1 Department of Gastric and Colorectal Surgery, General Surgery Center, The First Hospital of Jilin University, 130021 Changchun, Jilin, China
2 Department of Thoracic Surgery, The First Hospital of Jilin University, 130021 Changchun, Jilin, China
†These authors contributed equally.
Academic Editor: Vincenzo Lionetti
Abstract
Perioperative myocardial injury is a common complication caused by major surgery. Many pharmacological and nonpharmacological studies have investigated perioperative cardioprotection. However, the methods are insufficient to meet the increasing clinical needs for cardioprotection. The application of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes (MSC-Exos) is a novel cell-free therapeutic strategy and has significantly benefitted patients suffering from various diseases. In this review, we comprehensively analyzed the application of MSC-Exos to prevent myocardial infarction/injury by regulating inflammatory reactions, inhibiting cardiomyocyte apoptosis and autophagy, promoting angiogenesis, and mediating cardiac remodeling. Finally, we assessed the therapeutic effects and the challenges associated with the application of MSC-Exos from a clinical perspective.
Keywords
- mesenchymal stem cell
- exosomes
- cardioprotection
- myocardial injury
In an aging population, many perioperative patients suffer from cerebro-cardiovascular diseases, which result in high morbidity and mortality due to perioperative myocardial infarction (PMI) during anesthesia and surgery. PMI is a severe cardiovascular complication and contributes to non-fatal myocardial infarction, non-fatal cardiac arrest, and perioperative cardiac death in around 500,000~900,000 individuals, and also increases the risk of death due to cardiovascular complications every year in the first six months after major non-cardiac surgery [1, 2]. Irreversible short-term and long-term adverse outcomes caused by PMI increase the clinical need for perioperative cardioprotection during major surgery.
Perioperative cardioprotection has been applied for many years in cardiac and non-cardiac surgery and consists of pharmacological treatments, including beta-blockers, statins, alpha-2 agonists, aspirin, inhalation anesthetics, noble gases, and opioids [3], and nonpharmacological treatments, such as ischemic preconditioning (IPC), remote ischemic preconditioning (RIPC), and remote ischemic postconditioning (RIPostC) [4]. However, perioperative cardioprotection in cardiac and non-cardiac surgery remains a debated topic. Recently, mesenchymal stem cell therapy, which depends on the ability of self-renewal and secretion of regenerative cytokines, has been incorporated into the main therapeutic approaches in the regenerative medicine of cardiovascular diseases [5]. However, the problem of storage and transportation, and the risks of inducing tumorigenesis and deformity need to be addressed [6]. Exosomes primarily contribute to the efficacy of stem cells and are stable, easily stored, and not rejected by the immune system [7]. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes (MSC-Exos) were developed as a kind of novel cell-free therapy. They preserve the main biological features and functions of the parent cells and exhibit a strong cardioprotective effect [8]. We reviewed the studies related to MSC-Exos to improve the treatment of myocardial ischemia and investigated their ability to provide perioperative cardioprotection.
PMI is a kind of myocardial ischemia that mainly occurs during or a few days after surgery and might occur due to the usage of intense analgesia. Nearly 80% of patients sustaining PMI only show symptoms based on cardiac troponin but lack other typical ischemic symptoms, such as chest pain and changes in the ECG [9, 10]. Few PMI patients present atherosclerotic plaque rupture with thrombus formation and distal embolization. The flow-mediated hypoperfusion and supply-demand imbalance of oxygen promote PMI [11, 12].
Mesenchymal stem cells are found in many tissues, including adipose tissue, bone marrow, placenta, heart, peripheral blood, and umbilical cord [13]. They can regenerate by dividing and differentiating into several kinds of cells [14]. The application of MSCs in cardiovascular diseases has advanced considerably [5]. Exosomes, containing RNA, DNA, proteins, and lipids, are nano-sized lipid bilayer vesicles of endosomal compartments [15]. The biogenesis of exosomes is shown in Fig. 1. Besides having various exosome biogenesis-related functional proteins, MSC-derived exosomes contain surface markers, such as CD9, CD44, CD63, CD73, CD81, and CD90, specific markers of MSCs, proteins that act as signaling molecules [16, 17], and more than 850 unique gene products and miRNAs [18, 19]. Certain RNA cargos (mRNA and microRNA) that are sorted into MSC-derived exosomes are important for angiogenesis, cell differentiation, cell proliferation, cell survival, tissue remodeling, and immune system modulation [20, 21]. According to the results of RNA sequencing, MSC-Exos, isolated from different tissues, were found to have various species of tRNA [22] that affected the differences in the clinical efficacy of MSC-Exos. The five most abundant miRNAs in adipose-derived MSC (ASC) exosomes are miR-486–5p, miR-10a-5p, miR-10b-5p, miR-191–5p, and miR-222–3p. In bone marrow-derived MSCs (BMSCs), exosomes contain miR-143–3p, miR-10b-5p, miR-486–5p, miR-22–3p, and miR-21–5p. The miRNA sequencing data showed that the cardioprotection provided by endometrial MSCs was better than that provided by BMSCs and adipose-derived MSCs [23]; the cardioprotection-related miRNAs were upregulated (miR-29 and miR-24), while the cardiac-damage related miRNAs were downregulated (miR-21 and miR-15) [8, 24, 25].
