1 Department of Surgery, Breast Unit, DAME, University Hospital of “Santa Maria della Misericordia'', 33100 Udine, Italy
2 Ennergi Research (non-profit organisation), 33050 Lestizza, Udine, Italy
3 Academic Unit of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Department of Neuroscience, Rehabilitation, Ophthalmology, Genetics, Maternal and Infant Health, University of Genoa, 16132 Genova, Italy
4 Clinic of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Department of Medical Area, Academic Hospital of Udine, University of Udine, 33100 Udine, Italy
†These authors contributed equally.
Academic Editor: Michael H. Dahan
Abstract
Objective: Breast-conserving surgery (BCS) experienced a significant surge during the last decades due to the increase of early breast cancer detection. Central to the discussion is margin adequacy which represents one of the most significant predictive factors for local relapse. This paper aims to shed light on the problem of margins in breast surgery. Mechanism: We performed a systematic narrative review of the literature by conducting a search using Medline/PubMed, Scopus, and Embase. The following keywords were considered: “breast-conserving surgery” AND “margins”/“margin”. Findings in Brief: In the case of invasive breast cancer, “no ink on tumor” can be considered an adequate margin, while for ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), a distance of 2 mm from tumor should be obtained. Many novel tools have been developed based both on the latest radiological imaging techniques and on the tissue expression of certain markers, with the aim of precise navigation of tumor excision and intraoperative evaluation of cavity excision margins. Oncoplastic surgery can be considered oncologically safe while improving the cosmetic outcome and patients’ quality of life. The appropriate use of adjuvant treatments in the context of a multidisciplinary and personalized management of breast cancer is the only means to omit a second intervention in some carefully selected cases. Conclusions: Debate still exists concerning the definition of adequate clear margin following BCS for DCIS. Further studies are required to better assess multimodal treatment approaches in this condition.
Keywords
- breast-conserving surgery
- ductal carcinoma in situ
- margins
- oncoplastic breast surgery
- radiation therapy
Breast conservation is an increasingly important goal in breast cancer surgery. In fact, in addition to gaining quantity of life, modern oncology also aims to improve the quality of life of the patients it manages. As a consequence, starting from the 1990s, we have witnessed an increasingly conservative approach both at the breast and the axilla.
The considerable diffusion of conservative surgery of the breast (lumpectomy and quadrantectomy) and of the armpit (sentinel lymph node biopsy) has certainly been favored since the increase in the early diagnosis of breast cancer, especially after the worldwide introduction of systematic mammography screening programs [1, 2, 3, 4]. However, an important role has also been played by the implementation of adjuvant and neoadjuvant therapies. In fact, the recognition of breast cancer as a systemic disease has led the scientific community to develop and refine a multimodal strategy for de-escalating treatments, reducing the tumor to margin distance, and maintaining oncologic safety.
For instance, complementary breast irradiation after conserving surgery has demonstrated its indisputable value in local tumor control and breast cosmesis [5, 6, 7], experiencing during the passing of time many evolutionary stages, such as the reduction of the irradiation field (partial breast irradiation) [8], and of the irradiation sessions (hypofractionation) [6, 9].
Furthermore, the greater use of neoadjuvant treatments (in part, thanks to the increase in clinical trials relating to preoperative chemotherapy and radiotherapy), and the greater success of these treatments in terms of clinical response, have encouraged increasingly conservative surgical indications [1, 10].
Unsurprisingly, breast conservation has led to a major debate regarding the adequacy of margins, understood as the minimum distance of the tumor from the borders of surgical resection. Such debate includes considerations on the different histotypes and on the possible risk factors for the presence of further foci of disease in the preserved breast, which could cause a future relapse of the disease. Accordingly, this review focuses on the role of margins and on the concept of margin adequacy, with particular regard to specific groups of patients, such as those affected by ductal carcinoma in situ, those treated with neoadjuvant therapies, and those who previously underwent breast-conserving surgery for oncological reasons.
We performed a narrative review of the literature. The narrative review was considered the most appropriate format, given our project’s broad and explorative aim. We conducted a search using Medline/PubMed, Scopus, and Embase, considering the following keywords: “breast-conserving surgery”, “conservative surgery”, “margins”, and “margin”. Details about the queries are reported in Table 1. Only full-text articles published in English between Jan 1, 1990, and Aug 8, 2022, were considered. Additional sources were also evaluated based on author experience, examination of the reference lists of the included articles, and different searches (Fig. 1).
| Database | Query | Date | Number of items |
|---|---|---|---|
| PubMed | (breast-conserving surgery OR (“conservative surgery” AND breast)) AND (margin*) | 08.08.2022 | 3056 |
| Scopus | TITLE-ABS-KEY((breast-conserving surgery OR (“conservative surgery” AND breast)) AND (margin*)) | 08.08.2022 | 2154 |
| EMBASE | AB,TI((breast-conserving surgery OR (“conservative surgery” AND breast)) AND (margin*)) | 08.08.2022 | 3241 |
 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.Flow-chart of study selection.
