1 Department of Respiratory, Ningbo No.2 Hospital, 315000 Ningbo, Zhejiang, China
2 Department of Radiology, Ningbo No.2 Hospital, 315000 Ningbo, Zhejiang, China
Abstract
Background: The expression of vimentin as a marker of
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) has been speculated to be associated
with tissue heterogeneity and metastases of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Methods: This study utilized in vitro co-immunoprecipitation
with small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) against protein inhibitors of STAT system
type 1 (PIAS1) or SMAD4 in transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-
Keywords
- non-small cell lung cancer
- SUMOylation
- SMAD4
- PIAS1
- Vimentin
Lung cancer is the most common cancer globally, with 2.21 million cases in 2020 and over 1.8 million deaths from lung cancer, making it the most common cause of cancer-related deaths [1]. In China, the estimated age-standardized incidence rate of lung cancer is as high as 34.8 per 100,000, ranking the second-highest worldwide [2], to a large extent due to the drastic increase of inhalant carcinogens (cigarette smoking, for example) in the past few decades. Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) comprises the main histologic types of most lung cancer, with the most common ones being lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) and lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC). When diagnosed, over half of NSCLC cases are already in stage IV with metastasis [3]. Recent advancement in targeted therapy transforms disease management into an actionable molecular alteration. Targeted therapy in combination with chemotherapeutic agents indeed elongated the median survival (OS) of the selected patients’ group [4, 5]. However, due to universally developed resistance or the nature of lacking identifiable targets, the OS of patients with a metastasized situation is still as low as no more than two years [6, 7].
The oncogenic process in around 20% of patients with LUAD type of NSCLC is thought to result from mutations of epithelial growth factor receptor (EGFR) [8], thus molecules targeting tyrosine kinase (TK) of EGFR like Osimertinib has become a recommended treatment for patients falling into this category [9]. Since intrinsic and acquired resistance against these TK inhibitors (TKI) seems to be inevitable nonetheless [10, 11], and acquisition of mesenchymal proteins has been associated with more advanced stage and poorer prognosis [12], the role of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) has thus been extensively discussed in the treatment as well as its function in NSCLC and other cancers [13, 14]. EMT is a complex program of trans-differentiation necessary during embryogenesis and important for organ development. During this process, epithelial cells lose their characteristic apical-to-basal polarity as well as dense adhesion between cells and approach to more mesenchymal-like cells, gaining motility and resistance to apoptosis instead [15, 16]. Under precisely controlled mechanical and physiological induction, appropriate EMT is essential for early development and tissue regeneration or healing in later life [17]. However, cells undergoing inappropriate EMT could acquire the enhanced capacity to migrate and invade, which could be disastrous in tumor development and metastasis [14, 18].
In accordance with this hypothesis, increased mesenchymal characteristics could be observed across multiple different studies involving lung cancer cells with resistance to first-line drugs such as Gefitinib and Erlotinib, with universally increased expression of vimentin, a typical mesenchymal marker of intermediate filament [13, 19, 20, 21]. Metabolism-inhibiting drugs with EMT-inhibiting features are not new in the cancer treatment regimen [1]. Several EMT transcription factors have been identified and targeted as therapeutic candidates in cancer management [2, 3]. Emerging evidence has gradually established the role of vimentin in the occurrence of metastasis in NSCLC, especially in poorly differentiated large cell endocrine, adenosquamous and sarcomatous [22, 23, 24, 25].
SMAD4 protein is a significant transducer in transforming the growth factor-beta
(TGF-
An enzymatic cascade directed by small ubiquitin-like modifiers (SUMO) has been
shown to be important in directing SMAD4 activity: SUMOylation of SMAD4 has been
reported to stabilize SMAD4, thus enhancing/activating the TGF-
A great portion of the target proteins of SUMOylation can be directly recognized by at least one member of the protein inhibitors of the STAT system (PIAS) family. Several members of this family, such as PIASy, and PIAS1, have already been shown to interact with members of the SMAD family to some extent; the interaction in some cases was minimal or weak, but in certain situations was influential enough on the activity of SMAD [34, 35, 36].
