1 Department of Clinical Microscopy, Faculty of Medical Technology, Mahidol University, 73170 Nakhon Pathom, Thailand
2 Department of Surgery, Phramongkutklao Hospital and Phramongkutklao College of Medicine, 10400 Bangkok, Thailand
3 Department of Biological Engineering Program, Faculty of Engineering, King Mongkut’s University of Technology Thonburi, 10140 Bangkok, Thailand
4 Department of Clinical Microbiology anẠpplied Technology, Faculty of Medical Technology, Mahidol University, 73170 Nakhon Pathom, Thailand
Abstract
Background: Large-scale production of mesenchymal stromal cells is essential for sufficient therapeutic doses in regenerative medicine. However, long-term cultivation encounters limited cell growth and cellular aging. Therefore, an alternative cell culture approach that promotes proliferation and attenuates cell senescence is required. Human platelet lysate (HPL) is a potent supplement for in vitro cell expansion. Applying HPL as a coating material can potentially improve mesenchymal stromal cell cultures. Method: To examine the capacity of HPL, it was used to pre-coat a tissue culture plate for in vitro adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cell expansion. Alterations in biological features of adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) were investigated, including cell adhesion assays, cell proliferation, population doubling time, and cellular senescence. Results: ADSCs cultured on HPL-coated plates significantly increased cell adhesion rate, shortened population doubling time, and stimulated cell growth. The senescent cells were significantly decreased in ADSCs cultured in an HPL-coated plate, and the expression levels of senescence-associated genes, including p16, p21, and p53, were downregulated. Furthermore, Western blotting analysis revealed that HPL was enriched with fibronectin and vitronectin, essential cell adhesive proteins. Conclusions: HPL was effectively used as a coating material for ADSC expansions. Cellular cultivation on the HPL coating is an alternative approach for producing mesenchymal stromal cells.
Keywords
- mesenchymal stromal cell
- adipose-derived stem cell
- human platelet lysate
- coating substance
- cell senescence
Mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) offer great promise as advanced therapy medicinal products in regenerative medicine to repair or replace damaged tissues and organs [1]. MSCs gain marked therapeutic properties, such as high proliferation ability, multilineage differentiation potential, and secretion of various biological components, especially anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory molecules [2, 3]. MSCs have been successfully isolated from several sources, including bone marrow and gestational and adipose tissues [4]. According to the International Society for Cell and Gene Therapy (ISCT) criteria, MSC characteristics are defined by their differentiation potential and the expression of a set of stem cell markers [5, 6]. MSCs express CD73, CD90, and CD105 on the surface, yet they lack the expression of hematopoietic cell surface markers: CD45, CD34, CD14, CD19, and HLA-DR. In addition, MSCs can also differentiate into multi-lineage cells, such as chondrocytes, osteocytes, and adipocytes.
Most clinical applications use extensive MSC numbers to achieve effective outcomes; thus, large-scale expansion of MSCs in vitro is required to reach adequate therapeutic MSC doses [7]. Although MSCs expand with ease as conventional monolayer cultures, serially passaged MSCs begin to form alterations in their biological features and functions. After serial cell passaging, MSCs decrease in replication rate, alter their morphology, and express distinct transcriptome profiles [8]. In addition, late-passaged cells usually undergo senescence [9, 10]. These limitations make optimizing the MSC culture system necessary to enhance cell expansion and maintain cell functionalities.
MSCs are adherent cells that attach to the extracellular matrix or an artificial material of the cell culture surface. Generally, the polystyrene surface of cell culture plasticware is treated with corona discharge. This process generates a high-energy oxygen ion that allows the culture surface to become hydrophilic and negatively charged [11, 12]. In addition, the culture surface can be coated by various biological materials, including extracellular matrix and adhesion proteins, such as collagen, fibronectin, vitronectin, and laminin [13, 14, 15]. Therefore, surface modification possibly improves cell adhesion, enhances cell proliferation, and regulates cell behavior.
At present, many studies have revealed the efficiency of using human platelet lysates (HPLs) as supplements for expanding MSC growth [16, 17, 18]: HPLs were superior to fetal bovine serum (FBS) at enhancing higher growth rates [16], cellular viability [17], and differentiation potential [18]. HPL is derived from human platelets using repeated freeze and thawing cycles to disrupt the cell membrane. Increasing evidence has shown that HPL contains several growth factors and adhesion molecules supporting cellular adhesion and cell proliferation [19, 20]. Substituting FBS with xeno-free HPL can be an alternative nutrient for cell culture and is also suitable for cell-based therapies. The enrichment of several adhesion molecules in the HPL, including fibronectin, vitronectin, and collagen, has been reported [21]. Therefore, applying HPL to coat surfaces in cell culture may establish an appropriate environment for cell expansion [22].
Taken together, cultivating MSCs on HPL-coated surfaces may improve cell expansion, augment cell adhesion, and decrease cellular senescence in long-term cultures. This study aimed to modify cell culture surfaces to enrich adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) expansion in vitro, using HPL as a biological coating material. Changes in ADSC biological features such as cell adhesion, proliferation, and replicative senescence were determined. Moreover, the presence of key adhesive molecules in HPL samples, especially fibronectin and vitronectin, was identified by Western blotting analysis. The finding of this study could be applied to cell expansion during the manufacturing of ADSCs, which promotes cost savings by reducing the use of additional adhesion molecules or HPL volumes.
