1 Department of Plant Protection, Faculty of Agriculture, Vali-e-Asr University of Rafsanjan, 7718897111 Rafsanjan, Iran
2 Université de Reims Champagne‐Ardenne, Unité de Recherche Résistance Induite et Bio‐Protection des Plantes‐EA 4707‐USC INRAE1488, 51100 Reims, France
Abstract
Background: Phytopathogens, encompassing fungi, bacteria, viruses, and nematodes, pose a significant threat to the agricultural industry by causing substantial economic losses through severe plant diseases. The excessive use of synthetic fungicides to combat phytopathogens has raised environmental and human health concerns. Results: Consequently, there is an increasing demand for safe and environmentally friendly biopesticides to align with consumer preferences for uncontaminated food. One particularly promising alternative to synthetic fungicides involves harnessing biocontrol bacteria that produce extracellular hydrolytic enzymes. These enzymes serve to effectively manage phytopathogens while concurrently fostering sustainable plant protection. Among the pivotal hydrolytic enzymes generated by biocontrol bacteria are chitinase, cellulase, protease, lipase, glucanase, and amylase. These enzymes exert their influence by breaking down the cell wall, proteins, and DNA of phytopathogens, thereby establishing a dependable method of biocontrol. Conclusions: Recognizing the critical role of these hydrolytic enzymes in sustainable biocontrol, this review seeks to delve into their primary functions, contribution to sustainable plant protection, and mechanisms of action. Through an exploration of the potential presented by biocontrol bacteria and their enzymatic mechanisms, we can discern effective and environmentally conscious strategies for managing phytopathogens in agriculture.
Graphical Abstract
Keywords
- phytopathogens
- extracellular hydrolytic enzymes
- chitinase
- cellulase
- protease
- lipase
- biocontrol
Plant diseases have profoundly influenced the course of food production and the development of human civilizations over decades [1]. The ultimate consequence of these plant pathogens is reducing food quantity, quality, and security, exerting significant pressures on agricultural systems, and prompting adaptations and innovations to ensure sustainable food production [2, 3]. The severity of plant diseases can vary from mild to severe, depending on various factors such as environmental conditions, host resistance, pathogen aggressiveness, and the duration of infection [4]. Soil-borne phytopathogens pose a particularly severe threat as they cause extensive damage, resulting in a 30% loss across a wide range of plants. This not only leads to economic disasters for producers but also contributes to the risk of starvation, particularly in underdeveloped countries with limited access to disease management methods [5]. For instance, the devastating prevalence of potato late blight, caused by Phytophthora infestans, led to famine, starvation, death, and mass migration throughout history [6]. It is worth noting that the impact of phytopathogens on plants has been exacerbated by two key factors: global climate change and the globalization of markets. These factors have accelerated the spread of phytopathogens, increasing the likelihood of emerging diseases affecting crops [7]. Among plant phytopathogens, soilborne pathogens pose a significant challenge to plant protection [8, 9]. Soilborne plant pathogenic fungi, such as Fusarium sp., Sclerotinia sp., Phytophthora sp., Verticillium sp., Rhizoctonia sp., and Pythium sp. are reported to cause 50 to 75% yield loss for various horticultural and agricultural products [10]. In addition to soilborne phytopathogenic fungi, Ralstonia solani, which probably is the most destructive plant pathogenic bacterium globally, as well as Meloidogyne spp. and Heterodera spp., as the most damaging nematodes, have a tremendous effect on economic, political and cultural development [11, 12, 13]. Regardless of damages and losses caused by phytopathogens, another key challenge is developing efficient strategies that rapidly manage plant pathogens [14]. Synthetic pesticides have been the primary method for managing plant diseases for several decades because of their high effectiveness and ease of application [15]. However, the intensive and indiscriminate use of synthetic pesticides has led to several issues in modern plant protection. These include the emergence of pesticide-resistant strains, new disease outbreaks, and mounting concerns about the impact on health, environment, and contamination of soil and water [16]. As a result, there has been a revolution in plant protection to develop more sustainable and environmentally-friendly alternatives [15, 17, 18, 19]. Therefore, some eco-friendly management methods include soil solarization, crop rotation, soil steam sterilization, anaerobic soil disinfestation, resistant cultivars or grafted plants, biofumigants, soil fertility, and soil fertility biopesticides, have been developed to mitigate soilborne phytopathogens while maintaining the environment safe [20, 21]. Currently, sustainable agriculture is experiencing emerging opportunities such as the utilization of biological agents [22, 23, 24, 25, 26], integration of nanoscience [25, 27], advancement of resistant plants, and implementation of biopolymers [28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39]. Using soil microbial communities for biological control has emerged as a promising strategy for suppressing soilborne plant pathogens [40, 41, 42]. Biocontrol bacteria utilize diverse antagonistic strategies against phytopathogens, encompassing the synthesis of lytic enzymes, antibiotics, volatile organic compounds, siderophores, nutrient and spatial competition, as well as the initiation of host resistance [43]. Among these mechanisms, the extracellular enzymes, commonly referred to as hydrolytic enzymes, synthesized by diverse biocontrol bacteria, have a direct impact on phytopathogens by breaking down the structural components of their cell walls [44, 45]. Soil biocontrol bacteria can effectively manage plant diseases caused by soilborne pathogens by producing extracellular enzymes, including chitinase, cellulase, protease, amylase, and lipase. This process helps to break down organic matter in the soil, leading to the suppression of pathogenic microorganisms and promoting plant growth. Regardless of the indirect effect of bacterial biocontrol hydrolytic enzymes on the plant, some detected enzymes, including pectinases, chitinases, lipases, cellulases, and amylases, can directly affect plant growth by providing better colonization. The production of these enzymes is reported to be upregulated in the bacterial interaction with the host plant, involved in the recognition, attachment, and movement of beneficial bacteria through plant tissues which leads to the induction of the plant immune system against biotic stresses [46]. This review considers one of the primary biocontrol mechanisms employed by antagonistic bacteria in sustainable agriculture to manage various plant pathogens. This mechanism involves the production of cell-wall degrading enzymes and is crucial in meeting the increasing demand for safe and pathogen-free food for the world’s growing population.
