1 School of Basic Medicine, Gansu University of Chinese Medicine, 730000 Lanzhou, Gansu, China
2 Department of Scientific Research Office, Gansu Provincial Hospital, 730000 Lanzhou, Gansu, China
3 Department of Pathology, The 940th Hospital of Joint Logistics Support Force of Chinese People's Liberation Army, 730050 Lanzhou, Gansu, China
4 Department of Cardiology, Gansu Provincial Hospital, 730000 Lanzhou, Gansu, China
5 Department of Scientific Research Office, Gansu Provincial Hospital, 730000 Lanzhou, Gansu, China
Academic Editor: Vincenzo Lionetti
Abstract
Pulmonary endarterectomy (PEA) is used to treat chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH) patients, and it can effectively remove organized thrombotic materials and proliferative intima as well as improve hemodynamics. It has been reported that the levels of several inflammatory factors were altered in the peri-operative period of PEA. Even though their specific role remains unknown, this could have some relevance. In this study, we reviewed the recently published data addressing these factors in PEA, attempting to understand their potential implications.
Keywords
- inflammation
- pulmonary endarterectomy
- perioperative period
Pulmonary endarterectomy (PEA) surgery has been the primary treatment option for patients suffering from chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH) [1]. PEA was first proposed and popularized by a team from the University of California in San Diego, USA [2]. PEA surgery can clear organized thromboembolic materials and enhance the hemodynamic index of pulmonary circulation and prognosis among CTEPH patients [3, 4]. However, some potential complications are causing early postoperative mortality rates of 5%–23% [5]. It has been reported that PEA-associated hemodynamic instability during the perioperative period was usually correlated with cytokines overstimulation [6]. Additionally, several studies have revealed that the blood samples of CTEPH patients after PEA surgery contained a lot of inflammatory factors and cytokines [5, 7, 8]. With an increasing number of reports regarding PEA inflammation, it is essential to review recent data for further understanding the implications of PEA that are beneficial for patients.
Inflammation involves the pathogenesis of CTEPH and has a
critical role in the process of right heart failure. Many studies identified high
levels of inflammatory cytokines in the blood samples of CTEPH patients, such as
interleukin (IL)-6, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-
| Author | Samples | TNF- |
IL-6 | IL-8 | IL-10 | |||
| Preoperative | Postoperative | Preoperative | Postoperative | Preoperative | Postoperative | |||
| Langer F et al. (2004) [5] | 14 | Elevated in 8 patients | They decreased significantly within 24 h after PEA surgery in 12 patients | Elevated in 5 patients | A sharp peak immediately after surgery, decreased during the postoperative period but was higher than the baseline | - | Elevated in 4 patients | During surgery, the level increased significantly, followed by a drastic decrease. After 8 h of surgery, it reached its baseline levels |
| Maruna P et al. (2008) [11] | 32 | Reached its peak after 24 h sternotomy, returned to preoperative level after 48 h sternotomy | Elevated in 6 of 32 patients 24 h before surgery. | The peak level of IL-6 was 6 h after sternotomy. The level was higher than preoperative after 48 h sternotomy | Reached its peak 12 h after sternotomy. The level was higher than preoperative after 48 h sternotomy | - | - | |
| Lindner J et al. (2009) [6] | 36 | Elevated at the time of separation from CPB, returned to preoperative level after 48 h CPB | Elevated at the time of separation from CPB, the level was also higher than the preoperative level after 48 h CPB | Reached its peak 12 h after CPB, which was also higher than the preoperative level after 48 h CPB | - | - | ||
| Maruna P et al. (2009) [14] | 32 | Reached its peak 6 h after CPB | Reached its peak 6 h after CPB | Reached its peak 12 h after CPB | - | - | ||
| Maruna P et al. (2009) [12] | 22 | Reached its peak 12 h after CPB | Reached its peak 12 h after CPB, the level was higher than preoperative after 36 h CPB | Reached its peak 18 h after CPB | - | - | ||
