1 Department of Medical and Surgical Sciences, Magna Graecia University, 88100 Catanzaro, Italy
2 Cardiology Unit, “San Giovanni di Dio” Hospital, 88900 Crotone, Italy
3 CMR Unit, Royal Brompton and Harefield Hospital, UB9 6JH London, UK
4 Pediatric Cardiology Unit, Department of Children and Woman’s Health, University of Padua, 35128 Padua, Italy
Academic Editor: Jerome L. Fleg
Abstract
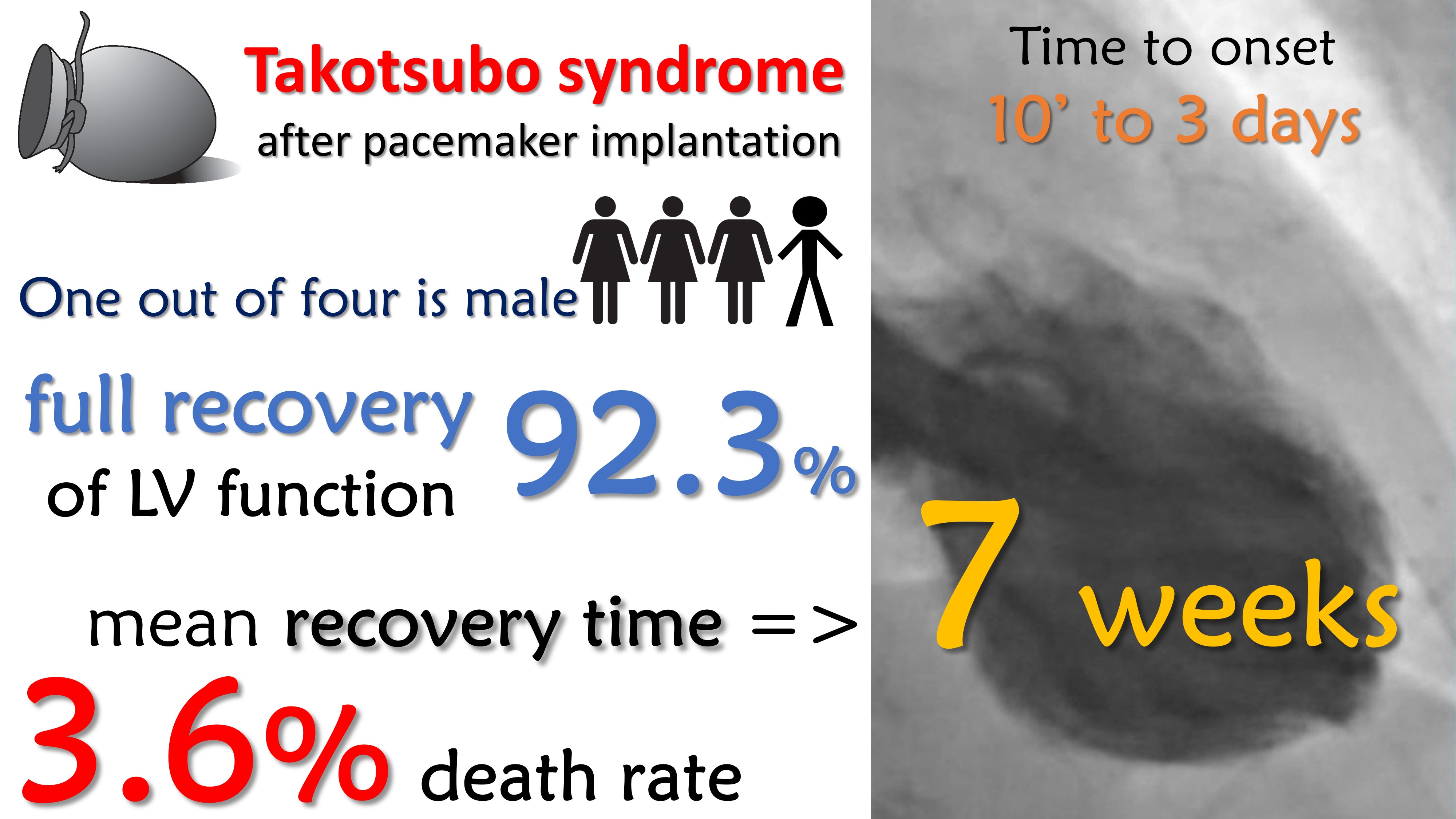
Background: Takotsubo syndrome (TTS) is an acute cardiac condition characterized by a temporary wall motion abnormality of the left ventricle that mimics an acute coronary syndrome (ACS). TTS usually occurs following emotional or physical triggering event. More recently, sporadic cases of TTS arising after pacemaker implantation were reported. Methods: We performed a systematic review of the available literature to provide a comprehensive overview of the current knowledge about pacemaker implantation-induced TTS. Results: The articles selected included case reports and one registry on 28 patients. Most cases occurred in women (75%), encompassing a broad age range. The mean age of the cases described was 74 years. Full recovery of cardiac function was reported in most cases (92.3%), with largely varying recovery times, on average 7 weeks. The most common comorbidity was arterial hypertension and the average ejection fraction at admission was approximately 62%. Clinical severity ranges from asymptomatic cases to severe clinical heart failure syndrome. Altogether the case fatality rate was 3.6%. Conclusions: For rare it might be, awareness about the potential to develop TTS after pacemaker implantation should prompt careful clinical monitoring, with daily electrocardiogram (ECG) monitoring and at least one echocardiographic examination prior to patients’ discharge to allow early diagnosis and minimize the clinical risk.
