1 Peking University Health Science Center, 100191 Beijing, China
2 Department of Cardiology, Peking University First Hospital, 100034 Beijing, China
3 Peking University Institute of Hematology, Peking University People's Hospital, 100044 Beijing, China
4 Peking University Third Hospital, 100191 Beijing, China
†These authors contributed equally.
Academic Editor: Brian Tomlinson
Abstract
Atherosclerosis is a risk factor for various cardiovascular diseases, and is linked to high rates of morbidity and mortality across the globe. Although numerous complex processes are involved in the development and progression of atherosclerosis, the exact mechanisms behind its pathogenesis remain unclear. Inflammation and endothelial cell damage exert a lasting effect on atherosclerosis, causing lipid and fibrous tissue accumulation in the intima of the artery to form plaques, and subsequently promoting atherosclerosis. Nod-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammatory corpuscle is thought to be the link between lipid metabolism and inflammation. Long Potassium outflow is a vital activator of NLRP3, with a simultaneous effect as a start-up and adjustment. The majority of existing drugs for atherosclerosis targeting the NLRP3 signaling pathway target IL-1, whereas drugs targeting the critical link of potassium efflux are relatively new. This review discusses the NLRP3 inflammatory corpuscle as a critical regulator of the immunological inflammatory pathway in atherosclerosis. Moreover, current knowledge on NLRP3 inflammatory corpuscle start and activation pathways were integrated, emphasizing potassium-involved outflow-related proteins. We highlight potential treatment approaches for NLRP3 inflammatory corpuscle pathways, specifically targeting potassium outflow channels of targeted drugs. Collectively, these insights indicate that targeting the NLRP3 inflammatory corpuscle is a vital anti-inflammatory therapy for treating atherosclerosis.
Keywords
- atherosclerosis
- NLRP3 inflammasome
- potassium efflux
- therapeutic target
Atherosclerosis is the most prevalent and important pathological condition in atherosclerotic vascular diseases, causing various cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), including coronary heart disease, hypertension, stroke, etc. These diseases constitute the global leading cause of death. In 2019, studies estimated that 17.9 million people succumbed to CVD, accounting for 32% of all global mortalities. Notably, 85% of these were attributed to coronary heart disease and stroke [1]. At present, CVD etiology remains unknown, due to a combination of multiple risk factors, including dyslipidemia, hypertension, diabetes, smoking, genetics, and obesity [2].
Atherosclerosis is thought to be caused by endothelial dysfunction and dysregulation of circulating lipid metabolism [3, 4, 5]. During its pathology, the earliest identifiable changes include focal deposition and oxidative modification of circulating lipoprotein particles dominated by low-density lipoprotein (LDL) under the endothelium [6]. After endothelial damage, circulating monocytes are selectively recruited into the endangium, where they differentiate into macrophages to eliminate the deposited lipoproteins. The deposited lipoproteins engulf the modified lipoproteins and become foam cells, forming early lipid streaks. An increase and decrease in circulating LDL and HDL levels, respectively, cause the formation of numerous foam cells. Consequently, smooth muscle cells in the tunica media vasorum are recruited to migrate. Migrating smooth muscle cells engulf the lesions that cannot be cleared. Under the stimulation of various cytokines, they generate collagen fibers, elastic fibers, and other fibrous caps wrapping the necrotic foam cells, forming typical atherosclerotic plaques. Notably, inflammation plays an indispensable role in the abovementioned atherosclerosis process [7, 8].