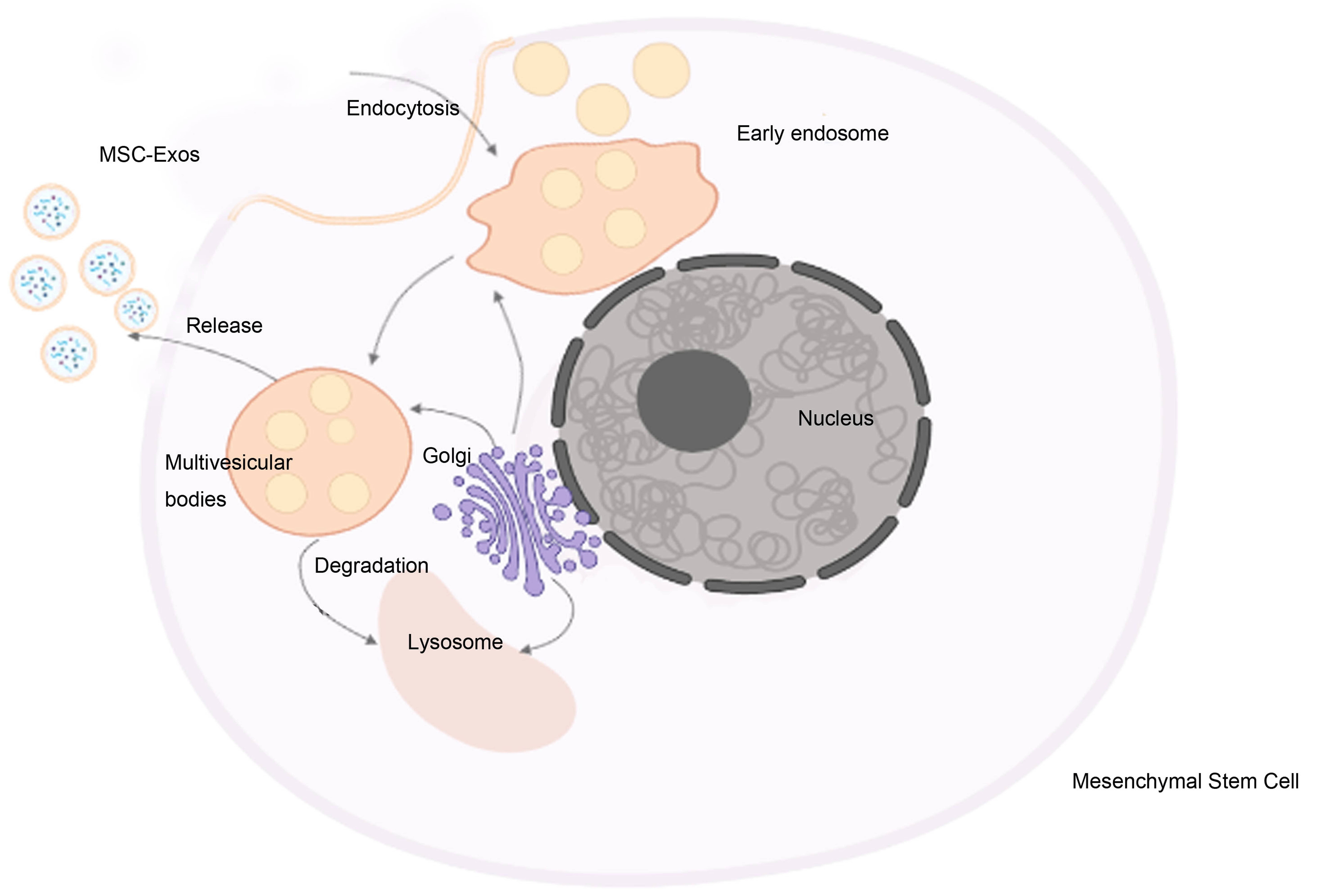 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.The biogenesis of MSC-Exos. First, the fusion of endocytic vesicles forms the early endosome. Then, early endosomes transform into multivesicular bodies. Finally, multivesicular bodies fuse with the plasma membrane to release exosomes via membrane budding. The MVBs might be transported to the Golgi for recycling endosomes and delivered to lysosomes for degradation.
