1 Department of Gynaecology, Huazhong University of Science and Technology Union Shenzhen Hospital/Shenzhen Nanshan Peopleʼs Hospital/the Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Shenzhen University Health Science Center, 518052 Shenzhen, Guangdong, China
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to investigate the risk factors associated
with complications following gynecologic laparoscopic surgery. Methods:
A retrospective analysis was conducted on patients who underwent gynecologic
laparoscopic surgery at Huazhong University of Science and Technology Union
Shenzhen Hospital between January 2005 and October 2021. The study population was
divided into four groups based on the type of surgery: adnexal surgery,
myomectomy/other uterine lesions, laparoscopically assisted vaginal hysterectomy
(LAVH)/total laparoscopic hysterectomy (TLH), and surgery for malignancy. The
rates of major and minor complications were compared and factors influencing the
occurrence of complications were analyzed. Results: A total of 15,308
patients were included in this study. The rates of major and minor complications
were 0.51% (78/15,308) and 4.64% (711/15,308), respectively. Multivariate
logistic regression analysis revealed that older age (31–60 years-old
vs. 18–30 years-old: adjusted odds ratio (aOR): 2.88, 95% confidence
interval (CI): 1.89–7.88;
Keywords
- gynecologic surgical procedures
- iatrogenic disease
- laparoscopic surgery
- risk factors
Laparoscopic surgery is commonly employed for the treatment of various benign and malignant gynecologic diseases. This approach offers several advantages over open surgery, including reduced trauma, faster postoperative recovery, and fewer complications than open surgery [1]. However, there are potential complications associated with gynecologic laparoscopic surgery, such as injuries to major blood vessels, bowel and genitourinary structures; incisional hernias; port-site metastases; and gas embolism [2, 3]. The overall complication rate of gynecologic laparoscopic surgery ranges from 0.69% to 6.22% [3, 4], with major complications occurring in approximately 2.84% of cases [2, 3]. Notably, many of these major complications arise during the entry stage of the procedure [5].
Factors known to increase the risk of major complications in patients undergoing
gynecologic laparoscopic surgery include advanced age, higher body mass index
(BMI), smoking, use of carbon dioxide, previous abdominal surgery, preoperative
diseases, American Society of Anesthesiologist score of III or higher, higher
predicted preoperative uterine weight (in cases of hysterectomy), and a
postoperative increase in fibrinogen level of
However, there is a lack of comprehensive data on the risk factors for major complications of gynecologic laparoscopic surgery in Chinese patients. Therefore, the objective of this study was to assess the incidence of complications in Chinese patients who underwent gynecologic laparoscopic surgery and identify the risk factors associated with both major and minor complications.
This retrospective study enrolled all patients who had undergone gynecologic laparoscopic surgery at Huazhong University of Science and Technology Union Shenzhen Hospital (Shenzhen, China) between January 2005 and October 2021. The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) age above 18 years; (2) underwent gynecologic laparoscopic surgery; (3) having been initially assessed in other departments through laparoscopy but later diagnosed with a gynecological disease, and transferred to the gynecological department for surgery. The exclusion criteria were: (1) combined with other surgeries; (2) open surgery; (3) incomplete data; (4) cases involving only laparoscopy or biopsy subsequent surgery, primarily for advanced ovarian cancer that was deemed inoperable; (5) simultaneous performance of other non-gynecological surgeries in different departments. This study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Huazhong University of Science and Technology Union Shenzhen Hospital (No. LW-2023-005) and informed consent were obtained. In adherence to the guidelines set forth by the journal, our data will be made available for independent analysis by a specifically chosen team, as determined by the Editorial Team. This will serve the purpose of conducting additional data analysis or facilitating the reproducibility of our study in other research centers, if such request is made.