Recognized risk factors, including smoking, hypertension, and obesity, among others, exacerbate the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Previous studies indicate that angiotensin II activates monocytes, releasing pro-inflammatory cytokines [9, 10]; nicotine causes inflammation in the endothelium [11, 12], whereas metabolic disorders, including increased visceral fat and insulin resistance, promote the release of inflammatory mediators [13]. At the same time, the abovementioned risk factors are involved in increased LDL levels [14, 15, 16, 17]. Through ROS accumulation in the intima of blood vessels, LDL undergoes oxidative modification to generate OX-LDL, which subsequently causes inflammation of the blood vessel wall by binding toll-like receptor (TLR) and scavenger receptor. Therefore, OX-LDL is a clinical marker of plaque inflammation. OX-LDL produces chemotactic intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1), which enhance the adhesion properties of endothelial cells and promote the binding of monocytes to endothelial cells. Consequently, inflammatory cells and monocytes release monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) to activate leukocytes and stimulate smooth muscle cell proliferation [18]. At the same time, cholesterol load also forms intracellular cholesterol crystals, which subsequently activate inflammasomes, and enhance the expression and release of numerous proinflammatory cytokines [19]. Previous experimental findings have shown that the deletion of inflammatory genes minimizes the risk of atherosclerosis development. During the late stages of atherosclerosis development, inflammatory cell secretions of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) become degraded patches of collagen fibrous caps rich in bursting lipid plaques. However, the necrotic tissue factor of the core is exposed to circulation in the blood, activating the blood coagulation cascade reaction, and causing blood clot formation as well as the development of tissue ischemia [20].
Considering the aforementioned pathogenesis, lowering LDL levels is currently
considered a basic treatment approach for atherosclerosis in clinical practice.
Although effective methods including statins and preprotein invertase
Bacillus subtilis invertase/Kexin9 (PCSK9) inhibitors inhibit the levels
of circulating LDL to a certain extent, they have been linked to various adverse
cardiovascular events, threatening the lives of patients [21]. For instance, a
2017 CANTOS trial [22] revealed that although canakinumab, a monoclonal antibody
that inhibits IL-1
The classic inflammasome refers to a polymeric protein complex, primarily
comprising sensor proteins, junction molecules, and effectors. Typical
inflammasome sensor proteins include nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain
(NOD), leucine-rich repeat (LRR) sequence receptors NLRP1,
NLRP3, NLRP6, NAIP/NLRC4, melanoma-2
