1 Department of General Surgery, Third People’s Hospital of Dalian, Dalian Medical University, 116033, Dalian, Liaoning, China
2 Department of Central Laboratory, Third People’s Hospital of Dalian, Dalian Medical University, 116033, Dalian, Liaoning, China
3 Department of Endocrinology, Second Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, 116021, Dalian, Liaoning, China
Academic Editors: Małgorzata Kotula-Balak and Edra London
Abstract
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis (HT) is the most common autoimmune disease involving the thyroid gland. HT often clinically manifest as hypothyroidism due to the destruction of thyroid cells mediated by humoral and cellular immunity. The pathogenesis of HT is a complex process in which environmental factors, hereditary inclination, trace elements immune factors, cytokines, and DNA and miRNA all play an important role. Herein, we summarize the precision factors involved in the pathogenesis of HT and offer an update over the past 5 years to provide a theoretical basis for further investigation of the relevant targets for HT treatment.
Keywords
- Hashimoto's thyroiditis
- autoimmunity
- cytokines
- pathogenesis
- environmental factors
- hereditary inclination
- trace elements
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis (HT) is also known as lymphocytic thyroiditis and chronic autoimmune thyroiditis [1]. HT is a disease characterized by the infiltration and destruction of lymphocytes in thyroid tissues [2], and is the most common autoimmune disease worldwide [3]. Patients with HT develop thyroid antibodies via a number of immune processes. As a result, thyroid tissues are attacked by these antibodies and fibrosis occurs, resulting in the gradual loss of thyroid function [1]. The main clinical manifestation of HT is primary hypothyroidism, which is caused by damage to the thyroid gland [4], and is accompanied by weight gain, constipation, increased sensitivity to cold, and dry skin [5]. HT can cause cardiovascular diseases, such as coronary heart disease [6]. HT is also a risk factor for the development of thyroid cancer [7]. The prevalence of HT is on the rise. Genetic susceptibility, environmental factors, immune factors, cytokines, and vitamin D are all known to have an important role in the pathogenesis of HT [8, 9, 10]. Here, we summarize the pathogenesis of HT to identify targets for interventional treatment and to improve the prognosis (Fig. 1).
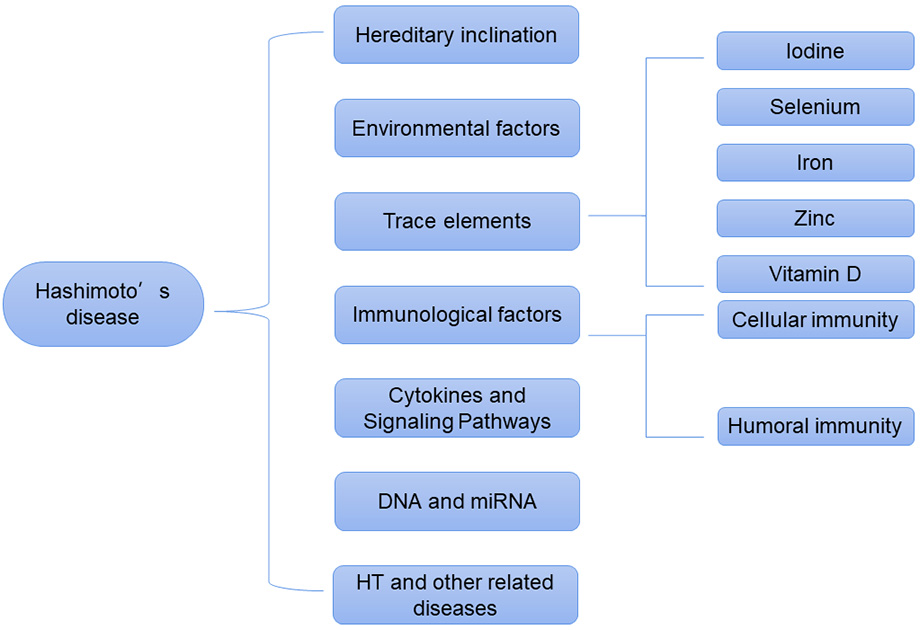 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.Pathogenesis of Hashimoto’s disease.
