1 Department of Dermatology, Affiliated Hospital of Nantong University, Medical School of Nantong University, 226001 Nantong, Jiangsu, China
2 Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Tandon School of Engineering, New York University, Brooklyn, NY 11201, USA
3 Medical School of Nantong University, 226019 Nantong, Jiangsu, China
4 Cancer Research Center Nantong, Nantong Tumor Hospital & Tumor Hospital Affiliated to Nantong University, 226361 Nantong, Jiangsu, China
†These authors contributed equally.
Abstract
Background: Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC) is the second most common malignancy of the skin, and its incidence is increasing annually. Once cSCC becomes metastatic, its associated mortality rate is much higher than that of cSCC in situ. However, the current treatments for progressive cSCC have several limitations. The aim of this study was to suggest a potential compound for future research that may benefit patients with cSCC. Methods: In this study, we screened the following differentially expressed genes from the Gene Expression Omnibus database: GSE42677, GSE45164, GSE66359, and GSE98767. Using strategies such as protein-protein interaction network analysis and the CYTOSCAPE plugin MCODE, key modules were identified and then verified by Western blotting. Subsequently, related signalling pathways were constituted in the SIGNOR database. Finally, molecular docking analyses and cell viability assay were used to identify a potential candidate drug and verify its growth inhibition ability to A431 cell line. Results: Fifty-one common differentially expressed genes were screened and two key modules were identified. Among them, three core genes were extracted, constituting two signalling pathways, both of which belong to the module associated with mitotic spindles and cell division. A pathway involving CDK1, the TPX2-KIF11 complex, and spindle organization was validated in a series of analyses, including analyses for overall survival, genetic alteration, and molecular structure. Molecular docking analyses identified the pyridine 2-carbaldehyde thiosemicarbazone (NSC689534), which interacts with TPX2 and KIF11, as a potential candidate for the treatment of cSCC. Conclusions: NSC689534 might be a candidate drug for cSCC targeting TPX2 and KIF11, which are hub genes in cSCC.
Keywords
- computational biology
- drug testing
- molecular docking simulation
- molecular structure
- skin neoplasms
Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC) is the second most common form of non-melanoma skin cancer and results from abnormal proliferation of keratinocytes from the epidermis or skin appendages [1, 2]. It accounts for 20% of all skin malignancies [3], has an increasing incidence [4], and is expected to continue to increase in the future with the aging population. cSCC is a malignant tumor that can progress from actinic keratosis and cSCC in situ to invasive or metastatic cSCCs [5, 6]. The majority of patients with primary cSCC, if treated early and appropriately, have an excellent prognosis with surgical excision and a 5-year cure rate of 90% [7]. However, a large single-center study of more than 900 patients with cSCC who were followed for approximately 10 years showed that the rates of recurrence, lymph node metastasis, and disease-related mortality were 4.6%, 3.7%, and 2.1%, respectively [8]. Factors, such as old age, male sex, immunosuppression, and lesions localized in the ear or lip, may increase the risk of recurrence and metastasis [9]. Once metastasis occurs, the prognosis is poor and there is a 70% mortality rate [10]. For the treatment of progressive cSCC, surgery in combination with radiotherapy is commonly applied in clinical practice. Obviously, there are limited options of treatment for progressive cSCC. For example, the choice of radiotherapy should take into account the lesion’s location, conventional chemotherapy led to limited therapeutic efficacy as well as high side effects [11], and the use of EGFR inhibitors in cSCC lacks evidence-based support because of unsatisfactory therapeutic outcomes [12]. To summarize, a better understanding of high-risk cSCC is necessary for the development of more effective treatments [13].
Based on previous basic research, cSCC frequently exhibits alterations in multiple important genes (e.g., TP53, CDKN2, and NOTCH1), as well as the activation of signaling pathways, such as the EGFR signaling pathway, RAS-RAF-MEK-ERK signaling, and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway [14]. Hence, the detection of hub genes and their involvement in signaling pathways is of great value in the investigation of therapeutic drugs for advanced cSCC. Gene expression analysis using microarray datasets from the public Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database provides an efficient method for studying the differences in gene expression between different classified samples [15]. Molecular docking analysis can help predict and match potential small-molecule compounds by constructing binding models and evaluating the binding capacity through computer simulation of the interaction between small-molecule compounds (ligands) and target molecules (receptors) [16], thus, discovering and confirming new drugs.
In this study, we used datasets from the GEO database to screen for differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between cSCC and adjacent normal tissue. Then, we constructed a protein-protein interaction (PPI) network and used two modules to identify hub genes among them. Finally, three core genes (targeting protein for Xklp2 [TPX2], cyclin-dependent kinase [CDK]1, and kinesis family member [KIF]11) that interact with each other were identified using SIGnaling Network Open Resource (SIGNOR3.0). These genes may constitute a pathway that plays a role in mitosis and DNA repair. Based on this pathway, NSC689534 was selected as a suitable small-molecule compound capable of acting on TPX2 and KIF11. Our results suggest that TPX2 and KIF11 could be therapeutic targets for cSCC, and NSC689534 might be a potential candidate drug targeting TPX2 and KIF11.
Datasets containing samples of both cSCC and normal skin tissue were downloaded
from the NCBI GEO database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/). Four datasets
based on the GPL571 platform, including GSE42677
(https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE42677), GSE45164
(https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE45164), GSE66359
(https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE66359), and GSE98767
(https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE98767), were finally
selected for this study. After removing samples, in which systemic treatments,
such as immunosuppression or chemotherapy, were used, a total of 46 cSCC samples
and 27 healthy skin tissue samples were included in the subsequent analysis
(Table 1). DEGs between the cSCC and control groups were identified in the
downloaded data matrices using the R package LIMMA (version 3.40.6; R Software
for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria). The screening criteria were set as
follows: fold change (FC)
| Accession No. | No. of cases | |
| Normal | Cancer | |
| GSE42677 | 10 | 10 |
| GSE45164 | 3 | 10 |
| GSE66359 | 5 | 8 |
| GSE98767 | 9 | 18 |
Gene Ontology (GO) functional enrichment analysis, pathway enrichment analysis
(including the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes, Reactome Gene Sets, and
WikiPathways), and disease enrichment analysis based on the DisGeNET database
were used, and data were plotted as bar graphs using METASCAPE
(https://metascape.org/gp/). A threshold of the enrichment number of genes
Interactions between the DEG-encoded proteins were analytically mapped using
STRING 12.0 (https://cn.string-db.org/) with a threshold of a combined score
The SIGnaling Network Open Resource (SIGNOR3.0), a repository of manually annotated causal relationships between human proteins, biologically relevant chemicals, stimuli, and phenotypes, provides advanced graphical tools to explore human cellular networks. By searching the hub genes in the key modules using the SIGNOR3.0 database (https://signor.uniroma2.it/), we created networks of potential signaling pathways. The causal relationships and mechanisms of how these proteins in the pathway act on the development of cSCC were further determined by searching the literature and analysing the molecular structure of functional domains obtained from the cBio Cancer Genomics Portal (cBioPortal).
The expression levels of TPX2, KIF11, CDK1, and pituitary tumor transforming gene (PTTG1) in squamous cell carcinoma of skin and other organs were validated using Gene Expression Profile Interaction Analysis (GEPIA; http://gepia.cancer-pku.cn/) based on The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) dataset. Kaplan–Meier plots were generated online (http://kmplot.com/analysis/index.php?p=service&cancer=pancancer_rnaseq) to plot overall survival curves based on the expression of four core genes in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSC); the best cutoff value was selected automatically. The Human Protein Atlas (HPA) (https://www.proteinatlas.org/) provided immunohistochemical expression maps of protein expression patterns in cSCC and normal skin tissues.
Genetic information, such as mutation rate, prognostic information, molecular structure and mutations, and post-translational modification sites for patients with cSCC were obtained from cBioPortal (https://www.cbioportal.org/). Samples were downloaded from two studies: Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma (MD Anderson, Clin Cancer Res 2014) and Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma (UCSF, NPJ Genome Med 2021).
Small molecule compound-gene interaction analyses were based on the Comparative Toxicogenomics Database (CTD) (downloaded in November 2016), and the network was visualized using the NetworkAnalyst website (https://www.networkanalyst.ca/).
The SDF format of NSC689534 was downloaded from the PubChem database, subsequently imported into ChemDraw 3D for energy minimization using the MM2 module to obtain the lowest energy advantage concept, and then saved as a mol2 file. Protein structures were downloaded from the UniProt database and visualized separately using the PyMOL Molecular Graphics System (Version 2.5, Schrödinger, LLC). Afterward, the ligands (NSC689534) and receptors (TPX2 and KIF11) were saved as pdbqt files using MGTools (Version 1.5.6, Center for Computational Structural Biology, Scripps Research, USA) after processing for dehydration, hydrogen addition, charge calculation, merging of non-polar hydrogens, and others. The ligands and receptors were docked using AutoDock Vina 1.1.2, [17, 18] with the docking parameters shown in Table 2. Then, concepts with higher scores were visualized using PyMOL and Discovery Studio (BIOVIA, Dassault Systèmes, FR). Pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness, and medicinal chemical analyses of NSC689534 were performed using the SwissADME algorithm. We analyzed drug-likeness on the basis of the Lipinski (Pfizer Inc., New York, NY, USA) rule of five [19], whereas the Abbot bioavailability score and gastrointestinal absorption were used to estimate the oral bioavailability of the drug [20].
| Center | Center_y | Center_z | Size_x | Size_y | Size_z | Exhaustiveness | Numb_modes | Energy_range | |
| 5lxm | 47.29 | −8.97 | 13.98 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 8 | 9 | 3 |
| 9tle | −19.12 | −10.13 | −10 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 8 | 9 | 3 |
The A431 (National Collection of Authenticated Cell Cultures, Beijing, China)
and HaCaT (Newgainbio, Wuxi, China) cells were grown in Dulbecco’s modified
Eagle’s medium (SH30022.01, HyClone, Logan, UT, USA) supplemented with 10% fetal
bovine serum (SH30074.03, HyClone) in 5% CO
Cells were washed twice in cold phosphate buffered saline and, then, lysed in radioimmunoprecipitation assay buffer for 30 min. After being boiled for 10 min, equal amounts of protein were separated via SDS-PAGE and transferred to polyvinylidene fluoride membranes. The membranes were blocked with 5% skim milk and 0.1% Tween 20 (P1379, Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO, USA) in tris-buffered saline with Tween-20 (TBST) and were then incubated overnight at 4 °C with antibodies against KIF11 (23333-1-AP, Proteintech, Rosemond, IL, USA) and TPX2 (11741-1-AP, Proteintech) in 5% skim milk. After being washed, the membranes were incubated in secondary antibodies for 2 h. Protein bands were detected using an enhanced chemiluminescence system.
The anti-cancer ability of NSC689534 was assessed using A431 cell line. 15,000 cells/well were seeded in 96-well plates for 24 h, treated by relevant concentration (0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1, 2.5, 5, 7.5 µM) of NSC689534 (obtained from MedChemExpress, Monmouth Junction, NJ, USA) for 8 h or 24 h. The cells were then incubated with fresh complete media containing 10% cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8) reagent (C6005, NCM, Suzhou, CHN) for 2 h. The absorbance at 450 nm was measured with the microplate reader manufactured by Bio-Tek Instruments (Winooski, VT, USA). Every group was repeated 3 times.
RNAs were extracted from HaCaT and A431 cells with 1 mL TRIzol (Cat. No.10296010CN, TRIzol™ LS reagent, Carlsbad, CA, USA) per sample. cDNA synthesis and qPCR were performed using HiScript® Ⅲ RT SuperMix for qPCR (R323, Vazyme, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China) and AceQ Universal SYBR qPCR Master Mix (Q511, Vazyme). GAPDH was tested for sample loading control. Primer (No.2514129018, Sangon, Shanghai, China) sequences were as follows: TPX2: TPX2-F GTCACCAAATCAGTTGACTTCC, TPX2-R AAGGATGCTTTCGTAGTTCAGA; KIF11: KIF11-F CATACTCTAGTCGTTCCCACTC, KIF11-R CAACCAAGTTCAACTTTCCGAT; GADPH: GAPDH-F CAGGAGGCATTGCTGATGAT, GAPDH-R GAAGGCTGGGGCTCATTT.
