substances were combined, they significantly reduced the infarct volume in rats 24 hours after reperfusion by increasing the expression of nuclear factor erythroid-associated factor 2 (Nrf2) and the antioxidant activity, which reduced levels of malondialdehyde (MDA) and reactive oxygen species (ROS) [8]. However, the application and mechanism of action of ASHP in CHD have not been reported.
In this study, we used network pharmacology and molecular docking to analyze ASHP and explore the pharmacodynamic mechanism of the herb pair in the treatment of CHD. The mechanism of illness and therapeutic activity is explained by network pharmacology from the broad perspective of biological networks. It is a new field created to see how medications interact with illness based on system pharmacology and bioinformatics. In this study, we finally obtained 20 major compounds of Astragalus and 188 corresponding targets, and 34 major components of Safflower and 216 corresponding targets through screening. We construct a sub-network of the main core compounds and targets, the results showed that a single chemical component could have multiple corresponding targets, and at the same time, different chemical components could intersect on the same target, which reflects the characteristics of ASHP with multiple targets and rich effects [30, 31, 32]. The main components of ASHP are quercetin (PubChem CID: 5280343), kaempferol (PubChem CID: 5280863) and apigenin (PubChem CID: 5280443) as shown by network pharmacology. The study showed that by controlling the SIRT3/PARP-1 pathway, quercetin preserved the mitochondrial activity and helped prevent heart hypertrophy [33]. Quercetin has been shown to decrease the effects of oxidative stress, vascular rarefaction, cardiomyocyte hypertrophy, cardiac fibrosis and cardiac fat storage brought on by High-fat diet (HFD) [34]. Studies have shown that quercetin can promote the conversion of cholesterol to bile acids and cholesterol efflux, reduce aortic plaque area, oxidized low density lipoprotein (ox-LDL) accumulation and foam cell formation, thus achieving the anti-atherosclerotic effect [35, 36]. According to the research, kaempferol medication prevents ventricular hypertrophy, and this cardio-protection may be partly attributed to kaempferol’s suppression of the ASK1/MAPK signaling pathway and its control of oxidative stress [37]. A large number of studies have shown that apigenin can play an anti-atherosclerotic effect by reducing blood lipids [38], regulating cholesterol metabolism [39], anti-inflammatory [40], improving endothelial cell dysfunction [41] .
Serum medicinal chemistry has become one of the main methods for studying the
basis of pharmacodynamic substances of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), and
the identification of blood components through serum medicinal chemistry can be
regarded as the main material basis for the effect of traditional Chinese
medicine [42]. We used UHPLC-QE-MS to analyze the blood components of ASHP on rat
drug-containing serum, and after comparing the obtained blood compounds with the
database, two compounds were analyzed, namely, calycosin (PubChem CID: 5280448)
and isorhamnetin (PubChem CID: 5281654). These two compounds, both of which
belong to the flavonoid family, may be the most important key components of ASHP
for the treatment of CHD. Flavonoids have been shown to reduce CVD mortality risk
[43]. Calycosin are flavonoids derived from astragalus that have been shown to
have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. The study shows that calycosin
promoted autophagy to prevent AS and improve plaque stability. By promoting
autophagy, calycosin reduced inflammation, apoptosis, and foam cell formation. A
previous study showed that calycosin’s inhibitory effects on AS were
mechanistically achieved by improving autophagy through modification of the
KLF2-MLKL signaling pathway [44]. Isorhamnetin, a 3’-methoxyflavonol, has been
reported in existing studies for its anti-atherosclerotic effects. Isorhamnetin
prevented the growth of AS plaque in ApoE
The most significant top 10 hub genes were obtained using the degree algorithm
in the cytoHubba plugin, respectively IL6, AKT1, IL1B, TP53, VEGFA,
PTGS2, MMP9, CCL2, CXCL8, and EGF. In the cardiovascular system,
several cell types respond to inflammation, angiotensin II, oxidative stress, and
vascular injury by producing IL-6. It has long been demonstrated that high levels
of hsCRP and IL-6 indicate poor prognosis in both acute coronary ischemia and
chronic secondary prevention [48]. Studies have confirmed that tocilizumab (an
antibody to IL-6R) achieves an anti-atherosclerotic effect through endothelial
dysfunction [49]. AKT1 plays a crucial role in the progression and development of
AS as a crucial node in the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. The survival,
proliferation, and migration of macrophages are all influenced by the PI3K/Akt
pathway, which may have an effect on atherosclerosis progression [50]. MiR-155-5p
performs a variety of biological cellular tasks in a wide range of pathologies,
such as cardiovascular disease. By controlling AKT1, miR-155-5p inhibits the
growth, movement, and invasion of VSMCs and HUVECs [51]. IL-1
The metascape database was used to enrich GO and KEGG pathways for the common
targets of ASHP and CHD. The results showed that the main signaling pathways
included fluid shear stress and atherosclerosis, IL-17 signaling pathway, HIF-1
signaling pathway, NF-kappa B signaling pathway, and necroptosis. At the branches
and curves of the arterial tree, where the blood flow pattern is disrupted,
atherosclerosis develops preferentially. Studies have shown that shear stress in
atherosclerosis regulates endothelial cell function through the SR-B1-eNOS
signaling pathway [55]. By causing endothelial cell mechanotransduction and by
regulating the near-wall transport pathways involved in atherosclerosis, wall
shear stress (WSS) has an impact on coronary artery atherosclerosis [56].