Genetic susceptibility plays an important role in the pathogenesis of HT [8]. Numerous studies have reported a genetic susceptibility to HT. HT is more prevalent in Latin America and less prevalent in Africa and Asians [9].
In the Swedish twin study, the HT concordance was 0.29 and 0.1 for monozygotic and dizygotic twins, respectively, with a heritability of 0.64 [8], the higher concordance among monozygotic twins can be hypothesized to be more heritable and susceptible than dizygotic twins [9].
Recombinant interleukin-2 receptor alpha (IL2RA), human leukocyte antigen (HLA), protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 22 (PTPN22), and cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen-4 (CTLA4) are susceptible sites for HT [11]. These loci have the potential to disrupt T-cell regulation and peripheral immune tolerance, and play an important role in the pathogenesis of HT [11].
HLA-B*46:01 is a prototypical immune response gene on the HLA complex,
and it was shown by experimental controls that the HLA-B*46:01 gene increased the
risk of HT in Han Chinese families [9]. In the thyroid tissue of HT patients,
IL-18 is expressed at high levels, which promotes INF-
STAT proteins mediate the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-6, which in turn affects dysregulated effector T cell responses [15]. Allele A of the STAT3 SNP rs744166 was significantly higher in HT patients than in controls, and compared to the control group, hypothyroidism in this group, demonstrating that allele A increased susceptibility to HT [16].
In a study of Chinese patients with immune thyroid disease, four HT susceptibility locus were identified at the genome-wide level, they were rs1265883 in SLAMF6, rs1024161 in CTLA4, rs1521 in the HLA-B region and rs5912838 in GPR174/ITM2A on chromosome X [17] (Table 1, Ref. [9, 11, 12, 17, 18]).
| High probability | Low probability |
| Latin America [9] | Africa and Asians [9] |
| Identical twins [9] | Dizygotic twins [9] |
| IL2RA, PTPN22 [11] | |
| HLA-B*46:01 [9] | |
| IL18 CG genotype [12] | |
| Allele A of the STAT3 SNP rs744166 [18] | |
| Mutation rs1265883 in SLAMF6 [17] | |
| Mutation s1024161 in CTLA4 [17] | |
| Mutation rs1521 in HLA-B [17] | |
| rs5912838 in GPR174/ITM2A at X chromosome [17] |
Environmental factors can also influence the pathogenesis of HT [8]. In autoimmune reactive diseases, hygiene without microbial agents has been shown to be strongly associated with the incidence of autoimmune diseases [19]. A study has shown that women born in the summer months will have a 2% higher incidence than the general female population [20]. A range of cigarette smoking and alcohol consumption is protective against HT [21]. Prolonged exposure to stressful situations can also increase the incidence of HT [22]. Specifically, meat is a major nutritional factor that has been shown to increase the risk of thyroid autoimmunity, while plant-based fat-free foods containing fiber and antioxidants reduce the risk of developing HT [23] (Table 2, Ref. [20, 21, 22, 23]).
Iodine plays an important role in endocrine diseases, especially thyroid diseases. Thyroid epithelial cells take up iodine from the blood and, catalyzed by hydrogen peroxide, iodize thyroid tyrosine molecules, and the iodized products are catalyzed by thyroid peroxidase (TPO) to form T3 and T4 [18]. Studies have shown that increased iodine intake enhances the risk of autoimmune thyroid disease [5]. Both salt iodization schedules and excessive levels of supplementation can cause HT [24]. The current speculated mechanisms may be as follows: (1) Prolonged exposure to high iodine may increase the immunogenicity of thyroglobulin. (2) It activates the autoimmune response and triggers signaling pathways leading to apoptosis, which leads to the destruction of thyroid tissue. (3) Leading to oxidative stress. (4) Inhibition of Tregs impaired peripheral tolerance [18, 25].
Selenium is an essential micronutrient that plays an important role in immune-related diseases [26]. The thyroid gland is the largest reservoir of selenium in the body [27]. SELENOS, a family of selenoproteins, is a susceptibility gene for HT that is expressed in thyroid follicular cells and encodes proteins involved in cellular stress and immune inflammatory responses [22]. Selenium supplementation has an immune-stimulating effect, and can inhibit HLA-DR expression in thyroid cells and reduces thyroid autoimmunity [5], as evidenced by increased T-cell proliferation and enhanced innate immune cell function [26]. Thus, selenium deficiency is also involved in the pathogenesis of HT. Moreover, there is a link between diet and the development of HT.