Publications were screened for title and abstract to assess their relevance. We managed references through Zotero (https://www.zotero.org/) and LibreOffice (https://www.libreoffice.org). We concentrated our search process on systematic reviews, meta-analyses, and randomized controlled trials. We chose articles based on their relevance and scientific merit. Scientific merit appraisal was established on full-text publication in peer-reviewed journals. The item relevance was based on the following compasses: pragmatism to enclose the most valuable articles to give a comprehensive overview starting from literature reviews; pluralism to include more perspectives as possible; contestation to examine conflicting data and debate arguments; and publication’s date to favor the most recent publications. Exclusion criteria were non-peer-reviewed items or retracted items. In case of disagreement about the included articles, a joint assessment of three senior authors was done, and an agreement was achieved.
Data from the included articles were assessed, including authors, publication year, type of article, metadata, setting, and findings. Data were collected in a predetermined form. Descriptive analysis and plots were done using R (version 4.2.1; R Core Team - 2022. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria - https://www.R-project.org/). The Scopus database was chosen for citation assessment because of the detailed citation counts and metadata. PubMed was selected for the publication time trend because whole counts of yearly included items were readily available.
A total of 8451 items were potentially suitable to answer the analysis question from the queried databases. Additionally, further 27 articles were selected from other sources. After removing duplicated and restricting for publication year, 4641 items remained. Titles and abstracts were screened, and 155 articles met the inclusion criteria. Details about the process are reported in Fig. 1.
All the included studies were published between 1990 and 2022 with peculiar
attention to the most recent publications in this field. According to the
preliminary analysis of the 4641 screened items, the annual growth rate of the
items was 8.53%. The top 5 contributing countries in Scopus were high-income
countries: the United States of America, Japan, Netherlands, United Kingdom,
Germany, and China. In Scopus, 80.9% of the items were full articles, 11.2%
reviews, and the other items were other types of documents such as conference
abstracts, book chapters, editorials, etc. Fig. 2 shows the annual incidence in
PubMed of the query results. From 1990 to 2001, there was a growing incidence of
