1 Department of Breast Medicine, Southern Medical University Affiliated Maternal & Child Health Hospital of Foshan, 528000 Foshan, Guangdong, China
†These authors contributed equally.
Abstract
Background: Ferroptosis, a distinct iron-dependent
form of regulated cell death, is induced by severe lipid peroxidation due to
reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation. Breast cancer patient survival is
correlated with the tumor-suppressing properties of Rho guanosine triphosphatase hydrolase enzyme (GTPase)-activating protein
6 (ARHGAP6). This study investigates the impact and mechanisms of ARHGAP6 on
ferroptosis in breast cancer. Methods: Using quantitative
RT-PCR, Western blotting, and immunofluorescence staining, ARHGAP6 expression was
detected in a gene expression dataset, cancer tissue samples, and cells. ARHGAP6
was overexpressed or silenced in breast cancer cell lines. Cell proliferation was
measured using 5-ethynyl-2-deoxyuridine (EdU) assay, and cell death rate was
determined using LDH cytotoxicity assay. As indicators of ferroptosis, Fe
Keywords
- breast cancer
- ARHGAP6
- ferroptosis
- p38 MAPK
Breast cancer leads to the fifth mortality rate among all female cancer diseases and has a 6.6% mortality rate [1, 2]. In recent years, breast cancer treatment includes refined surgical resection, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, targeted therapy, and endocrine therapy [3]. However, breast cancer patients’ survival remains unfavorable [4]. Therefore, extensive efforts are urgently needed to design and develop novel effective therapeutic strategies for breast cancer patients.
Ferroptosis is an iron-dependent type of nonapoptotic cell death accompanied by mitochondrial alterations due to increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation resulting from excessive lipid peroxidation [5]. Glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) converts reduced GSH to oxidized GSSG and reduces excess oxidized lipids due to the presence of ROS in the reaction [6]. Solute carrier family 7 member 11 (SLC7A11) as an anti-ferroptotic marker produces glutathione to regulate GPX4 activity [7]. Acyl-CoA synthetase long chain family member 4 (ACSL4), a positive regulator of ferroptosis, activates long-chain fatty acids for lipid synthesis, increasing cellular ferroptotic susceptibility [6]. Prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2 (PTGS2) and ChaC glutathione specific gamma-glutamylcyclotransferase 1 (CHAC1) are two well-documented biomarkers of ferroptosis [8]. Ferroptosis is closely related to cancer initiation and development and contributes to the therapeutic treatment responses of various cancers including breast cancer [9]. A promising therapeutic approach to breast cancer treatment is the induction of ferroptosis to eliminate cancer cells [10, 11].
Rho guanosine triphosphatase hydrolase enzyme (GTPases)-mediated signaling transduction is crucial for the progression of human malignances [12]. Rho GTPase-activating protein 6 (ARHGAP6) regulates actin polymerization, contributing to tumor growth and metastasis [13]. Previous studies revealed that ARHGAP6 downregulation may suppress tumor formation in bladder, breast, cervical, and lung cancer [14, 15, 16, 17], and evidence showed that ARHGAP6 expression is related to breast cancer patients’ survival [14]. Ras homolog family member A (RhoA) is a small GTPase protein that switches from GTP-bound state to GDP-bound state by hydrolyzing GTP [17]. Another study demonstrated an interaction between RhoA and p38 MAPK, which is activated in breast cancer [18]. RhoA and p38 MAPK are also associated with ferroptosis [19, 20, 21]. Nevertheless, the association of ARHGAP6 with ferroptosis and related regulatory mechanisms in breast cancer remains elusive.
This study detected ARHGAP6 expression in breast cancer tissue samples harvested
from hospitalized patients, and breast cancer cell lines to elucidate the
biological role of ARHGAP6. The impact of ARHGAP6 overexpression or knockdown on
ferroptosis was investigated by measuring the Fe
Gene expression data was obtained from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database (https://www.cancer.gov/about-nci/organization/ccg/research/structural-genomics/tcga) that included 1104 tumor tissues and 113 normal breast tissues. Using the gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) algorithm, pathways enriched between samples with low or high expression of ARHGAP6 were identified.
A total of 30 tumor and matched adjacent-normal tissue samples were collected from breast cancer patients at the Southern Medical University Affiliated Maternal & Child Health Hospital of Foshan. A signed informed consent was obtained from all patients. The medical ethics committee of Southern Medical University Affiliated Maternal & Child Health Hospital of Foshan (No. FSFY-MEC-2021-042) approved the present retrieval method of cancer tissue samples. To measure ARHGAP6 levels, a human breast cancer tissue microarray (Outdo Biotech Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) containing 75 tumor tissues and 20 adjacent normal breast tissues were used.
Human breast cancer tissue microarray was analyzed using immunohistochemistry.
Tissue slides were incubated with using anti-ARHGAP6 antibody (NBP2-49417, Novus
Biologicals, LLC, Centennial, CO, USA). Using the H-score system,
immunoreactivity was scored based on positively stained cells and staining
intensity [22]. Breast cancer patients were classified into high-expression
(H-score
Human breast cancer cell lines (BT-474, MCF-7, SKBR3, and ZR751) and a
nontumorigenic human breast epithelial cell line (MCF-10A) were obtained from the
American Type Culture Collection (ATCC, Manassas, VA, USA) and were maintained in
RPMI 1640 (11875119, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) media
supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum and 1% penicillin/streptomycin (Life
Technologies) in a humidified incubator with an atmosphere of 5% CO
RNA interference sequences targeting ARHGAP6 (siRNA#1 AGCAGAAGUCAUCAGACAAAG; siRNA#2 CAAUCAGUCUCGACUACUAGA; siRNA#3 CACCGAUCUUGAUGACAAUCA) and scramble siRNA sequence (GCCUGACCAUACACUCGCUCA) were synthesized and transfected into breast cells using Lipofectamine 2000 system according to the manufacturer’s protocol (11668500, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Human ARHGAP6 coding cDNA sequence was synthesized by Sangon Biotech as well and inserted into the pLVX-Puro vector (QYV0008, Beijing qualityard biotechnology Co., Ltd., China). Transfection was performed using the Lipofectamine 2000 system. Subsequently, 48 h after transfection, recombinant vector in the cell supernatant was collected and transduced into breast cancer cells.
