Academic Editor: Daphne Merkus
Background: Neuregulin-1 (NRG-1) is a stress-mediated transmembrane
growth factor. Reduced myocardial damage and higher NRG-1 levels upon treatment
with remote ischemic conditioning (RIC) has been described in rats. However, the
role of NRG-1 in patients with acute myocardial infarction (MI) is unknown. Thus,
we conducted a post hoc analysis of a randomized controlled trial that tested RIC
in patients with MI scheduled for primary percutaneous coronary intervention
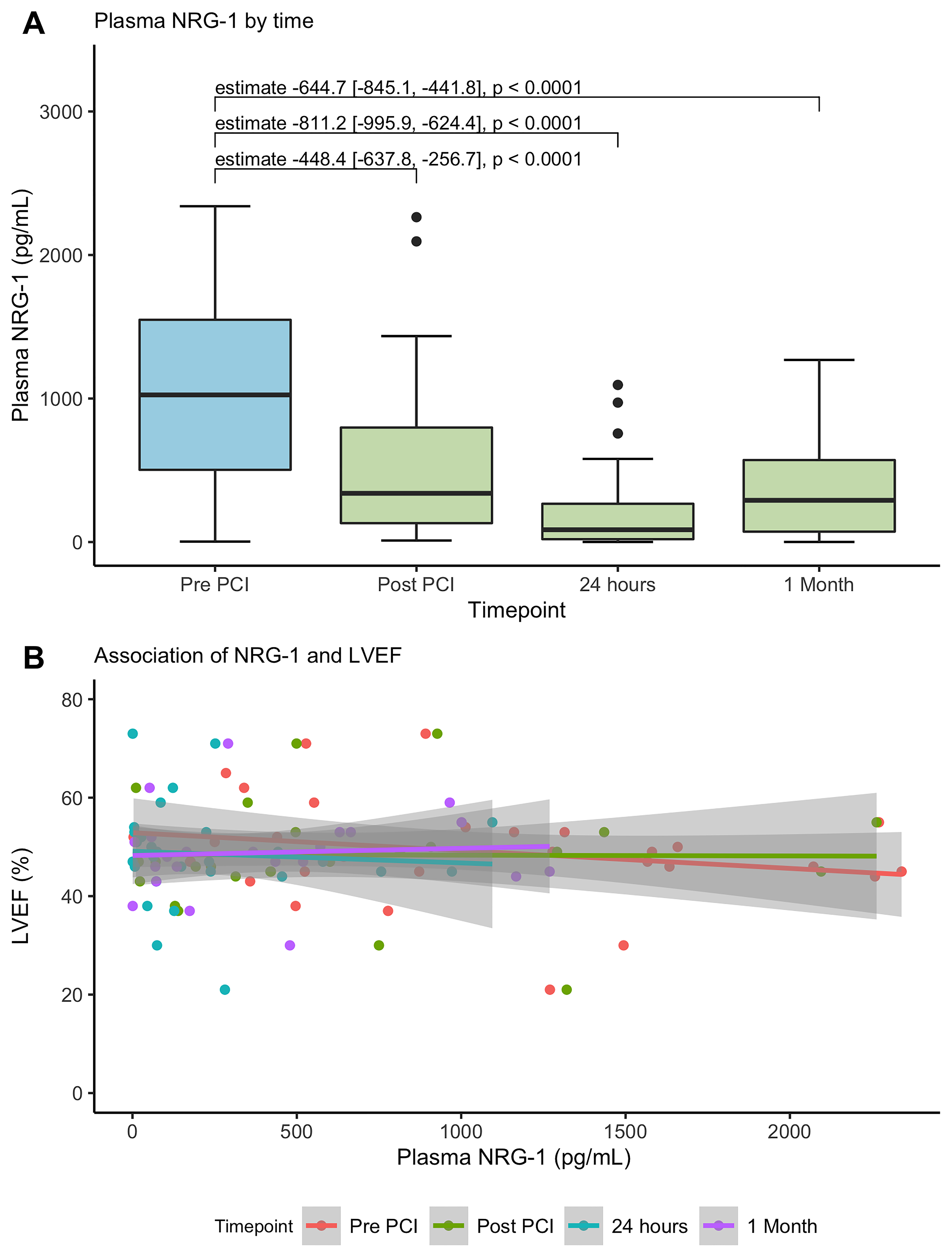
(PCI). Methods: Blood was drawn from 30 patients before RIC/PCI, within
1 hour, 4 days and 1 month later. Median left ventricular ejection fraction
(LVEF) in the overall study population following MI was 48.5%. Results:
NRG-1 plasma levels decreased significantly following PCI/RIC and remained
decreased up to 1 month following MI (p