1 School of Health Science and Engineering, University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, 200093 Shanghai, China
2 Chongming Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Medicine and Health Sciences, 202150 Shanghai, China
3 Collaborative Innovation Center for Biomedicine, Shanghai University of Medicine and Health Sciences, 201318 Shanghai, China
4 School of Pharmacy, Shanghai University of Medicine and Health Sciences, 201318 Shanghai, China
5 Department of Physiology and Biophysics, Dalhousie University, Halifax, NS B3H 4R2, Canada
Academic Editors: Kavindra Kumar Kesari and Dhruv Kumar
Abstract
The maintenance of intracellular and extracellular pH relies on multiple ion
transporters/channels. Proton-activated chloride channel (PAC) precisely
regulates extracellular and early/late endosomal pH by transporting chloride ion
(Cl
Keywords
- proton-activated chloride channel
- endosomes
- tissue acidosis
- hypothermia
The acid-base equilibrium is automatically adjusted in physiological conditions.
The pH of extracellular fluid, including the blood plasma, is tightly set between
7.32 and 7.42 by chemical buffers, the respiratory system, and the renal system
[1]. pH not only directly alters protein structure but also significantly
influences cell activity by modifying pH-sensitive enzymes/channels [2, 3, 4]. Under
pathological conditions, such as cancer, ischemic stroke, and hypoxia, the local
pH is usually acidic (~5.5–7.0) [5, 6, 7]. Several acid-sensitive
channels/exchangers (including acid-sensing ion channels (ASICs),
Na
Recently, the structure, molecular mechanism and function of PAC have been
characterized [11, 12, 13]. PAC exquisitely tunes the pH of extracellular milieu and
early/late endosomes by adjusting the chloride ion (Cl
The electrophysiological activity of PAC, also referred to acid-sensitive outwardly rectifying anion channel (ASOR) [19] or proton-activated outwardly rectifying anion channel (PAORAC) [20], was first observed in rat Sertoli cells [21]. The exact molecular identity and mechanism of PAC in maintaining acidic pH homeostasis remained ambiguous in last couple of decades. Three hypotheses were proposed, namely “PAC is a volume-regulated anion channel (VRAC)”, “PAC is chloride channel (CLC)-3” and “PAC is CLC-7” [22, 23, 24, 25, 26]. Until recently, the gene PACC1 encoding PAC channel was identified by cell-based fluorescence reporter assay and an unbiased RNA interference screening [2]. Meanwhile, it was confirmed that PAC is identical to transmembrane protein 206 (TMEM206) with the similar unbiased method.
PAC belongs to a unique and highly conserved family of ion channels that are
probably highly conserved in all vertebrate species and shares no significant
sequence with any other families of membrane proteins, such as cystic fibrosis
transmembrane regulator (CFTR), CLCs and NHE [2, 27]. PAC has been identified in
27 kinds of tissues in human including brain, kidney, testis, lymph node and bone
marrow [12]. PAC is activated at acidic pH and displays a strong outwardly
rectifying current-voltage (I-V) relationship. At the positive membrane
potential, PAC activation is time-dependent, and the order of ion permeability is
SCN
The structure of pufferfish PAC has been resolved by using single-particle
cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) [29]. Interestingly, PAC lacks obvious
sequence homology with any known Cl
Recently, the structure of PAC in the resting state (pH 7.5), activated state (pH 4.5) and desensitized state (pH 4.0) was investigated [31]. In three conformational states, PAC were assembled from symmetric trimers of TMEM206 subunits, including a large extracellular domain (ECD) which would be the luminal structural domain in endosomes, a transmembrane domain (TMD) containing two TM helices per subunit (TM1 and TM2) and an intervening juxtamembrane interface (JMI) which connects ECD to TMD. Under acidic condition, acidic clusters in ECD act as primary proton sensors and lead to the helical reorganization of TMD, inducing metamorphosis of transmembrane helices to fashion an ion transport pathway unique to the activated conformation [32]. The similar conformational change also occurs in ASIC1a, where clusters of negatively charged amino acids in ECD sense extracellular acidification and trigger transient channel opening [33]. Similarities and differences in the structures of PAC and ASIC1a have been clearly described [31]. Although they transport different ions, the similar activation mechanism and conformational change indicate that PAC and ASIC1a may work synergistically under acidic conditions. Indeed, coactivation of PAC and ASIC currents has been observed in chondrocytes under simultaneous hypotonic and acidic stimulation [34]. The details of cooperation between both channels will be discussed later. Reportedly, human PAC can be converted into a cation-selective channel and display inward rectification by replacing positively charged Lys319 residue on TM2 with glutamate residues, which indicates that Lys319 is the determinant of anionic selectivity and strong outward rectification [30].
