- Academic Editor
-
-
-
Background: In this study, we sought to detect the expression of
complement C3 and C4 in serum and maternal-fetal interface in patients with
unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion, and analyze their correlation, in
order to explore the clinical significance and role of C3 and C4 in unexplained
recurrent spontaneous abortion. Methods: In a prospective cohort study,
products of conception of 20 women who underwent curettage due to unexplained
recurrent spontaneous abortion in the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology at
the Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital from December 2021 to December 2022 were
chosen as the case group, and 23 healthy early-pregnancy women who underwent
elective abortion due to personal reasons during the same period were chosen as
the control group. Serum samples before curettage and decidual tissues samples
after curettage were collected. C3 and C4 levels in serum samples were detected
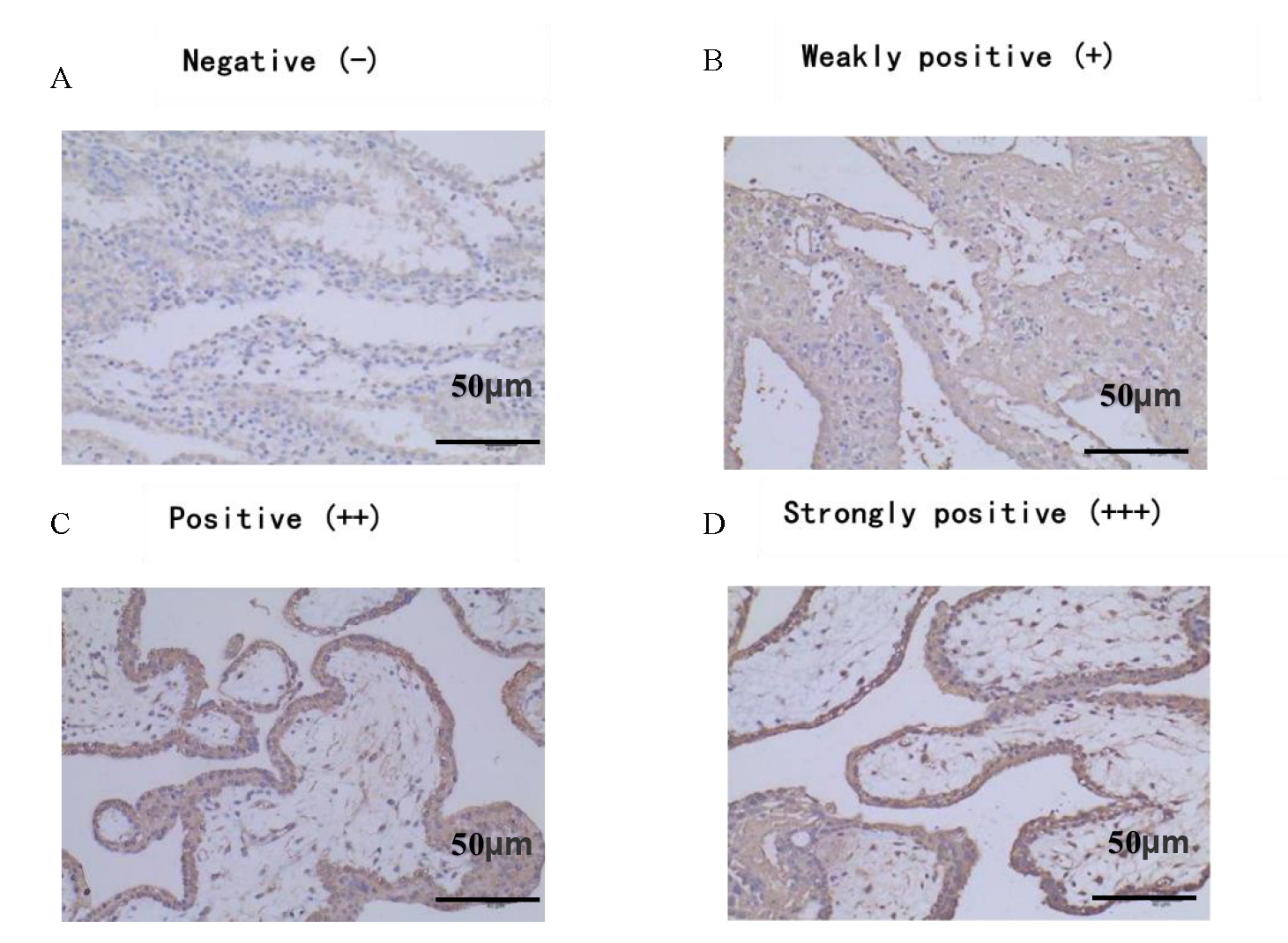
by immunoturbidimetry, and semi-quantitative scoring analysis was performed after
immunohistochemical staining of decidual tissues samples. The correlation between
C3 and C4 in serum and decidual tissues was analyzed. Results: The
levels of C3 and C4 in serum and decidual tissues in the case group were
significantly higher than those in the control group, and the differences were
statistically significant (p