The inflammatory cascade plays a pivotal role in the myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) process [26]. The local inflammation induces
pro-inflammatory cytokines and promotes cell proliferation and apoptosis [27, 28]. In turn, monocytes and macrophages secrete angiogenic cytokines and
anti-inflammatory cytokines to promote injury repair [29]. MSC-Exo, the main
efficient component of MSCs, participates in immune regulation [30]. Based on the
myocardial I/R mouse model, Zhao and Fatih Arslan discovered that bone
marrow-derived MSC-Exos could attenuate neutrophil infiltration [31, 32, 33], increase
the concentration of the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10, and decrease the
concentration of the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-6 in the heart tissues of mice.
More importantly, MSC-Exos promote the polarization of macrophages from the MI
phenotype to the M2 phenotype by exchanging miR-182 to downregulate TLR4 and
inhibit the relevant downstream signaling pathway (TLR4/NF-kB), while as the
sequence of signaling cascade PI3K/Akt signaling pathway was activated,
in vivo and in vitro [31]. MSC-Exos can increase the proportion
of M2 macrophages by upregulating IL-10 and downregulating IL-6 via miR-21–5p,
which reduces the inflammatory reaction in heart tissues [34]. MSC-Exos can
deliver miR-182–5p and downregulate Gasdermin D to reduce the inflammatory
cytokines (e.g., IL-1
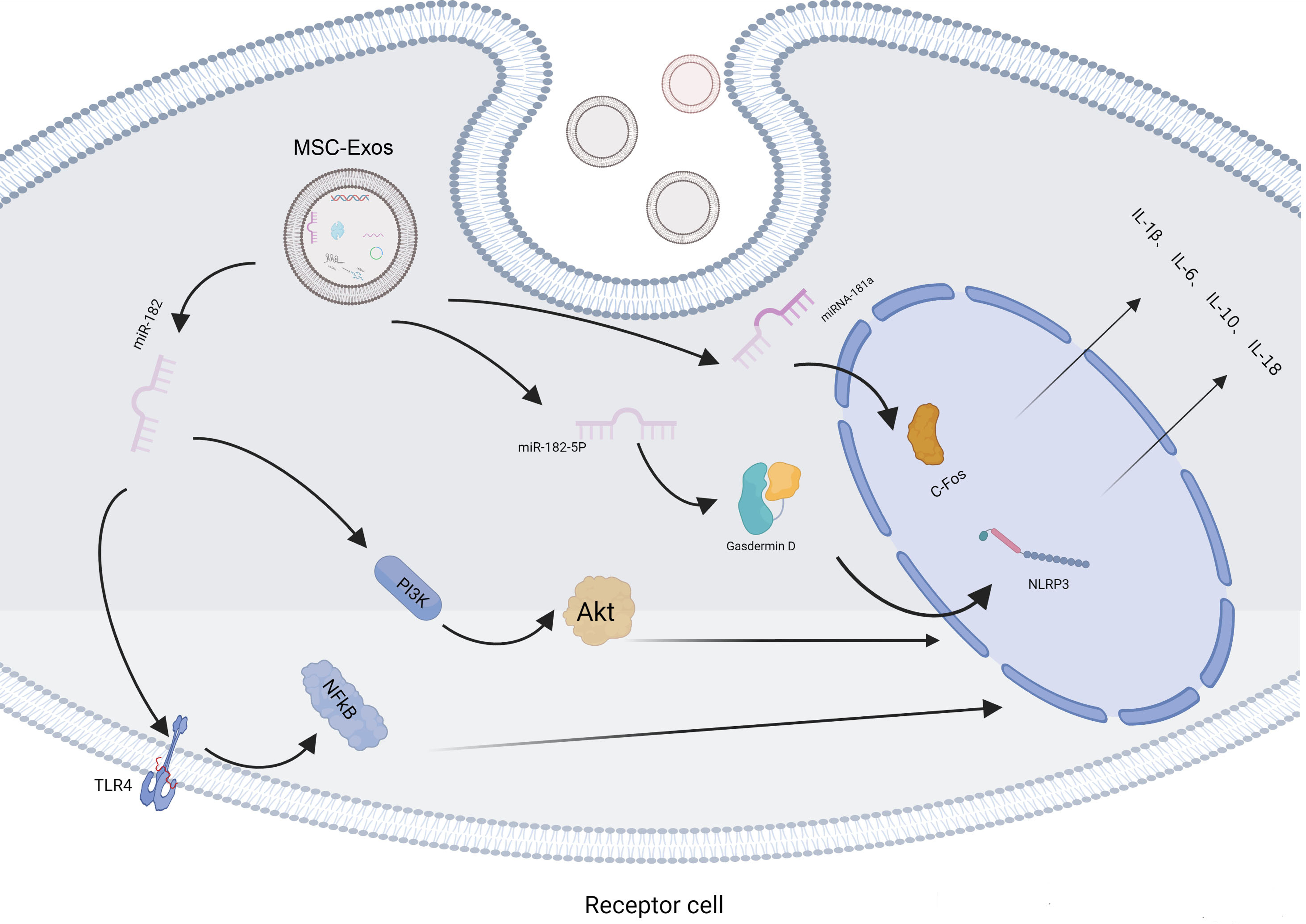 Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.MSC-Exos regulate inflammatory reactions in receptor cells. The
MSC-Exos enter the receptor cells and mediate the PI3K/AKT and TLR4/NF-kB
signaling pathways, and the release of IL-1
Inappropriate apoptosis in ischemia strongly influences myocardial injury
[37, 38, 39]. The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (AKT)
signaling pathway plays a pivotal role in myocardial cell apoptosis, which can be
reversed by enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2) [40]. In hypoxia, bone
marrow-derived MSC-Exos can ameliorate cardiomyocyte apoptosis [41]. Phosphatase
and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome ten (PTEN), the target mRNA of miR-144,
miR21, and miR-141, is downregulated in a hypoxic environment, which is reversed
by bone marrow-derived MSC-Exos in a dose-dependent manner, and activates the
downstream PTEN/p-AKT and PTEN/
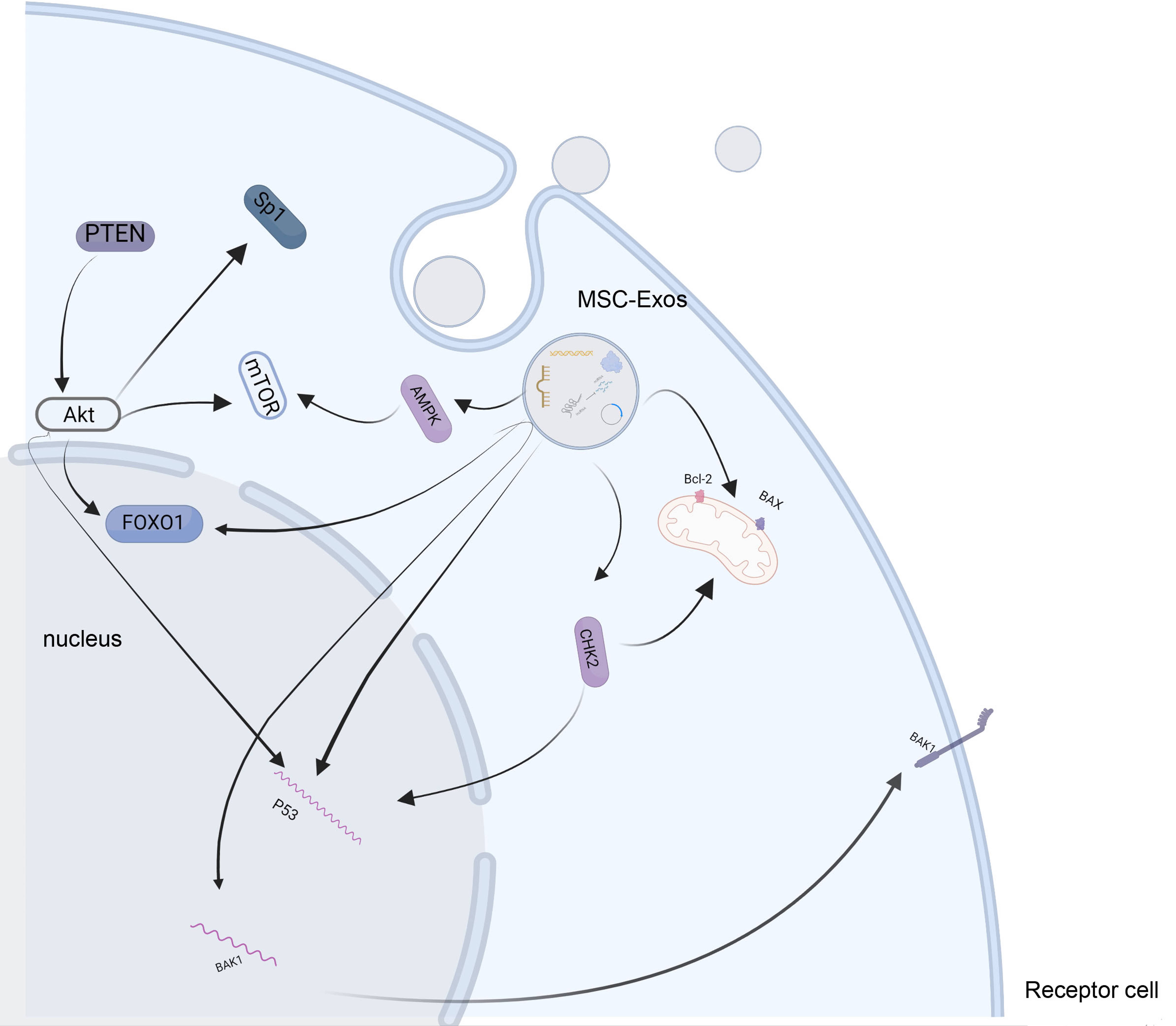 Fig. 3.