After receiving written informed consent, adipose tissue samples were harvested
from healthy subjects using lipoaspiration. The Ethical Committee approved the
procedure for Human Research on the Mahidol University Central Institutional
Review Board in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki (MU-CIRB
2018/202.1411). The lipoaspirate was washed with pre-warmed in phosphate-buffered
saline (PBS) to remove blood and oil, followed by digestion in 0.025% type I
collagenase (Worthington Biochemical Corporation, Lakewood, NJ, USA) at 37
°C for one hour with shaking. To separate the stromal vascular fraction
(SVF) containing ADSCs, the lipoaspirate was centrifuged at 300
The expired leukocyte-poor platelet concentrates (LPPCs) received from the blood
bank were used as a source for human platelet lysate (HPL) preparation. The study
was approved by the Ethical Committee for Human Research on the Mahidol
University Central Institutional Review Board in accordance with the Declaration
of Helsinki (MU-CIRB 2020/180.2307). HPLs were prepared using the freeze and
thawing technique. Briefly, frozen LPPC was thawed in a 37 °C water bath
for 90 minutes with shaking every 15 minutes. Then, LPPC was frozen at –80
°C for 24 hours. The freeze–thawing process was repeated to lyse the
platelets completely. For fibrin depletion, sterile 2 mM CaCl
To investigate the effects of HPL as a coating material for in vitro
ADSCs cultures, the experiments were divided into two groups: ADSCs cultured on
an uncoated surface and those cultured on an HPL-coated surface. For the
HPL-coated group, a 35 mm polystyrene tissue culture dish was pre-coated with 1
mL HPL and incubated at 37 °C in 5% CO
ADSCs at passage 5 were seeded at 1
To assess the effects of the HPL-coated surface on cell growth, ADSCs were
seeded at 1
To determine the growth curve of the ADSCs cultured on the HPL-coated surface,
the ADSCs were seeded at 1.5
For the cellular senescence assay and senescence-associated gene expression, 1
To assess whether the HPL-coated surface affected cellular senescence, the
senescence-associated
ADSCs were cultured in individual conditions until passages 5 and 10, as
described previously, were harvested for RNA extraction. RNA was collected using
TRIzol reagent (#15596026, Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA) and extracted through
the phenol–chloroform procedure. The RNA concentration was assessed using a
nanodrop spectrometer (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). The cDNA was
synthesized from 1 µg of RNA using iScript reverse transcription
(#170-8841, Bio-Rad Laboratories, CA, USA). The p16, p21, and
p53 mRNA levels were investigated using quantitative real-time PCR. Each
cDNA sample was mixed with the PCR master mix, containing forward and reverse
primers of the target genes (Table 1), nuclease-free water, and SYBR FAST qPCR
master mix (#KK4600, KAPA Biosystem, Wilmington, MA, USA). The expression levels
of the genes of interest were normalized to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
dehydrogenase (GAPDH), an internal reference control. The
difference in transcript levels of the senescence-associated genes was calculated
using the comparative CT method (2
| Gene name | Forward primer sequences | Reverse primer sequences |
| GAPDH | 5 |
5 |
| p16 | 5 |
5 |
| p21 | 5 |
5 |
| p53 | 5 |
5 |
For the Western blotting analysis, an equal amount of protein (20
µg) was separated on a 7% polyacrylamide gel and transferred to an
immobilon P transfer membrane (Merck Millipore, Burlington, MA, USA) using the
Mini-Protean© system (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Feldkirchen, Germany).
The membranes were incubated in 5% skimmed milk (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) for
2 hours to block any non-specific binding sites, followed by incubation with
anti-fibronectin (Ab268020) and anti-vitronectin (Ab45139) antibodies (Abcam,
Cambridge, UK) at 4 °C overnight.
All data are presented as mean
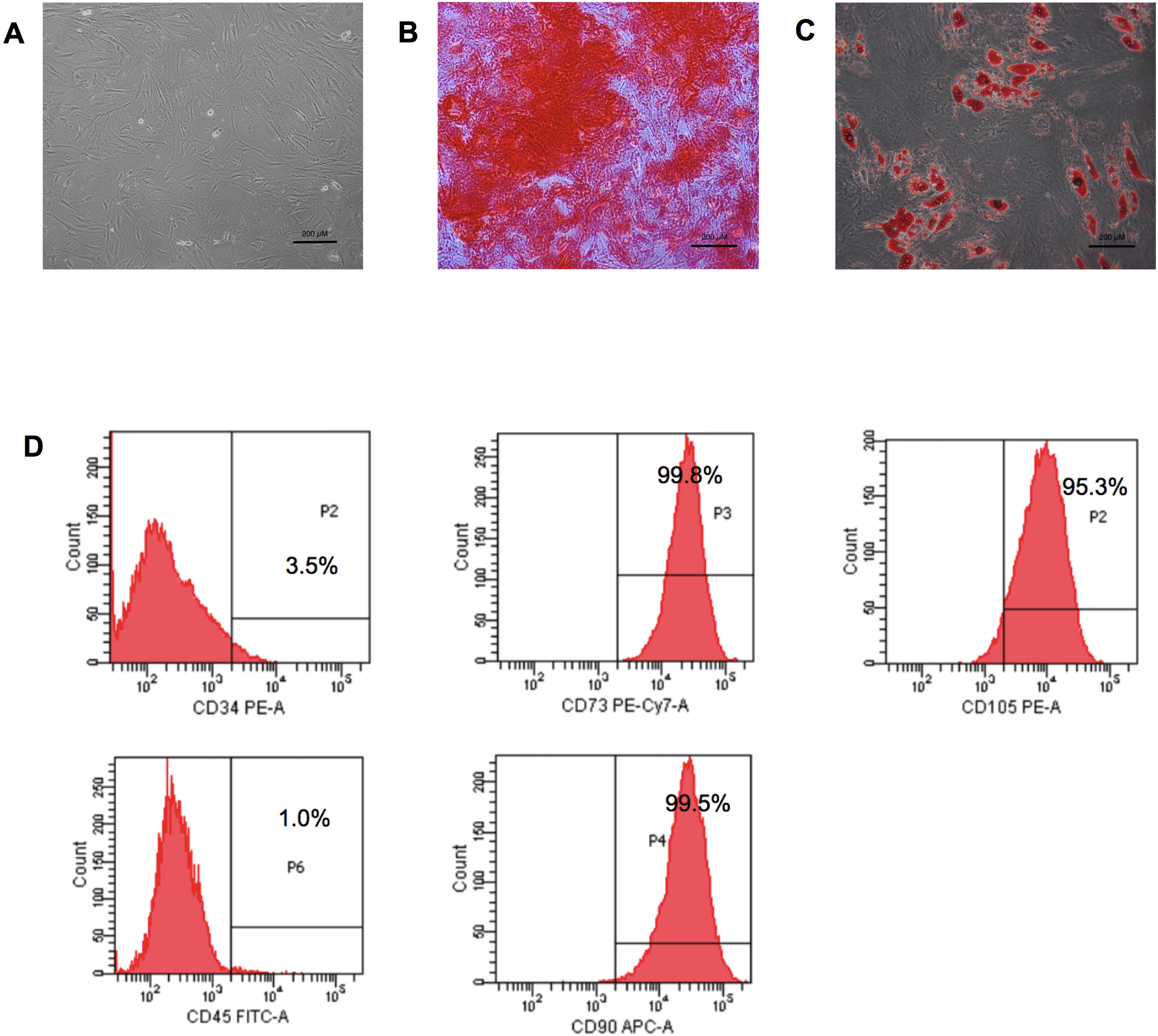
In vitro cultivation of adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) exhibited a spindle-shaped morphology with plastic adherent capacity (Fig. 1A). Multi-lineage differentiation properties of the ADSCs were evaluated by culturing the cells in osteogenic induction medium and adipogenic induction medium. The results showed that ADSCs could differentiate toward an osteoblast and adipocyte, as shown by the positive staining for Alizarin Red S (Fig. 1B) and Oil Red O staining (Fig. 1C), respectively. Immunophenotyping demonstrated that more than 95% of the ADSCs expressed mesenchymal stem cell surface markers, including CD105, CD90, and CD73. However, the cells rarely expressed both CD34 and CD45 hematopoietic markers (Fig. 1D).