MCF-7 cells transduced with indicated vectors were treated with or without 25 µM apoptosis inhibitor zVAD-fmk, 20 µM necroptosis inhibitor necrostatin-1, 10 µM ferroptosis inhibitor ferrostatin-1, or 1 µg/mL RSL3 (all from Selleck, Shanghai, China). BT-474 cells transfected with siARHGAP6 or siNC were treated with or without SB203580 (10 µM; Selleck). The cells were stained according to the instructions of the BeyoClick™ EdU Cell Proliferation Kit (C0071S, Beyotime Biotechnology, Shanghai, China). Cells were then incubated with DAPI solution and were observed using fluorescence microscopy.
MCF-7 cells transduced with indicated vectors were treated with or without 1 µg/mL RSL3. BT-474 cells transfected with siARHGAP6 or siNC were treated with or without 10 µM SB203580. Cell death rate was determined using the lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) cytotoxicity assay kit (Beyotime Biotechnology, Shanghai, China) as per manufacturer’s instructions and calculated as previously described [23].
MCF-7 cells transduced with indicated vectors were treated with or without 1
µg/mL RSL3. BT-474 cells transfected with siARHGAP6 or siNC were
treated with or without 10 µM SB203580. The level of lipid ROS was
quantified using C11-BODIPY (581/591) assay (D3861, Thermo Fisher Scientific,
Waltham, MA, USA). Briefly, the cell suspension was added with 10 µM
C11-BODIPY (581/591) and incubated for 30 min at 37 °C in the dark.
Fluorescence intensity was measured using an Accuri™ C6 flow
cytometer (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA, USA). To detect for Fe
Total RNA was extracted using TRIzol solution (Thermo Fisher Scientific). The
first-strand cDNA was synthesized using the Hifair® II 1st
Strand cDNA Synthesis SuperMix for qPCR (Yeasen Biotechnology (Shanghai) Co.,
Ltd., Shanghai, China) as per manufacturer’s instructions. Using the
Hieff® qPCR SYBR Green Master Mix (Yeasen Biotechnology
(Shanghai) Co., Ltd) on an ABI 7300 real-time PCR system (Applied Biosystems,
Foster, CA, USA), quantitative RT-PCR was performed. The primers used included
the following: ARHGAP6-F: 5
Proteins were lysed from tumor tissues and cell lines using radioimmunoprecipitation assay buffer (50 mM Tris, pH 7.4, 150 Mm NaCl, 1% NP-40, 100 mM NaF) with protease and phosphatase inhibitor cocktail. Proteins were separated by sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and transferred onto nitrocellulose membranes (Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA). Then, the membranes were incubated with primary antibodies against ARHGAP6 (Invitrogen; PA5-104106), ROCK1 (ab97592, Abcam, Waltham, MA, USA), GPX4 (ab125066, Abcam), PTGS2 (ab179800, Abcam), CHAC1 (ab217808, Abcam), ACSL4 (ab155282, Abcam), SLC7A11 (ab175186, Abcam), GAPDH (5174, Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA, USA), p-p38 (4511, Cell Signaling Technology), and p38 (9212, Cell Signaling Technology), followed by incubation with HRP-conjugated secondary antibodies (A0208, Beyotime Biotechnology).
MCF-7 cells were transduced with indicated vectors, and BT-474 cells transfected with siARHGAP6 or siNC were treated with or without Y-27632 (10 µM; Selleck), and the RhoA activity was measured using a Rho Activation Assay Biochem Kit (Cytoskeleton, Denver, CO, USA).
MCF-7 cells (5
Tissues samples collected from the xenograft tumor were incubated using anti-Ki67 (ab245113, Abcam) and Alexa Fluor 488-labeled Goat anti-mouse IgG (H + L) (A0428, Beyotime Biotechnology) antibodies, followed by DAPI (C1002, Beyotime Biotechnology) labeling. Using a confocal laser scanning microscope (Leica Microsystems, Inc., Deerfield, IL, USA), the positively stained cells were then visualized.
Statistical analysis was performed using GraphPad Prism 8.4.2 (GraphPad
Software, San Diego, CA, USA). All experiments were performed in triplicate, and
quantitative data were expressed as mean
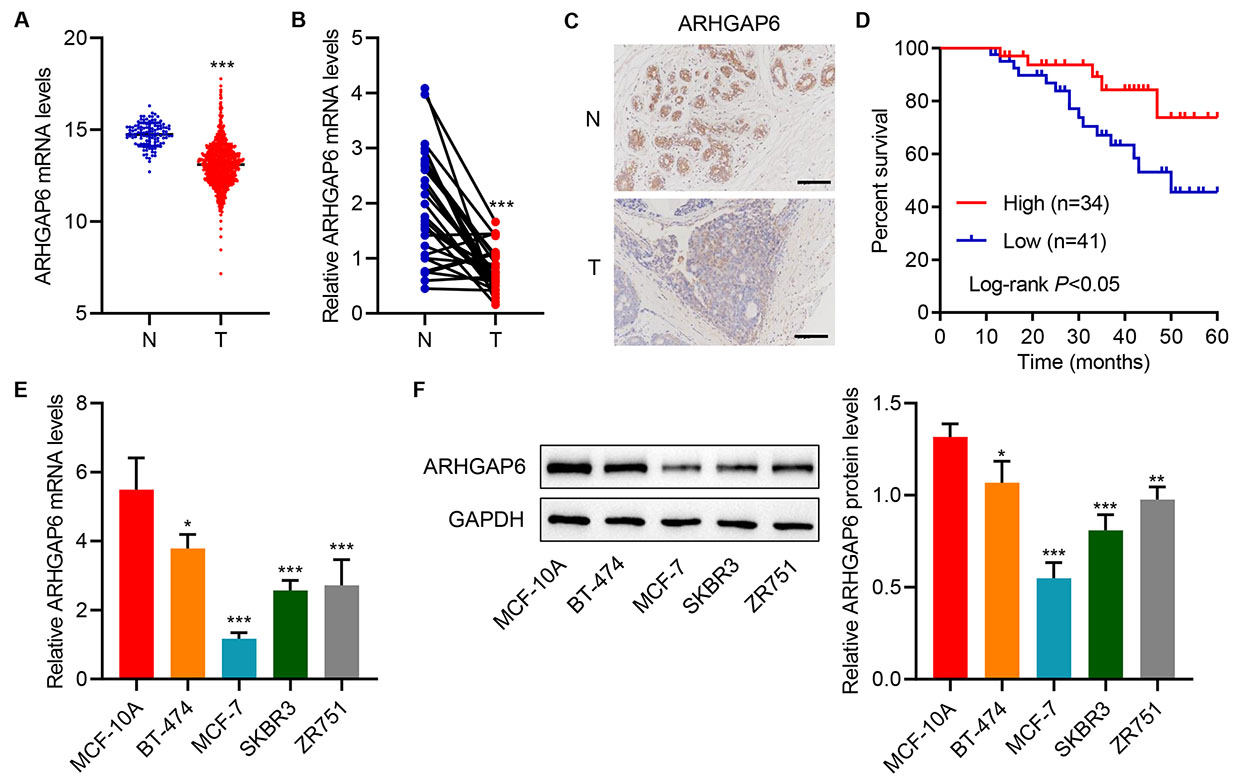
TCGA dataset gene expression data screening showed that ARHGAP6 mRNA level was
decreased in tumor samples compared with normal samples (Fig. 1A). Moreover, 30
clinical tumor samples were collected from hospitalized breast cancer patients.