(AIM2)-like receptors and PYRIN, a protein containing triangular motif
(TRIM) [25]. Each of the above responds to specific pathogen-associated
molecular patterns (PAMPs) or danger-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs). The
connector molecule is the apoptosis-associated speck-like protein ASC,
with a caspase recruitment domain (CARD). This complex recruits effector cysteine
proteases that generate inflammatory factors, including IL-1
NLRP3 comprising an N-terminal pyrin domain (PYD), a central ATPase
domain (NACHT), and a C-terminal LRR primarily exists in inflammatory
cells activated by inflammatory stimulation, including macrophages, monocytes,
dendritic cells, and splenic neutrophils. Also, it is expressed in bone marrow,
muscle, endocrine cells, and neurons. NLRP3 can either be activated by
PAMPs or DAMPs to open the PYD and interact with the PYD in ASCs.
Moreover, the CARD on ASCs combines with that on procaspase-1. Collectively,
these substances integrate, making up the NLRP3 inflammasome [27].
NLRP3 inflammasome formation causes self-cleavage of procaspase-1,
generating an active caspase-1p10/p20 tetramer, which subsequently cleaves the
cytokine precursors pro-IL-1
At present, NLRP3 inflammasome activation is considered a two-signal
model comprising prime activation and activation. In this model, NLRP3,
pro-IL-1
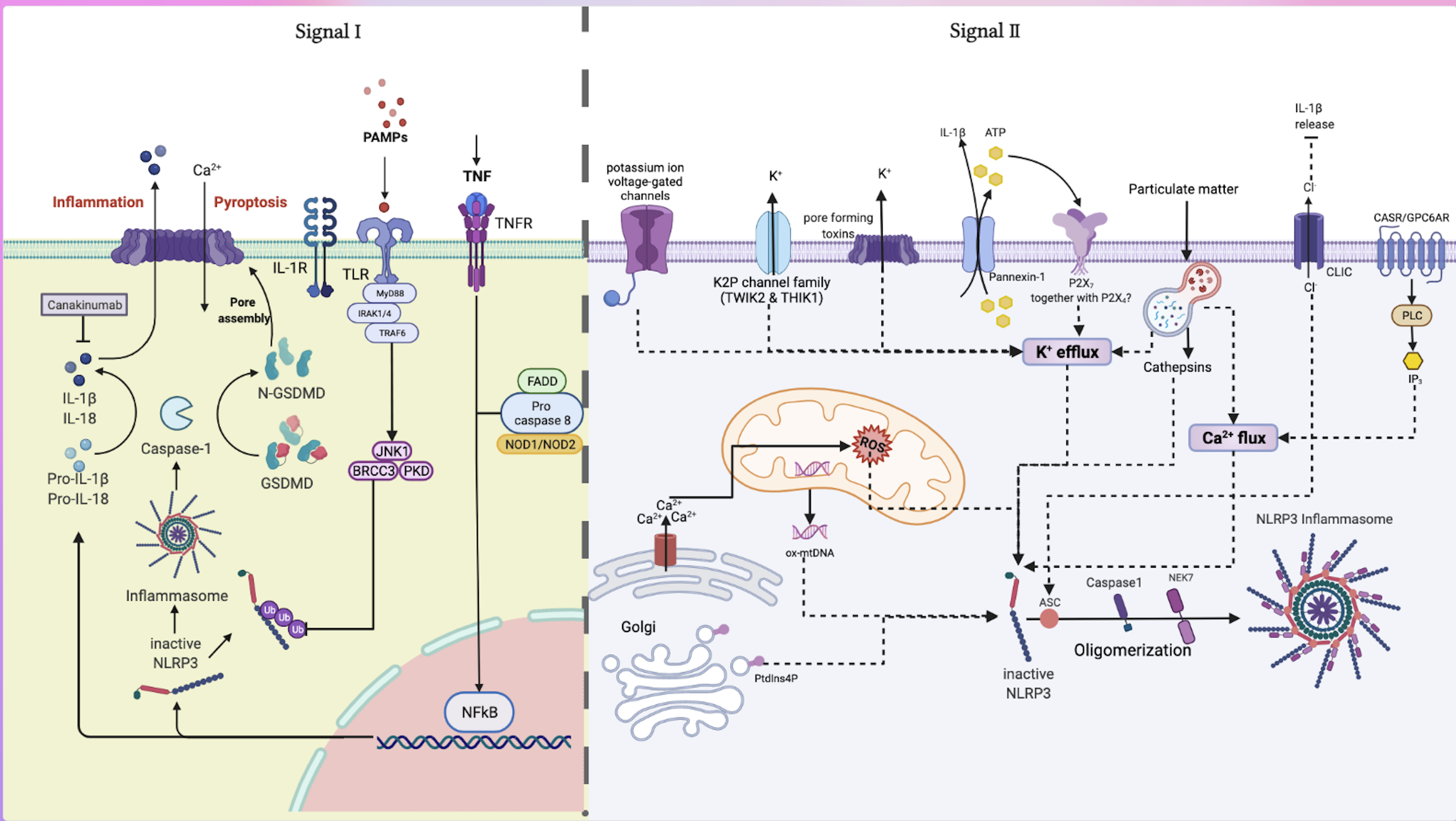 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.Classic activation pathways and common drug targets of NLRP3
inflammasome. The classic activation pathway of NLRP3 inflammasome is a
two-signal model. Signal I is induced by PAMP or DAMP stimulation of TLR and NLR,
which activates NF-
The inflammasome constitutes the innate immune system. Notably, Signa I is
activated by pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) recognizing harmful stimuli,
including PAMPs and DAMPs. PAMPs include common bacterial cell wall components,
viral products, and bacterial cell nucleus components, which primarily include
sugars and lipids, whereas DAMPs comprise endogenous cytokines released after
stimulation of tissues or cells by damage, hypoxia, stress, and other factors.
Atherosclerosis is mostly mediated by DAMPs. Harmful stimulation of TLR, NLR, and
cytokine receptor macrophages activates the transcription factor
NF-
Besides the aforementioned classical two-signal transcriptional activation
pathways, the critical role played by noncanonical and alternative activation of
the NLRP3 inflammasome has been documented (Supplementary Table 1). Specifically, the non-canonical NLRP3 inflammasome activation
pathway is mediated by caspase-11 in mouse cells or caspase-4/caspase-5 in human
cells in response to LPS in gram-negative bacteria. In humans, caspase-4 is
constitutively expressed in numerous non-monocytes and monocytes. Therefore,
cytoplasmic LPS activates non-classical inflammasomes without priming steps [34].