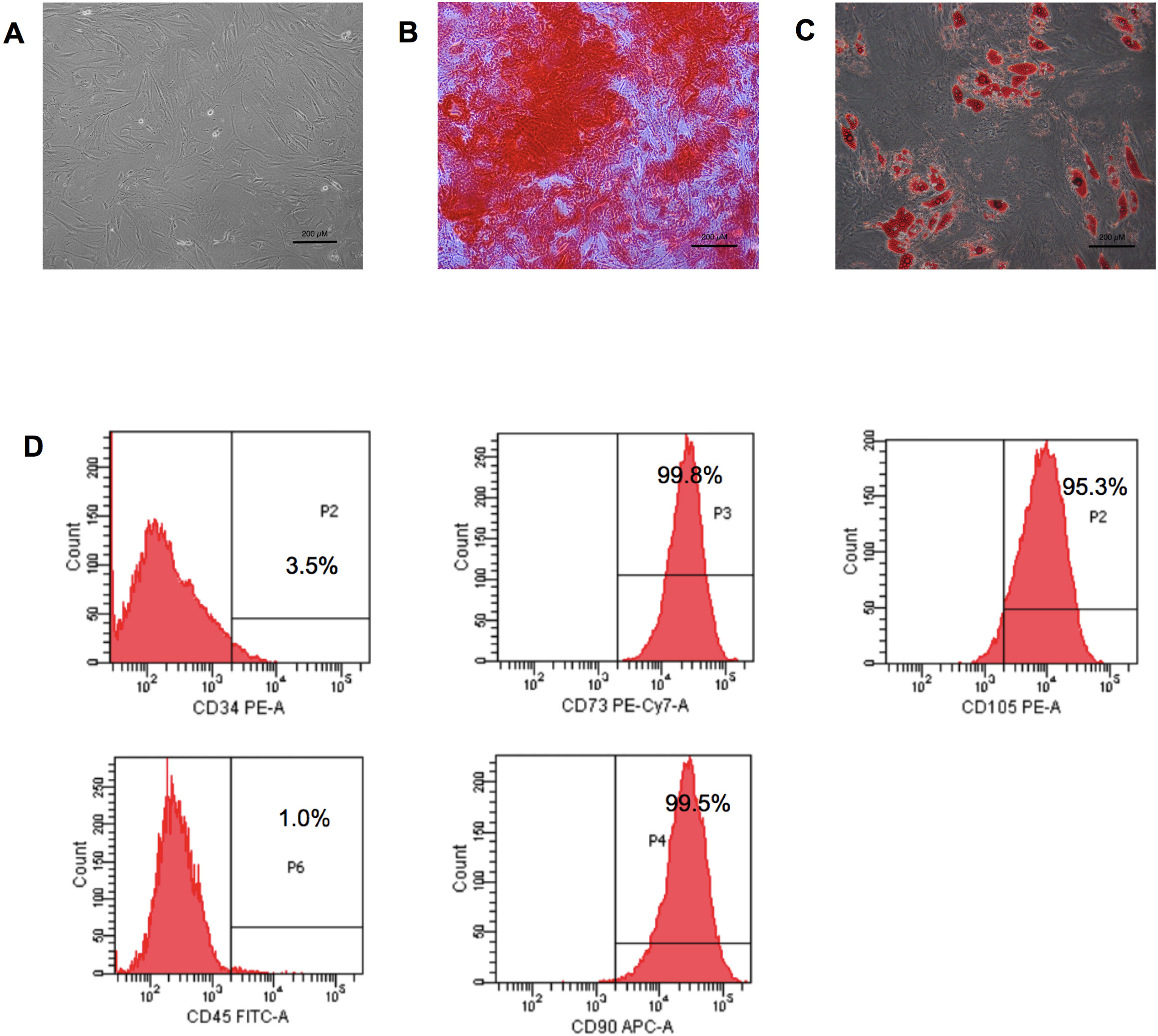 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.Adipose-derived stem cell characteristics. (A) Adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) displayed a fibroblast-like morphology. (B) Osteogenic differentiation of ADSCs after 21 days of differentiating—positive for Alizarin Red S staining. (C) Adipogenic differentiation of ADSCs after 14 days—positive for Oil Red O staining (scale bar = 200 µm). (D) Immunophenotyping of ADSCs demonstrated expressions of CD90, CD105, and CD73. PE-A, phycoerythrin; PE-Cy7-A, phycoerythrin-Cyanine7; FITC-A, fluorescein isothiocyanate; APC-A, allophycocyanin.
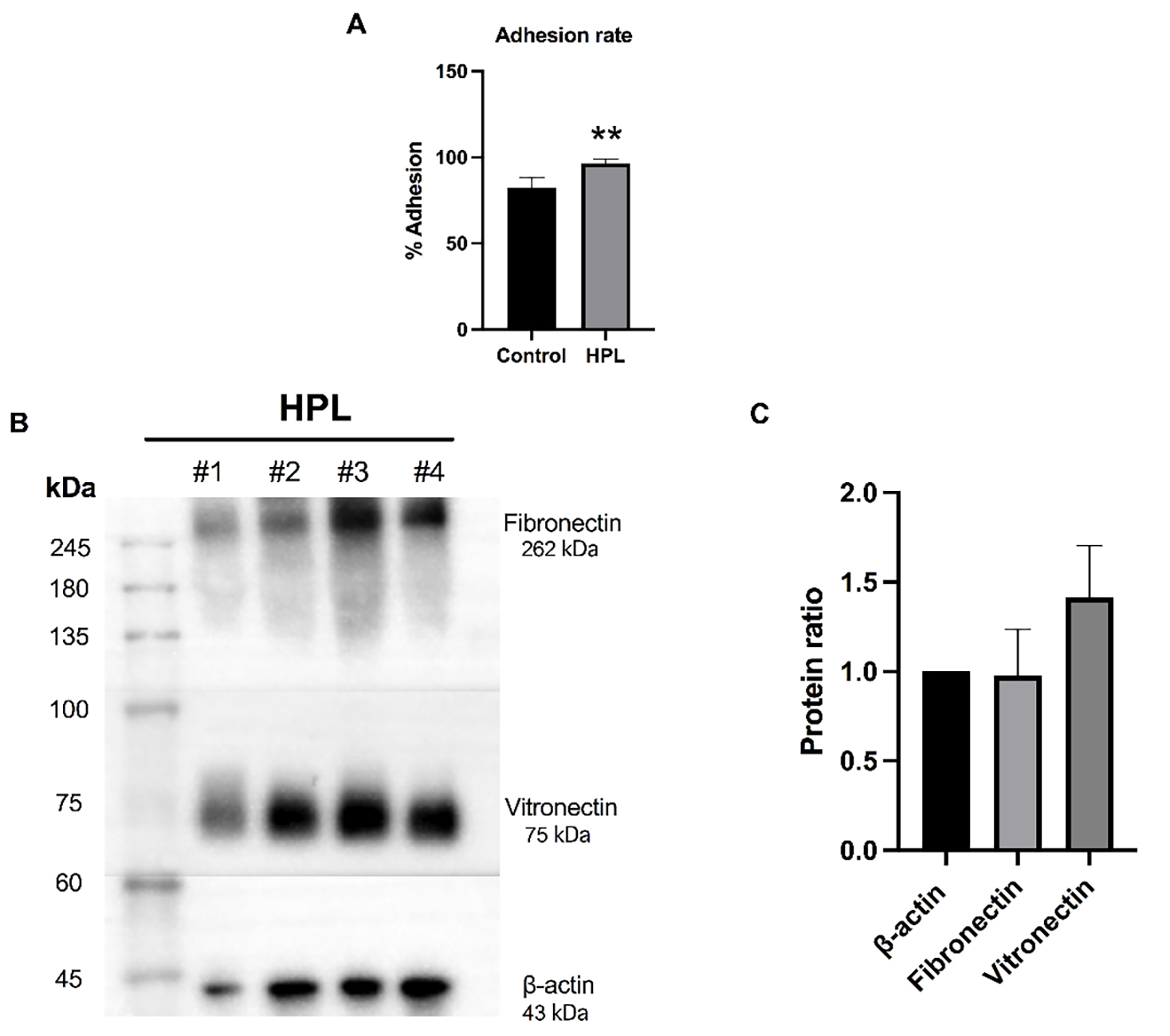
A cell adhesion assay was performed to investigate the alteration in the
biological features of ADSCs after being cultured on an HPL-pre-coated surface.
