1 Hematology Department, The Affiliated Cancer Hospital of Zhengzhou University & Henan Cancer Hospital, 450008 Zhengzhou, Henan, China
2 Central Laboratory, The Affiliated Cancer Hospital of Zhengzhou University & Henan Cancer Hospital, 450008 Zhengzhou, Henan, China
Abstract
Background: Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a recurrence-prone hematologic malignancy. The advent of molecularly targeted therapies provides new opportunities to enhance the effectiveness of AML treatments. Venetoclax, a selective inhibitor of the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2, has shown promising results; however, resistance often arises due to elevated expression of the Mcl-1 protein, among other factors. Overcoming this resistance to improve therapeutic outcomes is a pressing issue that requires further investigation. Studies have demonstrated that oridonin, by inhibiting AKT signaling that regulates Mcl-1 expression, can effectively suppress tumor cell growth. This study aims to investigate whether oridonin can synergistically enhance the anti-leukemic effects of venetoclax and explore the underlying mechanisms behind this effect. Methods: In vitro experiments were performed to evaluate the effects of the combination of oridonin and venetoclax on AML cell proliferation, apoptosis, cell cycle distribution, and mitochondrial membrane potential. Transcriptome sequencing was used to elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying the synergistic induction of AML cell apoptosis by the combination therapy. Western blotting and reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) techniques were used to validate the findings. Additionally, an AML mouse model was established to observe the synergistic anti-AML effects of venetoclax combined with oridonin in vivo. Results: Both venetoclax and oridonin individually exhibited inhibitory effects on AML cell proliferation, resulted in cell cycle arrest, and induced cell apoptosis. Moreover, combination of the two drugs resulted in a synergistic effect. We also observed that oridonin inhibited AKT phosphorylation, upregulated the expression of Bim and Bax proteins, facilitated Mcl-1 degradation, and enhanced the apoptotic effects of venetoclax in AML cells. Finally, in vivo experiments demonstrated that the combination of oridonin and venetoclax effectively inhibited the growth of AML xenograft tumors in mice and prolonged the survival time of tumor-bearing mice. Conclusions: Oridonin and venetoclax synergistically promote AML cell apoptosis by inhibiting AKT signaling.
Keywords
- oridonin
- venetoclax
- AKT signaling pathway
- acute myeloid leukemia (AML)
- apoptosis
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a malignant neoplasm of the hematopoietic system characterized by abnormal function, excessive proliferation, and impaired apoptosis of hematopoietic stem cells during their differentiation and maturation within human bone marrow. Until recently, chemotherapy and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation were mainstay treatments for AML [1]. However, with the emergence of targeted small molecule drugs in recent years, new opportunities for the treatment of elderly AML patients, patients unable to tolerate standard treatment, and individuals with relapsed or refractory AML have been made possible. Among these drugs, the Bcl-2 inhibitor venetoclax has gained significant attention due to its ability to induce high rates of complete remission (CR) when used in combination with hypomethylating agents, despite the absence of specific mutational targets.
Venetoclax, an orally administered Bcl-2 inhibitor, has been used in the induction and consolidation therapy of AML patients who are unable to tolerate standard chemotherapy. Although the single-agent CR rate for venetoclax is only 20%, when combined with hypomethylating agents or low-dose cytarabine, the composite CR rate (CR + CRi, complete remission with incomplete blood count recovery) increases to 66.4% [2]. In relapsed/refractory AML, the CR + CRi rate is 42% [3]. Despite these promising outcomes, approximately 30% of patients remain resistant to venetoclax, and studies have shown that this resistance is associated with elevated intracellular expression of Mcl-1 [4]. Additionally, other mechanisms such as dysregulation of Bcl-2 family members and apoptotic regulators have also been implicated in venetoclax resistance. Overcoming such venetoclax resistance represents an urgent clinical challenge.
Oridonin, a tetracyclic diterpenoid compound extracted from the Chinese medicinal herb Isodon rubescens, has demonstrated anti-inflammatory and anticancer effects [5, 6, 7]. Previous studies determined that oridonin exerts its antitumor activity by inhibiting tumor cell growth through the suppression of AKT signaling [5, 8, 9]. Additionally, it has been reported that the expression of Mcl-1, a protein associated with venetoclax resistance, is regulated by AKT signaling [10]. Based on these findings, we propose a hypothesis that the combined treatment of oridonin and venetoclax holds promise in overcoming venetoclax resistance.
The aim of this study was to investigate the synergistic pro-apoptotic effects of the combination of oridonin and venetoclax on AML using both in vitro and in vivo experimental models, and to explore the underlying mechanisms behind any observed effects. Results demonstrated that oridonin enhanced apoptosis effects induced by venetoclax in AML cells by inhibiting the AKT signaling. Additionally, in an AML mouse model, the combination of oridonin and venetoclax reduced tumor burden and significantly prolonged survival. These findings provide a new strategy to overcome venetoclax resistance in clinical settings, and also establish a theoretical basis for the combination therapy of oridonin and venetoclax in treating AML patients.
Monoclonal antibodies against Bcl-2 (#4223), Mcl-1 (#94296), Bim (#2819), Bax
(#5023), caspase3 (#14220), PARP (#9532),
AML cell lines used in the study were as follows: The THP-1 cell line was derived from human acute monocytic leukemia cells; OCI-AML3 cells were derived from human acute myeloid leukemia cells with DNMT3A and NPM1 mutations; U-937 is a cell line exhibiting monocyte morphology that was derived from histiocytic lymphoma; MOLM13 cells were derived from human acute monocytic leukemia cells with a Flt3-ITD mutation.
Cell lines were purchased from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC,
Manassas, VA, USA) and authenticated by short tandem repeat (STR) profiling and
cytochrome c oxidase gene analysis. All cell lines underwent mycoplasma testing.
OCI-AML3, MV4-11, and MOLM13 cells were cultured in complete growth medium
consisting of RPMI-1640 medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum and 1%
penicillin-streptomycin. THP-1 cells were grown in RPMI-1640 without calcium
nitrate, and with 0.05 mM
Normal human hematopoietic stem cells were obtained from peripheral blood
collected from healthy donors after mobilization with 5 µg/kg
granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF). CD34
Cells were seeded in 96-well plates (5
Apoptosis detection was performed using a commercial apoptosis assay kit
(#KGA1014, Nanjing KeyGen Biotech Co., Ltd., Nanjing, China). Venetoclax or
oridonin, was used alone or in combination to treat AML cell lines for 24h. A
blank (untreated) control group was run in parallel. Cells were collected,
centrifuged at 300 gravity (g) for 5 minutes at room temperature, washed twice
with phosphate buffer saline (PBS), and cell pellets were collected after
removing the supernatant. Each experimental group had 3 replicate wells with 2
Treatment with venetoclax or oridonin alone, or a combination of the two, was
applied to AML cells for 24 h. An untreated control group was also included in
these analyses. JC-1 solution was prepared according to the instructions provided
with the kit (#KGA604) from KeyGen Biotech Co., Ltd. (Nanjing, China). Cells
were centrifuged at 300 g for 5 minutes at room temperature, and the original
culture medium was removed. Each group had three replicate wells, and each well
contained 2
Cells were collected by centrifugation at 300 g for 5 minutes in a pre-cooled 4 °C centrifuge and washed with PBS. Each experimental group was conducted in 3 replicate wells. 1 mL of pre-cooled 75% ethanol solution were added to each well and cells were fixed overnight at –20 °C. Following this, cells were collected by centrifugation and the ethanol fixative was washed from the cells. A working staining solution was prepared using a ratio of Rnase A:PI of 1:9. 300 µL of staining working solution was added to each sample and the cells incubated at room temperature in the dark for 30–60 minutes. Staining intensity was recorded using a spectrophotometer at a wavelength of 488 nm.
