1 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, 215004 Suzhou, Jiangsu, China
2 Department of Chinese Medicine, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, 215004 Suzhou, Jiangsu, China
3 Department of Ultrasonography, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, 215004 Suzhou, Jiangsu, China
†These authors contributed equally.
Academic Editor: Michael H. Dahan
Abstract
Background: We speculated that stimulating the uterine cervix of patients may increase blood flow resistance of the uterine artery more significantly in women with endometriosis than those without. Accordingly, the resistance index (RI) of the uterine artery following stimulation of the cervix may offer a novel and promising non-invasive method for diagnosing endometriosis. In this prospective study, the aim was to determine the performance of the uterine artery resistance index (RI) following stimulation of the cervix in the diagnosis of endometriosis. Methods: This prospective cohort study included 270 patients with non-uterine diseases who were scheduled for laparoscopic surgery. Each patient underwent Doppler sonography for peak systolic velocity (PSV), end diastolic velocity (EDV), and RI before and after stimulation of the cervix, in addition to conventional ultrasound examination one day prior to laparoscopic surgery. The cervix was stimulated using a double convex array electronic vaginal probe for real-time tissue elastography. Results: Laparoscopic surgical evaluation revealed endometriosis in 91 (33.7%) patients. Following stimulation of the cervix, the RI of the uterine artery was significantly increased in the endometriosis group (p = 0.00), but no significant increase in the RI was observed in the control group (p = 0.45). The sensitivity and specificity of the post-stimulation RI for diagnosing endometriosis (using a cut off of 0.83) were 85.71% (95% confidence interval (CI): 76.45–91.88) and 88.83% (95% CI: 83.05–92.87), respectively. For peritoneal endometriosis (PEM), sensitivity and specificity were 86.96% (95% CI: 65.33–96.57) and 88.83% (95% CI: 83.05–92.87), respectively. The sensitivity and specificity of transvaginal ultrasonography (TVU) for diagnosing endometriosis were 63.74% (95% CI: 52.93–73.37) and 94.41% (95% CI: 89.68–97.14), respectively. The positive rate for TVU in diagnosing all endometrioses was 63.7%, and this was lower than that for the post-stimulation RI (84.6%, p = 0.001). Conclusions: Stimulation of the cervix leads to a significant decrease in uterine blood perfusion in women with endometriosis. TVU is a sensitive and specific method for the diagnosis of endometrioma, while the RI is a more sensitive parameter for diagnosing PEM than TVU. For the diagnosis of endometriosis, especially for PEM, the post-stimulation RI may prove to be a promising non-invasive diagnostic technique.
Keywords
- transvaginal ultrasonography
- cervix stimulation
- resistance index
- diagnosis
- endometriosis
Edometriosis is a disease characterized by the presence of endometrium-like epithelium and/or stroma outside the endometrium and myometrium, usually with an associated inflammatory process [1], and is classified according to the implant site: peritoneal endometriosis (PEM), ovarian endometriosis (OEM), deep infiltrating endometriosis (DIE), and other endometriosis types. The main symptoms of endometriosis, such as dysmenorrhea, infertility, dyspareunia, and chronic pelvic pain, are not specific [1]. As a result, it may take between 8 and 12 years before a patient receives a definitive diagnosis and starts treatment [2].
Transvaginal ultrasonography (TVU) is considered to be the most effective non-invasive method for the diagnosis of endometriosis [3, 4]. It is highly sensitive and specific for diagnosing OEM but has limited diagnostic value in PEM and DIE [5]. Given that PEM does not have any typical ultrasound imaging features, these patients are usually diagnosed by visual inspection of the pelvis at laparoscopy [6]. However, laparoscopy cannot be used as a routine screening method for endometriosis as it is expensive and invasive [7]. Consequently, an accurate non-invasive diagnostic method for PEM is urgently needed.
Excessive uterine activity has been reported in women with endometriosis [8, 9] expressed as more intensive myometrium contractions and higher intrauterine pressure when the uterus was stimulated by external factors than occurs in women without endometriosis [10, 11]. Intensive contractions of the myometrium decrease uterine blood perfusion [12]. In our clinical practice with laparoscopic surgery, we have found that the uterus of a patient with endometriosis becomes pale and inflexible immediately after the uterine manipulator is set in place. Thus, we speculated that stimulating the uterine cervix of patients may increase blood flow resistance of the uterine artery more significantly in women with endometriosis than those without. Accordingly, the resistance index (RI) of the uterine artery following stimulation of the cervix may offer a novel and promising non-invasive method for diagnosing endometriosis. Combined with TVU, the post-stimulation RI may therefore prove to be a sensitive tool in endometriosis diagnosis.
In this prospective study, the aim was to delineate the hemodynamic changes of uterine artery blood flow on stimulation of the cervix and to determine the performance of the post-stimulation RI in diagnosing endometriosis in women who were scheduled for laparoscopic surgery.
This prospective study enrolled patients who were scheduled for laparoscopic
surgery between August 1, 2015 and December 31, 2017 at the Department of
Gynecology of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University. Major
inclusion criteria were: women aged between 20 and 50 years with a sexual
history, regular menstrual cycles (21–35 days), and non-uterine gynecological
diseases requiring laparoscopic surgery. Major exclusion criteria were: the
presence of uterine diseases (myoma or adenomyosis), use of an intrauterine
device (IUD), an irregular menstrual cycle (
The study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committees of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University. All patients provided written informed consent. The study was registered at the Chinese Clinical Trial Registry (ChiCTR-DCD-15006719).
