1 School of Clinical Medicine, Changchun University of Chinese Medicine, 130117 Changchun, Jilin, China
2 State Key Laboratory of Electroanalytical Chemistry, Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 130022 Changchun, Jilin, China
Abstract
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) has a global prevalence of 25% and is a leading cause of cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. The prevalence of MASLD has been increasing, mirroring the global increase in diabetes and metabolic syndrome. MASLD is a chronic and progressive condition characterized by inflammation, oxidative stress, insulin resistance, and disruptions in lipid metabolism. Programmed cell death (PCD) plays a pivotal role in determining the pathological aspects of MASLD, including liver inflammation, fibrosis, and even the potential for malignant transformation. PCD is a dominant process that is fundamental for eukaryotic growth and serves as a regulatory factor in MASLD. PCD encompasses various pathways, including autophagy, ferroptosis, apoptosis, and pyroptosis. These PCD pathways can be activated at different stages of MASLD. The key effector molecules involved in these processes are central focal points in the development of therapeutic interventions for MASLD. Here, we comprehensively review the idea that targeted the modulation of the PCD pathway may be an effective approach for the prevention and/or treatment of MASLD.
Keywords
- autophagy
- ferroptosis
- apoptosis
- pyroptosis
- metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) is emerging as the leading chronic liver disease worldwide. It is estimated to afflict one billion individuals globally and may be present in approximately one in four of the world population [1]. However, there are notable disparities in the prevalence of MASLD across diverse geographic regions. The Middle East and South America exhibit the highest prevalence, while Africa reports the lowest prevalence of MASLD [2]. Globally, the prevalence of MASLD in individuals who are not classified as obese typically falls within the range of 10–30% in both Western and Eastern countries [3]. MASLD is therefore a worldwide health issue that imposes a significant socioeconomic burden.
MASLD is a leading contributor to liver-related morbidity and mortality, as well as being the fastest growing cause of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) [4]. This disease encompasses a spectrum of liver disorders, ranging from simple fat accumulation in the liver (non-alcoholic fatty liver, NAFL) to a more severe form known as metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH). The latter is characterized by inflammation and rapid progression of fibrosis, each with its own variable trajectory, but with the potential to progress to cirrhosis and HCC [5]. MASLD is also closely associated with the metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, extra-hepatic cancers, and its associated complications. The most severe among the extra-hepatic cancers cancer, mainly in the elderly [6]. The pathogenesis of MASLD involves a buildup of fats such as triglycerides in hepatocytes, accompanied by insulin resistance (IR), oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, lipotoxicity, mitochondrial dysfunction, hepatocyte lipoapoptosis, etc [7]. The pathogenesis of MASLD is complicated and involves multisystem abnormality and dysfunction. To date, there is still no ideal approved drug for the prevention and cure of this disease. Therefore, MASLD and its more severe forms constitute a growing worldwide epidemic with a high unmet medical need.
Cells can undergo two distinct modes of cell death: accidental cell death (ACD) and regulated cell death (RCD). RCD, commonly known as programmed cell death (PCD), is a strictly controlled form of cell death triggered by complex signaling [8]. PCD plays a crucial role in maintaining body homeostasis, but excessive activation or insensitivity to PCD can contribute to the development and progression of various diseases [9]. In the context of MASLD, PCD emerges as a pivotal factor that influences the severity and outcome of liver injury [10]. The death of hepatocytes is an important event in the progression of MASLD, causing inflammation that subsequently leads to fibrosis, cirrhosis, and even HCC [11]. Recent investigations have identified various types of PCD, including mainly apoptosis, autophagy, necroptosis, pyroptosis, and ferroptosis. All of these have been studied for their involvement in the pathogenesis of MASLD. They have unique characteristics while also exhibiting many similarities, overlap and crosstalk. Consequently, it is plausible that multiple types of PCD coexist. In this review, we discuss the known signaling cascades associated with each PCD and explore their implications in MASLD.
Autophagy is the process by which eukaryotic cells degrade their cytoplasmic proteins and damaged organelles by lysosomes under the control of autophagy-related genes [12]. On the one hand, autophagy can prevent cell damage and ensure that cells survive in the absence of nutrition. On the other hand, autophagy can respond to cytotoxic stimuli [13]. This form of PCD encompasses both basic autophagy occurring under physiological conditions, and induced autophagy triggered by stress conditions [14]. The former serves as a cellular self-protection mechanism, contributing to cell growth and development, and protecting cells from metabolic stress and oxidative damage. It plays a crucial role in maintaining intracellular homeostasis and governing the synthesis, degradation and recycling of cellular products [15]. However, it is worth nothing that while generally beneficial, autophagy can also potentially induce metabolic stress, facilitate the degradation of cellular components under certain circumstances and even contribute to cell death [16]. Studies have shown that autophagy plays a very important role in many physiological and pathological processes, including cell homeostasis, aging, immunity, tumorigenesis and neurodegenerative diseases [17].
MASLD is a clinicopathological syndrome with similar histological changes in the liver as to alcoholic liver disease, but without a patient history of excessive drinking [18]. Autophagy can regulate the homeostasis of the intracellular environment, and is therefore closely associated with development, progression and prognosis of MASLD [19]. Autophagy of liver endothelial cells in MASH patients is reduced compared to patients with simple steatosis or normal liver [20]. At present, drugs that can induce autophagy of hepatocytes may have potential therapeutic effects on MASLD [21]. However, the only treatment option for MASLD is still lifestyle intervention, which usually involves modification of diet and physical exercise [22]. Calorie restriction and physical exercise are the two main ways to stimulate autophagy [23]. MASLD is therefore closely related to autophagy.
Triglycerides (TG) in liver cells mainly exist in the form of lipid droplets. These droplets contain a lipid core composed of TG, with the surface covered by a single layer of phospholipids. The single layer of phospholipids is embedded with structurally-related PAT family proteins, including lipid droplet coating protein (perilipin) and lipogenesis-related protein [24]. Lipid droplets play an important role in lipid metabolism and storage, membrane transport and protein degradation. Moreover, autophagy has been shown to decompose fat and lipid droplets [25]. When the autophagy bodies surrounding lipid droplets fuse with lysosomes, the lipid droplets are degraded into free fatty acids, which are then oxidized in mitochondria to generate ATP [26]. Under starvation conditions, LC3 appears on the surface of lipid droplets and LC3II interacts with lipid droplet coating proteins to degrade lipids through autophagy. This is mediated by autophagosomes which recognize lipid droplet coating proteins on the surface of lipid droplets [27]. More recent research has showns that autophagy can regulate lipid metabolism, improve insulin resistance, reduce oxidative stress and improve MASLD [28]. Lipid metabolism in hepatocy is closely related to autophagy. Autophagy exerts a direct influence on lipid metabolism by facilitating the degradation of lipid droplets. Moreover, it indirectly regulates lipid metabolism by maintaining the normal functions of organelles and proteases that are integral to lipid metabolism [29]. The process of intracellular lipid transport through autophagosomes and leading to lysosomal decomposition is called lipophagy [30]. However, long-term chronic lipid deposition in MASLD leads to abnormal, autophagy function in hepatocytes [31]. Impaired autophagy function could therefore be one of the internal mechanisms of lipid deposition in MASLD hepatocytes. As lipids accumulate in the liver, the level of autophagy decreases, the membrane structure of autophagosomes changes, and the combination of autophagosomes with lysosomes is inhibited, thus affectings the role of autophagy in lipid degradation [32]. In an in vitro model of MASH, lipid metabolism and inflammatory reactions are elevated following the treatment of hepatocytes with the autophagy inhibitor 3-methylindole [33]. Other studies have shown that when the autophagy level is reduced due to excessive lipid accumulation in the liver, simple inflammation can evolve to MASLD and its associated complications. If lipid accumulation in the liver is reduced, the autophagy level can be restored and the occurrence of liver injury or MASLD and its complications can be prevented [34].