Recently, antagonistic microorganisms, especially biocontrol bacteria, have been extensively reported as the most promising strategies to guarantee plant health, quality and safety of fruits and vegetables [40, 47]. Several bacterial genera, including Bacillus, Pseudomonas, Serratia, Rhizobium, Xanthomonas, Streptomyces, Enterobacter, Agrobacterium, Erwinia, Alcaligenes, Stenotrophomonas, and Arthrobacter have demonstrated antagonistic activity in the biocontrol of various plant pathogens [3, 48, 49, 50, 51]. These bacteria suppress the development of plant pathogens through multiple mechanisms of action, which can be divided into direct and indirect mechanisms (Fig. 1).
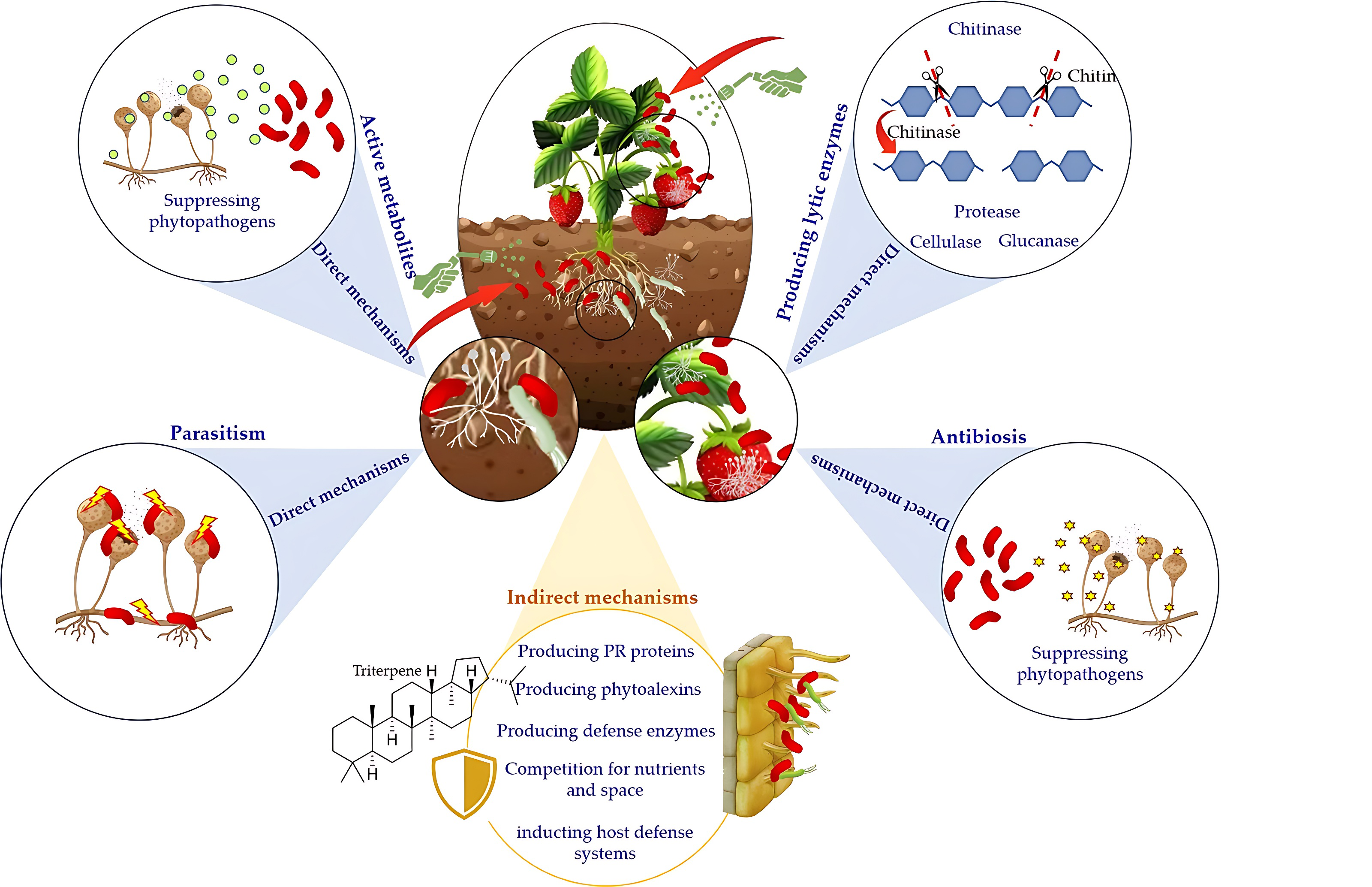 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.Multiple modes of action of biocontrol bacteria against phytopathogens.