Analyses and graphs were conducted with GraphPad Prism 9.4.1 (GraphPad Software,
Inc., San Diego, CA, USA). One-way ANOVA was used for data analysis in western
blotting while T-test in RT-qPCR. p
We downloaded conforming microarray datasets from the NCBI GEO database (Table 1) and examined shared genes that were differentially expressed between cSCC and
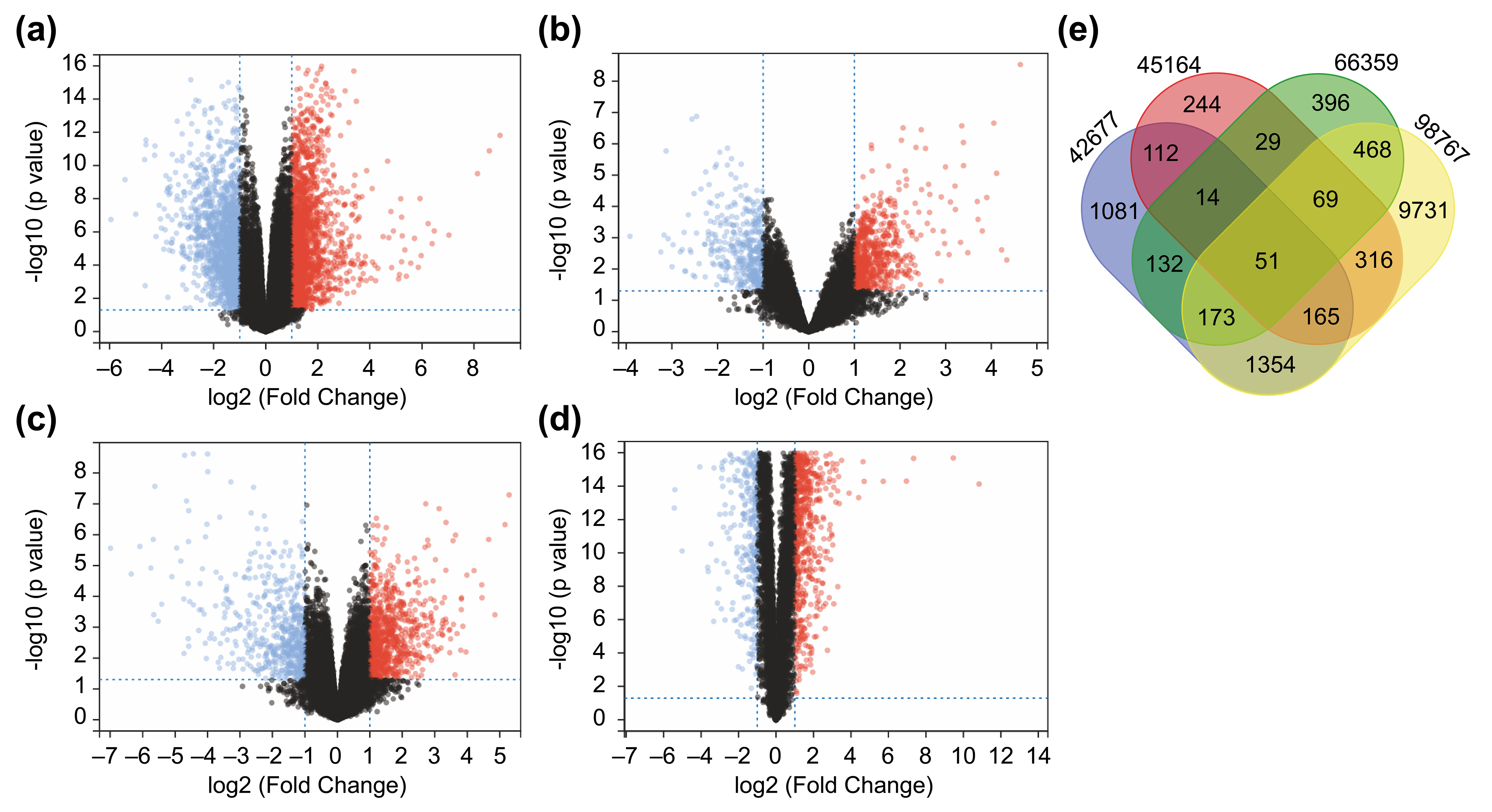
normal skin tissue in all datasets. All DEGs identified are shown as volcano
plots (Fig. 1a–d). Based on the matrices of the GSE42677, GSE45164, GSE66359,
and GSE98767 datasets, 3082, 1000, 1332, and 12327 DEGs, respectively, meeting
the threshold of
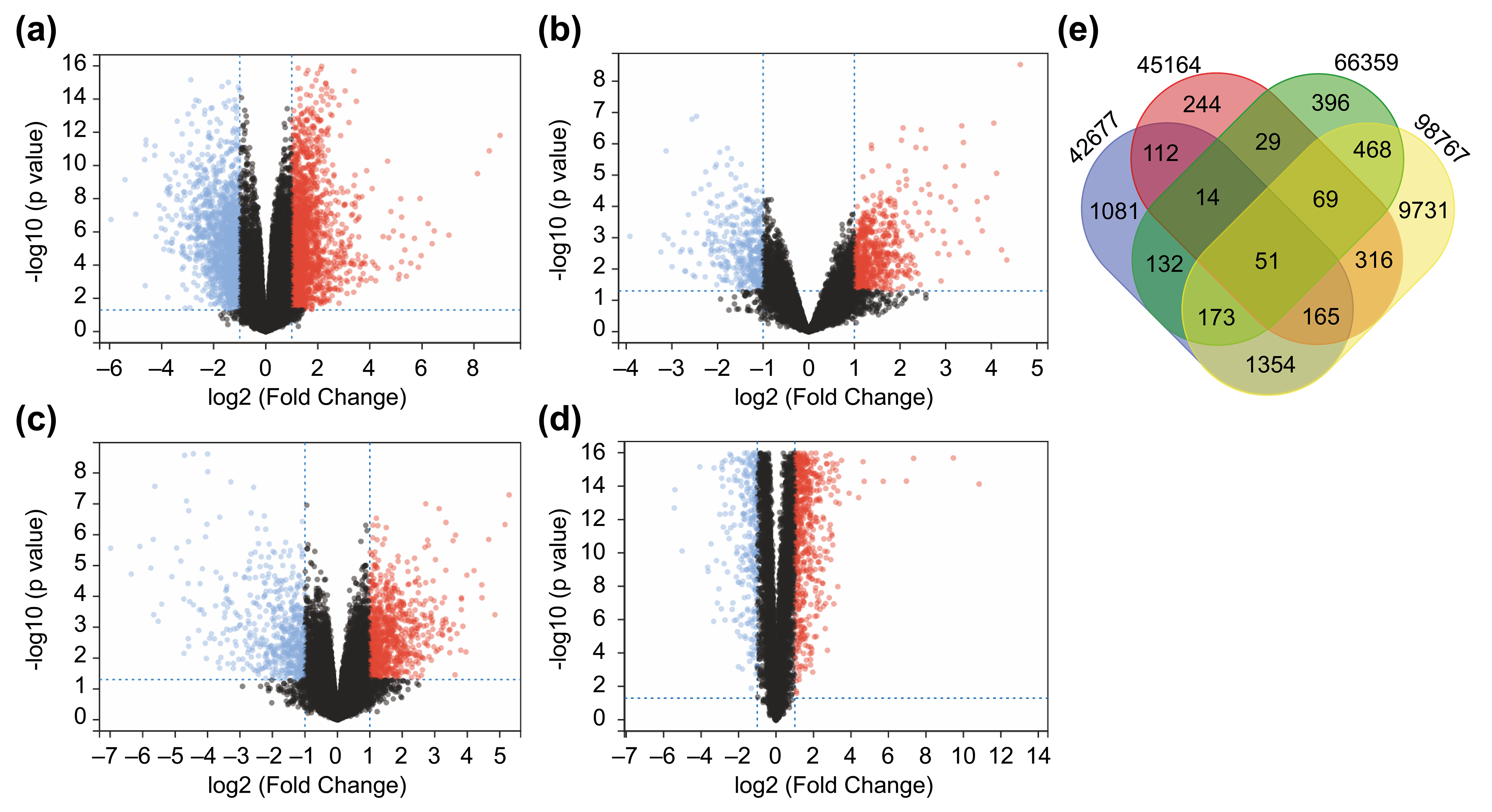 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.Identification of 51 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) from Four Datasets. (a–d) A total of 51 DEGs identified from four
datasets. Differentially expressed genes between cutaneous squamous cell
carcinoma (cSCC) and healthy tissue samples in the datasets GSE42677 (a),
GSE45164 (b), GSE66359 (c), and GSE98767 (d). DEGs were screened based on FC
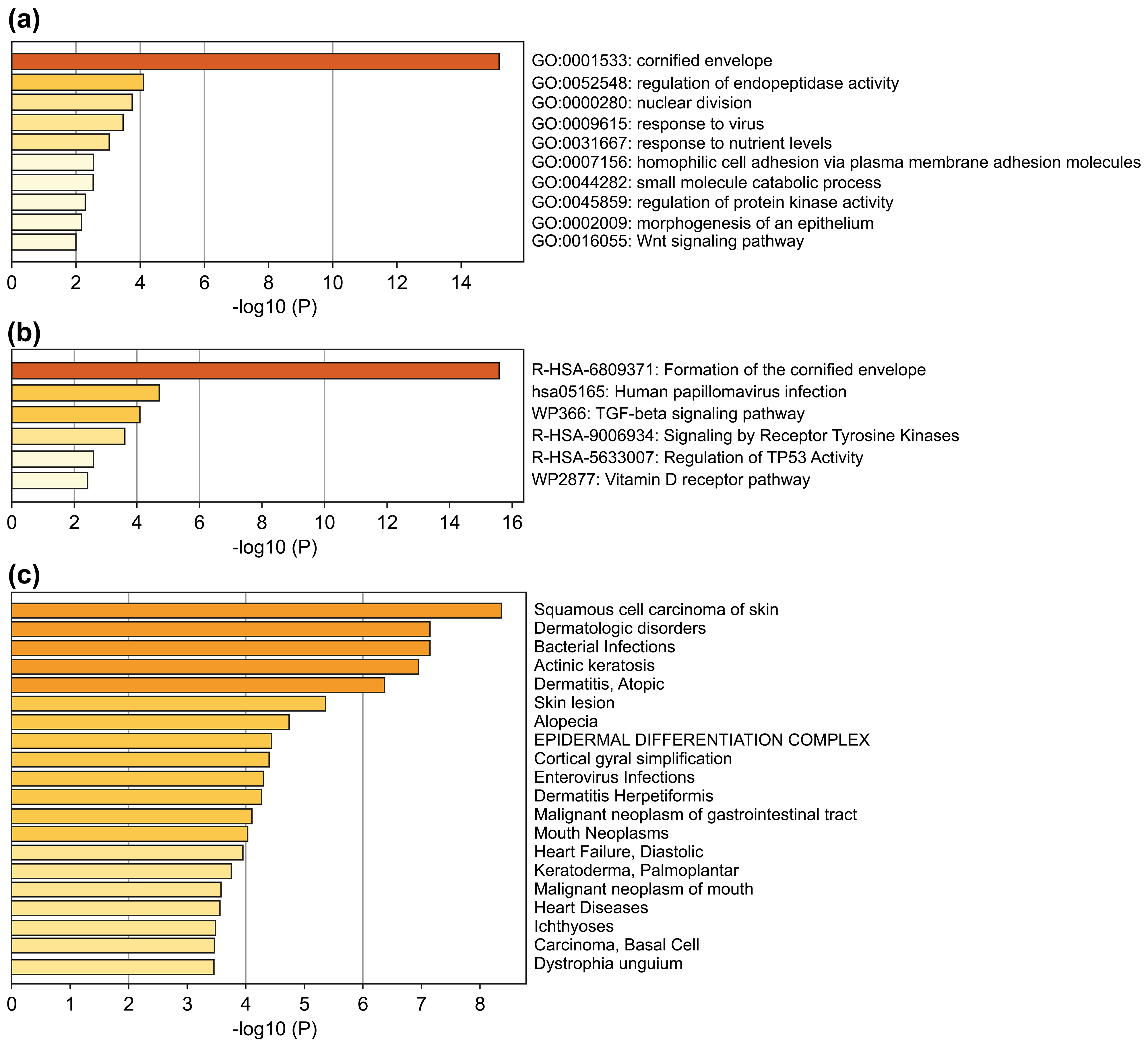
The 51 DEGs were significantly enriched in squamous cell carcinoma of the skin, actinic keratosis, and other skin-related disorders (Fig. 2a). GO and Reactome Gene Set analysis showed enrichment in cornified envelope/formation of cornified envelope (Fig. 2b,c), indicating that the screened DEGs were closely related to skin diseases. Pathway enrichment analysis also demonstrated that these 51 genes were associated with a variety of squamous cell carcinoma-related signaling pathways, including human papillomavirus infection, transforming growth factor beta signaling pathway, tyrosine kinase receptor signaling pathway, and regulation of the TP53-related pathway (Fig. 2c).
 Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.Enrichment analysis of the 51 DEGs. (a) Bar chart of
significant GO terms with DEGs. (b) Bar chart of significant enriched pathways.
(c) Bar chart of significant enriched diseases. The bar graphs were plotted using
METASCAPE with a threshold of the enrichment number of genes
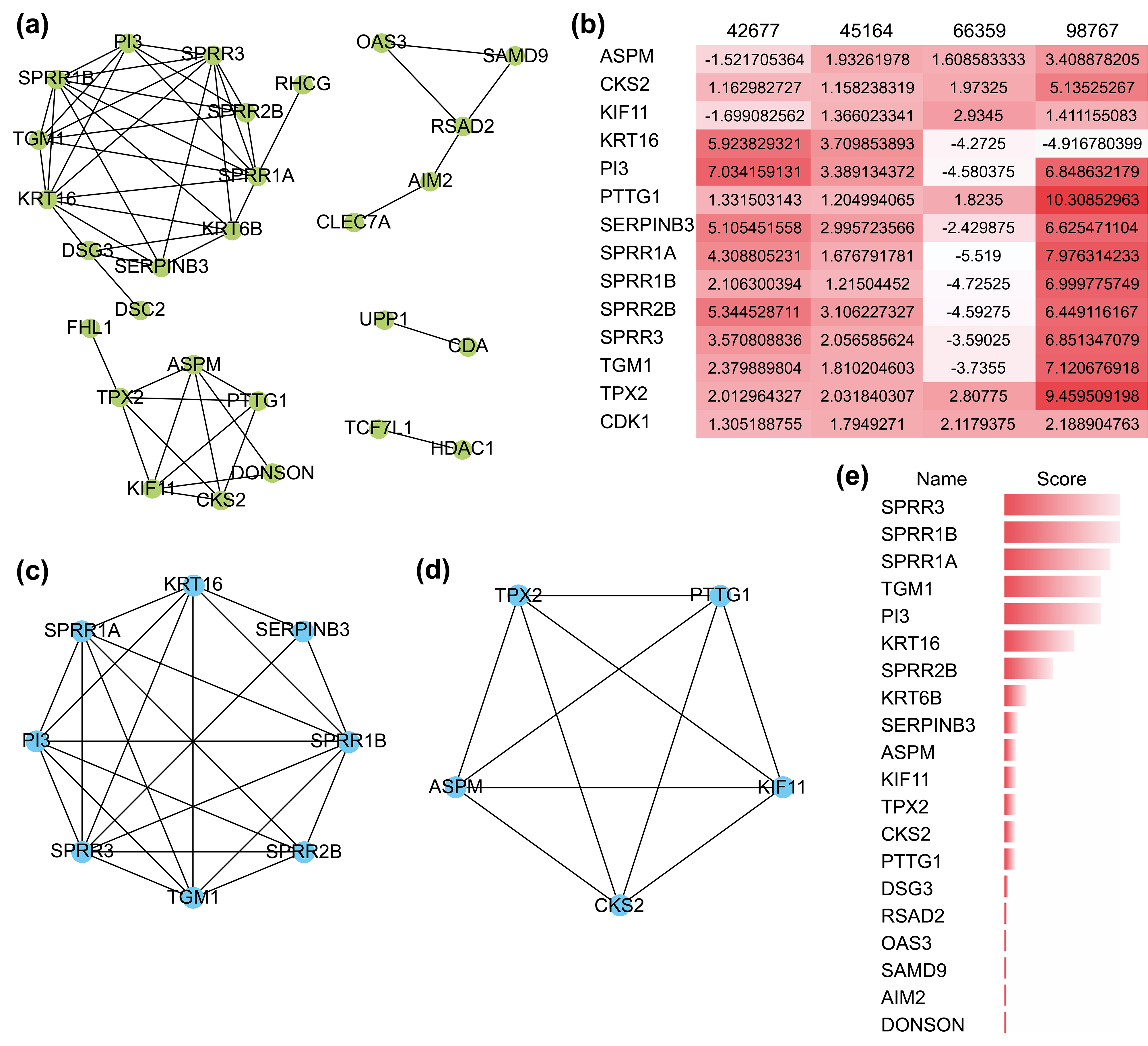
The PPI network comprizing these 51 genes contained 28 nodes and 53 interactions (Fig. 3a), and their GO functional enrichment analysis was mainly related to peptide cross-linking, keratinization, epidermal cell differentiation, and skin development. Using the MCODE plug-in of CYTOSCAPE, two functionally relevant key modules were extracted from the PPI network (Fig. 3c,d). Module A contained eight genes and 23 edges, whereas module B contained five genes and 10 edges. Nearly all 13 hub genes were highly expressed in the four GEO datasets (Fig. 3b). Genes in Module A were enriched in keratinization, peptide cross-linking, and keratin-forming cell differentiation, while those in Module B were mostly associated with spindle organization and polarization, mitotic spindles, and the cell cycle. In addition, we found that the scores of the genes in both modules were ranked in the top 15 when they were validated using the MCC algorithm of CYTOHUBBA, another plug-in for hub gene extraction (Fig. 3e). These results confirmed the reliability of the extracted hub genes.
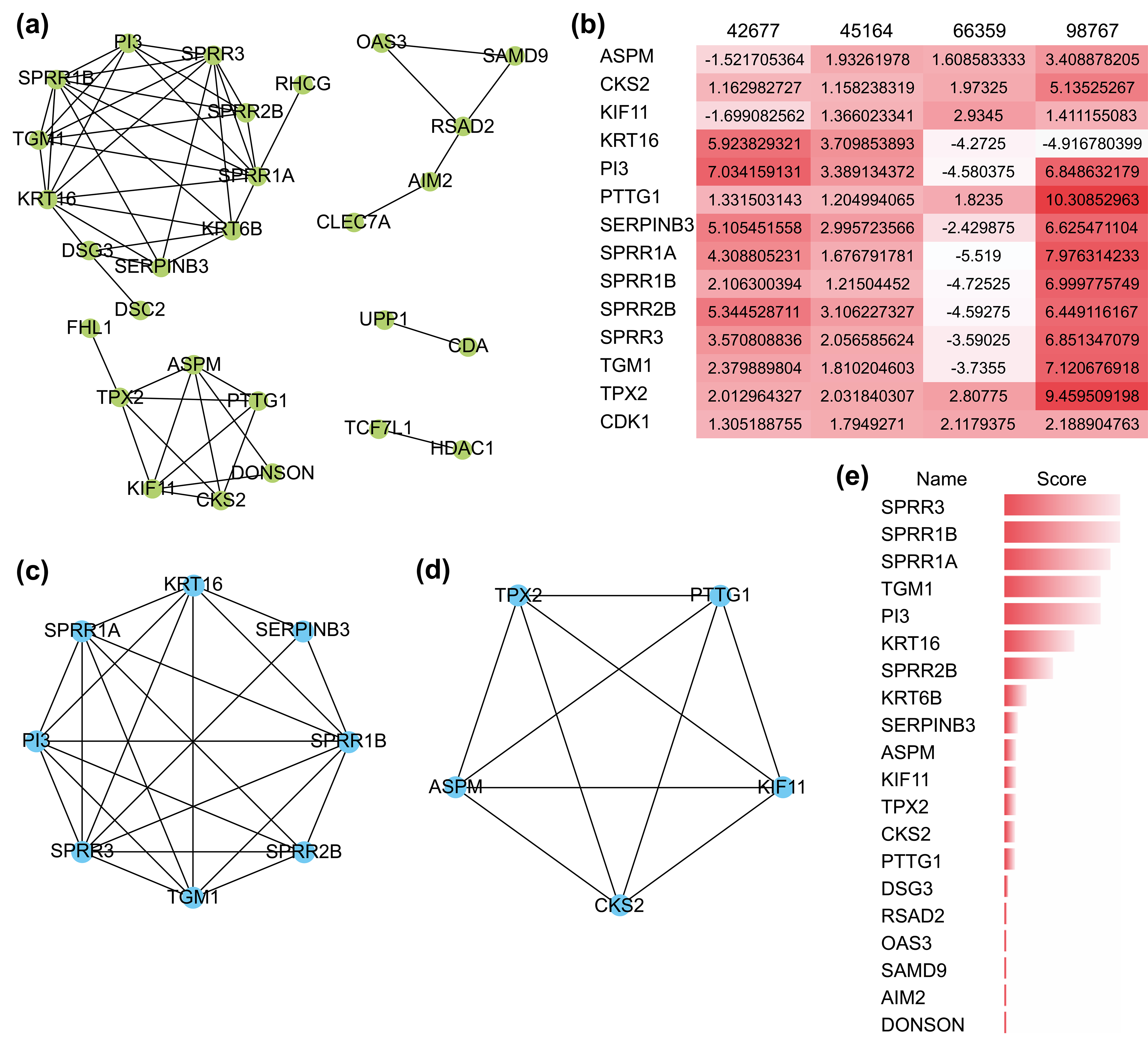 Fig. 3.
