1 School of Life Science, Northwest Normal University, 730070 Lanzhou, Gansu, China
2 Beijing Yanqing Market Supervision Inspection and Testing Monitoring Center, 102100 Beijing, China
3 Rural Development Academy, Northwest Normal University, 730070 Lanzhou, Gansu, China
4 Beijing Yanqing Center for Diseases Prevention and Control, 102100 Beijing, China
Abstract
Objective: An extract of Xanthoceras sorbifolium Bunge (XSB) oil called
nervonic acid (NA) was studied for its potential to ameliorate oxidative stress
and inflammation in people living with Parkinson’s disease (PD).
Recrystallization column chromatography was performed to isolate NA from the XSB
oil. Twenty-five C57BL/6 mice (8–10 weeks old) were randomly assigned to one of
five groups (control, model, low, medium, and high dosage). Methodology:
Except for the control group, all of the experimental animals received an
intraperitoneal injection of 1-Methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP).
The next phase was administering varied doses of NA produced from XSB oil to
mice. Control, model, low-dose, medium-dose, and high-dose groups were created at
random from SH-SY5Y and PC-12 cell cultures. Our study’s control groups exhibited
typical normative conduct. Research: Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was
used to examine oxidative stress (OS) and inflammatory factors (IFs) in cells. By the time recrystallization column chromatography had finished its
analysis, the concentration of NA had increased by a factor of roughly 26.
Results: The model and high-dose groups showed similar levels of
apoptosis in behavior (p
Keywords
- Parkinson's disease
- Xanthoceras sorbifolium Bunge
- nervonic acid
- inflammatory factors
- oxidative stress
Bradykinesia, rigidity, postural gait instability, and resting (or non-resting) tremor are some of the most notable clinical signs of Parkinson’s disease [1]. Although difficulties with movement are the most noticeable sign of Parkinson’s disease (PD), the sickness may also damage other sections of the brain, making it difficult for patients to pay attention, retain details, or even do the most basic of activities [2]. The sole choice for patients is long-term, ongoing medication to lower the severity of their symptoms since there is presently no therapy that can reverse the effects of PD in clinical settings [3]. Scientists need to develop a fresh means of diagnosing PD as soon as possible, and a therapy for the condition, so that people with PD may live with less anxiety [4].
Nervenic acid, often known as NA, is a substance implicated in the development and progression of several neurological disorders. Validation of NA’s effectiveness in treating PD mice and protecting them from dyskinesia is encouraging for the future of NA as a therapy option for illnesses of the nervous system [5]. The most dependable supply of NA, shark brains, are now illegal to harvest, making it harder for people to synthesize their own NA. Therefore, it is quite concerning that the synthesis of NA for therapeutic purposes is on the rise [6].
The woody oil plant species Xanthoceras sorbifolium Bunge (XSB) is endemic to China but is only found in a small number of provinces and autonomous regions. Included in this group are provinces like Henan and Ningxia and Gansu and the Northeast and Liaoning and Inner Mongolia [7]. Using a cold pressing technique, XSB may provide edible oil rich in unsaturated fatty acids (FAs) (like oleic acid, linoleic acid, NA, etc.). The risk of developing cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and other health problems is reduced in those who regularly drink XSB oil, according to studies [8]. XSB may be refined into edible oil and has the potential to be utilized as a raw material in many different industries. It is a key ingredient in many modern products, including lubricants, paints, plasticizers, and even cosmetics [9]. In recent years, China has seen a consistent increase in the area planted with XSB and, therefore, in the yield per acre. If we can devise a method that is both trustworthy and efficient, we will not only be able to effectively solve the problem of a large demand and a small supply of NA that exists today, but we will also be able to give patients new hope and a guarantee for the future treatment of patients suffering from a wide range of diseases affecting the nervous system [10].
Therefore, the purpose of this study is to provide a benchmark for the future acquisition of NA and the treatment of PD by extracting NA from XSB oil and evaluating its effect on PD. To determine whether NA derived from XSB has a beneficial impact on PD, this study aims to confirm this. The current clinical limitations of PD therapy will be alleviated, treatment efficacy will increase, and patients’ quality of life will improve.
He et al. [11], argue that “Oriental olive oil” is a particularly specific kind of oil that is pressed from the seeds of the oily woody shrub amellia oleifera. The chemical composition of olive oil from the Far East is not dissimilar to that of olive oil from Europe [12]. Camellia oil’s long-term usage is associated with lower chances of hypertension, liver, heart, and brain illnesses. Camellia oil has shown promise as a possible immune system booster. It has been investigated as a possible therapeutic for skin issues and even as a counter to the effects of aging on the skin [13]. The production process not only makes it very resistant to heat, but also gives it powerful antioxidant properties. This suggests it has commercial potential as an oil in all-natural skin care products. Camellia shells are a rich source of the basic ingredients used to produce chemicals including furfural, xylitol, tannin, and charcoal, which remove fluoride from water [14].
Ikram et al. [15], described that a fatty acid called N-(24)-hydroxy-N-(9)-nervonic acid has been identified. Because both are monounsaturated fatty acids, there is a structural resemblance to lignoceric acid (24:0). Aryal et al. [16], presented that the chemical is also known as selacholeic acid and cis-15-tetracosenoic acid. These two designations refer to the same underlying idea. The Latin term nervus, from which we get the English word “nerve”, really means “sinew” in Latin. Homem et al. [17], argue that it occurs spontaneously as a consequence of the elongation of oleic acid to 18:19. Erucic acid, a chemical, might be considered a direct precursor. Neronic acid is abundant in the white matter of animal brains and in peripheral nervous tissue, as well as in the myelin sheath that protects nerve fibers. Jayaraj et al. [18], research that Cerebrosides are a kind of glycosphingolipid that are abundant in the nervous system. This includes the brain, spinal cord, and other neural tissues. They are thought to account for around 40% of the fatty acids found in sphingolipids [19].