Laparoscopic surgery was conducted by two experienced surgeons between days five and seven of the menstrual cycle. During surgery, the abdominal and pelvic cavity were thoroughly examined in the following order: the left pelvic cavity, the anterior pelvic cavity, the right pelvic cavity, the right abdominal cavity, the diaphragmatic surface, the left abdominal cavity, the rectouterine fossa, the mesentery, the intestinal surface, the uterine surface, the ovaries, and finally the fallopian tubes. All clinical pathological types were carefully recorded including PEM, OEM, DIE, and other endometriosis types. The discovery of ectopic lesions during gynecological laparoscopic surgery confirmed the diagnosis of endometriosis with or without histological confirmation. All endometriotic foci were surgically removed.
On the day before laparoscopic surgery, Color Doppler sonography was performed
using a Hitachi EUB-7500 Ultrasound machine (Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan) with a
conventional transabdominal probe and a double convex array electronic biplane
rectal/vaginal probe. All measurements were taken by the same sonographer between
14:00 and 17:00 and between days five and seven of the menstrual cycle. Patients,
sonographers and gynecologists were all blinded to the patient data. The
sonographer started with color Doppler flow imaging (CDFI) and measured the
parameters of the uterine artery using transabdominal sonography prior to
stimulation of the cervix. A 3.5–5 MHz transducer was used with a wall filter
less than 100 Hz to reduce low frequency noise signals. Pulse repetition was at
7000 Hz and the sampling volume was 3 mm: equal to the internal diameter of the
uterine arteries. The uterine artery was identified as it passed lateral to the
uterus at the level of the internal os and then the probe angle was adjusted to
detect the maximum color intensity and amplitude. The angle between the acoustic
beam and the direction of flow was close to 0
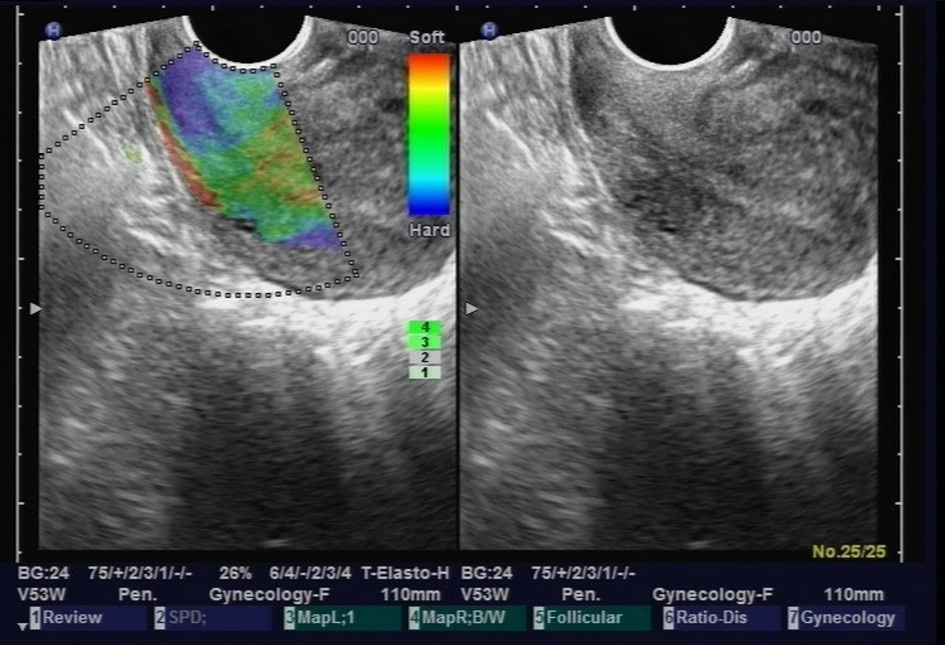
The end-fire ultrasound probe was used to stimulate the uterine cervix in the real-time tissue elastography mode. The probe was gently set perpendicular to the surface of the cervix and then pressure, set at stage 4 (3.7 N), was applied (see Fig. 1). Compression and decompression were then repeated 240 times/minute for 30 seconds in order to gain a stable frequency spectrogram. Once this had been acquired continuously for 3–5 cardiac cycles, the Doppler parameters of the uterine artery were measured within 10 minutes of stimulation of the cervix. The mean value of each parameter for three cardiac cycles was reported. In addition, only data from the right uterine artery was reported given that there was no statistical difference in Doppler parameters between the left and right uterine artery (data not shown).
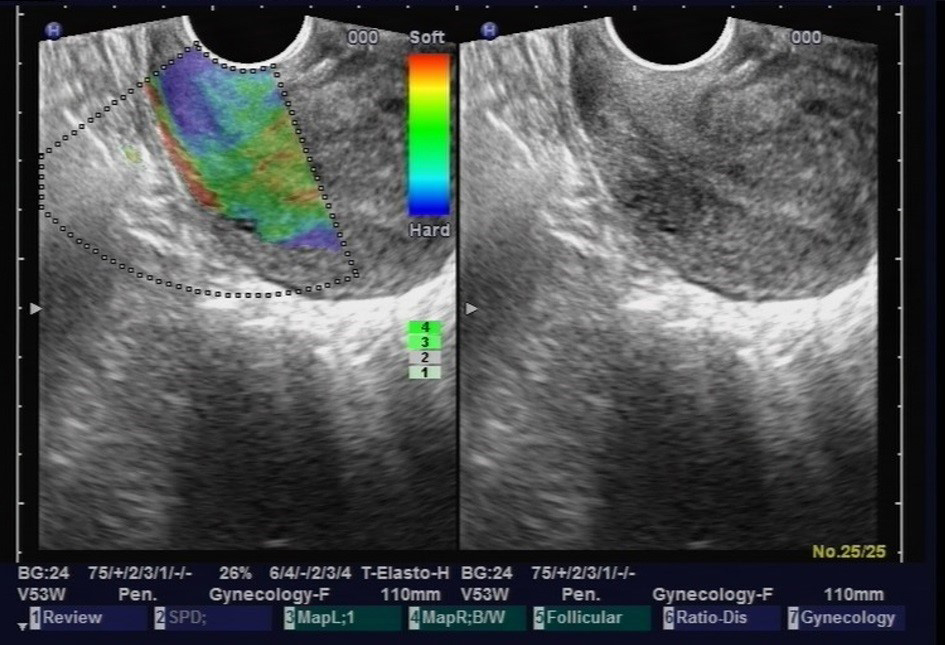 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.Cervical elastic ultrasound.
