1 Department of Cardiology, Beijing Hospital, National Center of Gerontology; Institute of Geriatric Medicine, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, 100730 Beijing, China
2 Department of Cardiology, Fuwai Hospital, National Center for Cardiovascular Diseases, Peking Union Medical College and Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, 100037 Beijing, China
3 PKU-HKUST Shenzhen-Hong Kong Institution, 518063 Shenzhen, Guangdong, China
†These authors contributed equally.
Academic Editors: Zhonghua Sun, Yung-Liang Wan and Brian Tomlinson
Abstract
Background: There are scarce published data reporting the effect of
rotational atherectomy (RA) on coronary microcirculation function.
Objectives: We aimed to evaluate coronary microcirculation function
indicated by the coronary angiography-derived index of microvascular resistance
(caIMR) in patients undergoing RA. Methods: RA procedures between
January 2013 and December 2021 were retrospectively analyzed. We investigated
coronary microcirculation function indicated by caIMR as well as peri-procedural
adverse events among the study population. All caIMR measurements were performed
using a FlashAngio system. The primary outcome was a composite of post-RA thrombolysis in myocardial infarction (TIMI)
flow grade
Keywords
- coronary artery disease
- percutaneous coronary intervention
- rotational atherectomy
- coronary microcirculation
- index of microvascular resistance
The effect of percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) on coronary microvascular function and the prognostic implication of pre and post-procedural index of microvascular resistance (IMR) has been shown in previous studies [1, 2, 3]. Coronary rotational atherectomy (RA) is an efficient way to facilitate balloon or stent delivery and optimize stent expansion by physical removal of hard plaque via lumen enlargement [4, 5]. Current PCI guidelines state that RA is a reasonable approach for the treatment of heavily calcified plaques that cannot be crossed by a balloon catheter or adequately dilated before stent implantation [6]. However, the RA procedure has previously been reported to be associated with microvascular disorder resulting from microcirculatory obstruction [5].
The pressure-temperature wire-derived coronary flow reserve (CFR) and IMR have constituted the reference standard to assess the status of coronary microcirculation thus far [7, 8]. Prior studies have indicated that there are major limitations to the pressure wire-derived CFR calculation; the maximal hyperemic coronary blood flow is strongly pressure-dependent, and the pressure wire-derived method appears to systematically underestimate the CFR values [9]. However, the pressure-temperature wire-derived IMR shows good specificity and reproducibility compared with CFR [10, 11], whereas the invasive measurement increases additional intracoronary performance and prolongs the operation time. Thus, to a certain degree, the invasive measurement raises unpredictable procedural risks, especially when faced with treating complicated lesions or in urgent situations. Alternatively, multiple pressure-wire-free tools, such as angiography-derived index of microcirculatory resistance, to assess coronary microvascular dysfunction have been developed [12]. The pressure-wire-free method was revealed to be well correlated with wire-derived IMR for estimation of microcirculatory function [13]. A novel coronary angiography-derived index of microvascular resistance (caIMR) shows good agreement with pressure-temperature wire-based IMR and has similar accuracy; thus, it has been proposed as a well-adopted non-invasive physiological assessment of coronary microcirculation function [14, 15, 16]. The effect of RA on coronary microcirculation function remains unclear, and this study aimed to investigate coronary microcirculatory function indicated by caIMR in patients undergoing RA.
Between January 2013 and December 2021, consecutive RA procedures in patients
with severe coronary artery calcification lesions and significant stenosis
(stenosis
Coronary RA was performed using a Rotablator Rotational Atherectomy System
(Boston Scientific, Marlborough, MA, USA). Standard techniques for PCI were
performed by an experienced operator. The most widely adopted institutional
protocol for rotablation was used. The preferred burr-to-artery ratio was 0.5,
and a smaller (1.25-mm) burr was initially used more often, followed by a larger
(1.50-mm, 1.75-mm) burr. Before approaching the target lesion, the burr advanced
at a low speed of 60,000 to 70,000 revolutions per minute (rpm). The working
rotational speed of the burr ranged from 130,000 to 180,000 rpm. When the target
lesion could not be fully dilated, a higher-speed (
The RA was performed when the target lesion was deemed undilatable by a balloon based on angiography and/or IVUS findings indicated the requirement of planned RA. RA procedures performed when it was not possible to fully expand the target lesion were regarded as rescue RA. The use of IVUS for the evaluation of lesion features and stent expansion was left to the discretion of the operator. After RA, patients received pre-dilation with conventional, scoring, or cutting balloons, as determined by the operator. When adequate pre-treatment results were achieved, one or more drug-eluting stents were implanted.