According to Hayes D et al. [20], Walnuts (Juglans regia), a tree species prized for its nuts and its woody oil, play an important role in Chinese agriculture. When it comes to both planted area and total yield, the country ranks first in the world. Due to the high oil content, walnuts are sometimes referred to as “oil depot on the tree”. Walnut oil, because of its high concentration of bioactive components, is an excellent dietary supplement and health care product for many different reasons, including its capacity to enhance the appearance of the skin and the body’s overall health and fitness [21]. In recent decades, the economic worth of walnuts has soared due in large part to the growing demand for new uses for walnut byproducts. The pomace, husk, and oil cakes from walnut trees may be processed into a variety of valuable components. The by-products of the walnut tree may be used to create activated carbon and color [22].
Chen et al. [8], considered that paeonia suffruticosa, popularly known as “Celestial Beauty, the king of flowers”, is a species of flower that is native to the area of China between the Yangtze and Yellow Rivers and is quickly increasing in population there. Similar to flaxseed oil, it contains the linolenic acid that has been shown to have positive benefits on cardiovascular health, brain and nerve function, and even cancer and inflammation. Peony seeds provide abundant and high-quality oil when crushed. Ingredients in peony seed oil may have used in medicine, cosmetics, and the food sector [23].
This research was conducted between October 2021 and February 2022 at Beijing Yanqing Market Supervision Inspection and Testing Monitoring Center (Beijing).
XSB, ordered from Lingbao Jiulin Garden Engineering Co., Ltd. (Sanmenxia, Hebei, China), was squeezed by a hydraulic oil press with a pressing pressure of 10–55 MPa. With this method, the oil yield of XSB seeds can reach about 25%.
Anhydrous sodium sulfate (Yuanye Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Shanghai) was added to XSB oil, which was placed for 24 hours and then filtered to obtain dry XSB oil. Then 40 g of XSB oil and 250 mL of sodium hydroxide-ethanol solution (72068, Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) were stirred continuously at 100 ℃ for 2 h. After cooling, petroleum ether (cas693-65-2, Yunbaihui Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Jinan, China) was added to extract unsaponifiable and the petroleum ether layer was discarded. Then sodium chloride solution (72068, Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) was utilized to adjust the pH value of the FA salt layer to 2–3, followed by standing, aqueous phase removal, washing with water till neutrality, and addition of anhydrous sodium sulfate (1614807, Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) for drying. Finally, XSB oil mixed fatty acid was prepared by recovery of petroleum ether via rotary evaporation at 45 ℃.
Using a synthetic analogue of meperidine may cause parkinsonism over time. Substantia nigra neurons were selectively harmed by the neurotoxin. Both the neurotoxicity caused by 1-Methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) and the transport of N-methyl-4-phenylpyridine was mediated by the mitochondria.
20.0 g XSB FA solution was immersed in 85% ethanol according to the ratio of 1:9 g/mL and refrigerated at 5 ℃ for 2 h for 4 times of repeated crystallization to obtain recrystallized mixed FAs, which were then placed in the upper layer of silica gel chromatography column and eluted according to the ratio of petroleum ether to ethyl acetate of 9:1 to obtain fractions for vacuum decompression, and the final sample was NA.
Twenty-five 8–10 week old C57BL/6 mice (Kexing Zhongwei Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China) were randomly split into 5 groups: The PD mouse model was developed by giving MPTP intraperitoneally once daily to all mice for 7 days (excluding the control group). Three groups of animals were administered either 20 mg/kg, 40 mg/kg, or 60 mg/kg of XSB oil-extracted NA (gavage once a day for 10 days), while two control groups received an equal amount of normal saline.
The collected mouse is then placed on a clean towel or other stable surface. The interscapular region is held still with the tentacles of the thumbs and fingers before needles are inserted. In this instance, three milliliters is just right. Subcutaneous (under the skin) injections are often administered in the genital area.
Pole-climbing test: The mouse was put on a rotarod, which was spun at a speed of 5 rpm/min–20 rpm/min for 180 seconds, and the time the mouse spent on the rotarod (latency) was recorded. The rotarod’s diameter was 9 mm, and its length was 1 m. The wooden pole was fastened vertically in the cage. Every half an hour, we ran the experiment again to get an average. In an open-field test, one mouse was given five minutes to explore a box that measured 50 by 50 by 40 centimeters and was outfitted with a camera to capture its every move. The number of times the mouse groomed itself and the number of times it stood up (meaning its front two legs left the floor or climbed a wall) were both noted. After each experiment, 75% alcohol was used to disinfect the testing area.
When severe behavioral issues are the sole source of suffering, it may be compassionate to put an animal to sleep. This is what is meant by the term “behavioral euthanasia”. Animal health and annoying behaviors like leash pulling and guest jumping are generally disregarded.
After the behavioral tests were finished, the mice’s throats were slit while they were still under anesthetic. Each group’s substantia nigra tissues were dehydrated with gradient ethanol, paraffin-embedded, and sectioned at 4 m before undergoing standard dewaxing to water and Terminal Deoxynucleotidyl Transferase mediated dUTP Nick-End Labeling (TUNEL) staining (ab66110, Abcam, Cambridge, UK). Apoptotic neurons were represented by red fluorescence in the visual field.
The American Type Culture Collection (ATCC) provided both the SH-SY5Y and PC-12
cell lines, and they have completed short tandem repeat (STR) and mycoplasma
testing, which confirmed that these cells are free of contamination. They were
maintained in a 37 °C, 5% CO
A control group, a model group, and groups given low, medium, and high doses were created from the collected cells. All groups (excluding the control group) used 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP+) to establish PD cell models. Both the control and experimental groups were first administered saline before the quantities of NA were varied between 5 and 20 mol/L.
The SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cell line is often used as an in vitro model in studies of Parkinson’s disease. A bone marrow biopsy from a 4-year-old with metastatic neuroblastoma was used to establish the first version of this cell line. It has undergone three further cycles of clonal selection since then. The SK-N-SH cell line was the seed from which these cells sprang.
40 cycles of denaturation (94 degrees Celsius for 30 seconds), annealing (94 degrees Celsius for 5 seconds), and extension were performed on RNA that had been extracted using the Trizol method (60 degrees Celsius for 30 seconds). As a consequence of this procedure, cDNA-based constructs were created. Two-Cycle Time (2-CT) analysis primers (Table 1) were developed and synthesized by Thermo Fisher Scientific (Shanghai, China).
| Genes | F (5′-3′) | R (5′-3′) |
| IL-6 | GATGTTGCTGCTTCACTTC | CCTTGTTGGCTTATGTTCTG |
| IL-8 | GGGCTGCATCTAAAGTAAATGG | CAGAACACTGCTGTAGAAGGTA |
| TNF- |
CTCTTCTCATTCCTGCTTG | CTCCACTTGGTGGTTTGCT |
| SOD | CACAACTGGTTCACCGCTTG | GCCCAACCAGACAGAGAATGA |
| GSH-Px | CGTGCAATCAGTTCGGACC | CCAGGCATCTCCCTTCCATTC |
| CTAAGGCCAACCGTGAAAAG | ACCAGAGGCATACAGGGACA |
IL-6, interleukin-6; IL-8, interleukin-8; TNF-
Cells were washed three times, and the final concentration was adjusted to 1
Cells were trypsin digested and resuspended in 100 um of binding buffer before being stained with 5 uL of Annexin V-FLTC (ab108194, Abcam, Cambridge, UK) and 5 uL of PI (ab14083, Cambridge, UK) for 15 minutes at RT in the dark. One way that fluorescence was measured was using a flow cytometer (CytoFLEX S, Beckman Coulter, Brea, CA, USA).