| Maruna P et al. (2011) [7] | 82 | The level elevated after surgery | Reached its peak 12 h after CPB, then fall | - | - | - | ||
| Maruna P et al. (2011) [13] | 24 | Reached its peak 12 h after CPB | Reached its peak 12 h after CPB, then fall | Reached its peak 18 h after CPB | - | - | ||
| Author | Samples | IL-1 |
C-reactive protein | Procalcitonin | Leptin | Soluble leptin receptor | |
| Preoperative | Postoperative | ||||||
| Maruna P et al. (2008) [11] | 32 | Elevated 6 h after surgery, not have statistically significant | Elevated 12 h after sternotomy, reached a peak level 48 h after sternotomy | Normal | Transient initial decline 3 h after sternotomy, reached a peak level 24 h after sternotomy. The level was higher than preoperative after 48 h sternotomy | - | - |
| Lindner J et al. (2009) [6] | 36 | Elevated at the time of separation from CPB, returned to preoperative level after 48 h CPB | - | - | - | - | - |
| Maruna P et al. (2009) [14] | 32 | Elevated 6 h after surgery, not significantly different from the initial levels | - | - | - | Transient initial decline 3 h after sternotomy, reached a peak level 24 h after sternotomy. The level was higher than preoperative after 48 h after sternotomy | Transient initial decline 3 h after sternotomy, returned to initial level 24 h after surgery |
| Maruna P et al. (2009) [12] | 22 | Elevated 6 h after surgery, not statistically significant | Elevated with a peak level at 48 h after CPB. The level was higher than preoperative after CPB 72 h | - | - | - | - |
| Maruna P et al. (2011) [7] | 82 | - | Elevated with a peak level at 48 h after CPB. The level was higher than preoperative after CPB 72 h | Minimal PCT concentrations were found after the last DHCA, reaching a peak level 24 h after the end of surgery. The level was higher than preoperative after CPB 72 h | - | - | |
| Maruna P et al. (2011) [13] | 24 | - | Elevated with a peak level at 48 h after CPB | - | - | - | - |
| Author | Samples | Cortisol | Hepcidin | Pro-hepcidin |
| Maruna P et al. (2009) [14] | 32 | Reached its peak 6 h after sternotomy, remained elevated 48 h after the start of surgery | - | - |
| Maruna P et al. (2009) [12] | 22 | - | - | The initial decline after DHCA reached its minimal after CPB, returned to initial levels within 24–48 h after the separation from CPB |
| Maruna P et al. (2011) [7] | 82 | - | - | - |
| Maruna P et al. (2011) [13] | 24 | - | Elevated from the start of surgery to 72 h after surgery, but the level was higher than preoperative 120 h after surgery | - |
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha (TNF-
Upregulated IL-6 could not correlate with the hemodynamic status pre-operation [11]. Since PEA surgery could inflict significant damage to the pulmonary vascular endothelium, the release of IL-6 originates from the pulmonary vascular endothelium [18]. Therefore, IL-6 expression could be caused by systemic vasoplegia in CTEPH patients after PEA [5]. It has also been described that postoperative IL-6 significantly correlated with preoperative mean pulmonary artery pressure and pulmonary vascular resistance levels of CTEPH [5]. Although the IL-6 levels increased and peaked at 6–12 h after the operation and then decreased, they were still higher than before the procedure [5, 6, 7, 11, 12, 13]. Moreover, several studies revealed that IL-6 significantly correlated with the vasopressor (norepinephrine) [6, 13]. This may indicate that cytokine activation may be neurohumoral, which is responsible for the hemodynamic changes in CTEPH patients after PEA [6]. IL-6 also correlates with the proliferation of pulmonary vascular smooth cells [19] and is essential in pulmonary vascular remodeling, which induces pro-inflammatory and pro-angiogenic transcriptional programs by activating the janus kinase (JAK) pathways and signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) signaling [20]. Additionally, IL-6 also correlates with right ventricular function [21]. The IL-6 knockout model depicted decreased cardiac hypertrophy, fibrosis, and inflammation after angiotensin II stimulation [22]. Another study pointed out that an increased level of IL-6 can predict residual pulmonary hypertension after PEA surgery [23]. Numerous members of the IL-6 family and their levels also change during the perioperative period.