The ability of ADSCs to attach to HPL-coated surfaces was investigated after
being incubated for 12 hours. As shown in Fig. 2A, ADSCs cultured on HPL-coated
surfaces had significantly higher cell adhesion rates than those cultured on the
uncoated surfaces (96.49%
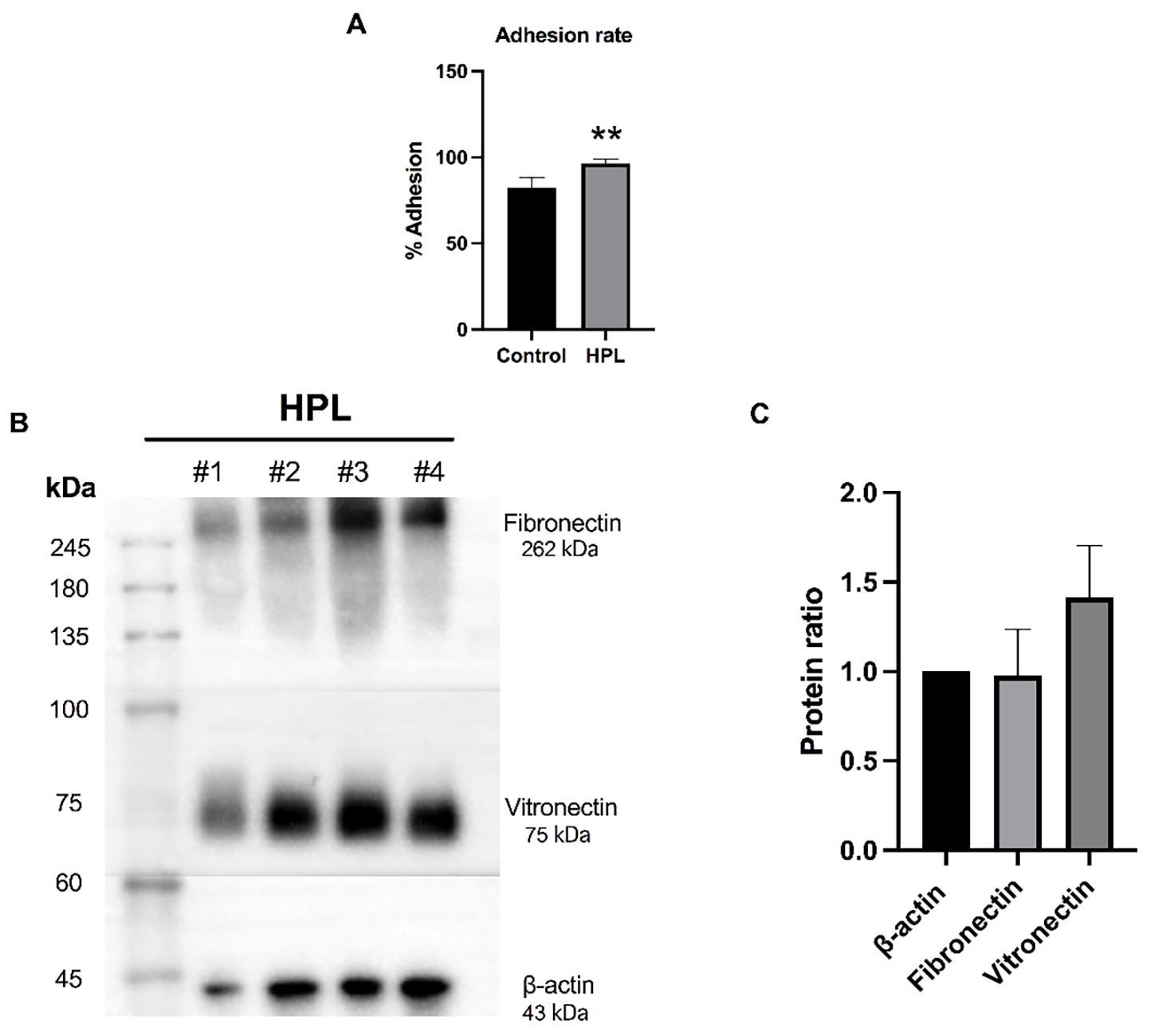 Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.Effects of human platelet lysate (HPL) coating on cell
adhesion and the expression of adhesive molecules. (A) The ADSC cell adhesion