Iron plays an important role in hemoglobin and myoglobin, and it is involved in many important metabolic processes [28]. TPO can only be activated after binding to repair heme I, which is involved in thyroid hormone synthesis [18], therefore, iron content affects the synthesis of T3T4 [29]. The thyroid-gut axis has recently been found to be closely associated with HT [30], hypothyroidism may lead to digestive abnormalities, impaired intestinal function, and reduced iron absorption. After iron deficiency, it seriously affects the iodine regulation of thyroglobulin and the coupling of iodotyrosine molecules, which leads to the decrease of T3 and T4 production [18], it causes hypothyroidism HT is often associated with autoimmune gastritis [31], there are a large number of anti-parietal cell antibodies in serum. With the increase of disease course, it gradually evolves into severe atrophic gastritis, and gastric acid secretion is greatly reduced [32], causing the body to be unable to effectively absorb iron from food, leading to iron malabsorption [18].
Zinc is a trace element closely related to thyroid metabolism [33]. It promotes the synthesis of hypothalamic thyrotropin-releasing hormone and thyroid stimulating hormone, it is also a structural component of the T3 receptor [33]. It also acts as a thyroid hormone-binding transcription factor that regulates the expression of thyroid hormones [34]. Dietary deficiency of zinc and low serum zinc concentration can lead to changes in thyroid hormone metabolism and even thyroid structure [33]. Zinc deficiency reduces serum free T3T4 levels [30]. And zinc and thyroid function can affect each other, zinc deficiency leads to decreased thyroid function, thyroid insufficiency leads to inadequate zinc absorption [30].
Vitamin D deficiency is one of the causes of HT, whereby the greater the vitamin
D deficiency, the greater the likelihood of HT [35]. Vitamin D concentrations are
positively correlated with serum TNF-