C-reactive protein (CRP), an acute-phase hepatic protein, immediately responds
to inflammatory reactions within the disease organs [24]. Furthermore, high
levels of CRP negatively correlated with the 6-minute walk test distance and
right ventricular (RV) function in a sizeable CTEPH cohort [25]. In addition, CRP
levels
IL-8 is an effective pro-inflammatory cytokine that is released by endothelial cells, monocytes, T cells, etc [29]. It has been reported that high baseline levels of IL-8 are negatively associated with the survival of CTEPH patients (but not all CTEPH patients had high levels of IL-8 at baseline) [30]. The changes in IL-8 occurred slightly later than in IL-6 (Table 1A,1B,1C). IL-8 levels significantly correlated with the levels of cardiac Troponin I. It indicated that IL-8 plays a role in cardiac injury after cardiac surgery [31]. IL-8 can elevate the adhesion between cells and increase the infiltration of neutrophils [32]. It has also been described that IL-8 is associated with the hemodynamic status after PEA surgery, whose concentration reaches its peak 12 h after separation from the cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) [6].
IL-10 as an anti-inflammatory cytokine can prevent inflammatory cell
infiltration and smooth muscle cell proliferation in patients with pulmonary
hypertension [33]. It has been revealed that IL-10 reduces cardiac hypertrophy
and fibrosis and protects cardiac function and vasculature [22]. IL-10 expression
also elevated reactively preoperative along with the elevated levels of
TNF-
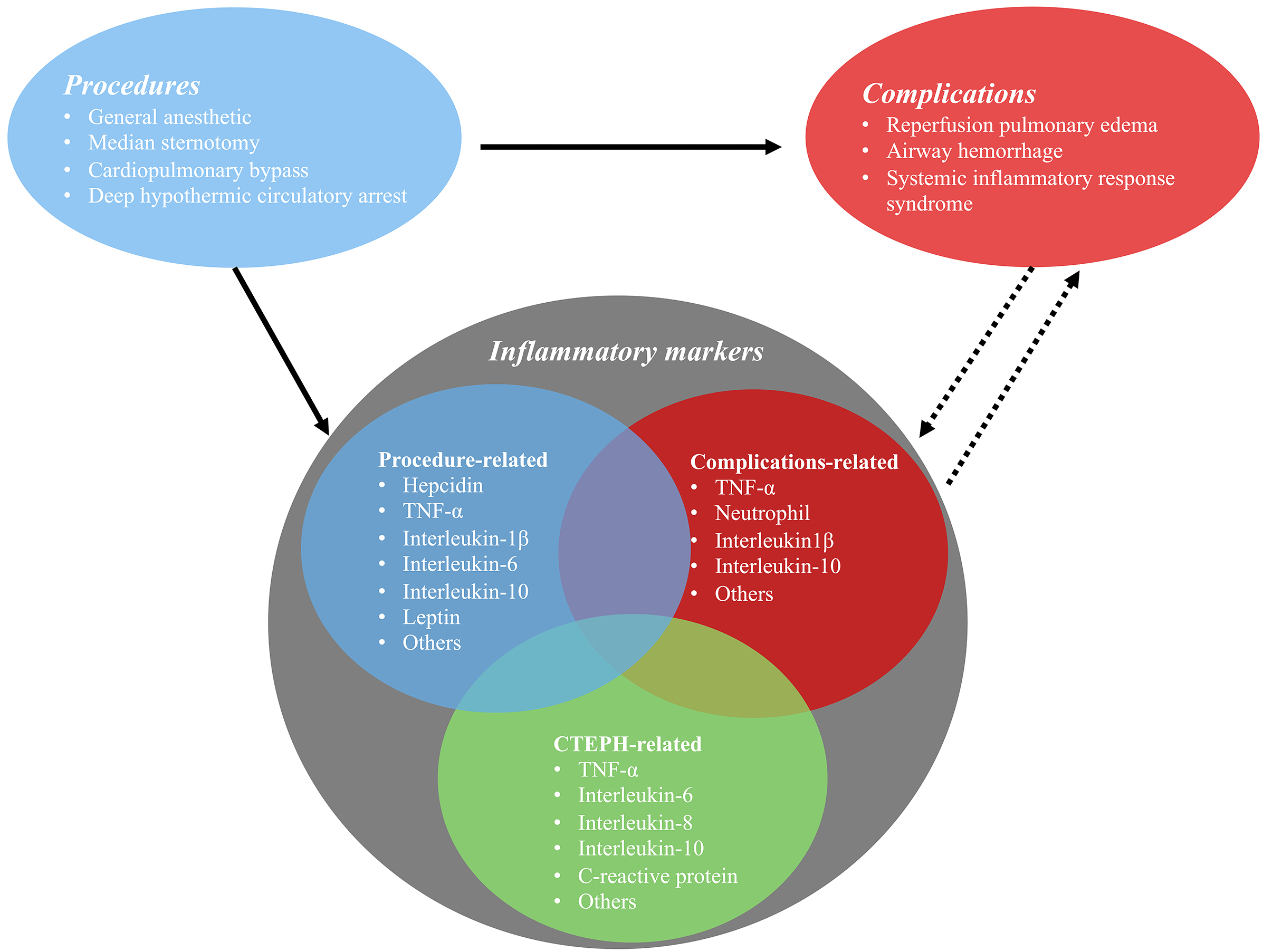
PEA surgery cures CTEPH patients, and the survival rates reach 90% after five years of surgery [34]. PEA surgery includes a general anesthetic, median sternotomy, CPB, and deep hypothermic circulatory arrest (DHCA) [35, 36]. These procedures had been to be reported to affect the immune system [6, 37] and contributed to the increasing levels of inflammatory cytokines (Fig. 1).