Fig. 3.The protein-protein interaction (PPI) network and its key
modules extracted from the DEGs. (a) PPI network of DEGs using the STRING
website. (b) Expression level of 13 hub genes in the four GEO datasets. A darker
color represents a higher level of expression. (c,d) Key modules extracted by the
MCODE plug-in with a degree cutoff
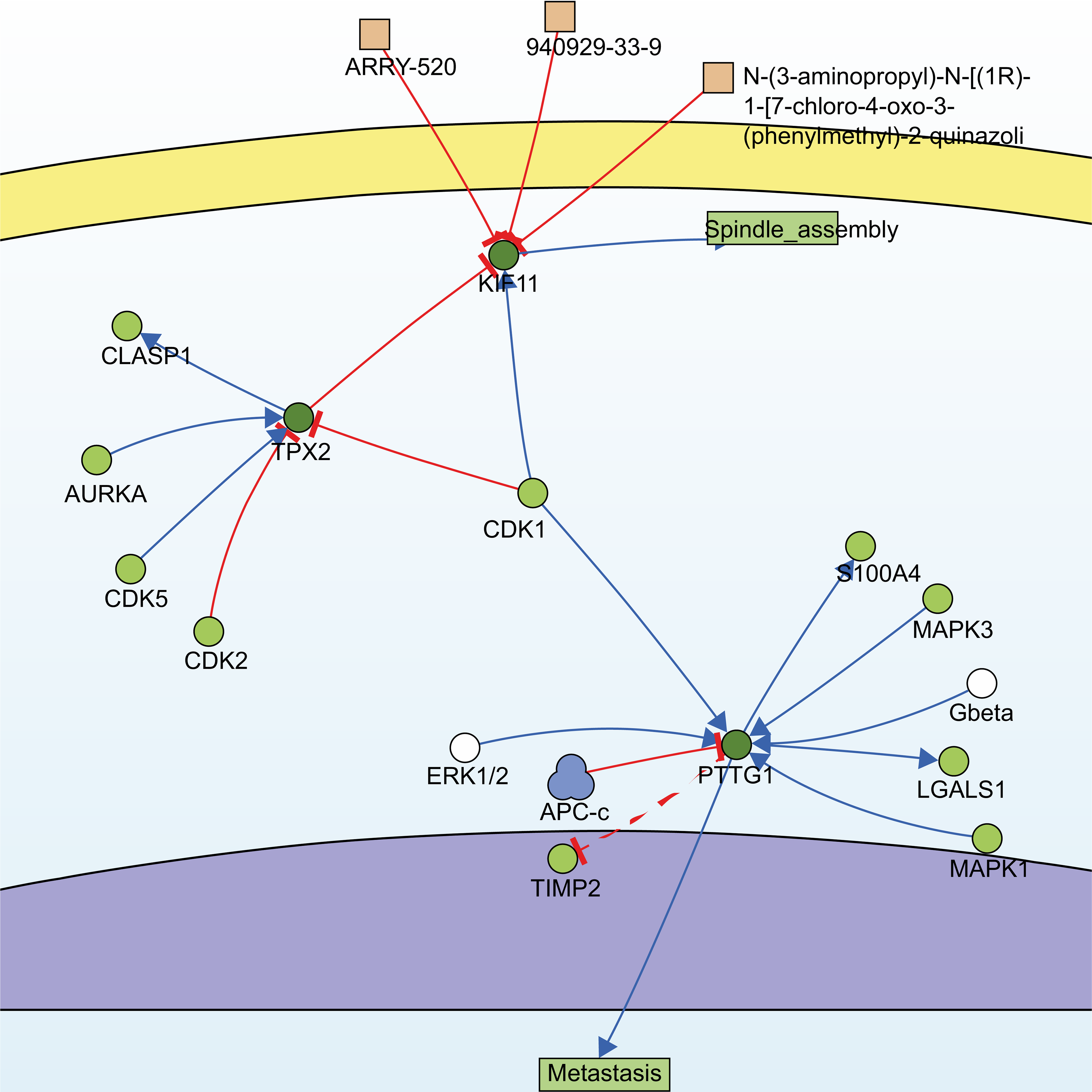
Utilizing the information of the SIGNOR3.0 database, an open-source signaling network that manually stores annotated causal relationships between human proteins, biologically relevant chemicals, stimuli, and phenotypes, TPX2, KIF11, PTTG1, and another non-modular gene, CDK1, were extracted from 13 hub genes, forming two possible signaling pathways (Fig. 4).
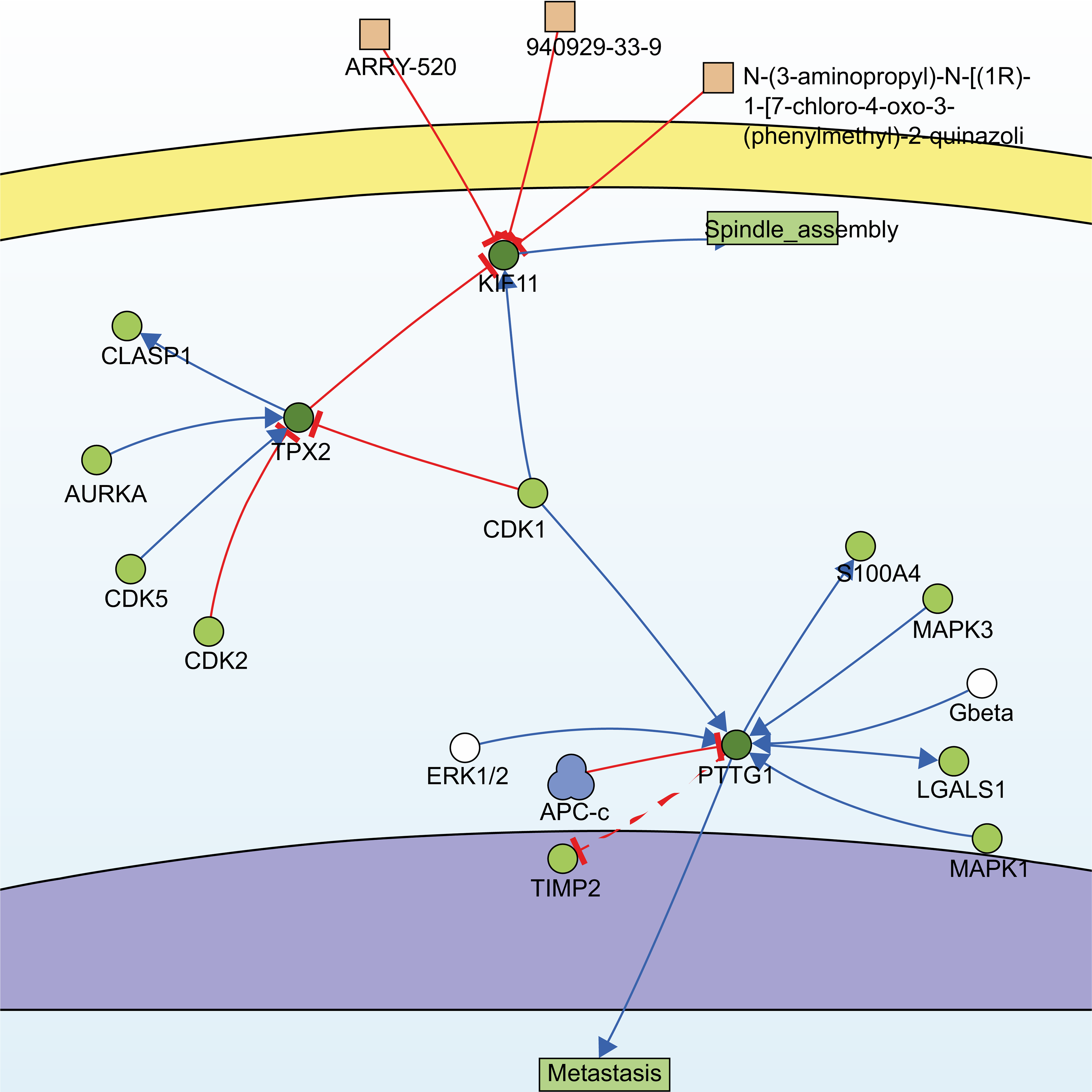 Fig. 4.
Fig. 4.Signaling pathways constructed by SIGNOR3.0. Searching for the 13 hub genes in the SIGNOR3.0 database. Two signaling pathways containing three of the hub genes were automatically generated for further analysis.
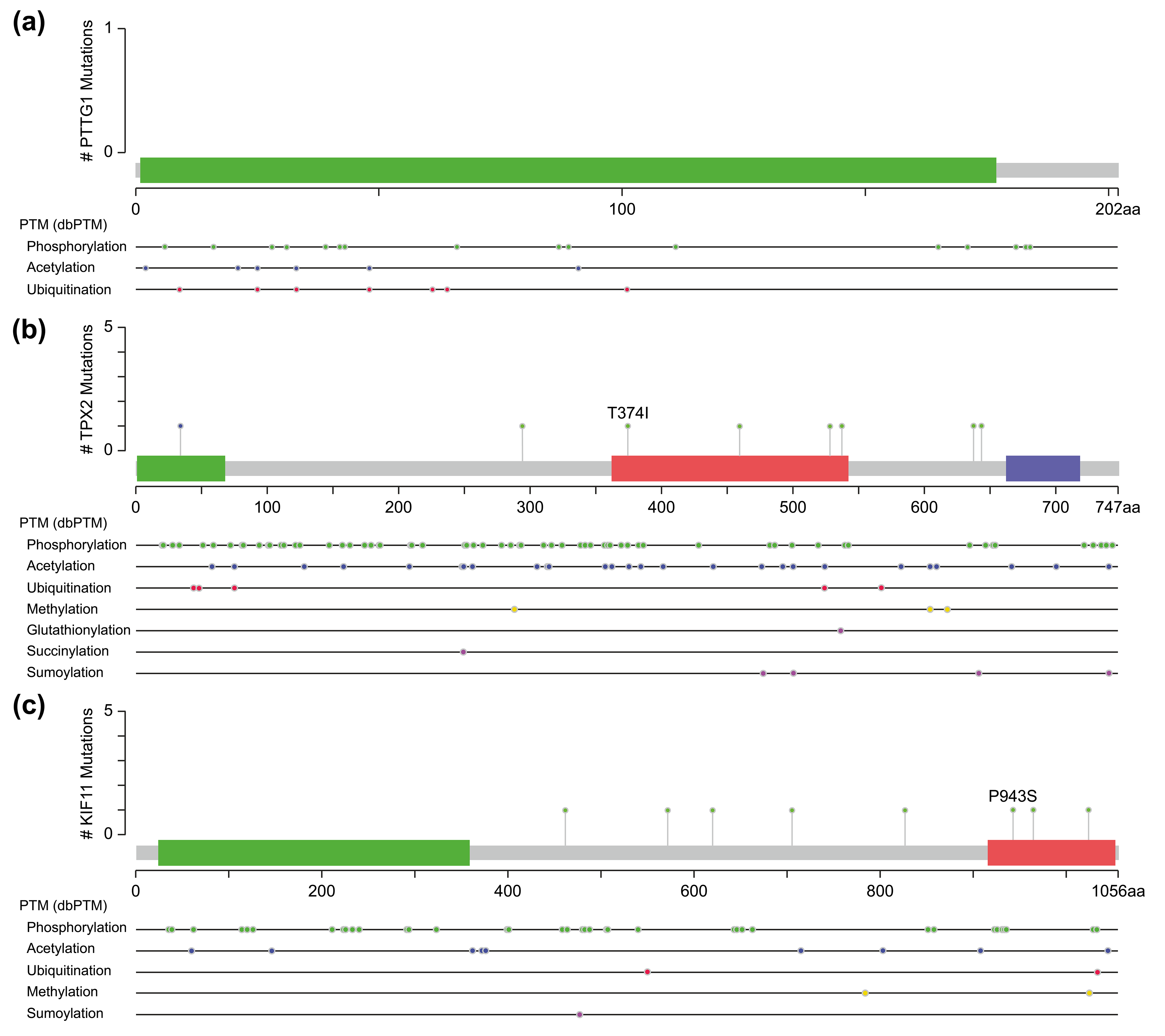
One of them comprised the CDK1, PTTG1, and mitogen-activated protein kinases/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (MAPK-ERK) signaling pathway. PTTG1 has been shown to be highly expressed in various neoplastic diseases, such as hepatocellular carcinoma, cholangiocarcinoma, and breast cancer [21, 22, 23], and is associated with tumor invasion and metastasis [24]. Both CDK1 and MAPK are kinases, whereas PTTG1 has sites for phosphorylation modification (Fig. 5a). However, activation of PTTG1 through phosphorylation by MAPK has not been confirmed in vivo, and there is a lack of studies on the PTTG1-MAPK-ERK-related pathway in cSCC.