We established a dedicated RA database to record demographic, angiographic, and
procedural data, including characteristics of RA and peri-procedural events, as
well as hospitalization information. Peri-procedural adverse events (PPAEs)
including coronary slow flow or no flow post-RA, coronary dissection, burr
entrapment, side branch occlusion, peripheral vascular complications,
contrast-induced nephropathy, procedure-related myocardial infarction (MI), and
in-hospital death were recorded. Coronary slow flow/no flow refers to instant
thrombolysis in myocardial infarction (TIMI) flow grade
A three-dimensional mesh of the target artery was reconstructed based on two
coronary angiographic projections which were at least 30° apart and had
no vessel overlap. In theory, the caIMR (unit: mmHg
In the above equation, Pd
Continuous variables are expressed as the mean
A total of 192 consecutive patients who underwent RA between January 2013 and
December 2021 were enrolled in this study. Thiry-seven patients with coronary
angiography involving unclear contrast opacification, marked vascular overlap or
distortion of the targeted vessel, poor-quality angiographic images, or lack of
two images that were
| Variables | n = 155 | |
| Clinical baseline characteristics | ||
| Age (years) | 70.1 | |
| Male gender | 94 (60.6) | |
| Hypertension | 118 (76.7) | |
| Diabetes mellitus | 76 (49.0) | |
| Current smoker | 52 (33.5) | |
| Previous MI | 22 (14.2) | |
| Prior PCI | 72 (46.5) | |
| UAP | 87 (56.1) | |
| eGFR (mL·min |
73.8 | |
| LVEF | 61.1 | |
| Angiographic and procedural characteristics | ||