Immediately following the hemodynamic study of the uterine artery, the uterus, the adnexa, the vagina, the recto-vaginal space, the uterosacral ligaments, the recto-sigmoid, and the urinary bladder were examined using dimensional TVU during a standard ultrasound examination. The presence of a unilocular cyst with homogeneous low-level echogenicity (ground-glass echogenicity) or deep nodules provided a sonographic diagnosis of endometriosis [13].
The SPSS 19.0 software package (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) was used for data
analysis. The Kolmogorov–Smirnov test was used for testing normality. For
normally distributed data, an independent samples t-test was used for
analyzing the differences between the endometriosis group and the control group. The Mann–Whitney U test was used in cases of
non-normally distributed data. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves of
the RI were obtained along with areas under the curve (AUC) and the 95% CI, and
these were analyzed using the Hanley–McNeil nonparametric method. The ROC cutoff
value was chosen by maximizing the sum of the sensitivity and specificity.
Sensitivity, specificity, the positive and negative predictive values (calculated
based on the prior probability of 0.30), the positive and negative likelihood
ratios (conventional), and the 95% CI were calculated using Clinical Calculator
1 [14] after choosing the optimal cutoff. The Kappa test was used as a
consistency test, and the McNemar test was used as a test of significance. A
value of p
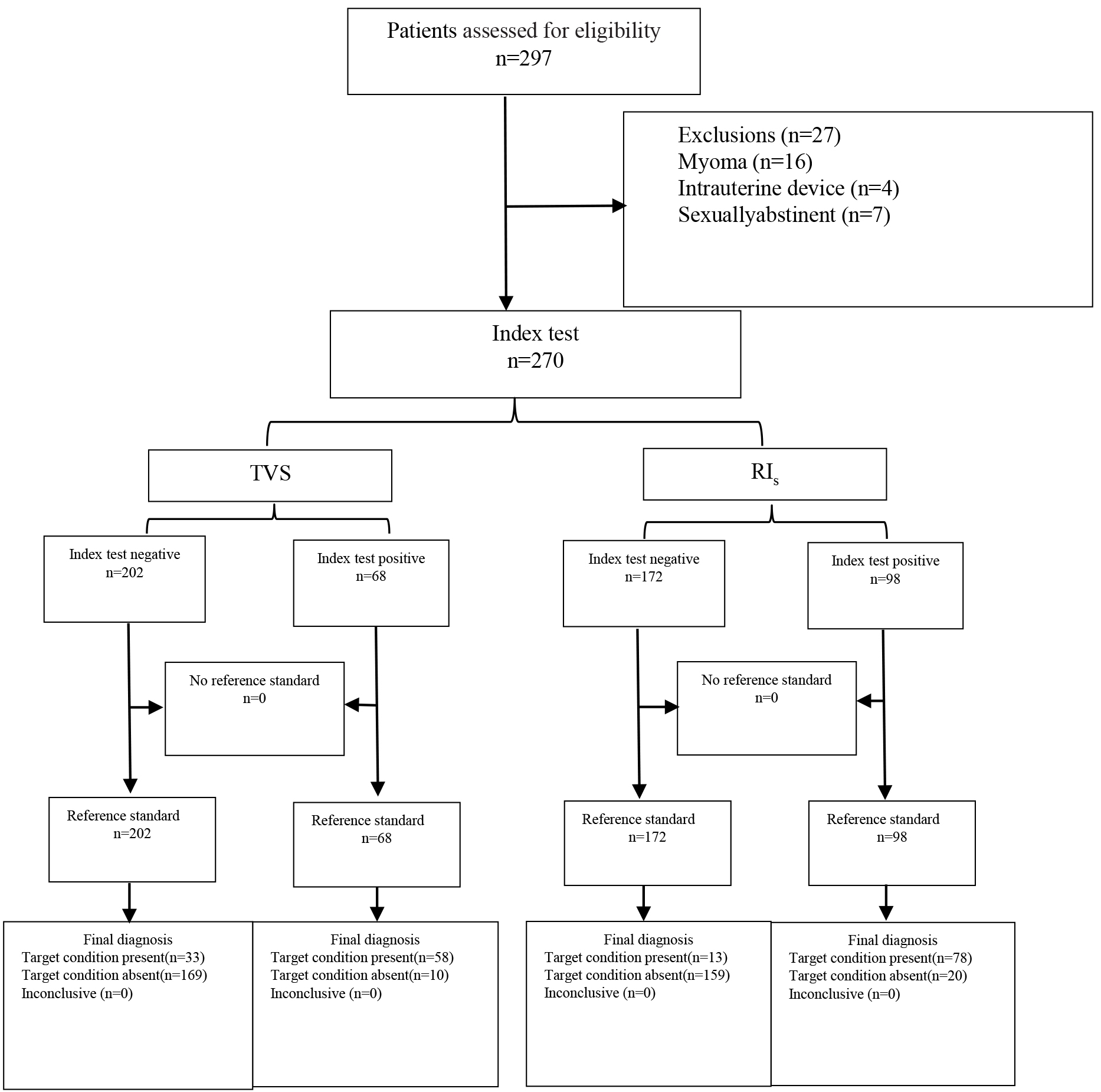
The study flowchart is shown in Fig. 2. A total of 297 patients were screened for eligibility. No patient reported pain or any other discomfort during the ultrasound examination. Twenty-seven patients were excluded due to the following reasons: 16 had myoma, 4 used an IUD, and 7 were sexually abstinent. A total of 270 patients were enrolled. Ninety-one (33.7%) patients were diagnosed with endometriosis during gynecological laparoscopic surgery. They included 23 (25.3%) cases of PEM, 51 (56.0%) cases of OEM, and in 17 (18.7%) cases a compound type of endometriosis was present: PEM + OEM in 7 cases, PEM + DIE in 2 cases, OEM + DIE in 3 cases, and PEM + OEM + DIE in 5 cases (Table 1).