Because HT is an autoimmune disease characterized by thyroid-specific autoantibodies, inflammatory infiltration of T and B cells is the main pathogenesis [9]. It is reasonable to assume that in the context of genetic predisposition and environmental factors, errors in innate immune surveillance function produce antibodies against thyroid antigens that can cause both cytotoxic damage to thyroid cells and immune dysfunction, resulting in cellular and humoral immune responses and destruction of thyroid epithelial cells, thus causing disease.
Some autoreactive T cells escape immune regulatory control and enter the
peripheral tissues, which leads to autoimmune disease, where stimulation by
peripheral antigens, co-stimulatory factors, or specific cytokines activates T
cells, resulting in the formation of different subpopulations of T cells [37]. Th
cells and regulatory T cells (Tregs) are important T cells involved in the
autoimmune response [38]. Tregs and Th cells are key regulators of inflammation
and play an important role in immune tolerance [39]. CD4 is the main marker on
the Th surface, with T helper 1 (Th1), T helper 2 (Th2), T helper 17 (Th17), and
follicular helper T-cell subsets closely associated with the development of HT
[40]. Th17 is capable of secreting IL17, which causes cell infiltration and
tissue destruction [41]. Tregs consist mainly of CD4
Antibodies against TG and TPO are present in nearly all HT patients [21]. AbTPO
is predictive of hypothyroidism, and patients with high serum AbTPO titers are at
increased risk of HT [27]. AbTPO antibodies are capable of producing two types of
cytotoxicity (antibody- and complement-dependent cytotoxicity; 44). Indeed, such
cytotoxicity destroys thyroid tissue, thus causing thyroid cell death and
hypothyroidism [27]. An exosome is a new diagnostic marker with physiologic
effects, such as antigen presentation and inflammatory activation [50]. Exosomes
are involved in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases [51]. In HT patients,
exosomes carry TPO and Tg, and deliver the MHC-IITPO/Tg complex to dendritic
cells (DCs; 47). DCs accept antigen, bind TLR2/3, and result in an inability of
CD4
The cytokines affecting HT are produced by subsets of Th1, Th2, and Th3 cells