articles in breast-conserving surgery resection margins. After that, a plateau
was achieved with a mean of 11.77 (
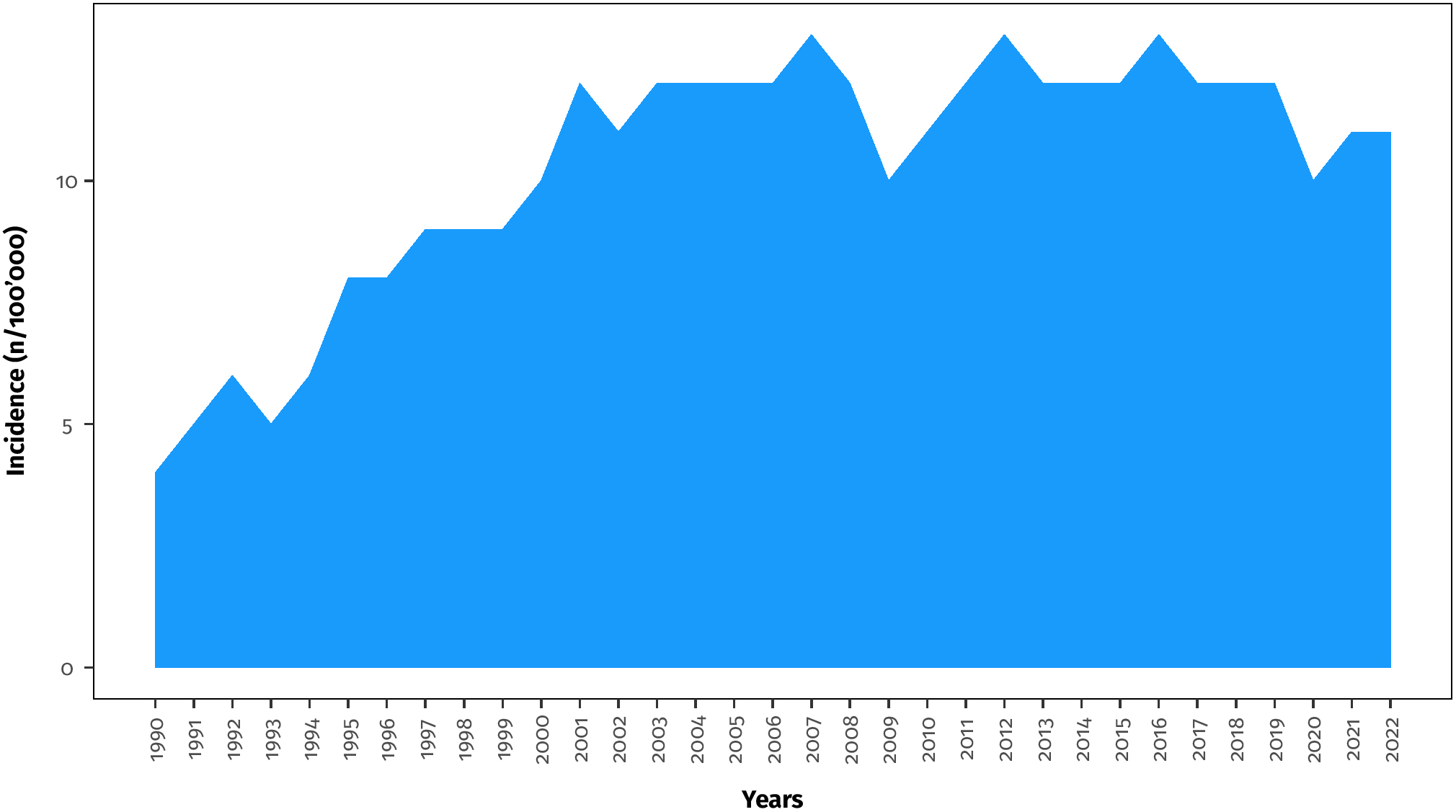 Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.The annual incidence of items in PubMed/Medline about margins in breast-conserving surgery. The annual incidence is reported as the number of items every 100,000 PubMed/Medline entries subdivided by year.
In the literature, “no ink on tumor” in invasive breast cancer was found to be an acceptable margin status [11, 12, 13]. Meanwhile, a distance of 2 mm from the tumor margin was considered adequate for ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) [13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18].
Table 2 shows the overview of the methods used in non-palpable tumors to mark and remove the area of interest in conservative breast surgery [19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28].
| Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Hook wire | Placement of a hook wire through the tumor, subsequently used to guide surgical excision. |
| ROLL (radio-guided occult lesion localization) | Injection of peritumoral radiocolloid before surgery used to localize the neoplastic lesion during surgery. |
| Intraoperative ultrasound guidance | Use of ultrasound imaging intraoperatively to locate non-palpable lesions and guide surgical removal. |
| Guiding-Marker System | Stainless steel hook connected to a magnetic marker used by a handheld device to better localize the tumor during excision. |
| MagSeed | Paramagnetic steel seed inserted at the tumor site and used to guide surgical excision. |
| LOCalizer radiofrequency identification system (RFID) | Insertion of a LOCalizer RFID tag by ultrasound guidance to better localize the tumor by a handheld device during tumor excision. |
| Intraoperative fluorescence detection | Intravenously systemic administration or local peritumoral administration of indocyanine green (ICG) to better localize the tumor by a handheld fluorescence detector during tumor excision. |
| SAVI-SCOUT localization system | The SAVI-SCOUT reflector is positioned under ultrasound or mammogram guidance using a 16-gauge introducer needle. The reflector can be localized by an infrared emitting handheld detector that also provides the distance from the reflector. |
Table 3 shows an overview of the methods developed to evaluation of cavity excision margins or the tissue specimen excised margins [29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56]. A growing number of devices were using radiomic, nanotechnology, mass spectrometry, spectroscopy, or optical signatures to improve the accuracy of margins assessment.