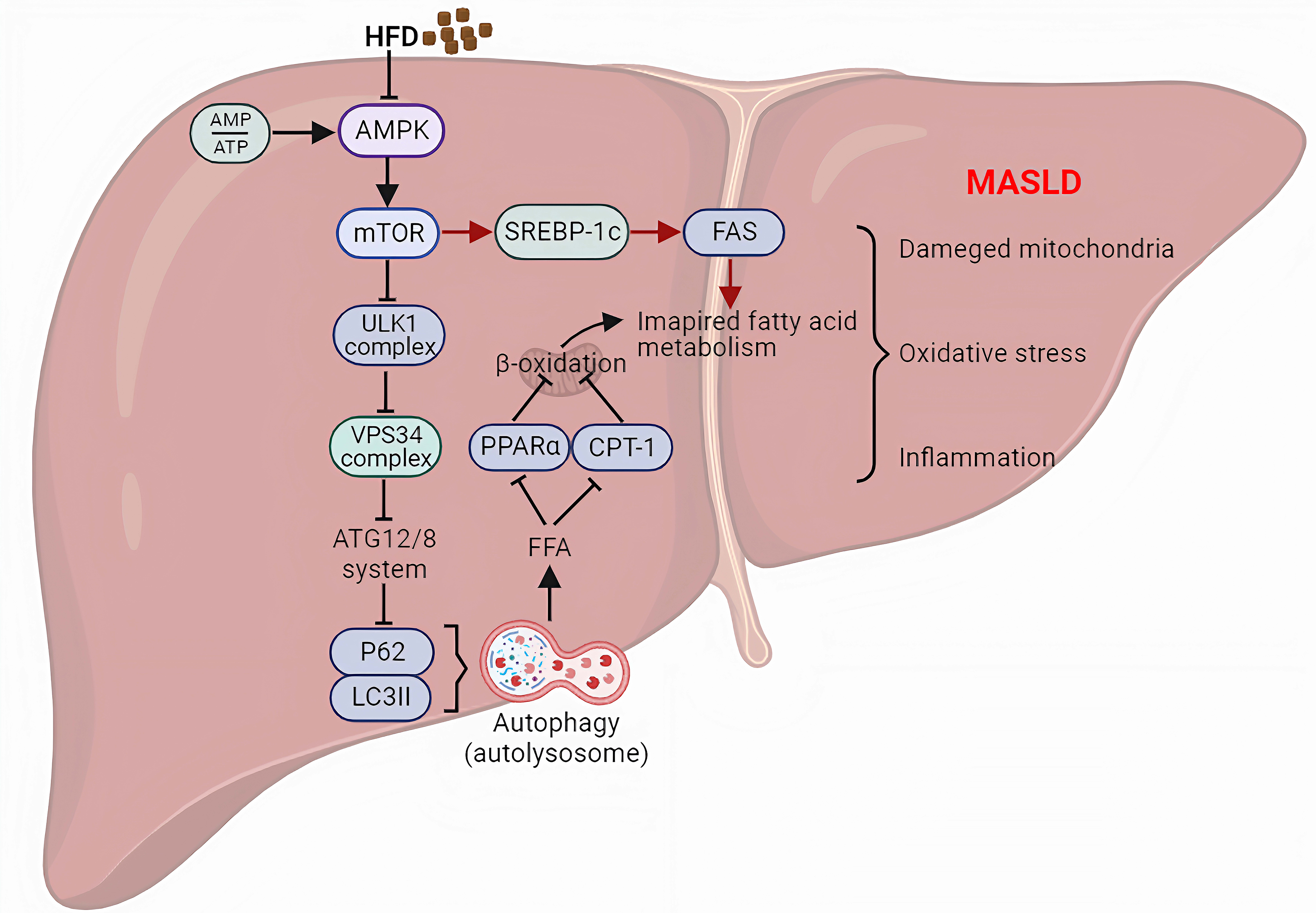
Recent studies have shown that activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)
can increase the autophagy level of hepatocytes and promote fatty acid oxidation
[35]. Under conditions of sufficient glucose, active mammalian target of
rapamycin (mTOR) inhibits the activation of unc-51-like kinase 1 (ULK1) and the
initiation of autophagy by phosphorylating a specific site in ULK1 (Ser 757),
thereby destroying the interaction between ULK1 and AMPK. Under conditions of
glucose deficiency, AMPK is activated, the phosphorylation of mTOR is inhibited
by AMPK, and ULK1 can interact with AMPK and be phosphorylated by AMPK, thus
enabling the activated ULK1 to start autophagy [36, 37, 38]. Liver Kinase B1
(LKB1) is an upstream regulatory protein of AMPK (Fig. 1). Following activation
of the LKB1-AMPK-mTOR pathway, the mRNA levels of CPT1
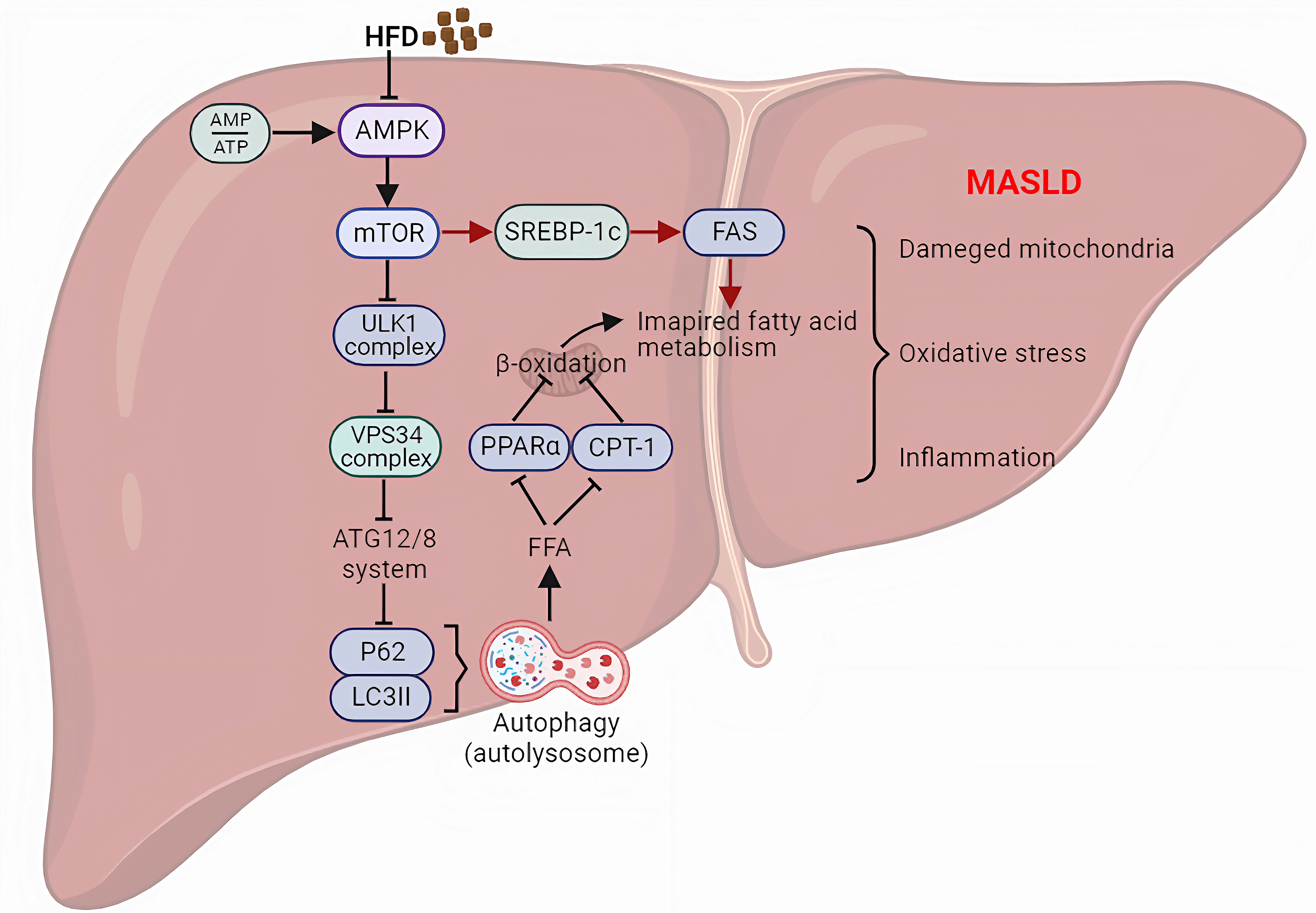 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.Autophagy and MASLD. The AMPK pathway is considered a
key factor in slowing the progression of MASLD. When excessive fat accumulates in
the liver, AMPK is inhibited. This promotes hepatic fatty acid synthesis, while
concurrently suppressing fatty acid oxidation and hence reducing fatty acid
consumption. This increases intracellular lipid accumulation and favors the onset
and progression of MASLD. AMPK also regulates autophagy through its effects on
the clearance of cellular waste and the maintenance of energy balance. AMPK
activation can directly phosphorylate ULK1 to initiate autophagy. AMPK can also
indirectly promote autophagy by inhibiting mTOR. Thus, AMPK-meditated autophagy
facilitates the degradation of cellular waste, such as fatty acids.
Abbreviations: MASLD, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease;
HFD, high-fat diet; AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; ULK1, unc-51-like kinase
1; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; LC3, microtubule-associated proteins
1A/1B light chain 3; FFA, free fatty acids; SREBP-1c, sterol regulatory element
binding protein 1c; FAS, fatty acid synthase; PPAR
The influence of obesity-induced liver lipid metabolism disorders on human health has attracted much attention in recent years. The research described above shows that autophagy plays a key role in hepatic lipid metabolism, mainly by degrading intracellular lipid droplets and reducing lipid accumulation in the liver, thereby improving lipid metabolism disorders (Fig. 1). Study of the molecular mechanism of autophagy in hepatic lipid metabolism should clarify the pathogenesis of liver lipid metabolism disorder caused by obesity and lead to improvement in drug treatments.