10 mL of mobilized human peripheral blood was decanted into a 50 mL sterile
centrifuge tube. CD34
Cells in logarithmic growth phase were seeded at a density of 3
| Gene | Primer | Sequence |
| Bcl-2 | forward | 5 |
| reverse | 5 | |
| Mcl-1 | forward | 5 |
| reverse | 5 | |
| Bim | forward | 5 |
| reverse | 5 | |
| Bcl-xl | forward | 5 |
| reverse | 5 | |
| b-actin | forward | 5 |
| reverse | 5 |
Logarithmically growing cells were seeded at a density of 3
Female immunodeficient NTG mice
(NOD/ShiLtJGpt-Prkdc
To investigate the effects of venetoclax and oridonin on AML cell proliferation, we initially used the CCK-8 assay to quantify the effects of different concentrations of venetoclax (Fig. 1A,C) and oridonin (Fig. 1B,D) on the proliferation of MOLM13, OCI-AML3, U937, and THP-1 cell lines at 12 h, 24 h, and 48 h pot-treatment. Results obtained indicate that venetoclax or oridonin alone can inhibit the viability and proliferation of AML cells, exhibiting both time and concentration-dependent effects. The half-maximal inhibitory concentrations (IC50) values were calculated using Graphpad Prism 6 software (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA) (Fig. 1E) and showed that in these four cell lines, the IC50 value of Venetoclax for the MOLM13 cells at 24 h was 4.7 nM, indicating that MOLM13 cells were significantly sensitive to venetoclax. In contrast, the measured IC50 values of venetoclax for the OCI-AML3, U937, and THP-1 cells at 24 h were 3.9 µM, 5.0 µM, and 4.3 µM, respectively. These findings indicate resistance to venetoclax in these 3 AML cell lines. The IC50 values (95% confidence interval) of oridonin for the four cell lines showed relatively small changes and ranged from 0.5 µM to 5 µM.
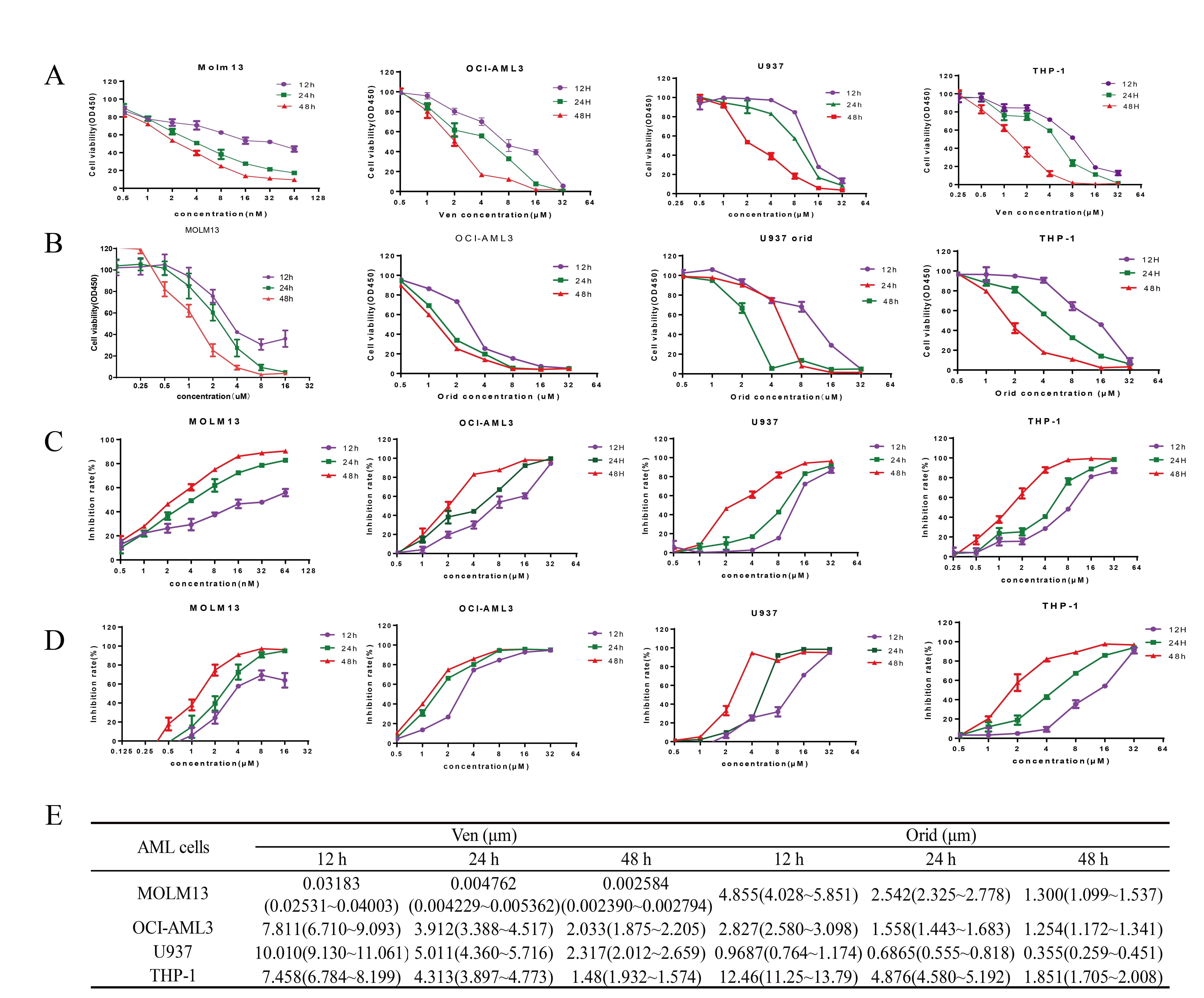 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.The inhibitory effects of venetoclax and oridonin on acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cell line proliferation using a CCK8 assay. MOLM13, OCI-AML3, U937, THP-1 cells were treated with venetoclax (concentrations ranging from 0.5 nM to 64 µM) or oridonin (concentrations ranging from 0.125 µM to 64 µM). (A) Cell viability of AML cells after treatment with different concentrations of venetoclax for 12 h, 24 h, and 48 h. (B) Cell viability of AML cells after treatment with different concentrations of oridonin for 12 h, 24 h, and 48 h. (C) Proliferation inhibitory rate of AML cells after treatment with different concentrations of venetoclax. (D) Proliferation inhibitory rate of AML cells after treatment with different concentrations of oridonin. (E) IC50 (95% confidence interval) values of venetoclax and oridonin on AML cells after 12 h, 24 h, and 48 h of treatment. Each experiment was repeated independently three times. Con, control; Ven, venetoclax; Orid, oridonin; Comb, combination of Ven and Orid.