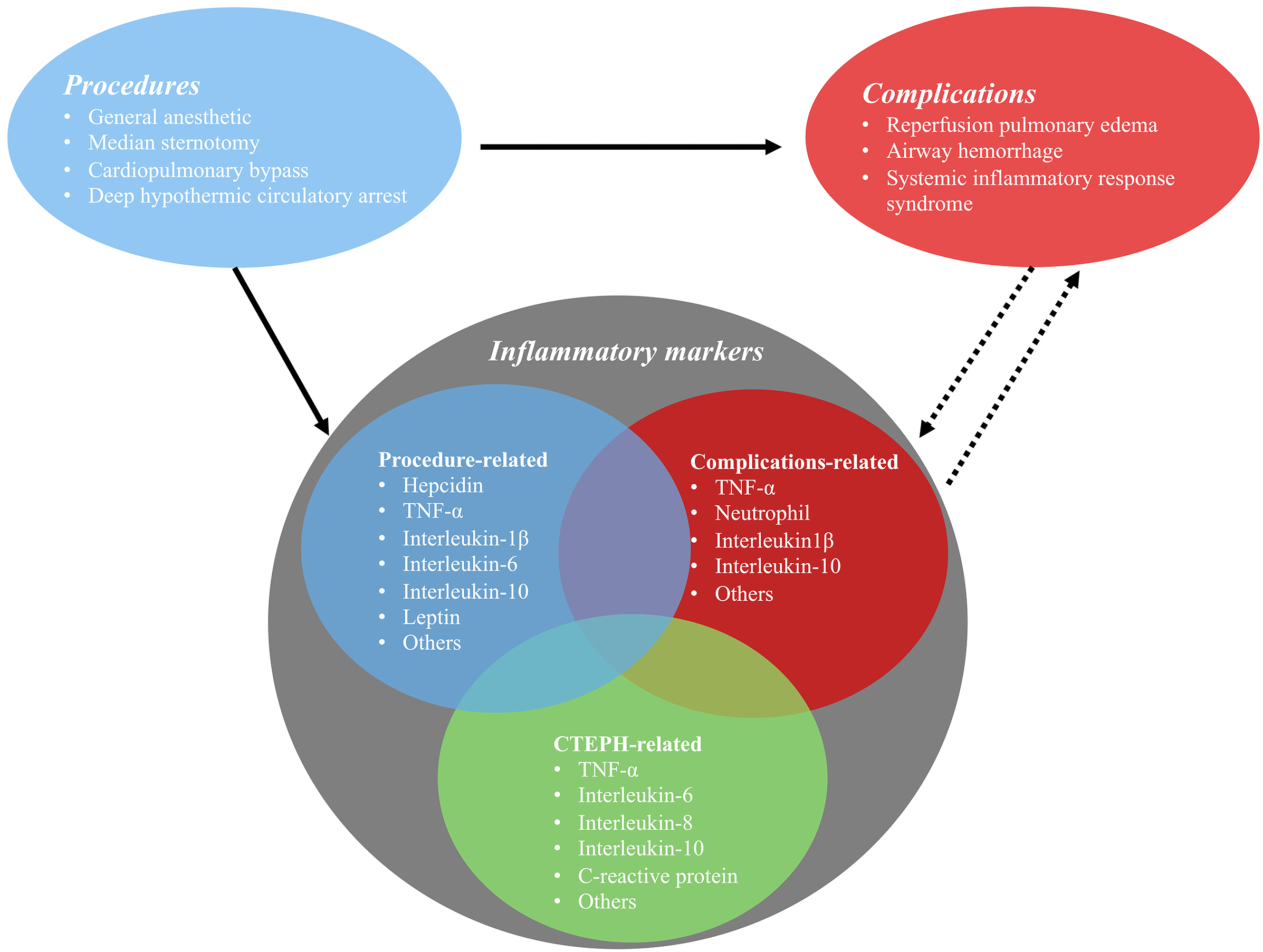 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.The relationship between pulmonary endarterectomy and perioperative inflammatory markers.