The study collected demographic and clinical data from medical records,
including age, BMI, history of prior abdominal surgery, year of surgery, type of
surgery, procedural characteristics, length of hospital stay, minor
complications, and major complications. Age was divided into three groups:
Complications arising from laparoscopy were categorized as major and minor. Major complications were defined as those occurring during laparoscopy or the postoperative period that necessitated additional intervention, such as laparoscopy or laparotomy. These included injuries to the intestine, urinary bladder, ureter, or major blood vessels, significant bleeding (with a volume exceeding 600 mL within 24 hours of the perioperative period), severe infective complications, and pulmonary edema. Minor complications encompassed mild bleeding or infection, fever, nerve damage, abdominal wall hematoma, urinary tract infection or retention, paralytic ileus, subcutaneous emphysema, genital edema, uterine perforation, and pain of unknown origin. Postoperative evaluations were conducted for all patients. Diagnostic criteria for serious infective complications included: (1) signs of infection, such as fever; (2) concurrent organ dysfunction, such as hypotension (referred to as shock blood pressure, with systolic blood pressure below 90 mmHg and diastolic blood pressure below 60 mmHg); (3) alterations in mental state; (4) respiratory failure accompanied by rapid breathing; and (5) reduced urine output, indicating poor kidney blood supply and impaired urine excretion [10, 11].
The analyses were conducted using SPSS 26.0 (SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA).
Statistical significance was defined as p-values
This study conducted a review of 29,253 gynecological surgeries that took place
between January 2005 and October 2021. Out of these surgeries, 15,407 patients
underwent gynecological laparoscopic surgery. However, 82 cases involving other
surgical procedures and 17 cases involving laparoscopy alone were excluded (Fig. 1) from the analysis. Ultimately, a total of 15,308 patients who underwent
effective gynecological laparoscopic operations were enrolled (a mean age of
42.25
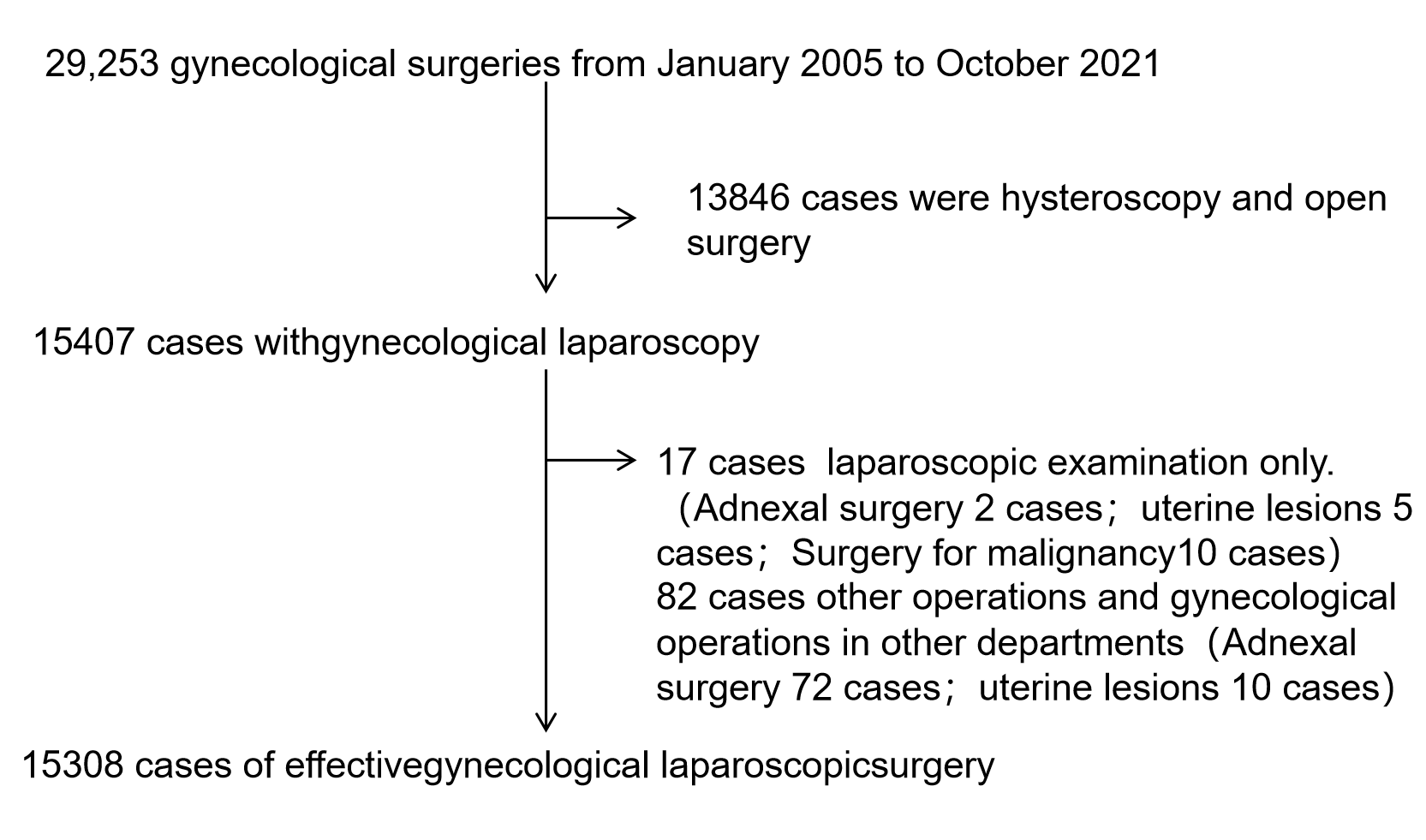 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.Flow charts of patients.