PAC was initially reported to be distributed in the plasma membrane. The
swelling and death of HeLa cells and mouse cortical neurons induced by prolonged
exposure to an acidic extracellular milieu were attenuated using nonspecific
blockers of chloride channels [19, 28]. It was proposed that cell swelling
induced by extracellular acidity is caused by the osmotic gradient generated by
PAC-mediated Cl
Regarding its strong pH dependence, PAC may localize not only in the plasma
membrane, but also in the luminal compartments of endocytic and secretory
vesicles with lumen pH of ~4.5–6.5, such as lysosomes and late
endosomes [20]. Actually, PAC is actively transferred from the cell surface to
endosomes in a canonical YxxL motif-dependent manner, and mainly localizes in the
early and late endosomal membranes, and a small amount locates in the plasma
membrane [13]. By cooperating with vacuolar-ATPase (V-ATPase), CLCs and NHE, PAC
regulates endosomal pH by precisely controlling the Cl
 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.Channels to maintain pH in endosomes. V-ATPase maintains
luminal pH by inducing the influx of proton. CLC 2Cl
Under physiological conditions, the pH of extracellular fluid is maintained at ~7.32–7.42 and PAC cannot be activated because of its acidic threshold. However, acidic microenvironment is often found in most tissues in pathological situations including: (1) The extracellular pH at the inflammatory site can be as low as 5.5 due to the production of protons by activated neutrophils and macrophages [38]. (2) Even in presence of sufficient oxygen, cancers tend to produce energy by anaerobic oxidation instead of oxidative phosphorylation, the so-called Warburg effect [39], resulting in the extracellular pH even below 6.0 [40]. (3) When the blood supply to the brain is compromised, protons accumulate locally with available ATP being consumed, which makes the brain tissue more susceptible to ischemic injury. During ischemia, seizure and hyperglycemia, the extracellular pH can be reduced to less than 6.0 [6, 41].
The intracellular and extracellular pH of cancer cells are out of balance, cancer cells operate at alkaline cytoplasmic pH higher than 7.4 and acidic extracellular pH around 6.7–7.1 [42]. It has been demonstrated that the acid-base equilibrium of the cancer microenvironment involves in the occurrence of numerous abnormalities of cancer cells. This reversed pH gradient facilitates tumorigenesis and development including proliferation, metabolic homeostasis, migration, and invasion [5, 9, 43, 44, 45]. On the other hand, more attentions have been directed to pH homeostasis within intracellular secretory or endo-lysosomal compartments regarding to cancer growth, metastasis, and drug resistance [46, 47, 48]. Genomic data indicate that endosomal pH regulation plays critical role in cancer survival, prognosis, and resistance to chemoradiation therapy. Mechanistically, growth factors, cytokines and other ligands initiate the genesis and development of cancer cells by binding to receptors on the plasma membrane. The ligands are separated from their receptors in the acidic pH of the endosomal compartments and then delivered to lysosomes for degradation to complete signal termination. Alternatively, the receptor-ligand complex can be removed from early endosomes for rapid return to the plasma membrane or be sorted into perinuclear recycling compartments for slow delivery to the plasma membrane. Therefore, as an important hub of cancer cell signaling, endosomes can determine the fate of cancer cells by terminating or prolonging oncogenic signals [10, 49, 50]. Because abnormal pH is a common finding in cancers, interventions aimed to manipulate the acidic extracellular microenvironment and endosomal pH of cancer cells may provide new therapeutic perspective. Thus, key channels or transporters (such as V-ATPase [51], CLCs [52], NHE [53] and PAC) to regulate extracellular/endosomal pH may be therapeutic targets for cancers treatment.
TMEM206 has significant modulating effects on cancer: (1) The silencing of
TMEM206 can downregulate Wnt/
Targeted delivery to PAC via pH-sensitive nano-systems is a highly promising therapeutic strategy, the development of bio-responsive materials that undergo conformational or solubility changes in acidic environments offers great promise for the development of smart targeted drug delivery nano-systems [56]. However, at present, only some nonspecific drugs targeting chloride channels, such as 4,4’-diisothiocyano-2,2’-stilbenedisulfonic acid (DIDS), niflumic acid (NFA), phloretin and 5-nitro-2-(3phenylpropylamino) benzoic acid (NPPB) are available, while specific drugs targeting PAC in the endosomal pathway have not been reported [2, 12]. More research is needed to establish the specific carcinogenic effect of endosomal pH in different types of cancer, which is crucial for the development of endosomal inhibitors and activators that are PAC-specific and have minimal off-target effects.