Graphical Abstract
Keywords
- Takotsubo
- pacemaker
- procedural complication
Takotsubo syndrome (TTS) was first described in Japan in the 1990s and is usually characterized by transient wall motion abnormalities of the left ventricle (LV) mimicking an acute coronary syndrome (ACS) [1]. Traditionally, TTS has been typically reported after an emotional or physical trigger event [2]. However, growing clinical experience revealed that several alternative mechanisms can be responsible for TTS, including catecholamine-induced myocardial stunning and inflammation, coronary microvascular dysfunction, and myocardial microinfarction [3, 4], making up a prevalence of 1–3% among all patients presenting with suspected ST-Elevation coronary syndrome [5, 6].
Initially believed of being a very rare condition, it has gradually emerged that several different stimuli can elicit TTS, including pacemaker implantation. The increasing complexity in the assessment of TTS has recently prompted the development of standardized diagnostic criteria, such as the score proposed by the international consensus on TTS (InterTAK Score), as reported in Table 1 [7].
| 1. Transient left ventricular dysfunction (hypokinesia, akinesia, or dyskinesia) presenting as apical ballooning or midventricular, basal, or focal wall motion abnormalities that usually don’t correspond to a single epicardial vascular distribution. Right ventricular involvement can be also present. |
|---|
| 2. The acute event is usually preceded by a stressor (either emotional or physical). |
| 3. Neurologic disorders (particularly vascular disease) as well as pheochromocytoma can also be triggers for takotsubo syndrome. |
| 4. Electrocardiogram (ECG) usually shows new abnormalities (particularly in the ST-T tract). |
| 5. Cardiac biomarkers (troponin and creatine kinase) are usually elevated as well as brain natriuretic peptide. |
| 6. Significant coronary artery disease could also be diagnosed in patients with takotsubo syndrome and does not represent an exclusion criterion for the diagnosis. |
| 7. Patients should have no evidence of infectious myocarditis. Cardiac magnetic resonance could be helpful in distinguish the two conditions. |
| 8. Postmenopausal women represent the majority of takotsubo cases. |
In this context, our aim was to provide a comprehensive overview of the current knowledge about pacemaker-induced TTS.
For this purpose, we performed a review of the literature on PubMed and Google Scholar. The following keywords have been used for the research: (“takotsubo cardiomyopathy” [MeSH Terms]) OR (takotsubo syndrome [MeSH Terms]) OR (takotsubo pacemaker [Title]) AND (pacemaker [Text Word]) AND (English [Language]). Search results were screened according to the PRISMA protocol by two investigators (AS, IL) independently to identify eligible articles. Divergencies were resolved though discussion on study methodology until consensus was reached. Studies were selected if they fulfilled all the pre-defined inclusion criteria reported. Criteria for inclusion were: (i) original data; (ii) presence of apical ballooning; (iii) exclusion of obstructive CAD; (iv) other cardiomyopathies ruled out or unlikely; and (v) occurrence shortly following pacemaker implantation. Exclusion criteria were: the diagnosis of Takotsubo syndrome wasn’t confirmed nor sufficiently discussed; no relationship with pacemaker implantation was reported; systematic review or meta-analyses. Data extraction was performed by two independent authors (AS, SDR), with divergences resolved by consensus. Baseline characteristics were extracted, including age, gender, cardiovascular risk factors, timing of TTS onset respect to pacemaker implantation, clinical presentation and symptoms, clinical outcome and recovery time.
