1 Central Laboratory, The Tenth Affiliated Hospital of Southern Medical University, 523059 Dongguan, Guangdong, China
2 Dongguan Key Laboratory of Chronic Inflammatory Diseases, The First Dongguan Affiliated Hospital, Guangdong Medical University, 523808 Dongguan, Guangdong, China
3 Dongguan Key Laboratory of Stem Cell and Regenerative Tissue Engineering, Guangdong Medical University, 523808 Dongguan, Guangdong, China
†These authors contributed equally.
Abstract
Male infertility, age-related changes, and tumors have been increasingly studied in the field of male reproductive health due to the emergence of environmental stressors, declining fertility rates, and aging populations. Numerous studies have demonstrated that the ERK1/2 signaling pathway plays a significant role in male reproduction. The ERK1/2 pathway is associated with several signaling pathways and has a complex interplay that influences the spermatogenic microenvironment, sperm viability, gonadal axis regulation, as well as resistance to testicular aging and tumors. Moreover, the ERK1/2 pathway directly or indirectly regulates testicular somatic cells, which are crucial for maintaining spermatogenesis and microenvironment regulation. Given the critical role of the ERK1/2 signaling pathway in male reproductive health, comprehensive exploration of its multifaceted effects on male reproduction and underlying mechanisms is necessary. This study aims to provide a solid foundation for in-depth research in the field of male reproduction and further enhance the reproductive health of males.
Graphical Abstract
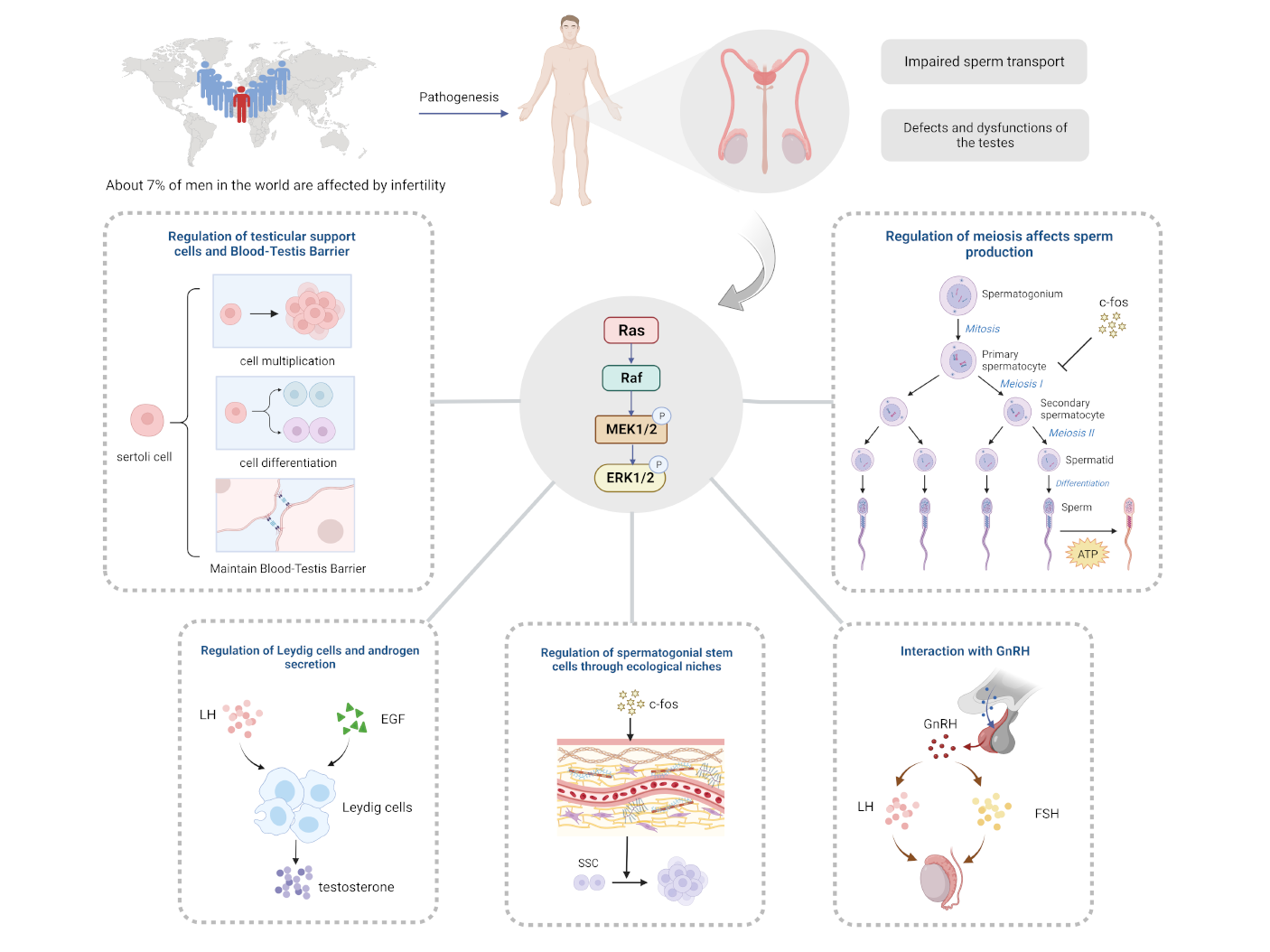
Keywords
- ERK1/2 signaling pathway
- male reproduction
- mechanism of action
- aging
- tumor
Presently, the world is experiencing a decrease in population growth, and in addition to the decline in fertility intentions, infertility remains a prominent obstacle preventing individuals from having children. In 2018, an epidemiological review reported [1] that over 186 million people worldwide suffer from infertility, with the highest prevalence found in developing countries. While male factor infertility accounts for 40% to 50% of all cases, approximately 7% of men worldwide are affected [2]. Among the most common causes of male infertility are defective and dysfunctional testes, followed by impaired sperm delivery. Furthermore, industrial development has increased the risk of endocrine disruptors and environmental toxins, which pose a significant threat to the structure and function of male reproduction. Unfortunately, current research on infertility primarily pertains to women, resulting in limited methods and effects for treating and preventing male infertility. Current mainstream therapeutic drugs primarily target the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis, such as gonadotropins and aromatase inhibitors. However, studies on their efficacy remain relatively sparse, which limits their conclusive effectiveness [3]. As such, it is clear that there is substantial research space in the field of male reproduction. Recent studies have explored the growing significance of the extracellular regulated protein kinase (ERK1/2) signaling pathway in male reproduction, which has shown non-negligible potential in addressing male sterility, aging, and tumors.