IL-17/IL-17R signaling modality plays an important role in the pathogenesis of
CAD. Li et al. [57] reported that hyperglycemia may aggravate coronary
atherosclerosis by triggering TBK1-HIF-1-mediated IL-17/IL-10 signaling.
Proinflammatory cytokines, chemokines, and matrix metalloproteinases produced by
the IL-17 cytokine family play crucial roles in the development of inflammation.
Kido et al. [58] reported that HIF-1
Cell death plays an irreplaceable role in the growth and development of the organism and other physiological functions. Programmed cell death includes apoptosis, necroptosis, proptosis, ferroptosis, and autophagy. Non-programmed death mainly includes necrosis. Proptosis is a recently identified caspase-dependent programmed cell death, which occurs in response to inflammation. The classical proptosis pathway is a Caspase-1-dependent pathway. A recent study found that apoptosis, necroptosis, and scorch death were closely associated with each other and cross-regulated by each other [62].
Necrotrophic signals can lead to IL-1
We selected the core components in the ASHP and the key molecules of the
signaling pathway mediated by NLRP3 inflammasomes, and the results showed that
quercetin, kaempferol and apigenin can have good docking thermal energy with
NLRP3 and caspase-1. We then validated it using vivo experiments. The results of
the study showed that in the myocardial tissue of mice with CHD, inflammatory
cells infiltrate, nuclear contraction, and the above situation was significantly
improved after the intervention of ASHP. It was found in our study that the
expression levels of NLRP3, caspase-1, GSDMD and IL-1
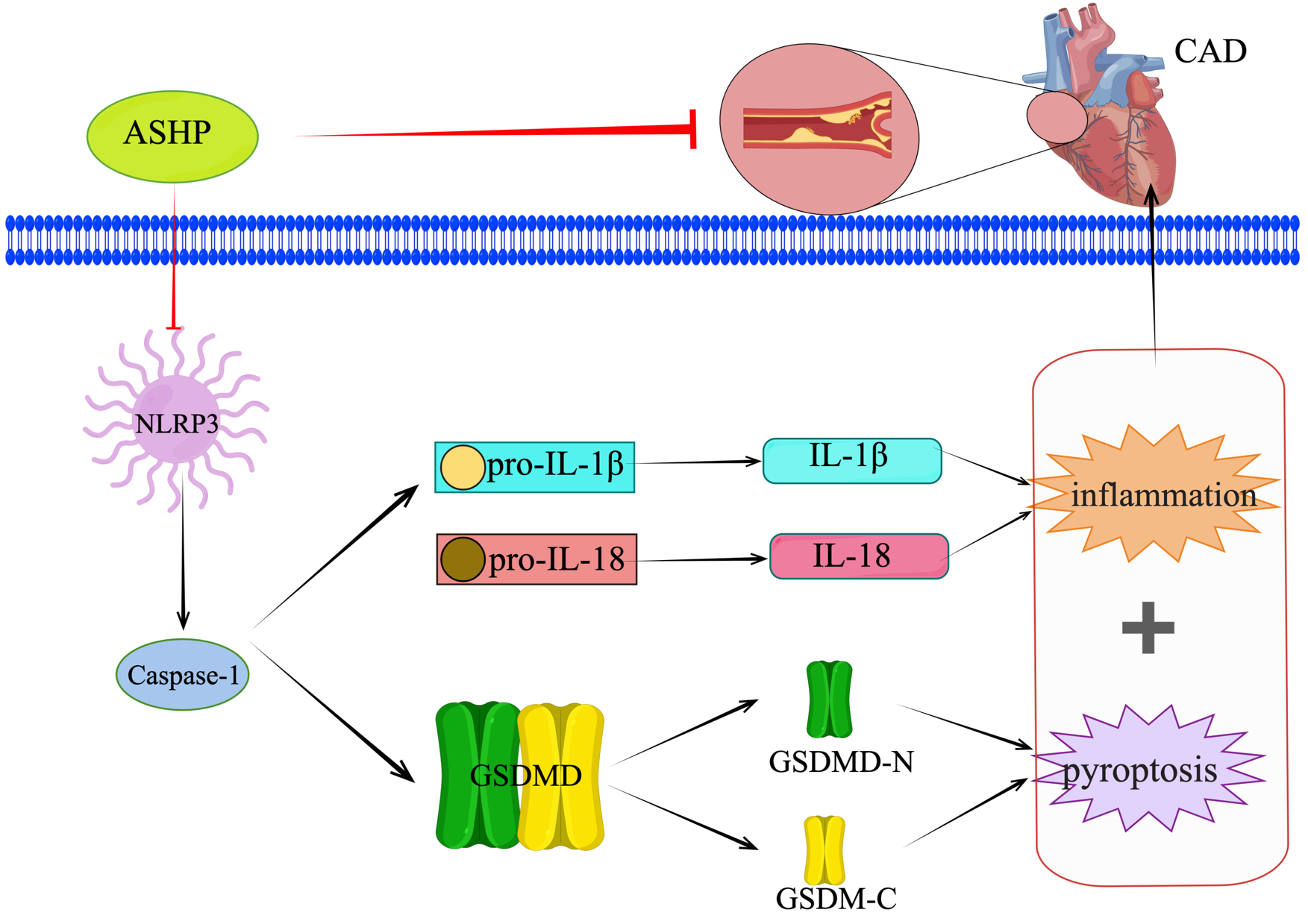
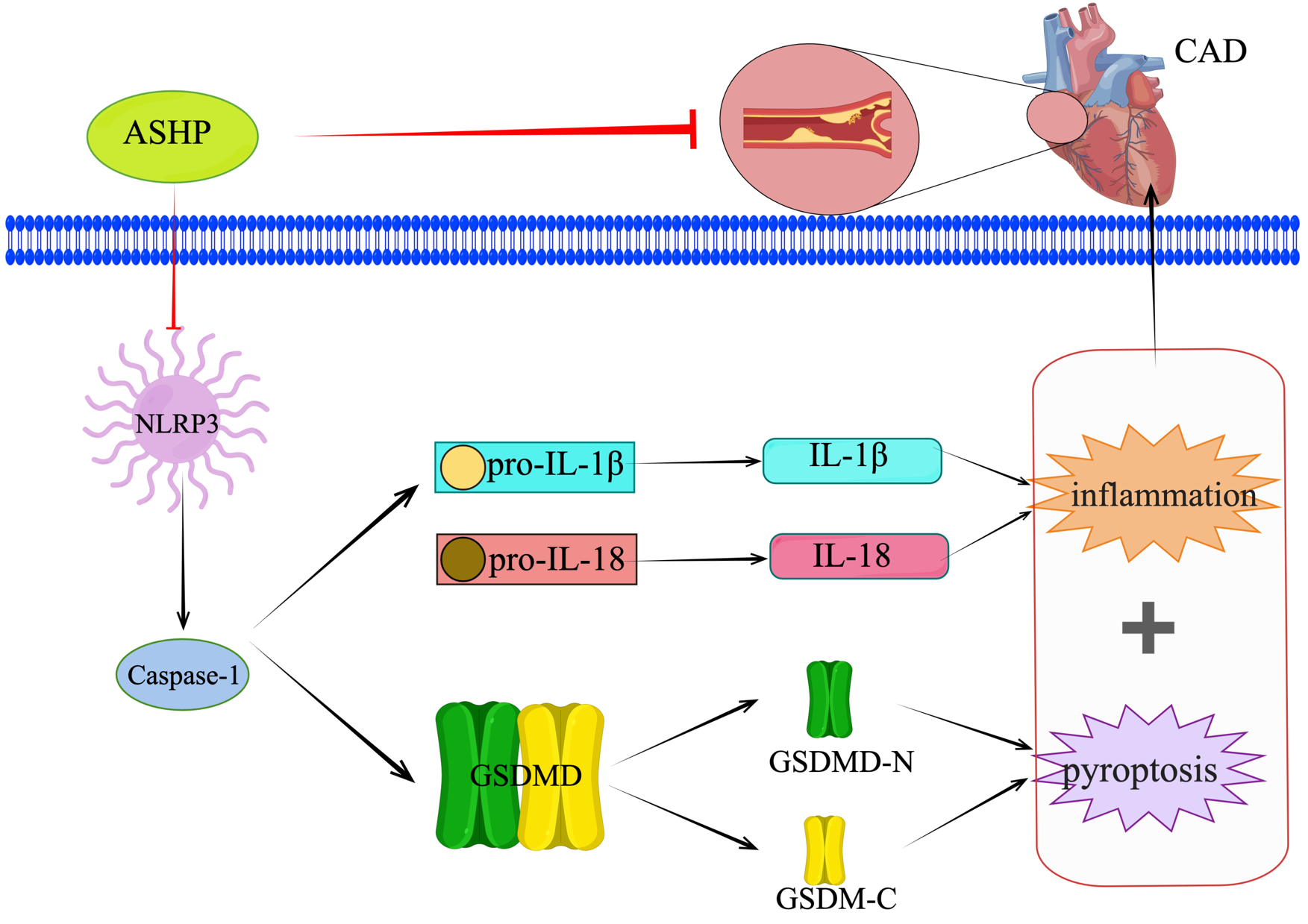 Fig. 15.