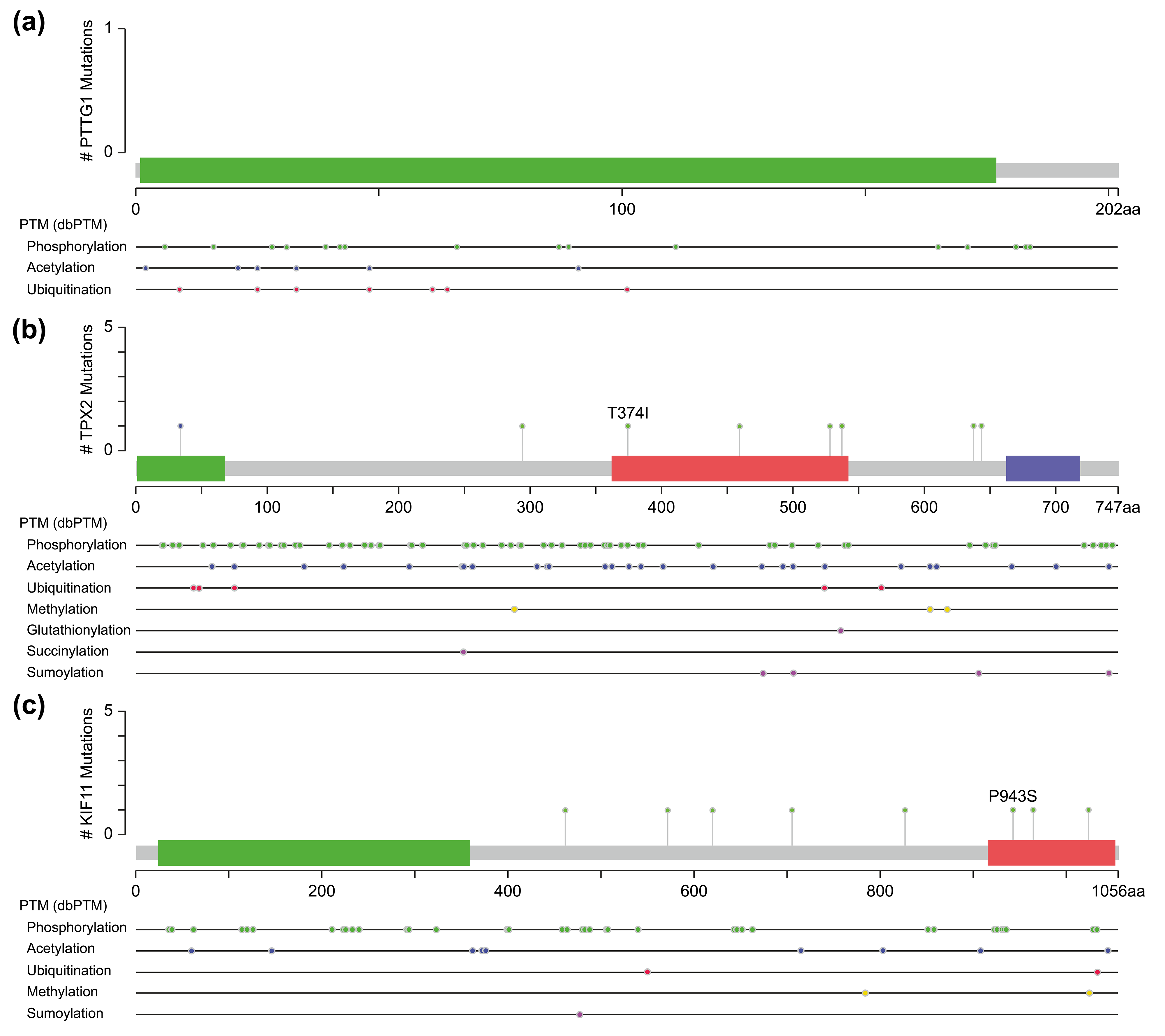 Fig. 5.
Fig. 5.Molecular structure and post-translational modification sites of PTTG1 (a), TPX2 (b), and KIF11 (c) according to cBioPortal.
Another pathway contained three genes, TPX2, KIF11, and CDK1, of which TPX2 and KIF11 are involved in the biological processes of spindle organization, mitotic spindle pole, and mitosis in the GO functional annotation. TPX2 includes three major functional domains: the N-terminal Aurora A kinase binding domain, the nuclear localization signal (NLS) structural domain, and the TPX2 structural domain (Fig. 5b). Among them, the TPX2 structural domain mediates the localization of Xklp2 to the mitotic spindle in Xenopus Leavis [25]. KIF11, a member of the Eg2 (KIF15) homolog family, is homologous to Xklp2. Therefore, it is reasonable to speculate that TPX2 interacts with KIF11 through the TPX2 domain and affects the function of the mitotic spindle, thereby leading to chromosomal instability [26], which is an important event in tumorigenesis. Regarding the role of CDK1 in the pathway, both TPX2 and KIF11 have a large number of sites for phosphorylation modification (Fig. 5b,c), especially TPX2, whose phosphorylation has a considerable effect on its function [27].
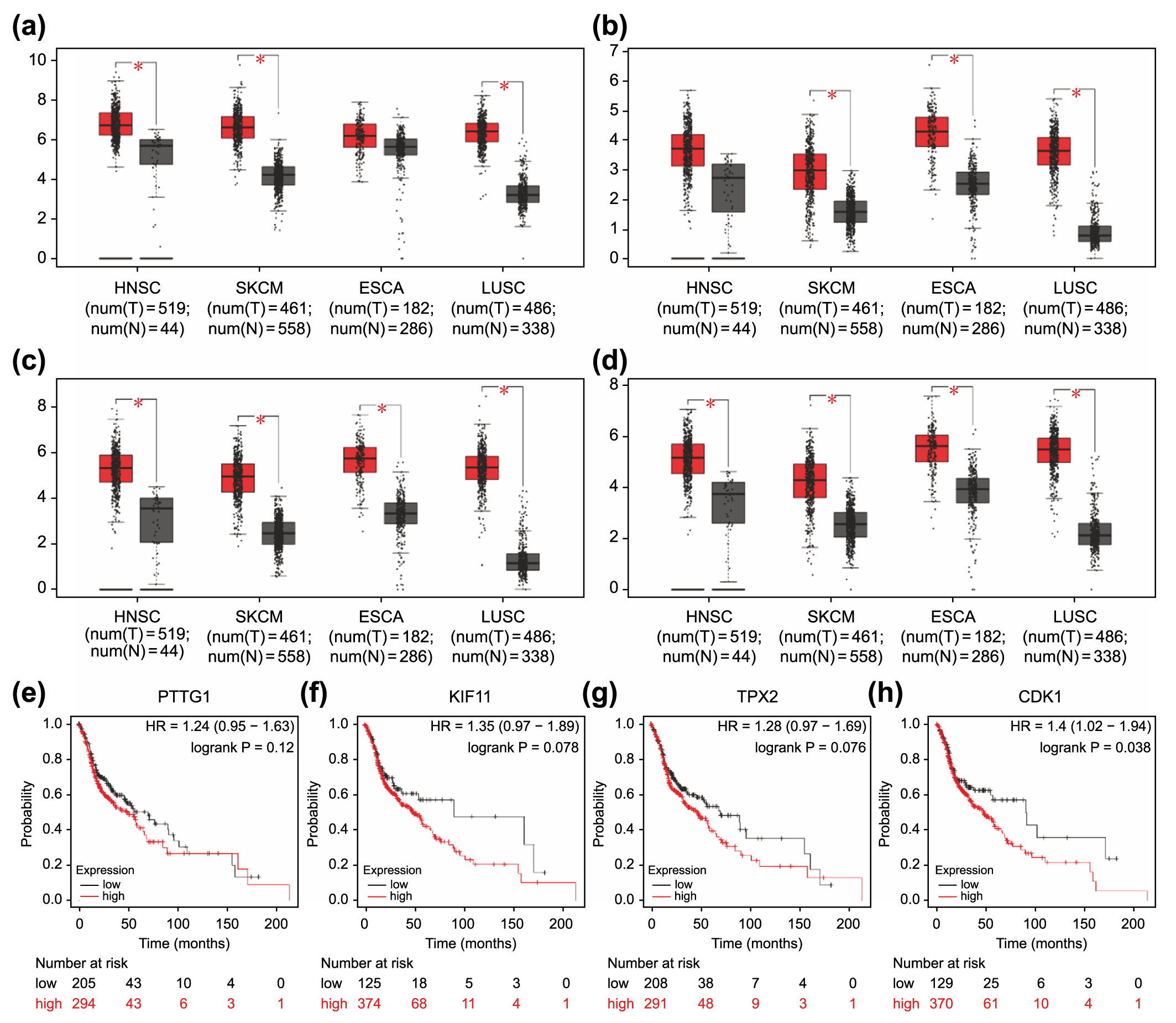
TPX2, KIF11, PTTG1, and CDK1 were
consistently highly expressed in the four selected GEO datasets (Fig. 3b). Owing
to the lack of a database involving prognosis-related clinical information for
cSCC, we validated the expression levels and prognostic relevance of these four
genes in a variety of squamous cell carcinomas of other tissues and cutaneous
malignant melanoma that was homozygous for cSCC (Fig. 6a–h). HNSC, which refers
to squamous cell carcinoma occurring mostly in the mucosal areas of the head and
neck, such as the tongue, pharynx, and larynx, is broadly classified as squamous
cell carcinoma of the skin. TCGA-based analyses showed that these four genes were
highly expressed in most squamous cell carcinomas, as well as cutaneous melanoma
(Fig. 6a–d). Moreover, elevated expression of these genes except for
PTTG1 was correlated with poorer overall survival in HNSC (p
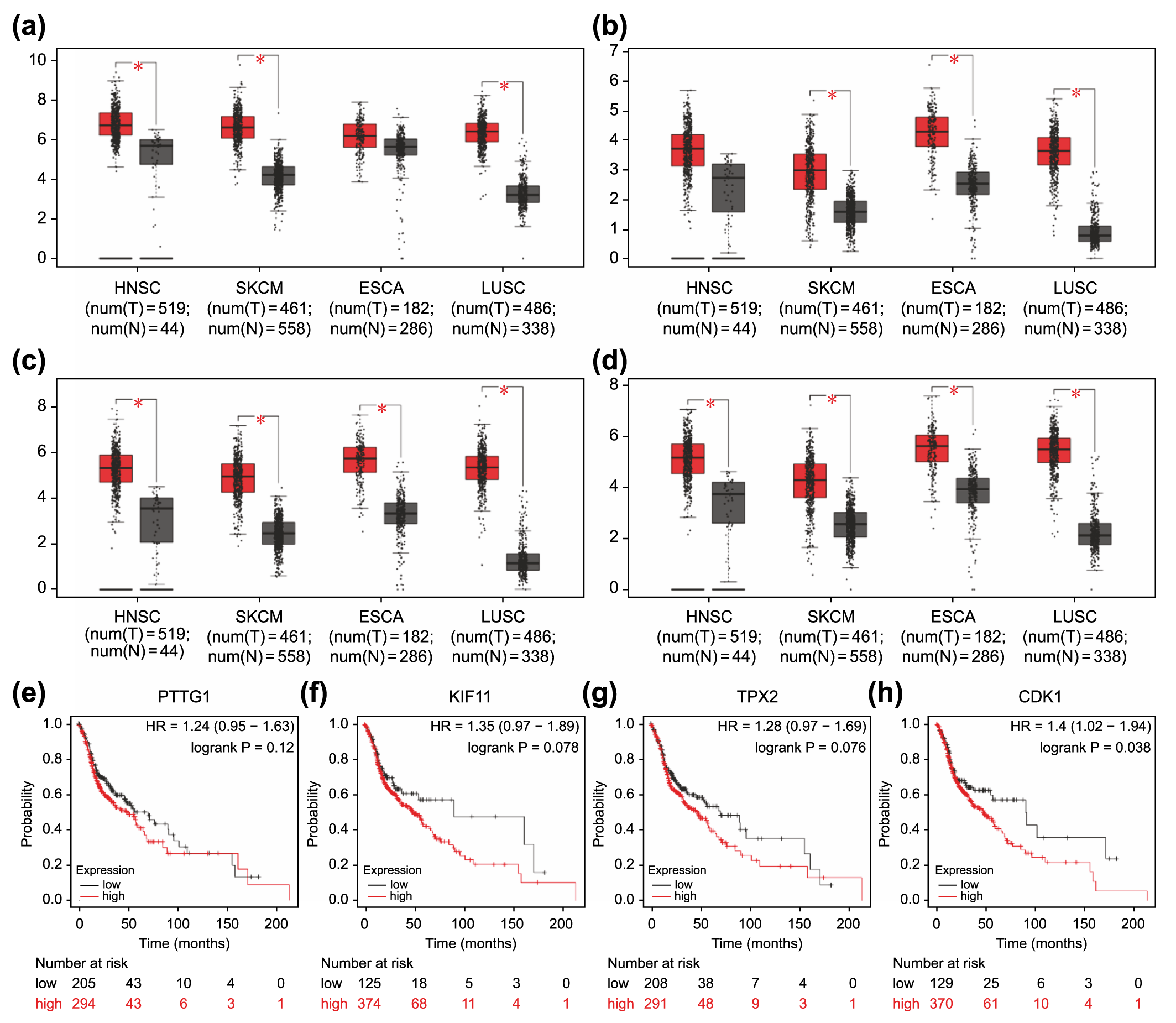 Fig. 6.
