- Academic Editors
-
-
-
Background: Small vessel disease (SVD) widely exists in patients with
acute coronary syndrome. However, the plaque characteristic of SVD has not been
investigated. Methods: Optical coherence tomography (OCT) of culprit
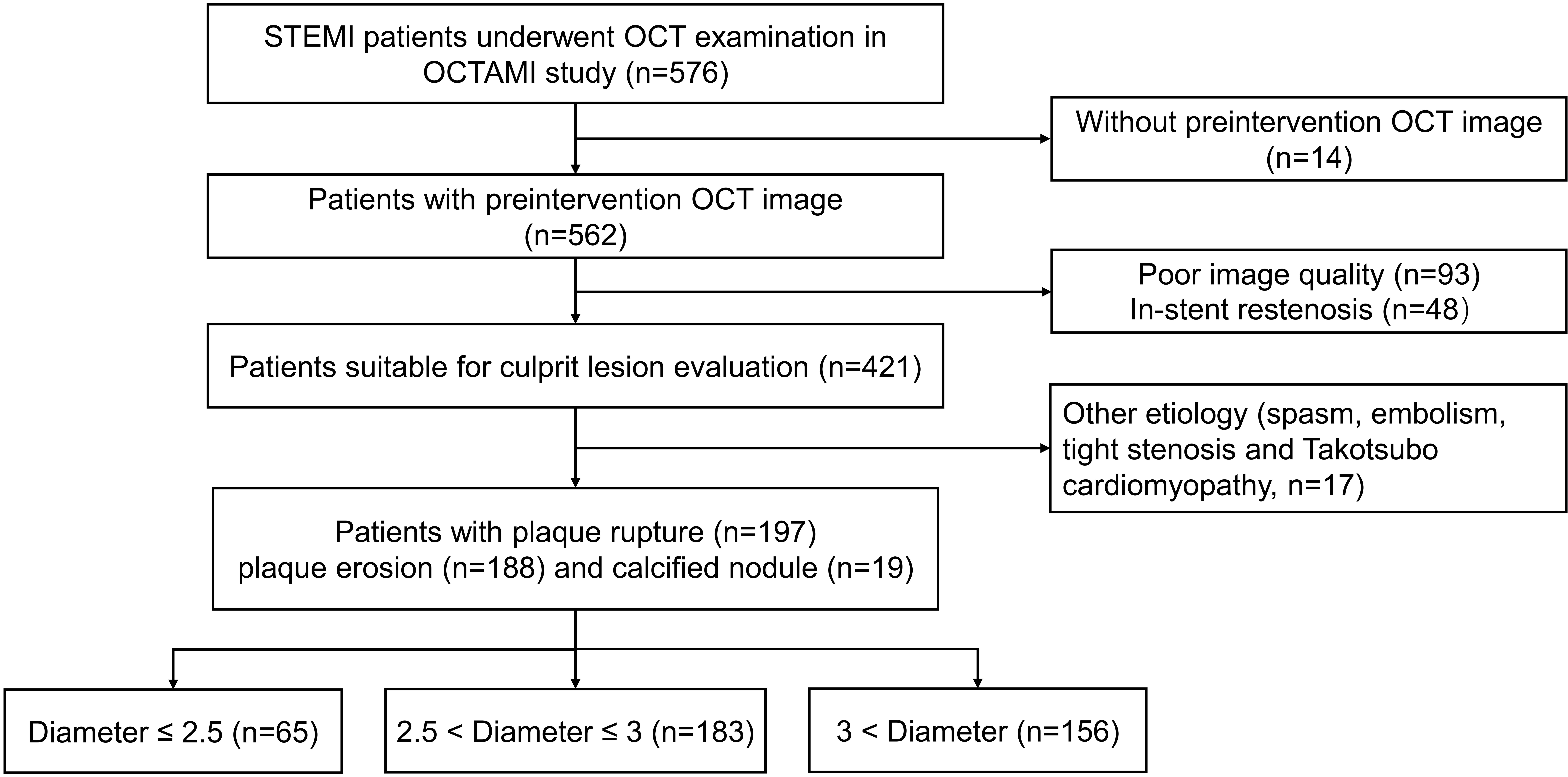
lesion was examined in 576 patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial
infarction (STEMI) and finally 404 patients with qualified images were analysed of plaque
phenotypes and microstructure. The cohort was divided into three groups according
to vessel diameters of culprit lesion which were measured by OCT. Major adverse
cardiac events (MACEs) were recorded of each patient and compared among patients
with different vessel diameters and plaque phenotypes. Results: Gender,
age and body mass index (BMI) were significantly different among patients with
different diameters of culprit vessels (98.4% vs. 85.7% vs.71.4%, p