Total protein was extracted from lysed cells using Radio-immunoprecipitation assay (RIPA) (89901, Thermo Fisher, Shanghai, China). Following that, the proteins were transferred to a polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) membrane using sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) (12% gel). Nonfat dried milk (5%), used to seal the membrane, was mixed with water and let to sit for 2 hours before being poured into a container and chilled to 4 degrees Celsius. Abcam, an American business, was where we ultimately purchased the antibody (ab52939, ab278716, ab211061, ab32537, ab17942, ab8227, 1:1000, Abcam, Cambridge, UK). We utilized an enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL) luminescence reagent to process the film in the darkroom.
Statistical analysis was performed in SPSS (v22.0, IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA), and the findings were shown as (mean standard deviation). We used a mixed-model analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by a Bonferroni-Seltzer test to determine the statistical significance between the groups. If the p-value is less than 0.05, then there is a statistically significant difference between the groups.
The high-dose group showed obviously improved behavior test results than the
model group, with a lower neuronal apoptosis rate (p
Compared with the original Wenguan fruit oil, the NA content was greatly improved after low-temperature recrystallization, and the content of linoleic acid is reduced (Table 2).
| Before and after extraction | Types of fatty acids | Retention time (min) | Content (%) |
| Before extraction | Linoleic acid | 17.534 | 45.14 |
| Oleic acid | 17.036 | 28.22 | |
| Erucic acid | 22.841 | 8.36 | |
| Eicosaenoic acid | 19.894 | 6.28 | |
| Palmitic acid | 14.362 | 5.64 | |
| nervonic acid (NA) | 26.354 | 2.58 | |
| Stearic acid | 16.357 | 2.03 | |
| Tetracosanoic Acid | 19.228 | 1.04 | |
| Others | - | 0.89 | |