Above results indicate that both venetoclax and oridonin can inhibit the growth
of AML cells. To investigate whether the combination of these two drugs has a
synergistic effect on promoting AML cell apoptosis, we used an Annexin V-FITC and
PI double staining assay to measure apoptosis when AML cells were treated with
the two drugs alone or in combination. The results indicated that both venetoclax
(Fig. 2A) and oridonin (Fig. 2B) alone induce AML cell apoptosis. After treatment
with a combination of the two drugs, the induction of cell apoptosis was further
enhanced. Specifically, the combination index (CI) values, calculated using
Compusyn software, indicated a CI of less than 1, indicating a synergistic effect
on promoting apoptosis (Fig. 2C). The CI theorem of Chou-Talalay offers a
quantitative definition for additive effect (CI = 1), synergism (CI
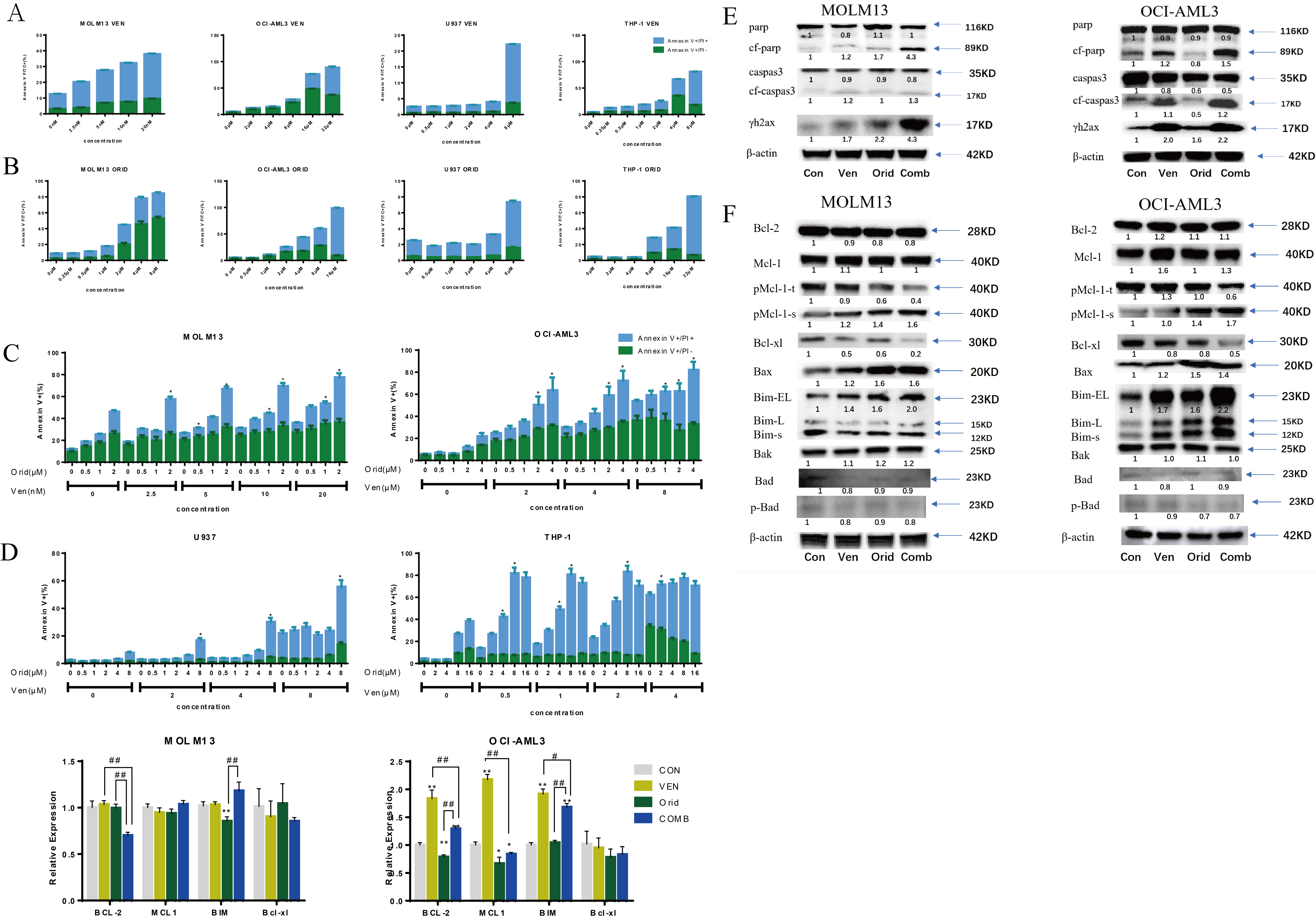 Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.Annexin V-FITC and Propidium Iodide (PI) double staining assay
was used to quantify apoptosis in AML cells treated with different concentrations
of venetoclax and oridonin. (A) Apoptosis rate of AML cells treated with
venetoclax (0~32 µM) for 24 h. (B) Apoptosis rate of AML
cells treated with oridonin (0 µM~32 µM) for 24 h.
(C) Changes in AML cell apoptosis following treatment with different
concentrations of venetoclax and oridonin for 24 h, and the combination index
(CI) was calculated. * indicates CI
Based on the synergistic induction of cell apoptosis by the two drugs, we
selected 2.5 nM venetoclax and/or 2 µM oridonin for single or combined
treatment of MOLM13 cells, and 4 µM venetoclax and/or 4 µM oridonin
for single or combined treatment of OCI-AML3 cells. Further, we used RT-qPCR to
detect changes in expression of Bcl-2 family-related genes in drug-treated cells.