Fig. 6.Association of overexpressed core differentially expressed genes
in different types of carcinomas with poor prognosis. Expression levels of
PTTG1 (a), KIF11 (b), TPX2 (c), and CDK1 (d)
in four carcinoma types (HNSC, SKCM, ESCA, and LUSC). *p
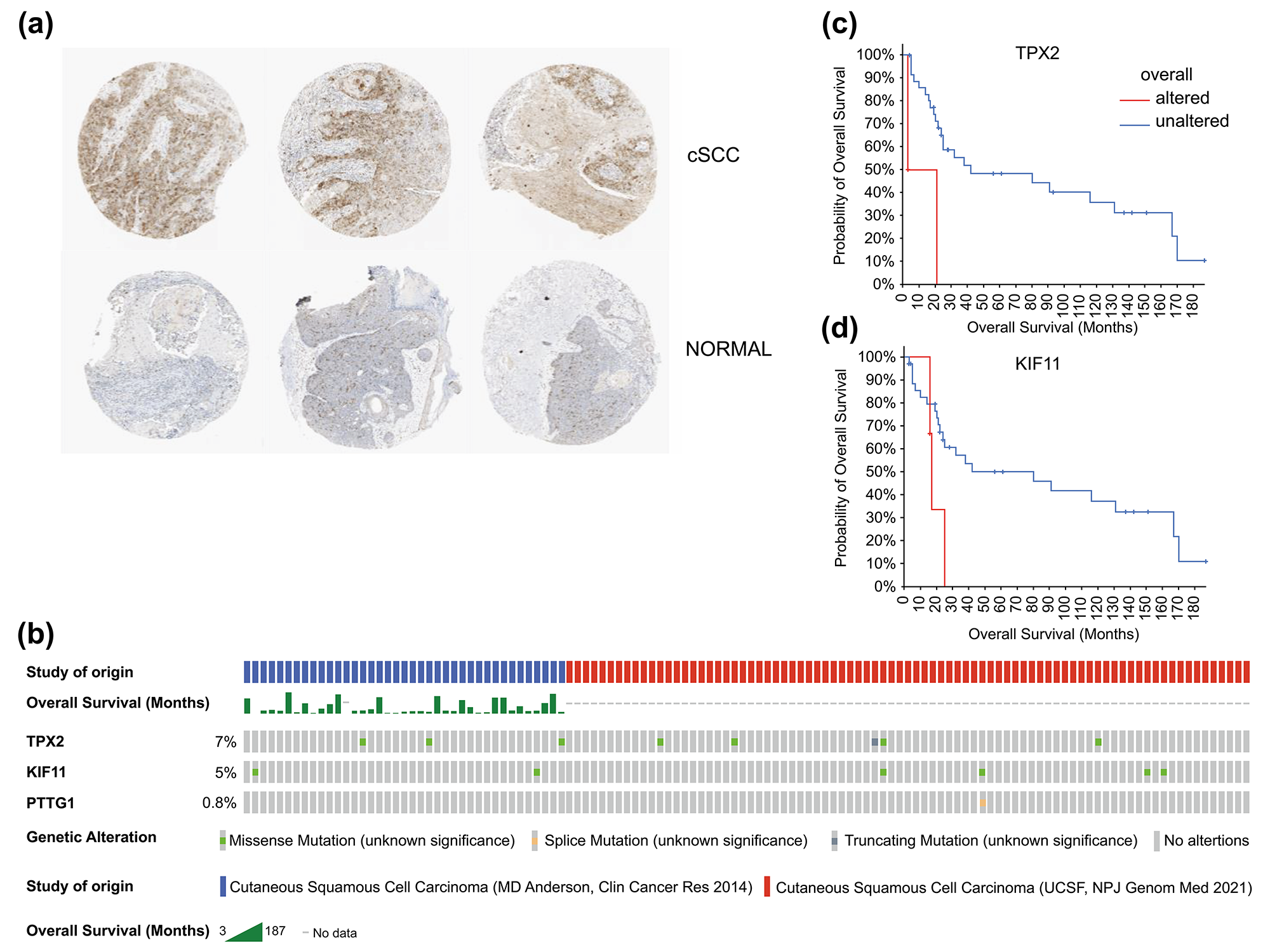 Fig. 7.
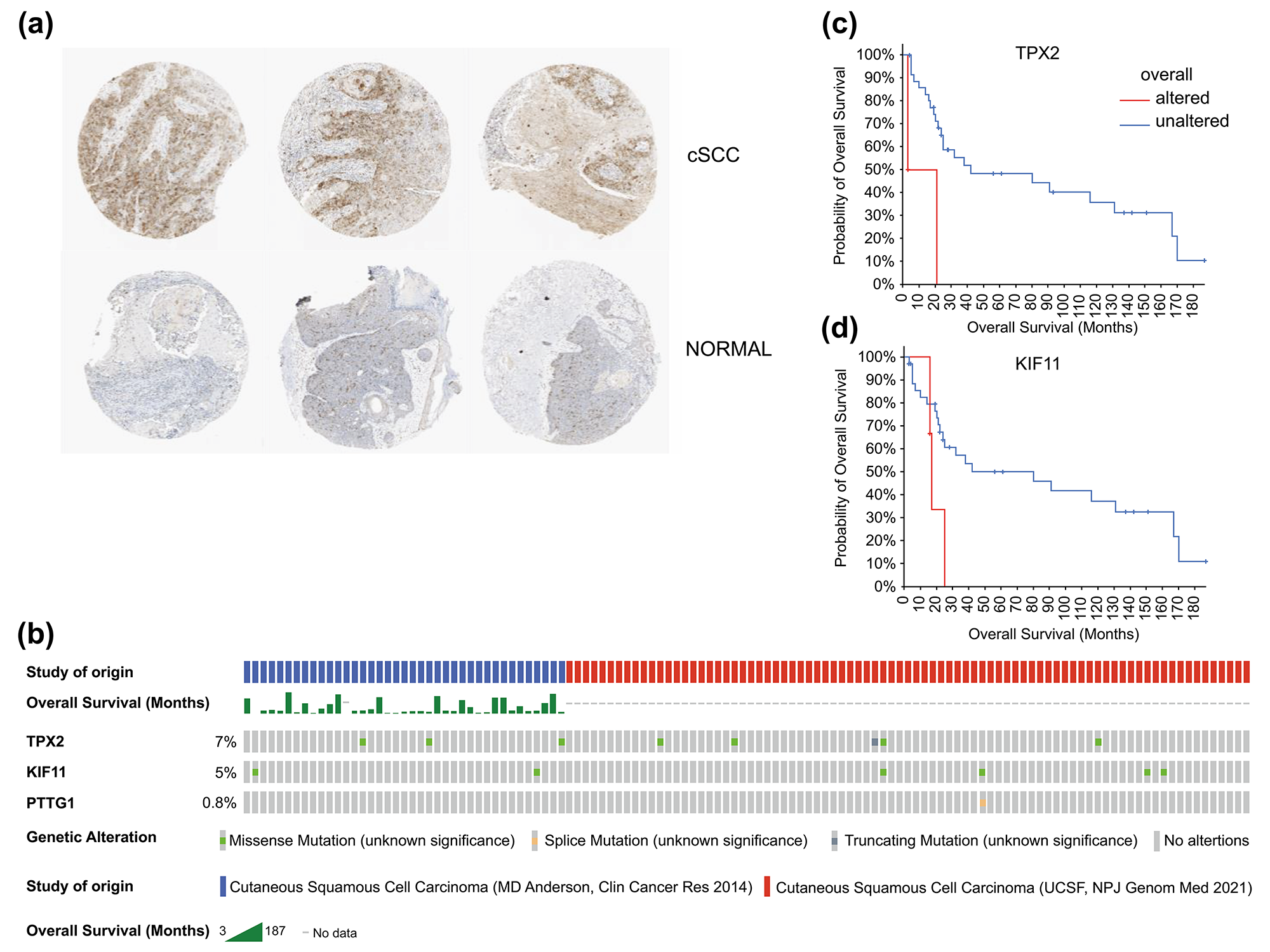
Fig. 7.Histological expression levels and mutation likelihood of TPX2 and KIF11 according to the HPA database and cBioPortal. (a) Histological expression levels of KIF11 in the HPA. (b) Mutation rates of TPX2, KIF11, and PTTG1 in cSCC. (c,d) Mutation-prognosis curves of TPX2 and KIF11. cSCC, cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma; HPA, Human Protein Atlas; KIFF, kinesin family member 11; TPX2, targeting protein for Xklp2.
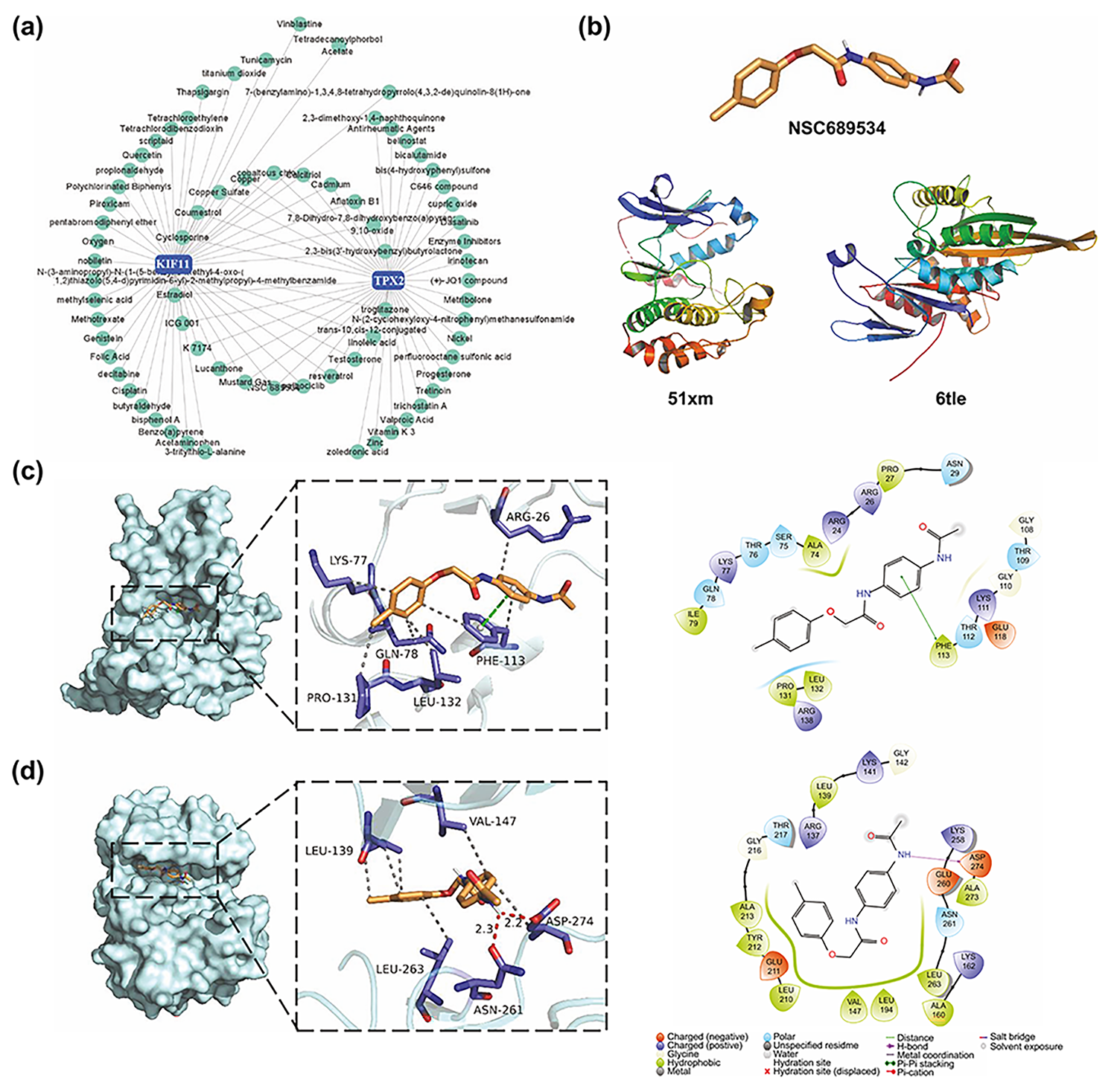 Fig. 8.