In this study, we uncovered the interactions of PIAS1 with SMAD4 protein and confirmed that SUMOylation of SMAD4 by PIAS1 favors the migration ability of A549 cells. We also speculate that the modification of SMAD4 further contributes to the metastasis of NSCLC partially through upregulating the expression of vimentin and promoting the process of EMT.
NSCLC line A549 cells were maintained in an ATCC-formulated F-12K medium
supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS, 10099141C, Thermo Fisher,
Waltham, Illiniwek, US) in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO
Plasmids expressing hemagglutinin-tagged PIAS1 (HA-PIAS1), c-Myc-tagged SUMO1 (Myc-SUMO), and FLAG-SMAD4 were purchased from Sino Biological. Full-length cDNA clones of PIAS1 (1956 bp), SMAD4 (2388 bp), and SUMO1 (306 bp) were constructed between the KpnI and XbaI sites on mammalian expression vector pCMV3 separately. PIAS1 and SMAD4 siRNAs were synthesized by Thermo Fisher Scientific. General transfection was conducted using Lipofectamine 3000 transfection reagents (Invitrogen). Processes involving siRNAs were carried out using RiboJuice siRNA transfection reagent (Sigma Aldrich) following the instructions of the manufacturers.
The following antibodies were employed in this study:
Rabbit DYKDDDDK tag antibody (ProteinTech, Wuhan, Hubei, China,
Cat#80010-1-RR), rabbit anti-Myc-Tag antibody (ProteinTech, Wuhan, Hubei, China,
Cat#10828-1-AP), rabbit anti-HA antibody (ProteinTech, Wuhan, Hubei, China,
Cat#51064-2-AP), rabbit anti-PIAS1 antibody (ProteinTech, Wuhan, Hubei, China,
Cat#23395-1-AP), rabbit anti-SMAD4 antibody (ProteinTech, Wuhan, Hubei, China,
Cat#10231-1-AP), rabbit anti-SUMO1 (ProteinTech, Wuhan, Hubei, China,
Cat#10329-1-AP), rabbit anti-
Cells were co-transfected with Myc-SUMO1, HA-PIAS1, or FLAG-SMAD4, in the presence or absence of PIAS1si or SMAD4si or both. At 48 hours post-transfection, cells were collected and lysed with 1 mL of Triton lysis buffer (150 mM NaCl, 0.2% Triton X-100, 1 mM EDTA, 10% Glycerol, 50 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.5) supplemented with protease inhibitor cocktail (Sigma Aldrich, Chengdu, Sichuan, China) and phosphatase inhibitor cocktail (Sigma Aldrich) at 4 °C for 15 min with gentle rocking. Cell extracts were centrifuged at 14,000 rpm for 10 min at 4 °C. The supernatants were immunoprecipitated with ANTI-c-MYC Affinity Gel, ANTI-FLAG M2 Affinity Gel, or Anti-HA Affinity Matrix (Millipore Sigma, Massachusetts, Burlington, US) with gentle rocking at 4 °C overnight. Immunoprecipitates were then washed three times with cold Triton lysis buffer and were analyzed by western blotting.
Cell lysates prepared in Triton lysis buffer were diluted in Laemmli buffer (10% (w/v) glycerol, 2% sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), 10% (v/v) 2-mercaptoethanol, and 62.5 mM Tris-HCl pH 6.8), boiled for 10 min, and separated on a 10% SDS- polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PDGE, Bio-Rad, Hercules, California, US) followed by transfer onto polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membranes (Millipore Sigma). Before blocking the membrane for 1 h with 5% non-fat milk in Tris-buffered saline with Tween 20 (TBST), membranes were briefly stained with 0.1% Ponceau-S in 5% acetic acid to represent total protein content. Membranes were subsequently incubated overnight with a 1:1000 dilution of appropriate primary antibodies at 4 °C. Membranes were then incubated with peroxidase-conjugated with secondary antibodies for 1 hour at room temperature (RT) at a 1:250 dilution. Membranes were washed three times with TBST for 10 min each and revealed using ECL (GE Healthcare, Chicago, Illiniwek, US) as the manufacturer instructed.