The results showed that there was no significant effect of venetoclax on the
transcription levels of Bcl-2 and Mcl-1 in MOLM13 cells, but that venetoclax
induced an increase in Mcl-1 transcript abundance in OCI-AML3 cells. However,
when combined with oridonin, the transcription level of Mcl-1 decreased
significantly in OCI-AML3 cells. The gene expression levels were represented as
Mean
Western blotting was also used to detect changes in expression of
apoptosis-related proteins and Bcl-2 family regulatory proteins following drug
treatment. Results obtained indicate that venetoclax alone increased the levels
of various markers of apoptosis such as cleaved (cf) Caspase3, cf-PARP, and
The expression levels of Bcl-2 family proteins were examined using western blotting. Results obtained are shown in Fig. 2F. In regards to Mcl-1, treatment with venetoclax alone increased the expression of Mcl-1, with a lower increase in sensitive MOLM13 cells compared to more resistant OCI-AML3 cells. Various Mcl-1 phosphorylation sites can alter the funcrion of this protein. For example, Mcl-1 phosphorylation at Ser159 (Mcl-1s) makes the Mcl-1 protein unstable and easily degraded, while phosphorylation at Thr163 (Mcl-1t) increases Mcl-1 stability and promotes an anti-apoptotic role [12]. In this study, after treatment with venetoclax alone, the abundance of Mcl-1t decreased in MOLM13 cells, while the abundance of Mcl-1s increased. In OCI-AML3 cells, Mcl-1s did not exhibit a significant change, but Mcl-1t was observed to be increased. When venetoclax was combined with oridonin, both cell lines showed an increase in Mcl-1s and a decrease in Mcl-1t abundance. We also observed that after 24 h of treatment with venetoclax, the abundance of the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-xl decreased, and this effect was further enhanced when combined with oridonin. When we studied the pro-apoptotic protein Bax we noted that treatment with venetoclax or oridonin alone increases Bax abundance, and Bax abundance levels further increased when these two drugs were combined. Similarly, the pro-apoptotic protein Bak showed that with oridonin alone an increase in Bak abundance was noted. Taken together, these findings indicate that oridonin can synergize with venetoclax to promote AML cell apoptosis by, in part, downregulating anti-apoptotic proteins.
Mitochondria play an important role in the activation of apoptosis. In the early
stages of apoptosis, the permeability of the mitochondrial membrane changes and
the opening of permeability transition pores cause a decrease in the
mitochondrial transmembrane potential. In normal cells, the mitochondrial
membrane potential is maintained at a relatively high level, resulting in the
accumulation of the dye JC-1 in the mitochondrial matrix and the formation of
JC-1 aggregates that produces red fluorescence that can be detected by flow
cytometry. During early apoptosis, the mitochondrial membrane potential
decreases, preventing the accumulation and aggregation of JC-1 in the
mitochondrial matrix. As a result, JC-1 exists as monomers, leading to the
production of green fluorescence [13]. We sought to detected the effects of
venetoclax and oridonin on the mitochondrial membrane potential of AML cells. The
results (Fig. 3A,B) showed that when venetoclax was combined with oridonin, there
was a significant decrease in mitochondrial membrane potential in the MOLM13,
OCI-AML3, U937, and THP-1 cell lines, and the differences were statistically
significant (p
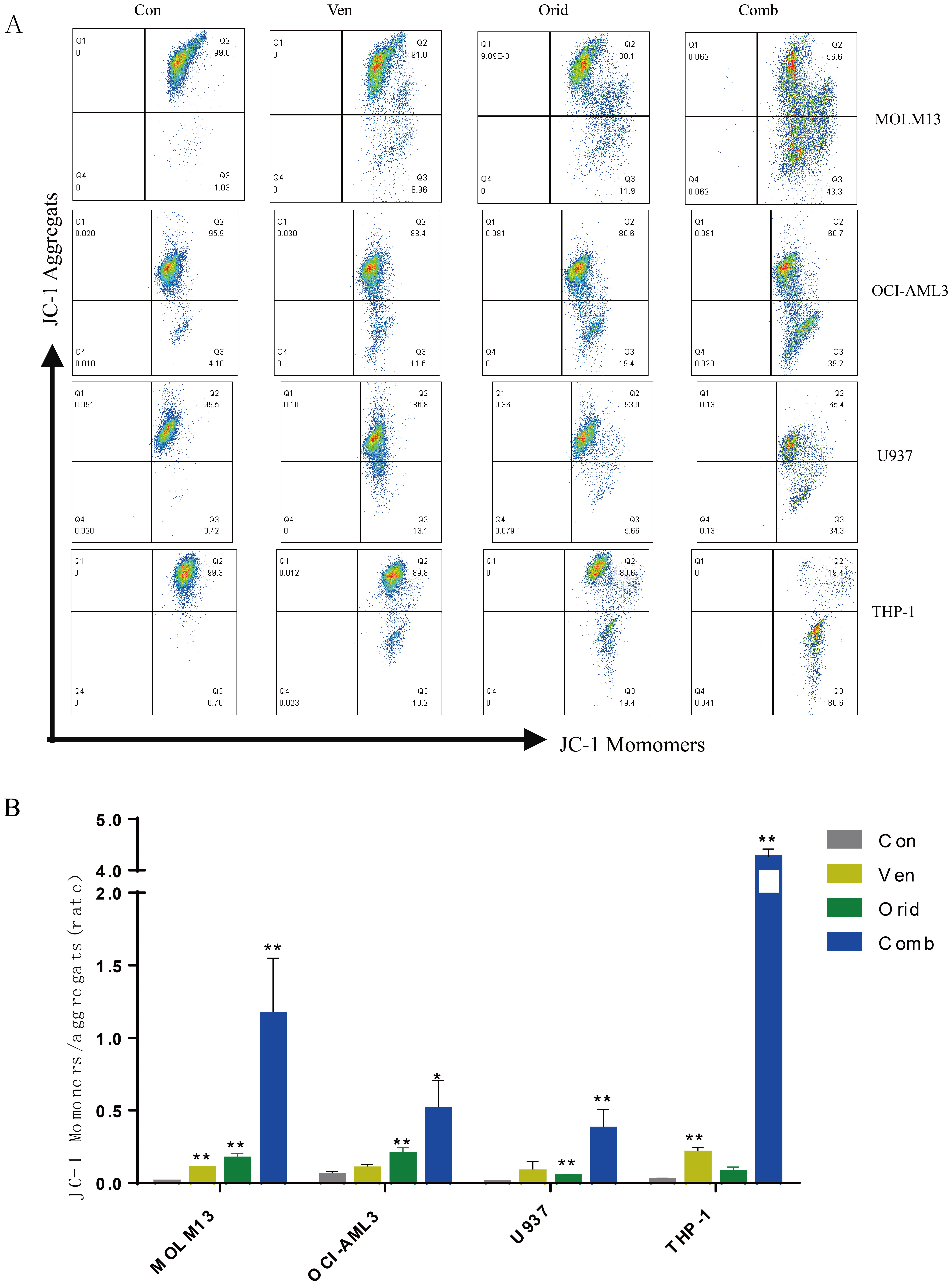 Fig. 3.