that participate in HT cellular and humoral immunity [55]. The main role of Th3
is to synthesize TGF
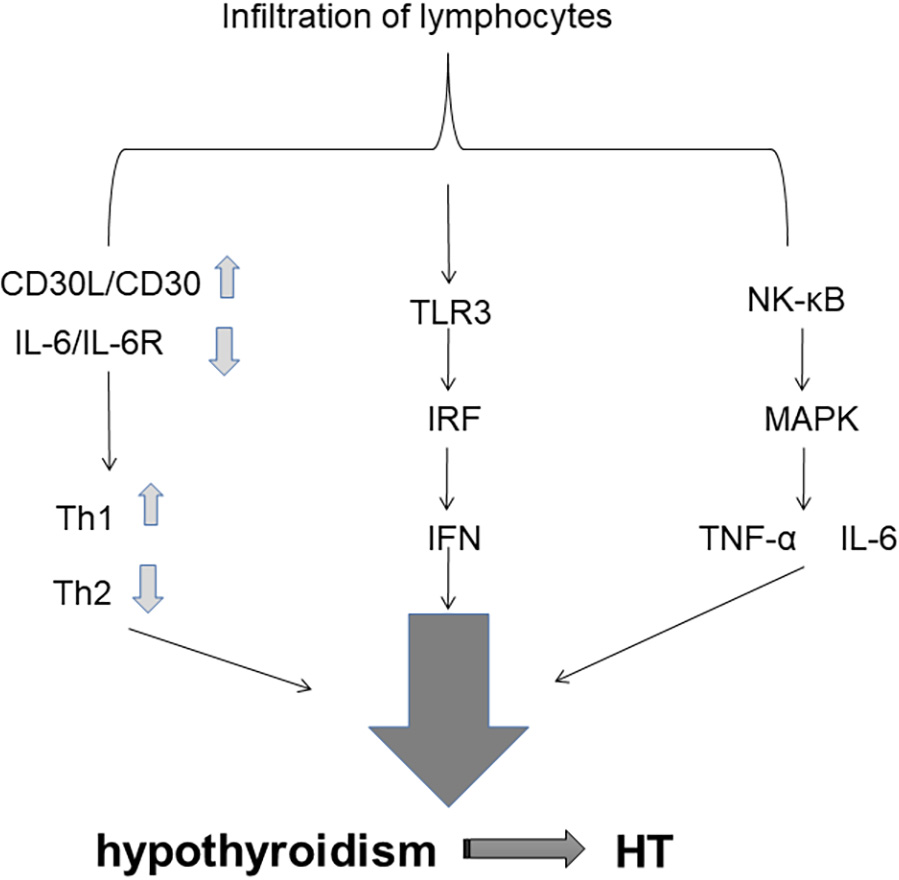 Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.Cytokines and Signaling Pathways.
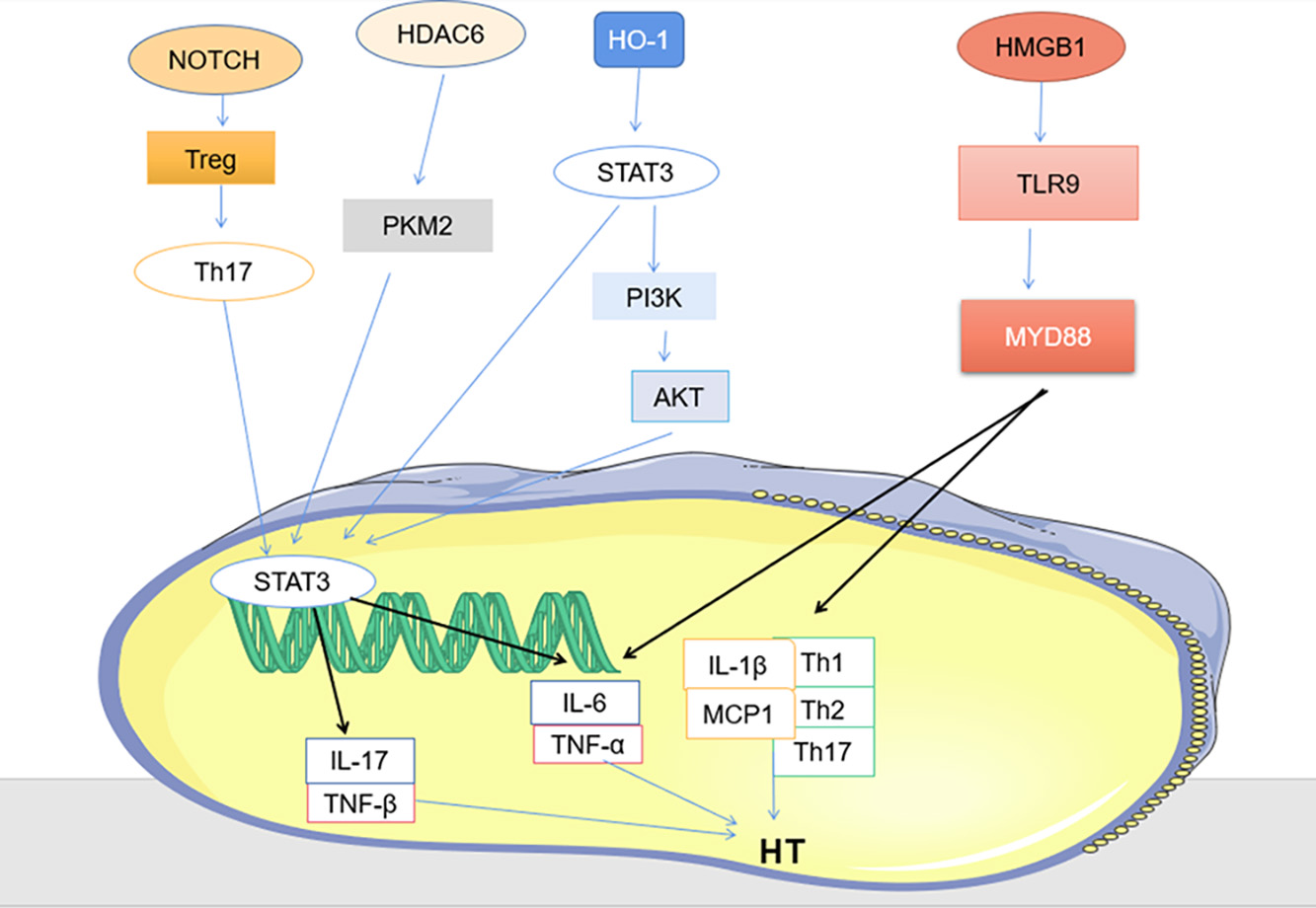 Fig. 3.
Fig. 3.Other signaling pathways (PKM2/ STAT3, HMGB1 / TLR9/MYD88 and HMGB1/TLR9/MYD88).
Environmental factors and genetics act synergistically to determine HT. Inactivation of some genes is associated with DNA methylation. In children and
adolescents with HT, DNA methylation has been shown to act on the PTPN22 gene,
thereby affecting thyroid function [83]. Some histone alterations affect the
expression of some genes. Tri-methylated histone H3 lysine 4 (H3K4me3) is a
marker of gene activation and an overall alteration of H3K4me3 was found in HT
patients, with H3K4me3 enrichment in the follicular cells of the thyroid gland of
HT patients [84]. These processes are all environment-dependent [21]. The release
of genomic DNA from dead cells can activate innate immunity, and it is the H2B
histone of DNA that has been shown experimentally to be closely associated with
innate immune activation [9]. The miRNA is a novel regulatory gene regulator that
is involved in the pathogenesis of many autoimmune diseases [85]. MiR-451
promotes the apoptotic process and accelerates cell death through the expression
of caspase-3 [86]. Apoptosis is also a pathogenic mechanism underlying HT.
Inhibition of miR-451 expression is effective in reducing the incidence of HT
[87]. Thus, miR-451 is an important molecule in the pathogenesis of HT. MiR-296
is overexpressed in HT patients and is capable of causing hypothyroidism, thus
miR-296 is also involved in the pathogenesis of HT [87]. The female advantage in
HT is associated with inactivation of the X chromosome [88]. FOXE1 is a
transcription factor that is involved in the developmental and differentiation
processes of the thyroid gland, such as the genes for TPO and Tg [27]. FOXE1
mutations may cause thyroid dysplasia, making the thyroid gland hypothyroid [89].