Total RNA was extracted by TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen, Los Angeles, California, US). The cDNA was synthesized using the QuantiTect Reverse Transcription kit (Qiagen, Shenzhen, China). Quantitative RT-PCR experiments were performed with TaqMan Multiplex master mix (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, Illiniwek, US) using Applied Biosystems ViiA 7 Real-Time PCR System; the following primers were used: human vimentin F: AGGCAAAGCAGGAGTCCACTGA, human vimentin R: ATCTGGCGTTCCAGGGACTCAT. Human glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) was used as a control; the primer set was GAPDH F: GTCTCCTCTGACTTCAACAGCG, GAPDH R: ACCACCCTGTTGCTGTAGCCAA. Controls without reverse transcriptase were assessed for all samples.
Cell migration ability was evaluated with a wound-healing assay. 3 days post-transfection, cells were collected by brief trypsinization and were seeded in Ibidi wound-healing two-well Culture Inserts (Ibidi, Fitchburg, Wisconsin, US) into 24-well plates. Cells were grown to confluence in DMEM containing 10% FBS for another 12 h before the Ibidi wound-healing two-well Culture Inserts were removed. The cells were washed twice with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) to remove the cell debris and grown in DMEM containing 1% FBS. The cell migration into the gap area was observed and photographed at time points 0 h, 24 h, and 48 h. The closure of the gap was measured using a phase-contrast