Fig. 3.Changes in mitochondrial membrane potential of AML cells treated
with venetoclax or oridonin alone, or in combination. (A) Venetoclax and
Oridonin were applied to four cell lines, including MOLM13, OCI-AML3, U937, and
THP-1 for 24 h (the concentration of venetoclax was 2.5 nM, 4 µM, 8
µM, 1 µM in MOLM13, OCI-AML3, U937, and THP-1 cells, respectively;
the concentration of oridonin was 2 µM, 4 µM, 8 µM, 4 µM,
respectively), and the ratio of JC-1 monomers/polymers was detected by flow
cytometry. (B) Statistical differences between experimental groups and control
groups were compared using t-test (*: p
We next conducted transcriptome sequencing to explore the molecular mechanism
that governs the synergistic effect of oridonin and venetoclax in promoting
apoptosis in AML cells. Previous results determined that different AML cell lines
have different sensitivities to venetoclax, with MOLM13 being sensitive and
OCI-AML3, U937, and THP-1 showing resistance. Our findings indicate that oridonin
can synergize with venetoclax to induce apoptosis in AML cells; thus, to
investigate the mechanism that controls this sensitivity to venetoclax, we
selected venetoclax-sensitive MOLM13 cells, venetoclax-resistant OCI-AML3 cells,
and normal peripheral blood CD34
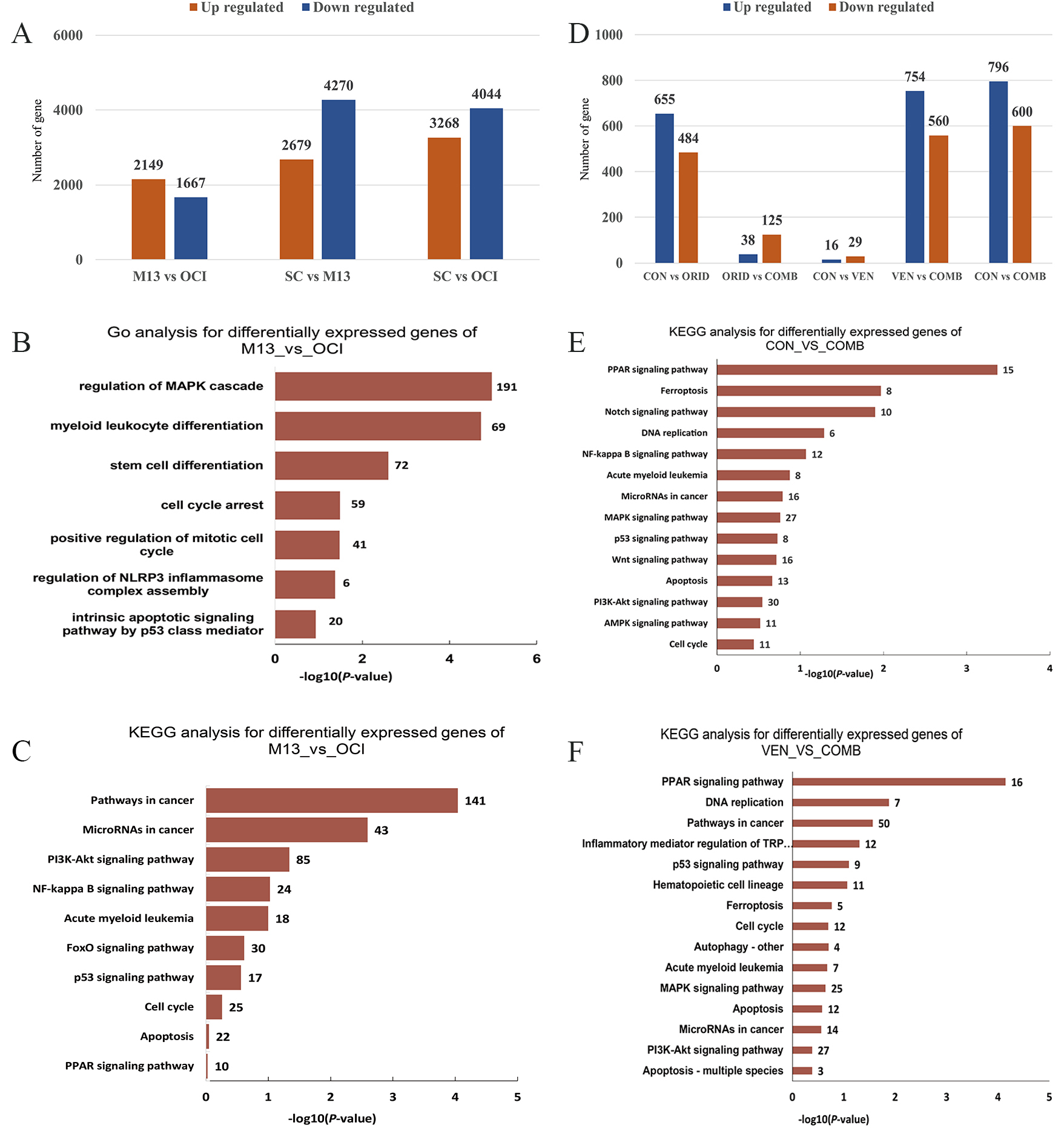 Fig. 4.
Fig. 4.Differential gene expression analysis and enrichment results of transcriptome sequencing. (A) Differential gene expression in OCI-AML3, MOLM13, and normal hematopoietic stem cells. (B,C) Gene Ontology (GO) enrichment analysis and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment analysis of differentially expressed genes between MOLM13 and OCI-AML3. (D) Differential gene expression before and after drug treatment of OCI-AML3 cells. (E) KEGG enrichment analysis of differential gene expression between combination drug treatment and control groups. (F) KEGG enrichment analysis of differential gene expression between th4 combination drug group and venetoclax monotherapy group. SC, stem cells from healthy person; Con, control; Ven, venetoclax; Orid, oridonin; Comb, combination of Ven and Orid.
To investigate which of these differences contribute to drug resistance, we treated OCI-AML3 cells with 4 µM venetoclax, 4 µM oridonin, or a combination of both, and explored their molecular mechanisms through transcriptome sequencing. The results showed that the quantitative gene expression changes induced by venetoclax were less than those induced by oridonin in OCI-AML3 cells after drug treatment (Fig. 4D). Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analysis revealed that compared with the venetoclax single-drug group, the combination therapy group also contained differentially expressed genes in the p53 and MAPK signaling pathways as well as cell cycle regulation (Fig. 4E,F). These transcriptome sequencing results suggested that the PI3K/AKT and p53 signaling may affect the sensitivity of AML cells to venetoclax.