Ischemic acidosis is a sensitive metabolic indicator of cerebral ischemic injury
progression in ischemic stroke. The pH of ischemic core tissue can be as low as
pH 6.0, whereas the pH of penumbra tissue around infarction fluctuates between pH
6.5 and 6.9 [57]. TMEM206 has the highest expression in cerebral cortex [2], and
three different approaches have demonstrated that PAC activity can be considered
to play a major role in ischemic brain injury in vivo: (1)
Acidosis-induced neuronal injury is largely prevented by pharmacological blockage
of PAC using DIDS or phloretin in mouse cortical neurons [28], and
ischemia-reperfusion induced neuronal injury is also alleviated by DIDS in
hippocampal CA1 neurons [58]. (2) Hypothermia inhibited the PAC activity of mouse
cortical neurons and reduced acidotoxic neuronal death [28]. (3) PAC knockout
abolished the proton-activated Cl
For cerebral acidosis caused by ischemic stroke, a model describing the
synergistic action of multiple channels can be proposed. Sustained extracellular
acidification activates both ASIC1a and TRPM7, leading to Na
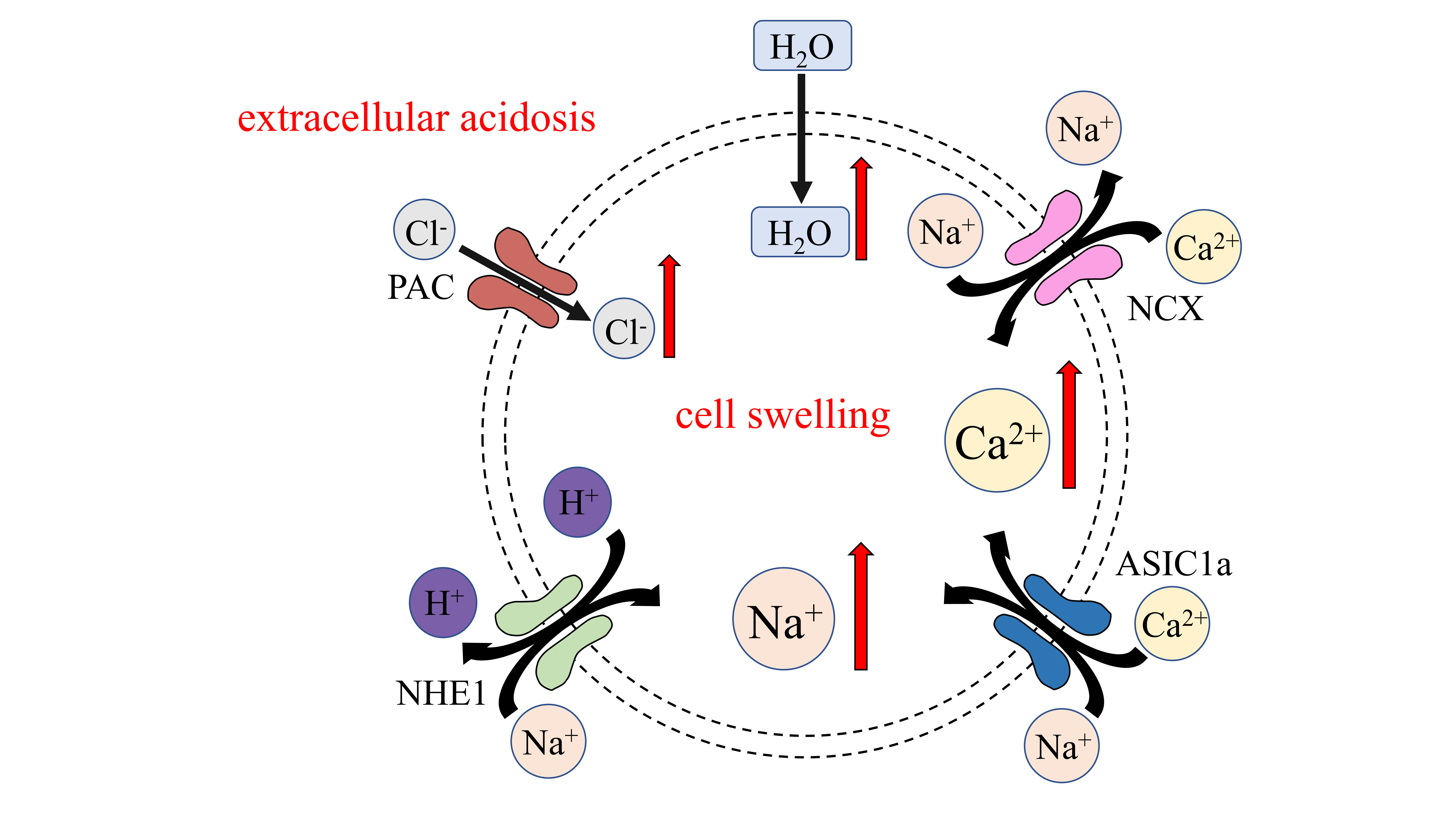 Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.Ion channels pertaining to cell edema caused by acidosis.