Quantitative RT-PCR showed that the mRNA level of ARHGAP6 was markedly decreased
in tumor samples compared with adjacent-normal tissues (Fig. 1B).
Immunohistological staining also demonstrated a low ARHGAP6 protein expression
levels in tumor samples compared with adjacent-normal tissues from human breast
cancer tissue arrays (Fig. 1C). The patients with high ARHGAP6 expression
(H-score
 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.Rho GTPase-activating protein 6 (ARHGAP6) expression is
decreased in tumor tissues and cell lines. (A) ARHGAP6 expression in tumor
tissues (T; n = 1104) and adjacent-normal tissues (N; n = 113) in the TCGA
database. (B) ARHGAP6 mRNA levels in tumor tissue (T; n = 30) and corresponding
adjacent-normal tissue (N; n = 30) in the hospitalized breast cancer patient
cohort. (C) ARHGAP6 expression in tumor tissue arrays. (D) Survival of breast
cancer patients. (E,F) ARHGAP6 expression in human breast cancer cell lines
(BT-474, MCF-7, SKBR3, and ZR751) and nontumorigenic human breast epithelial cell
line (MCF-10A) was determined (n = 3). GTPase, guanosine triphosphatase hydrolase enzyme.
Scale bar: 100 µm. *p
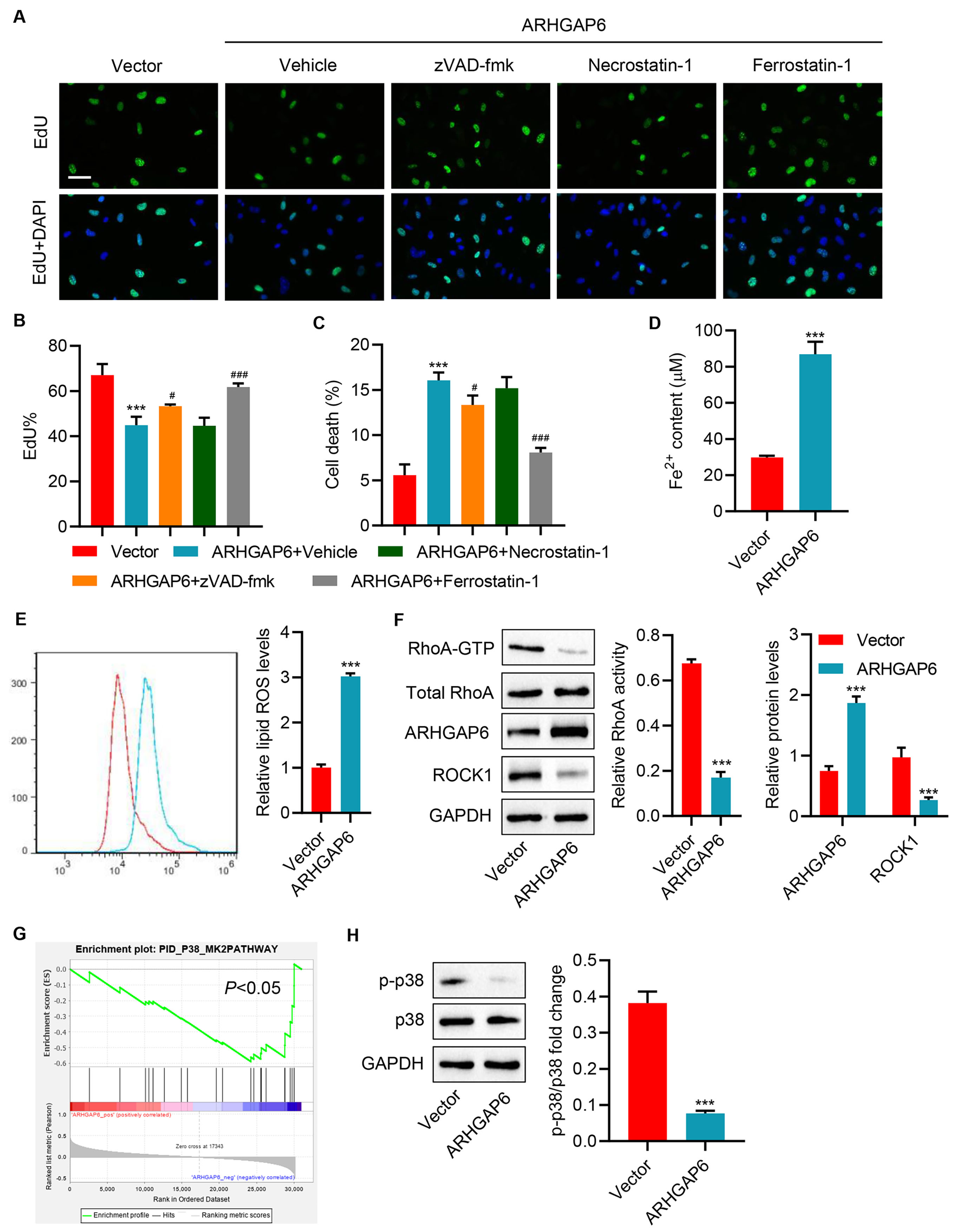
To eamine the role of ARHGAP6 in breast cancer, MCF-7 cells with the lowest
ARHGAP6 expression compared with other breast cancer cell lines were transduced
with ARHGAP6 expression vector to overexpression ARHGAP6. Following the
successful establishment of ARHGAP6 overexpression, ARHGAP6 mRNA and protein
levels were significantly increased (Supplementary Fig. 1A–C). At 48 h
post-transduction, cell proliferation was decreased, and cell death was increased
in ARHGAP6-overexpressing MCF-7 cells (Fig. 2A–C). To determine the cause of
ARHGAP6 overexpression-induced cell death, several cell death inhibitors were
tested. Ferroptosis inhibitor ferrostatin-1 markedly inhibited ARHGAP6
overexpression-induced cell death; however, apoptosis inhibitor zVAD-fmk only
mildly inhibited ARHGAP6 overexpression-induced cell death (Fig. 2A–C). To
further examine the effects of ferroptosis on ARHGAP6 overexpression-mediated
cell death, Fe
 Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.ARHGAP6 overexpression promotes ferroptosis in MCF-7 cells.