CPB results in a hemodynamic state of loss of pulsatile flow
and micro-embolism [38]. Blood exposure to CPB circuits leads to the systemic
inflammatory response, leukocyte activation, and the release of pro-inflammatory
and anti-inflammatory cytokines [39], ultimately causing multi-organ function
failure. The CPB of PEA surgery was performed with a non-pulsatile flow [40].
Studies have shown that non-pulsatile perfusion causes a decrease in hemodynamic
energy, resulting in capillary collapse, microvascular shunting, and the
activation of inflammatory mediators [40, 41]. Another study compared the
centrifugal pump and roller pump induced inflammatory cytokines in CPB after PEA
surgery. It was concluded that the non-occlusive centrifugal pump was associated
with reduced inflammation [42]. These findings warrant further studies exploring
the changes in inflammatory cytokines after CPB during PEA surgery. Elevated
levels of IL-10 were associated with pre-operative steroid injections in CPB
surgery, which reduced myocardial injury [43], attenuated the inflammatory
response to cardiac surgery and CPB, and enhanced hemodynamic changes [44].
IL-1
DHCA provides surgeons with a relatively clear view to allow for precise
dissection and removal of obstructive material during PEA surgery [49].
Neurological injury is the most common complication caused by DHCA [50]. It has
been reported that the incidence of perioperative neurological injury of PEA was
within the range of 3%–12% [50, 51, 52]. The longer time of DHCA may inflict
neurological injury [53] and acute kidney injury [54]. Surgeons should remove the
thrombosis materials as soon as possible to minimize the times and duration of
the circulatory arrest. In the PEACOG (PEA and COGnition) trial, the affection of
PEA to cognitive function was investigated, and data revealed that PEA with DHCA
at 20 °C provided excellent lung and brain results using other standard
procedures [51]. DHCA also contributed to the release of inflammatory cytokines
such as TNF-
Anesthetics are critical to the surgical procedure. It is a challenge for anesthesiologists to use anesthetics in CTEPH patients during PEA surgery due to the risk of right heart failure [56]. Sevoflurane is used in CTEPH (PEA) patients because of its cardio-protective effects in patients with little or no ischemic heart disease as a result [57]. It has been reported that anesthetics can regulate the immune system, including apoptosis of lymphocytes and impairment of neutrophil phagocytosis [58], which could be involved in PEA surgery.
Surgery-related trauma can specifically induce neutrophil extracellular trap
formation that causes endothelial cell damage and impairment of vascular
integrity, eventually resulting in postoperative multi-organ function failure
[59]. High levels of IL-6 and IL-10 induced by surgical-related trauma correlated
with the incidence of multi-organ function failure and mortality [60].
Furthermore, the increased levels of IL-6 during the perioperative period can
impair cognitive function during the postoperative phase [61]. However,
inflammatory cytokines are not only detrimental to cardiac remodeling, sometimes
they can play protective roles in cardiac remodeling. For example, IL-6 plays a
protective role in the heart by activating glycoprotein (GP)130 [62], thereby
leading to a cellular protective response in the heart, which preserves cellular
and interstitial structural integrity [63]. Alterations in the immune system
induced by surgical trauma correlated with postoperative recovery [59]. Leptin is
similar to other acute phase reactants and can upregulate the levels of
proinflammatory cytokines such as TNF-
The most common complications of PEA surgery include reperfusion pulmonary edema [37], airway hemorrhage, and systemic inflammatory response syndrome [65] (Fig. 1). Inflammation is critical in these processes. Pulmonary hemorrhage is a rare and serious complication and is associated with a mortality rate approaching 70% [66]. This can be caused by tears or disruption in the intima of the pulmonary artery (surgical struma), bleeding due to the rupture of fragile bronchopulmonary collateral, damage to the blood-airway barrier, and reperfusion pulmonary edema [67]. Other risk factors correlated with hemorrhage have not been investigated thoroughly.