Dixony first introduced the concept of ferroptosis in 2012 to describe a form of
iron-dependent, non-apoptotic cell death observed in cancer cells with
KRAS mutations. The cellular features of ferroptosis include: (a) Iron
homeostasis, (b) lipid peroxidation, and (c) depletion of glutathione peroxidase
4 (GPX4) [43]. Several key biological processes in the human body are based on
the ability of iron to fluctuate between oxidized (Fe
Free extracellular Fe
Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) are the primary substrates for peroxidation
in cell membranes during ferroptosis. Elevated PUFA synthesis enhances
susceptibility to ferroptosis by a process that is positively modulated by acyl
coenzyme A (CoA) synthetase long-chain family member 4 (ACSL4) [52]. Lipid
peroxidation can cause great damage to cells. The accumulation of propylene
glycol, the end product of lipid peroxidation, can cause polymerization of
proteins and nucleic acids, leading to irreversible damage to membrane structure
and ultimately to cell death [53]. Glutathione (GSH) functions as a substrate for
the antioxidant enzyme GPX4, which mitigates the presence of toxic lipid ROS
during ferroptosis. GPX4 is an intracellular antioxidant that catalyzes the
transformation of GSH into oxidized glutathione while concurrently converting
phospholipid hydroperoxides (PLOOH) into corresponding phospholipid alcohols.
This enzymatic process effectively inhibits lipid peroxidation and is a pivotal
mechanism in the prevention of ferroptosis. Additionally, the transmembrane
protein system Xc
MASLD is a progressive liver disease that can progress to MASH, liver fibrosis, and even to HCC [55]. The liver is an important organ for fat metabolism and nutrient metabolism. It is also an important site for iron storage, accounting for about one-third of the body’s stored iron reserve. Iron in the liver has a dual role in that hepatocytes maintain iron homeostasis through the production and secretion of hepcidin (Hepc), while iron metabolism and excessive accumulation of lipid peroxides in hepatocytes also causes ferroptosis [56]. Ferroptosis occurs during the progression of various types of liver diseases, such as alcoholic liver disease, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, and HCC [57]. These are characterized by iron deficiency or iron overload in hepatocytes [58]. Specific inhibition of lipid peroxidation, modulation of iron metabolism and GPX4 (Fig. 2), and amelioration of excessive ferroptosis in the liver have become important approaches to combat MASLD.
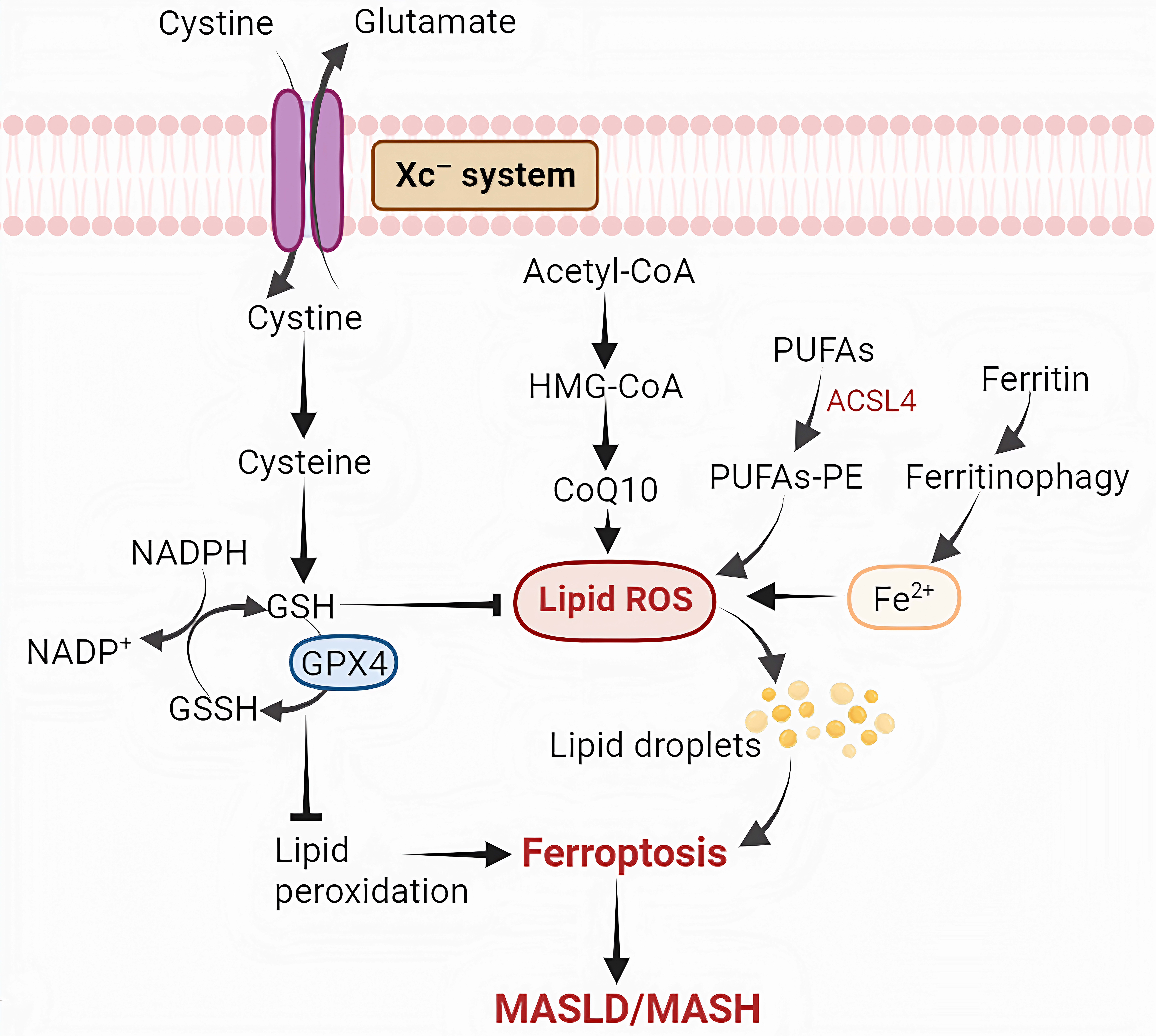
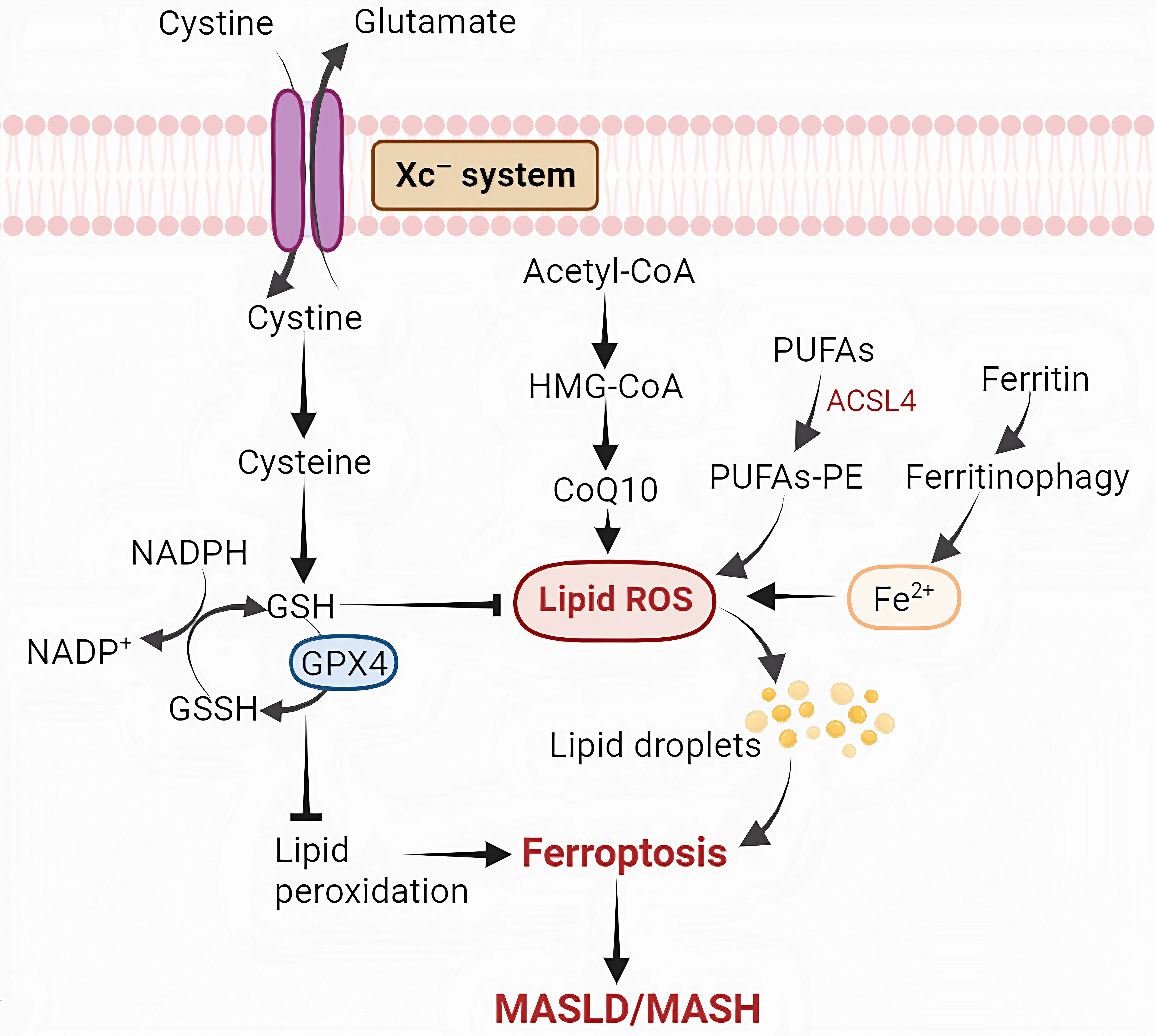 Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.Ferroptosis and MASLD. Ferroptosis can be initiated by
inhibiting the Xc
As the main iron storage organ in the body, the liver is important for
maintaining iron homeostasis. Normally, iron is stored in hepatic ferritin. By
binding to ferritin and transporting it to the lysosomes, NCOA4 causes iron
overload, resulting ultimately in the releases of large amounts of Fe
It has also been shown that ferroptosis and damage to liver cells can occur in
the absence of iron overload. The multifunctional protein polyr (C) binding
protein (PCBP1) is a receptor that acts as a cytoplasmic iron chaperone and binds
and transfers iron to mammalian cells. GSH binds Fe
Oxidative stress caused by lipid peroxides is thought to be one of the important
factors in the development of MASLD, and the accumulation of lipid peroxides is