In this pathway, extracellular LPS activates TLR4, induces type Ⅰ
interferon response, and complements the C3-C3aR axis, thereby upregulating
caspase-11 expression. Previous findings indicate that Caspase-11 directly
recognizes lipid A in the conserved structure of cytoplasmic LPS, causing its
oligomerization and automatic proteolysis [35]. This process is followed by
gasdermin D (GSDMD) generation, which causes cell lysis and pyrosis [36], and ATP
release from pannexin-1 [37]. Consequently, this activates the P2X7 receptor,
resulting in potassium outflow, activating NLRP3-caspase-1-dependent
IL-1
An alternative inflammasome activation pathway occurs in human monocytes and
secretes IL-1
NLRP3 inflammasome activation involves various ion flux events, including potassium outflow, calcium mobilization, chloride outflow, and sodium inflow. Among them, is potassium outflow, which functions upstream of NLRP3 inflammasome activation; this is extensively considered a necessary condition and common feature of classic NLRP3 inflammasome activation. That is, potassium outflow occurs before NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Studies have shown that high extracellular potassium also inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation [44], whereas other scholars indicate that NLRP3 inflammasome activation is unrelated to potassium outflow [38, 45]. Despite extensive research, the specific molecular mechanisms by which potassium outflow causes NLRP3 inflammasome activation to remain poorly understood. Elsewhere, researchers have hypothesized that potassium outflow may be associated with conformational changes in NLRP3, mitochondrial dysfunction, and mtROS production that promote NLRP3 inflammasome activation [46].
Previous studies indicate that the P2X7 receptor, pannexin-1, K2P channel, and
GSDMD are closely related to this process [47]. Additionally, LPS binds to
complement components in vivo, forming membrane-attacking complexes on
the cell membrane. On the other hand, C3a binds to receptors on monocytes to
release ATP, whereas particle irritants, including alum, silica crystals, and
calcium pyrophosphate crystals directly cause the outflow of potassium ions [48].
The P2X7 receptor is an ATP-gated non-selective cation channel with a
pore-forming motif similar to that of a potassium ion channel, that can be
activated by extracellular ATP for direct outflow of potassium ions. Its
deficiency is linked to the inhibition of IL-1
Of note, pannexin-1 is a non-selective macroporous channel, whose relationship
with the NLRP3 inflammasome remains puzzling. Nonetheless, it is closely
associated with apoptosis. Previous studies indicate that annexin-1 releases
IL-1
The two-pore domain potassium (K2P) channels are an important family of mammalian potassium channels that maintains the resting membrane potential in nearly all cells. Previous studies indicate that TWIK2, a member of the K2P channel family, has a synergistic effect with P2X7 in macrophages. The former causes calcium and sodium ions to flow in to change the membrane potential, whereas the latter causes potassium ions to flow out to activate the NLRP3 inflammasome. THIK1 is another member of the K2P channel family that activates the NLRP3 inflammasome in microglia [55]. Also, potassium ion voltage-gated channels KCNA3 and KCNB2 as well as potassium ion inward rectifier channels KCNJ3, KCNMA1, and KCNN4 are involved [56].