| Technique | Application | Description |
| Frozen section of surgical specimen | Ex-vivo | Intraoperative, histological, macroscopic and microscopic assessment of tumor-resected margins. |
| Surgical cavity margins shaving | Ex-vivo | Removal of cavity margins after tumor removal and subsequent histological assessment. |
| Intraoperative flow cytometry | Ex-vivo | Sample collection by margin brushing (tumor resected margins), fine-needle aspiration of the tumor, and peripheral blood sample. Tumor cells were identified using flow cytometry to compare the sample ploidy status with the control. |
| Intraoperative fluorescence imaging using a tumor specific exogenous agent (multiple approaches) | Ex-vivo, In-vivo | -Tumor specific agent delivered locally to the surgical specimen and subsequent imaging of the surgical specimen (e.g., enhancing acrolein, a product of oxidization reactions) [ex-vivo]. |
| -Imaging of the surgical specimen and imaging of the surgical cavity after systemic 5-ALA administration (ex-vivo and in-vivo in humans). | ||
| -Imaging of the surgical cavity after systemic pegulicianine fluorescence guided system administration (in-vivo in humans). | ||
| -Breast cancer mouse model in vivo assessment and imaging of the surgical specimen (using Hepatitis B Core virus-like particles modified with Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) capable of targeting angiogenesis-expressed proteins to deliver indocyanine green specifically to the tumor region). | ||
| -Cancer mouse model in-vivo and ex-vivo lesion localization by near infrared imaging using an exogenous nanotechnology agent. Pseudomonas aeruginosa azurin derived peptide p28 that specifically targets cancer cells was combined with indocyanine green. | ||
| ClearEdge (proprietary method) | Ex-vivo | This is a handheld portable imaging system based on bio-impedance spectroscopy sensitive to dielectric properties that allows to localize abnormal tissue at the margin of the tumor specimen (tumor resected margins). |
| Margin-Probe (proprietary method) | Ex-vivo | Based on dielectric spectroscopy, this measures the dielectric properties of a medium and allows to differentiate normal tissue from breast cancer up to 1mm depth and to assess the surgical specimen margin status. |
| Diffuse reflectance spectroscopy | In-vivo, Ex-vivo | Characterization of tumor tissue according to light tissue interactions (surgical specimen, ex-vivo, in-vivo, in humans). |
| Cancer diagnostic probe (proprietary method) | In-vivo | Handheld probe to detect hypoxia glycolysis in the surgical cavity (real-time, label-free, in-vivo, in humans). Specifically, the device records the Hydrogen Peroxide produced during pyruvate formation using carbon nanotubes-based electrodes. |
| MasSpec Pen (proprietary method) | Ex-vivo, In-vivo | Handheld mass spectrometry (in-vivo, in a porcine model). |
| ClearSight | Ex-vivo | Mobile magnetic resonance imaging system to assess intraoperatively the surgical specimen margins. |
| Nuclear magnetic resonance relaxometry | Ex-vivo | Assessment without spatial discrimination (no imaging) of T1 nuclear magnetic relaxation dispersion that is influenced by tissue composition (water/protein/lipids) and allows discrimination between cancer and normal tissue (ex-vivo) in the surgical specimen. |
| Magnetic particle imaging | In-vitro | Hypothesized model based on systemic injection of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle tracer specifically coated to target the breast tumor, actively allowing in-vivo monitor of tumor excision with free margins. |
| High frequency ultrasound | Ex-vivo | Pulsed high frequency (50 MHz) amplitude mode ultrasound of surgical specimen. |
| Photoacoustic imaging | In-vivo, Ex-vivo | This procedure is an imaging technique founded on the photoacoustic effect. Specifically, the non-ionizing laser pulses are delivered into biological tissue. Part of the energy is absorbed and converted into heat, leading to transient thermoelastic expansion, thus permitting ultrasonic emission. These ultrasonic waves are detected by ultrasonic transducers and converted into bidimensional images. The target of optical absorption can be: |
| - endogenous (e.g., hemoglobin). | ||
| - exogenous contrast agent (e.g., Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) tripeptide sequence functionalized melanin nanoparticles for targeting integrin |
Considering the evidence in the literature, oncoplastic surgery was found to have low recurrences while improving the cosmetic outcome and patients’ quality of life [10, 57, 58, 59, 60, 61, 62, 63, 64, 65, 66, 67].
Adjuvant treatments were introduced in the context of a multidisciplinary and personalized management of breast cancer. They were essential to omit a second intervention in some carefully selected cases while obtaining conservative management and an adequate oncological outcome [68, 69].
Since the introduction of lumpectomy during the 90s, breast-conserving surgery (BCS) followed by whole breast irradiation has been demonstrated to be safe and comparable to mastectomy in terms of local recurrences [70, 71]. Moreover, in the absence of any subsequent radiation therapy (RT), the local recurrence rate after BCS resulted as high as 40%, supporting the suspicion of tumorigenic cells in the tissue surrounding the tumor, otherwise known as “field cancerization” [71, 72, 73, 74].
Complementary breast irradiation has undergone numerous changes over time in order to reduce radiation side effects without affecting the tumor relapse rate. In particular, the traditional whole breast irradiation has been replaced in some selected cases by partial breast irradiation, which has the possibility of intraoperative administration [75]. In addition, several modalities have been designed that permit the reduction of dose fractionation [76], up to the administration of a single dose within clinical trials [77].
However, a recent meta-analysis demonstrated that, even if combining BCS with subsequent RT, the local recurrence rate is about 10%, suggesting that not all tumorigenic cells surrounding the tumor are sensible to breast irradiation [78, 79]. Subsequently, although some authors recently elected to omit reintervention (as more than half of patients underwent potentially unnecessary re-excision) [80], the adequacy of margins after BCS still represents an argument of great interest.