also a cause of ferroptosis. Thus ferroptosis may be a contributing key factor to
MASLD [64]. Lipid peroxidation products can damage hepatocytes, and there
may be a synergistic relationship between the lipid peroxidation substrate
arachidonic acid (AA) and Fe
Oxidative stress is one of the most important mechanisms of liver injury in
MASLD. Large amounts of ROS are generated and target the double bonds of PUFAs,
resulting in the formation of lipid peroxides that can induce ferroptosis and
exacerbate hepatocyte injury. GSH/GPX4 is an antioxidant system that targets
lipid peroxide accumulation. Inhibition of the GSH/GPX4 system leads to
peroxidative damage to cell membranes and ferroptosis (Fig. 2). GPX4 activators
were found to be effective at alleviating MASH [65]. Nuclear factor E2-related
factor 2 (Nrf2) is an alkaline leucine zipper protein and a key transcription
factor for many antioxidant proteins. Nrf2 can
directly regulate GPX4 transcription, and is also an important regulator of
de novo GSH synthesis. Studies have shown that Nrf2 expression is
reduced in MASLD mice, and enhancing the Nrf2-HO1 pathway can effectively prevent
the development of MASLD [66, 67]. Knockdown of Nrf2 in MASLD mice effectively
reduces lipid accumulation and decreases PPAR
Numerous studies have confirmed that ferroptosis is involved in the progression of MASLD/MASH. Moreover, pathological processes such as lipid accumulation, hepatic steatosis, inflammatory cell infiltration, fibrosis, and mitochondrial damage are associated with ferroptosis in MASLD. Iron overload and oxidative stress-induced lipid peroxidation may mediate the progression of MASLD, and the major antioxidant mechanisms and iron metabolism regulators may be potential targets in future studies.
Apoptosis exhibits distinctive morphological features, including cellular shrinkage, a dense cytoplasm with tightly packed organelles, and pyknosis resulting from characteristic condensation and fragmentation of chromatin [69]. The biochemical process of apoptosis is induced by the activation of both initiator and executioner caspases. These caspases facilitate cell demise by cleaving proteins and subsequently activating nucleases, which in turn cleave DNA into shorter, uniform fragments. A recent study found a strong correlation between active caspases 3 and 7, increased expression of Fas receptors in MASH specimens, and the subsequent association of hepatocyte apoptosis with the progression of MASH [70]. Activation of caspase 3 and the occurrence of hepatocyte apoptosis are well-established hallmarks observed in various experimental models of MASLD, and in human MASLD [71] (Fig. 3). These phenomena have consistently shown a positive correlation with the severity of the disease.
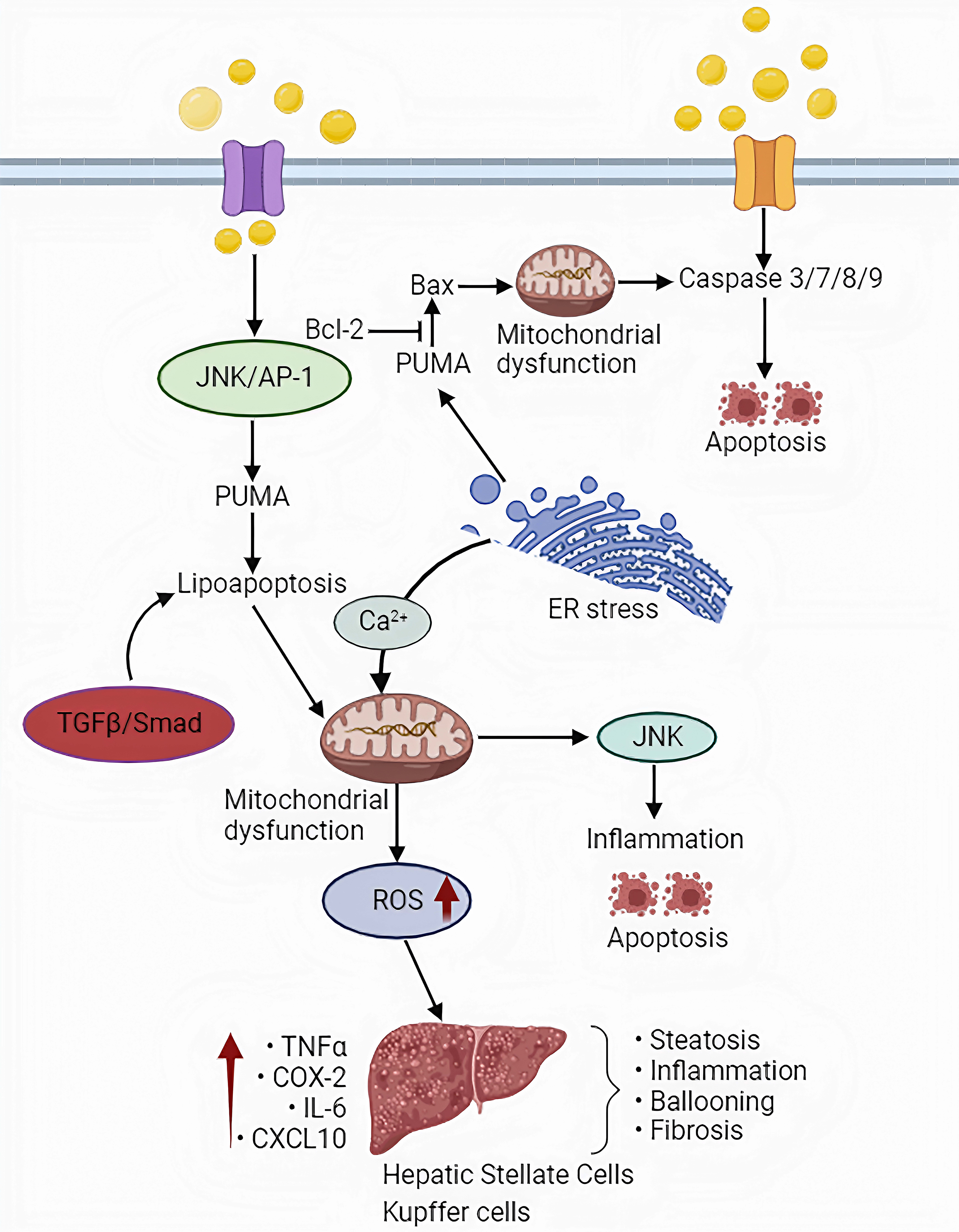
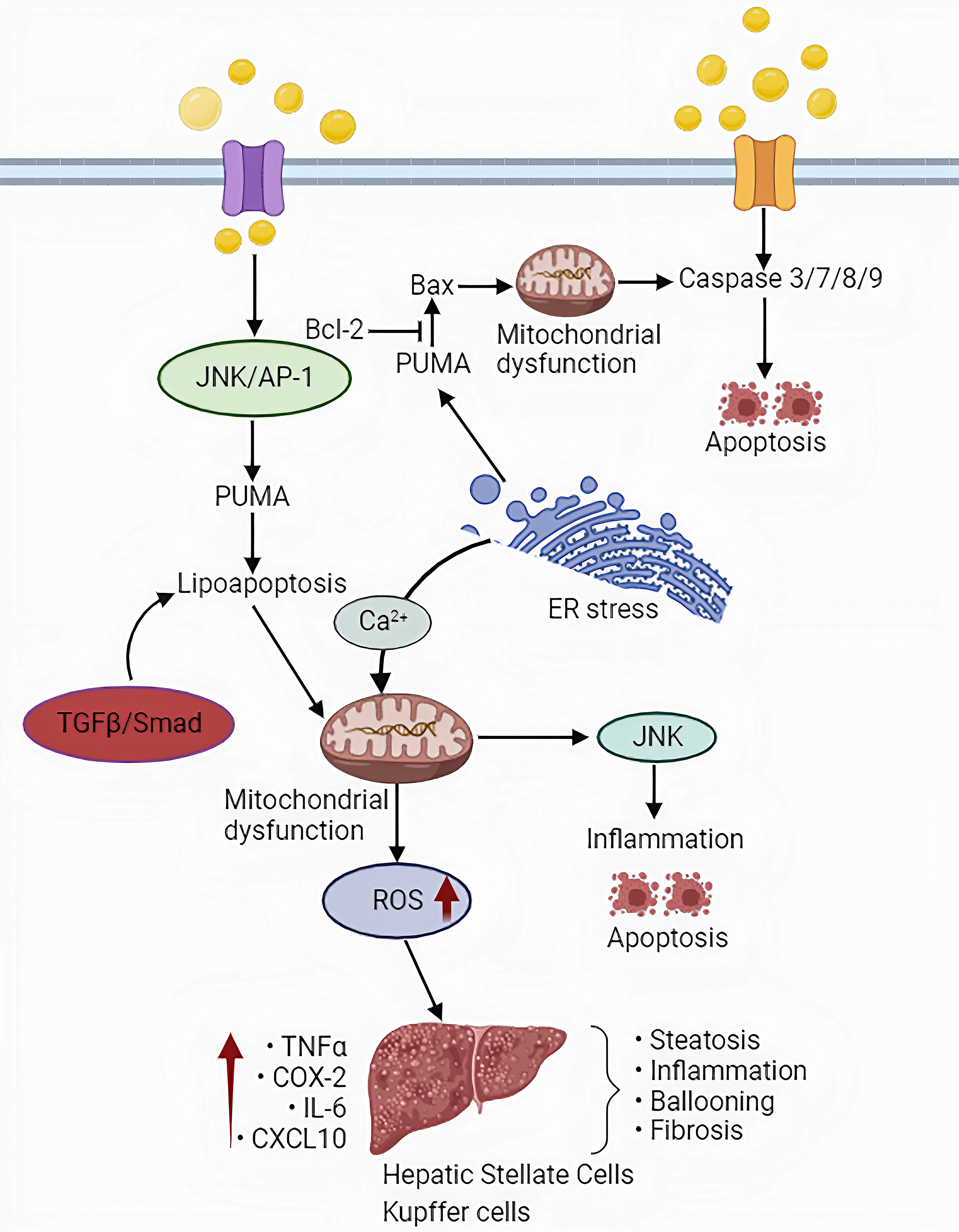 Fig. 3.
Fig. 3.Apoptosis and MASLD. Saturated FFAs exacerbate hepatocyte
lipoapoptosis linked to JNK activation by promoting the activity of proapoptotic
Bcl-2 proteins, notably Bax. Among these proteins, Bax assumes a pivotal role in
initiating the intrinsic apoptotic pathway. Additionally, the
apoptosis-modulator, PUMA, participates in FFA-induced lipoapoptosis in
hepatocytes through the JNK/AP-1 complex. The transcriptional upregulation of
PUMA, coupled with subsequent Bax activation, represents a critical step in the
initiation of apoptosis mediated by saturated FFAs. Consequently, mitochondria