| After extraction | Linoleic acid | 17.962 | 5.98 |
| Oleic acid | 17.061 | 4.15 | |
| Erucic acid | 22.686 | 8.33 | |
| Eicosaenoic acid | 19.542 | 2.42 | |
| Palmitic acid | 14.811 | 7.54 | |
| NA | 26.238 | 66.97 | |
| Stearic acid | 16.706 | 2.04 | |
| Tetracosanoic Acid | 25.171 | 1.95 | |
| Others | - | 0.62 |
Early on, we found that the latency times and durations of the rats’ spontaneous
movements were much shorter in the model group compared to the control group
(p
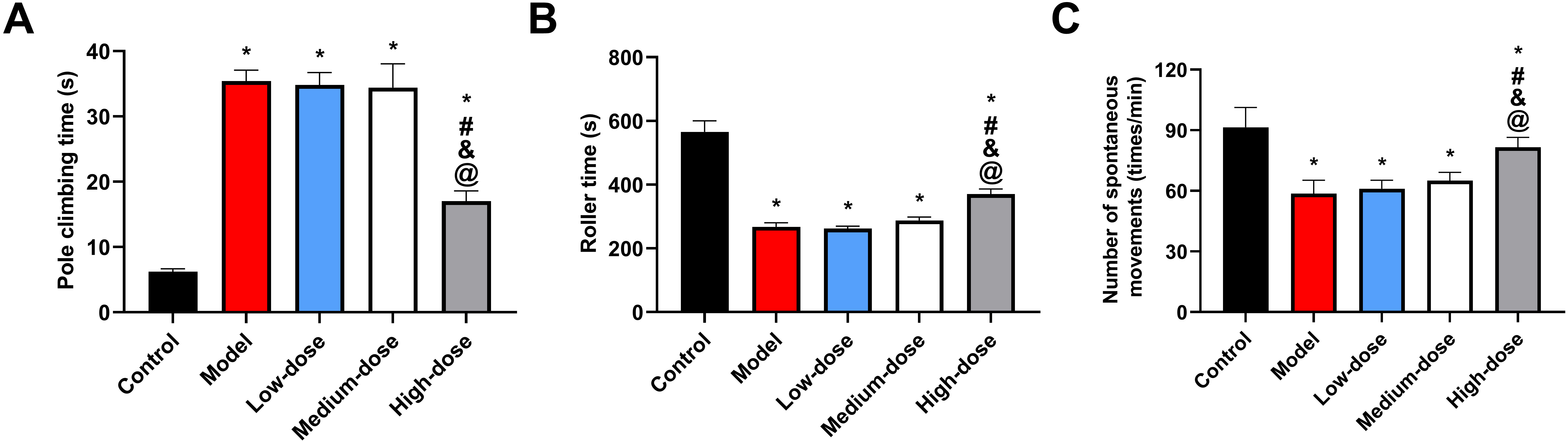 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.Alterations in behavioral disorders in a mouse model. (A)
Comparison of pole climbing time. (B) Comparison of latency. (C) Comparison of
the number of spontaneous movements. *: Compared with the control group, there is
a difference
Neuronal apoptosis was observed to be significantly reduced in the low-,
medium-, and high-dose groups relative to the control group. Yet, in contrast to
the control group, the model group was shown to have statistically significant
higher levels of neuronal apoptosis (p
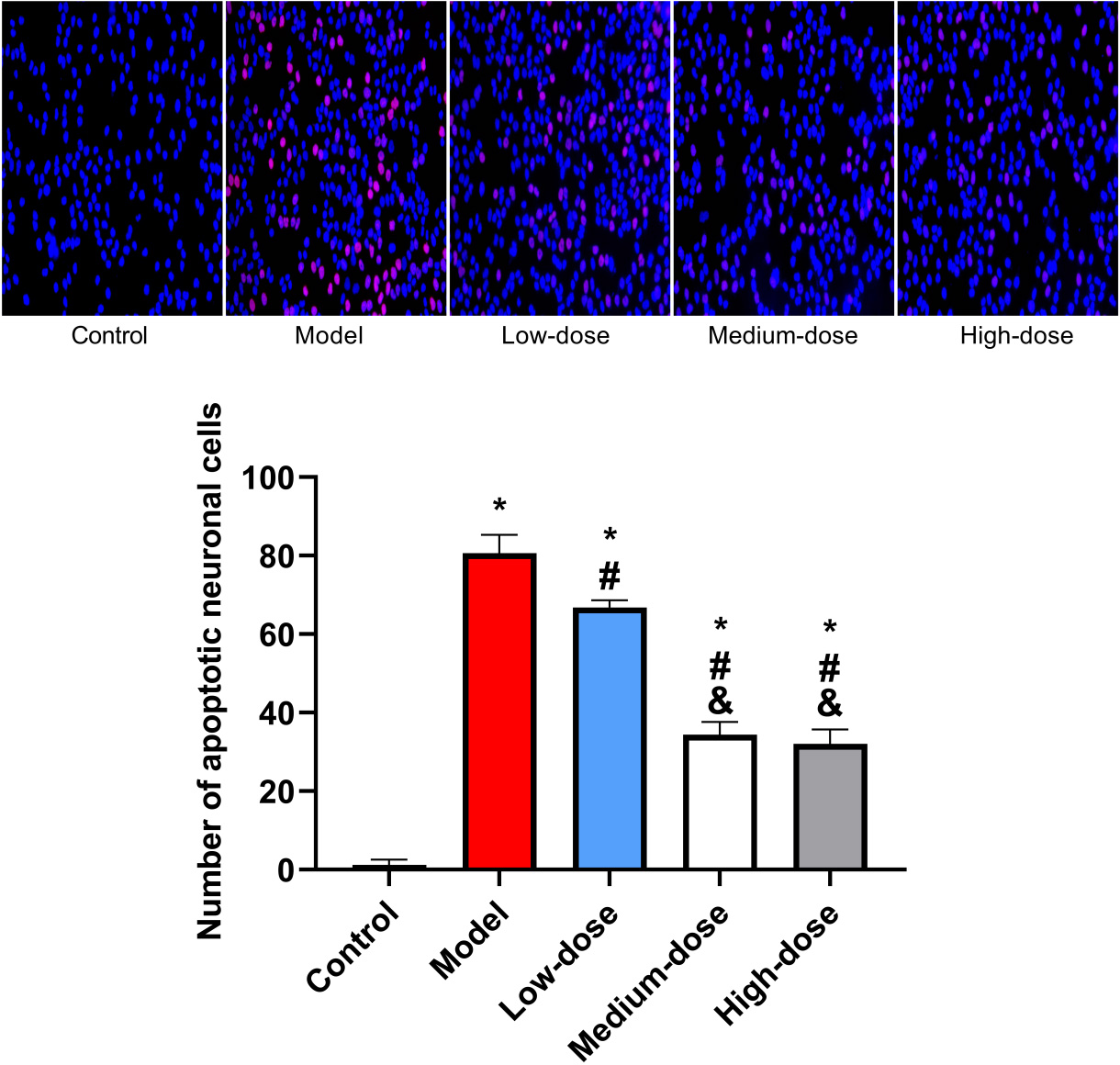 Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.Apoptosis of mouse neurons by TUNEL staining. *: Compared with
the control group, there is a difference
The model group had substantially higher levels of interleukin-6 (IL-6),
interleukin-8 (IL-8), and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-
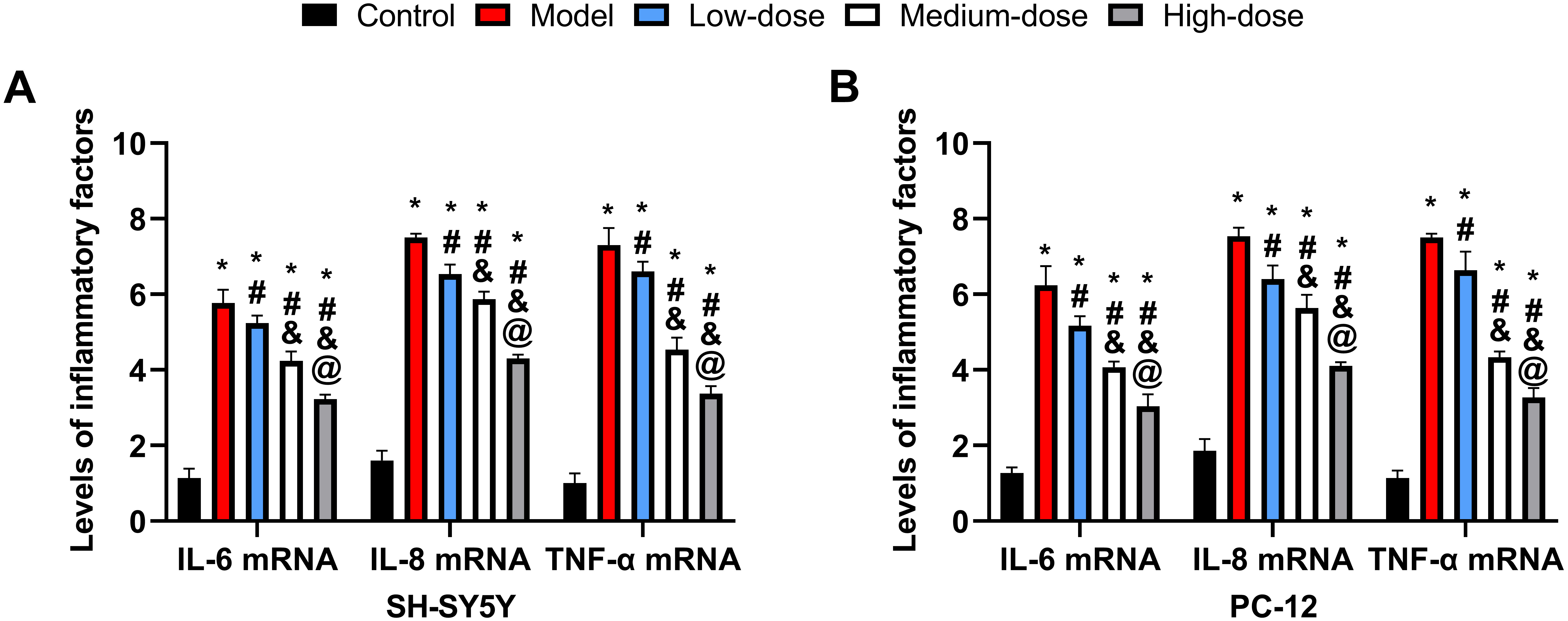 Fig. 3.
Fig. 3.Cellular inflammatory reaction. (A) Comparison of inflammatory
factor levels in SH-5Y5Y. (B) Comparison of inflammatory factor levels in PC-12.
*: Compared with the control group, there is a difference
SOD and GSH-Px mRNA levels were significantly reduced in the
model group compared to the other groups (p
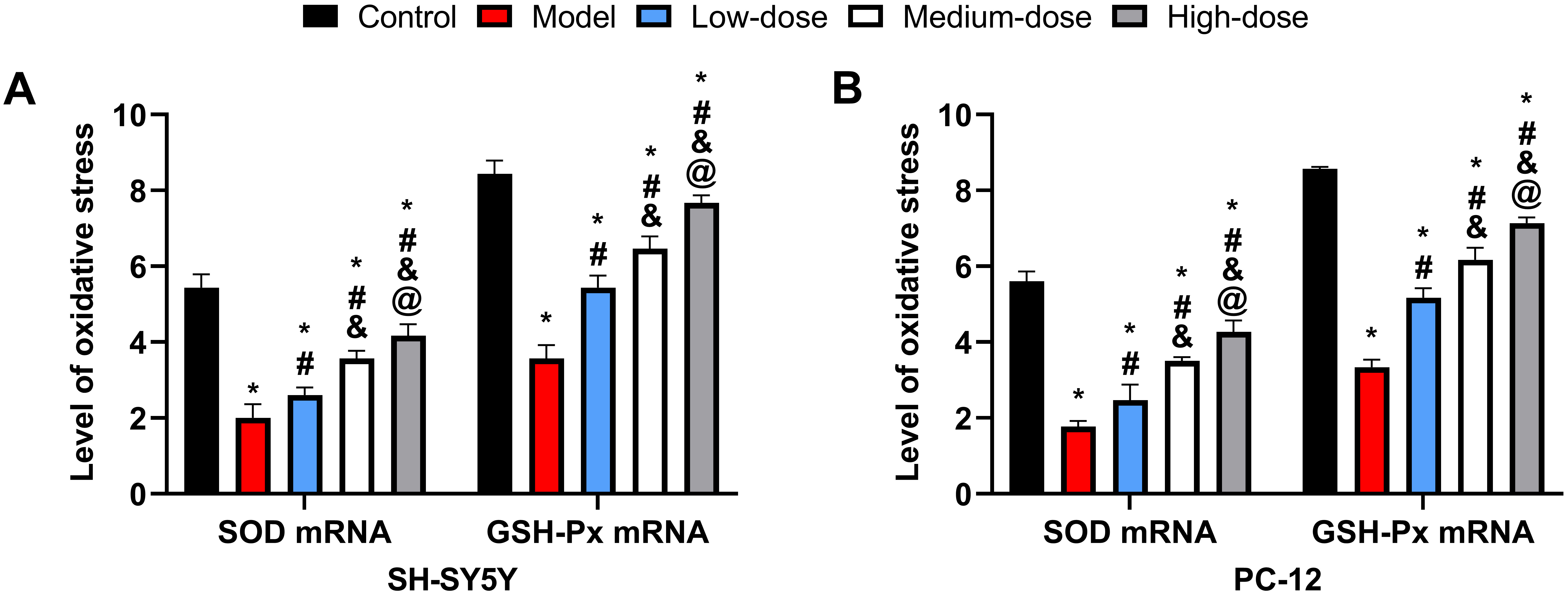 Fig. 4.