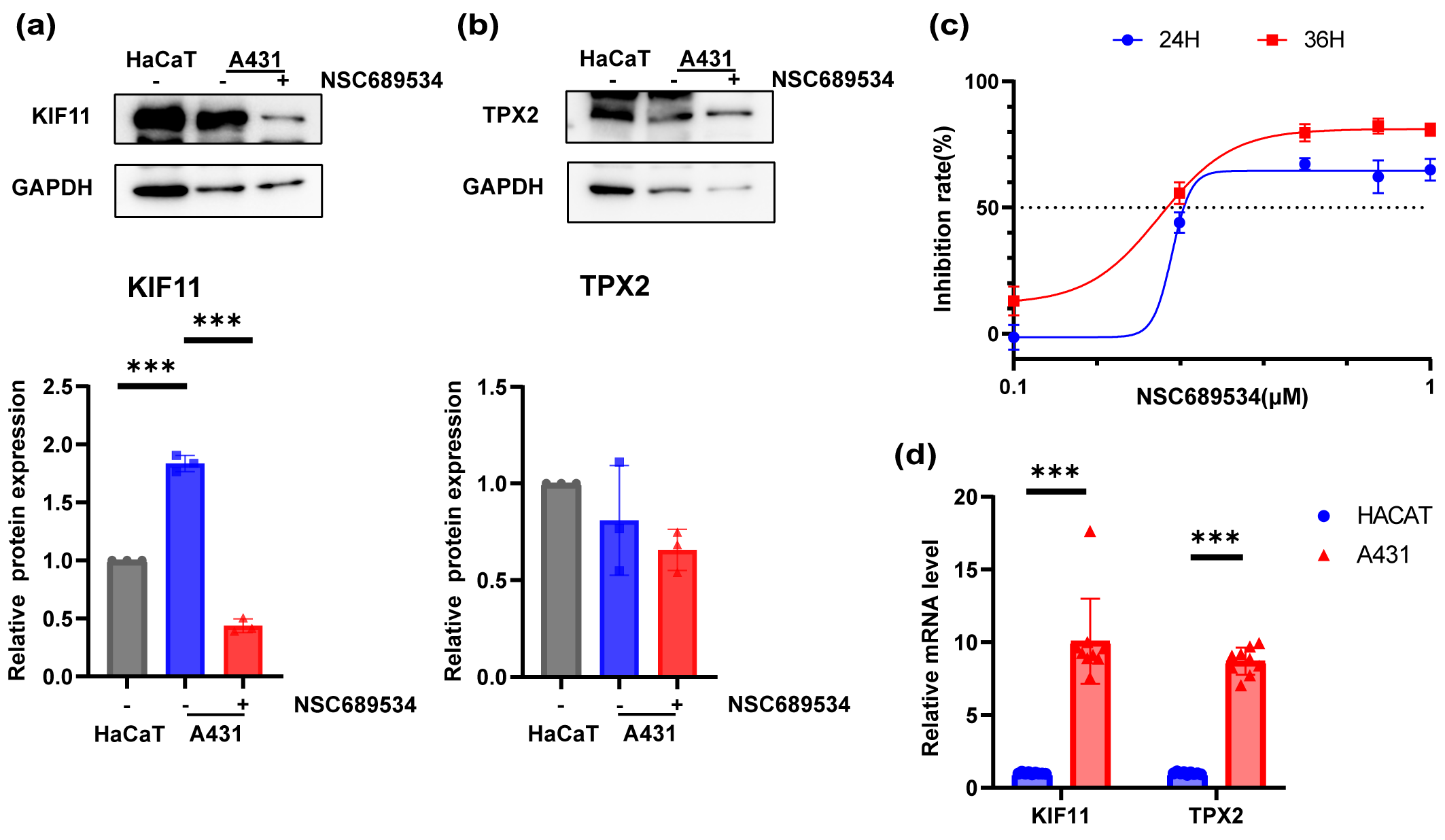
Fig. 8.In vitro vertification of the inhibition ability to
A431 cell line of NSC689534. (a,b) Expression levels of KIF11 (a) and TPX2 (b)
in HaCaT cell line, A431 cell line and A431 cell line with treatment of NSC689534
at 0.25 µM for 24 h by Western Blot. ***p
We also queried the mutation status of these genes in patients with cSCC using
cBioPortal. Except for PTTG1 with a mutation rate
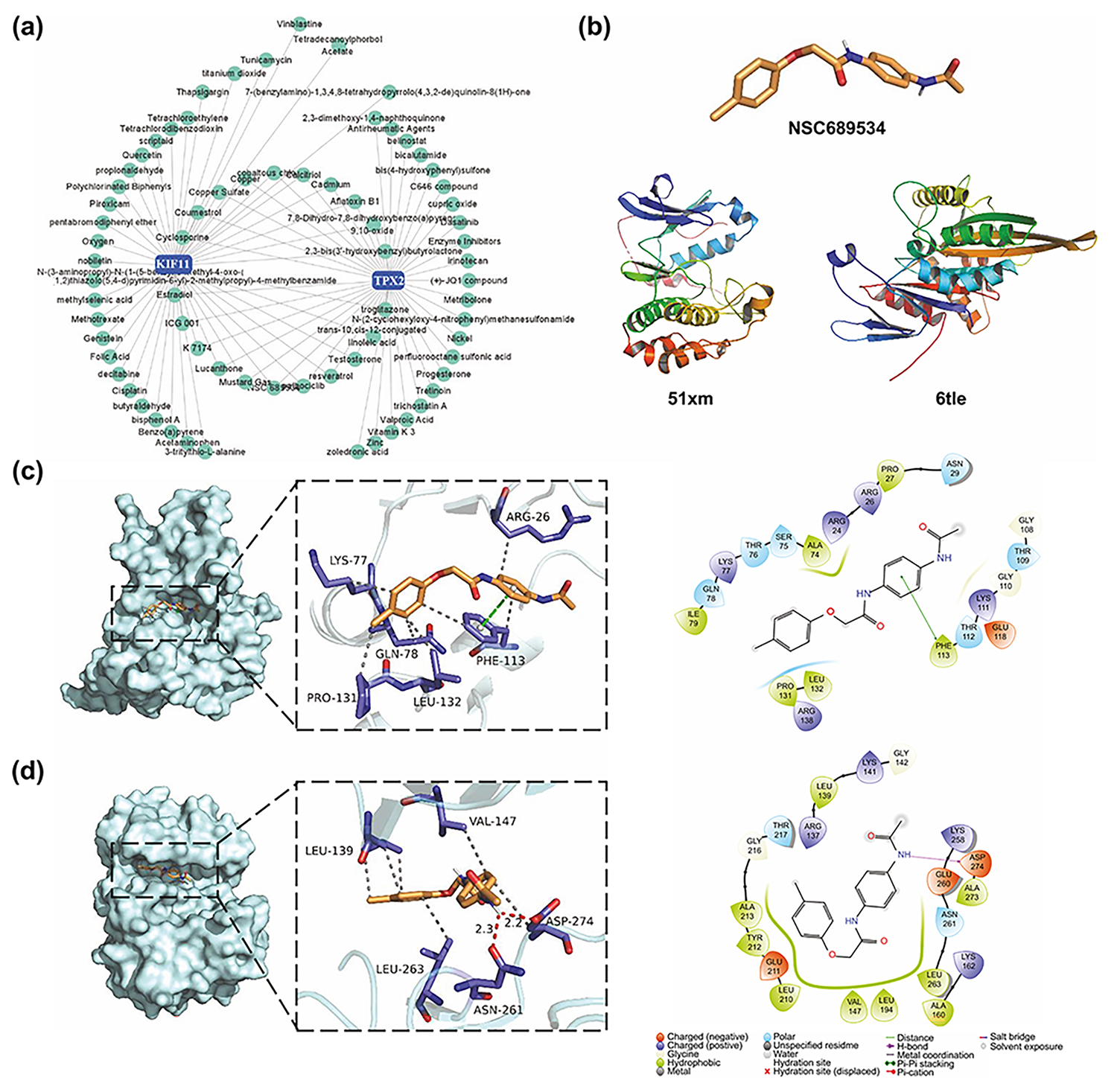
Based on the CTD database, interactions between small molecular compounds and
the gene TPX2 and KIF11 networks were visualized using the
NetworkAnalyst website (Fig. 9a). In total, 21 common small molecule compounds
were identified. After further analysis with the help of PubChem and published
literature, we excluded compounds that were inherently toxic (e.g., troglitazone
and mustard gas) and have been studied in cSCC (e.g., cyclosporine) [28, 29]. We
selected the pyridine 2-carbaldehyde thiosemicarbazone (NSC689534) (Fig. 9b) as
the target for further studies. Molecular docking analyses identified the
potential of NSC689534 to interact with KIF11 (Fig. 9c). Although TPX2 could not
dock directly with NSC689534, the TPX2-Aurora A complex, which affects spindle
length in human somatic cells [30], was able to interact with NSC689534 through
hydrophobic interactions (LEU139, VAL147, LEU263, and ASP274) and hydrogen bonds
(ASN216 and ASP274) with strong binding ability (Fig. 9d and Table 3). Likewise,
KIF11 bound NSC689534 strongly through four hydrophobic interactions and one
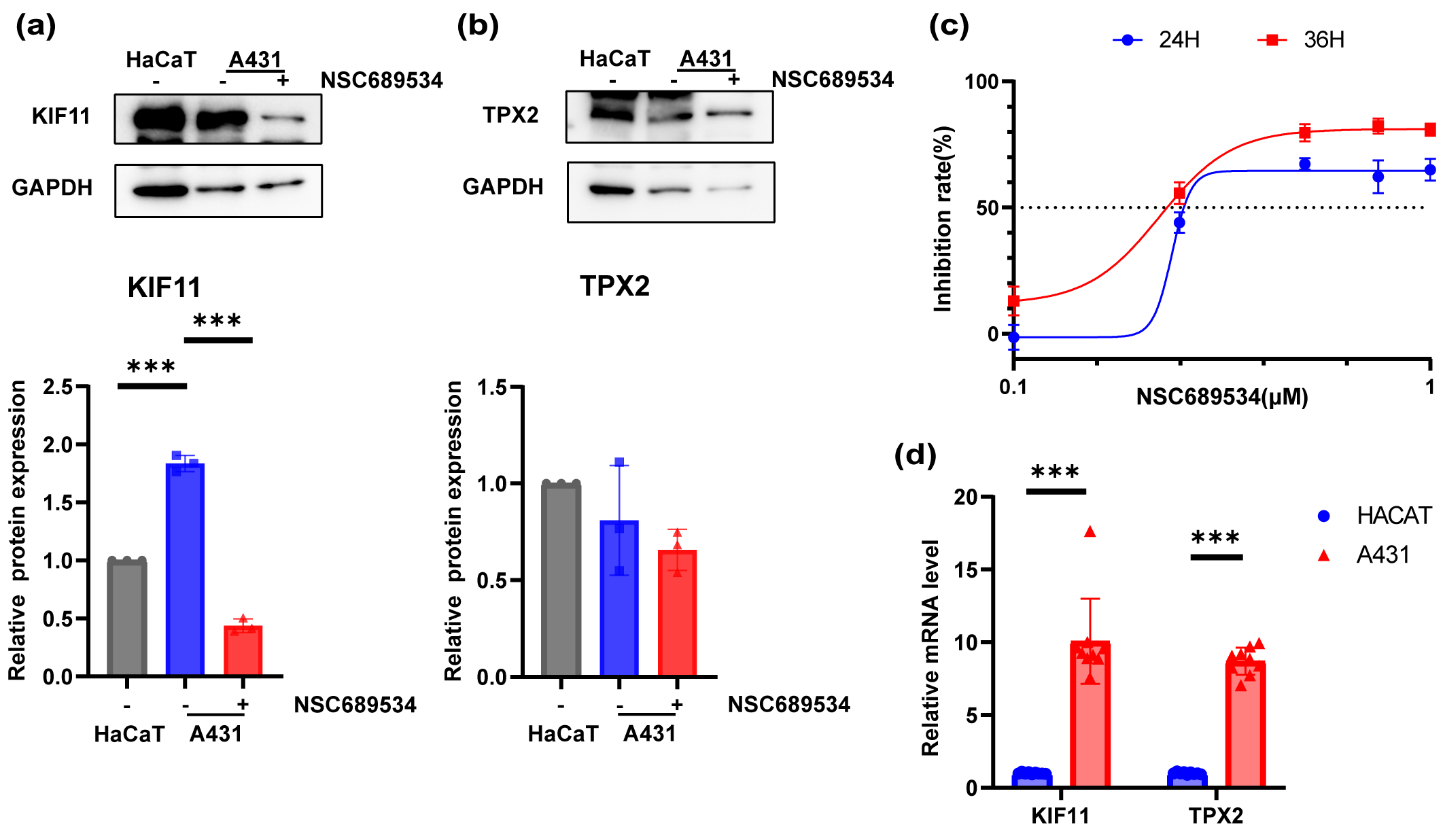 Fig. 9.