MCF-7 cells were infected with indicated lentiviral vectors and treated with 25
µM apoptosis inhibitor zVAD-fmk, 20 µM necroptosis inhibitor
necrostatin-1, or 10 µM ferroptosis inhibitor ferrostatin-1, and
the (A,B) cell proliferation and (C) cell death were determined (n = 3).
MCF-7 cells were infected with indicated lentiviral vectors, and the (D)
Fe
RhoA activates downstream Rho-related protein kinase 1 (ROCK1) and modulates the accumulation of ROS [24, 25]. To detect whether RhoA/ROCK1 signaling pathway was affected by ARHGAP6 overexpression in breast cancer cells, this study applied active small GTPase pull-down assays. As a result of ARHGAP6 overexpression, it showed that RhoA activity and ROCK1 protein levels were diminished (Fig. 2F).
Pathway enrichment analysis using the GSEA algorithm revealed that p38 MAPK pathway was significantly enriched in patients with low ARHGAP6 expression (Fig. 2G). In response to ARHGAP6 overexpression, p38 MAPK phosphorylation was dramatically reduced (Fig. 2H).
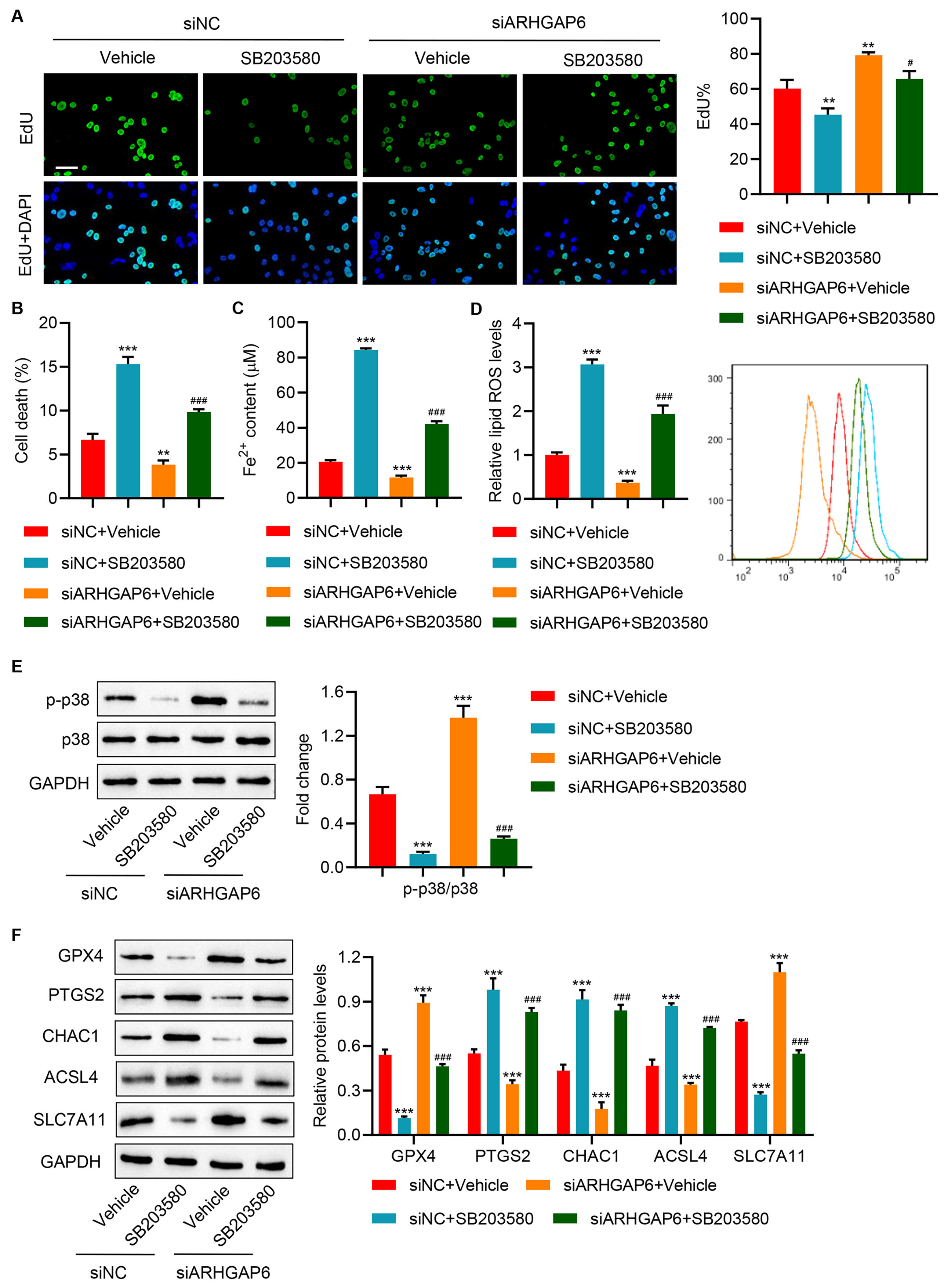
To further understand the regulatory role of ARHGAP6 in ferroptosis, BT-474
cells with the highest ARHGAP6 expression compared with other breast cancer were
transfected with ARHGAP6 siRNA to knockdown ARHGAP6. BT-474 cells transfected
with siARHGAP6 successfully eliminated ARHGAP6 mRNA and proteins
(Supplementary Fig. 1D–F). Cell proliferation significantly increased,
while the level of cell death, Fe
 Fig. 3.