The margin status in BCS has been shown to be a significant predictive factor in local relapse rates [81, 82], representing a moment of great discomfort for patients and commonly requiring breast demolition. However, there is disagreement as to the role of margins on distant recurrences, which are instead a life-threatening occurrence. In fact, some authors excluded a correlation of margin involvement with an increased risk of distant relapse [83]. Conversely, some authors reported that positive surgical margins in stage II triple negative breast cancer patients negatively impacted metastasis free survival and overall survival [84].
In the literature, the prevalence of reinterventions for margin infiltration has significant variability, ranging from 10% to 70% [85, 86, 87, 88, 89, 90, 91, 92, 93, 94, 95, 96]. Nevertheless, the desirable prevalence rate has been stated to be under 20% [82]. The reduction of the reintervention rate would have a strongly positive economic impact [97, 98] while reducing patient discomfort.
To reduce the reintervention rate after BCS, it is imperative to better determine the type of intervention preoperatively, as well as to adopt some intraoperative shrewdness [99, 100]. For better planning of breast surgery, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has been widely applied with encouraging results, by lowering the re-excision rate after BCS [101] and by prompting an appropriate upgrade to mastectomy in a considerable number of cases, when warranted for cancer extent [102, 103]. In patients affected by triple-negative breast cancer, MRI improved the local recurrence rate after BCS [104]. In selected cases of radiotransparent adipose breasts, tomosynthesis and contrast-enhanced mammography (CEM) appear to be the most accurate techniques [105, 106].
Numerous predictors of surgical margin involvement following BCS have been proposed. Various prediction models (i.e., nomograms) have been designed, demonstrating an impressive ability to predict positive margins after BCS and thereby reduce the reintervention rate [107, 108]. However, there is lack of agreement on their routine use in clinical practice [109, 110]. Among risk factors for margin inadequacy, the lack of a definitive presurgical diagnosis was associated with a two-fold increase of inadequate margins in BCS, while other demonstrated risk factors were high mammographic breast density, large-sized invasive cancers, and intraductal histology [111, 112].
In the case of infra-clinical, non-palpable tumors, it is possible to mark the area of interest with a hook wire placed through the tumor or the injection of a radiotracer (radio-guided occult lesion localization – ROLL) [19]. Recently, the use of handheld superparamagnetic devices, such as MagSeed or the Guiding-Marker System, have provided an accurate and reliable localization method in BCS with favorable surgical outcomes [20, 21, 22] (Table 2). Other alternative, non-radioactive, wire-free localization methods, developed to increase the likelihood of complete tumor removal, include intra-operative ultrasound guidance [23], the LOCalizer radio-frequency identification (RFID) system [24, 25], reflector-guided localization through SAVI-SCOUT [26, 27], and fluorescence detection after intralesional indocyanine green (ICG) solution injection [113] or intravenous administration was used [28] (Table 2).
Intraoperatively, it is possible to submit the surgical specimen to radiography or ultrasound to confirm the presence of the breast lesion within it [114, 115, 116, 117]. This procedure may be especially helpful in the case of DCIS diagnosed by microcalcifications or in the case of complete regression after neoadjuvant chemotherapy by the presence of a clip, previously placed in the tumor site [118].
Another typical intraoperative approach to reduce reinterventions after BCS is the frozen-section analysis of lumpectomy margins [29], as well as of cavity shaving margins around lumpectomy [30] (Table 3). Routine circumferential cavity shaving ensures microscopic clearance, reduces the reintervention rate, and offers superior surgical outcomes without any impact on operating time or patient satisfaction [31, 32, 33, 34, 35]. For what concerns the extemporary specimen processing for invasive breast cancer, the analysis of shaving margins seems to be adequate to exclude ink on the tumor. Conversely, in the case of in situ carcinoma (including both DCIS and pleiomorphic lobular carcinoma in situ), a radial evaluation of margin distances may be more appropriate with the aim to exclude a distance of the tumor from margins lower than 2 mm. However, intraoperative frozen-section analysis of margins is still contentious: some authors have recently proposed to omit this procedure, as there is some evidence that in selected cases can be omitted without burden the patient management [36].
The literature has proposed many other approaches to intraoperatively assess margin status and reduce the reintervention rate. Recently, intraoperative flow cytometry was found to be a reliable technique for evaluating lumpectomy margins. This technique was found to be a low-cost method with an accuracy of 94.2% and which does not rely on the expertise of a pathologist or cytologist [37].