Based on the results of our sequencing, we used flow cytometry to detect changes
in cell cycle distribution after drug treatment in MOLM13 and OCI-AML3 cells. The
effects of these drugs on cell cycle dynamics were different in the various AML
cell lines used. We observed that venetoclax had no significant effect on cell
cycle distribution. In contrast, oridonin arrested MOLM13 cells
in the G1 phase and OCI-AML3 cells in the G2 phase of the cell cycle. In
addition, when the two drugs were used in combination, the cell cycle arrest
effect observed with oridonin treatment alone was further enhanced in both MOLM13
cells (arrested in the G1 phase) and OCI-AML3 cells (arrested in the G2 phase)
(p
Furthermore, we used western blotting to detect changes in the expression of several cell cycle-related proteins. Namely, we examined p21, CDK2, phospho-CDK2, and c-Myc in MOLM13 and OCI-AML3 cells after drug treatment. The results showed that the expression of p21 was down-regulated after venetoclax alone, most notably in MOLM13 cells. Oridonin was found to up-regulate p21 when used alone, and the combination of the two drugs increased the expression of p21 compared to venetoclax alone. Oridonin down-regulated the expression of cyclin D1, and both drugs down-regulated the expression of c-Myc. When used together, this effect was further enhanced as the two drugs had no significant effect on the total protein expression of CDK2, but oridonin could inhibit the phosphorylation of CDK2 in MOLM13 cells. This led to a decrease in the level of phospho-CDK2 and G1 cell cycle arrest. In OCI-AML3 cells, oridonin up-regulated phosphorylation of CDK2, leading to an increase in the level of phospho-CDK2. This finding may help explain the different cell cycle arrest stages induced by venetoclax and oridonin in these two cell lines (Fig. 5C).
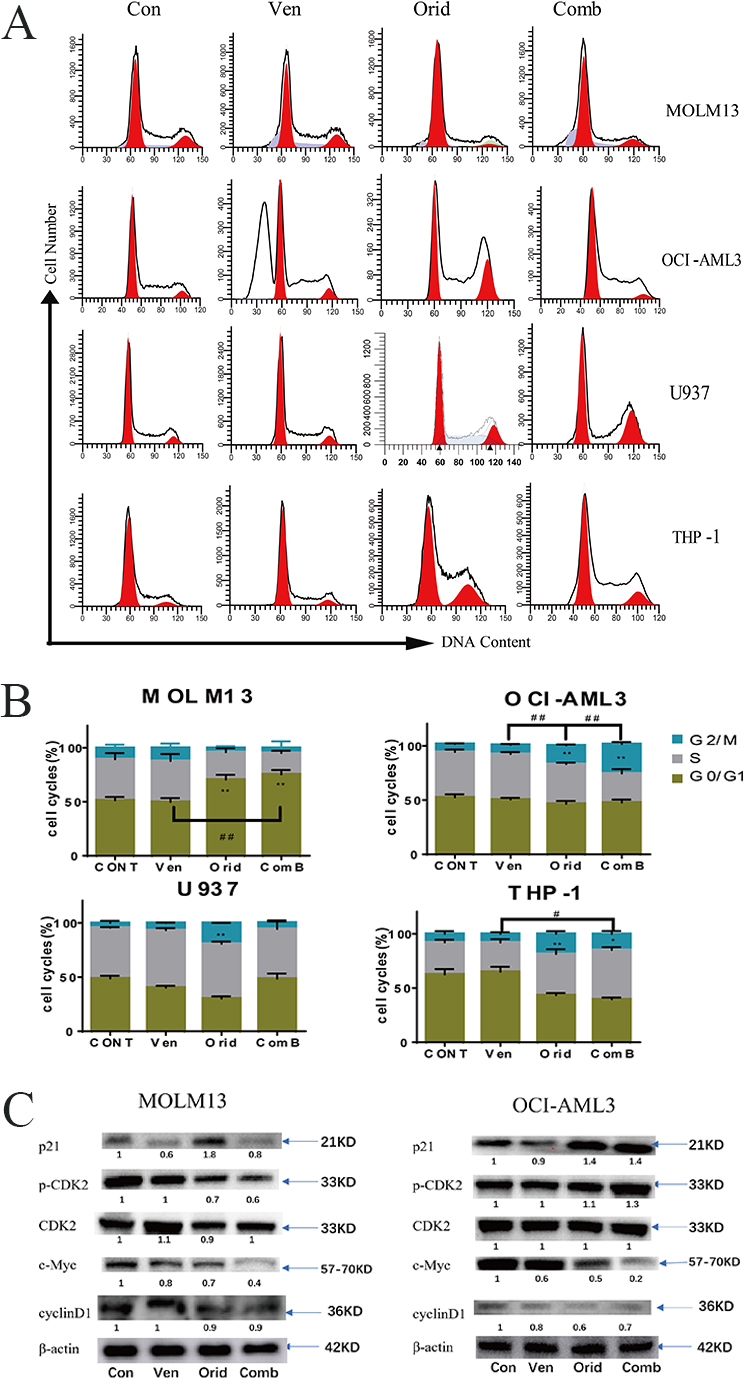 Fig. 5.
Fig. 5.Cell cycle alterations in AML cells treated with venetoclax or
oridonin alone, or in combination. (A) Venetoclax and oridonin were applied to
MOLM13, OCI-AML3, U937, and THP-1 for 24 h. The concentration of venetoclax was
2.5 nM, 4 µM, 8 µM, 1 µM in MOLM13, OCI-AML3, U937, and THP-1
cells, respectively. The concentration of oridonin was 2 µM, 4 µM, 8
µM, 4 µM, respectively. Cell cycle dynamics were obtained by flow
cytometry. (B) Statistical differences between experimental groups and control
groups, as well as between combination groups and single drug groups, in each
cell line were compared using t-test (* experimental group vs control
group; # combination group vs single drug group; */#: p
The results of transcriptomic sequencing suggested that the PI3K/AKT and p53 signaling pathways may affect the sensitivity of AML cells to venetoclax. To investigate the mechanism of action, we harvested MOLM13 and OCI-AML3 cells treated with venetoclax, oridonin, or combination for 24h, extracted total protein, and performed western blotting analysis. The results showed that both venetoclax and oridonin can inhibit AKT phosphorylation, decrease phospho-AKT abundance. However, we noted that this effect is enhanced in MOLM13 cells. When the two drugs were used in combination, the inhibitory effect was further increased (Fig. 6A).
 Fig. 6.
Fig. 6.Expression of key molecules in the MAPK/AKT and p53 pathways.
(A) The effects of venetoclax and oridonin on indicated protein abundance in AML
cells was investigated by western blotting. (B) Western blotting was used to
examine AKT phosphorylation following 4 µM oridonin. Note this effect was
reversed by pre-treatment with 10 µM SC-79 for 1 h. (C) Flow cytometry was
used to detect that oridonin could induce apoptosis in OCI-AML3 cells, but this
effect was abrogated by pre-treatment with SC-79 for 1 h (**: p
To verify the role of the AKT signaling in this process, we added the AKT agonist SC-79 to overcome the inhibitory effect of oridonin on AKT. SC-79 is an AKT agonist that induces phosphorylation of AKT at Thr308 and Ser473 in the cytoplasm and promotes downstream signaling pathway activity. We performed this experiment using the OCI-AML3 cell line which is resistant to venetoclax, and treated cells with 4 µM oridonin alone, 10 µM SC-79 alone, or the combination of the two by pre-treating cells with SC-79 for 1 h before adding oridonin. The level of AKT phosphorylation and cell apoptosis rate were measured 24h later. The results showed that SC-79 alone could increase the abundance of phospho-AKT, and when used in combination with oridonin, it could reverse the inhibitory effect of oridonin on AKT phosphorylation (Fig. 6B). Co-culturing SC-79 with oridonin reduced the apoptotic response induced by oridonin (Fig. 6C).