Fig. 3.MSC-Exos inhibit the apoptosis and autophagy of cardiomyocytes. MSC-Exos enter the receptor cells that mediate the mTOR signaling pathway and increase the BCL-2/BAX ratio, thus regulating the expression of FOXO1 and p53.
Myocardial injuries occur due to the dysfunction of angiogenesis and restriction of blood supply [56]. MSC-Exo has a robust proangiogenic ability, both in vivo and in vitro [57]. The GO analysis and the Panther pathway analysis aimed at the MSC-Exo proteome revealed canonical angiogenesis-related pathways, such as Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF), Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), Platelet-derived Growth Factor (PDGF), and cadherin [58]. In a study, Sun showed that MSC-Exo with abundant HIF-1a can increase the mRNA and protein levels of proangiogenic factors (e.g., VEGF and PDGF) and enhance neovessel formation to provide cardioprotection [59]. Hypoxic conditions can enhance this function [60]. Wang et al. [44] found that these proangiogenic effects were induced by the upregulation of miRNA-221–3p. In vivo, MSC-Exos were administered to ischemic limbs via intramuscular injection. Laser Doppler Perfusion Imaging showed that blood perfusion in limb ischemia was restored by nearly 85%, and the bioinformatics analysis suggested that proangiogenic effects might be induced by miR-7116–5p [61]. In the human umbilical vein endothelial cell model, MSC-Exo influenced capillary tube formation and promoted angiogenesis [60]. Although the mechanism is unclear, MSC-Exo can treat mouse hearts with a higher capillary density, which can protect the myocardium from ischemic injury [62, 63]. Intriguingly, Hemin (a potent heme oxygenase-1 inducer)-treated MSC-Exo had a superior effect in enhancing the capillary density compared to MSC-Exo [48]. Hemin pretreatment can upregulate miR-183–5p in MSC-Exo. Exosomal miR-183–5p can partially regulate the HMGB1/ERK pathway and inhibit ischemia-induced cardiomyocyte senescence to enhance the cardioprotective effects by regulating mitochondrial fission. Several experiments have confirmed that MSC-Exo can deliver miR-543 to reduce the expression of COL4A1 and lead to the proliferation, migration, invasion, and angiogenesis of cardiac microvascular endothelial cells [64].