| Parameter | Value (n (%)) | |
| Age (years), mean |
42.25 | |
| Body mass index (kg/m |
23.62 | |
| Prior surgery, n (%) | 2589 (16.91) | |
| Type of surgery, n (%) | ||
| Adnexal surgery | 9812 (64.10) | |
| Myomectomy or surgery for other uterine lesions | 3412 (22.29) | |
| LAVH or TLH | 1572 (10.27) | |
| Surgery for malignancy | 512 (3.34) | |
| Length of hospital stay (days) | 8.31 | |
| 5–7 days, n (%) | 13,104 (85.60) | |
| 8–10 days, n (%) | 1560 (10.19) | |
| 644 (4.21) | ||
SD, standard deviation; LAVH, laparoscopically assisted vaginal hysterectomy; TLH, total laparoscopic hysterectomy.
The overall incidence of major complications and minor complications in this study was 0.51% (78/15,308) and 4.64% (711/15,308), respectively. Table 2 summarizes the types of major and minor complications experienced by the patients. The most common major complications were bleeding (71.79% of all major complications), visceral organ injury (12.82%), infection (10.26%), and blood vessel injury (3.85%). Further details of the major complications can be found in Table 3. The most frequent minor complication was bleeding (3.01%). Intraoperative findings led to the conversion of the procedure to laparotomy in four patients (0.03%), including the discovery of an ovarian malignant tumor in two cases and the discovery of a large uterus and extensive pelvic adhesions in two cases. Additionally, one patient (0.01%) required conversion to laparotomy due to bleeding complications (Tables 2,3).
| Complication | Value (n = 15,308) | ||
| Major complications | 78 (0.51) | ||
| Vascular injury | 3 (0.02) | ||
| Bladder injury | 3 (0.02) | ||
| Intestinal injury | 3 (0.02) | ||
| Ureteral injury | 4 (0.03) | ||
| Serious bleeding complications | 56 (0.37) | ||
| Serious infection | 8 (0.05) | ||
| Acute pulmonary edema | 1 (0.01) | ||
| Minor complications | 711 (4.64) | ||
| Severe anemia requiring transfusion | 152 (0.99) | ||
| Minor bleeding | 461 (3.01) | ||
| Minor infection | 4 (0.03) | ||
| Wall abscess | 2 (0.01) | ||
| Vaginal vault abscess | 1 (0.01) | ||
| Pelvic abscess | 1 (0.01) | ||
| Nerve lesion | 2 (0.01) | ||
| Fever | 46 (0.30) | ||
| Pain of undetermined cause | 6 (0.04) | ||
| Subcutaneous emphysema | 3 (0.02) | ||
| External genitalia edema | 2 (0.01) | ||
| Paralytic ileus | 1 (0.01) | ||
| Hernia at trocar site | 3 (0.02) | ||
| Urinary tract infection | 6 (0.04) | ||
| Urinary retention | 9 (0.06) | ||
| Hematoma (postoperative) | 10 (0.07) | ||
| Postoperative abdominal wall hematoma | 8 (0.05) | ||
| Postoperative vaginal vault hematoma | 2 (0.01) | ||
| Uterine perforation | 6 (0.04) | ||
| Conversion to laparotomy due to intraoperative findings | 4 (0.03) | ||
| Conversion to laparotomy because of complications | 1 (0.01) | ||
Data are presented as n (%).