The signaling pathways in AML cells influenced by oridonin and venetoclax are shown in Fig. 7.
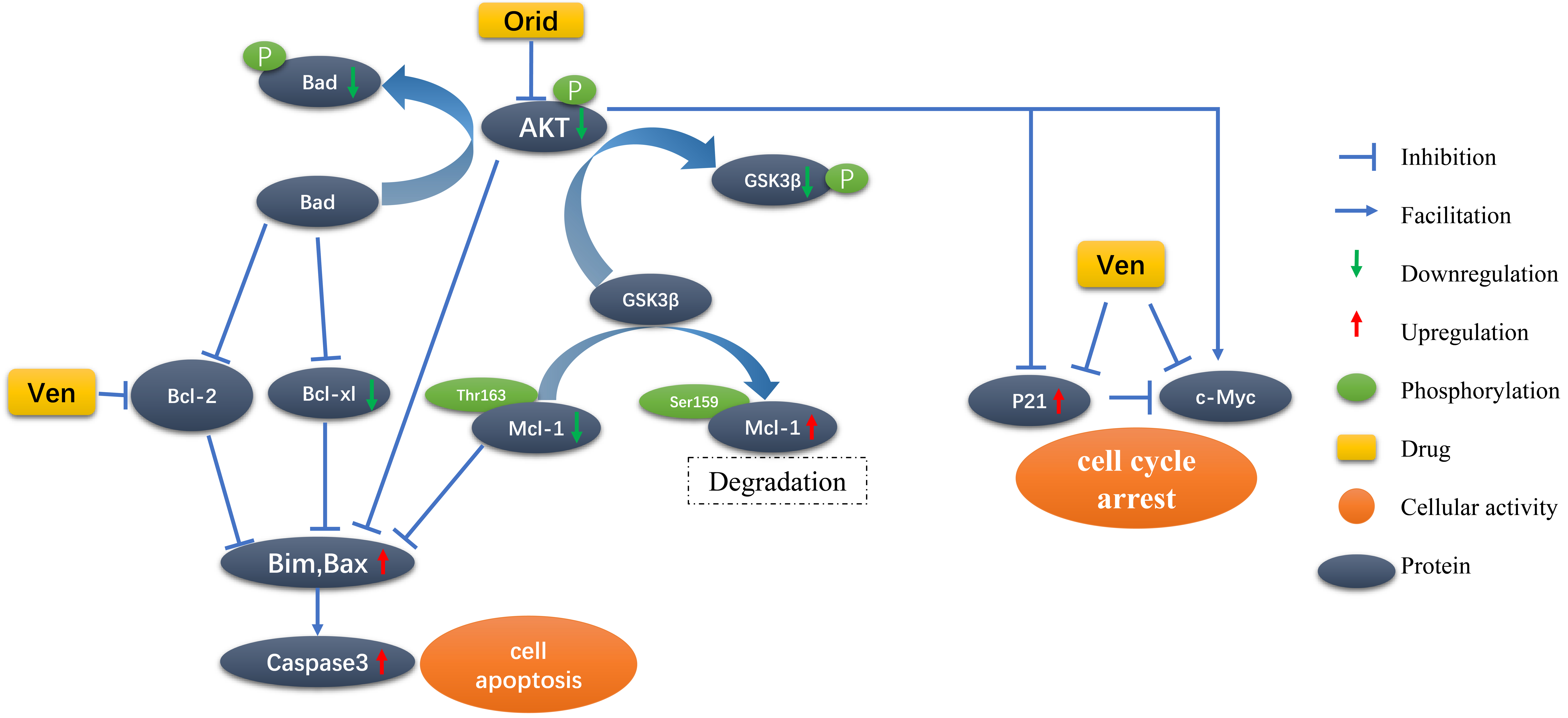 Fig. 7.
Fig. 7.The signaling pathways impacted by combination treatment with venetoclax and oridonin in AML cells. Orid, oridonin; Ven, venetoclax.
A total of 5
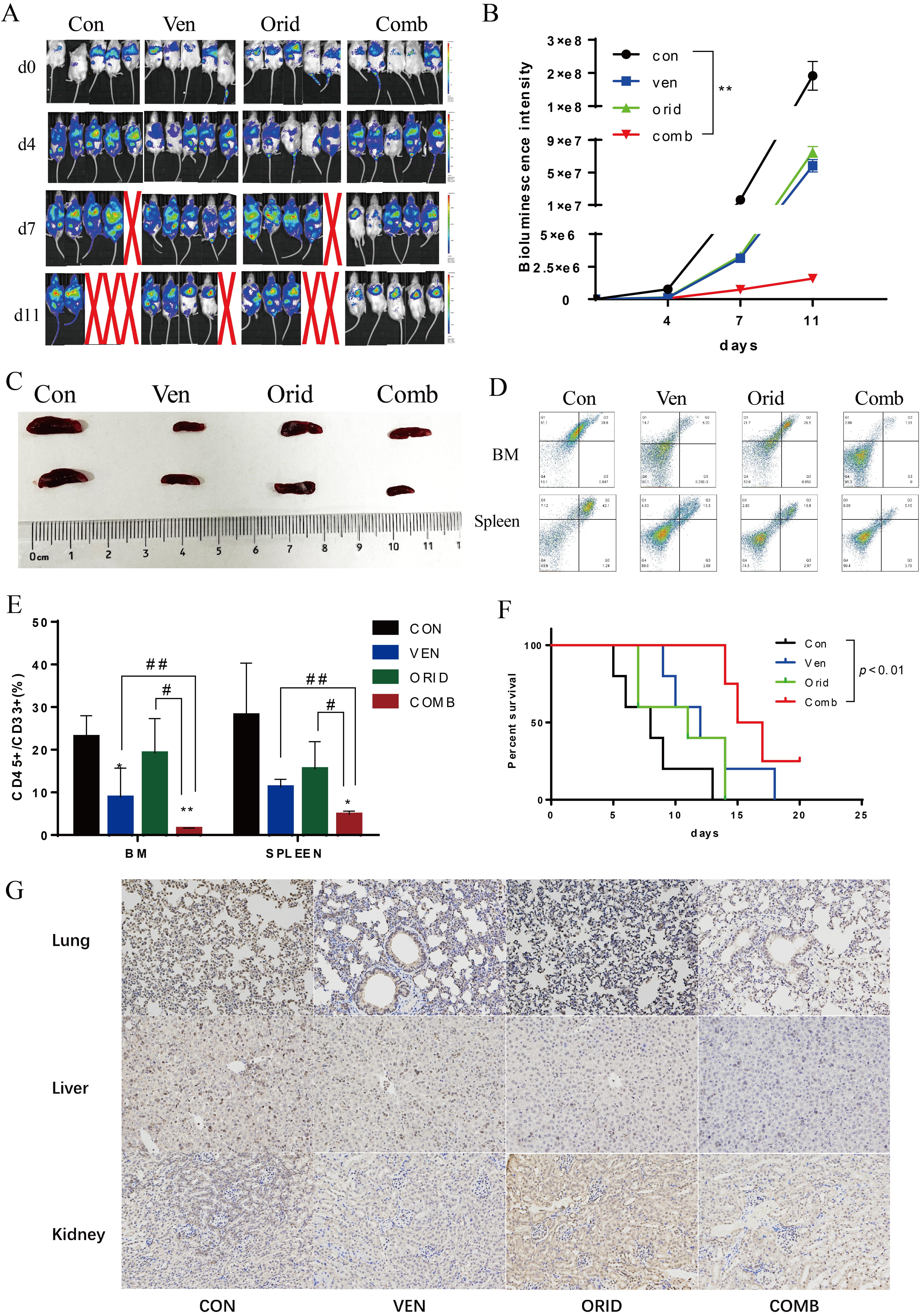 Fig. 8.