ERK1/2 belongs to a crucial member of the serine-threonine protein kinase (MAPK) family. ERK1 and ERK2 exhibit kinase activity, and when activated, phosphorylate a series of proteins within the cell [4]. The ERK1/2 signaling pathway specifically refers to the RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK cascade reaction pathway within the MAPK signaling pathway, which has become the most extensively studied cell transduction pathway in the ERK family. In this pathway, the ERK1/2 signaling pathway plays a critical role in cell proliferation, survival, growth, metabolism, migration and differentiation, among other biological and cellular processes. It also plays an important role in anticancer drug targets [5]. A growing body of evidence suggests that the ERK1/2 signaling pathway is ubiquitously distributed and activated at multiple sites throughout the male reproductive system and plays an important role in various stages of male reproduction, including development, maturation, and aging. As such, the ERK1/2 pathway is poised to play an important regulatory role in the regulation of male germ cells.
In this review, we aim to investigate the impact of ERK1/2 on male reproductive function, explore its basic mechanism of action, and finally summarize the potential applications of ERK1/2 in male reproductive aging and tumors. This will provide a solid foundation for subsequent research in this field, thus contributing to the theoretical basis and reference value of clinical treatments for male infertility disorders, the development of reproductive tumors, and the field of geriatric reproductive medicine.
ERK1 and ERK2 share many sequences and functional similarities and are therefore often discussed and studied as “ERK1/2”. Organisms require the presence of both alleles for survival, as lack of either will lead to poor embryonic development [6]. The specific functions of each kinase and their relationship remain unclear. Research suggests that their expression varies in response to different stimuli, shedding light on some phenomena. For instance, exposing mouse testicular germ cells to varying doses of molybdenum resulted in a relatively increased expression of ERK1 with increasing dosage, suggesting its involvement in cell proliferation and differentiation. Conversely, ERK2 expression demonstrated an opposite trend, indicating its role in molybdenum-induced cellular damage [7].
In addition to the effects of the signaling pathway itself, the ERK1/2 signaling pathway is closely associated with other signaling pathways in the family, such as the JNK pathway and the P38 MAPK pathway. Some studies have shown that spermatozoa in cryopreservation lead to the activation of the phosphorylation of p53 protein through the p38 MAPK signaling pathway, decreasing the phosphorylation levels of ERK1/2 and JNK, and thus affecting spermatozoa quality and apoptosis. This suggests that p38 MAPK may be a common action pathway of ERK1/2 and JNK [8]. Resveratrol administration to rats can simultaneously inhibit the phosphorylation levels of ERK1/2 and JNK, thus preventing cisplatin-induced testicular damage and reproductive dysfunction [9]. In addition, the co-activation of ERK1/2 and JNK pathways may have the effect of decreasing the activity of testicular supportive cells. This suggests that there is a coordinated relationship between ERK1/2 and JNK in terms of the male reproductive system [10, 11]. Therefore, their synergistic or antagonistic effects often serve as important mechanisms in the pathogenesis of many male diseases. In addition, crosstalk between ERK1/2 signaling pathway and other signaling pathways also collectively explains the mechanisms of cell proliferation, differentiation, autophagy and apoptosis under different circumstances, commonly the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. AKT is an important downstream molecule of PI3K, and the phosphorylation levels with ERK can be co-regulated by certain substances. For example, decreasing the activity of sphingomyelin synthase 2 (SMS2), which is localized in the male reproductive organs, plays a key role in inhibiting and increasing the phosphorylation levels of AKT and ERK, which can affect the motility and activity of male spermatozoa or even lead to their apoptosis [12]. mTOR is a downstream substrate of PI3K/AKT and, in testosterone-mediated cell proliferation in L6 cells, it involves mechanism of association between ERK and mTOR signaling, whereas the AKT pathway does not play a role here [13]. Another study showed that the ERK1/2 pathway in testicular tissues would be activated by BPA exposure, along with inhibition of the AKT/mTOR pathway, leading to a decrease in germ cell mass in adult male rats [14]. In addition to this, co-up-regulation of ERK1/2 and PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling plays an important role in testicular injury and apoptosis in rheumatoid arthritis patients [15]. Notably, although the ERK1/2 signaling pathway is closely associated with the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway, ERK1/2 and the mTOR signaling pathway can have a mutually non-interfering operational relationship in regulating cellular autophagy [16]. From the above reports, it can be seen that the relationship between the ERK1/2 pathway and the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway is complex, and its regulation of cells shows diversity, which may have greater potential research value.
Several reports have demonstrated a close association between the ERK1/2 signaling pathway and glycogen synthase kinase 3-
While the ERK1/2 signaling pathway plays a role in regulating cell proliferation and apoptosis, it also has complex and ingenious connections with other signaling pathways. Due to the abundance of the ERK1/2 signaling pathway and the wide distribution of receptors, it has a significant impact on the mechanism of action of male germ cells, and it has also made people realize the great clinical application prospect of the ERK1/2 signaling pathway (Fig. 1). At present, more and more researchers have carried out in-depth exploration and research on the ERK1/2 signaling pathway and its related pathways and male germ cells, and a number of related specific inhibitors have already been put into use, taking a solid step toward the treatment of male infertility, anti-aging, anti-tumor and other major directions.