Fig. 3.ARHGAP6 silencing promotes cell proliferation and inhibits
ferroptosis of BT-474 cells by activating the p38 MAPK signaling pathway. BT-474
cells were transfected with siARHGAP6 or siNC with or without p38 MAPK inhibitor
SB203580 (10 µM) treatment, and the (A) cell proliferation, (B) cell
death, (C) Fe
Furthermore, to determine whether RhoA/ROCK signaling mediated the effect of ARHGAP6 on p38 MAPK signaling, siARHGAP6-transfected cells were exposed to RhoA/ROCK inhibitor Y-27632. ARHGAP6 silencing evidently improved RhoA activity and the phosphorylation of p38 MAPK signaling, which were counteracted by exposure to RhoA/ROCK inhibitor Y-27632 (Supplementary Fig. 2A,B). This indicates that RhoA-ROCK1-p38 MAPK signaling mediates the effects of ARHGAP6 on ferroptosis in breast cancer.
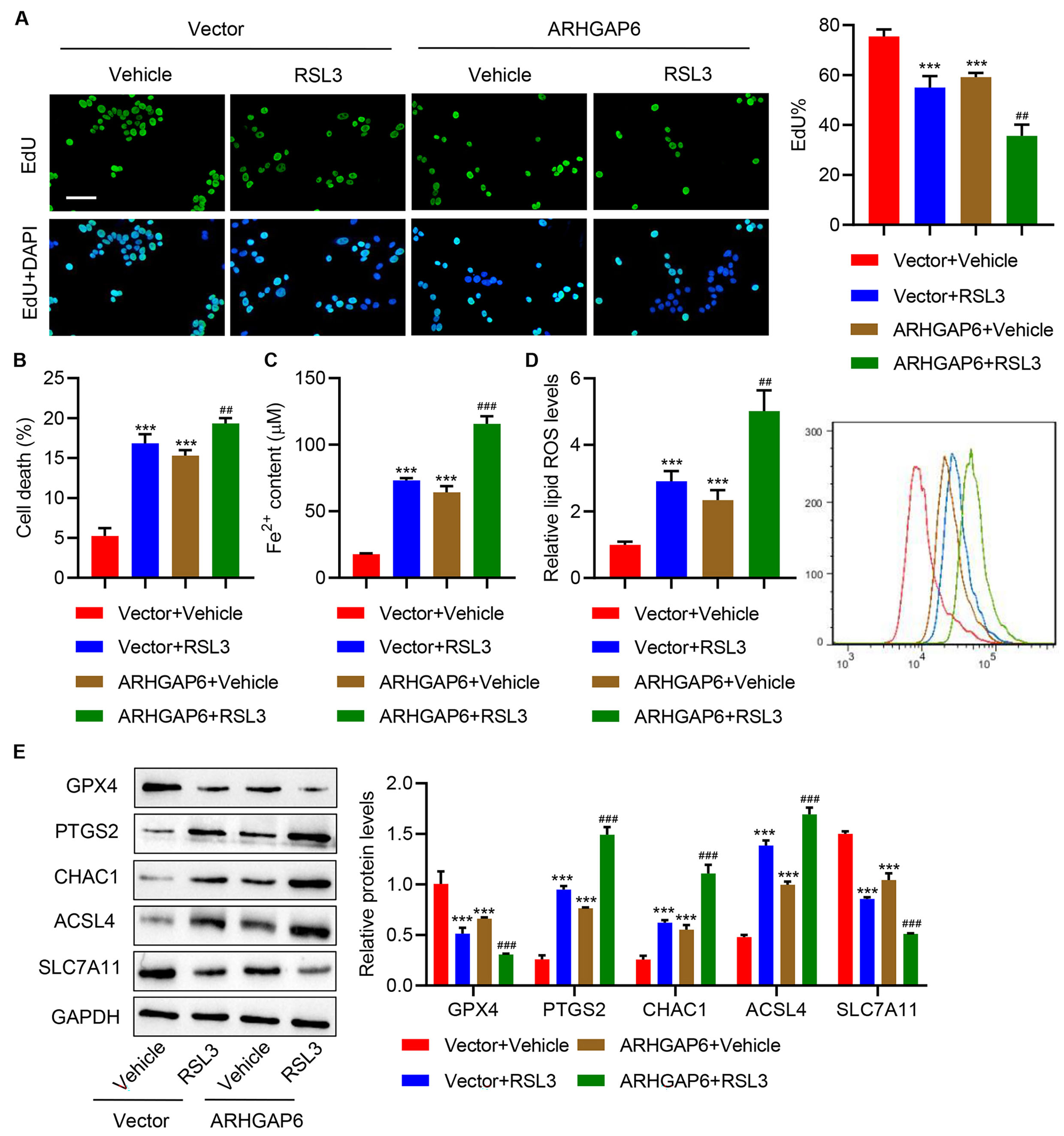
To evaluate the effects of ARHGAP6 and RSL3 co-treatment on ferroptosis,
ARHGAP6-overexpressing MCF-7 cells were stimulated by the ferroptosis-inducer
RSL3. This demonstrated that in the MCF-7 cells transduced with
pLVX-Puro-ARHGAP6, RSL3 stimulation further decreased cell proliferation (Fig. 4A), enhanced cell death (Fig. 4B), Fe
 Fig. 4.