Indirect modes of action include colonization of the infection site followed by competition for nutrients and space and, more importantly, induction of host defense systems [52]. Pseudomonas spp. are among the most reported beneficial bacteria used as biopesticides due to several relevant properties, including their potential capability to trigger plant defense responses, strong biocontrol activity against a wide range of phytopathogens and their high ecological fitness [53]. Fluorescent pseudomonads have the potential to colonize not only the rhizosphere but also the phyllosphere and endosphere, outcompete other microorganisms for nutrients and space, and contribute to plant growth promotion, disease suppression and nutrient cycling [54]. For instance, better nutrient utilization and growth rate of P. fluorescens EPS62e compared to Erwinia amylovora reduced bacterial infection [55]. Under nutrient deficiency, especially the limitation of iron, Pseudomonas spp. suppress pathogenic microorganisms through a siderophore-mediated competition mechanism [56]. In addition, Pseudomonas spp. are known as dominant bioactive metabolites producers like enzymes, antibiotics, and cyclic peptides, playing significant antagonistic roles [57]. The induction of plant systemic resistance (ISR) is one of the most important indirect mechanisms activated by Pseudomonas spp., which confers plants with resistance to multiple pathogens via the stimulation of induced systemic resistance. ISR activates the plants’ defense responses and primes them for a more effective defense response. For instance, Pseudomonas fluorescens PTA-CT2 activated the ISR mechanism in grapevines. As a result, the plants developed increased resistance against Botrytis cinerea and Plasmopara viticola, two common pathogens [58]. Also, a relevant trait of Bacillus species is their capability to elicit ISR, enhancing plant defense mechanisms against a variety of pathogens [59]. Besides these two important genera, species of Lactobacillus spp., Pantoea spp. and Streptomyces spp. are among the most studied bacteria with biological control activity through a wide variety of mechanisms [60, 61, 62].
The direct mechanisms are based on liberating antioxidants, lipopeptides,
antibiotics, hormones, biosurfactants, volatile compounds, and cell wall
degrading enzymes, reducing pathogens’ growth or metabolic activity [60, 61, 62].
Further, the production of various highly active antimicrobial metabolites, such
as bacteriocins, pyrrolnitrin, pyoluteorin, dialkylresorcinols, and
phloroglucinols have been reported to be contributed directly to the biological