 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.ERK signaling pathway cross-linking. Stimulatory factors such as cytokines activate intracellular receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) by binding to the corresponding receptors and thus activating the RAS pathway in response to the guanine nucleotide exchange factor SOS. Activated RAS binds mitogen-activated protein kinase, and activated MEK leads to ERK phosphorylation, which in turn activates the ERK pathway, allowing the activated ERK to enter the nucleus. JNK mainly consists of JNK1/2/3, and this signaling pathway is activated by MAPKKK, which sequentially activates MEK4/7, which in turn phosphorylate and activates JNK. The p38 MAPK kinase is mainly activated by ERK3/6 phosphorylation. These three pathways regulate the cell cycle and promote cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis by affecting multiple substrates and regulating related gene expression. In addition, ERK1/2 is closely associated with the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway as well as GSK3
The testis is the most important reproductive organ in the male reproduction. The development and function of the testis depends on the development of testicular somatic cells (Sertoli cells and Leydig cells, etc.) and germ cells (spermatogonia, spermatocytes and sperms, etc.). This is because the number of Sertoli cells determines the limit of sperm production [25]; Leydig cells determine androgens for male development, and the development of germ cells is essential for the production of spermatozoa, while sperm capacitation and the acrosome reaction are closely related to successful fertilization. Notably, testicular somatic cells can develop normally and produce testosterone even in the absence of germ cells. In contrast, the development of spermatogenic cells is entirely dependent on somatic cells [26]. For example, Sertoli cells play their role in maintaining the spermatogonial stem cells (SSC) niche, spermatogonial cell population, meiosis, spermatogenesis, sperm fertilization, and release of mature spermatozoa [27]. In recent years, an increasing number of studies have focused on the role of ERK1/2 signaling in testis development and its role in the fertilization process. To illustrate the association between ERK1/2 signaling and testicular development and the fertilization process and the possibility of further mechanistic studies, we have summarized the current relevant literature in Table 1 (Ref. [28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51, 52, 53, 54, 55]).
| Involved substance | Change in ERK1/2 | Result | Effects of ERK1/2 on different cells of testis | ||
| Germ cells | Spermatogonial stem cells (SSC) | GDNF, GFR | Increases ERK1/2 phosphorylation | Promote SSC proliferation | The binding of GDNF and GFR |
| GDNF | Activate the MEK/ERK pathway | Induce SSC migration | High levels of GDNF are expressed in the testis of sexually mature mice, perhaps through activation of the MEK/ERK signaling pathway to induce SSC migration [29]. | ||
| FGF, GDNF, GFR | Activate the MEK/ERK pathway | Promote SSC self-renewal | FGF cooperates with GDNF to promote SSC self-renewal by inducing GFR | ||
| FGF5, CyclinA2, CyclinE1 | Activate ERK1/2 signaling pathway | Promote SSC proliferation | FGF5 activates ERK and AKT signaling pathways to promote mouse SSC proliferation through CyclinA2 and CyclinE1 expression [31]. | ||
| FGF, GDNF, Retinoic acid, FOXO1 | Activate ERK1/2 signaling pathway | Maintain undifferentiated SSC | FGF may activate ERK1/2 signaling in cooperation with GDNF and Retinoic acid, maintaining undifferentiated SSC through the downstream expression of FOXO1 [32]. | ||
| Spermatocytes | – | Activate ERK1/2 signaling pathway | Promote G2/M transition | The activity of ERK1 is specifically stimulated during G2/M cellular turnover in murine spermatocytes. ERK1/2 is all activated at the G2/M transition [33]. | |
| Shp 2, Sycp 3, Dmc 1 | Increases ERK1/2 phosphorylation | Block meiosis | The deletion of Shp 2 inhibits the phosphorylation of AKT and ERK, thereby inhibiting Sycp 3 and Dmc 1 [34]. | ||
| L-GILZ | Potentiate ERK1/2 signaling | Accelerate spermatogonia proliferation | Depletion of the L-GILZ gene potentiates ERK1/2 signaling and accelerates the proliferation of undifferentiated spermatogonia [35]. | ||
| Sperm | Progesterone | Increases ERK1/2 phosphorylation | Promote acrosome reactions | Progesterone concentrations promote the onset of acrosome reactions and involve increased ERK1/2 phosphorylation [52]. | |
| Superoxide anion radicals | Activate ERK1/2 signaling pathway | Promote sperm capacitation | Superoxide anion radicals activate the ERK1/2 signaling pathway, promoting sperm capacitation via tyrosine phosphorylation [53]. | ||
| Hsp 90 | Activate ERK1/2 signaling pathway | Promote sperm capacitation | Sperm capacitation involves Hsp 90 via ERK1/2 and p38MAPK pathways [54]. | ||
| Sperm binding to zona pellucida | Activate EGFR/ERK1/2 phosphorylation | Promote sperm capacitation | Sperm binding to zona pellucida may activate EGFR-ERK1/2 phosphorylation, further phosphorylation of EGFR in a positive feedback manner, and accelerated completion of the acrosome reaction [55]. | ||
| Testicular somatic cells | Leydig cells (LCs) | luteinizing hormone (LH), cAMP | Increases ERK1/2 phosphorylation | Promote androgens secretion | LH can stimulate Leydig cells to produce cAMP, enhance the phosphorylation of ERK1/2, and then promote the secretion of androgens [36, 37]. |
| GSK-3 | Decrease p-ERK1/2 levels | Inhibit androgens secretion | A decrease in p-ERK1/2 levels leads to a decrease of phosphorylation levels of GSK-3 | ||