| PCI access | ||
| Transradial | 126 (81.3) | |
| Transfemoral | 29 (18.7) | |
| Three-vessel coronary disease | 112 (72.2) | |
| Contrast volume (mL) | 266.5 | |
| Target vessel | ||
| LAD | 127 (81.9) | |
| LCX | 7 (4.5) | |
| RCA | 21 (13.5) | |
| 128 (82.6) | ||
| Bifurcation lesion | 84 (54.2) | |
| Planned RA | 109 (70.3) | |
| Rescue RA | 46 (29.7) | |
| IVUS use | 73 (47.1) | |
| Number of rotational times | 4 (3, 5) | |
| Maximum RA time of each pass (seconds) | 17.0 | |
| Maximum rotational speed (10,000 rpm) | 15.8 | |
| Number and size of burrs | ||
| 1 | 138 (89) | |
| 2 | 17 (11) | |
| 1.25 mm | 103 (59.9) | |
| 1.50 mm | 68 (39.5) | |
| 1.75 mm | 1 (0.6) | |
| Number of stents | 2 (2, 2) | |
| Myocardial injury | 37 (23.9) | |
| Peri-procedural adverse events | 33 (21.3) | |
| Instant TIMI flow grade |
13 (8.4) | |
| No flow | 1 (0.6) | |
| Procedure related-MI | 17 (11) | |
| In-hospital death | 1 (0.6) | |
| The primary outcome | 61 (39.3) | |
| Values are mean The primary outcome was a composite of TIMI flow | ||
There were no significant differences in pre-RA caIMR measurements between the
target and reference vessels (15.2
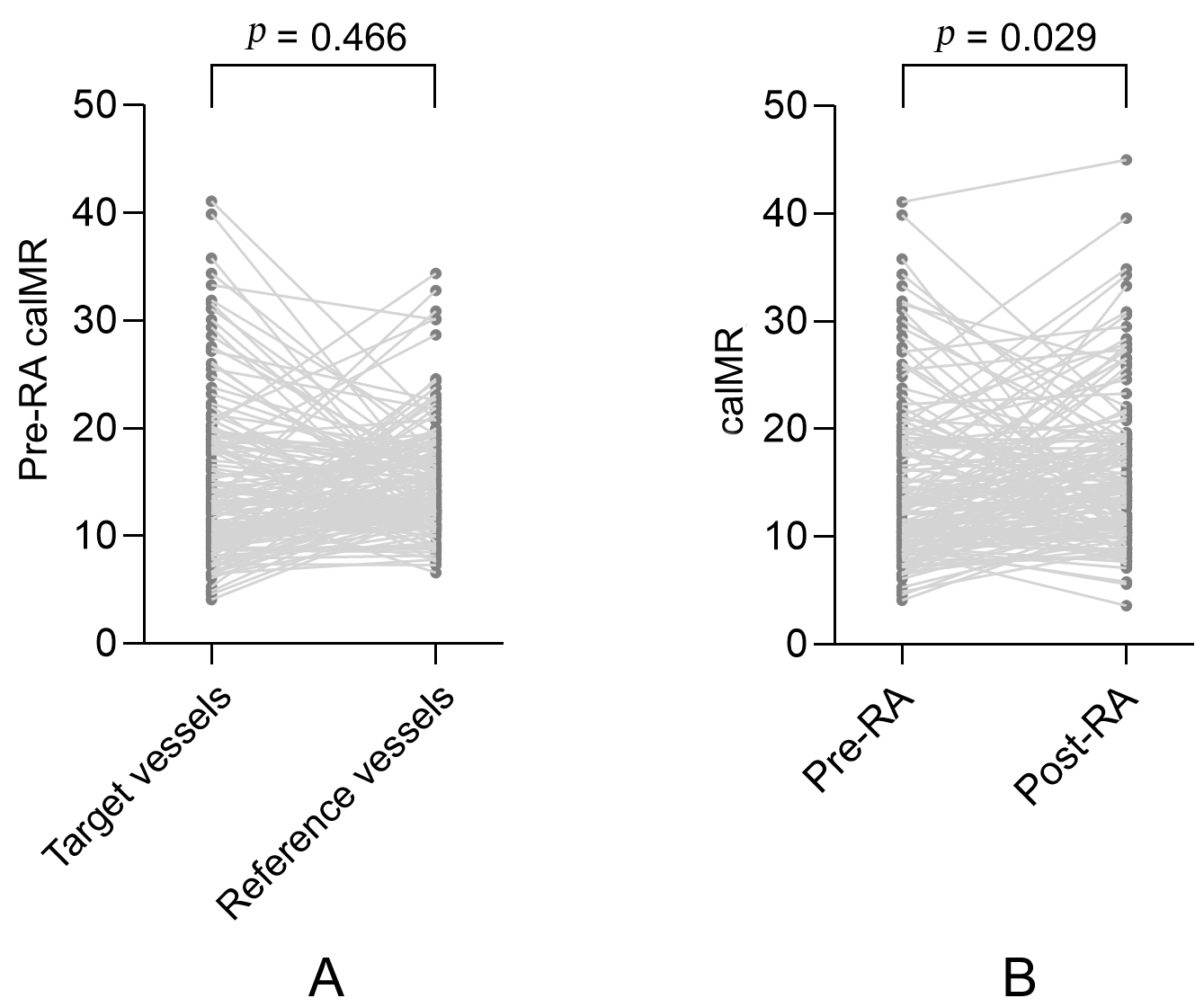 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.A paired comparison of caIMR in the target and reference vessels. (A) A paired comparison of pre-RA caIMR between the target and reference vessels. (B) A paired comparison of pre-RA and post-RA caIMR in the target vessels. MI, myocardial infarction; caIMR, coronary angiography-derived index of microvascular resistance; RA, rotational atherectomy.