Furthermore, intraoperative fluorescence imaging using tumor-specific exogenous agents has been widely investigated (Table 3). This technique was found to be a simple, low-cost, time-saving strategy to refine surgical navigation, consistent with or superior to other methods used in BCS to reduce second surgery [38]. However, locating the optimal fluorescent probe is challenging [38]. Intraoperative fluorescence imaging has been used in-vivo, ex-vivo, or with both approaches simultaneously (Table 3). For example, ex-vivo, the surgical specimen was treated to enhance acrolein, a product of oxidization reactions that can highlight tumor tissue [38]. Some recent studies reported the use in humans of 5-aminolevulinic acid (5-ALA) to assess the surgical specimen in-vivo with the aim of finding residual tumor tissue in the surgical cavity margins [39]. Moreover, a pegulicianine fluorescence-guided detection system was recently tested in humans to establish the presence in-vivo of residual tissue in the surgical cavity after tumor removal [40]. In addition, animal models have been used to develop nanotechnology-based approaches to target the tumor. For example, a tailored Hepatitis B Core virus-like protein was designed to target angiogenesis and hence highlight the tumor tissue, allowing in-vivo imaging guidance of excision and residual tumor assessment at the cavity margins as well as ex-vivo surgical specimen assessment to establish the consistency of the tumor-free margins [41] (Table 3). Pseudomonas aeruginosa azurin-derived peptide p28 is known to target cancer cells specifically and has been used in combination with indocyanine green as a nanotechnology-based exogenous agent in a cancer mouse model (in-vivo and ex-vivo) to localize the lesion and provide tumor-free margins using near-infrared imaging [42].
Spectroscopy has also been widely used. In detail, spectroscopy is the broad field that studies the electromagnetic spectra that result from the interaction between electromagnetic radiation and matter (Table 3). Among the devices based on spectroscopy, a tool with the capability to detect real-time cellular abnormalities on the surgical specimen is the so-called ClearEdge [43]. The spectroscopy system known as MarginProbe can detect patterns of relative abundances of molecules, distinguishing clusters of benign tissue and cancer in surgical resections that has subsequently reduced positive margins by over 50%; however, its performance should be corroborated by the pathology report [44, 45, 46, 47, 48](Table 3). Some authors demonstrated the potential of diffuse reflectance spectroscopy, an optical technology based on light tissue interactions, to characterize tissue during surgery and to detect malignant tissue. In the case of DCIS, such an approach is particularly helpful for surgical guidance [49] (Table 3). A custom handheld mass spectrometry was used ex-vivo to assess the margins of the surgical specimen in breast cancer [50]. The same method was also proposed in an animal model for in-vivo assessment [50, 51].
Another group of techniques is based on nuclear magnetic resonance. Recently, the mobile MRI system ClearSight has been developed to intraoperatively examine the specimen based on a diffusion-weighted imaging protocol with an overall diagnostic accuracy of 80% [52]. The fast field-cycling nuclear magnetic resonance relaxometry allows the determination of the tissue proton relaxation rates as a function of the applied magnetic field, which are affected by changes in the composition of the mammary gland tissue occurring during the development of neoplasia. The technique thus has the potential to improve intraoperative margin assessment [53]. Other new powerful tools for breast cancer imaging and precise surgical navigation include magnetic particle imaging based on a passively or actively tumor-targeted iron oxide agent [54]. For example, an in-vitro model was developed using a superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle tracer specifically coated to target the breast tumor [54].
A device based on nanotechnology is the cancer diagnostic probe that was observed to efficiently detect breast cavity side margins in real-time as well as after neoadjuvant treatment [55]. This device assesses the presence of hypoxia glycolysis associated with the tumor tissue [55]. Another approach based on an exogenous nanotechnology contrast agent (water-soluble melanin nanoparticles conjugated with cyclic Arg-Gly-Asp peptides) and photoacoustic imaging was proposed to guide surgery in vivo and assess free margins ex-vivo or in-vivo [56].
In summary, developing a diagnostic assessment of breast lumpectomy tissues using radiomic, nanotechnology, mass spectrometry, spectroscopy, or optical signatures provides promising techniques that are attractive solutions for intraoperative residual cancer detection [119, 120]. The primary limitation of these novel techniques is the cumbersome problem of translating the collected information into clinical pathology data due to inter-and intra-patient variability, calibration, or technical issues [121].
The NSABP B-06 trial was the first to successfully introduce the concept of “no ink on tumor” [11]. In 2014, the Society of Surgical Oncology (SSO) and the American Society of Radiation Therapy (ASTRO) then released guidelines considering adequate a margin with “no ink on tumor” in the case of invasive breast cancer [12]. Finally, in 2017, the St. Gallen International Expert Consensus Conference defined as adequate margin “no ink on tumor” for invasive histotypes and 2 mm for DCIS [13].