emerge as central regulators in facilitating the elimination of fatty acids and
inducing changes that enable hepatocytes to counteract excessive fat
accumulation. Impaired mitochondrial function is implicated in various
pathogenetic mechanisms of MASH. Abbreviations: JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase;
AP-1, activator protein-1; Bcl-2, B-cell lymphoma-2; Bax, Bcl2-associated X;
PUMA, p53-upregulated modulator of apoptosis; TNF
The pharmacological pan-caspase inhibitor VX-166, an inhibitor of hepatic apoptosis, can decrease liver cell death in mice suffering from MASH. This could ultimately prevent the development of fibrosis [72]. Patients with MASH display increased levels of active caspase 2, active caspase 3, and apoptosis in their livers [71]. In additionally, ballooned hepatocytes downregulate caspase 9, which is a crucial enzyme responsible for initiating mitochondrial apoptosis [73]. The absence of caspase 8 in hepatocytes attenuates the methionine-choline deficient (MCD)-induced increase in apoptosis, resulting in decreased production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, and reduced infiltration in the liver [74]. These observations highlight the crucial role of caspase 8 in MASH pathogenesis. Caspase 2 is considered an initial trigger in the process of lipid-induced cytotoxicity, specifically lipo-apoptosis, contributing significantly to MASH pathogenesis [75]. Its involvement in hepatocyte apoptosis induced by lipids is closely linked to the generation of apoptosis-associated fibrogenic factors. Furthermore, mice with MASH, show reduced levels of free CoA in the liver. This decrease correlated with elevated caspase 2 activity, and was associated with more severe liver cell death, inflammation, and fibrosis [75].
In patients with MASH, liver injury is associated with two key factors:
apoptosis and the activation of NF-
The onset of ER stress-associated c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) initiates apoptosis by modulating the expression and function of pro-apoptotic members from the Bcl-2 family. This includes Bcl-2 homology 3 (BH3) proteins like Bim and the p53-upregulated modulator of apoptosis (PUMA) [78]. PUMA, in turn, facilitates the activation of Bax, leading to permeabilization of the mitochondrial outer membrane and causing these pro-apoptotic factors to relocate to the cytosol [78]. The interaction between phosphorylated JNK and mitochondrial Sab results in compromised respiration, the generation of ROS, prolonged JNK activation, and apoptosis in the presence of lipid-induced lipotoxicity. These ultimately contribute to the pathogenesis of MASH [79] (Fig. 3). Therefore, the JNK signaling pathway plays a crucial role in the apoptosis that occurrs during MASLD and MASH.
Overexpression of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptors 1 and 2 aggravate
hepatic steatosis and fibrosis. At the same time, they promote hepatic induction
of TNF-
Additionally, studies have suggested the preesence of oxidized
phosphatidylcholine within apoptotic hepatocytes in the livers of patients with
steatotic disorders. This implies that oxidized phosphatidylcholine is generated
within hepatocytes that have been subjected to oxidative damage [85]. Moreover,
transforming growth factor
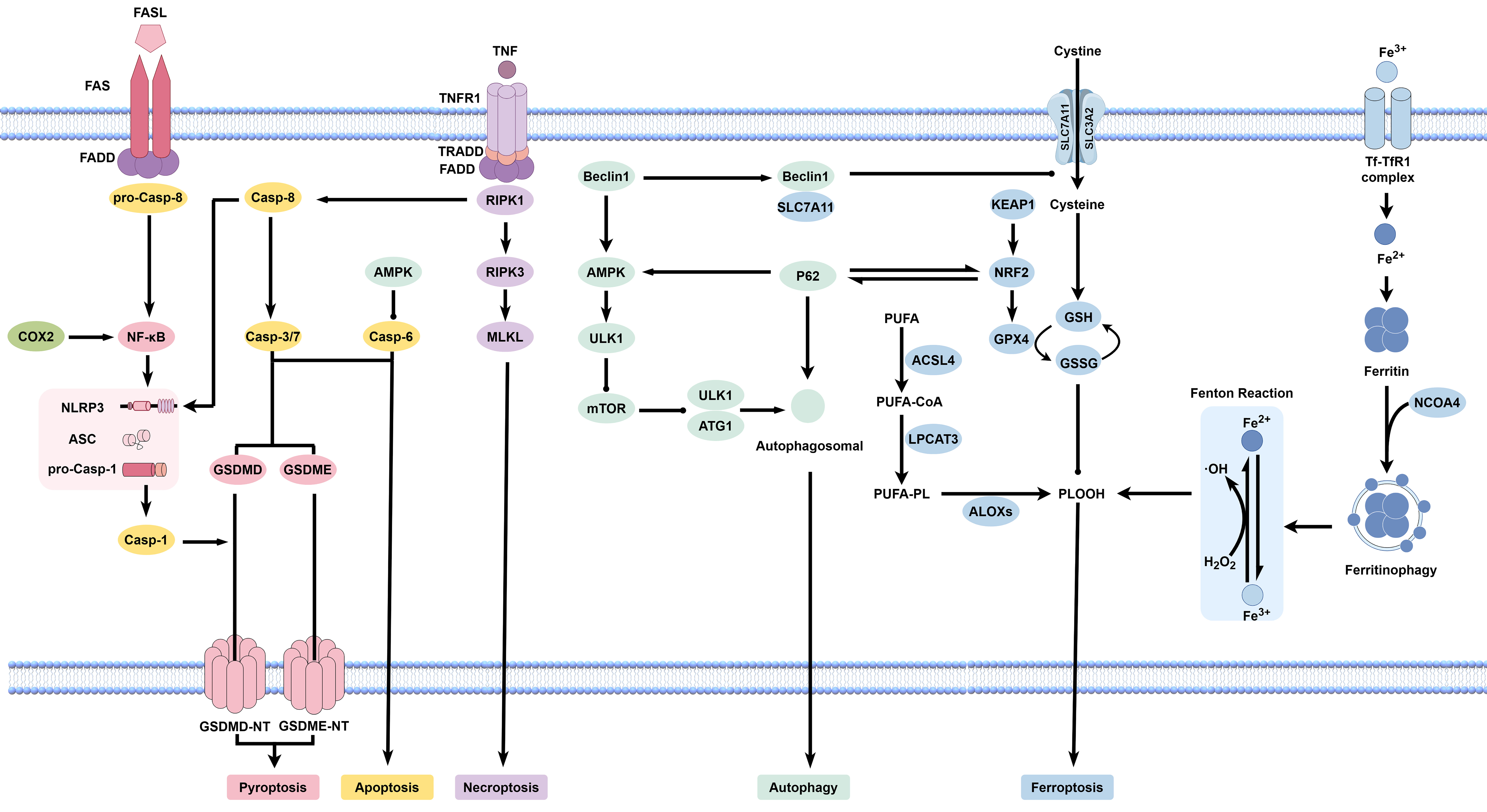
Pyroptosis is a highly inflammatory form of PCD triggered by inflammatory
microsomes. These can detect cell cytosolic contamination or disturbance.