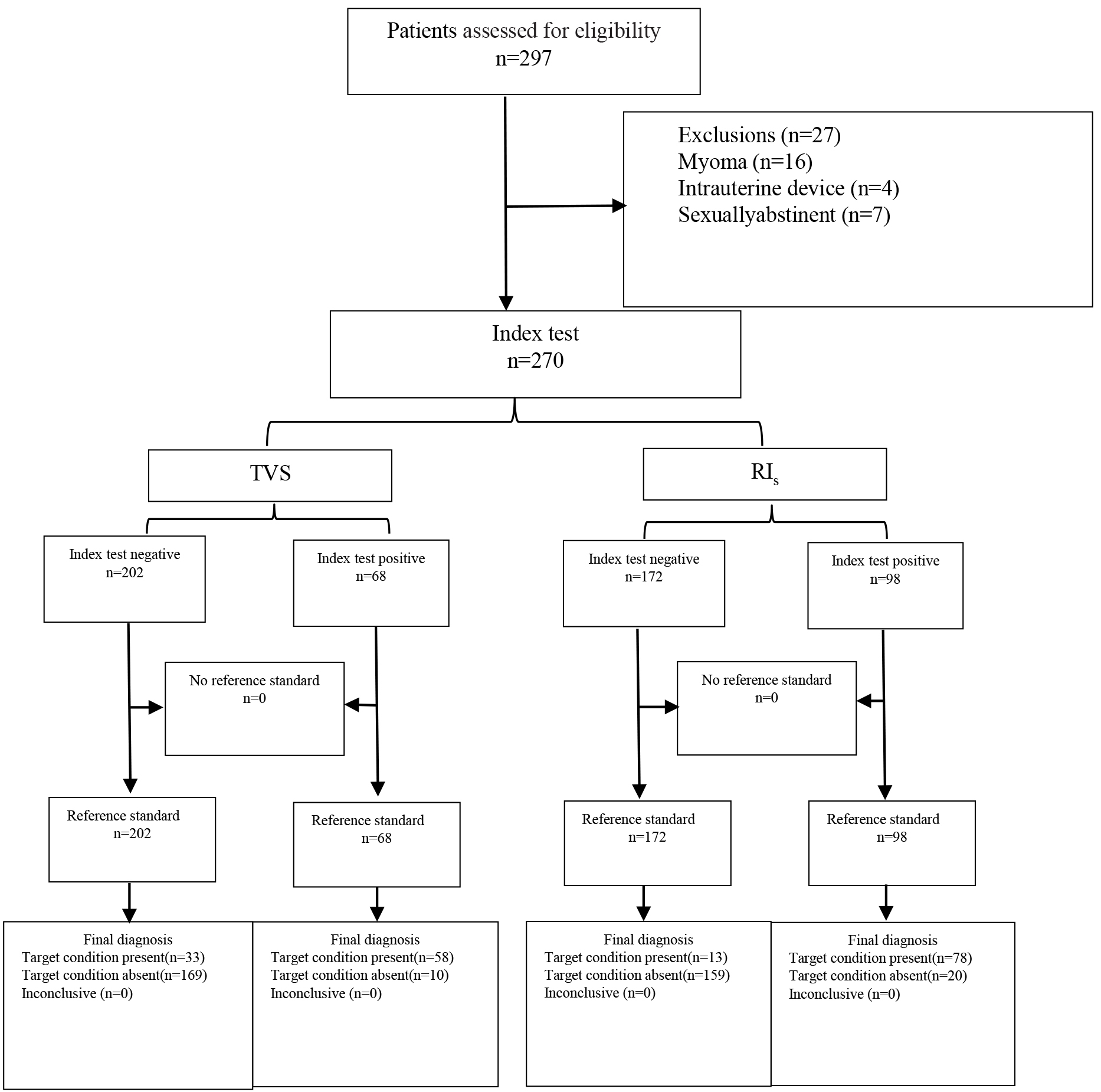 Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.The study flowchart.
| Postoperative Diagnosis (Preoperative diagnosis by TVS) | Endometriosis | Non-endometriosis | Total | ||||||||
| PEM | OEM | DIE | CEM | Benign ovarian tumor | Borderline or malignant ovarian tumor | Hydrosalpinx | Infertility | Inflammatory mass | |||
| Endometriosis | PEM | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| OEM | 0 | 45 | 0 | 10 |
6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 63 | |
| DIE | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| CEM | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | |
| Non-endometriosis | Pelvic cyst | 17 |
6 |
0 | 0 | 148 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 176 |
| Infertility | 6 |
0 | 0 | 2 |
0 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 16 | |
| Other | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 10 | |
| Total | 23 | 51 | 0 | 17 | 154 | 5 | 10 | 8 | 2 | 270 | |
| Note: 91 patients (the endometriosis group) were confirmed to have
endometriosis during gynecological laparoscopic surgeries and 179 patients (the
control group) were confirmed to have no endometriosis. | |||||||||||
One hundred seventy-nine (66.3%) patients did not have endometriosis. They included 54 cases of teratoma, 48 cases of serous cyst endometrioma, and in 77 cases other diseases were present.