microscope. Wound healing was analyzed using the “MRI Wound Healing Tool” plugin in ImageJ (version 1.52 LOCI, University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI, USA) and estimated as a percentage of the starting wound area.
All experiments were performed in biological triplicates or quadruplicates.
One-way, two-way analyses of variances (ANOVA) or unpaired t-test with
two-tailed p value was applied accordingly. Data were presented as mean
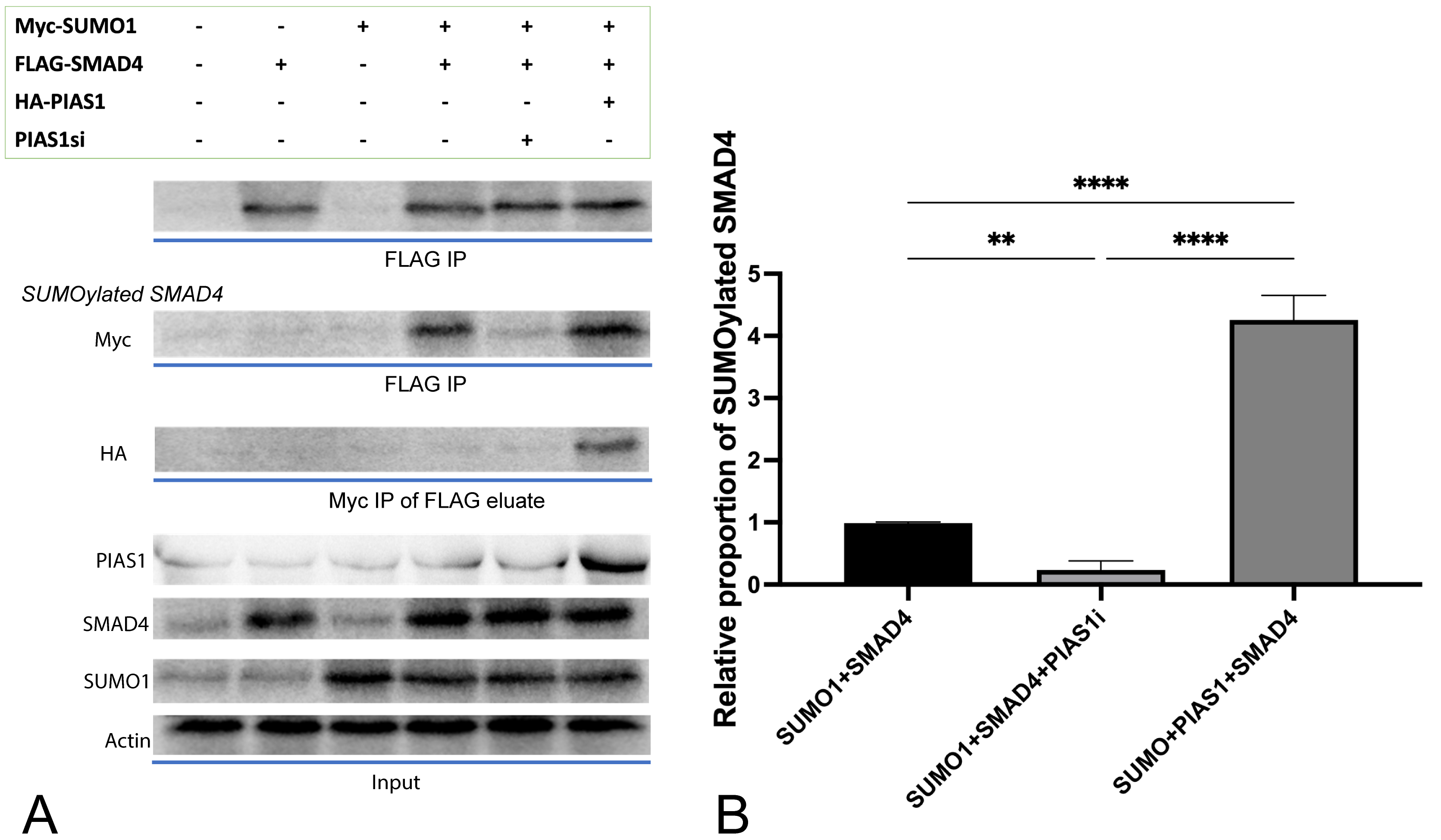
SMAD4 was indeed SUMOylated, confirmed by our in vitro SUMOylation
assay conducted in NSCLC cell line A549 (Fig. 1B, column 1), and such
modification was enhanced obviously (p