Our search retrieved 54 articles, published between 2006 and 2022. Of those, 18 papers were eligible for inclusion. Thirty-six publications were excluded from the original search. Exclusion criteria are reported in detail in the PRISMA flowchart (Fig. 1) and includecase reports of Takotsubo syndrome not related to device implantation, duplicate studies. The articles selected included 17 case reports and one monocentre registry including altogether 28 patients (21 female and 7 male) that developed TTS after a pacemaker (PM) implantation, mean age 74 years (range 0–91 years), the most common comorbidity was arterial hypertension followed by atrial fibrillation and diabetes mellitus. In almost all the articles included in our review, the only echocardiographic feature reported was the left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF). In the most case it was in the normal range with few cases that presented a mild reduced LVEF, among the cases where it was reported the mean value was approximately 62% (range 50–75%) [8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25].
 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.PRISMA Flowchart describing articles’ screening and selection processes.
In 19 cases the indication to PM implantation was atrioventricular (AV) conduction defect (AV block) or atrial fibrillation (AF) with slow ventricular response), and Sick Sinus Syndrome (SSS) in the remaining 9 cases. Most of devices implanted were dual chamber PM (n = 23). Clinical details on all cases included are reported in Table 2 (Ref. [8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25]). Usually, TTS occurs in postmenopausal women and only in 9.7% of cases it affects men [26]. It’s interesting that, in this specific setting, men represent approximately 25% of the population. ECG changes were recorded in almost all cases, except for very few cases [12, 13, 16, 23, 24] in which ventricular pacing probably masked its ECG markers. A recent study [27] has documented that persistent ST elevation (PSTE), defined as
| Authors | Sex | Age | Indication for PM implantation | Type of PM | Clinical presentation | Recovery | Time for recovery | ECG abnormalities | Time to onset of symptoms after PM implantation | Complications of TTS | Death |
| Kurisu et al. [8] | Female | 89 | AV block | Dual chamber | Chest discomfort | No | Permanent dysfunction | ST-segment elevation in leads I, aVL and V2–6 | 10 minutes | AHF | No |
| Female | 77 | AV block | Dual chamber | Orthopnea | No | Permanent dysfunction | ST-segment elevation in leads V2–6 | 3 days | AHF | No | |
| Chun et al. [9] | Female | 77 | SSS | Dual chamber | Asymptomatic | Yes | 6 weeks | inverted T waves V2–4 | - | No | No |
| Abu Sham’a et al. [11] | Female | 86 | AV block | Dual chamber | Acute pulmonary edema | Yes | 1 week | prolongation of the QTc interval | 1 day | Acute pulmonary edema | No |
| Kohnen et al. [10] | Female | 83 | SSS | Dual chamber | Dyspnea | Yes | 9 weeks | ST-segment elevations in the inferior and precordial leads | Few Hours | Left ventricular thrombus | No |
| Golzio et al. [14] | Female | 67 | AV block | Dual chamber | Chest pain | Yes | 12 weeks | ST-segment elevation in V2, T-wave inversion in leads DII-DIII-aVF and V3–V6 | 1 day | No | No |
| Female | 64 | SSS | Dual chamber | Asymptomatic | Yes | 12 weeks | ST-segment elevation in leads DII, DIII, aVF and V2–V6 | - | No | No | |
| Brunetti et al. [12] | Female | 65 | AV block | Dual chamber | Dyspnea | Yes | 1 week | Paced | Few Hours | AHF | No |
| Mazurek et al. [13] | Male | 77 | AV block | Dual chamber | Dyspnea | Yes | 1 day | Paced | Few Hours | Acute pulmonary edema | No |
| Gardini et al. [15] | Female | 75 | AV block | Dual chamber | Chest pain and Dyspnea | Yes | Some days | ST segment elevation in inferior and anterior leads. | Few Hours | No | No |
| Postema et al. [16] | Female | 61 | AV block | Dual chamber | Chest pain and orthopnoea | Yes | 3 weeks | Paced | 1 day | AHF | No |
| Kinbara et al. [18] | Female | 69 | AV block | Dual chamber | Chest pain and syncope | - | - | VT | 3 days | VT, VF, Acute pulmonary edema | Yes |
| Dias et al. [17] | Female | 72 | AV block | - | Nausea and lightheadedness | - | - | - | Few Hours | AHF | No |
| Daswood et al. [19] | Female | 76 | SSS | Dual chamber | Chest pain, Hypotension | Yes | 24 weeks | Global deep T wave inversions | 1 day | Hypotension, Hypoxia | No |
| Lazzari et al. [20] | Female | 67 | SSS | Dual chamber | Asymptomatic | Yes | 6 weeks | ST-segment elevation of 1 mm in the precordial leads V2-5, rapidly changing to negative T-waves, and widespread repolarization abnormalities | - | No | No |