| Site of complication (n) | Type of surgery (n) | Diagnosis (n) | Surgical access (n) | Additional information |
| Vascular injury (3) | Radical hysterectomy for cervical cancer (3) | Intraoperative (3) | Laparoscopy (3) | Injury occurred during separation of minor vascular branches (common iliac veins) and adhered tissue (external iliac vein). Vessels successfully repaired by suturing in all cases. |
| Left common iliac vein (1) | ||||
| Right common iliac vein (1) | ||||
| External iliac vein (1) | ||||
| Bladder injury (3) | Total hysterectomy with adhesiolysis (3) | Intraoperative (3) | Laparoscopy (3) | Intraoperative repair was successful in all three cases. |
| Intestinal injury (3) | Radical hysterectomy for cervical cancer (1) | Postoperative (1) | Transvaginal (1) | Rectovaginal fistula diagnosed after yellow-green vaginal discharge developed on post-op day 5; transvaginal repair was successful. Colonic injuries were detected and repaired intraoperatively. |
| Rectovaginal fistula (1) | Total hysterectomy for adenomyosis (2) | Intraoperative (2) | Laparoscopy (2) | |
| Colonic injury (2) | ||||
| Distal ureteral injury (4) | Radical hysterectomy for cervical cancer (1) | Intraoperative (1) | Laparoscopy (2) | Repaired by ureterovesicostomy. |
| Total hysterectomy (2) | Postoperative (1) | Laparotomy (1) | Diagnosed by CT urography after development of fever and abdominal pain. Repaired by uretero-ureterostomy. | |
| Broad ligament myomectomy for 8-cm leiomyoma (1) | Intraoperative (2) | Laparoscopy and laparotomy (1) | Initial repair by laparoscopic uretero-ureterostomy failed. Subsequent repairs carried out via laparotomy at 2 and 5 months. Patient recovered well. | |
| Serious bleeding (56) | Adnexectomy for endometriosis (4) | Intraoperative (56) | Laparoscopy (56) | Most cases occurred in patients undergoing technically difficult operations. |
| Myomectomy (10) | ||||
| Total hysterectomy (16) | ||||
| Radical hysterectomy (26) | ||||
| Serious infection (8) | Myomectomy (1) | Postoperative (8) | Wound dressing changes. Vaginal drainage, antibiotics (8) | Most cases were infected abdominal incisions in patients with obesity. |
| Wall abscess (6) | Hysterectomy (2) | |||
| Vaginal vault abscess (1) | Radical hysterectomy (3) | |||
| Pelvic abscess (1) | Radical hysterectomy (1) | |||
| Radical hysterectomy (1) | ||||
| Acute pulmonary edema (1) | Radical hysterectomy (1) | Intraoperative (1) | Diuretic and other drugs (1) | Operative duration was long, and substantial blood transfusion was needed. |
CT, computed tomography.
Bivariate analysis revealed several factors associated with major complications.
These factors included patient age (p = 0.027), year of surgery
(p = 0.035), prior abdominal surgery (p = 0.038), obesity
(p = 0.021), and type of surgery (p
| Factor | Major complications (78) n (%) | Minor complications (711) n (%) | |
| Age | |||
| 18–30 years | 9 (11.54) | 325 (45.71) | |
| 31–60 years | 58 (74.36) | 285 (40.08) | |
| 11 (14.10) | 101 (14.21) | ||
| p | 0.027 | 0.142 | |
| Period of surgery | |||
| 2005–2011 | 48 (61.54) | 420 (59.07) | |
| 2012–2021 | 30 (38.46) | 291 (40.93) | |
| p | 0.035 | 0.029 | |
| Prior abdominal surgery | |||
| Yes | 30 (38.46) | 76 (10.69) | |
| No | 48 (61.54) | 635 (89.31) | |
| p | 0.038 | 0.187 | |
| Obesity | |||
| Yes | 16 (20.51) | 36 (5.06) | |
| No | 62 (79.49) | 675 (94.94) | |
| p | 0.021 | 0.358 | |
| Type of surgical procedure | |||
| Adnexal surgery | 4 (5.13) | 26 (3.65) | |
| Myomectomy/other uterine lesions | 12 (15.38) | 257 (36.14) | |
| LAVH/TLH | 25 (32.05) | 216 (30.38) | |
| Surgery for malignancy | 37 (47.44) | 212 (29.83) | |
| p | |||
Data are presented as n (%).