control of plant pathogens [63]. Flury et al. [64] reported the
involvement of pyoluteorin and hydrogen cyanide produced by Pseudomonas
spp. in the biocontrol of some phytopathogens. Pseudomonas spp. produce
cyclic lipopeptides, which are antimicrobial compounds that can harm plant
pathogens by disrupting their cell membranes. This disruption can result in
cytolysis and leakage, ultimately leading to the death of the pathogen [63]. For
example, plant pathogens such as Pythium, Phytophthora, and
Rhizoctonia have been managed using orfamides produced by P.
protegens [65]. Lytic extracellular enzymes, such as cellulase,
The second most exploited antagonistic bacteria as biopesticides are Bacillus species. Their wide distribution in different habitats, such as plant surface and soil, endospore forming ability and the production of a wide variety of antimicrobial compounds, and the stimulation of plant immune system are considerable traits for their application in plant protection [67]. Several bacteriocins, such as subtilin A, subtilin B, subtilin, amysin, thuricin, amylocyclicin, and amylolysin produced by Bacillus spp. exhibit antimicrobial activity by forming spores in the cell membrane or preventing the cell wall synthesis [68]. More than that, many Bacillus species produce cyclic lipopeptides like surfactins, fengicins, and iturins, which are key factors in suppressing fungal phytopathogens [69]. Bacillus spp. strains can also liberate extracellular enzymes such as protease, lipase, chitinase, glucanase, cellulase, and chitosanase, that important factors in the biocontrol of bacterial and fungal pathogens [59].
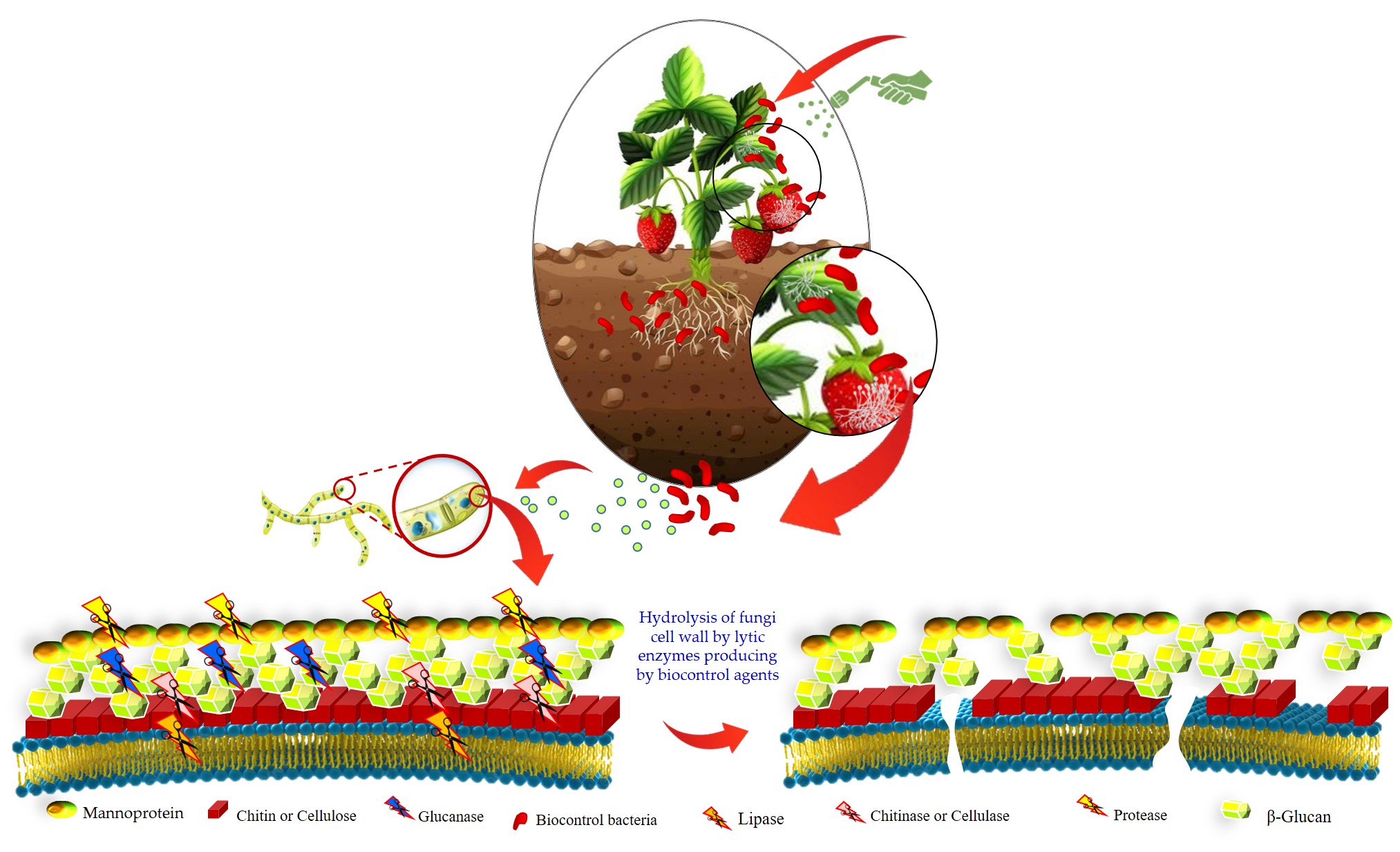
Among these modes of action, extracellular enzymes, also known as hydrolytic enzymes, produced by various biocontrol bacteria directly affect phytopathogens via the degradation of cell wall structural compounds of most pathogens [44]. In fact, Hydrolytic enzymes play a crucial role in breaking down fungal pathogen spores and mycelia [70]. Bacterial lytic enzymes, such as chitinase, b-1,3-glucanase, catalase, cellulase, and proteases, break down polymeric compounds like chitin, glucan, cellulose, proteins, DNA, and hemicellulose which are the main compounds in the cell wall structure of phytopathogens [71]. Fig. 2 depicts the effects of hydrolysis enzymes on the degradation of cell membranes and cell walls of phytopathogenic fungi.
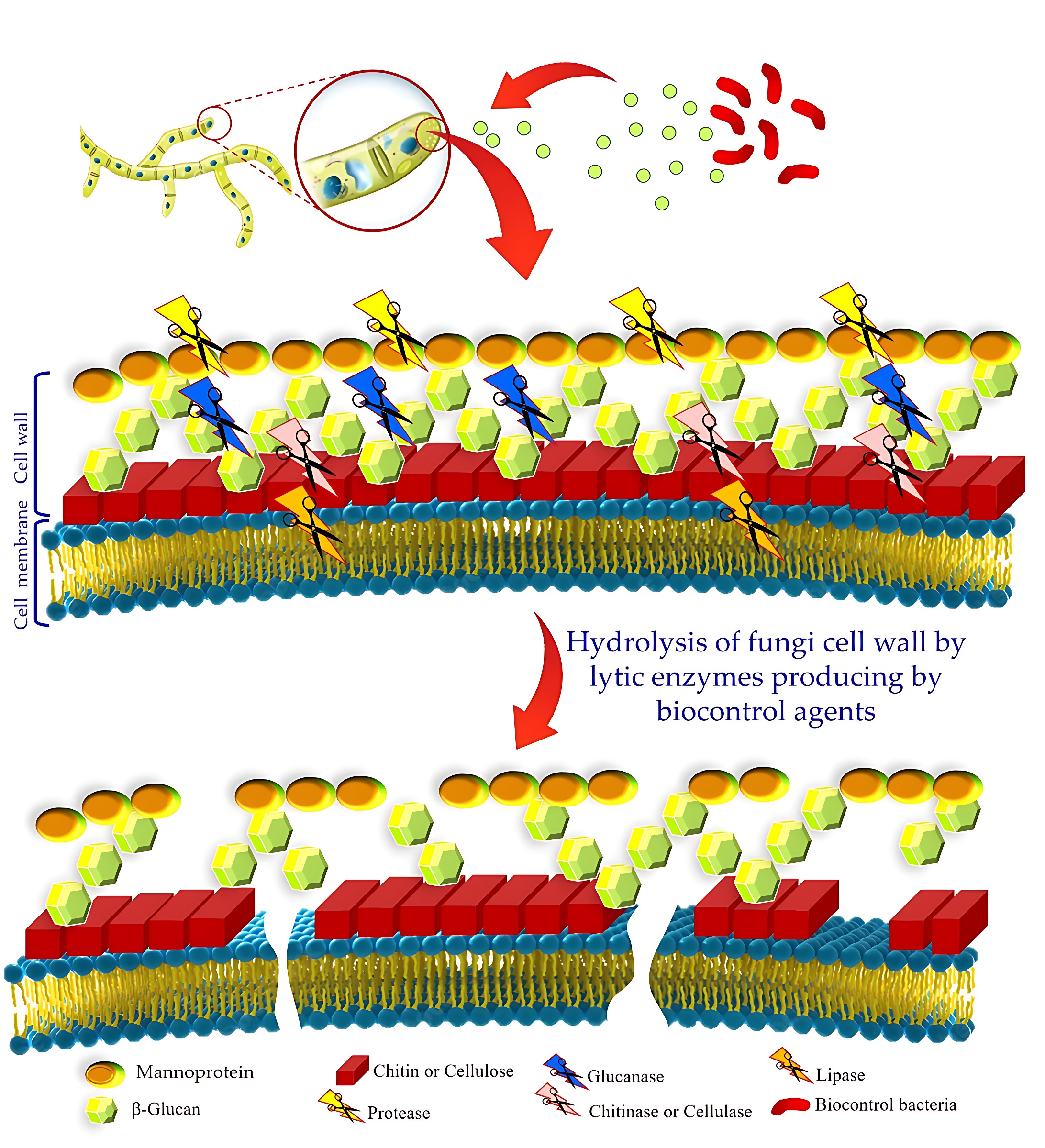 Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.The effects of hydrolysis enzymes on the degradation of the cell membrane and cell walls of phytopathogenic fungi.