MAGI3 is a newly identified group of genetic markers that is associated with an
increased risk of progression from TPO antibody positivity to hypothyroidism, and
implies an association with the pathogenesis of HT [90]. Long non-coding RNAs
have recently been recognized as critical for the regulation of genomic
expression [91]. Abnormalities in lncRNAs are often associated with immune system
diseases [92]. MAFTRR is the transcription product of lncRNAs, a
chromatin-associated Th1-specific expression product [93]. Th1 cells are able to
activate macrophages and cytotoxic lymphocytes, thus destroying thyroid
follicular cells and causing hypothyroidism. MAFTRR has two roles: (1) promoting
the differentiation of CD4T cells to Th1 cells and (2) promoting the production
of IFN-
The pathogenesis of HT is further clarified by understanding the familial
correlation with other diseases. Six diseases (autoimmune hemolytic anemia,
chronic glomerulonephritis, chronic rheumatic heart disease, immune
thrombocytopenic purpura, aspergillosis, and Takamatsu disease) are specifically
present in the offspring of patients with HT disease in a study of
family-associated autoimmune diseases in HT offspring [97]. Arthropathy and
connective tissue disease are more common in adults with HT, while type I
diabetes and celiac disease are more common in adolescents with HT [63].
Glutamate dehydrogenase is a key autoantigen in type I diabetes, and studies have
demonstrated that HLA-II is able to bind TPO and glutamate dehydrogenase, which
together lead to the activation of T cells, which may be the pathogenesis of HT
[98]. Celiac disease is a chronic autoimmune disease in which specific T-cell
antigens can be detected in the mutated peritoneal mucosa of patients with celiac
disease. After a number of immune reactions, Th1 cells are stimulated to secrete
pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-
The most common way to control HT is to take levothyroxine (L-T4) to control the disease [100]. Long-term use of 1.6–1.8 mg per kg to achieve normal levels of thyrotropin in the body [21]. Pregnant women and infants should be treated with liquid L-T4, which is much more bioequivalent than tablets [101]. When the condition is more urgent, prednisone can also be used for shock therapy [102]. Traditional Chinese medicine also plays a significant role in the treatment of HT, Xiaoying Daotan decoction can effectively down-regulate Notch protein, up-regulate Treg cytokines, down-regulate Th17 cytokines, and reduce immune attack on thyroid gland [42]. It can be used as an effective drug for the treatment of HT. Histone deacetylase 6 specific inhibitor (HDAC6i) inhibitor reduces Th17 cell differentiation by regulating PKM2/STAT3 axis, and successfully reduces thyroid tissue damage [80]. HT is closely related to trace elements and dietary fiber, so appropriate diet, healthy lifestyle, adequate sleep and appropriate vitamin D supplementation can improve the condition [103]. PI3K inhibitor LY294002, Akt inhibitor triciribine or STAT3 inhibitor WP1066 all significantly reduced the severity score of thyroiditis [75], all can be considered as therapeutic agents for HT. Edaravone is a drug that scavenges hydroxyl radicals [104], it acts on the STAT3/PI3K/Akt pathway to effectively improve autoimmune thyroiditis and has become an emerging drug for the treatment of HT [104]. PV-mediated HMGB1 inhibition decreased the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and suppressed the HMGB1-TLR9 signaling pathway in, while downregulating the proportion of Th1, Th2 and Th17 cells in splenocyte, provides a potential therapeutic value for HT [81], the lignan component of PV has a strong affinity for the disease protein of HT, and quercetin has a strong affinity for serum thyroid peroxidase (TPO), further confirming that PV can effectively treat HT [100].
HT is an autoimmune disease caused by a variety of factors, such as
environmental factors, genetic susceptibility, and immune factors. The thyroid
gland of HT patients is often infiltrated by lymphocytes and fibrosis, and often
presents clinically as a painless, diffuse goiter and hypothyroidism. The current
treatment for HT is based on thyroid replacement therapy. Among them, the
specific mechanism of MicroRNA in relation to the development of HT has not been
clarified, the mechanism of elevated MAFTRR in HT patients has not been
elucidated, and how MAF damages IFN-
The supporting materials have been included in the article.
BJ searched the literature and wrote the article. ZF designed the manuscript. ZF and SW revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81701965, 82200886).
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Publisher’s Note: IMR Press stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.