Pyroptosis serves as a crucial component of the innate immune response. It has a
significant role in promoting inflammation by releasing cytokines such as
interleukin 1
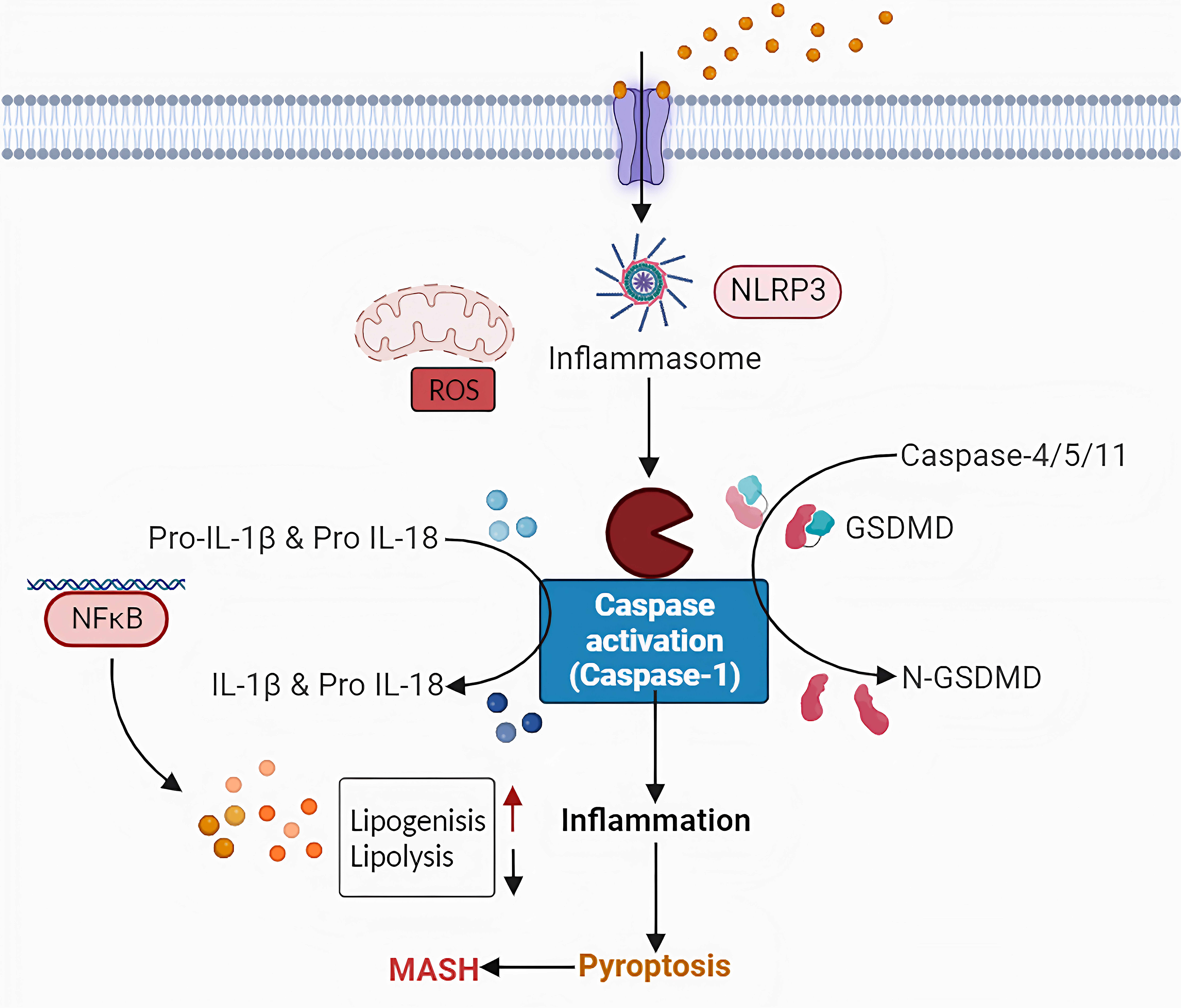
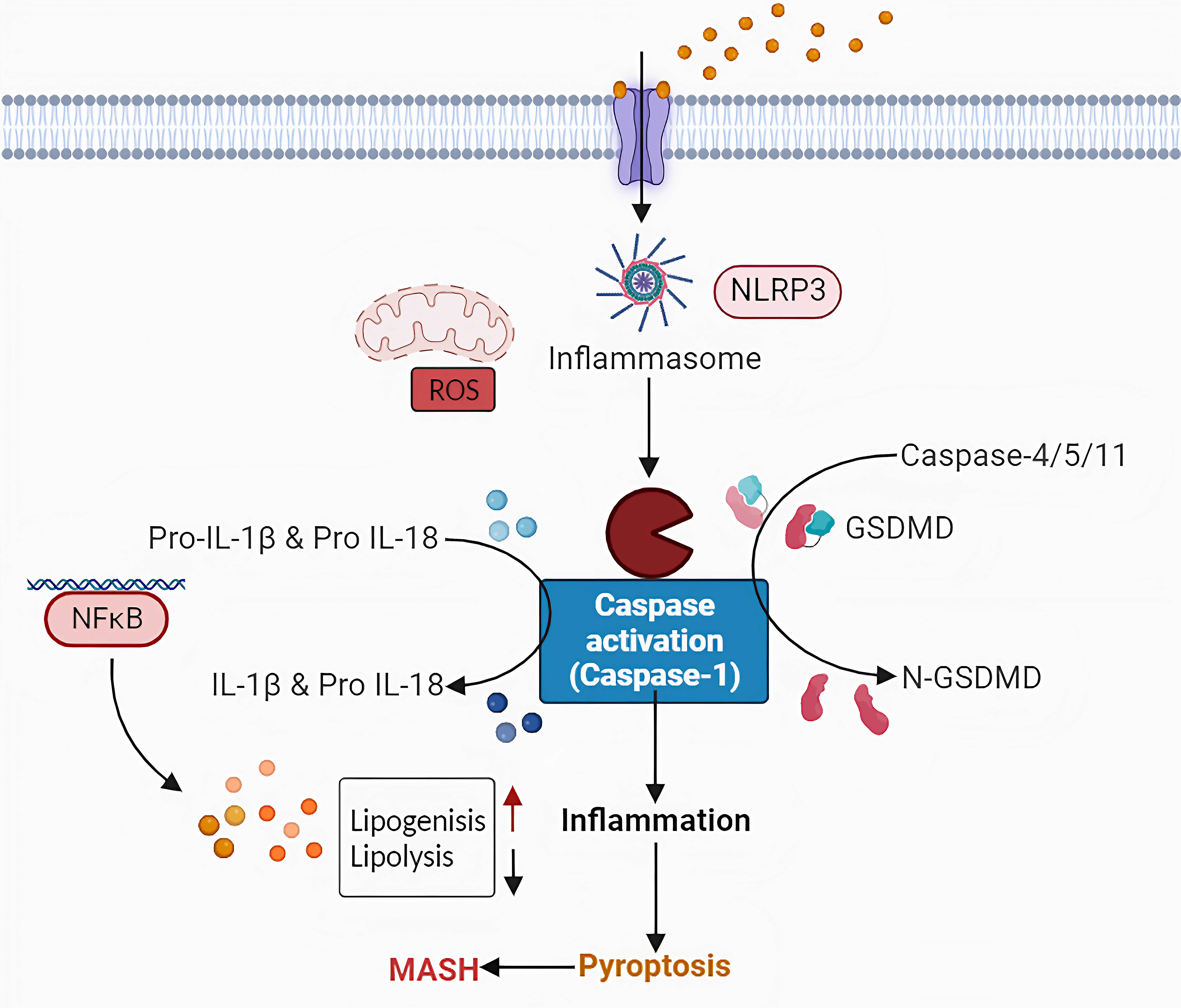 Fig. 4.
