-
- Academic Editors
-
-
-
†These authors contributed equally.
Background: Left atrial appendages (LAAs) play an important role in
regulating left atrial function, and much evidence supports the possibility that
changes in left atrial structure may cause or worsen mitral regurgitation. This
study intended to investigate the outcomes of patients with mitral regurgitation
who underwent left atrial appendage closure (resection or endocardial closure)
during isolated surgical ablations. Methods: Patients with mild or
moderate mitral regurgitation who received isolated surgical ablations for atrial
fibrillation (AF) in our center from 2013 to 2022 were referred. During
follow-up, each clinical visit was composed of medical interrogation, a 24 h
Holter, and echocardiographic evaluation. Death, atrial fibrillation, worsening
of mitral regurgitation, and stroke were evaluated as outcomes. Freedom from
outcomes whose results were adjusted by inverse probability of treatment
weighting for causal effects after acquiring propensity scores. Results:
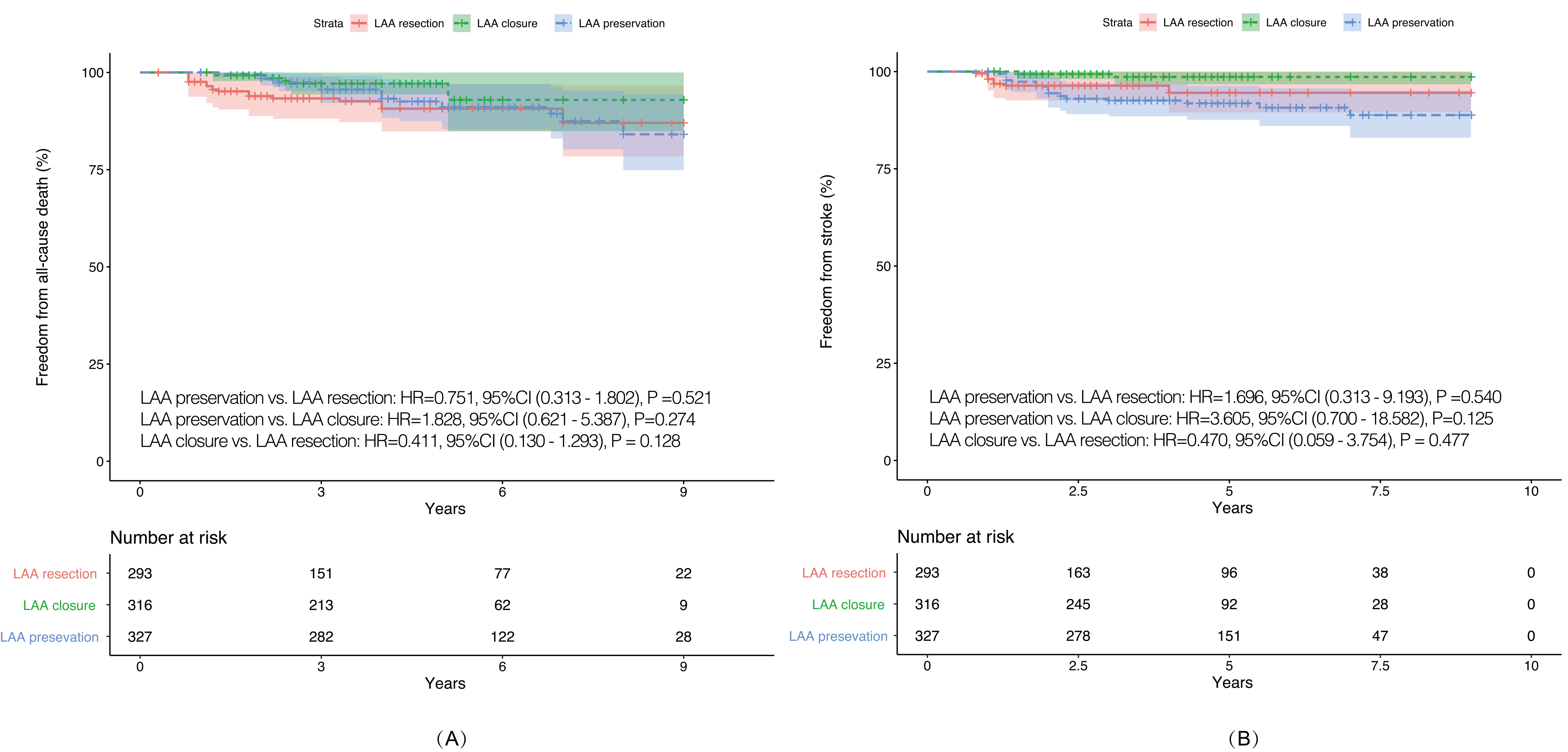
A total of 456 patients were enrolled in this study. During a median follow-up of
48 months, 30 deaths and 11 cases of stroke were observed. After adjustments, no
significant differences in terms of death or stroke were observed among the three
groups. Patients who underwent resection or endocardial closure during surgical
ablations had a higher risk of mitral regurgitation worsening during follow-up
(p