| The diabetic rats | The ratio of p-ERK1/2 to total ERK1/2 decreases | Inhibition of the function of LCs | The ratio of phosphorylated ERK1/2 to total ERK1/2 in the total testis content of diabetic rats tended to decrease [38]. | ||
| Propofol, Cyp11a1, Cyp17a1 | Block ERK1/2 phosphorylation | Inhibit androgens secretion | The anesthetic propofol may down-regulate the expression of key steroidogenic enzymes (Cyp11a1 and Cyp17a1) in rat Leydig cells by blocking the phosphorylation of ERK1/2 [39]. | ||
| Nano-Tio2 | Increase ERK1/2/PKA/PKC signaling pathway | Inhibit testosterone production | The inhibition of testosterone secretion in Leydig cells by nano-Tio2 may be related to ERK1/2/PKA/PKC signaling pathway dysfunction [40]. | ||
| Sertoli cell (SCs) | Estrogen, GPR30, ER | Activate GPR30/EGFR/ERK1/2 signaling pathway | Promote SCs proliferation | Estrogen can promote the proliferation of Sertoli TM4 cells by up-regulating GPR30 and ER | |
| Relaxin, CAMP | Activate ERK1/2 signaling pathway | Promote SCs proliferation | Relaxin secreted by SCs during SCs immaturity inhibits CAMP expression, activate ERK1/2 signaling pathway to promote SCs proliferation [42]. | ||
| FSH, CAMP, CREB | Inhibit ERK1/2 signaling pathway | Inhibit SCs proliferation | After SCs mature, relaxin release is reduced, allowing FSH to activate the CAMP/CREB pathway to stimulate cell differentiation, inhibit the ERK1/2 pathway, and inhibit SC proliferation [42]. | ||
| Melatonin, GDNF | Increase ERK1/2 phosphorylation | Promote SCs proliferation | Melatonin and GDNF increases ERK1/2 phosphorylation and induces SCs proliferation [43, 44]. | ||
| Bta-miR-34b, MAPK1 | Activate ERK1/2 signaling pathway | Promote SCs proliferation | Bta-miR-34b, by targeting over-expression of MAPK1, in the ERK1/2 signaling pathway that mediates cell proliferation and testis development [45]. | ||
| Testosterone, Dehydroepian drosterone | Activate ERK1/2 signaling pathway | Promote the formation of BTB tight junctions | Testosterone activates ERK1/2-CREB-ATF-1, promoting claudin-1 and claudin-5 formation [47]. Dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate activates the ERK1/2 cascade response via GPCR, stimulating the expression of claudin-3 and -5 [48]. | ||
| Non-receptor tyrosine phosphatase SHP2 | Increases ERK1/2 phosphorylation | Maintain BTB integrity | Non-receptor tyrosine phosphatase SHP2 may phosphorylate ERK1/2 through SRC kinase, regulating actin cytoskeleton and maintaining BTB integrity [46]. | ||
| CD95-containing germ cells | Activate ERK1/2 signaling pathway | Induce apoptosis of CD95-containing germ cells | CD95L-expressing SC induces apoptosis of CD95-containing germ cells, a process that requires the involvement of ERK1/2 activation [49]. | ||
| Inflammatory factor IL-1b | Activate ERK1/2 signaling pathway | Promote lactate secretion by SC | Inflammatory factor IL-1b stimulation or heat stress activates ERK1/2, which increases lactate dehydrogenase and enhances heat shock protein 70 expression induced by heat stress, respectively, promoting lactate secretion by SC and protecting germ cells [50, 51]. | ||
The term “niche” describes the intricate short- and long-term stimulus interactions between stem cells, their differentiated daughter cells, neighboring cells, and the extracellular matrix that together form the microenvironment that controls stem cell behavior. The composition of the SSC niche includes Leydig cells, Sertoli cells, peritubular cells, extracellular matrix, and blood vessels [56]. In this microenvironment, its composition secreted chemicals and activated cell signaling pathways jointly regulate cytological behaviors such as SSC proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis. Among them, Sertoli cells are the most important structure of the niche, and the glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) produced by Sertoli cells plays a key role in determining the behavior and outcome of SSC. Meng et al. [57] discovered in 2000 that GDNF plays a crucial role in the regulation of self-renewal in SSC. He et al. [28] found that GDNF and GFR
Further study of the SSC niche has identified potential regulators in the form of CSF1, NODAL, WNT3A and FGF that serve to co-regulate SSC outcomes [30]. Among them, more and more studies have begun to focus on the relevant mechanisms of FGF in regulating SSC. Studies have revealed that FGF cooperates with GDNF to promote SSC self-renewal by inducing GFR
 Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.The ERK1/2 signaling pathway regulates the spermatogenic microenvironment and spermatogenic cells. (a) FGF, as a regulator of the SSC niche, synergizes with GDNF to regulate relevant mechanisms in the SSC. In particular, Sertoli cells supply GDNF and FGF2, myoid cells provide GDNF, fibroblasts produce FGF5, and vascular-generated GDNF and FGF2 signaling also occurs in the differentiation of germ cells. (b) In SSC, transcription of c-fos, upregulation of gene Etv 5 and Bcl6b expression, upregulation of FOXO1, and enhanced expression of CyclinA2 and CyclinE1 could all promote the proliferation and self-renewal of SSC. GFR
In conclusion, ERK1/2 signaling pathway plays an important role in regulating the particular microenvironment of SSC niche. In addition to FGF and GDNF, there are other niche regulators that deserve attention and intensive investigation. Therefore, revealing their association with the ERK1/2 signaling pathway will help to further understand the mechanism of the biological behavior of SSC, and then lay a solid theoretical foundation for the treatment of infertility, the development of male contraceptives, and the elucidation of the etiology of spermatogonic-related tumors.