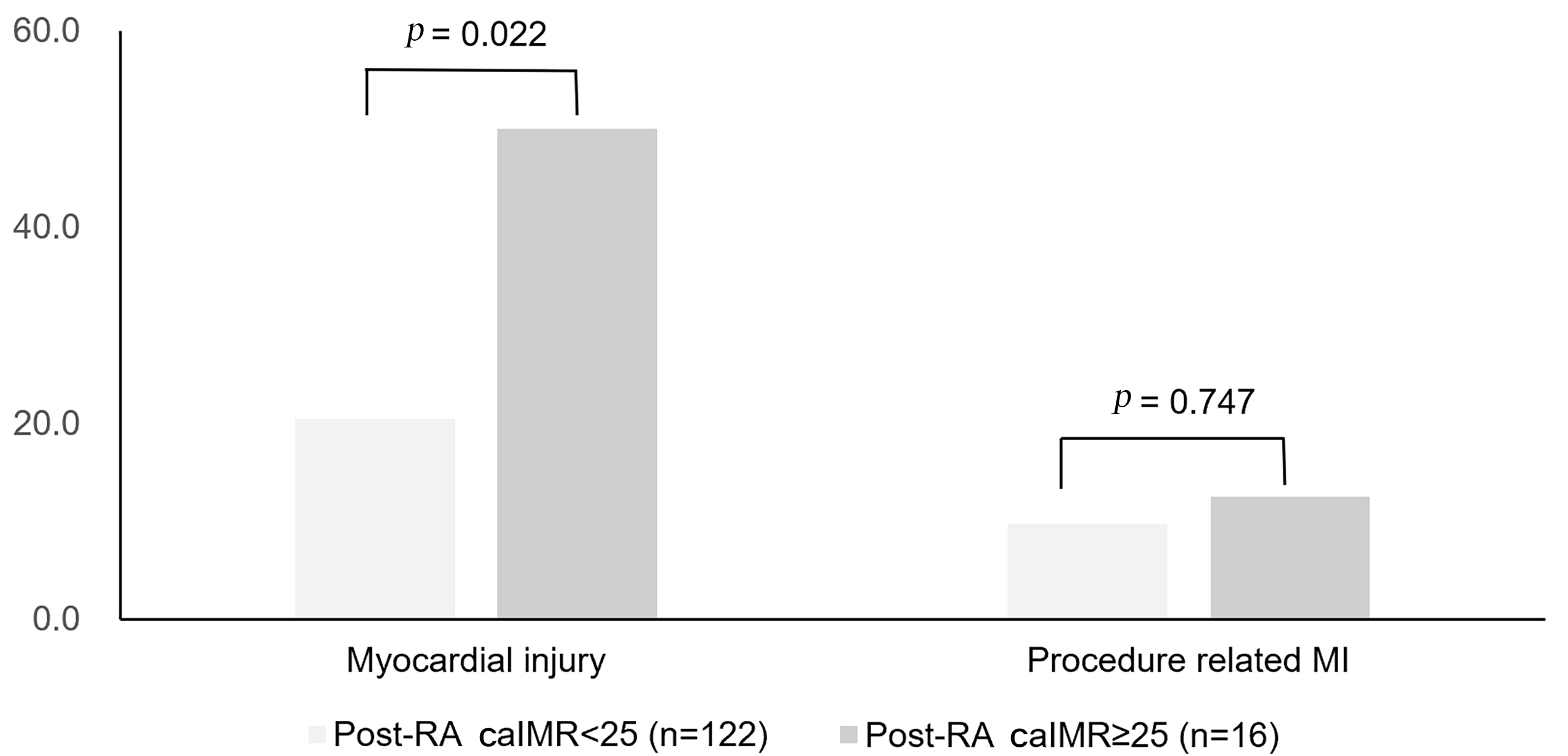 Fig. 2.
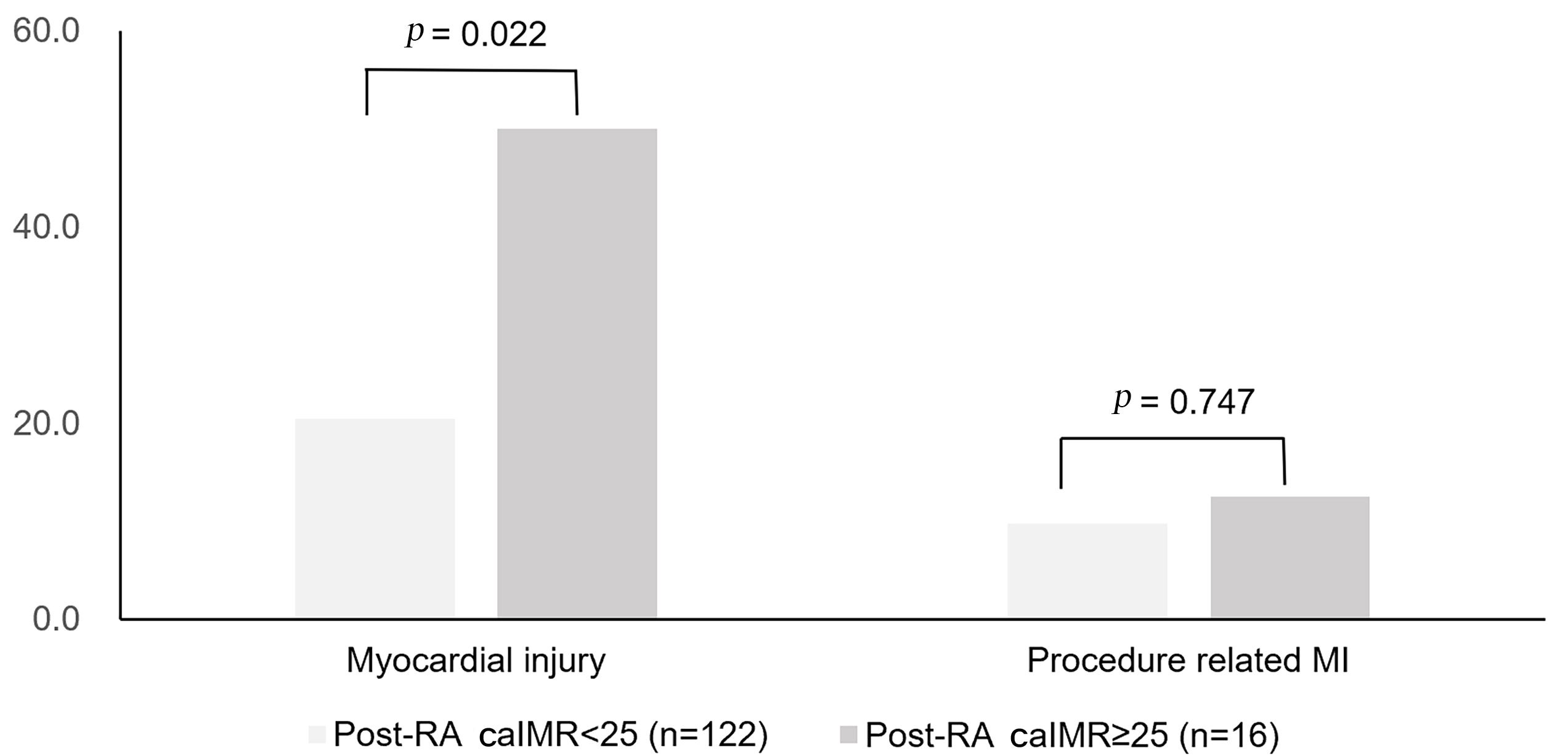
Fig. 2.Occurrences of myocardial injury and procedure-related MI among
patients with pre-RA caIMR
Patients with post-RA TIMI flow grade
| Variables | post-RA TIMI flow grade |
post-RA TIMI flow grade 3 | p value | |
| (n = 13) | (n = 142) | |||
| pre-RA caIMR | 23.5 |
13.7 |
0.005 | |
| 8 (61.5) | 9 (6.3) | |||
| 5 (38.5) | 133 (93.7) | |||
| post-RA caIMR | 25.6 |
15.1 |
||
| 7 (53.8) | 10 (7.0) | |||
| 6 (46.2) | 132 (93.0) | |||
| Myocardial injury | 5 (38.5) | 32 (22.5) | 0.342 | |
| Procedure-related MI | 4 (30.8) | 13 (9.2) | 0.040 | |
| Values are mean | ||||
Candidate predictors in the univariate analysis included age, hypertension,
diabetes mellitus, previous MI, estimated glomerular filtration rate, number of
diseased vessels, lesions
| Variable | Univariate OR (95% CI) | p value | Adjusted OR (95% CI) | p value |
| Age (years) | 1.034 (0.997–1.073) | 0.075 | ||
| Hypertension | 1.420 (0.649–3.110) | 0.380 | ||
| Diabetes mellitus | 0.989 (0.518–1.886) | 0.973 | ||
| Previous MI | 1.028 (0.991–1.066) | 0.136 | ||
| eGFR (mL·min |
0.990 (0.976–1.004) | 0.165 | ||
| number of diseased vessels | 1.017 (0.985–1.049) | 0.305 | ||
| lesions |
1.368 (0.571–3.281) | 0.482 | ||
| bifurcation lesion | 0.994 (0.520–1.897) | 0.985 | ||
| RA strategy (planned or rescue RA) | 1.449 (0.720–2.914) | 0.298 | ||
| number of rotational times | 1.127 (0.999–1.271) | 0.053 | ||
| maximum RA time of each pass (seconds) | 1.121 (1.021–1.230) | 0.016 | 1.127 (1.025–1.239) | 0.014 |
| maximum rotational speed | 1.000 (1.001–1.100) | 0.705 | ||
| pre-RA caIMR | 1.027 (0.984–1.073) | 0.219 | ||
| pre-RA caIMR |
3.227 (1.125–9.253) | 0.029 | 3.254 (1.054–10.048) | 0.040 |
| post-RA caIMR | 1.018 (0.973–1.066) | 0.441 | ||
| post-RA caIMR |
3.592 (1.269–10.166) | 0.016 | 2.834 (0.958–8.386) | 0.060 |
| RA, rotational atherectomy; OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval; MI,
myocardial infarction; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; caIMR,
coronary angiography-derived index of microvascular resistance. The primary
outcome was a composite of TIMI flow | ||||
The aim of this study was to evaluate coronary microcirculation function
indicated by caIMR in patients undergoing RA. Our main findings are as follows:
(1) Post-RA caIMR, which indicates coronary microcirculation function, was
greater than pre-RA caIMR in the treated vessels. Patients with
It has been demonstrated that RA facilitates procedural success in treating calcified plaques, especially in complex ostial lesions and bifurcation lesions, which feature bulky plaque and unfavorable geometry for stent deployment [24, 25]. While there have always been concerns regarding microcirculatory dysfunction associated with RA, analyzing the CFR and coronary microvascular resistance using intracoronary Doppler guidewire has been considered to be the most reliable method for coronary microcirculation assessment [26, 27]. However, intracoronary Doppler guidewire is unavailable in current practice. The pressure-temperature wire-derived CFR is associated with variations in measurement and has unsatisfied reproducibility [9, 28]. The pressure-temperature wire-derived measurements of coronary microcirculation, indicated by IMR, seem impracticable with regard to real-world applicability, particularly when applied in urgent situations or complex PCI. Previous studies have demonstrated that caIMR is a feasible alternative for the evaluation of coronary microcirculatory function [14, 15, 16].
In the present study, post-RA caIMRs were significantly higher than pre-RA
caIMRs in the treated vessels. Nearly 1/8th of patients without demonstrated
microcirculatory dysfunction indicated by pre-RA caIMR
In our study, we observed that among patients without microcirculation
dysfunction reflected by pre-RA caIMR
Slow flow or no flow is not a rare phenomenon during RA, with reported rates
varying from 7–10% [32, 33]. The incidence of instant TIMI flow grade
In our adjusted analysis for various related variables, patients with maximum RA
time of each pass had a significantly increased risk of the primary outcome.
Prolonged rotational duration does not necessarily confer beneficial effects,
which is consistent with a prior report which found that adopting an aggressive
RA strategy did not offer advantage, and was sometimes even detrimental [35].
Notably, our study revealed that pre-RA caIMR
This study has several limitations. First, this was a single-center
retrospective observational study, and the lack of a control group weakened the
strength of the study’s implications. However, we performed a self-control