Multivariate logistic regression analysis was conducted to investigate the relationship between various factors and the occurrence of major complications. The findings revealed that individuals aged 31–60 years had a significant higher adjusted odds ratio (aOR) of 2.88 (95% CI: 1.89–7.88) for major complications compared to those aged 18–30 years. Similarly, individuals over 60 years had a significantly higher aOR of 2.92 (95% CI: 1.67–5.65) for major complications compared to those aged 18–20 years. Other independent risk factors for major complications included previous abdominal surgery (aOR: 3.58, 95% CI: 1.38–6.54), obesity (aOR: 2.52, 95% CI: 1.39–7.28), and surgical complexity. Specifically, myomectomy or surgery for other uterine lesions had an aOR of 1.56 (95% CI: 1.23–3.45) compared to adnexal surgery. Additionally, LAVH or TLH had an aOR of 3.87 (95% CI: 1.99–8.23) compared to adnexal surgery. Finally, malignant tumor surgery had an aOR of 7.62 (95% CI: 3.61–13.63) compared to adnexal surgery. The type of surgical procedure was also associated with minor complications: LAVH/TLH had an aOR of 2.21 (95% CI: 1.20–5.42) and surgery for malignancy had an aOR of 4.56 (95% CI: 2.77–9.49) (Table 5).
| Factor | Adjusted odds ratio (95% confidence interval) | ||
| Major complications | Minor complications | ||
| Age | |||
| 18–30 years | 1 | 1 | |
| 31–60 years | 2.88 (1.89–7.88) | 0.66 (0.35–0.92) | |
| 2.92 (1.67–5.65) | 0.72 (0.47–1.21) | ||
| Period of surgery | |||
| 2005–2011 | 1 | 1 | |
| 2012–2021 | 0.52 (0.27–1.09) | 0.71 (0.32–1.31) | |
| Prior abdominal surgery | 3.58 (1.38–6.54) | 0.86 (0.43–2.12) | |
| Obesity | 2.52 (1.39–7.28) | 0.95 (0.43–2.28) | |
| Type of surgical procedure | |||
| Adnexal surgery | 1 | 1 | |
| Myomectomy/other uterine lesions | 1.56 (1.23–3.45) | 1.26 (0.38–4.65) | |
| LAVH/TLH | 3.87 (1.39–8.23) | 2.21 (1.20–5.42) | |
| Surgery for malignancy | 7.62 (3.61–13.63) | 4.56 (2.77–9.49) | |
A previous meta-analysis of 27 prospective randomized clinical trials demonstrated that laparoscopic surgery was associated with several benefits compared to laparotomy, including a significant reduction in pain, with an 80% decrease in the rate of surgical site infection. Additionally, patients who underwent laparoscopic surgery experienced a shorter hospital stay by two days and a faster return to physical activity by two weeks. Furthermore, laparoscopic surgery was found to reduce the rate of postoperative adhesions by 60% when compared to laparotomy [12].
However, gynecologic laparoscopic surgery carries a risk of complications. In this study, the incidence of minor complications was found to be 4.64%, which aligns with previous studies [3, 4, 13]. The rate of major complications was only 0.51%, lower than what has been reported by others [2, 3]. One possible explanation for this discrepancy is that the majority of patients in our study underwent adnexal surgery or myomectomy, which are relatively less complex procedures. Notably, the incidence of complications was higher during the period of 2005–2011 compared to 2012–2021, suggesting a progressive improvement in the skill level of our surgeons over time. This finding is consistent with previous research indicating that the surgeon’s annual case load influences the rate of complications [8].