The adoption of the SSO-ASTRO Consensus Guidelines on margins for BCS with whole breast irradiation resulted, as expected, in the reduction of both margin positivity rate and reintervention rate [122, 123, 124], especially in elderly patients [125]. However, some topics remained controversial, such as the definition of a focal infiltration that certain Dutch authors demonstrated not to be correlated with local recurrences [126, 127]. The multiple infiltration of a margin was more frequently associated with residual disease than the isolated one [128]. In addition, if the circumferential margin infiltration has been confirmed to be a significant predictive factor for local recurrence, the superficial and deep margins were not associated with local recurrence after BCS for invasive breast cancer [129].
Numerous definitions of “close margin” have been proposed during the last decade [96, 130, 131, 132, 133, 134, 135, 136]: some authors considered it as an infiltrated one in terms of local recurrence rate [128], while others equated it to a negative one [137].
Oncoplastic techniques following BCS experienced a significant surge during the last decades, with the aim to improve cosmetic results with acceptable oncologic outcome and complication rate. This kind of surgery is also associated with better patient-reported outcomes, which are of paramount importance for social and psychological wellbeing and quality of life [57]. These techniques have demonstrated promising results as a safer tool to handle large, complex tumors and lesions in difficult anatomical locations, whether multifocal or progressing on neoadjuvant therapy. As expected, the application of oncoplastic techniques has witnessed the emergence of new problems with margin adequacy due to the unavoidable displacement or replacement of residual breast tissue surrounding the excised tumor, according to excision size and location [58, 59, 60]. Regardless, the current literature demonstrates that oncoplastic surgery is a safe option in terms of re-excision, completion mastectomy rates, and local and distant recurrence [10, 61, 62, 63, 64, 65, 66]; such surgery is oncologically safe and has been recommended in the case of DCIS [67].
Finally, the local recurrence rate is inevitably influenced by adjuvant therapies. For example, a significant reduction in the ipsilateral breast recurrence rate after BCS in patients affected by HER2-positive breast cancer has been observed following the administration of 1-year adjuvant/neoadjuvant trastuzumab treatment [68]. Nonetheless, it is important to underscore the issue of elderly patients who should receive the same therapies of younger ones, if their general health status allows it; in the context of multidisciplinary management, it is vital to prevent their risk of local recurrence [69].
The local recurrence rate results are clearly higher in the case of DCIS compared with invasive carcinoma [138]. This discrepancy is likely attributable to the peculiar features of this kind of tumor which are more frequently multifocal or multicentric and thus able to spread through the ducts. DCIS represents a challenge for the breast radiologist and the breast surgeon for the difficulty in preoperatively recognizing its real extent through radiological investigations and in intraoperatively defining its boundaries in the absence of objective findings.
Many trials have confirmed that tumor margins are the main prognostic factor of local recurrence for DCIS patients treated with BCS with or without subsequent RT, together with tumor size, nuclear grading and patient age [135, 136]. In the era of genetic signatures, Oncotype Breast DCIS Score and DCISionRT have been developed, providing information that has significantly changed the recommendations to add or omit RT in comparison with traditional clinicopathologic features and patient preference [139, 140, 141]. Patterns of adjuvant therapy indicated after BCS for DCIS may also depend on institutional policies and available facilities in certain geographic areas [142].
Various definitions of “close margin” have been used to define the optimal distance to obtain from the tumor, ranging from 1–10 mm [130, 131, 132, 133, 134, 135, 136], until the SSO-ASTRO Consensus Guidelines definitively stated this distance as 2 mm [14, 15]. As expected, the further implementation of margin consensus guidelines for DCIS resulted worldwide in a consistent increase in re-excisions and mastectomy conversions [143], but not without numerous challenges. For instance, although negative margins in BCS for DCIS reduced the odds of local recurrence, in some cohorts, the minimum margin distances above 2 mm seemed not significantly associated with further reduced odds of local recurrence in women receiving RT [144]. Accordingly, the American Society of Breast Surgeons approved the margin adequacy for DCIS in the case of “no ink on tumor” [145, 146]. In fact, patients affected by DCIS with “no ink on tumor” who receive RT showed no significant increased risk of local recurrence at 10 years follow-up [145].
Considering the high number of negative findings in the specimens of reoperations, some authors retrospectively observed that, especially in the case of close margins after BCS for DCIS, individual assessment should be used in decisions on reoperation, as opposed to rigid adherence to guidelines [16]. Similarly, while deciding which patients truly may benefit from margin re-excision, other authors suggested the use of clinical judgment, based on patient and tumor characteristics [17, 18].