Nek7 is a member of the mammalian NIMA-related kinase (Nek) family
recognized as an essential mediator in downstream activation of the
NLRP3 inflammasome by potassium outflow. It is a multifunctional kinase
that influences processes, including centrosome replication, mitochondrial
regulation, intracellular protein transport, DNA repair, and mitotic spindle
assembly. For instance, He et al. [57] reported that as an NLRP3 binding
protein, Nek7 acts downstream of potassium ion outflow and regulates
NLRP3 oligomerization and activation. In the absence of Nek7,
caspase-1 activation and IL-1
Previous research findings have shown that atherosclerosis is globally
recognized as a chronic inflammatory disease. Moreover, its course is nearly free
of microbial infection; thus, atherosclerosis-associated inflammation is
frequently considered an aseptic inflammation [59, 60]. Aseptic inflammation is
majorly caused by inflammasome activation, among which studies on the
NLRP3 inflammasome have reached maturity. Clinical and basic study
results have shown that the NLRP3 inflammasome is expressed in
endothelial cells, immune cells, smooth muscle cells, and other cells involved in
the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. However, its products IL-1
Although the role of NLRP3 in atherosclerosis has not been fully
established, several studies have shown that it modulates the early stages of
disease development. Endothelial injury is the first step of atherosclerosis,
whereas expression of NLRP3 and ASC in endothelial cells increases under
the action of nicotine, ultimately causing pyroptosis [11]. The vascular ECs
cover the intima of blood vessels, forming a semipermeable barrier between
circulating blood and the extravascular matrix. IL-1
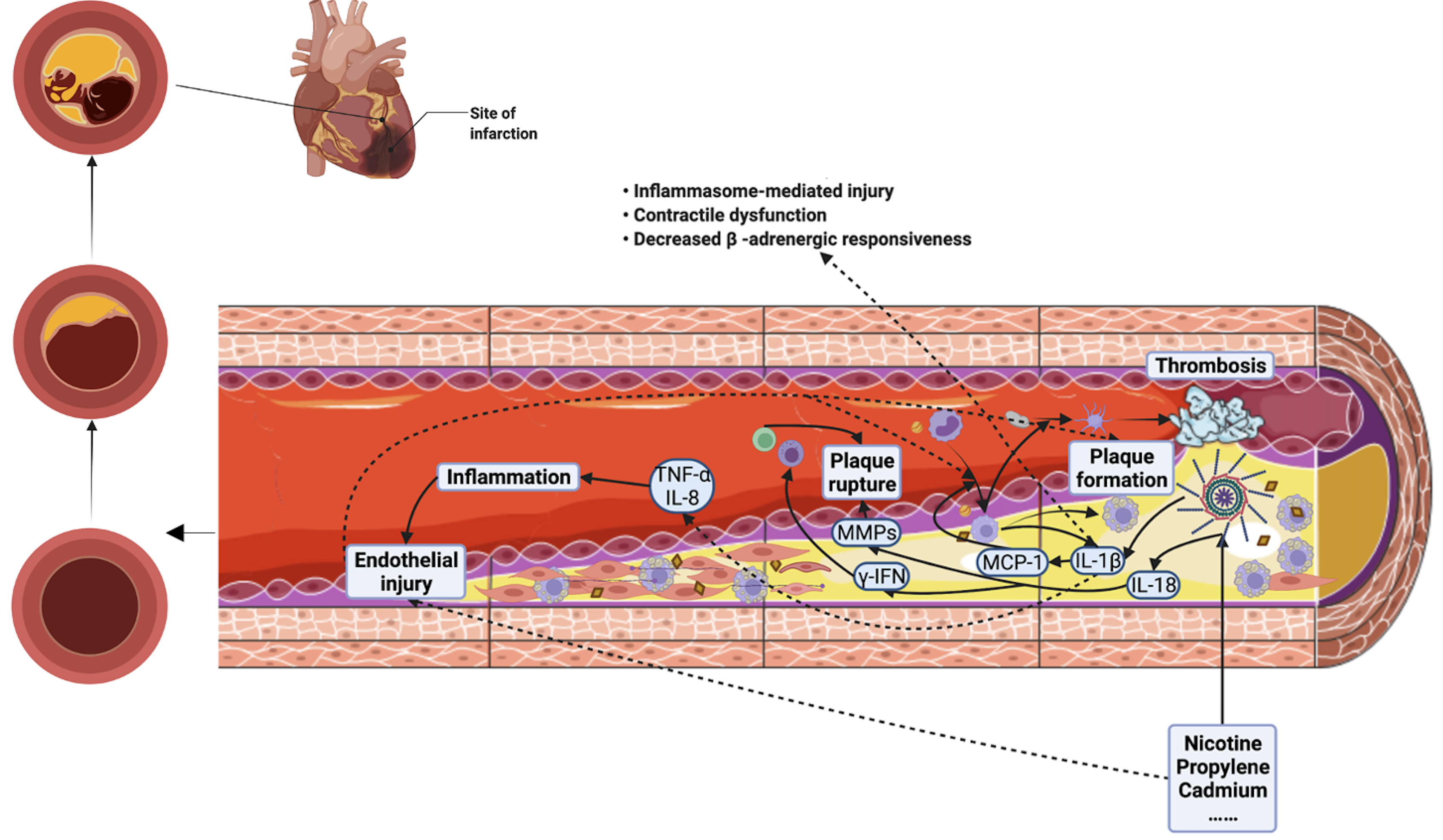 Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.Relationship between NLRP3 inflammasome and atherosclerosis and
acute myocardial infarction. NLRP3 inflammasome plays a role in promoting
different stages of atherosclerosis: (1) During plaque formation, NLRP3
inflammasome can destroy endothelial cells directly by itself or by causing
inflammatory reactions, leading to deposition of ox-LDL and cholesterol, while
IL-1
Several pieces of evidence have shown that NLRP3 inflammasome
activation enhances lipid deposition and migration in macrophages as well as
accelerates foam cell formation [71]. As mentioned above, macrophages
phagocytosing ox-LDL or cholesterol to form foam cells are associated with
