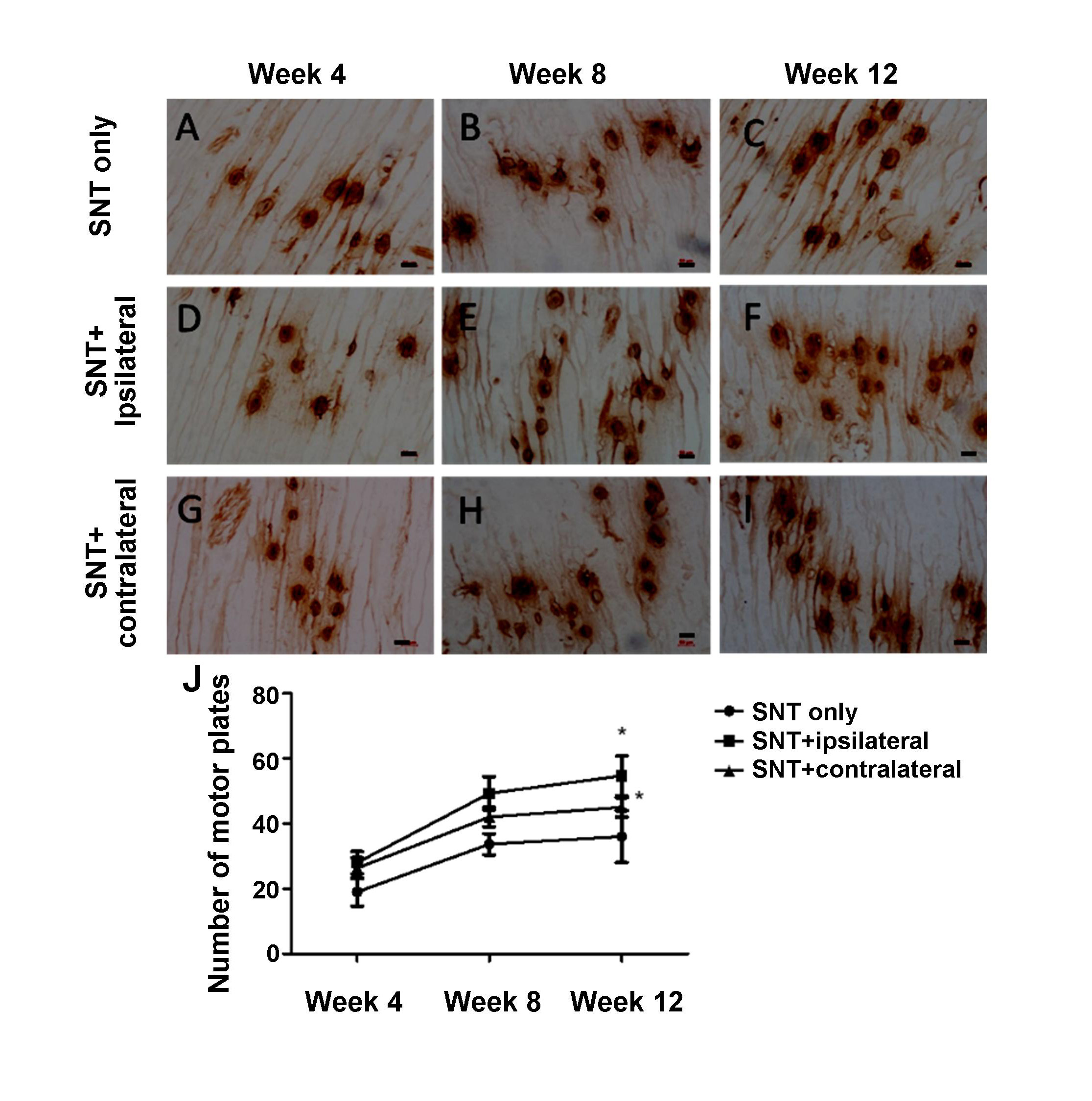
Previous studies showed that brain trauma promotes repair of peripheral nerve injury by reducing scar in nerve endings. The effect of brain injury at different locations on ipsilateral rat sciatic nerve regeneration in Sprague-Dawley rats was found to promote the repair of ipsilateral sciatic nerve injury, thus providing further experimental evidence for the unveiling of traumatic brain injury promoting peripheral nerve regeneration.