Fig. 4.ARHGAP6 and RSL3 cooperatively inhibit cell proliferation and
promote ferroptosis of MCF-7 cells. MCF-7 cells were infected with
indicated lentiviral vectors and treated with ferroptosis inducer RSL3 (1
µg/mL), and the (A) cell proliferation, (B) cell death, (C)
Fe
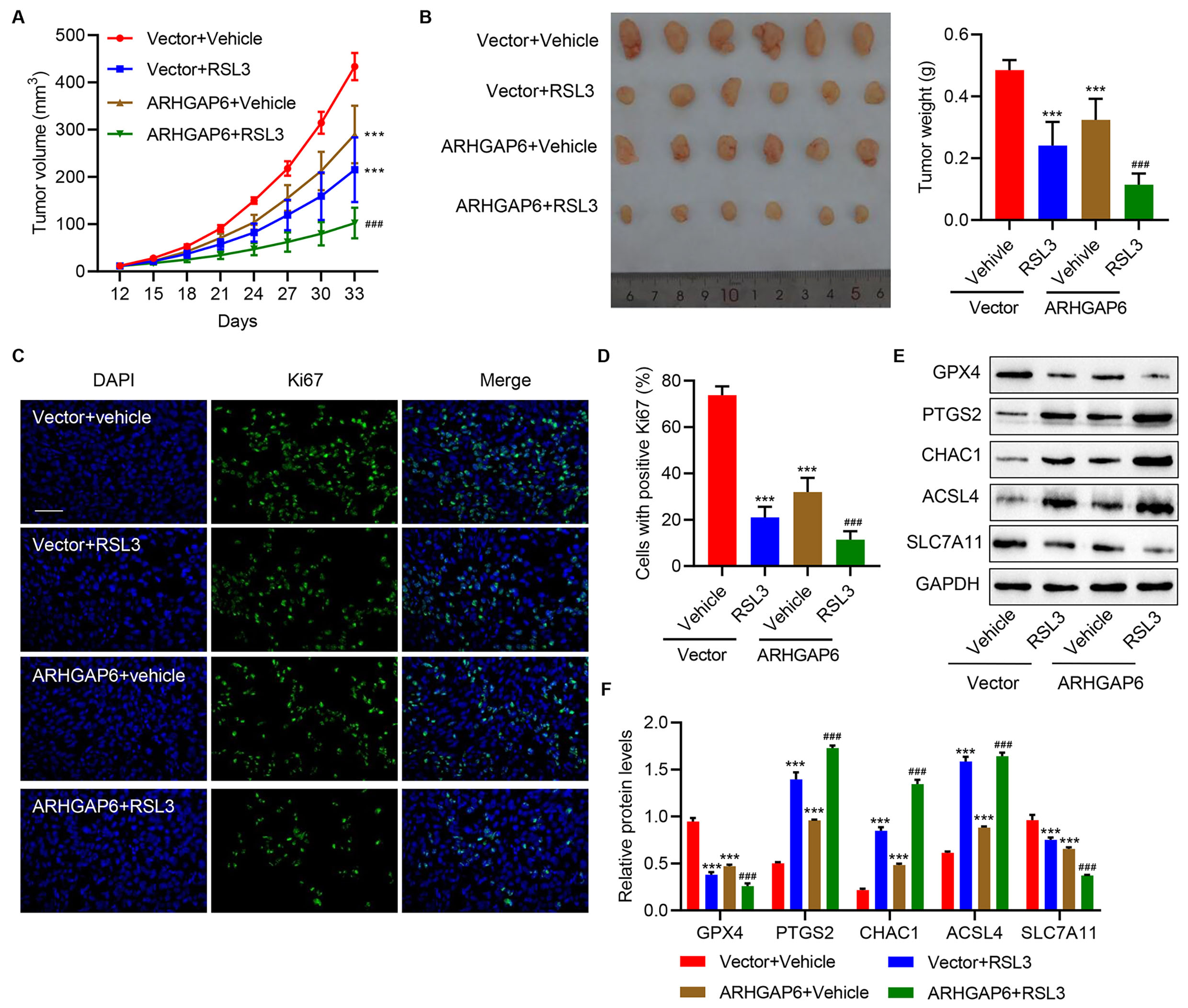
To further evaluate the effects of ARHGAP6 overexpression and RSL3 on tumor growth in vivo, the mouse-xenograft models were established by subcutaneous injection of MCF-7 cells transduced with ARHGAP6 expression vector and treat with RSL3. Fig. 5A,B shows that the mice with ARHGAP6 overexpression or treated with RSL3 treatment had observably smaller tumor volumes and reduced tumor weights compared to vehicle-treated mice. The combination of two treatments further decreased the tumor volume and weight compared to either treatment alone. Tumor cell proliferation was measured using Ki67 immunofluorescence staining. Either ARHGAP6 overexpression or RSL3 treatment alone significantly suppressed tumor cell proliferation (Fig. 5C,D). Moreover, the combined treatments further suppressed tumor cell proliferation than the induced suppression of each treatment alone (Fig. 5C,D). Protein levels of GPX4, SLC7A11, ACSL4, PTGS2, and CHAC1 were detected in tumor tissue samples harvested from the mice models. A significant decrease in GPX4 and SLC7A11 protein and a significant increase in PTGS2, ACSL4, and CHAC1 expression were found in mice with ARHGAP6 overexpression or receiving RSL3 injection compared to vehicle mice (Fig. 5E,F). The combined treatments caused more significant changes in these ferroptosis biomarkers compared with each treatment alone (Fig. 5E,F). These observations revealed that ARHGAP6 and RSL3 co-treatment is a better therapeutic strategy for breast cancer than either treatment alone by promoting ferroptosis.
 Fig. 5.