percentage when cultured on HPL (HPL group) for 12 hours compared to ADSCs
cultured on an uncoated surface (control group). Data are presented as the mean
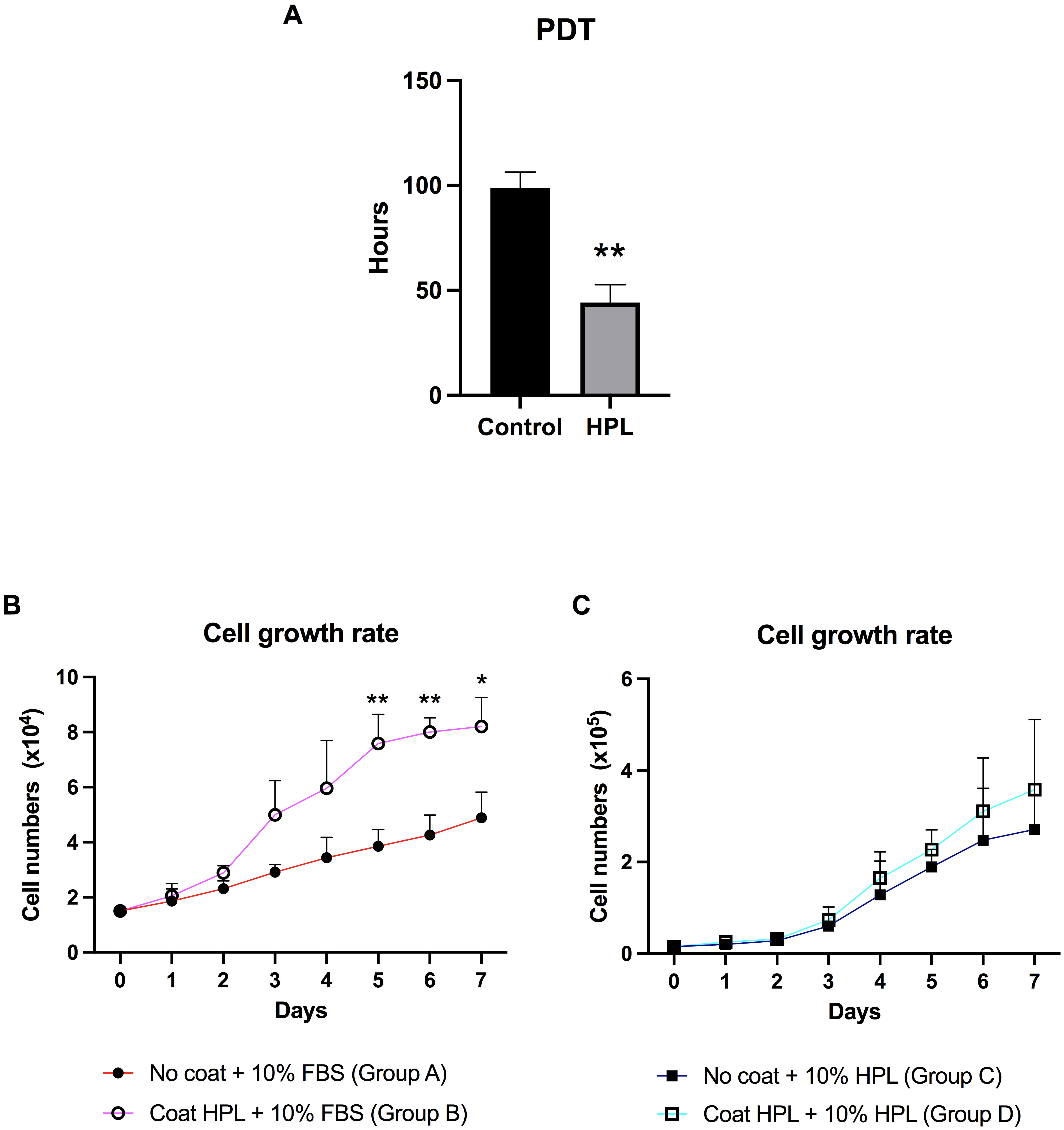
To investigate the effect of HPL coating on the growth rate, the ADSC population
doubling times (PDTs) when cultured in the presence or absence of HPL were
evaluated. Analysis of the PDTs revealed that HPL coating significantly decreased
the PDT of ADSCs to 44.17
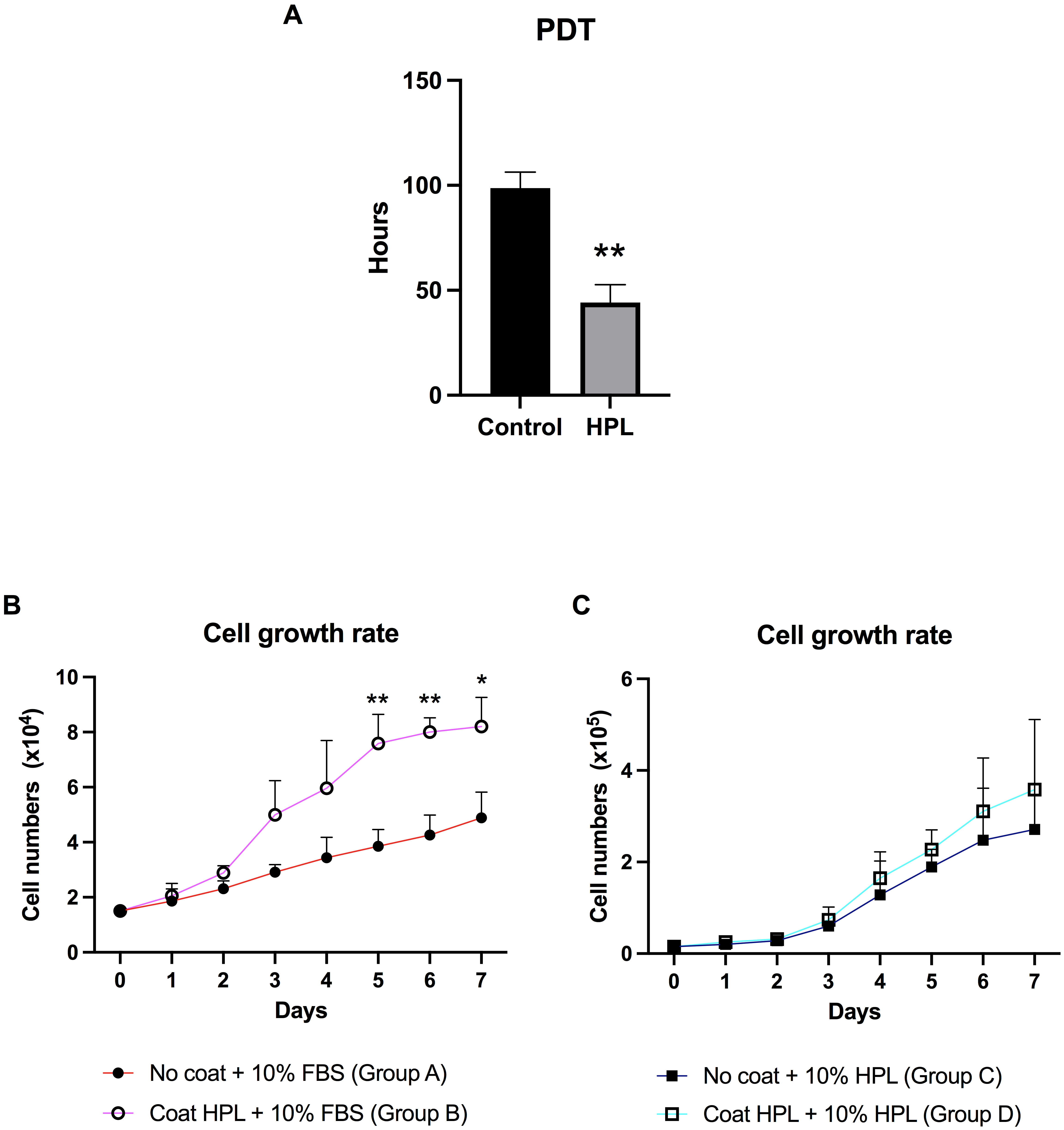 Fig. 3.