In this study, the main factors associated with major complications were older age, prior abdominal surgery, and type of surgical procedure (which was used as an indicator of surgical complexity). Elderly patients, who often experience tissue degeneration and compromised visceral function, along with a history of multiple previous surgeries, face challenges in tissue separation during surgical procedures. These difficulties can lead to an increased risk of bleeding and potential damage to surrounding organs. The above findings agree well with prior research [3, 6, 8]. Other studies have also suggested that operation type, surgical complexity and degree of pelvic adhesions may affect the incidence of complications [13, 14, 15, 16, 17].
In this study, the primary factors associated with major complications were older advanced age, previous abdominal surgery, and the type of surgical procedure, which served as an indicator of surgical complexity. These findings align with previous research studies [3, 6, 8]. Additionally, other studies have indicated that the type of operation, surgical complexity, and the extent of pelvic adhesions may influence the occurrence of complications [13, 14, 15, 16, 17].
Gynecologic laparoscopic procedures have been identified as the cause of over half of all iatrogenic injuries to the ureters [18]. The incidence rate of gastrointestinal injury during gynecologic laparoscopic surgery has been estimated to range from 0.13% to 1% [19, 20]. Among these injuries, the small intestine is the most commonly affected site (55.8%), followed by the large intestine (38.6%) and the stomach (3.9%) [20]. A study involving 12,354 patients undergoing laparoscopic surgery reported 15 cases of rectal injury [21]. In our study, one patient who had undergone two previous surgeries required transvaginal repair of a rectovaginal fistula, resulting in a yellow-green vaginal discharge. Two additional patients experienced colonic injuries during total hysterectomy. Common strategies for managing rectal injuries include laparotomic or laparoscopic colostomy, one-stage repair, low anterior resection, and partial rectal resection [4, 22, 23, 24]. To minimize the risk of injury during laparoscopic surgery, it is crucial to ensure that the separation of the intestine is performed as close to the uterus as possible.
Three cases of vascular injury were observed in this study. Blood vessels can sustain damage during the separation of adhesions or trocar insertion [25]. Only five patients (0.03%) necessitated conversion to laparotomy in this study. Two cases were due to the intraoperative discovery of an ovarian malignant tumor, one case was due to extensive hemorrhage from a cesarean scar pregnancy, and two cases were attributed to a large uterus and extensive pelvic adhesions. The rate of conversion to laparotomy in this series was significantly lower than the previously reported value of 5% for patients undergoing hysterectomy for benign gynecologic disease [15]. The lower rate observed in this study may be attributed to the majority of operations being technically straightforward procedures such as adnexal surgery or myomectomy.
This study encompassed a substantial number of patients who received consistent treatment and management within the same hospital. However, it is important to acknowledge several limitations of this study. Firstly, being a retrospective study, there is a possibility of selection bias or information bias affecting the findings. Secondly, the generalizability of the results is uncertain due to the study being conducted at a single center. Lastly, there may be additional parameters not considered in the analysis that could have acted as confounding factors influencing the results.
The findings suggest that meticulous separation of adhesions and regular examination of the bladder, ureter, bowel, blood vessels, and other vital organs may effectively mitigate the risk of complications. These results contribute valuable data on the risk factors associated with major complications in gynecologic laparoscopic surgery among Chinese patients. Furthermore, these findings could aid in the appropriate selection of patients for preventive measures.
The occurrence of minor and major complications following gynecologic laparoscopic surgery is relatively low. Moreover, increased surgical difficulty and a history of previous surgeries are identified as risk factors that contribute to a higher incidence of major complications. Additionally, older age, prior abdominal surgeries, and the complexity of the surgical procedure are associated with an increased likelihood of major complications.
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
AL carried out the studies, participated in collecting data, and drafted the manuscript. YX and JC participated in acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data. AL participated in reviewing and proofreading papers. All authors contributed to editorial changes in the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. All authors have participated sufficiently in the work and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
This work has been carried out in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki (2000) of the World Medical Association and approved by Huazhong University of Science and Technology Union Shenzhen Hospital (approval number: LW-2023-005). All patients were aware of the potential risks of this clinical study and agreed to offer the data and the information.
Not applicable.
This study was supported by a grant from the Shenzhen City Technology Creative Committee (No. JCYJ20190809104403566).
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Publisher’s Note: IMR Press stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.