Fig. 9.NSC689534, a potential drug candidate targeting TPX2 and KIF11. (a) Small molecular compound-gene interaction network visualized on the NetworkAnalyst website. (b) Structure of NSC689534, KIF11, and TPX2. (c,d) Three-dimensional and two-dimensional structures of ligand (NSC689534)–receptor (KIF11, TPX2) interactions. KIFF, kinesin family member 11; TPX2, targeting protein for Xklp2.
| Ligand | Receptor | PDB ID | Binding affinity (kcal/mol) | Bonding length | Amino acid residues | Interaction |
| 689534 | TPX2 | 5lxm | −8.1 | 2.2 | ASP274 | Hydrogen bond |
| 2.3 | ASN264 | Hydrogen bond | ||||
| 689534 | KIF11 | 6tle | −7.3 | 3.7 | PHE113 | Π-stacking |
| Physicochemical properties | ||
| Formula | C | |
| Molecular weight | 362.45 g/mol | |
| Pharmacokinetics | ||
| Gastrointestinal absorption | High | |
| Blood-brain barrier permeant | No | |
| Drug-likeness | ||
| Lipinski | Yes; 0 violations | |
| Ghose | Yes | |
| Veber | Yes | |
| Egan | Yes | |
| Muegge | Yes | |
| Bioavailability score | 0.55 | |
| Medicinal chemistry | ||
| Synthetic accessibility | 3.22 | |
A431 cells were cultured in 96-well plates and exposed to different concentrations of NSC689534 for 24 h or 48 h. After determining the cell viability with CCK8 reagent, the inhibition ability of NSC689534 to A431 cells was confirmed (Fig. 8c). It was possible to achieve very impressive inhibition rate even at a low concentration of 0.5 µM. Subsequently, the protein expression of TPX2 and KIF11 was compared among normal keratinocytes, A431 cells and cSCC cells treated with NSC689534. It was found that NSC689534 could reduce the expression of KIF11 but not TPX2 (Fig. 8a,b). Combining results of molecular docking analysis (Fig. 8c,d), we consumed that NSC689534 interacted with KIF11 and then reduced its expression in cSCC cells. Our results suggested that NSC689534 could inhibit the proliferation of A431 cells and reduce the expression of KIF11.
In this study, we aimed to suggest a potential compound for future research that may benefit patients with cSCC. NSC689534 might be a candidate drug for cSCC targeting TPX2 and KIF11. cSCC is the second most common cutaneous malignancy among nonmelanoma skin cancers [32]. Most patients are in the early stages of the disease at the time of consultation and can be cured by surgical excision. However, cSCC has the ability to metastasize [10] and contributes to 20% of the mortality among skin tumors [33]. Once a tumor metastasizes, surgical treatment is often insufficient. For instance, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, EGFR inhibitors, and immune checkpoint inhibitors (e.g., the PD-1 inhibitor cemiplimab) can be selected as adjuvant therapies or combined for systemic therapy. Unfortunately, satisfactory long-term outcomes remain difficult to achieve [12]. Moreover, few articles using bioinformatics have been devoted to identify potential drugs for cSCC. Screening for DEGs that distinguish cSCC from normal skin tissue using public databases can help search for new biomarkers for cSCC and targets for the subsequent discovery of potential drugs using molecular docking analysis.
Here, we identified in four microarray datasets 51 shared DEGs that were significantly associated with skin diseases and enriched in multiple signaling pathways in cSCC. Based on the PPI network constituted by String and the plug-in MCODE, two key functionally relevant modules were extracted, where the genes were all associated with mitosis and cell cycle. With the aid of protein causality annotations stored in the SIGNOR3.0 database, we identified two signaling pathways.
One of the pathways consisted of the CKD1, PTTG1, and MAPK-ERK signaling pathways. PTTG1 was isolated from rat pituitary tumor cells in 1997 [34], and its overexpression has been reported in a variety of endocrine-related tumors and non-endocrine-related cancers involving the central nervous, pulmonary, and gastrointestinal systems [35, 36, 37, 38, 39]. PTTG1 has been recognized as a key signature gene associated with tumor metastasis [40]. PTTG1 phosphorylation is important for protein activation [41], and cell cycle-dependent phosphorylation during mitosis may be associated with cell migration [42]. MAPK has the ability to phosphorylate PTTG1 in rats, which is associated with the transactivation of PTTG1 [43]. Accordingly, CDK1 and MAPK were inferred to be capable of phosphorylating PTTG1 at different sites with distinct effects. In turn, the activation of PTTG1 can also contribute to tumor metastasis via the MAPK-ERK signaling pathway [22]. It has been reported that in cSCC, PTTG1 might be a biomarker for tumor metastasis associated with mutated p53 protein, but its value for the prediction of prognosis is unknown [44]. Consistently, our overall survival analysis based on the TCGA database revealed no statistically significant impact of PTTG1 expression levels on HNSC prognosis. Consequently, this signaling pathway was not selected for further investigations in subsequent screenings of small-molecule compounds. Nevertheless, considering that HNSC represents only a section of all cSCCs and that the involvement of PTTG1 in the MAPK-ERK signaling pathway in cSCC has not been experimentally examined, a prognostic value of PTTG1 in cSCC cannot be completely rejected.
Another pathway involved two core genes, TPX2 and KIF11, as well as CDK1, which is not considered a core gene but differed in the four datasets. Both TPX2 and KIF11 are involved in mitosis [45]. They are able to interact in certain ways, but there is no unified perspective on the mechanism of their interaction and impact [45, 46, 47, 48]. In a recent study, TPX2 was shown to regulate spindle motility through a C-terminal interaction with KIF11 [46], which was the first report of a direct interaction between TPX2 and KIF11. Unfortunately, no study to date has verified this interaction in the context of human cSCC. TPX2 consists of three major functional domains: the N-terminal Aurora A kinase binding domain, single NLS domain, and TPX2 structural domain, of which the NLS domain is associated with the nuclear expression of TPX2 [49]. We hypothesize that CDK1 interferes with the nuclear transport process of TPX2 by phosphorylating its NLS domain, which ultimately affects the formation of the TPX2-KIF11 complex.
Subsequently, NSC689534 was selected as a potential small-molecule compound that
can act on both TPX2 and KIF11, based on the CTD database and available
literature. The results of molecular docking analyses showed that NSC689534 was
capable of strongly binding to KIF11 with a binding energy of –7.3 kcal/mol,
whereas it could not bind to TPX2 directly. In the next validation in
vitro, the expression of KIF11 but not TPX2 was down-regulated with the
treatment of NSC689534. Meanwhile, the compound had properties of suitable
molecular weight, lipophilicity, pharmacokinetic effects, drug-likeness, and good
synthetic accessibility. As to side effects, there were no studies reporting on
the toxicity. While in an in vivo research, NSC689534 did not lead to
any loss in animal models [31]. The above analysis suggested that this compound
had the potential to be an effective inhibitor of KIF11. Various
thiosemicarbazones, such as Triapine, have been explored as anti-tumor agents
[25, 50]. NSC689534 was reported to be capable of inducing cell death associated
with reactive oxygen species generation and depletion of cellular glutathione
[51, 52], whereas Cu
Overall, our study suggests that CDK1, TPX2, and KIF11 may play a role in the development of cSCC by forming a signaling pathway that affects spindle organization and mitosis through their interactions. NSC689534 may be a potential drug candidate for the treatment of cSCC owing to its satisfactory bioavailability, synthetic accessibility, and relatively strong binding ability with KIF11, and the efficiency in vitro.
However, it should be noted that in vivo validation experiments are lacking, which is the main limitation of the present study. Moreover, our study suggested the compound’s effect on the interaction and expression of KIF11. Whether NSC689534 inhibited cell proliferation by affecting mitosis through interactions with KIF11 or induced apoptosis through oxidative stress as suggested in other essays remained to be shown. Thus, the detailed mechanism of NSC689534 needed more experiments to confirm. In the future, we will focus on validating the function of the two core genes in vivo and the mechanism of NSC689534 in vivo.
Based on the study findings, we propose a potential signaling pathway involved in the development of cSCC, where TPX2 and KIF11 may play an important role. This pathway ultimately affects spindle organization and mitosis. Both of them were proved to be highly expressed in mRNA level in the A431 cell line. Thus, NCS 689534 may be a potential drug candidate targeting KIF11 in this pathway. However, the hypothesis regarding the mechanism and specific role of NSC689534 in cSCC still requires further experimental validation. Our findings suggest a potential drug for progressive cSCC and prove the value of NSC689534 for further research, which provide new insights into systemic therapy for progressive cSCC.
CTD, Comparative Toxicogenomics Database; cSCC, cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma; DEG, differentially expressed gene; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; FC, fold change; GEO, Gene Expression Omnibus; GO, gene ontology; HNSC, head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; HPA, Human Protein Atlas; KIFF, kinesin family member 11; MCC, Matthews Correlation Coefficient; NLS, nuclear localization signal; PPI, protein-protein interaction; PTTG1, pituitary tumor transforming gene; SIGNOR, SIGnaling Network Open Resource; TBST, tris-buffered saline with Tween-20; TCGA, Cancer Genome Atlas; TPX2, targeting protein for Xklp2.
The data involved in this study could be obtained from publicly available online database. The online sites include the following: GEO (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/); GO (https://www.geneontology.org/); KEGG (https://www.genome.jp/kegg/); Reactome Gene Sets (https://reactome.org/); WikiPathways (https://www.wikipathways.org/); STRING (https://cn.string-db.org/); SIGNOR (https://signor.uniroma2.it/); TCGA (https://portal.gdc.cancer.gov/); cBioPortal (https://www.cbioportal.org/); The Human Protein Atlas (https://www.proteinatlas.org/); CTD (https://ctdbase.org/); PubChem (https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/); UniProt (https://www.uniprot.org/). All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
YM and XDC designed and conducted the study. CS analyzed the data and collated the figures. XZ, QQL, AYP, and WMZ contributed to analysis of data and the original draft. XYW helped prepare the figures. HYQ provided financial support for the research and interpretation of data. YM, CS, HYQ and XDC contributed to editorial changes in the manuscript. All authors have contributed to editorial changes in the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. All authors have participated sufficiently in the work and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Not applicable.
The authors thank all individuals who participated in this study. We would like to thank Editage (www.editage.cn) for English language editing.
This study was funded by the Foundation of Nantong Science and Technology Bureau (JC2020025), Health Committee of Nantong (MB2020021), and Clinical Medicine Special Program of Nantong University (2019JY017). The funding sources were involved in the collection, analysis, and interpretation of data; the preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript; and the decision to submit the manuscript for publication.
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Publisher’s Note: IMR Press stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.