The demographics and baseline characteristics of the study population are shown
in Table 2. Demographic and baseline variables were comparable between the two
groups (p
| Variables | Control | Endometriosis | p value |
| No. | 179 | 91 | |
| Mean age, years (SD) | 37.35 (6.80) | 36.27 (5.56) | 0.19 |
| Mean BMI, kg/m2 (SD) | 22.95 (2.12) | 23.33 (2.25) | 0.40 |
| Median number of pregnancies (IQR) | 1 (2) | 2 (2) | 0.15 |
| Median number of term pregnancies (IQR) | 1 (1) | 1 (2) | 0.32 |
There was no statistical difference in PSV between the control group and the endometriosis group prior to stimulation of the cervix (p = 0.73, see Table 3). The PSV in the endometriosis group was significantly lower following stimulation of the cervix as compared with before stimulation and was comparable with the PSV in the control group after stimulation (p = 0.00 for both).
| Parameters | Control (n = 179) | Endometriosis (n = 91) | p value |
| PSV | |||
| Non-stimulated | 49.30 (38.00) | 59.00 (15.40) | 0.73 |
| Stimulated | 54.80 (32.00) | 47.10 (15.00) | 0.00 |
| EDV | |||
| Non-stimulated | 13.00 (8.80) | 7.30 (6.90) | 0.00 |
| Stimulated | 14.70 (12.80) | 1.10 (6.00) | 0.00 |
| RI | |||
| Non-stimulated | 0.76 (0.17) | 0.87 (0.12) | 0.00 |