Extracellular acidosis activates PAC, causing Cl
Based on the characteristics and mechanisms of PAC, there are two proposing
therapeutic strategies. First, the application of pH-driven and bio-responsive
nanomaterials in solid tumor therapy has inspired the application of
nanotechnology in the treatment of ischemic stroke [69, 70]. Tissue acidosis in
ischemic stroke can act as a trigger to selectively deliver PAC-specific blockers
to the ischemic penumbra via pH-responsive smart nano-systems, promising
treatment at the site of injury without adverse off-target effects [71]. Second,
since 1987, therapeutic hypothermia has been recognized as one of the most
effective neuroprotective strategies for protecting the brain from ischemia,
excitotoxicity, or traumatic brain injury [72, 73, 74]. Numerous preclinical studies
have shown that hypothermia exerts neuroprotective effects mainly by reducing the
cerebral metabolic rate [75], but it is also involved in cell death, inflammatory
response, and white matter integrity [76], and PAC’s temperature sensitivity may
be one of the underlying mechanisms [59]. Precise cooling of acidotic brain
tissue in ischemic stroke by therapeutic hypothermia can increase the opening
threshold of PAC, thereby shutting the channel, reducing Cl
Iron is essential to produce hemoglobin, the oxygen carrier in erythrocytes. Transferrin delivers iron into cells through receptor-mediated endocytosis, so transferrin receptor-mediated endocytosis is important in erythropoiesis through its iron uptake function [78, 79]. After iron binds to transferrin, it binds to cell surface receptors, forming transferrin-receptor complex into the endocytosis pathway. The endosomal pH is less than 6.0, which is conducive to the dissociation of iron from transferrin. Iron-free transferrin is then recycled back to the cell surface, where it rapidly dissociates from its receptor at neutral pH and enters the subsequent iron transport cycle [80]. Endosomal alkalization inhibits the dissociation of iron from transferrin, causing the undissociated iron-transferrin conjugate to return to the cell surface and bind closely to the receptor, reducing the binding rate of transferrin and iron [81]. PAC affects the efficiency of iron dissociation from transferrin by regulating pH in the endosomal lumen [13]. Knockout of PAC results in endosomal hyper-acidification, which improves the dissociation efficiency and cell surface receptor accessibility, and thus increases uptake of transferrin.
In addition, the role of PAC is conserved in long-term hypoxia adaptation. The
results of exome sequencing in Tibetan highland population showed that PACC1 was
one of the genomic regions with the highest frequency variation compared with
ethnic Han Chinese population [82]. Natural selection for PACC1 has also been
observed in pigs at high altitudes, allowing them to adapt to hypoxia [83]. The
regulatory role of PAC after transferrin enters the endocytosis pathway provides
a potential mechanism for these phenomena. However, the possibility of direct
regulation of transferrin-receptor-mediated endocytosis by endosomal Cl
PAC is widely expressed in various cells and tissues, and highly conserved in
mammals. The molecular properties, structures and functions of PAC were briefly
reviewed. And emerging evidence has suggested that PAC may play critical roles in
cancer, ischemic stroke and hypoxia by mediating the Cl
(1) Further studies are needed to determine the molecular mechanisms responsible for both the endocytosis and recycling of PAC back to the plasma membrane.
(2) More research is required to determine the potential roles of PAC in other acidic intracellular organelles in the secretory and endocytic pathways.
(3) The protective or adverse effects of PAC in different types of cancer are uncertain, and further research is needed on the specific mechanism of PAC in cancer.
(4) The development of PAC-specific targeting drugs bears great prospects for the treatment of cancer and ischemic stroke.
(5) It would be interesting to investigate whether PAC affects other cargoes entering the endocytosis pathway, as is the case for iron uptake by erythrocytes via transferrin.
Conceptualization—FP, YW, XD and PH; writing - original draft preparation—FP; writing - review and editing—XD and PH. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Not applicable.
We apologize to colleagues whose works are not cited due to space limitations.
This research was funded by Shanghai Municipal Health Commission Foundation grant [20204Y0379] to Y.W.
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Publisher’s Note: IMR Press stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.