Reactive fibrosis, followed by the loss of cardiomyocytes,
occurs in most myocardial injuries and contributes to the remodeling of
post-myocardial injury [65, 66]. Collagen I promoted myocardial fibrosis in
myocardial injury [67]. MSC-Exo can alleviate myocardial fibrosis and improve
cardiac function more effectively than MSC [8, 40, 68, 69]. In the
epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) process, epithelial cells are gradually
transformed into mesenchymal cells. EMT facilitates the pathogenesis of fibrosis
[70]. MSC-Exo can downregulate EZH2 and upregulate High Mobility Group AT-Hook 2
(HMGA2); thus, activating the PI3K/AKT pathway that can delay EMT and fibrosis in
myocardial tissues, increase the left ventricular end-diastolic internal diameter
(Dd), and end-systolic internal diameter (Sd), and increase the cardiac function
[40]. In diabetic patients, MSC-Exo can reduce fibrosis and damage to the
myocardial tissue by inhibiting the TGF-
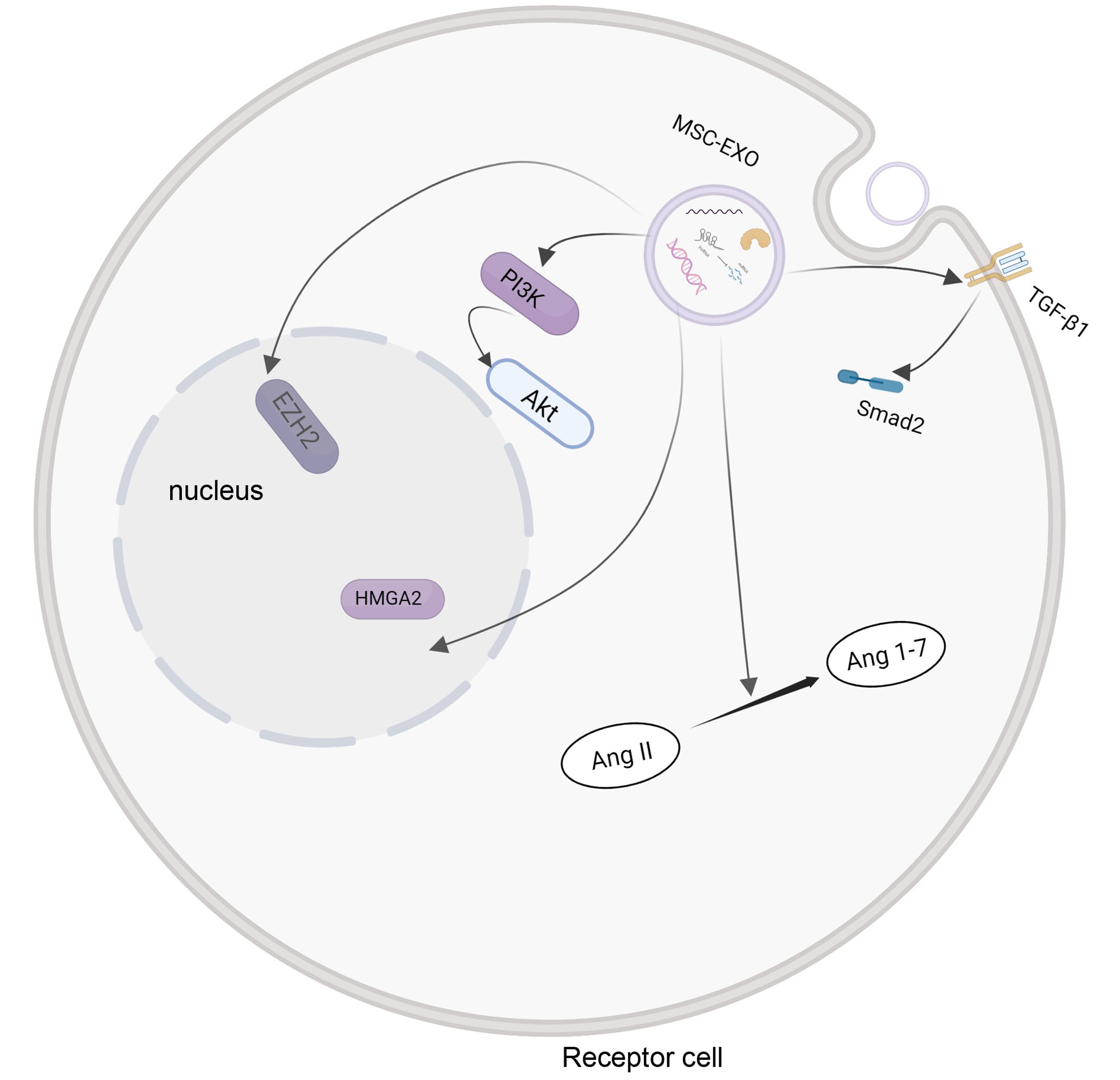 Fig. 4.