Normal meiosis is an important step in the production of healthy sperm, and abnormal meiosis is a major cause of male infertility. Since the end of the 20th century, several studies have suggested that ERK1 is specifically activated during the G2/M transition in mouse spermatocytes and is required for chromosome condensation associated with meiotic metaphase progression. Shortly thereafter, the results of Inselman A et al. [33] further showed that ERK1/2 are all activated at the G2/M transition and that this result is independent of MEK activation. This suggests that the activation of ERK1/2 is somehow related to meiosis in spermatocytes. Recent studies have found that the ERK1/2 signaling pathway may play a certain role in the process of meiosis by regulating the genes involved in meiosis. For example, loss of SHP2, an important regulator of ERK1/2 signaling, suppresses phosphorylation of AKT and ERK, thus expression of meiotic genes Sycp3 and Dmc1, which may provide a potential therapeutic target for male infertility [34]. Moreover, deletion of L-GILZ gene enhances ERK1/2 signaling and accelerates the proliferation of undifferentiated spermatogonia. Meanwhile, after knockout of this gene, meiotic cells undergo massive apoptosis, and the differentiation of spermatogonia is abnormal. Considering that ERK1/2 signaling pathway is widely involved in cell proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis, the enhanced connection of this phenomenon with ERK1/2 signaling cannot be excluded [35]. In fact, the ERK1/2 signaling pathway and spermatogonial proliferation and apoptosis have been reflected in the mechanism of male infertility caused by endocrine disruptors such as perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) [61], exogenous estrogen bisphenol A [62], and 17
Leydig cells, a type of steroid-producing cell, are the main source of testosterone in the testis. Androgens promote the development of male reproductive organs, spermatogenesis, and maintenance of secondary sexual characteristics. Testosterone is one of the important androgens and its reduction will lead to male infertility [64]. Currently, there is an increasing number of cases of infertility in males due to decreased testosterone levels or decreased sensitivity of Leydig cells response to luteinizing hormone (LH). However, exogenous testosterone usually inhibits LH secretion, leading to reduced testosterone production by Leydig cells, which inhibits spermatogenesis, and recovery of spermatogenesis after cessation of treatment usually takes 6–15 months or longer [65]. Therefore, it is even more important for men with decreased testosterone levels to address such male infertility by increasing endogenous testosterone. It is worth noting that more and more studies have shown that the ERK1/2 pathway has an important promoting effect on the increase of endogenous testosterone.
The ERK1/2 pathway regulates androgen secretion by Leydig cells by affecting the transcriptional expression of related molecules and their phosphorylation levels. Pogrmic-Majkic et al. [36] found that cAMP can enhance ERK1/2 phosphorylation thereby increasing androgen secretion by Leydig cells. Luteinizing hormone has been proven to maintain steroidogenesis in adult Leydig cells by stimulating cAMP production in Leydig cells and activating the ERK1/2 pathway [37]. Karpova et al. [38] in studying the mechanism of the effect of hyperglycemia on male reproductive function, proposed that the ratio of phosphorylated ERK1/2 to total ERK1/2 in the total testicular content of diabetic rats tended to decrease in comparison with the control group, whereas by increasing phosphorylated ERK1/2 was effective in improving the functioning of Leydig cells in the experimental group. In addition, a study found that a reduction in the level of phosphorylated ERK1/2 impaired its inhibitory effect on glycogen synthase kinase 3
Based on the above, it can be inferred that ERK1/2 expression plays an important role in steroid production and that decreasing ERK1/2 expression interferes with testosterone production in Leydig cells. The mechanism of the action of LH on ERK1/2 is currently unclear, whereas the positive effect of ERK1/2 on testosterone production in Leydig cells and its mechanism is certain, with its regulation of steroidogenesis through the regulation of Cyp11a1 and Cyp17a1 and StAR (Fig. 3a). Therefore, further study of how ERK1/2 is involved in the regulatory mechanism of the LH-CAMP-Leydig cells-testosterone hormone secretion pathway may provide some help and hints for male infertility caused by low testosterone levels.
 Fig. 3.
Fig. 3.Effect of ERK on Leydig cells and the blood-testis barrier. (a) LH interacts with EGF receptors and activates the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathway to stimulate androgen production in Leydig cells. cAMP production by LH-stimulated Leydig cells plays an important regulatory role in this process. In addition, membrane-linked protein A5 and EGF can activate ERK1/2 phosphorylation, thereby upregulating Cyp11a1 and Cyp17a1 and promoting testosterone production. In addition, ERK1/2 can promote testosterone production by inhibiting GSK-3
Sertoli cells (SCs) regulate the development of spermatogenic structures and spermatogenesis in various ways and play a crucial role in ensuring the quality of spermatozoa, which is why they have been referred to as “nurse cells” [67]. The deficiency and abnormal function of SCs is one of the major causes of male infertility.
A number of experiments have revealed that ERK1/2 can be involved in the proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis of SCs under the stimulation of different hormones, especially sex hormones. For example, estrogen can not only bind to the classical estrogen receptor (ER) on SCs, but also promote the proliferation of Sertoli TM4 cells by up-regulating G protein-coupled receptor 30 (GPR30) and ER
Furthermore, it is known from reviewing a large amount of literature that ERK1/2 can also regulate three important functions of SCs thus affecting the quality of male semen and fertility.
First, ERK1/2 are involved in the blood-testis barrier (BTB) formed by SCs. The blood-testis barrier formed by the SCs acts as a selective restriction of molecular entry (permeability barrier) and circumvents the immune system (immune barrier) through tight junctions, gap junctions, and special adhesion-linked structures, thus guaranteeing normal proliferation and differentiation of spermatogonia. Kinase-mediated signaling cascades have been identified as important for the maintenance of the BTB, with ERK1/2 being one of them [46] (Fig. 3b). A non-receptor tyrosine phosphatase, SHP2, may regulate the actin cytoskeleton through phosphorylation of ERK1/2 by SRC kinases and is also a key regulator in maintaining BTB integrity [46]. The tight junction structure is closely related to the expression of the claudin family, and the interaction of ouabain with different subunits of the sodium-potassium pump can activate the ERK1/2 signaling pathway, which in turn regulates claudin-11 [73, 74] and claudin-1 [73] in the rat SCs. Testosterone binding to the ZIP9 transporter protein receptors on SCs activates the nonclassical testosterone pathway ERK1/2-CREB-ATF-1, which promotes claudin-1 and claudin-5 formation [47] (Fig. 3c). The dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate is a steroidal non-classical signaling pathway that activates the ERK1/2 cascade response via G-protein-coupled receptors, stimulating the expression of claudin-3 and -5 [48]. ERK1/2 also regulates the expression of connexin 43 in SCs, which is involved in the formation of gap junctions [74, 75]. In addition, different isoforms of transforming growth factor
Second, ERK1/2 activates the “scavenger” role of the SCs. In addition, SCs have scavenger or macrophage-like activity, which can quickly remove residual vesicles and apoptotic germ cells produced by differentiated spermatocytes to maintain a good spermatogenic environment. Among them, SCs expressing CD95L induce apoptosis of CD95-containing germ cells, a process that requires the involvement of ERK1/2 activation [49]. In addition, Cyanidin-3-O-glucoside in anthocyanins can attenuate the number of oxidative stress and apoptotic cells, promote the integrity of the BTB in the testis, and also increase levels of p-JNK2 and p53 by inhibiting activation of p-ERK and p-JNK1, which in turn has a protective effect on SCs and spermatogenesis [78].