| Stimulated | 0.75 (0.14) | 0.97 (0.11) | 0.00 |
| PI | |||
| Non-stimulated | 1.65 (0.74) | 1.64 (0.56) | 0.98 |
| Stimulated | 1.72 (0.76) | 1.65 (0.71) | 1.00 |
| Note: | |||
EDV in the endometriosis group was significantly lower than that of the control
group prior to stimulation of the cervix (p = 0.00). Following
stimulation, there was a significant reduction in the EDV in the endometriosis
group (p = 0.00 vs. before stimulation) while no such significant
decline was observed in the control group (p = 0.11). The RI of the
uterine artery in the endometriosis group was significantly higher than that of
the control group both before and after stimulation of the cervix (p =
0.00 for both, see Fig. 3). The RI of the uterine artery increased significantly
in the endometriosis group after stimulation of the cervix (p = 0.00 vs.
before stimulation), but no significant increase in RI was observed in the
control group after stimulation (p = 0.45 vs. before stimulation). No
significant differences were observed in the PI between the endometriosis group
and the control group both before and after stimulation of the cervix (p
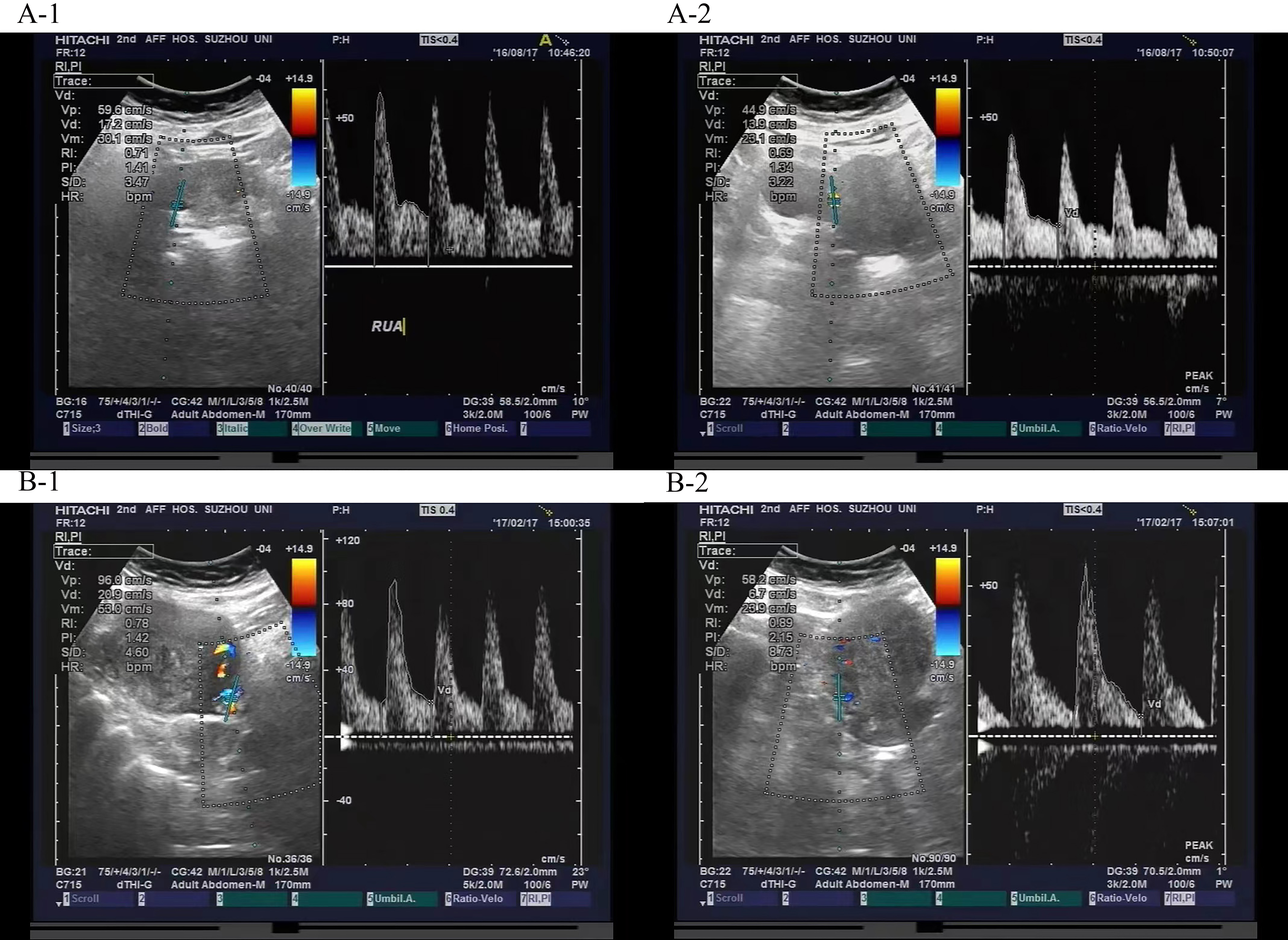
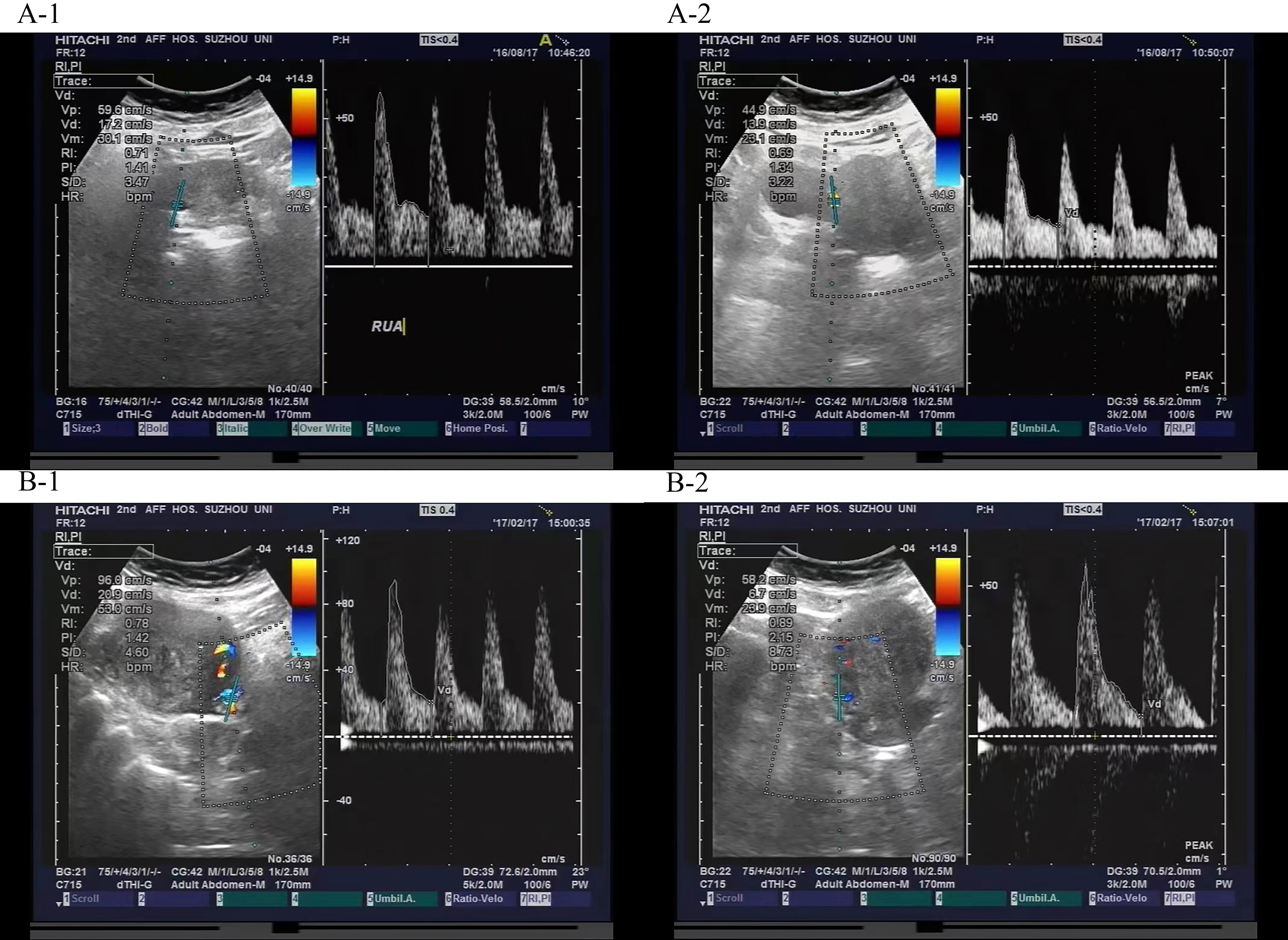 Fig. 3.