Fig. 4.The mechanism of cardiac remodeling is mediated by MSC-Exos. MSC-Exos help to regulate the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway, the conversion of Ang II to Ang 1–7, and the expression of EZH2 and HMGA2.
| Study | Design | Myocardial injury model | Intervention | Result | Mediator | Signalling pathways |
| Zhao J 2019 [31] | mice | Ligating LCA | bone marrow-derived MSC-Exo | Converting macrophages to M2 phenotype and alleviating cardiac inflammation | miR-182 | TLR4/NF-κB/PI3K/Akt |
| Arslan F 2013 [32] | mice | Ligating LCA | huES9.E1 derived MSC-Exo | reducing WBC count | activate adenosine receptors | PI3K/Akt |
| Pei Y 2021 [33] | mice | cecalligation puncture induced myocardial impairment | bone marrow-derived MSC-Exo | reducing the inflammatory infiltration and cell apoptosis | miR-141 | PTEN/ |
| Shen D 2021 [34] | mice | Ligating LCA | C57BL/6 mouse derived MSC-Exo | promote the polarization of macrophages to the M2 phenotype | miR-21-5p | Not given |
| Yue R 2022 [35] | mice | Ligating LAD | bone marrow-derived MSC-Exo | Reducing GSDMD-dependent cell pyroptosis and inflammation | miR-182-5p | Not given |
| Wei Z 2019 [36] | mice | Ligating LAD | human umbilical cord blood-derived MSC-Exo | Reducing inflammatory cell infiltration | miRNA-181a | TNF- |
| Jiao W 2022 [40] | rat | Ligating LAD | bone marrow-derived MSC-Exo | Reducing fibrosis | EZH2 | PI3K/AKT |
| Zhu LP 2018 [41] | mice | Ligating LAD | bone marrow-derived MSC-Exo | ameliorating cardiomyocyte apoptosis | miR-125b | p53 and BAK1 |
| Wen Z 2020 [42] | H9C2 CMCs of rat cardiac origin | Cells were incubated in the hypoxic container for 48 h at 37 |
bone marrow-derived MSC-Exo | protect H9C2 cells from apoptosis | MiRNA144 | PTEN/AKT |
| Shi B 2018 [43] | cardiac stem cells of the rat | CSCs are treated with 100 |
bone marrow-derived MSC-Exo | protection against oxidative stress-triggered cell death | miR-21 | PTEN/PI3K/Akt |
| Wang Q 2021 [44] | rat | Ligating LAD | human umbilical cord blood-derived MSC-Exo | Promoting the survival and angiogenesis in cardiomyocytes | miR-221-3p | Not given |
| Liu C 2021 [45] | mice | Cecal Ligation and Puncture | bone marrow-derived MSC-Exo | protect cardiomyocytes of inflammation model | miR-146a-5p | MYBL1 |
| Chen H 2020 [46] | cells | Human-induced pluripotent stem cell (hiPSC)-derived cardiomyocytes | human adipose-derived MSC-Exo | protecting cardiomyocytes from apoptosis | miR-142-3p | LncRNA-NEAT1/miR-142-3p/FOXO1 |
| Mao S 2022 [47] | rat | Ligating LAD | bone marrow-derived MSC-Exo | protecting cardiomyocytes from apoptosis | miR-183-5p | FOXO1 |
| Li T 2020 [54] | mice | Ligating LAD | bone marrow-derived MSC-Exo | regulating autophagy under cardiac injury | miRNA-29c | PTEN/AKT/mTOR |
| Chen G 2021 [55] | rat | H9c2 cells were administrated to established the cellular hypoxia-reoxygenation model | bone marrow-derived MSC-Exo | Reducing cell apoptosis | miR-143-3p | CHK2-Beclin2 |
| Ju C 2018 [61] | mice | Ligating LAD | cardiac derived MSC-Exo | Promoting cardiomyocyte proliferation, and preserves heart function | Not given | Not given |
| Yang M 2021 [64] | rat | Ligating LAD | Human mesenchymal stem cells derived exosome | Promoting cardiac microvascular endothelial cell angiogenesis | miR-543 | COL4A1 |
| Lin Y 2019 [71] | rat | diabetes mellitus-induced myocardial injury myocardial injury | bone marrow-derived MSC-Exo | Reducing myocardial injury and fibrosis | Not given | TGF- |
| Xiao M 2021 [72] | rat | H9c2 cells | bone marrow-derived MSC-Exo | Improving cardiac remodeling and cardiac function | Not given | renin-angiotensin system |
| Note: left anterior descending coronary artery LCA; left anterior descending LAD. | ||||||
Exosomes are endocytic vesicles that play a key role in communication between cells. The biogenesis, uptake, composition, and physiological features have been discussed in previous reviews [73, 74, 75]. Although the exact mechanism is unknown, exosomes are extracellular nanovesicles mainly involved in cardioprotection. In a prospective clinical study executed in Policlinico Hospital of Bari and “G. Monasterio” Foundation of Massa showed that distinct exosomal proteins playing their roles of cardioprotection in older cardiac surgery patients regardless of surgery type [76]. Lucio Barile proved cardiac progenitor cells (CPC) derived exosome possessed the capacity to reduce cardiomyocyte apoptosis, enhance angiogenesis, and improve LV ejection fraction in the rat myocardial infarction model [77]. In-depth study revealed that pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A existed in CPC derived exosomes played a significant role in reducing scar size and improving ventricular function in rats’ permanent coronary occlusion model [78]. The data of Valentina Casieri’s research indicated ticagrelor can be leveraged to modulate release of anti-hypoxic exosomes from resident human cardiac-derived mesenchymal progenitor cells (hCPCs) [79]. It is remarkable that, recently, MSC-Exos were also shown to provide effective cardioprotection as a cell-free treatment [80]. In our review, we comprehensively analyzed the feasibility of the application of MSC-Exos in perioperative cardioprotection, as it can regulate inflammatory reaction [30], mediate cardiomyocyte apoptosis and autophagy [81], promote angiogenesis [57, 58, 60, 82], and improve cardiac remodeling [32].