Reperfusion lung injury is common among PEA patients and usually leads to
postoperative morbidity and mortality [68, 69]. Reperfusion injury is a specific
complication that usually appears within 48 h after surgery, which is similar to
acute lung injury. The main characteristic is pulmonary hyperemia in the
revascularized pulmonary areas [70]. It has previously been reported that the
neutrophil could induce the reperfusion of lung injury [71]. It has been
demonstrated that increased neutrophils exist in bronchial alveolar lavage of
patients with lung injury compared with those without lung injury [72]. Blocking
the neutrophil selectin-mediated adhesion on the day of surgery reduced the
reperfusion injury incidence [72]. These findings suggested that inflammation
could induce reperfusion injury. Also, pulmonary reperfusion after PEA surgery
made patients more susceptible to infection [7]. Administration of cylexin to
CTEPH patients undergoing PEA reduces the incidence of postoperative reperfusion
lung injury. However, no significant effect was observed on the overall clinical
outcome [72]. In the latest study, predictively injecting erythropoietin to
patients with CPB surgery effectively reduced lung injury after CPB and reduced
the pro-inflammatory factors TNF-
Residual pulmonary hypertension is the most common reason for postoperative mortality and morbidity in CTEPH patients after PEA surgery [52, 75]. It results from distal chronic thromboembolic disease or small-vessel vasculopathy that is not cured by endarterectomy [76]. Within the international CTEPH registry, persistent pulmonary hypertension affected 16.7% of patients and was related to a higher early mortality rate [52]. In addition, patients can also re-present with CTEPH and pulmonary hypertension, which is caused by a further thrombotic episode after successful PEA [3, 77] and usually correlates with irregularly anticoagulation [3]. Until now, there is no clear guidance for CTEPH patients undergoing PEA surgery to detect recurrent pulmonary hypertension [77].
It has been reported that preoperative parenchymal lung disease decreased the
perioperative pulmonary reserve and was a predictor of perioperative mortality
after PEA [78]. A small study (86 cases) revealed that the incidence of
prolonged mechanical ventilation was nearly 50% after PEA
surgery, which also correlated with higher rates of postoperative complications
and higher hospital medical expenses [79]. Prolonged tracheal intubation is
common after PEA. Thus, it is expected that ventilator-associated pneumonia would
be prevalent in CTEPH patients after PEA [78]. Furthermore, a longer time of
ventilatory support and a longer stay in the intensive care unit would increase
the possibility of nosocomial or care-related infections, leading to death [80].
Procalcitonin (PCT) is a highly specific marker for the
diagnosis of clinically relevant bacterial infections and sepsis [11], and is
used as a predictive factor for postoperative complications following cardiac
surgery [81, 82]. Plasma levels of PCT are elevated due to the systemic
inflammatory responses [83] and act as a predictive factor in distinguishing
inflammatory and noninflammatory complications. The expression of PCT reaches its
peak at 24 h after the end of the surgery, along with the downregulated
pro-inflammatory mediators such as IL-6 and TNF-
Pulmonary endarterectomy is an effective treatment for chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension patients. Perioperative inflammatory cytokines are crucial to improve the prognosis of patients. Furthermore, the existence of inflammatory mediators in removed PEA materials could further suggest that inflammatory cytokines are involved in the pathogenesis of CTEPH. In a word, the exact role of involved inflammation peri-PEA remains unknown and should be explored in the future.
PEA, Pulmonary endarterectomy; CTEPH, Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary
hypertension; CPB, Cardiopulmonary bypass; DHCA, Deep hypothermic circulatory
arrest; TNF-
QL and ZZ searched the literature and collected the data. QL, ZZ, and JY wrote the first draft of the manuscript. YC and MZ contributed to the study conception, design, and polished the draft. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
Thanks for supporting of National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 81860059).
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Publisher’s Note: IMR Press stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.