Fig. 3.Population doubling time (PDT) and growth curve of ADSCs
cultured on HPL coating. (A) The population doubling time (PDT) of ADSCs derived
from the HPL coating group compared to the control group. (B) The growth curve of
ADSCs was maintained on an HPL-coated surface (group B) for 7 days, compared to
an uncoated surface (group A). Cells in both groups were supplemented with
stromal medium and 10% FBS (fetal bovine serum). (C) The growth curve of ADSCs was maintained on an
HPL-coated surface (group D) compared to those cultured on an uncoated surface
(group C), although both had FBS substituted for 10% HPL. Data are presented as
mean
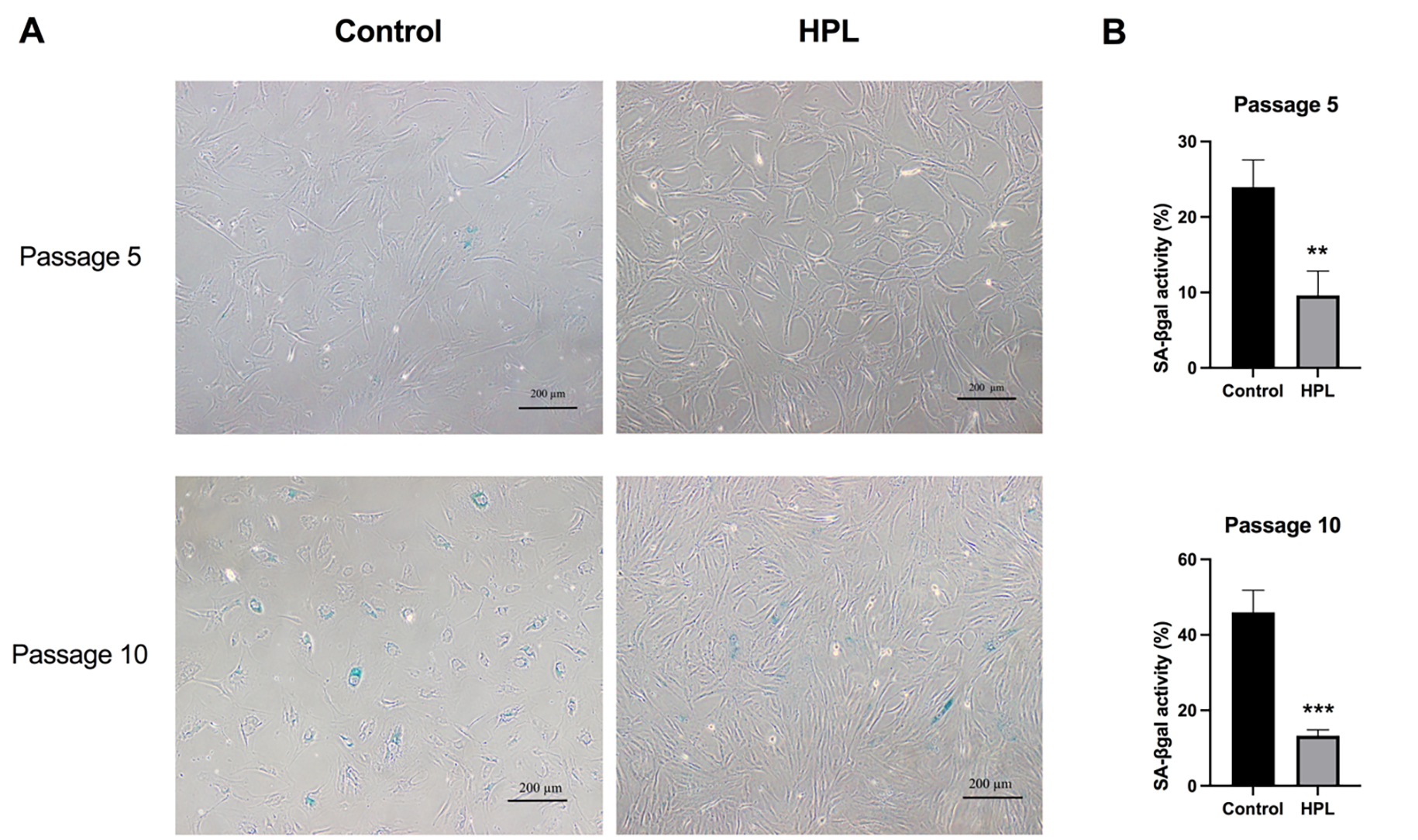
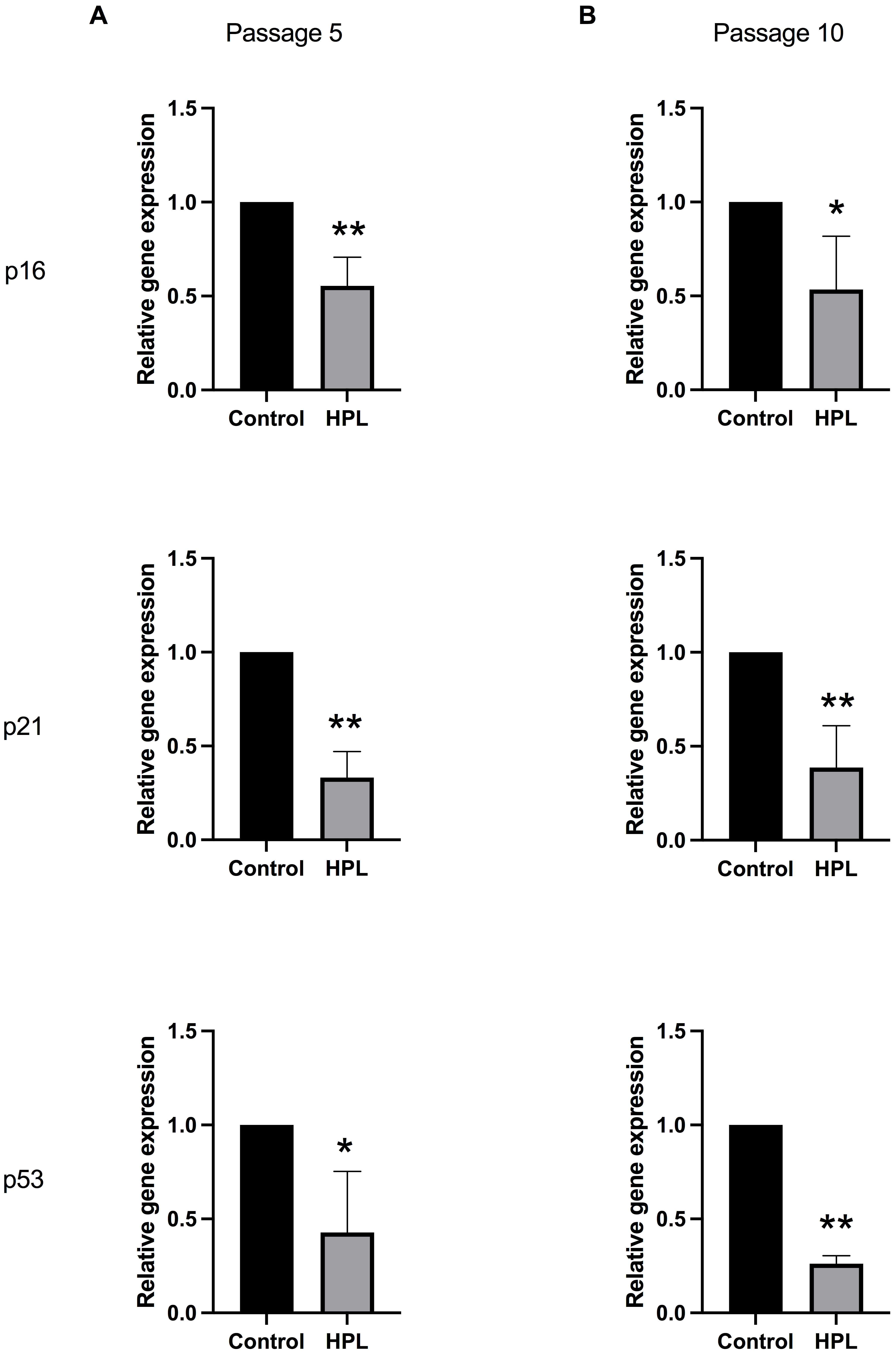
To determine whether HPL coating affects ADSC senescence rates after serial
passage, senescent cells were visualized using senescence-associated
beta-galactosidase (SA-
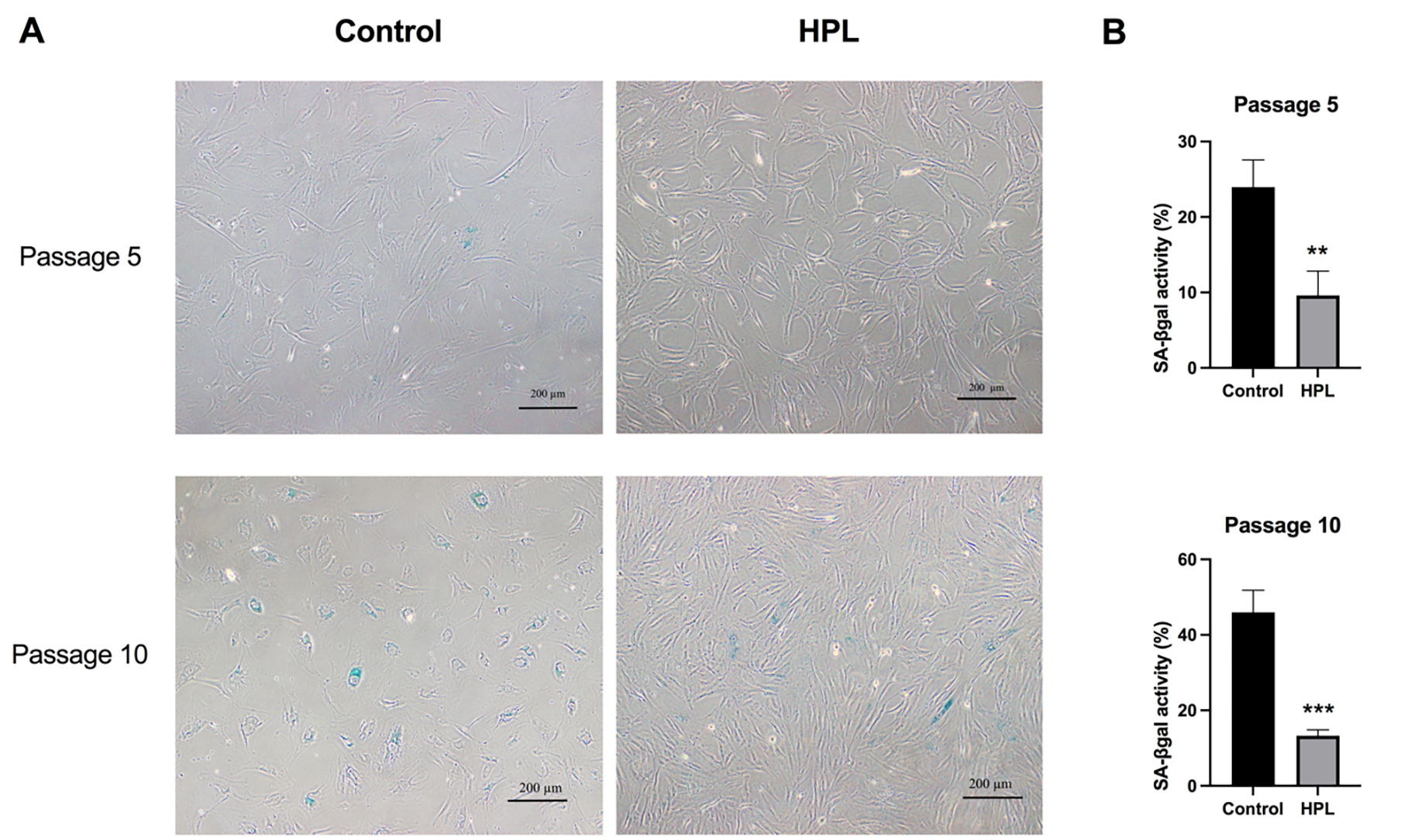 Fig. 4.
Fig. 4.Effects of HPL coating on ADSCs senescence after serial
passages. (A) Positive
The previous results demonstrated a decrease in the number of senescent ADSCs
maintained on the HPL-coated surface. Thus, to clarify whether HPL coating
influenced the activation of the senescence signaling pathway during cellular
aging, the transcription levels of p16, p21, and p53
were investigated in P5 and P10 ADSCs. Gene expression analysis showed that the
p16, p21, and p53 mRNA levels were significantly
downregulated in ADSCs cultured on HPL-coated plates for five passages compared
to the control group (0.501
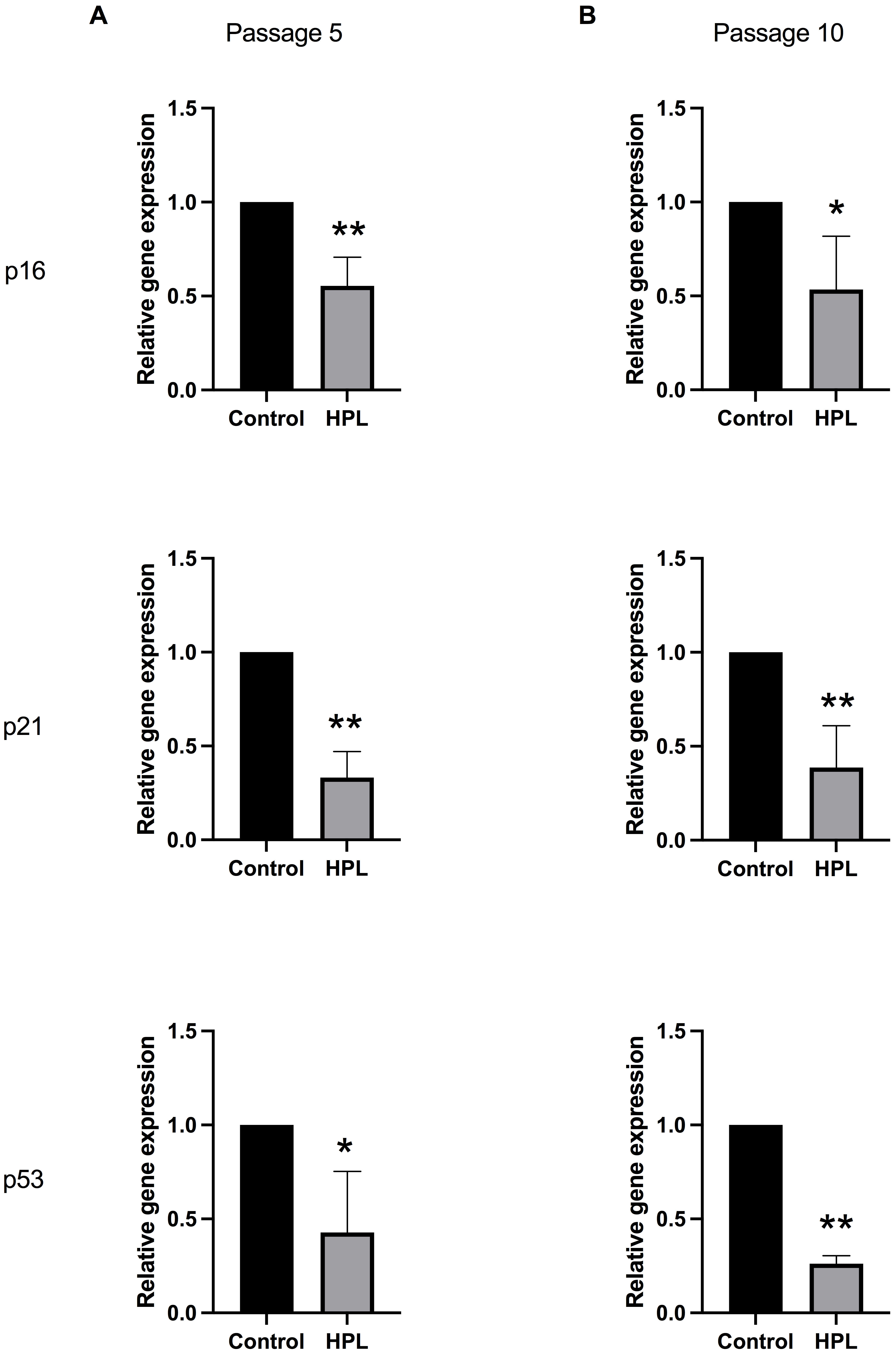 Fig. 5.
Fig. 5.Alteration of senescent-associated gene expressions in ADSCs
cultured on HPL coating. (A) Passage 5 and (B) passage 10 populations maintained
on HPL-coated surfaces. Data are presented as mean
This study demonstrated the role of HPL as a coating material in supporting in vitro ADSC expansion. Changes in the biological features of ADSCs, including cell adhesion, cell proliferation, and cellular senescence, were investigated at different periods of ADSC growth on pre-coated HPL plates. HPL supplements have beneficial effects on MSC growth; however, the cells had difficulty attaching to the plastic surface of tissue culture vessels. According to a recent study, MSCs cultured in FBS medium interacted more with the tissue culture vessel than those cultured in HPL [24]. The MSCs cultured in FBS had a significantly higher amount of focal adhesion than those cultured in the HPL additive.