Fig. 3.Hemodynamic parameters of the uterine artery in patients with or without endometriosis before and after stimulating the cervix. (A) In patients with no endometriosis: before stimulating the cervix, the hemodynamic parameters were PSV 59.6 cm/s, EDV 17.2 cm/s, RI 0.71 (A-1); after stimulating the cervix, the hemodynamic parameters were PSV 44.9 cm/s, EDV 13.9 cm/s, RI 0.69. There was no significant difference of EDV, PSV and PI between before and after stimulating the cervix (A-2). (B) A representative case of PEM: before stimulating the cervix (B-1), the hemodynamic parameters were PSV 96.0 cm/s, EDV 20.9 cm/s, RI 0.78, respectively; after stimulating the cervix, the uterine artery perfusion resistance significantly increased, PSV 58.2 cm/s, EDV 6.7 cm/s, RI 0.89 (B-2).
The AUC for the RI following stimulation of the cervix was 0.93 (95% confidence interval (CI): 0.89–0.96) and this was significantly higher than that for the RI prior to stimulation (0.79; c: 0.73–0.84, p = 0.00). The diagnostic value of the post-stimulation RI was further analyzed and it was found that, with a cut off of 0.83, the sensitivity and specificity for diagnosing all types of endometriosis were 85.71% (95% CI: 76.45%–91.88%) and 88.83% (95% CI: 83.05%–92.87%), respectively. In addition, in the diagnosis of PEM, sensitivity and specificity of the post-stimulation RI were 86.96% (95% CI: 65.33%–96.57%) and 88.83% (95% CI: 83.05%–92.87%), respectively. When the post-stimulation RI was used for the diagnosis of OEM, the sensitivity and specificity were 84.31% (95% CI: 70.86%–92.52%) and 88.83% (95% CI: 83.05%–92.87%), respectively. When the post-stimulation RI was used for the diagnosis of compound endometriosis (CEM), the sensitivity and specificity were 88.24% (95% CI: 62.25%–97.94%) and 88.83% (95% CI: 83.05%–92.87%), respectively.
Endometriosis was diagnosed by TVU prior to surgery in 58 (63.73%) of 91 patients with confirmed endometriosis. The sensitivity and specificity of TVU in diagnosing endometriosis were 63.74% (95% CI: 52.93%–73.37%) and 94.41% (95% CI: 89.68%–97.14%), respectively. The sensitivity and specificity of TVU for diagnosing PEM were 0.00% (95% CI: 0.00%–17.81%) and 94.41% (95% CI: 89.68%–97.14%), respectively. When TVU was used for diagnosing OEM, the sensitivity and specificity were 88.24% (95% CI: 75.44%–95.13%) and 94.41% (95% CI: 89.68%–97.14%), respectively. When TVU was used for diagnosing CEM, the sensitivity and specificity were 88.24% (95% CI: 62.25%–97.94%) and 94.41% (95% CI: 89.68%–97.14%), respectively (see Table 4).
| 1,Parameters | Sensitivity % (95% CI) | Specificity % (95% CI) | PPV (95% CI) | NPV (95% CI) | PLR (95% CI) | NLR (95% CI) | Kappa (95% CI) |
| RI | |||||||
| ALL | 85.71 (76.45–91.88) | 88.83 (83.05–92.87) | 0.36 (0.31–0.0.42) | 0.64 (0.58–0.69) | 7.67 (5.03–11.69) | 0.16 (0.10–0.27) | 0.73 (0.65–0.82) |
| PEM | 86.96 (65.33–96.57) | 88.83 (83.05–92.87) | 0.20 (0.15–0.26) | 0.80 (0.74–0.85) | 7.78 (5.00–12.11) | 0.15 (0.05–0.42) | 0.57 (0.39–0.72) |
| OEM | 84.31 (70.86–92.52) | 88.83 (83.05–92.87) | 0.27 (0.22–0.34) | 0.73 (0.66–0.78) | 7.55 (4.91–11.60) | 0.18 (0.09–0.33) | 0.68 (0.56–0.79) |
| CEM | 88.24 (62.25–97.94) | 88.83 (83.05–92.87) | 0.18 (0.13–0.24) | 0.82 (0.76–0.87) | 7.90 (5.05–12.36) | 0.13 (0.04–0.49) | 0.52 (0.32–0.70) |
| TVS | |||||||
| ALL | 63.74 (52.93–73.37) | 94.41 (89.68–97.14) | 0.25 (0.20–0.31) | 0.75 (0.69–0.80) | 11.41 (6.13–21.25) | 0.38 (0.29–0.50) | 0.62 (0.50–0.73) |
| PEM | 0.00 (0.00–17.81) | 94.41 (89.68–97.14) | 0.05 (0.02–0.91) | 0.95 (0.91–0.97) | 0.00 (0.00–NaN) | 1.06 (1.06–1.06) | 0.07 (0.04–0.11) |
| OEM | 88.24 (75.44–95.13) | 94.41 (89.68–97.14) | 0.24 (0.19–0.30) | 0.76 (0.70–0.81) | 15.79 (8.58–29.08) | 0.12 (0.05–0.26) | 0.80 (0.71–0.88) |
| CEM | 88.24 (62.25–97.94) | 94.41 (89.68–97.14) | 0.13 (0.09–0.18) | 0.87 (0.82–0.91) | 15.79 (8.44–29.56) | 0.12 (0.03–0.46) | 0.68 (0.48–0.84) |
| Note: PEM 23, OEM 51, DIE 0, CEM 17 (PEM + OEM 7, PEM + DIE 2, OEM + DIE 3, OEM + DIE + DIE 5). | |||||||
The consistency and differences between the results of the post-stimulation RI and TVU were further analyzed. In the diagnosis of all endometriosis types, the positive rate when using TVU and the post-stimulation RI was 63.7% and 84.6%, respectively (p = 0.001), and the Kappa value was 0.159 (p = 0.077). For PEM alone, the positive rate of using TVU and the post-stimulation RI was 0.000% and 87.0%, respectively, and the Kappa value was 0 (p = 1.000). For OEM alone, the positive rate of using TVU and the post-stimulation RI was 88.2% and 84.3%, respectively (p = 0.754), and the Kappa was 0.175 (p = 0.206). For CEM alone, the positive rate of using TVU and the post-stimulation RI was 88.2% in both cases (p = 1.0), and the Kappa value was 0.133 (p = 0.582).