Third, ERK1/2 is tightly linked to the paracrine effects of SCs. It was found that the paracrine action of SCs itself also plays a key role in spermatogenesis. For example, either inflammatory factor IL-1b stimulation or heat stress activates ERK1/2, which increases lactate dehydrogenase and enhances heat shock protein 70 expression induced by heat stress, respectively, promoting lactate secretion by SCs and protecting germ cells [50, 51]. In addition to lactate, SCs secrete substances such as IGF-1 [79], androgen-binding protein and transferrin [80]. Although there are no studies directly proving whether these substances are also regulated by ERK1/2 in SCs, it is undeniable that ERK1/2 is involved in their production regulatory mechanisms in all other cells.
Therefore, ERK1/2 not only plays a significant role in the formation of intact BTB in SCs, but also has important implications for its paracrine function.
The morphology, motility, quantity and viability of spermatozoa, along with their capacity to effectively undergo the energizing and acrosome reactions within the female reproductive tract, are essential in determining the strength of male fertility and the likelihood of conception. In the male reproductive system, Leydig cells, Sertoli cells, hormones, among other factors, impact sperm motility. Following ejaculation into the female reproductive tract, sperm motility primarily involves capacitation and acrosome reactions preceding the process of fertilization with the egg cell. It has been determined that ERK1/2 are typically localized in the tail [64] and head [65] of developed human spermatozoa. The capacitation and acrosome responses arise from multiple enzymatic activities on the flagella of the head and tail of the spermatozoa, leading to the activation of cell signaling cascades [12]. As a result, the sperm-related energizing and acrosome reactions may be closely interconnected with ERK1/2, which is being validated by an increasing number of studies. ERK has been found to be closely associated with the process of the acrosome reaction [64]. High concentrations of progesterone can promote this process by inducing an increase in ERK1/2 phosphorylation [52]. It has been reported that superoxide anion radicals facilitate sperm capacitation through tyrosine phosphorylation via the ERK1/2 signaling pathway [53]. Recently, Sun et al. [54] discovered for the first time that Hsp90 is also involved in regulating human spermatogenesis through the ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK pathways. During the acrosome reaction, the binding of sperm to the zona pellucida may trigger the phosphorylation of EGFR/ERK1/2 in spermatozoa, which in turn promotes the inward flow of calcium ions. This further leads to the phosphorylation of EGFR in a positive feedback manner and accelerates the completion of the acrosome reaction [55]. Moreover, research has indicated that elevated leukocytes present in the female reproductive tract can contribute to reduced sperm motility and infertility in humans. This phenomenon may be attributed to the formation of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) upon leukocyte demise, which can impede sperm motility [81]. Recently, Wei et al. [82] corroborated this finding in pigs and posited that NETs release is linked to the ERK1/2 signaling pathway. This may serve as a basis for further investigations into the mechanisms underlying sperm-NETs interactions in humans. Hence, it is clear that the phosphorylation of ERK1/2 is actively involved in regulating sperm vitality and fertilization. Consequently, proper activation of the ERK1/2 signaling pathway is crucial in maintaining optimal sperm motility. Notwithstanding, the precise mechanisms by which ERK1/2 signaling positively influences sperm motility and fertilization remain incompletely elucidated, warranting further studies.
The aforementioned results demonstrate that the ERK1/2 signaling pathway is intricately linked to normal testicular development and male reproductive health. This pathway plays a crucial role in regulating the SSC ecological niche, spermatogonial cell proliferation and differentiation, sperm motility and fertilization, as well as androgen secretion from mesenchymal stromal cells, thereby directly or indirectly impacting male reproductive health. Given that somatic cells are responsible for testosterone secretion and the development of spermatogenic cells, and that testicular somatic cells continue to regulate the process from spermatogenesis to fertilization, it is imperative to further investigate the intrinsic connection between the ERK1/2 signaling pathway and testicular somatic cells.
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) is a hypothalamic decapeptide hormone that acts as a primary regulator of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis (HPGA). This hormone binds to the gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor (GnRHR) in a pulsatile manner, thereby stimulating the production of LH and FSH. These hormones modulate the production of steroid hormones in the peripheral target gonads, regulate gametogenesis, and control animal reproductive activity [83]. GnRH promotes the transfer of ERK1/2 from the cytoplasm to the nucleus, increasing the transcription of GSU subunits, LH, and FSH through GnRHR. Inhibition of ERK1/2 activation results in decreased transcription of FSH and LH under GnRH stimulation [84]. The activation pattern of ERK1/2 by GnRH and their frequency-dependent effects play a crucial role. Previous studies have shown that changes in the frequency and amplitude of GnRH pulses have different effects on the synthesis and release of FSH and LH [85], which may be related to the pattern of ERK1/2 activation by GnRH and the different roles of ERK1/2 in the frequency-dependent effects. For instance, Kanasaki et al. [86]identified that when GnRH pulses have a lower frequency, ERK1/2 activation is more rapid, its duration is longer, and dephosphorylation is slower.