| Wei et al. [21] | Female | 72 | AV block | Dual chamber | Chest pain and Dyspnea | Yes | 16 weeks | T waves inversion in the pericardial leads | 1 day | AHF | No |
| Wakatsuki et al. [22] | Female | 81 | SSS | Dual chamber | Onset with ventricular tachycardia | Yes | 2 weeks | giant negative T waves and a prolonged QT interval | 1 day | VT, VF | No |
| Niewinski et al. [23] | Female | 75 | AV block | Dual chamber | Chest pain | Yes | - | Paced | 2 days | No | No |
| Male | 73 | AF with slow ventricular response | Single chamber | Hypotension | Yes | - | LAH | Fews hours | AHF | No | |
| Female | 87 | AV block | Dual chamber | Asymptomatic | Yes | - | Paced | - | No | No | |
| Female | 88 | SSS | Single chamber | Hypotension | Yes | - | ST segment denivelation | Fews hours | AHF | No | |
| Male | 80 | AV block | Dual chamber | Dyspnea | Yes | - | Paced | Fews hours | AHF | No | |
| Male | 75 | AF with slow ventricular response | Single chamber | Asymptomatic | Yes | - | ST segment denivelation | - | No | No | |
| Male | 89 | SSS | Dual chamber | Asymptomatic | Yes | - | Q-waves | - | No | No | |
| Female | 77 | AF with slow ventricular response | Single chamber | Dyspnea | Yes | - | ST segment denivelation and pronlonger QT interval | Fews hours | AHF | No | |
| Male | 92 | SSS | Dual chamber | Dyspnea, chest pain | Yes | - | LBBB | Fews hours | Elevation pacing thresholds | No | |
| Iqbal et al. [24] | Female | 84 days | AV block | Dual chamber | - | Yes | 8 weeks | Paced | - | No | No |
| Moinudddin et al. [25] | Male | 65 | AV block | Dual chamber | Syncope | Yes | 4 weeks | Paced/LBB | Fews hours | Hypotension | No |
| AV block, atrioventricular block; SSS, sick sinus syndrome; AF, atrial fibrillation; VT, ventricular tachycardia; VF, ventricular fibrillation; LAH, left anterior hemiblock; LBBB, left bundle brunch block; AHF, acute heart failure | |||||||||||
Iqbal et al. [2] reported the case of a new-born who underwent PM implantation for congenital heart block and hemodynamic instability that developed TTS and apical ballooning early after the procedure. The documented wall motion abnormalities (WMAs) at echocardiography persisted at 20 days follow-up, followed by partial recovery, after starting pharmacological therapy, at 23 days follow-up and complete recovery at ten months of age.
Mean recovery time for LV systolic function among the reported cases was approximately 7 weeks, although Kurisu et al. [8] described two cases of persistent LV dysfunction following TTS. Lack of recovery of LV function could be explained either by a too short follow-up period (maximum 4 months) or by an additive potential harmful effect induced by pacing in the context of TTS. Ventricular pacing could in fact cause alterations in electrical and mechanical activation [28, 29, 30, 31, 32]. Data reported in literature showing that chronic pacing at a threshold of 40% pacing burden is cause of LV dysfunction.
In addition, we observed longer recovery times in those cases, compared to the remaining cases described in the literature. Unfortunately, the authors who described the above cases did not report the percentage of ventricular pacing, information that could have made this observation more significant and support the hypothesis of a negative effect on the recovery times of LV function in the setting of TTS in case of a high percentage of ventricular pacing.
LV apical oedema and inflammation, common characteristics in TTS, could be the cause, in the acute setting, of transient dysfunction of the device [33, 34]. Probably myocardial oedema is able to increase local tissue impedance and therefore causing increased pacing threshold, particularly, with bipolar pacing [34, 35]. This hypothesis seems to be supported by the significant correlation between corrected QT interval (QTc) an indirect sign of myocardial oedema, and ventricular pacing thresholds. However, Brunetti et al. [36] reported a case of delayed transient ventricular pacing failure in a patient with TTS discharged after partial recovery of LV function, who was referred after 4 weeks with pacing failure, due to a concomitant increase in pacing threshold, subsequently returned within normal ranges after complete LV function recovery. In the case described by Brunetti et al. [36] report probably, delayed evidence of pacing failure may coincide with further delayed QT prolongation, which usually peaks in the subacute phase of TTS rather than in the acute phase [37]. Alternatively, it is possible that other conditions beyond QTc prolongation may have influenced ventricular pacing threshold and QT length.