Fig. 4.Cellular oxidative stress response. (A) Comparison of oxidative
stress levels in SH-5Y5Y. (B) Comparison of oxidative stress levels in PC-12. *:
Compared with the control group, there is a difference
There was a statistically significant difference (p
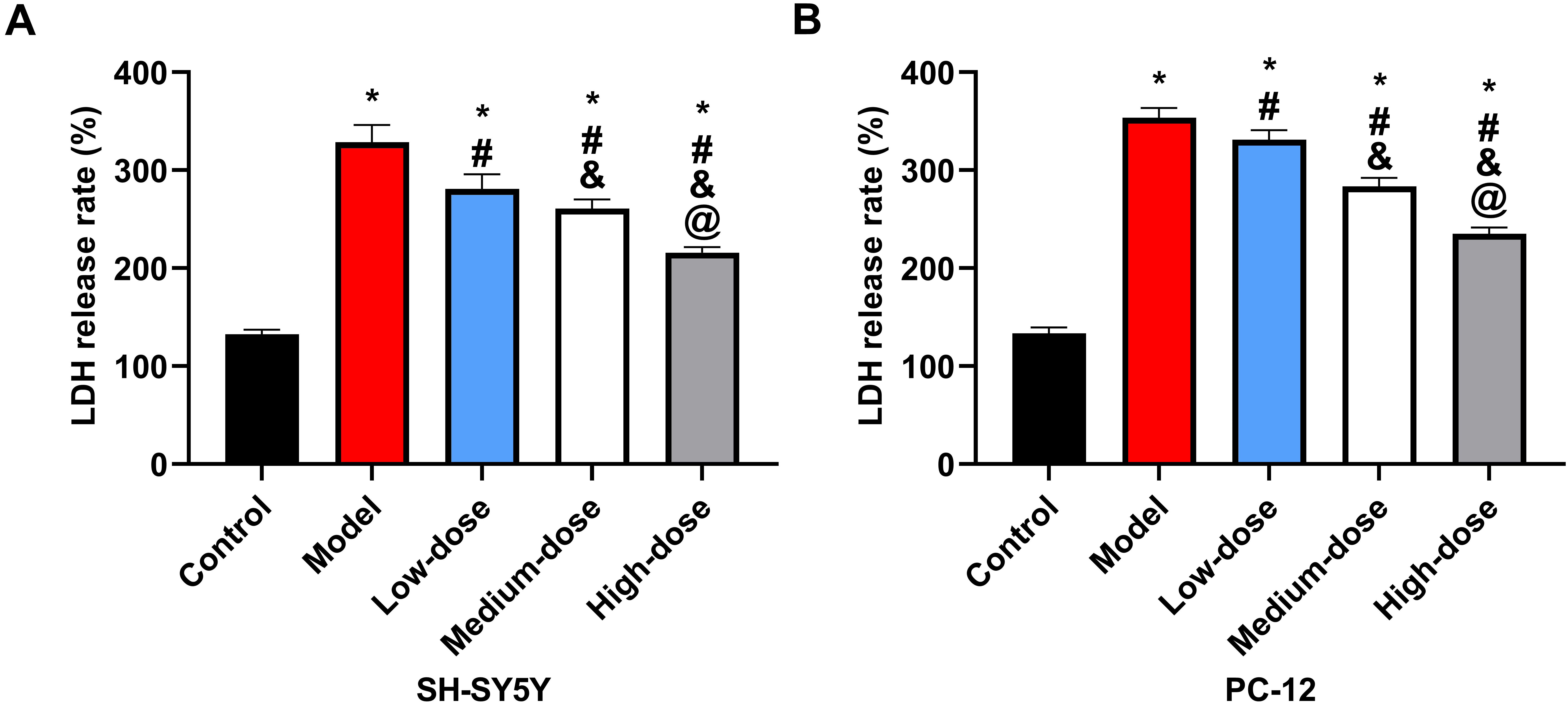 Fig. 5.