Fig. 4.Pyroptosis and MASLD. Cellular damage occurs during the
progression of MASH due to factors such as oxidative stress, endoplasmic
reticulum stress, and inflammatory responses. This can activate the formation of
inflammasomes, with NLRP3 being a common factor. Activated inflammasomes, through
the activation of caspase-1, subsequently induce the cleavage of Gasdermin D and
the triggering of pyroptosis. Pyroptosis leads to cell rupture and the release of
cellular contents, including pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1
In a mouse model fed the MCD diet, inflammasome-mediated dysbiosis was found to
modulate the pathogenesis of MASLD and obesity. Aaggravation of liver injury was
also apparent in interleukin-18 knockout (IL-18 KO) mice. Notably, when
NLRP3 deficiency was selectively confined to the immune system, the severity of
MASH was not significantly different to wild-type animals [90]. MCC950, an NLRP3
inhibitor, attenuated the elevated levels of aspartate transaminase (AST) and
alanine transaminase (ALT) in a mouse model of MASH, leading to reduced
activation of NF-
HSCs are key players in liver fibrosis, which is a common feature of advanced MASLD. PCD in activated HSCs encompasses autophagy, necroptosis, and pyroptosis. These may contribute to the resolution of fibrosis, or exacerbate tissue damage. While an association between autophagy and fibrosis is acknowledged, a correlation with hepatic fibrosis remains inconclusive. A recent study found that inducing autophagy in HSCs can hold promise for alleviating liver fibrosis. This therapeutic effect is attributed to a decrease in the secretion of extracellular vesicles carrying fibrotic components derived from activated HSCs [93]. Furthermore, the significance of mitophagy in the context of liver fibrosis deserves attention, thereby highlighting an additional dimension to the intricate processes involved in this pathological condition. Studies have indicated that the suppression of mitophagy in HSCs significantly activates these cells, thereby worsening hepatic fibrosis [94]. Conversely, another study reported that enhancement of autophagy in HSCs accelerates their activation, thereby promoting liver fibrosis [95]. Similarly, the formation of inflammasomes during pyroptosis can lead to liver injury and fibrosis, while inhibition of their activity can potentially reduce hepatic fibrosis caused by MASLD [96]. The activation of HSCs by inflammasomes released during hepatocyte pyroptosis constitutes a pivotal mechanism in liver fibrosis. Pyroptosis-induced dead hepatic cells can release high mobility group-1 (HMGB1), which serves as a damage-associated molecular pattern (DAMP), thereby promoting the activation of HSCs. Inhibiting pyroptosis typically reduce inflammation and liver fibrosis [97].
Necroptosis is a variant of programmed lytic cell death and has parallels with necrosis. Both modalities share similar characteristics, including enlarged cell volume, organelle swelling, and compromised membrane integrity. These lead to the release of DAMPs, which in turn induce inflammatory responses and consequential secondary injury [98]. In the context of MASH, necroptosis serves to intensify inflammation. DAMPs from necroptotic hepatocytes play a pivotal role in tissue inflammation and in triggering the activation of HSCs. However, the role of necroptosis in HSCs appears to be different to that in hepatocytes. Previous research has shown that induced necroptosis in HSCs substantially reduces liver fibrosis [99]. In summary, the modulation of PCD in HSCs may be a potential therapeutic approach to regulate liver fibrogenesis in MASLD.
KCs are resident macrophages in the liver responsible for identifying tissue damage and initiating an inflammatory response. KCs are closely associated with MASLD. The inflammatory response triggered by fat accumulation in MASLD may activate KCs [69], causing them to release inflammatory factors and thus further exacerbating liver inflammation and damage. KCs also play a role in clearing free radicals and responding to oxidative stress, thereby maintaining the hepatic redox balance [100]. The increased oxidative stress in MASLD can challenge the antioxidant function of KCs. Pyroptosis appears to be more prominent in macrophages during liver injury induced by MASLD/MASH, and it also contributes to the progression of liver fibrosis. The DAMP SA1008 is elevated in fibrotic liver tissue and has the capacity to mediate pyroptosis of KCs [101]. SA1008, released from deceased macrophages, activates HSCs, thereby promoting liver fibrosis. The pyroptosis of KCs effectively alleviates liver fibrosis by suppressing the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase (NOX2)/NLRP3 pathway [102].
Autophagy within KCs is a robust protective mechanism for liver homeostasis
during the initiation and progression of hepatic fibrosis. The autophagic process
in KCs has a safeguard effect on hepatocytes during instances of hepatic injury.
This protective role is manifested through the suppression of hepatic
inflammation and fibrogenesis, as shown by the inhibition of ROS-induced
IL-1
There are clear parallels between apoptosis and necroptosis in the context of liver injury, particularly in MASH. Specifically, the upregulation of activating transcription factor 3 in MASH induces increased expression of receptor-interacting serine-threonine kinase 3 (RIPK3) [105]. As a consequence, this molecular change prompts a transition in the predominant mode of cell death within hepatocytes, shifting from apoptosis to necroptosis and thereby aggravating hepatic steatosis. In contrast to pyroptosis, necroptosis represents a distinct form of PCD characterized by distinctive triggering factors and morphological features. Both modalities exhibit shared features in terms of membrane rupture and the initiation of inflammation within the context of MASLD/MASH [10]. Additionally, caspase-10 intricately regulates both pyroptosis and necroptosis by cleaving RIPK1, thereby hindering the assembly of the NLRP3 inflammasome in hepatic macrophages [106]. This regulatory mechanism markedly reduces the incidence of necroptosis and pyroptosis in macrophages, leading to a concomitant reduction in the release of inflammatory cytokines (Fig. 5). As a result, this action attenuates cirrhosis and suppresses the activation of HSCs. The three distinct modes of cellular death, namely apoptosis, necroptosis, and pyroptosis, collectively constitute the pro-inflammatory form of PCD known as PANoptosis. Caspase-6 and caspase-8 are the two most important regulators of PANoptosis (Fig. 5). This phenomenon has been implicated in the context of liver fibrosis, whereby RIPK1 is as a key driver of PANoptosis within KCs. NASH subsequently intensifies and is characterized by steatosis, inflammation, and fibrosis [107]. Experimental evidence indicates that inhibition of PANoptosis in hepatocytes is effective at ameliorating liver injury and fibrosis induced by fatty liver disease associated with metabolic dysfunctions [107].
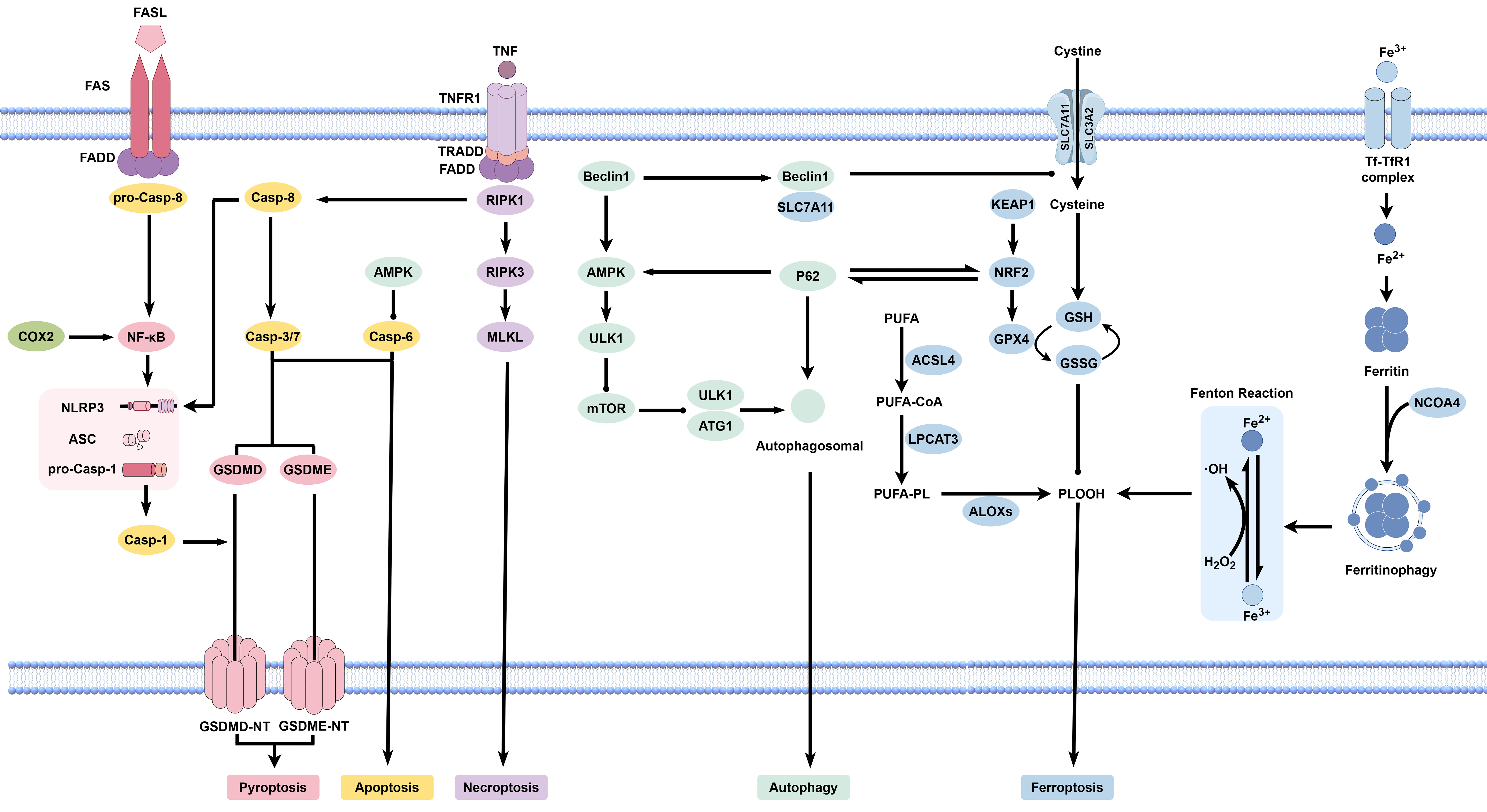 Fig. 5.