A wide variety of plant biocontrol bacteria can remarkably represent a mutually helpful interaction with microbial microorganisms by synthesizing various extracellular enzymes that can change their environment in a self-beneficial manner. The production of cell wall degrading enzymes has been reported in different groups of bacteria isolated from the rhizosphere and phyllosphere of different plant species. For instance, Bibi et al. [72] reported the isolation of amylase, lipase, protease, and cellulase-producing bacterial strains of various genera from the leaves, roots, and soil of mangroves.
In addition to producing extracellular enzymes, biocontrol bacteria can also disrupt the quorum-sensing system of pathogens by producing inhibitor enzymes, such as chitinase, pectinase, cellulase, and lactonase. These inhibitors prevent the synthesis or degradation of signal molecules required for the pathogens to infect their host plants. This interference with the quorum-sensing system can reduce the virulence of the pathogens and limit the damage they cause to the plants [73].
The most dominant bacteria belong to the genera Vibrio, Halomonas,
Alteromonas, Marinobacter, Erwinia, Microbulbifer, Chromohalobacter,
Psychrobacter, Aidingimonas, Isoptericola, and Bacillus. Some of them,
including Bacillus, followed by Halomonas, Marinobacter, and
Microbulbifer species, were also active against fungal pathogens, such as
P. capsica, P. ultimum, F. oxysporum, and A. mali. Evaluating
the potential of the bacterial flora associated with maize in Brazil’s main
maize-producing regions for producing hydrolytic enzymes indicated that these
bacterial strains belong to the phyla Proteobacteria, Firmicutes, and
Actinobacteria. Moreover, Pantoea dispersa and Massilia timonae
were the new producers of lipase and amylase, respectively [74]. While conducting
a study across three distinct regions of Tami Nuda in India, numerous bacterial
strains displaying hydrolytic enzyme production were successfully isolated. Out
of 72 bacterial isolates, 20.83% were found to produce amylase, cellulase, and
inulinase simultaneously. Most isolates exhibiting enzyme activities were
identified as Bacillus cereus, B. thuringiensis, and B.
anthracis [75]. Many strains of B. subtilis depict the capability to suppress
several plant pathogens through the secretion of extracellular enzymes such as
Extracellular hydrolytic enzymes are a highly heterogenous group of enzymes, including lyases, esterases, glycosyl-hydrolases, and oxidoreductases. Microorganisms with degrading activities toward plant cell wall polysaccharides are the most source of hydrolytic enzymes for industrial applications. Although, large- scale industrial production of microbial enzymes as biopesticides in the management of phytopathogens has been considered by many researchers. Among rhizosphere microbes, various bacterial strains produce cell wall degrading enzymes, including chitinase, cellulase, proteases, lipases, and amylases, in response to phytopathogen attacks, which are fully discussed in the following sections (Table 1, Ref. [40, 79, 80, 81, 82, 83, 84, 85, 86, 87, 88, 89, 90, 91, 92, 93, 94, 95, 96, 97, 98, 99, 100, 101, 102, 103, 104, 105, 106, 107]). These enzymes can either be applied indirectly by manipulating genes coding enzymes, purified enzyme proteins, or directly applying on phytopathogens.