NLRP3 in the following ways [72]: (1) lysosomes release ROS and
proteases to activate NLRP3; (2) TLRs recognize ox-LDL and free fatty
acids to induce NF-
Acute inflammation is often caused by PAMPs (infection, non-sterilized
inflammation) and DAMPs (cellular stress, trauma). This process occurs over a
short period and is characterized by severe manifestations. Previous studies have
identified IL-6, TNF-
During the normal inflammatory response, inflammatory response subsides upon
removal of the stimulus. Nonetheless, acute inflammation is regulated by social,
psychological, environmental, and biological factors, which impede its regression
and instead promote the development of chronic inflammation in a low-level,
non-infectious (i.e., sterile) condition [75]. Chronic inflammation, usually
caused by DAMPs, including metabolic disorders, and tissue damage, among others,
is age-related causing persistent damage to an organism. Chronic inflammation
characterized by metabolic disorders, including type 2 diabetes (T2D), obesity,
atherosclerosis, and AD, promote diabetes occurrence, whereas NLRP3
inflammasome mediates obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance [82].
Previous studies have shown that molecules, including high glucose, islet amyloid
polypeptides, saturated fatty acids, and mitochondrial ROS activate the
NLRP3 inflammasome and promote T2D pathogenesis [82, 83, 84].
Additionally, A
In conclusion, inflammasomes play a double-edged sword in inflammation, whereas their activation in acute inflammation helps in eliminating necrotic cells and initiating tissue repair. Nevertheless, sustained activation of inflammasomes in chronic disease is detrimental, resulting in metabolic disorders and damage to tissues [85].
Through extensive pathogenicity analysis, scholars have confirmed that atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory disease. The inflammasome plays a crucial role in this process, specifically with the NLRP3 inflammasome being extensively studied. Consequently, there has been an emergence of multiple targeted therapies targeting NLRP3 inflammasome complex cascade signals [86]. These include inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation and upstream signaling, blocking inflammasome assembly, inhibition of caspase-1 activation, blocking GSDMD cleavage, and neutralization of inflammatory cytokines. Although specific inhibitors of the NLRP3 inflammasome have significant therapeutic potential, no drugs have so far been approved for direct NLRP3 inflammasome inhibition.