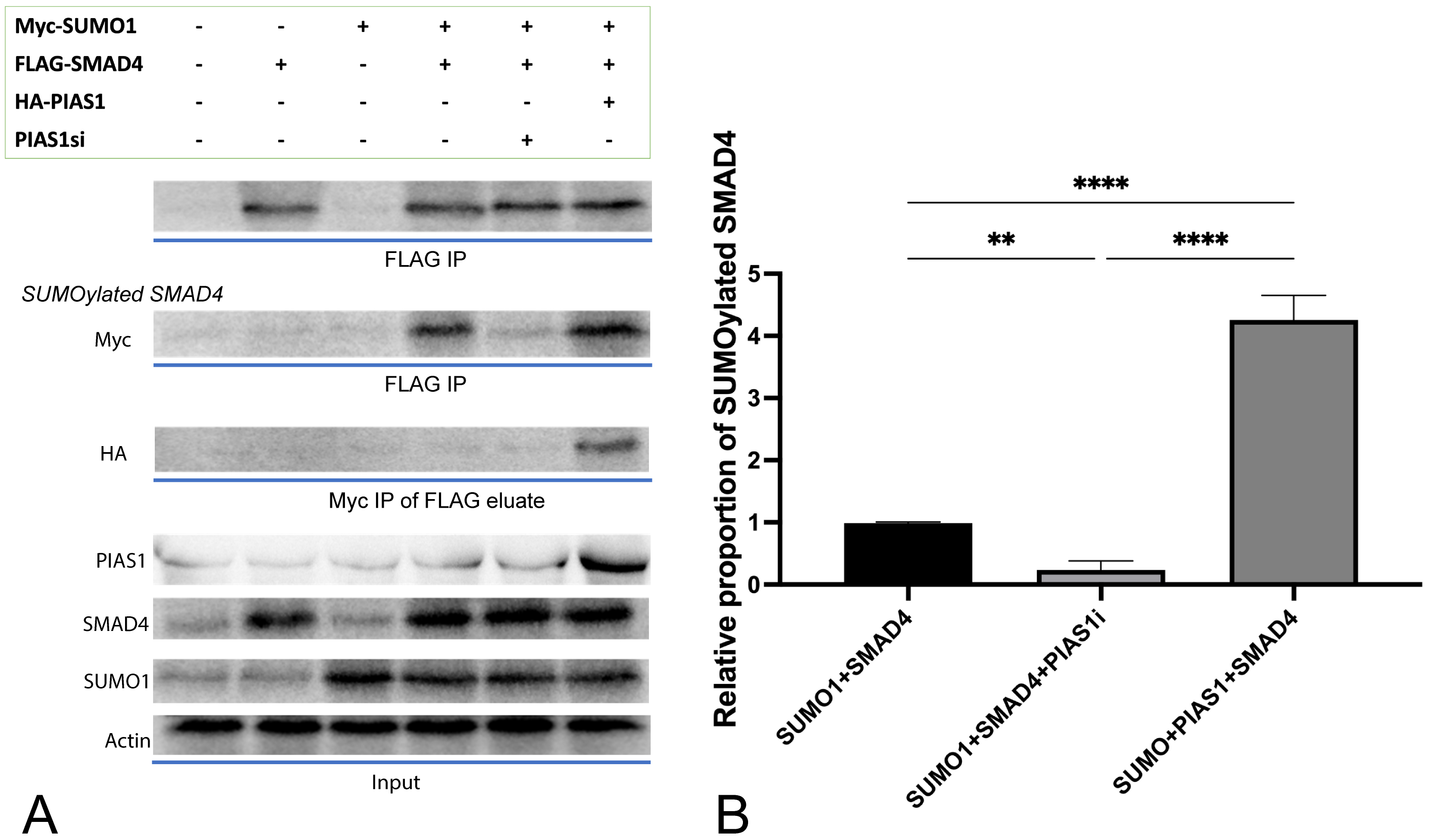 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.PIAS1 enhances SMAD4 SUMOylation by forming PIAS1-SUMO1-SMAD4
multiprotein complex. (A) Cell lysates transfected with vector control or a
plasmid containing cDNA encoding Myc-SUMO1, FLAG-SMAD4, and HA-PIAS1, alone or in
combination, were subjected to SMAD4 immunoprecipitation (FLAG IP) followed by
SMAD4 or Myc immunoblotting (IB). At the same time, 10% lysates were subjected
to SMAD4, PIAS1, SUMO1 IB as the input, and
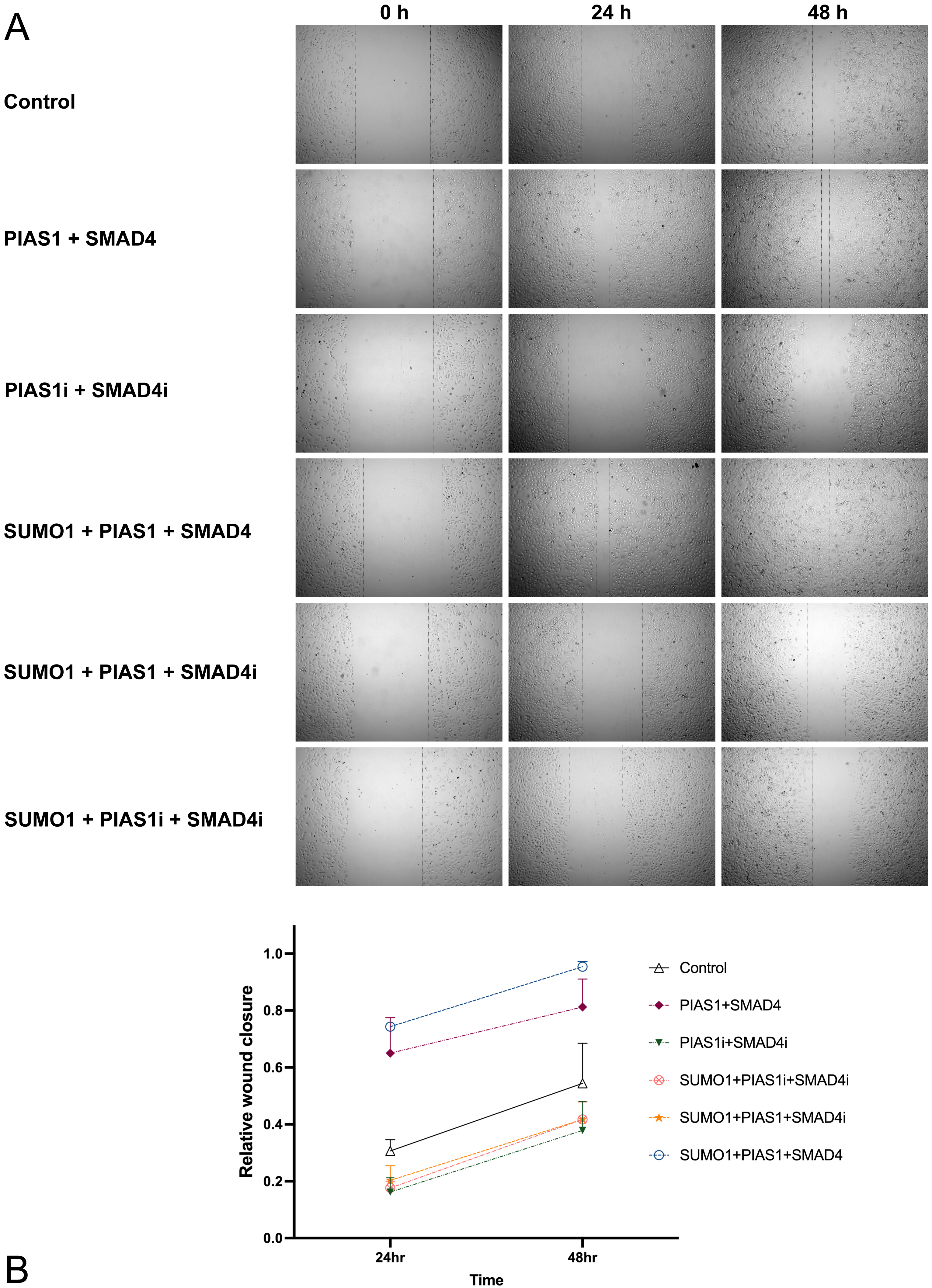
To elucidate whether upregulated SUMOylation of SMAD4 is related to metastasis
of NSCLC, we tested the effect of different combinations of plasmid transfection
on cell migration ability through a wound-healing assay. The maximally enhanced