| Biocontrol bacteria | Hydrolytic enzyme | Target pathogen | Reference |
| Streptomyces isolate CT02 | Chitinase | Aspergillus niger, A. oryzae | [82] |
| Streptomyces albus, S. flavogriseus, S. fumosus | Chitinase | Fusarium. graminearum, Magnaporthe oryzae, Rhizoctonia solani, Botrytis cinerea, Puccinia species | [83] |
| Streptomyces cellulosae | Chitinase | Sclerotium rolfsii | [84] |
| Pseudomonas putida, B. subtilis | Chitinase | M. phaseolina | [80] |
| Pseudomonas fluorescens | Chitinase | Magnaporthe grisea | [85] |
| Pseudomonas fluorescens, Enterobacter cloacae | Chitinase, cellulase, lipase, protease | Phytophthora capsici | [79] |
| Bacillus velezensis | Chitinase, protease, |
Verticillium daliae | [86] |
| Bacillus velezensis NKG-2 | Protease, Lipase | Gaeumanomyces graminis Var. tritici, Gaeumannomyces graminis var. tritici | [40] |
| Paenibacillus elgii HOA73 | Chitinase | B. cinerea | [81] |
| B. subtills TD11 | Chitinase, cellulase | Colletotrichum, Aspergillus, Fusarium, Rhizoctonia. | [93] |
| Bacillus velezensis NKG-2 | Chitinase, |
Alternaria alternata, Botrytis cinerea, Fusarium oxysporum, F. graminearum, Ustilaginoidea virens, Fulvia fulva | [87] |
| Bacillus spp. | Chitinase, protease, glucanase | Rhizoctonia solani, M. phaseolina | [89] |
| Basillus spp. | Chitinase, |
F. oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici | [88] |
| B. cereus | Chitinase | F. verticillioides | [90] |
| Serratia plymuthica | Chitinase | Pythium myriotylum | [92] |
| B. aerius, Geobacillus, Thermodenitrificans | Chitinase | P. capsici | [91] |
| B. cereus, B. subtillis, Pantoea agglomerans | Chitinase | Colletotrichum, Rhizoctonia, Aspergillus, Fusarium | [93] |
| Bacillus simples, B. subtilis | Cellulase, chitinase, pectinase, xylanase | Fusarium spp. | [94] |
| B. velenzensis TSA32-1 | Cellulase, protease | F. fujikuroi, F. graminearum, Diaporthe actinidiae, A. alternata, Pythium ultimum | [95] |
| B. subtilis | Cellulase, chitinase, glucanase | Colletotrichum gloeosporioides OGC1 | [96] |
| Pseudomonas spp. | Cellulase, glucanase, xylanase | Verticillium dahliae | [97] |
| Bacillus pumilus | Protease, cellulase | Fusicoccum aesculli, Phomopsis macrospora, Cytospora chrysosperma. | [98] |
| B. cereus | Protease | Bursaphelenchus xylophilus | [100] |
| B. cereus BCM2 | Protease, chitinase | Meloidogyne incognita | [99] |
| P. aeruginosa FG106 | Protease, lipase | Xanthomonas euvesicatoria pv. perforans, R. solani, P. infestans, A. alternata, B. cinerea, Clavibacter michiganensis subsp. Michiganensis, P. colocasiae | [101] |
| P. putida ASU15 | Lipase, protease, chitinase | Uromyces appendiculatus | [102] |
| B. cereus | Rhizoctonia cerealis | [103] | |
| B. cereus SCB-1 | Fusarium, Alternaria, Curvularia, Neodeightonia, Saccharicola, Cochliobolus, Phomopsis | [104] | |
| Staphylococcus warneri, B. velezensis, B. megaterium, Caballeronia glebae, B. licheniformis | Amylase | Ralstonia solanacearum | [105] |
| One Bacillus and one Pseudomonas isolate | Amylase, protease | R. solanacearum | [106] |
| P. syringae, P. fluorescens, P. aeruginosa | R. solanacearum | [107] |
Chitinase enzymes, which can be classified as exochitinases, endochitinases,
Cellulase extracellular enzymes are glycoside hydrolyses that cleavage
Proteases are enzymes that break down proteins and are vital in biological
control processes and in protecting plants from disease-causing microorganisms.
Proteases degrade proteins into peptide chains and amino acids, resulting in the
breakdown of the cell wall. This occurs because the fibrils of
Lipases are vital lipolytic enzymes many microorganisms produce, from procaryotes to eucaryotes. These enzymes belong to the alpha and beta hydrolase superfamily with many catalytic characteristics, such as alcoholysis, transesterification, decarboxylation, and aminolysis [117]. Their mechanism of action catalyzes the hydrolysis of different lipid substrates. Various bacterial strains representing lipase production can be considered as biological control agents. The lipases produced by these bacteria affect phytopathogens directly and induce plant defense mechanisms by liberating lipids [71]. Lipases produced by P. aeruginosa FG106, isolated from the rhizosphere of tomato plants, improved its biocontrol activity in managing Xanthomonas euvesicatoria pv. perforans, R. solani, P. infestans, A. alternata, B. cinerea, Clavibacter michiganensis subsp. Michiganensis, and P. colocasiae [101]. Admassie et al. [79] reported lipases as one of the most important antagonistic compounds liberated by Pseudomonas fluorescens and Enterobacter cloacae in the control of P. capsici. The P. putida strain AUS15, isolated from fresh beans, represented direct biocontrol efficacy against Uromyces appendiculatus through lipolytic, chitinolytic, and proteolytic activities [102]. Streptomyces puniceus with strong lipase activity exhibited significant inhibition to the growth of Verticillium dahliae, and Valsa mali [118]. Evaluating the ability of several isolates of Bacillus (B. subtilis, B. licheniformis, B. firmus, B. lentus, B. circulans, and B. aeruginosa) and Pseudomonas (P. fluorescens, P. luteola, and P. aeruginosa) to inhibit the mycelia growth of F. oxysporum f. sp. ciceris showed different rates of inhibition due to the excretion of different hydrolytic enzymes including lipase [119]. A study by Mota et al. [120] isolated bacteria from different plant species and soils which were identified as B. cereus, B. subtilis, B. thuringiensis, Paenobacillus polymyxa, Pseudomonas poae, Pseudochrobactrum saccharolyticum, P. putida, B. amyloliquefaciens, Bacillus spp. and Pseudomonas spp. killed juveniles of Mesocriconema xenoplax by the production of extracellular lytic enzymes such as lipases. Similarly, lipase production activity was observed in bacteria isolated from different sources, which were identified as Bacillus sp., Pantoea sp., Pantoea vegans, Burkholderia cepacian, Acinetobacter sp., P. putida, Staphylococcus warneri, B. licheniformis, B. amyloliquefaciens, Paenibacillus cineris and Oceanobacillus oncorhynchi. These bacteria exhibited antagonistic activity against Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae, the causal agent of bacterial leaf blight of paddy [121]. Consequently, lipases play a vital role as an important lytic enzyme in the plant protection mechanism employed by many biocontrol bacteria.