Only a few drugs targeting potassium channels in NLRP3 inflammasome
activation have been developed. The sulfonylurea compound glibenclamide is an
extensively studied compound targeting potassium channels. Glibenclamide is an
oral hypoglycemic drug with anti-inflammatory effects through NLRP3
inflammasome inhibition, reduction of proinflammatory cytokine production, and
inflammatory cell recruitment as well as inhibition of NO production. This drug
has therapeutic effects against respiratory, digestive, urinary, heart, and
central nervous system inflammatory diseases as well as ischemia-reperfusion
injury processes [87]. Glibenclamide is an ATP-sensitive potassium channel
(K
Different specific agents for P2X7 receptor and NLRP3 inflammasome inhibition
have been developed. None of these drugs is currently approved for therapeutic
use; a few are at early clinical stages. Berberine is a bioactive base extracted
from various herbal components with enormous pharmacological effects, including
antibacterial, anticancer, anti-inflammatory, blood-glucose-lowering, and
lipid-lowering effects [91]. Antiatherosclerotic effects of berberine have been
explored via multiple animal and clinical studies. Previous findings have shown
that berberine disrupts the NF-
Colchicine effectively hinders pore formation induced by P2X7 receptors, thereby
abrogating potassium ion flow from the cytoplasm [94, 95]. Colchicine exhibits
broad anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting microtubule formation, mitosis,
leukocyte motility and the release of inflammatory cytokines. Colchicine inhibits
the assembly of the NLRP3, thereby reducing the production of downstream
IL-1
Additionally, the P2X7 receptor is blocked by novel biological agents, including
antibodies and nanoantibodies, with high specificity in various inflammatory
models [101]. Pannexin-1 is associated with P2X7 receptor activation, hence, its
inhibitors also block NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Probenecid is a
prevalent pannexin-1 antagonist. In vitro treatment of macrophages with
probenecid reduces NLRP3 inflammasome-dependent IL-1
Kv1.3 voltage-gated potassium channel is a primary potassium channel in
macrophages, and its activation causes potassium ion outflow. NLRP3
inflammasome is a downstream molecule of the Kv1.3 voltage-gated potassium
channel. Kv1.3 is involved in apoptosis, migration, proliferation, and activation
of macrophages. Blocking Kv1.3 with Margatoxin, its specific inhibitor prevents
macrophages from converting into foam cells in atherosclerosis [105]. Previous
findings indicate that NLRP3, ASC, and caspase-1 expression are
significantly upregulated in colitis; inhibition of the NLRP3 inflammasome
pathway effectively reduces the severity of colitis [106]. Recent studies reveal
that PAP-1 (a Kv1.3 channel-specific blocker) downregulates Kv1.3 expression in
macrophages in mice with colitis and inhibits macrophage activation [107].
Moreover, PAP-1 effectively inhibits the expression of NLRP3,
ASC, caspase-1p20 and IL-1
K2P channel modulators have been extensively investigated in recent years.
Xiao-yan Wu et al. [109] used various K2P channel modulators, including
quinine, fluoxetine, DCPIB, ML365, ML335, and TKDC to evaluate their effects on
K2P channels. As a result, quinine and fluoxetine were non-selective and weak
blockers of all K2P channels. ML365 showed a high selective inhibitory effect on
TWIK2 via dose-dependent inhibition of ATP-induced NLRP3 inflammasome
activation. Moreover, ML365 administration decreased the levels of
IL-1
At present, clinical treatment of NLRP3-related diseases primarily
targets IL-1
Studies have shown that several small molecular compounds including MCC950, BHB, and Bay 11-7082 inhibit NLRP3 inflammasome activation in vitro. Nonetheless, the majority of these inhibitors are relatively non-specific with low efficacy. Supplementary Table 2 presents recent pharmacological targets and associated clinical trials of NLRP3 inflammasome pathway inhibitors.
Incidence of atherosclerosis is projected to increase owing to increase in aging population and current changes in lifestyle. Studies report that atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory disease, associated with a variety of adverse cardiovascular events. NLRP3 inflammasome is an important component of innate immune system that links lipid metabolism to inflammation. Lipid deposition, ox-LDL, macrophage transformation into foam cells and other events associated with atherosclerosis interact with the NLRP3 inflammasome to promote progression of the disease. Initiation and activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome is a two-signal model in which potassium outflow is an indispensable process in signal 2. Only few drugs have been developed that target NLRP3 inflammasome due to the unknown mechanism of potassium outflow and activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome.
Currently, most drugs against NLRP3 inflammasome target IL-1
Conception and design—ZYA, YJJ; drafting the manuscript—ZYA, YJJ, XCL, ZXS; revision—ZYA, YJJ, XCL, ZXS; final approval—ZYA, YJJ, XCL, ZXS.
Not applicable.
We acknowledge the support from the Education Depatment of Peking University Health Science Center. Figures are created with BioRender.com.
This research received no external funding.
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Supplementary material associated with this article can be found, in the online version, at https://doi.org/10.31083/j.rcm2308268.
References
Publisher’s Note: IMR Press stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.