Bearing in mind that breast surgery following neoadjuvant therapy (NAT) should be determined not only according to biological and anatomical parameters at diagnosis, but should be tailored according to the response to therapy, breast surgeons are becoming more confident with BCS after NAT. Some authors performed BCS in 82% of cT3 patients in whom BCS appeared feasible on post-NAT MRI, resulting in an excellent local control of the disease; they reported an increased risk of positive margins in the case of luminal tumors, non-mass enhancement on MRI and lobular histotype [147].
Recent studies have demonstrated that current NAT schemes for patients affected by triple-negative or Her2-positive breast cancers succeed in achieving a complete response in more than half of cases [148]. Consequently, an appropriate tumor identification and marking is essential before starting any treatment.
There is some evidence that tumor marking before neoadjuvant chemotherapy improves the rate of satisfactory margins in patients undergoing BCS after NAT [149]. To reduce the need for re-excision in the case of BCS after NAT, MarginProbe, associated with a lower re-excision rate, was tested [150]. Recently, radioactive iodine-125 seed has been tested to perform BCS and improve detection of residual axillary disease in patients treated with NAT [151]. However, cavity specimen radiography after NAT proved inadequate for intraoperative margin assessment but remains useful to document removal of the biopsy site clip [152].
The application of oncoplastic techniques proved safe after NAT [153, 154]. Recently, the omission of surgery has been explored in the case of exceptional NAT responders [155].
Malignant phyllodes tumors and radio- and non-radio-induced sarcoma represent rare entities among breast malignancies. In the absence of a standard of care regarding adjuvant treatment, surgical resection is the cornerstone of their treatment. Regardless, the therapy should be multidisciplinary and possibly managed by a specialized center [156, 157, 158].
Some authors reported positive margins in 87.5% of patients with non-epithelial breast tumors operated with BCS who consequently underwent mastectomy [157]. The issue of margins in this type of neoplasms may be due to an incorrect preoperative diagnosis or to an inexact preoperative assessment of the extent of disease.
Although local recurrences after BCS traditionally require breast demolition, repeated lumpectomy with reirradiation has recently been considered in selected patients presenting with an ipsilateral breast tumor recurrence with multidisciplinary input with low rates of postoperative complications and equivalent survival outcomes at a short-term follow-up [159]. Partial breast reirradiation was also investigated and found to be safe and efficient in obtaining an excellent local control of the disease, and thus a well-tolerated and reasonable alternative to mastectomy [160].
Obviously, in the case of repeated BCS, the role of margins becomes absolutely crucial, in order to reduce the number of reinterventions as well as patient discomfort in the case of a further recurrence.
Breast-conserving surgery cannot disregard the question of margins, as they represent a recognized, significant predictive factor for local recurrence. Many novel tools have been developed that are based both on the newest radiological imaging techniques and on the tissue expression of certain markers, with the aim of precisely navigating tumor excision and intraoperatively evaluating cavity excision margins. BCS can be safely applied after neoadjuvant treatments when residual tumor size permits. Oncoplastic surgery can be considered oncologically safe while improving the cosmetic outcome and patient quality of life. The appropriate use of adjuvant treatments in the context of a multidisciplinary and personalized management of breast cancer is the only means to omit a second intervention in some carefully selected cases. In the case of invasive breast cancer, “no ink on tumor” can be considered an adequate margin, while in the case of DCIS, a distance of 2 mm from tumor should be obtained. However, significant disagreement remains concerning the definition of adequate clear margin after BCS for DCIS, and further studies are required to better assess the multimodal treatment approach in this condition.
5-ALA, 5-aminolevulinic acid; ASTRO, American Society of Radiation Therapy; BCS, breast-conserving surgery; CEM, contrast-enhanced mammography; DCIS, ductal carcinoma in situ; ICG, indocyanine green; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; NAT, neoadjuvant therapy; NSABP, National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project; RFID, radio-frequency identification; ROLL, radio-guided occult lesion localization; RT, radiation therapy; SSO, Society of Surgical Oncology.
Substantial contributions to conception, design, acquisition of data, analysis and interpretation of data (SB, APL, CC). Contributions to conception, design and interpretation of data (SB, APL, JADN, FL, BB, LLV, MN, DA, CC). Drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content (SB, APL, JADN, FL, BB, LLV, MN, DA, CC). All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
The present study is exempt from ethical approval since this review only involves anonymous data which has already been published.
The authors would like to thank the whole staff collaborating in clinical practice and in the study.
This study was supported by Ennergi research non-profit association.
The authors declare no conflict of interest. Ambrogio P Londero and Serena Bertozzi is serving as one of the Guest editors of this journal. We declare that Ambrogio P Londero and Serena Bertozzi had no involvement in the peer review of this article and has no access to information regarding its peer review. Full responsibility for the editorial process for this article was delegated to Michael H. Dahan.