Fig. 5.Interplay among diverse forms of PCD gives rise to a complex regulatory network influencing the fate of cells. Key nodes in this intricate interaction, crucial for the survival or demise of macrophages, include AMPK, mTOR, Caspase-8, RIPK3, Bcl-2, and p62. These components play pivotal roles in the interconnection of pyroptosis, apoptosis, necroptosis, autophagy, and ferroptosis within the cell death network. Abbreviations: ASC, apoptosis-associated speck-like protein; NCOA4, nuclear receptor coactivator 4; NLRP3, NOD-like receptor thermal protein domain associated protein 3; COX-2, cyclooxygenase-2; TFR1, transferrin receptor 1; NRF2, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2. By Figdraw.
A distinctive feature of ferroptosis involves the increased levels of
intracellular ROS. This shared characteristic extends across diverse forms of
PCD, encompassing apoptosis, necroptosis, and pyroptosis. It implies the presence
of interactive regulatory relationships between ferroptosis and other pathways of
PCD. A previous study reported that administration of a GPX4 inhibitor can induce
ferroptosis and concurrently activate apoptosis by upregulating early growth
response-1 (EGR1) expression. Ferroptosis subsequently initiates necroptosis
through the generation of ROS. The therapeutic efficacy of ferroptosis inhibition
in the context of MASLD is demonstrated by improvement of apoptosis, necroptosis,
and pyroptosis [108, 109]. Overexpression of yes-associated protein (YAP)
facilitates liver fibrosis, ferroptosis, and necroptosis in MASLD/MASH and can be
mitigated by the administration of exosomes derived from huMSC cells [109]. These
exosomes have the capacity to secrete Beclin-1, an autophagy regulator, by
mediating ferritinophagy, thereby diminishing the system Xc
The process of autophagy in hepatocytes initiates apoptosis, subsequently triggering the transdifferentiation of HSCs into myofibroblasts. The facilitation of mitophagy enhances apoptosis in HSCs, thereby mitigating liver fibrosis [95]. Furthermore, the induction of necroptosis is also contingent upon autophagic processes. In the presence of ATG5, necroptosis has the capability to eliminate activated HSCs, thereby mitigating liver fibrosis [110]. While the complex interplay between autophagy and pyroptosis in the context of liver fibrosis remains incompletely elucidated, valuable insights into their interaction can be gleaned from observations in other liver diseases. For example, increasing the level of autophagy in hepatocytes promotes pyroptosis of in an arsenic-induced MASLD animal model. Conversely, the suppression of mitophagy has been shown to alleviate the pyroptosis of hepatocytes in FFA-induced MASH [111]. Given the associations between various types of PCD and MASLD mentioned above, we have compiled the therapeutic applications of different types of PCD inducers for MASLD, as illustrated in Table 1 (Ref. [10, 107, 112, 113, 114, 115, 116, 117, 118, 119, 120, 121, 122, 123, 124, 125]).
| Drugs | Effects on the PCD | Benefits of MASLD | Refs |
| Ferrostatin-1 | A ferroptosis inhibitor and prevents lipid ROS accumulation and inhibits lipid peroxidation | Ameliorate MASLD/MASH and fibrosis | [112] |
| Liproxstatin-1 | As a ferroptosis inhibitor, serves as a radical-trapping antioxidant to impede the process of lipid peroxidation | Alleviates MASLD | [113] |
| Deferoxamine | As an iron chelator, has affinity with Fe |
Ameliorate MASLD/MASH and fibrosis | [114] |
| Deferasirox | As an iron chelator, suppresses oxidative stress and HSC activation | Ameliorate MASLD/MASH and fibrosis | [115] |
| Deferiprone | As an iron chelator, attenuates hepatic inflammation | Alleviates MASLD | [107] |
| Necrostatin-1 | As a necroptosis inhibitors, attenuates hepatic inflammation | Alleviates liver injury and ischemia reperfusion injury in MASLD | [116] |
| Necrosulfonamide | As a necroptosis inhibitors, decreases hepatic de novo fat synthesis and chemokine ligand expressions | Has protective effects in MASH | [117] |
| Emricasan | As an apoptosis inhibitor, decreases ALT and biomarkers | Has protective effects and ameliorate fibrosis in MASH | [118] |
| GS-9450 | As an apoptosis inhibitor, decreases ALT | Has protective effects in MASH | [119] |
| Disulfiram | As a pyroptosis inhibitor, modulates the gut microbiota and bile acid metabolism | Ameliorates MASH | [120] |
| PX-478 | As a pyroptosis inhibitor, reduces weight and abdominal adipocyte hypertrophy | May ameliorate fatty liver disease | [121] |
| Rapamycin | As an autophagy activator, attenuates steatosis, inflammation, and increases fatty acid oxidation | Ameliorates MASH and fibrosis | [122] |
| Trehalose | As an autophagy activator, increases transcription of genes, regulates mitochondrial energy metabolism | Ameliorates MASLD and inflammation | [123] |
| Metformin | As an autophagy activator, alleviates hepatic steatosis, protects of hepatocyte necroptosis, and induces lipophagy | Ameliorates MASLD and fibrosis | [10] |
| Spermidine | As an autophagy activator, enhances mitochondrial activity and fatty acid |
Ameliorates MASH | [124] |
| Resveratrol | As an autophagy activator, improves glucose metabolism, lipid profile, and steatosis | Ameliorates MASLD/MASH and liver fibrosis | [125] |
PCD, Programmed cell death; MASLD, Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease; MASH, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis; ALT, alanine transaminase.
The concept of PCD has brought about a paradigm shift in our comprehension of cell death, while stimulating an entire realm of research in MASLD. Accumulating evidence indicates that PCD plays a significant role in metabolic liver disease and holds promise as a therapeutic target for MASLD/MASH. In the context of MASLD, PCD is a major driving force for fat accumulation, liver inflammation, liver injury and fibrosis. Nevertheless, several crucial questions still need to be addressed through experimental research prior to clinical applications. Further research is needed to fully elucidate the molecular conditions in which the various PCD mechanisms regulate cell death. Understanding the precise signaling pathways that govern PCD in MASLD should enable researchers to target therapeutics to specific molecules, thereby mitigating subsequent liver injury, inflammation, and fibrosis. More importantly, various PCD modes coexist in MASLD, and hepatocytes are able to transition between different death subroutines. Future investigations should aim to understand the substantial crosstalk among the various PCD modes and signaling cascades in MASLD. A better understanding of the intricacies and connections involved in the pathogenesis of MASLD will be instrumental for the development of targetedt therapeutics.
SSZ and XZY designed the study. SSZ, YG and XZY collected and analyzed the literatures. SSZ and XZY wrote the manuscript. YG and XZY discussed and critically revised the manuscript. All authors contributed to editorial changes in the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. All authors have participated sufficiently in the work to take public responsibility for appropriate portions of the content and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to its accuracy or integrity.
Not applicable.
The main figures were created with the assistance of the tools BioRender and/or Figdraw.
This work was supported by the Science and Technology Development Plan of Jilin Province (20210204029YY and YDZJ202201ZYTS151).
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Publisher’s Note: IMR Press stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.