Fig. 5.Cooperative effects of ARHGAP6 and RSL3 on tumor growth
in vivo. Mice were injected with MCF-7 cells infected with indicated
lentiviral vectors, followed by RSL3 (100 mg/kg) injection. The (A) tumor volume
(n = 6), (B) tumor weight (n = 6), (C,D) Ki67 immunofluorescence staining (n = 6),
and (E,F) the expression of GPX4, PTGS2, CHAC1, ACSL4, and SLC7A11 (n = 3) were
measured. Scale bar: 100 µm. ***p
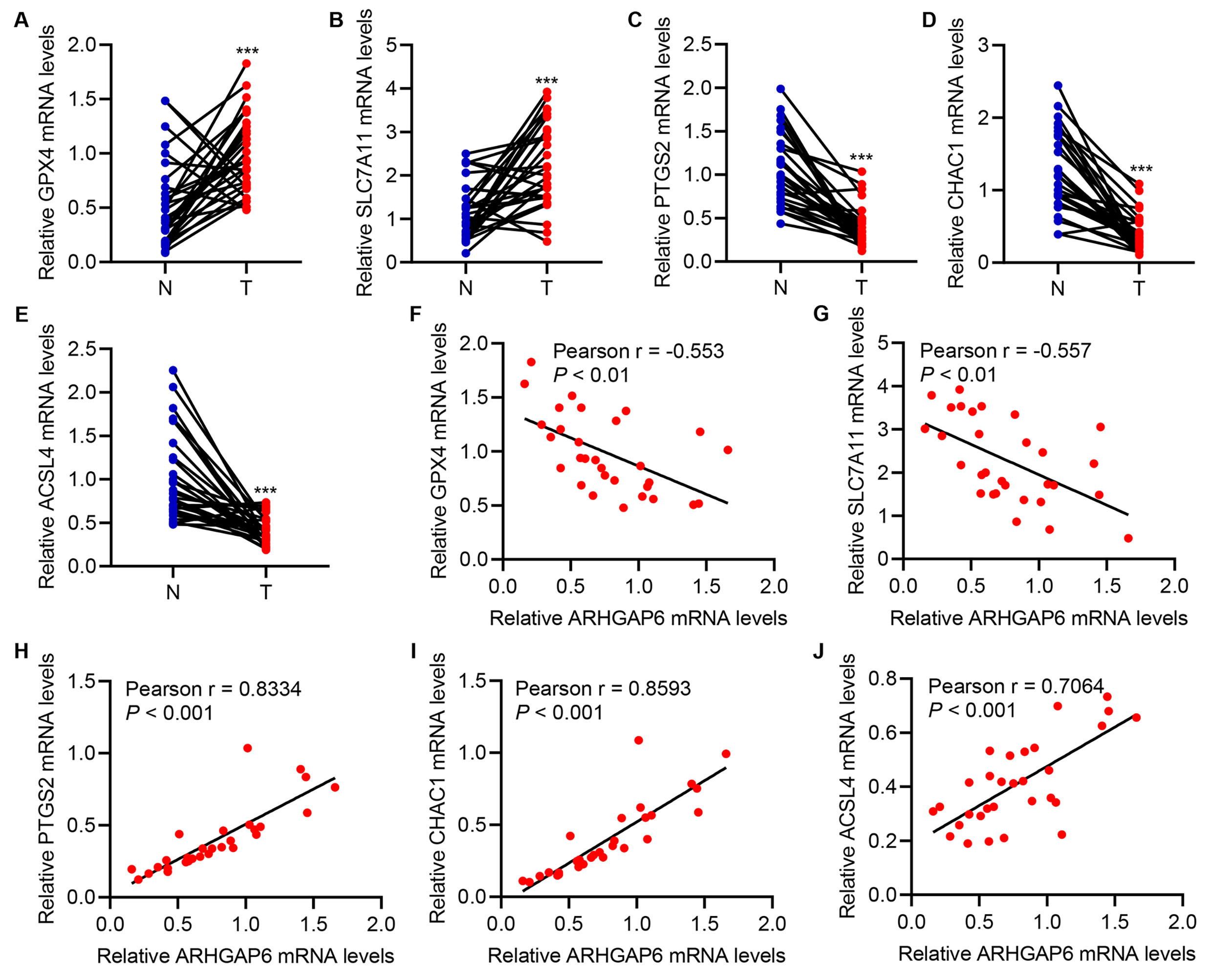
The correlations of GPX4, PTGS2, and CHAC1 with ARHGAP6 in breast cancer tissue and the corresponding adjacent-normal tissue were analyzed. GPX4 as well as SLC7A11 mRNA level was markedly increased, while the mRNA level of PTGS2, ACSL4, and CHAC1 was markedly decreased in cancer tissue compared with adjacent-normal tissue (Fig. 6A–E). This suggests the inhibition of ferroptosis in breast cancer. GPX4 and SLC7A11 mRNA levels were negatively correlated with the ARHGAP6 mRNA level (Fig. 6F,G). Conversely, PTGS2, ACSL4, and CHAC1 mRNA level was positively correlated with ARHGAP6 mRNA level (Fig. 6H–J). These results demonstrated that ARHGAP6 expression has a significant positive correlation with ferroptosis indicators in breast cancer. Additionally, ARHGAP6 is significantly associated with tumor stage (p = 0.034), ER status (p = 0.017), PR status (p = 0.020), and HER2 status (p = 0.011; Table 1).
 Fig. 6.
Fig. 6.Correlation analysis in tumor tissues. (A–E) Expression of
GPX4, SLC7A11, PTGS2, CHAC1, and ACSL4 in breast cancer tissues (T; n = 30) and
the corresponding adjacent-normal tissues (N; n = 30) in the hospitalized breast
cancer patient cohort. (F–J) Pearson correlation scatter plots of tumor
tissues (n = 30). ***p
| Variable | ARHGAP6 | |||
| High (n = 34) | Low (n = 41) | p value | ||
| Age (years) | 0.066 | |||
| 17 | 29 | |||
| 17 | 12 | |||
| Histological type | 0.078 | |||
| Ductal | 22 | 30 | ||
| Lobular | 8 | 11 | ||
| Other | 4 | 0 | ||
| Tumor site | 0.069 | |||
| Left | 18 | 30 | ||
| Right | 16 | 11 | ||
| American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) stage | 0.272 | |||
| I | 5 | 2 | ||
| II | 22 | 26 | ||
| III | 7 | 11 | ||
| IV | 0 | 2 | ||
| Tumor stage | 0.034 | |||
| T1 | 13 | 5 | ||
| T2 | 18 | 25 | ||
| T3 | 2 | 7 | ||
| T4 | 1 | 4 | ||
| Lymph node status | 0.087 | |||
| Metastasis | 14 | 25 | ||
| No metastasis | 20 | 16 | ||
| ER status | 0.017 | |||
| Positive | 13 | 27 | ||
| Negative | 21 | 14 | ||
| PR status | 0.020 | |||
| Positive | 10 | 23 | ||
| Negative | 24 | 18 | ||
| HER2 status | 0.011 | |||
| Positive | 16 | 31 | ||
| Negative | 18 | 10 | ||
Ferroptosis induction contributes to tumor growth suppression and, therefore, holds great potential for anticancer therapy [26]. This study revealed that ARHGAP6 was downregulated in the breast cancer dataset, cancer tissue samples, and cell lines in accordance with previous findings [14, 15]. ARHGAP6 overexpression or knockdown strengthened or inhibited ferroptosis, respectively, in breast cancer cells via RhoA-ROCK1-p38 MAPK signaling. Moreover, ARHGAP6 combined with a ferroptosis inducer had cooperative effects on promoting ferroptosis in vitro and suppressing tumor growth in vivo. This study reports a previously undescribed role of ARHGAP6 in regulating ferroptosis in breast cancer. It expands our understanding on the induction mechanisms of ferroptosis and has significant implications for developing ferroptosis-mediated therapeutic strategies for breast cancer treatment.