Fig. 15.ASHP treats CHD by inhibiting the NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis pathway.
Based on the multiple network components between ASHP and CHD, we identified the main potential active components and action targets of ASHP and the related pathways, which may provide new ideas for further in-depth exploration of its action mechanism, though further experimental verification is required in the later stage.
However, the study still has some limitations. First, in the database search of drug ingredients and disease targets, only one was selected. In future research, it can be considered to search multiple drug ingredient target databases and disease target databases to make the study more comprehensive. Secondly, only the conventional dose of ASHP was selected in this study, and we all know that TCM has a positive dose-effect relationship, so it is necessary to increase the number of different doses to compare. At the same time, the ASHP should be compared with Astragalus and Safflower. Finally, in terms of experimental verification, only some indicators of in vivo experiments were selected for verification, and cell experiments needed to be added to further explore the mechanism.
A network pharmacology approach and molecular docking were used to investigate the effective components and key targets of ASHP in treating CHD. Multiple target genes and pathways were involved in the action of ASHP against CHD. Quercetin, kaempferol, apigenin, calycosin and isorhamnetin were shown to be the main effective compounds for the treatment of CHD, possibly exerting anti-CHD effects by inhibiting the NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis pathway. This study provides a more comprehensive understanding of the active components and targets of action of ASHP, which is beneficial for further optimization of CHD medication in the future.
CHD, coronary heart disease; TCM, Traditional Chinese medicine; CVD, cardiovascular disease; CAD, coronary artery disease; NLRP3, NLR family pyrin domain containing 3; I/R, ischemia-reperfusion; OB, oral bioavailability; DL, drug-likeness; PPI, protein-protein interaction; BP, biological process; CC, cell composition; MF, molecular function; KEGG, Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes; HQ-HH, Huangqi-Honghua, Astragalus-Safflower; ASHP, Astragalus-Safflower herb pair; Ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography coupled with Q-Exactive MS/MS, UPLC-QE-MS/MS; ECs, endothelial cells; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; HUVECs, human umbilical vein endothelial cells; SRA, Scavenger receptor A; KLF4, krüppel-like factor 4; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; ox-LDL, oxidized low density lipoprotein; HFD, High-fat diet; AMI, acute myocardial infarction; SAP, stable angina pectoris; PBMCs, peripheral blood monocytes; SMCs, smooth muscle cells.
Data are all contained within the paper and supplementary materials.
YY is responsible for the drafting of the manuscript and the theoretical part of Traditional Chinese Medicine. HL is responsible for animal experiments and experimental data statistics. QM is responsible for the figures and grammar revision of the article. YY and HL have contributed equally to this work. Editorial modifications to the work were made by all writers. All the authors had read and approved the final manuscript. All authors have participated sufficiently in the work and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
The Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Hainan Medical University approved all animal experimentation techniques (Number: HYLL-2021-140). The animal experiment followed Guidelines for Ethical Review of the Welfare of Laboratory Animals in the People’s Republic of China [GB/T 35892-2018].
The authors thank Science Experiment Center and Clinical Skills Experimental Teaching Center of Hainan Medical University gave support to the lab research.
This study was supported by the Open Project Fund of Hainan Provincial Key Laboratory of Tropical Brain Research and Transformation (JCKF2021001); The Natural Science Foundation of Hainan Province Youth Project (No.821QN401); Hainan Province Health and Health Industry Research Project (No.21A200344); The First Affiliated Hospital of Hainan Medical University Youth Incubation Fund (No. HYYHYPY202006).
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Supplementary material associated with this article can be found, in the online version, at https://doi.org/10.31083/j.fbl2805094.
References
Publisher’s Note: IMR Press stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.