Some clinical research organizations conducted a series of exosome-related clinical trials. In a study, Dai, et al. [83] reported that ascites-derived exosomes (Aex) were administered in the immunotherapy of colorectal cancer in phase I clinical trials. Aex combined with Granulocyte-macrophage Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) was shown to have strong antitumor effects. Subsequent clinical trials showed that Dendritic cell-derived exosomes (Dex) have strong antitumor effects in melanoma and non-small cell lung cancer [84, 85, 86]. From a clinical perspective, MSCs have beneficial curative effects in some non-neoplastic diseases. The phase II/III clinical pilot studies in Sahel Teaching Hospital showed that MSC-Exos applied to grade III-IV chronic kidney diseases can inhibit inflammatory immune reactions and improve kidney function [87]. Moreover, clinical trials on bronchopulmonary dysplasia, macular holes, type 1 diabetes, and acute ischemic stroke are underway. Due to large inter-individual variability and technological limitations, MSC-Exos have not been widely applied in clinical treatment. Fortunately, other applications of exosomes in oncologic therapy have verified the safety and effectiveness of MSC exosomal therapy.
The bioactive cargoes in MSC-Exos are also being investigated. Several studies
have shown that exosomal miRNAs and proteins are responsible for the
cardiovascular protection and repair of MSC-Exos [21]. Exosomal miRNA is an
important bioactive cargo in MSC-Exo and is transferred to the recipient cells
and specifically combined with the complementary mRNA target; thus, it can
regulate the expression of related genes. The result of miRNA analysis based on
the NanoString platform showed that the predictable top 23 miRNAs of human bone
marrow-derived MSC-Exo targeting 5481 genes enriched in the PDGF, TGF-
MSC-Exos regulate inflammatory reactions, inhibit cardiomyocyte apoptosis and autophagy, promote angiogenesis, and mediate cardiac remodeling to prevent myocardial injury. MSC-Exos show therapeutic potential for ischemic cardiac injury and have a good application prospect in Cardioprotection. However, exosomes alone are not enough to reverse cardiac dysfunction after myocardial injury. Further study of the molecular mechanism can better guide the clinical transformation.
MSC-Exo, Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosome; PMI, perioperative myocardial infarction; IPC, ischemic preconditioning; RIPC, remote ischemic preconditioning; RIPostC, remote ischemic postconditioning; I/R, ischemia-reperfusion; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; Aex, ascites-derived exosomes; hMSC-Exo, human umbilical cord MSC-Exo; EMT, Epithelial to mesenchymal transition; Sd, end-systolic internal diameter; Dd, end-diastolic internal diameter; RAS, renin-angiotensin; BMSC, bone marrow-derived MSCs; ASC, adipose-derived MSCs; FOXO1, forkhead box O1; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome ten; GM-CSF, granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor; Dex, dendritic cell-derived exosomes; FGF, fibroblast growth factor; EGFR, Epidermal growth factor receptor; PDGF, platelet-derived growth factor; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; HMGA2, high mobility group at-hook 2.
WL and SW designed the research study. JL and SY performed the research and wrote the manuscript. MT and XG provided help and advice on figures. All authors contributed to editorial changes in the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Not applicable.
The figures were created in BioRender.com. We would like to express our gratitude to all those who helped us during the writing of this manuscript. Thanks to all the peer reviewers for their opinions and suggestions.
This research was funded by the Development Center for Medical Science & Technology, National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China (Grant No: WA2020RW18); Wu Jieping Medical Foundation (Grant No: 320.6750.19092-1); Jilin Province Scientific and Technological Department, International Scientific and Technological Cooperation Project (20190701043GH).
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note: IMR Press stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.