TTS was traditionally considered a benign disease. However, recent data demonstrated that rates of cardiogenic shock and death are comparable to ACS patients treated according to current guidelines [38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44] and despite long-term follow-up data are missing, the clinical consequences should not be underestimated. In fact, in 4 of the reported cases the patient had haemodynamic instability [9, 14, 23]. Moreover, in other 2 of the reported cases the patient had ventricular tachycardia/fibrillation [22] and of these one died acutely [18].
Interestingly, the absence of symptoms at onset did not always predict a benign course. Indeed, in the case described by Wakatsuki et al. [22] the patient was asymptomatic, but she developed polymorphic ventricular tachycardia later. For these reasons, routine investigations are suggested to early identify potentially life-threatening complications even in asymptomatic patients.
Niewinski et al. [23] recently conducted a retrospective analysis in one high volume implantation centre, identifying nine cases of TTS following PM, with a prevalence of 0.54% in the analysed period (1655 devices implanted between 2013–2017). In their study, female gender was not predictive of TTS, while the presence of any cognitive decline and frailty syndrome were independent risk factors or TTS occurrence in the described cohort [23].
Evidence-based guidelines for the treatment of TTS are lacking, and current therapeutic strategies are mainly based on clinical experience and expert consensus documents.
One open question is whether there might be predicting elements to risk-stratify patients. However, only a multicentre prospective study could provide an answer to this question. Based on currently available information, despite the clinical course was benign in most cases, we should focus our efforts on early diagnosis. In fact, even if symptomatic cases generally presented a benign course, early diagnosis might be crucial in specific cases. What might the most efficient and effective strategy to identify similar cases? Looking at the available data, the onset of TTS was between a few minutes up to three days after device implantation. However, most cases manifested very early after the implantation procedure. In fact, 86% of patients manifested signs or symptoms of TTS within the first 24 hours after PM implantation (Fig. 2). This would render the probability of missing a diagnosis rather low, as a simple fast echocardiogram at discharge would very efficiently identify TTS-related signs. Of course, more solid clinical evidence, ideally from prospective studies is needed to better inform clinical practice in this setting.
 Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.TTS onset time after pacemaker implantation.
The main limitation of this review is that most of the information comes from case reports (17 out of 18 articles) and only one monocentre registry. Therefore, a systematic collection of the clinical and instrumental characteristics of the patients was not performed. Furthermore, no long-term follow-up data are available. However, despite the limited duration of follow up available, the evidence of full recovery of cardiac function in 92.3% of cases is reassuring.
As pacemaker implantation was recently described as a potential trigger for TTS, we performed a systematic revision of the published literature. Our findings suggest the incidence of TTS after is not so rare as one might think. In fact, the picture showed by our results is a case rate of approximately 0.5%, which could be an underestimation. Furthermore, it is possible that the characteristics of patients affected by TTS after PM implantation reported here do not fully mirror the general population. Several questions still remain open. For example, the typical inflammation and oedema usually found in TTS could be the cause of transient device malfunction. Looking at the clinical course of all clinical cases described so far, daily ECG monitoring and an echocardiogram targeted to wall motion examination prior to patients’ discharge might be helpful to minimize the risk of missing this infrequent, yet dreadful complication of PM implantation.
AV block, atrioventricular block; SSS, sick sinus syndrome; AF, atrial fibrillation; VT, ventricular tachycardia; VF, ventricular fibrillation; LAH, left anterior hemiblock; LBBB, left bundle brunch block; AHF, acute heart failure.
AS—conceptualization. AS and SDR—study design, project management and manuscript draft. AS, IL, SDR, JS, LRR, GC, CC—data collection and analysis. AS, SDR, IL, CI—critical revision. All authors discussed the results and contributed to the final manuscript.
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
This research received no external funding.
The author declares no conflict of interest. Salvatore De Rosa is serving as one of the Editorial Board members and Guest editors of this journal. Ciro Indolfi is serving as Guest Editor of this journal. We declare that Salvatore De Rosa and Ciro Indolfi had no involvement in the peer review of this article and has no access to information regarding its peer review. Full responsibility for the editorial process for this article was delegated to Jerome L. Fleg.