In cell-based therapy, expanding ADSCs holds significance in cell manufacturing procedures. An alternative approach to enhancing growth during this process involves surface coating with adhesion molecules. Notably, utilizing HPL coating has emerged as a strategic method for MSC expansion [25], one which closely mimics the natural cellular environment through the enrichment of adhesion molecules [19, 20]. Interestingly, the findings in our recent study clearly showed that HPL coating could promote the adhesion of ADSCs. Western blot analysis of the HPL samples indicated that they possess key adhesive molecules, including fibronectin and vitronectin. This finding agrees with those in prior studies, which showed that HPL has a biological richness and contains various growth factors, cytokines, and extracellular matrix proteins that can positively influence cell behavior, which is crucial for cell growth and differentiation [26, 27, 28]. Moreover, recent studies that thoroughly characterized protein contents of HPL samples following proteomic analysis revealed a remarkable richness in multiple growth factors and adhesion molecules [19, 20]. Adhesive molecules, such as laminin, vitronectin, and fibronectin, have been shown to play roles in improving cellular adhesion and promoting colony formation [29, 30]. Thus, it seems possible that the increase in the cell adhesion ability of ADSCs cultured on HPL-coated plates is partly due to the presence of key adhesive molecules in the HPL samples, including fibronectin and vitronectin.
Evidence supporting the substitution of FBS with HPL supplements could enhance
MSC proliferation [16, 31] and facilitate MSC differentiation [18]. We further
investigated whether minimal amounts of HPL that remained as a coating substance
could promote ADSC growth. Our finding first reported that the PDT of ADSCs
cultured on HPL-coated plates was reduced, which led to robust increases in ADSC
growth. Likewise, the growth curve of the ADSCs cultured in HPL-coated plates
demonstrated a significant increase in ADSC numbers [32]. HPL as a coating
material successfully enhanced in vitro ADSC expansion. Moreover, adding
HPL supplements to HPL-coated plates slightly increased ADSC numbers. However, no
significant differences were found. HPL is enriched with an abundance of growth
factors, such as insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), platelet-derived growth