Fig. 5.LDH release rate of cells. (A) Comparison of LDH release rate
in SH-5Y5Y. (B) Comparison of LDH release rate in PC-12. *: Compared with the
control group, there is a difference
Among the six groups, the control group had the lowest apoptosis rate
(p
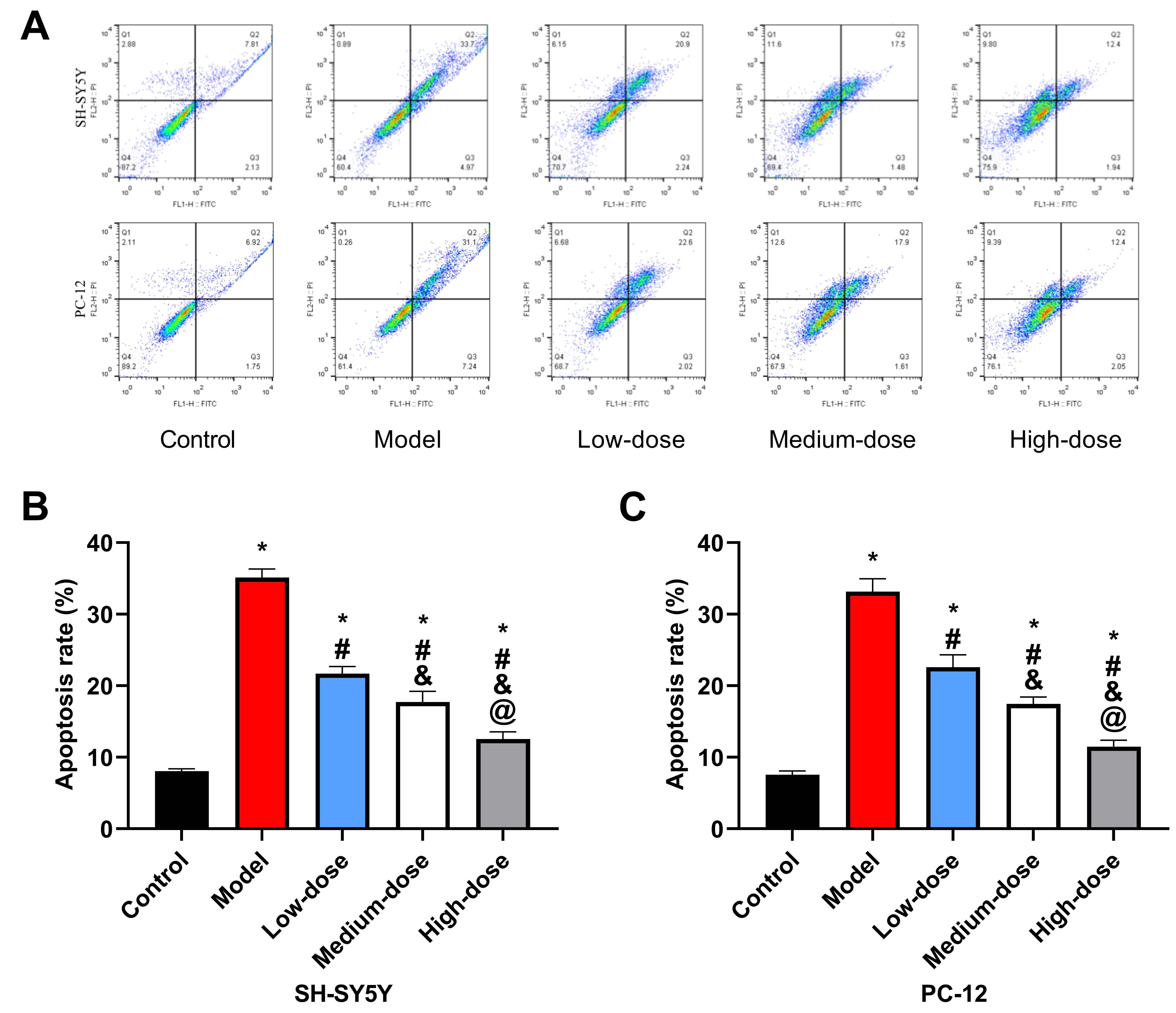 Fig. 6.
Fig. 6.Apoptosis rate detected by flow cytometry. (A) Results of flow
cytometry. (B) Comparison of apoptosis rate in SH-5Y5Y. (C) Comparison of
apoptosis rate in PC-12. *: Compared with the control group, there is a
difference
Protein levels of Ras, MEK/p-MEK, and ERK/p-ERK were all found
to be lower in the model group (p
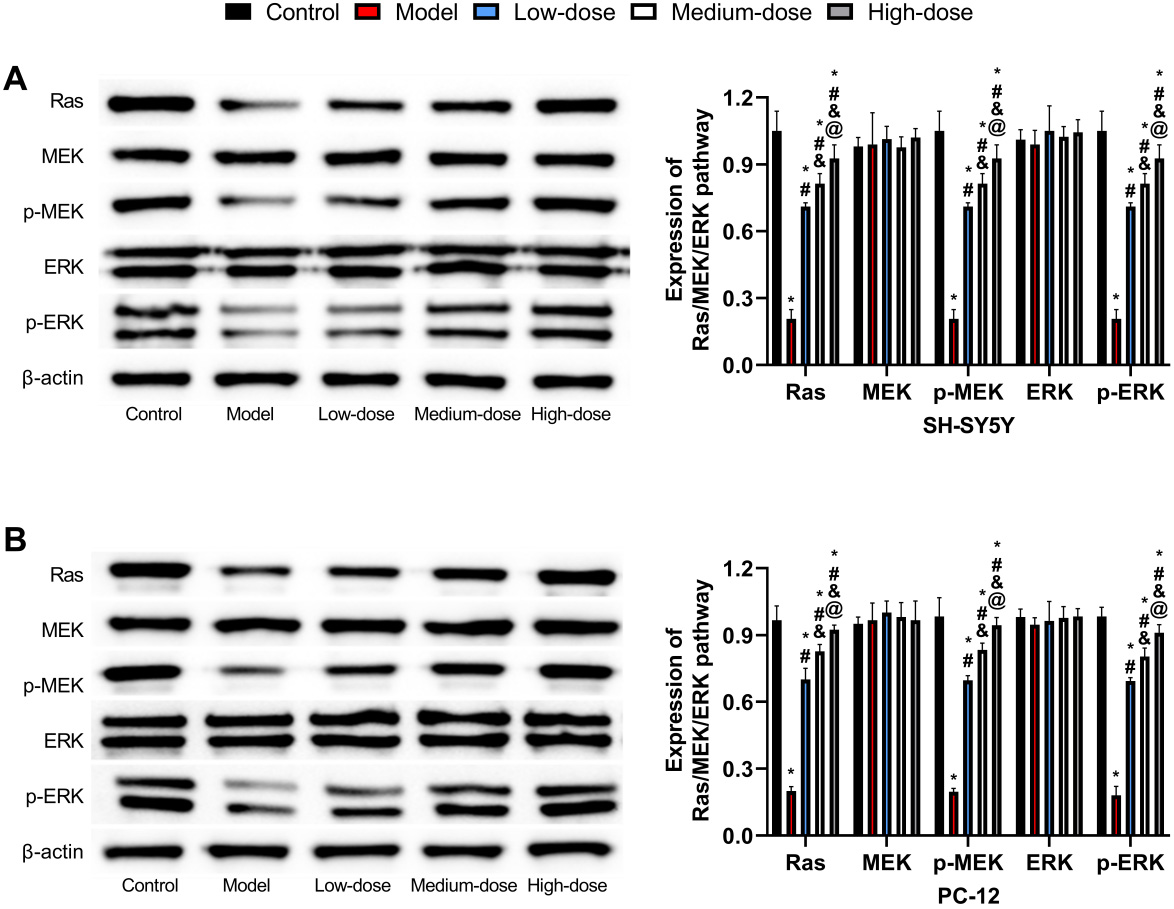 Fig. 7.