Furthermore, GnRH activates the FSH
The pathogenesis of male infertility is complex, and there is no unified conclusion at present. Free radical theory is one of the generally accepted theories at present. Normal levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) contribute to sperm capacitation, acrosome reaction and sperm-oocyte fusion [91]. Whereas under pathological conditions, excessive accumulation of ROS can damage the plasma membrane of spermatozoa while affecting DNA integrity, leading to high levels of DNA fragmentation [92]. In addition, oxidative stress is closely related to apoptosis, and high ROS levels lead to enhanced and dysregulated apoptotic responses, disrupting the normal ratio between Sertoli cells and germ cells [93]. Autophagy, one of the important pathways for removing misfiring proteins from cells, can recycle damaged ROS-producing mitochondria to regulate oxidative stress [94]. Studies have shown that oxidative stress in human spermatozoa activates the autophagic response, and autophagy blockade leads to increased oxidative damage and sperm death [95]. Interestingly, the inflammatory response in the male reproductive system is inextricably linked to oxidative stress. Certain ROS and/or reactive nitrogen species (RNS) can activate intracellular signaling cascades that promote the activation of pro-inflammatory genes. In addition, inflammatory activation in the reproductive tract attracts immune cells, leading to a burst of excess reactive substances that exacerbate oxidative stress [96]. Meanwhile, it has been demonstrated that autophagy can attenuate the inflammatory response through a variety of mechanisms. Autophagy can inhibit signaling via RIG-I-like receptors by directly conjugating the receptors to ATG5-ATG12 complexes and through elimination of dysfunctional mitochondria, and it can also inhibit NLRP3 activation by removing permeabilized or ROS-producing mitochondria [97]. Bharath et al. [98] found that enhancing autophagy as well as restoring mitochondrial function is an important strategy for alleviating aging-related inflammation.
The above studies suggest that oxidative stress, autophagy, and inflammation are interrelated pathophysiological processes that are involved in the development of male infertility. However, the mechanism of their crosstalk is currently unknown. Interestingly, the ERK1/2 signaling pathway plays an important role as a signaling pathway shared by oxidative stress, autophagy, and inflammation. Thus, elucidating the relationship between the ERK1/2 signaling pathway and these three is expected to provide new insights into the treatment of male infertility.
ROS play an important role in apoptosis through a variety of cell signaling pathways and altered mitochondrial function, and ERK1/2 are often involved in this process as important downstream factors. It has been shown that the ERK1/2 signaling pathway localized in mitochondria is involved in the regulation of mitochondrial depolarization, swelling, apoptosis and calcium homeostasis [99]. Whether it is possible to change the level of ROS in cells and the function of mitochondria by regulating the phosphorylation level of ERK1/2, thus realizing the anti-aging of cells, has become a hotspot of current research in the field of male reproduction. It has been found that a certain concentration of xylene induces ROS production, prevents LH in immature Leydig cells from binding to its receptor, prevents epidermal growth factor from activating the ERK1/2 cascade in the cells, and reduces the level of phosphorylation of steroidogenic StAR and GSK-3
 Fig. 4.
Fig. 4.Mechanism of ERK1/2 signaling pathway regulating proliferation or differentiation of Leydig cells. Xylene induces ROS production, prevents the luteinizing hormone from immature Leydig cells from binding to its receptor, prevents epidermal growth factor from activating the cellular ERK1/2 cascade, and reduces the phosphorylation levels of steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR) and GSK-3
In germ cells, overexpression of inflammatory factors such as TNF-
Triggered by the activation of single or multiple signaling pathways in response to internal and external environmental stimuli, autophagy fuses, degrades, and recycles vesicles containing organelles and other protein structures with lysosomes, thereby fulfilling the need for cellular renewal and preventing malignant transformation of cells as a form of cell death. This process is manifested in multiple aspects of spermatogenesis and endocrine processes in men, and mediating spermatogenesis by targeting autophagy may be an effective strategy for treating male infertility [110]. The ERK1/2 signaling pathway is one of the classical autophagy regulatory pathways, and a large number of studies have demonstrated that both upregulation and inhibition of this pathway contribute to autophagy [111]. It has been suggested that exposure to organic toxicants such as perfluoroalkanoic acid may down-regulate the phosphorylation level of ERK1/2, which in turn may promote autophagy in mesenchymal cells while delaying their differentiation [112]. Genc et al. [113] suggest that blocking the lysophosphatidic acid receptors and inhibiting the activation of the AKT/ERK/mTOR pathway may promote autophagy in prostate cancer cells, thereby delaying cancer progression. Chen et al. [114] found that Cox7a2 inhibits StAR expression in the ERK1/2 signaling pathway and reduces LH-induced testosterone secretion in a state of overexpression in testicular mesenchymal stromal cells of mice, which was shown to be possibly related to the level of phosphorylation of the autophagy signaling factor P70S6K. In contrast to the inhibition of ERK1/2, it has been experimentally demonstrated that the ERK1/2 signaling pathway may be phosphorylated at elevated levels in response to zearalenone induction, thereby activating autophagy in TM4 cells [115]. Lee et al. [116] found a similar phenomenon (Fig. 5).
 Fig. 5.
Fig. 5.Mechanism of ERK1/2 signaling pathway regulating male germ cell proliferation or apoptosis. Activation of the Nrf2/HO-1/ERK signaling pathway inhibits ROS production by hyperhomocysteinemia and also inhibits apoptosis of smooth cavernous muscle cells, which in turn improves erectile dysfunction in rats. The number of testicular spermatogonial stem cells was significantly reduced in a high ROS environment, and the mechanism may be that ROS promotes transcription, translation, and cleavage of the epidermal growth factor receptor ligand spitz, increases its binding to the receptor, activates downstream molecules including ERK1/2, and initiates early stem cell differentiation. The function of macrophages in the testis to recognize and produce inflammatory factors requires LPS binding to cellular receptors. It induces activation of AP-1, a signaling pathway induced by the MAPK family. Radiation stimulates Toll-like receptors in SCs, which upregulates ERK1/2 phosphorylation levels, activates AP-1 transcription factors, and induces overproduction of inflammatory factors. Betulinic acid inhibits the inflammatory response in the testis. Zearalenone induces testicular inflammation by activating the ERK1/2 pathway, and the ERK1/2 signaling pathway may have elevated zearalenone-induced phosphorylation levels, activating autophagy in TM4 cells. Autophagy may reduce the production of inflammatory factors and decrease ROS levels.