Amylases are classified into three main groups including,
The main action mechanism of different extracellular lytic enzymes liberated by
biocontrol bacteria catalyzes the hydrolysis of phytopathogens’ cell wall,
proteins, and DNA, leading to the outflow of intracellular materials and cell
death [124]. The cell wall of pathogenic microorganisms maintains their cells’
physical integrity, composed of proteins, different carbohydrates, chitin,
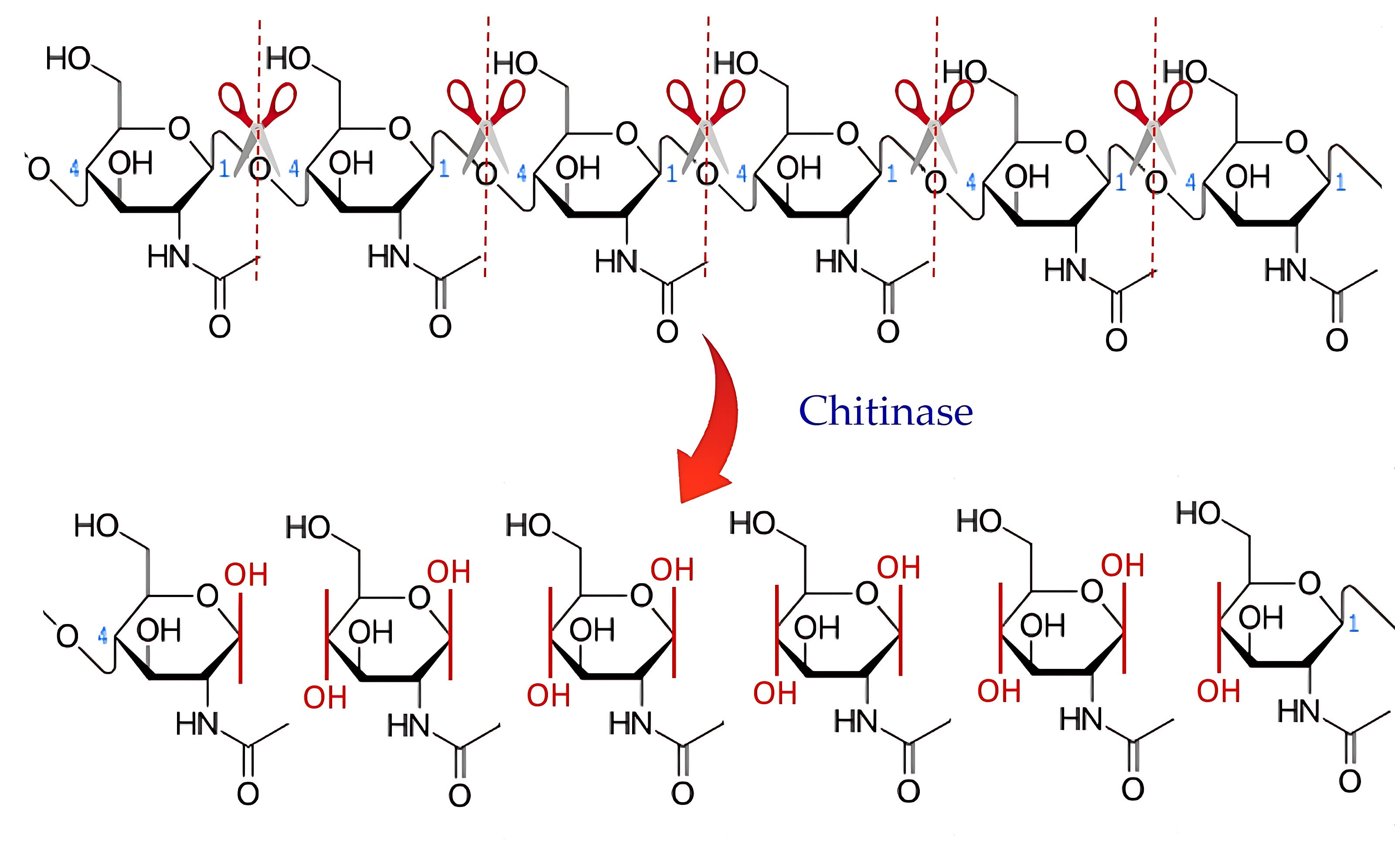 Fig. 3.
Fig. 3.The action mechanism of chitinase.