Fig. 7.Western blot detection of Ras/MEK/ERK signaling pathway
expression. (A) Comparison of Ras/MEK/ERK signaling pathway expression
in SH-5Y5Y. (B) Comparison of Ras/MEK/ERK signaling pathway expression
in PC-12. *: Compared with the control group, there is a difference
Although NA is widely recognized as a breakthrough in the therapeutic treatment of neurological illnesses, its acquisition remains a pressing issue owing to its limited availability and high level of complexity. Low-temperature crystallization, the urea inclusion technique, metal salt precipitation, etc. are being employed for NA separation and extraction in clinical settings. However, there is still much debate regarding the best approach to extraction since there are no widely accepted standards. We investigated the NA separation and extraction strategy to better understand its clinical application implications and to give a more intuitive reference and guiding meaning for the clinic. We also constructed PD animal and cell models for validation to demonstrate the long-lasting impact of XSB oil-extracted NA in PD.
After optimizing the purification procedure in this experiment, the NA content reached 22.53% after selecting low temperature crystallization settings. The concentration may rise to around 30.81% after 4 rounds of recrystallization. Previous research showed that the NA percentage of XSB oil produced by straight pressing was only 2%–4%. The NA content was raised by a factor of 26 after being subjected to the recrystallization-column chromatography technique of processing. However, this approach has the limitation that it can only be utilized in the lab and cannot be industrialized.
The question of whether or not NA derived from XSB oil has the same stellar performance as regular NA remains unanswered. As a result, we conducted further tests on animals to investigate the effects of NA derived from XSB oil on the abnormal behavior of PD mice. While the medium- and low-dose groups showed no statistically significant improvement in their mice’s behavior, the high-dose group clearly exhibited reduced PD-related behavioral disorders, as evidenced by a shorter pole climbing time and statistically increased latency and spontaneous movement times. We hypothesized that since the XSB oil-extracted NA in this experiment was not completely pure, there were some variations with respect to the conventional NA. NA derived from XSB oil at the same dosage is impacted by other FAs compared with the conventional NA, which may explain why it has no discernible effect on behavioral impairments in PD mice. When the NA from XSB oil is administered in high enough doses, it plays a significant role in the therapy and repair of PD, which in turn helps to alleviate the behavioral abnormalities seen in mice. Previous research has shown that NA may prevent neuronal death in animals with PD [24]. Thus, we also analyzed the effect of NA on neuronal apoptosis in each strain of mice. NA derived from XSB oil also exhibited a protective effect on neuron cells, with certain therapeutic application potential, as shown by the data showing a significant improvement in apoptosis in the high-dose group of mouse neuron cells.
Our cell assays also showed that the MPP+-induced PD cell model exhibited pathological alterations typical of PD, including an increase in the rates at which LDH is released and apoptosis occurs. Consistent with previous studies, we found that NA produced from XSB oil greatly alleviated the pathological changes of PD when a specified dosage was obtained, with the highest-dose group showing the most considerable improvement. A breakthrough that might one day lead to a permanent clinical cure for Parkinson’s disease. A insight into NA’s function in PD may be gained by considering the data that it stimulates the Ras/MEK/ERK axis. Moreover, the expression of proteins implicated in the Ras/MEK/ERK axis was analyzed to confirm that NA produced from XSB oil had an impact on PD model cells. Protein levels of Ras, mitogen-activated protein kinase, and extracellular signal-regulated kinase are all significantly decreased in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. One hypothesized mechanism by which NA from XSB oil impacts PD cells is via reactivation of the Ras/MEK/ERK axis.
However, whether the same substantial benefit is shown in human trials remains unknown because of variations between animal models and humans and the limited clinical application research due to the difficulty of acquiring NA. More tests are required to determine how NA influences PD. Finally, different methods may also have positive NA extraction effectiveness, since there is no universal NA extraction guide at home and overseas. They want us to move rapidly on doing more studies on the therapeutic potential of NA so that we can make informed recommendations. Lastly, the following were the experimental conditions that inhibited the detection of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and Glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px): Extensive future study is needed to find markers like malondialdehyde (MDA) and reactive oxygen species (ROS) to completely understand the function that NA plays in the oxidative stress damage found in PD.
NA extracted from XSB oil can ameliorate the pathological changes of PD mice and cell models, reduce inflammatory reaction and improve antioxidant capacity, possibly, which is expected to become a new clinical treatment scheme for PD that can provide a more reliable guarantee for patients’ health.
The datasets used during the current study are available from the corresponding author.
JZ designed the research study. DH performed the research. YC provided help and advice on data collection. DH analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript. All authors contributed to editorial changes in the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. All authors have participated sufficiently in the work and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and the protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of Beijing Yanqing Center for Diseases Prevention and Control (approval number: 2021-YL021-02).
Not applicable.
This research received no external funding.
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Publisher’s Note: IMR Press stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.