The above evidence suggests that the ERK1/2 signaling pathway plays a non-negligible role in oxidative stress, inflammation and autophagy. It has been illustrated that inactivation of MAPK family proteins may contribute to the prevention of ferroptosis in Sertoli cells induced by testicular ischemia reperfusion, which provides a new clinical theoretical basis for the clinical treatment of male infertility [40].
With the increasing number of studies demonstrating the association of ERK1/2 with male fertility decline, many studies have suggested that the ERK1/2 pathway may have potential clinical applications in the treatment of male fertility decline. Sokanovic’s group [117] suggests that ERK1/2 is involved in androgen reduction after aging in rats by targeting NUR77 and StAR to affect steroid synthesis. Subsequently, this group also proposed that long-term use of PDE5 inhibitors such as sildenafil helps to reduce ERK1/2, improve testicular microcirculation and testosterone production, and reverse testicular mesenchymal cell senescence in rats [117]. One study [118] reported that intranasal administration of nerve growth factor (NGF) could regulate GnRH release through the PKC/p-ERK1/2/p-CREB signaling pathway, thereby promoting testosterone production and restoring fertility in senescent male mice. This mode of intranasal administration of NGF may become an alternative therapy for hypogonadism and replace exogenous testosterone therapy. In addition, neuropeptide P can stimulate the proliferation of GC-2 SPG cells (a spermatogonia cell line) by activating the ERK1/2 signaling pathway, which is expected to provide a new therapeutic strategy for male infertility [119]. In Traditional Chinese Medicine, an animal study reported that the Chinese herb Pueraria may be a potential alternative for the treatment of busulfan-induced impairment of male fertility by inactivating the testicular MAPK pathway, thereby inhibiting the phosphorylation of p38, ERK1/2, and JNK in the testis, laying the groundwork for the use of Pueraria to address male infertility induced by chemotherapy or other factors [120]. Moreover, electroacupuncture treatment stimulating the Shenshu and acupoints Guanyuan may attempt to modulate ERK expression and scavenge free radical damage, thereby improving the microenvironment and testosterone synthesis in senescent testicular mesenchymal cells [121]. Furthermore, ERK1/2 can also function as a molecular marker. A clinical study suggests that the combined assessment of ERK1/2 and prolactin-induced peptide may be a useful molecular marker for FSH in male idiopathic infertility, and the discovery of these markers can help adjust FSH and reduce associated healthcare costs during treatment [122]. Based on the above studies, it is easy to understand that the ERK1/2 signaling pathway has greater clinical application space in male reproductive aging and is worth further exploration by researchers.
Tumor is a big problem that troubles all walks of life. At present, the clinical treatment of most tumors is still very limited. The results of several studies show that the activated ERK pathway is associated with malignant tumors, such as lung cancer, liver cancer, breast cancer, gastric cancer, etc. [123, 124, 125, 126]. Since tumor growth and metastasis are strongly dependent on neoangiogenesis, this study focused on the relationship between ERK and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in anti-angiogenic therapy. Related studies have reported the complex relationship between ERK and VEGF, such as activating ERK can promote VEGF-dependent angiogenesis [127], or the vascular remodeling of VEGF through PKA/RAS/ERK/HIF 1
In conclusion, although the current ERK1/2 in male reproductive aging and tumor-related research is relatively less in number, but ERK1/2 signaling pathway to reverse male reproductive aging and tumor potential has been reflected from the above studies, so the future is worth further research in the field of male reproduction, make it can really be for clinical application.
In summary, ERK1/2 and many signaling pathways such as PI3K/AKT/mTOR, regulation of related pathways can affect the apoptosis and proliferation of male germ cells. Meanwhile, ERK1/2 can be stimulated by internal and external environmental substances such as gonadal axis hormones and Endocrine Disruptors, through the oxidative stress, release of inflammatory factors and autophagy, to realize the regulation of the formation, development, differentiation and other processes of various cells in the male reproductive system. Therefore, in the future, the crosstalk relationship between ERK1/2 pathway under the regulation of gonadotrophins such as LH, autophagy, oxidative stress and inflammation-related pathways such as PI3K/AKT/mTOR can be deeply explored. How this dysfunctional relationship affects testicular Sertoli cells and Leydig cells and further mediating the progression of male reproductive senescence also deserves further study in the future. We are exploring new therapies for the ERK pathway in the last field of aging and tumor in the field of male reproduction for better clinical application.
XC, YD, CY, YW and YH: conceptualization, literature collection, and writing-original draft; ZW, JQ and ZM: data acquisition, analysis, review and editing; WQZ and XLC: prepared all figures; WZ, JZ, ZG and MZ: literature analysis, picture processing, review and editing. All authors contributed to editorial changes in the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. All authors have participated sufficiently in the work and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
This research was funded in part by a grant from the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (Nos. 2021B1515140012 and 2023A1515010083), the Dongguan Science and Technology of Social Development Program (No. 20211800905342), the Research and Development Fund of Dongguan People’s Hospital (No. k202005), the Guangdong Medical University Students’ Innovation Experiment Program (Nos. 2021ZZDS006, 2021ZCDS003, 2022ZYDS003, 2022FYDB009, and 2022FCDS003), the Guangdong Medical University Students’ Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program (Nos. GDMU2021003, GDMU2021049, GDMU2022031, GDMU2022047, GDMU2022063, GDMU2022077, GDMU2022078), the Provincial and National College Students’ Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program (Nos. 202210571008, S202210571075, 202310571031, S202310571047, S202310571078, S202310571063, S202310571077), the Guangdong Medical University-Southern Medical University twinning research team project (No. 4SG23033G), and the Cai Limin National Traditional Chinese Medicine Inheritance Studio.
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Publisher’s Note: IMR Press stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.