The second hydrolytic enzyme discussed in this article is cellulase, hydrolyzing
1,4-
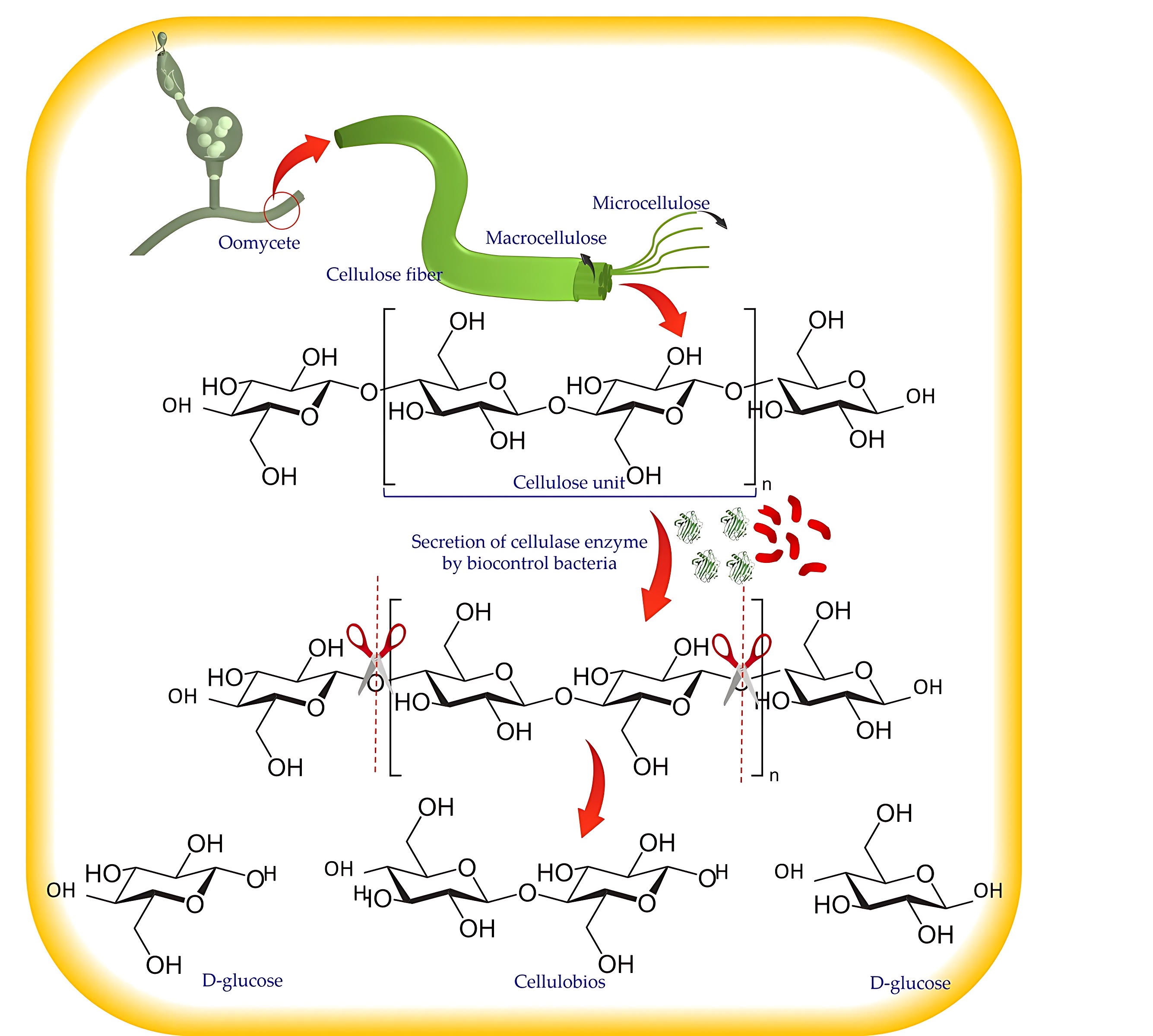 Fig. 4.
Fig. 4.The action mechanism of cellulase.
With the increasing global population and growing demand for agricultural products, finding alternatives to synthetic pesticides has become a top global priority. Antagonistic microorganisms, especially biocontrol bacteria, have emerged as promising strategies to ensure plant health, food safety, and sustainable agriculture. These biocontrol bacteria, belonging to genera like Bacillus, Pseudomonas, Streptomyces, and others, exhibit antagonistic activity against various plant pathogens through multiple modes of action, particularly those producing hydrolytic enzymes. Hydrolytic enzymes, such as chitinase, cellulase, protease, lipase, and amylase, play a critical role in breaking down components of phytopathogens’ cell walls, leading to their degradation. Moreover, some of these enzymes can directly affect plant growth and promote colonization by beneficial bacteria, triggering the plant’s immune system against biotic stresses. This mechanism of action not only combats pathogens, but also enhances plant defense responses and overall health. Looking forward, the perspective of harnessing hydrolytic enzymes as a cornerstone of plant protection strategies is highly promising, with ongoing research on identifying novel and potent hydrolytic enzymes to efficiently degrade a wide range of pathogenic organisms, ultimately enhancing the effectiveness of biocontrol agents. Additionally, integrating these enzymes into various formulations, such as sprays or coatings, could facilitate easy application. As these enzymes work through a fundamentally different mechanism from chemical pesticides, it significantly reduces the likelihood of pathogens developing resistance, ensuring a sustainable and long-term solution. Scaling up production processes for these enzymes using advanced biotechnological methods is another avenue that holds great potential. However, challenges include maintaining the stability and activity of enzymes under different conditions, as well as ensuring their safe use without any adverse effects on non-target organisms or the environment. Continued research, technological innovation, and field trials will be instrumental in realizing the full scope of benefits that hydrolytic enzymes can offer in sustainable agriculture and disease management.
RSR, and MH, conceptualization; MV, MH, and EAB, data collection and analysis; RSR, and MH, visualization; EAB, format analysis; MV, MH, and EAB, original draft preparation; MV, MH, and EAB, review and editing; RSR, supervision. All authors contributed to editorial changes in the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. All authors have participated sufficiently in the work and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
This research received no external funding.
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Publisher’s Note: IMR Press stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.