This study has shown that the post-stimulation RI of women with endometriosis was significantly higher than that of women without endometriosis (p = 0.00). The post-stimulation RI was an effective index for diagnosing endometriosis, especially for PEM, while TVU was an effective method for diagnosing OEM.
Serum CA125 has been the most valuable index used in the diagnosis of endometriosis. However, it still cannot serve as a routine screening index as only a small proportion of patients with advanced endometriosis have an elevated CA125 [15, 16]. TVU is currently the most effective method for the diagnosis of endometriosis, especially for OEM [3]. It is the preferred imaging modality for evaluation of adnexal masses as it correctly characterizes most adnexal masses solely based on gray scale and power or color Doppler features [17]. However, it still has limited diagnostic sensitivity for PEM and in endometriosis where cysts are less than 2 cm [18]. In this study, 58 of the 91 patients (63.73%) were diagnosed with endometriosis by TVU prior to surgery, including 2 patients with endometrioma 2 cm in size, and the proportion of patients diagnosed by TVU prior to surgery is similar to other reports in the literature [19, 20, 21]. Although the specificity for TVU in diagnosing endometriosis is as high as 94.4%, the sensitivity is still somewhat limited at 63.7%.
Transabdominal and transvaginal CDFI are important methods for evaluating uterine blood perfusion [22, 23]. The uterine artery blood flow parameters are affected by many factors including benign and malignant uterine tumors [24], intrauterine adhesions [25], IUDs [26], the menstrual cycle [27], sex hormones [28], cerebrovascular disease [29], vasoactive drugs [30], and other factors [31]. This study included women of childbearing age with no uterine diseases in order to ensure reproducibility and stability of the results. All ultrasound examinations were performed between days five and seven of the menstrual cycle. In addition, all the uterine artery hemodynamic parameters were transabdominally determined in order to avoid stimulation of the cervix, thus allowing these parameters to be ascertained under quiescent conditions. It was found that the RI of the endometriosis group prior to stimulation of the cervix was significantly higher than that of the control group. This indicated that blood flow resistance in patients with endometriosis was higher than that of controls, and this is consistent with previous reports [8, 10]. This may be due to the fact that under quiescent conditions, the frequency and intensity of uterine contractions in women with endometriosis is higher than in normal women, and uterine artery blood perfusion is lower [27, 31]. More importantly, stimulation of the cervix significantly reduced the uterine artery diastolic blood flow of women with endometriosis and even caused the disappearance of EDV. Following stimulation of the cervix, the RI increased both in the endometriosis group and the control group, but the increase seen in the endometriosis group was significantly higher than in the control group. This demonstrates that uterine activity is greater in women with endometriosis as compared with women without the disease [8, 9].
In this study, the post-stimulation RI demonstrated its value in the diagnosis of endometriosis (AUC = 0.93) with a sensitivity and specificity of 85.71% and 88.83%, respectively. Most importantly, the sensitivity of the post-stimulation RI for the diagnosis of PEM was 86.96%, and this was significantly higher than that for TVU (0.00%). In OEM and CEM, the diagnostic value of the post-stimulation RI and TVU was similar. This result shows that the post-stimulation RI is a more sensitive parameter than TVU in the diagnosis of PEM.
This study did not include patients with uterine lesions. The diagnostic value of post-stimulation RI in women with endometriosis and uterine lesions needs further study. In addition, in order to accurately compare the effect of stimulation of the cervix on uterine blood flow, TVU was used to detect uterine artery blood flow, while it is simpler and more convenient to use TVU to measure uterine artery blood flow in the future.
This study shows that following stimulation of the cervix, the decrease in uterine blood perfusion in patients with endometriosis is significantly greater than that in the control group, although the cause is still unknown.
In conclusion, stimulation of the cervix leads to a significant decrease in uterine blood perfusion in women with endometriosis. TVU is a sensitive and specific method for the diagnosis of endometrioma, while post-stimulation RI is a more sensitive parameter than TVU for the diagnosis of PEM. Post-stimulation RI may be a promising non-invasive diagnostic technique for the diagnosis of endometriosis, especially for PEM.
We declared that materials described in the manuscript, including all relevant raw data, will be freely available to any scientist wishing to use them for non-commercial purposes, without breaching participant confidentiality. The datasets used and analysed during the current study available from the corresponding author.
Conception and design of the research—Q-ZR, QM, S-HJ, HS, YW. Acquisition of data—QM, Y-MJ, S-HJ, YW. Analysis and interpretation of the data—Q-ZR, YW. Statistical analysis—M-FS, YX. Obtaining financing—Q-ZR, HS, S-HJ. Writing of the manuscript—Q-ZR, YW. Critical revision of the manuscript for intellectual content—Q-ZR, YW. All authors read and approved the final draft.
This study was conducted with approval from the Ethics Committee of The Second Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University (approval number: 110). This study was conducted in accordance with the declaration of Helsinki. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants.
We would like to acknowledge the hard and dedicated work of all the staff that implemented the intervention and evaluation components of the study.
This work was supported by The National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81270678), Suzhou science and technology planning project (No. SS201633, SYSD2019106, SYS2020134), The Jiangsu Provincial Commission of Health and Family Planning (No. F201922), Suzhou Wumen medical school research special scientific research fund (No. SKJYD2021190).
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Publisher’s Note: IMR Press stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.