ARHGAP genes turn off Rho-like GTPases that perform multiple functions in the initiation and progression of cancer [14]. It was noteworthy that ARHGAP6 suppresses tumor growth in lung cancer [15, 27]. Consistent with these findings, this study showed that in mouse models, ARHGAP6 exhibited a suppressive effect on breast cancer tumor growth, thus proving its role as a tumor suppressor. Ferroptosis is characterized by increased lipid peroxidation and lipid ROS levels and the inactivation of GPX4 responsible for scavenging lipid peroxides [28]. SLC7A11, a subunit unique to system xCT, can synthesize GSH in the intracellular environment and maintain the antioxidant activity of GPX4 [29]. PTGS2 encodes cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2) that is upregulated in ferroptosis cells and has been shown to be a downstream target of ferroptosis [30]. Ferroptosis inhibition inactivates the COX-2/prostaglandin E2 pathway [31]. CHAC1 plays an important role in glutathione degradation and is involved in apoptosis, oxidative stress, and ferroptosis [32]. The ACSL4, a crucial lipid metabolism enzyme, contributes to ferroptosis execution [33]. This study found that ARHGAP6 overexpression increased ferroptosis, as indicated by the elevated lipid ROS levels, decreased GPX4 and SLC7A11 proteins, and increased protein levels of PTGS2, ACSL4, and CHAC1. Moreover, the present study provided evidence that ARHGAP6 aggravated RSL3-induced ferroptosis, thereby suppressing tumor growth. Additionally, in tumor tissues, ARHGAP6 mRNA level was negatively correlated with that of GPX4 and SLC7A11 but was positively correlated with that of PTGS2, ACSL4, and CHAC1. This further demonstrates the positive correlation between ARHGAP6 expression and ferroptosis indicators.
RhoA/ROCK signaling pathway is involved in actin–myosin contraction, thereby regulating cellular growth, migration, and differentiation [34]. RhoA/ROCK signaling plays an important role in modulating breast cancer progression by affecting the migration and proliferation of cancer cells [35, 36]. A recent study reported that ARHGAP6 influenced the downstream RhoA/ROCK signaling to induce gastric cancer cell death [37]. Similarly, this study found that ARHGAP6 overexpression inhibited RhoA/ROCK1 signaling, indicating that RhoA/ROCK1 signaling mediates ARHGAP6-induced ferroptosis and tumor suppression. p38 MAPK signaling is a key regulator for cancer cell survival and has been widely known as a potential therapeutic target [38]. A significant body of literature provides evidence supporting the regulatory mechanisms of ferroptosis involved in p38 MAPK signaling [19, 20]. Consistent with the results of previous studies, this study demonstrated that p38 MAPK signaling mediates ARHGAP6 effect on ferroptosis. Moreover, the difference between p38 MAPK activation and RhoA activity induced by ARHGAP6 silencing indicated that other Rho GTPase factors such as Cdc42 or Rac1 may also contribute to the ARHGAP6 silencing-induced p38 MAPK activation [39]. Therefore, further investigation is required to elucidate the role of ARHGAP6-Cdc42/Rac1- regulated p38 MAPK activation in breast cancer.
RhoA/ROCK signaling has been known to activate the downstream p38 MAPK signaling
pathway [40, 41]. This study showed that RhoA/ROCK signaling inhibition
ameliorated the phosphorylation of p38 MAPK induced by ARHGAP6 knockdown in
breast cancer cells. Moreover, it revealed that RhoA/ROCK signaling mediates the
effect of ARHGAP6 on p38 MAPK signaling, indicating that RhoA-ROCK1-p38 MAPK
signaling is an important regulatory mechanism underlying the ARHGAP6 promotion
of ferroptosis and suppression of breast cancer tumor growth. Furthermore,
evidence revealed that ARHGAP6 upregulation inhibits the downstream STAT3
signaling in regulating the proliferation, migration, and invasion of lung cancer
cells [27]. p38 MAPK/NF-
In conclusion, our results showed that by using in vitro and in vivo experiments, ARHGAP6 inhibits breast cancer tumor growth by strengthening ferroptosis via the targeting of RhoA-ROCK1-p38 MAPK signaling. This study demonstrates the relationship between ARHGAP6 and ferroptosis and advances our knowledge of the regulatory signaling pathways implicated in ferroptosis. ARHGAP6 alone, or in combination with ferroptosis-inducing agents, may be an attractive therapeutic strategy targeting breast cancer.
All data presented in this study are included within the paper and its Supplementary files. The data utilized and/or examined in the present study can be obtained from the corresponding author upon a reasonable request.
XC and DZ designed the research study. XC and JZ performed the research. ZZ, XF, RL, and HL provided help and advice on the acquisition of data and supervision. JZ, XL, and JC analyzed the data. XC and DZ wrote the manuscript. All authors contributed to editorial changes in the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. All authors have participated sufficiently in the work to take public responsibility for appropriate portions of the content and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to its accuracy or integrity.
The medical ethics committee of Southern Medical University Affiliated Maternal & Child Health Hospital of Foshan (No. FSFY-MEC-2021-042) approved the present retrieval method of cancer tissue samples. All patients provided signed informed consent. All animal experiments were performed in accordance with the animal ethics guidelines of the Animal Care and Use Committee of Shanghai Rat@Mouse Biotech Co., Ltd., China [No. 202103(11)].
We sincerely thank all who participated in this study.
This study is supported by Innovation Project of Women and Children medical research center affiliated to Foshan Institute of Fetal Medicine (FEYJZX-2020-006), Foundation of Bureau of Science and Technology of Foshan (2020001005568 and 2220001004898), and Medical Research Project of Foshan Health Commission (20230819A010163).
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Supplementary material associated with this article can be found, in the online version, at https://doi.org/10.31083/j.fbl2901006.
References
Publisher’s Note: IMR Press stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.