factor (PDGF), transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-
Serial cell expansions and prolonged cell culture times usually lead to cellular
aging [35]. However, cellular senescence is induced by repetitive passaging and
high glucose levels [36]. The alterations in cellular behaviors during senescence
can be demonstrated by morphological changes and increased senescence-associated
Our experiments demonstrated the beneficial effects of HPL coating on ADSC expansion. Culturing ADSCs using an HPL-coating system resulted in increased cell adhesion, enhanced cell proliferation, and reduced cellular senescence. This study has also identified the presence of key adhesive molecules in HPL. This study strengthens the idea that cell culture surface modification by HPL coating would be an additional method for expanding in vitro ADSC growth. Minimal HPL volumes are required to improve ADSC growth during long periods of in vitro cell culture.
ADSCs, adipose-derived stem cells; MSCs, mesenchymal stromal cells; FBS, fetal bovine serum; HPL, human platelet lysate; PDT, population doubling time.
All data generated and/or analyzed in this study are included in the published article and supplementary information.
WK and AS designed and conceptualized the research study. PT, NC and SH performed the research. CP performed sample collection and the data analysis. PT, SH, and KN participated in collecting and analyzing the data. WK and AS supervised the experiments and analyzed the data. PT, WK and AS wrote and edited the manuscript. AS made significant revisions and proofread the manuscript. All authors contributed to editorial changes in the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. All authors have participated sufficiently in the work and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
This study was approved by ethical committee for human research of the Mahidol University Central Institutional Review Board in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki (MU-CIRB 2018/202.1411 and MU-CIRB 2020/180.2307).
We would like to express our sincere gratitude to our colleagues for their advice on the article. Thanks to all those who helped us during the writing of this manuscript.
This research project is supported by Mahidol University (NDFR 30/2564).
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Publisher’s Note: IMR Press stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.