analysis and measured caIMR in the reference vessels. Second, the decision to
perform RA was at the discretion of the interventionist, and there was sustained
improvement in the RA techniques across the cases. Thus, the results of our study
should be interpreted with caution. Third, as the caIMR measurement was related
to Pd
There were significant changes in the coronary microcirculation function of the
target vessel after receiving RA, as indicated by a increase in post-RA caIMR
compared with pre-RA caIMR. Post-RA TIMI flow grade
RA, rotational atherectomy; caIMR, coronary angiography-derived index of microvascular resistance; PCI, percutaneous coronary intervention; CFR, coronary flow reserve; CMR, coronary microvascular resistance; IMR, index of microvascular resistance; ACS, acute coronary syndrome; PPAE, peri-procedural adverse event; MI, myocardial infarction; rpm, revolutions per minute; TIMI, thrombolysis in myocardial infarction; cTn, cardiac troponin; CFD, computational fluid dynamics; MAP, mean aortic pressure.
Study conception and design—H-PZ, HA. Acquisition of data—H-PZ, XP, LL, G-DT, YZ, G-JY, N-XZ, F-CS. Analysis and interpretation of data (e.g., statistical analysis, computational analysis)—HL, XP, H-PZ, HA. Writing, review, and/or revision of the manuscript—HL, XP, Y-DF, H-PZ. Study supervision—H-PZ. All authors contributed to editorial changes in the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
The study was approved by the institutional Ethics Committee (Approval No. 2019BJYYEC-021-02), all patients signed informed consent to undergo coronary angiography and the intervention procedure. Because data on caIMR were collected retrospectively, informed consent on the use of caIMR was waived given the institutional ethics regulations with regard to observational study nature.
Not applicable.
The present study was supported by National High Level Hospital Clinical Research Funding (BJ-2018-201), Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences (Grant Number 2021-I2M-C&T-A-019), and Beijing Municipal Science & Technology Commission, Administrative Commission of Zhongguancun Science Park (Grant Number Z211100002921008).
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Publisher’s Note: IMR Press stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.