Fig. 8.The effect of venetoclax and oridonin on AML xenografts in
mice. (A) In vivo imaging of AML-implanted mice treated with venetoclax
and oridonin alone, or in combination. (B) Fluorescence intensity values measured
in AML-implanted mice. (C) Spleens were obtained after euthanasia on day 11. (D)
Flow cytometry scatter plot of CD33
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a malignant tumor of hematopoietic stem progenitor cells, and the sustained proliferation of leukemia cells is related to dysregulated maturation and differentiation functions [14]. Venetoclax is an orally administered, highly selective Bcl-2 inhibitor that is currently widely used in the treatment of AML patients who cannot tolerate high-intensity chemotherapy. These patients display a remission rate of approximately 70% in newly diagnosed patients.
The Bcl-2 protein is an important member of the Bcl-2 family of apoptosis modulators. When Bcl-2 and Bax form heterodimers, they inhibit cell apoptosis and thus exhibit an anti-apoptotic role. In contrast, when Bax forms homodimers, it induces cells to undergo apoptosis [15]. When Bim binds to Bcl-2 it blocks the apoptosis process, but when it dissociates from Bcl-2, it can induce cells to undergo apoptosis. Bad can also bind to Bcl-2 to promote Bim dissociation, while Mcl-1 can bind to dissociated Bim to promote an anti-apoptotic role [4, 16]. Studies have shown that venetoclax resistance is related to Mcl-1 overexpression and that the activity of Mcl-1 is related to its phosphorylation site [12]. Phosphorylation of Ser159 residue of Mcl-1 (Mcl-1s) promotes Mcl-1 ubiquitination and degradation leading to decreased Mcl-1 abundance and promotion of cell death. In contrast, phosphorylation of the Thr163 residue of Mcl-1 (Mcl-1t) increases its stability and cellular abundance, thereby exerting an anti-apoptotic effect.
This study found that the combination of venetoclax and oridonin has an
inhibitory effect on AML cell proliferation and induces an apoptotic response.
However, the degree to which it inhibits AML cell proliferation varies is
dependent upon the cell line used. After treatment with venetoclax for 24h, the
abundance of Mcl-1s increased and the abundance of Mcl-1t decreased in
venetoclax-sensitive MOLM13 cells. This results in Mcl-1 being readily degraded,
which may be responsible, in part, to this cell line’s sensitivity to venetoclax.
In contrast, OCI-AML3 cells, which are resistant to venetoclax, showed the
opposite effect with an increase in Mcl-1t abundance, a decrease in Mcl-1s
abundance, increased in Mcl-1 stability, and an enhanced anti-apoptotic effect.
Oridonin can inhibit the generation of Mcl-1t, reduce the resistance of OCI-AML3
cells to venetoclax, and synergistically enhance its anti-apoptotic effect.
Oridonin functions by inhibiting AKT phosphorylation and this results in
decreased abundance of activated phospho-AKT. Activated phospho-AKT
phosphorylates GSK-3
Activated AKT can also phosphorylate Bad to form phospho-Bad, which cannot bind to Bcl-2 and prevent the release of Bim and Bax. Through this mechanism phospho-Bad serves an anti-apoptotic role [12]. Oridonin reduces the formation of phospho-Bad by inhibiting AKT activation and, in turn, this increases the amount of non-phosphorylated Bad and promotes apoptosis.
Activated AKT can also directly suppress the expression of pro-apoptotic proteins such as Bim and Bax [17]. Oridonin upregulates the cellular abundance of Bim and Bax proteins, downregulates the expression of the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-xl by inhibiting AKT phosphorylation/activation, and this leads to the promotion of AML apoptosis.
The cell cycle is a complex biochemical process controlled by interaction among
various cell cycle regulatory factors. p21, CDK2, c-Myc, and cyclin D1 are
closely related to cell cycle control. It has been reported that cyclin D1, which
regulates growth through the G1 phase can be suppressed by the AKT/GSK-3
The objective of this study was to explore the mechanism of synergistic anti-leukemia effects of venetoclax and oridonin. Our research yielded three findings. First, oridonin was found to induce apoptosis of AML cells, block the cell cycle progression of AML cells, and synergistically enhance the anti-leukemia activity of venetoclax. Second, oridonin was shown to promote apoptosis by inhibiting AKT phosphorylation, regulating the phosphorylation status of Mcl-1, and promoting its degradation. Third, the combination of venetoclax and oridonin significantly inhibited the progression of AML in xenografted mice and significantly prolonged their survival time. The study suggests that the combination of venetoclax and oridonin may be a promising therapeutic approach for the treatment of AML.
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
LC and XW designed the research study. LC performed the research, analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript. DL and XG provided help and advice on RNA sequencing. CC provided help on performing the research. All authors contributed to editorial changes in the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. All authors have participated sufficiently in the work and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee of Henan Cancer Hospital (approval No. 2019-KY-0017-001). The animal experiment was conducted in accordance with the project permit (No. 20200322) granted by the Zhengzhou University Committee on Life Science Ethics, and complied with the Zhengzhou University guidelines for animal care and use. Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
We would like to express our sincere gratitude to the healthy volunteers who generously donated their peripheral blood stem cells for this study. Their participation and contribution to this research are invaluable. Without their dedication, this study would not have been possible.
This research was funded by Henan Medical Science and Technology Research Project (NO. SBGJ202003012) & (LHGJ20210185).
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Publisher’s Note: IMR Press stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.