migration ability (compared to control, p
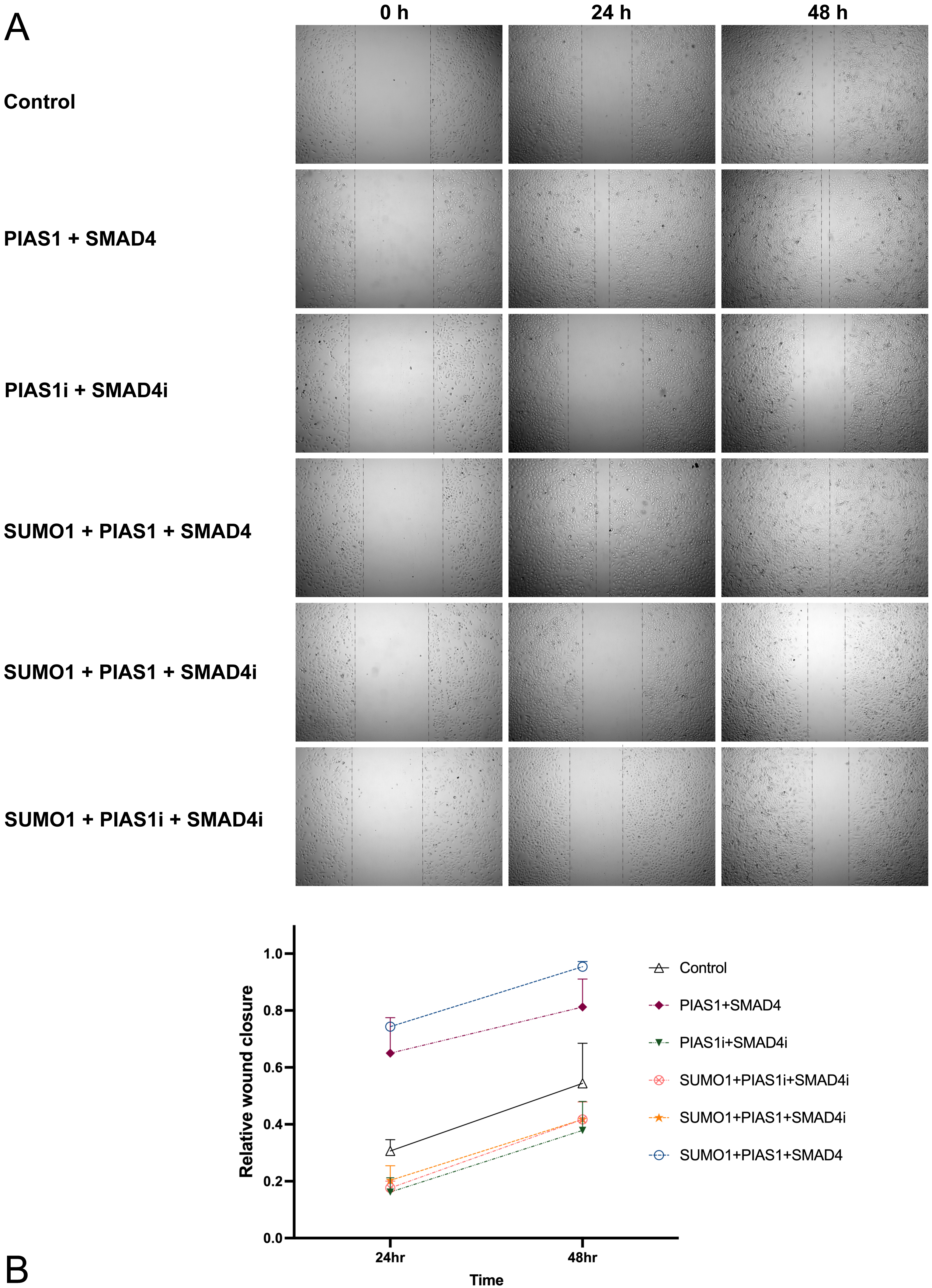 Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.PIAS1mediated SUMOylation of SMAD4 boosted the migration ability of A549 cells. (A) A549 cells were transfected with vector control or a plasmid containing cDNA encoding Myc-SUMO1, FLAG-SMAD4, HA-PIAS1, alone or in combination with siRNA against PIAS1 or SMAD4, and wound healing assay was performed. The photographs were taken at 0 h, 24 h, and 48 h. Cell migration was quantified by measuring the difference in area between the leading edge and the initiation edge of the experiment. The wound area was assessed by ImageJ software, quantitative data analyses were conducted in Prism 9.0, and the results were shown as (B).
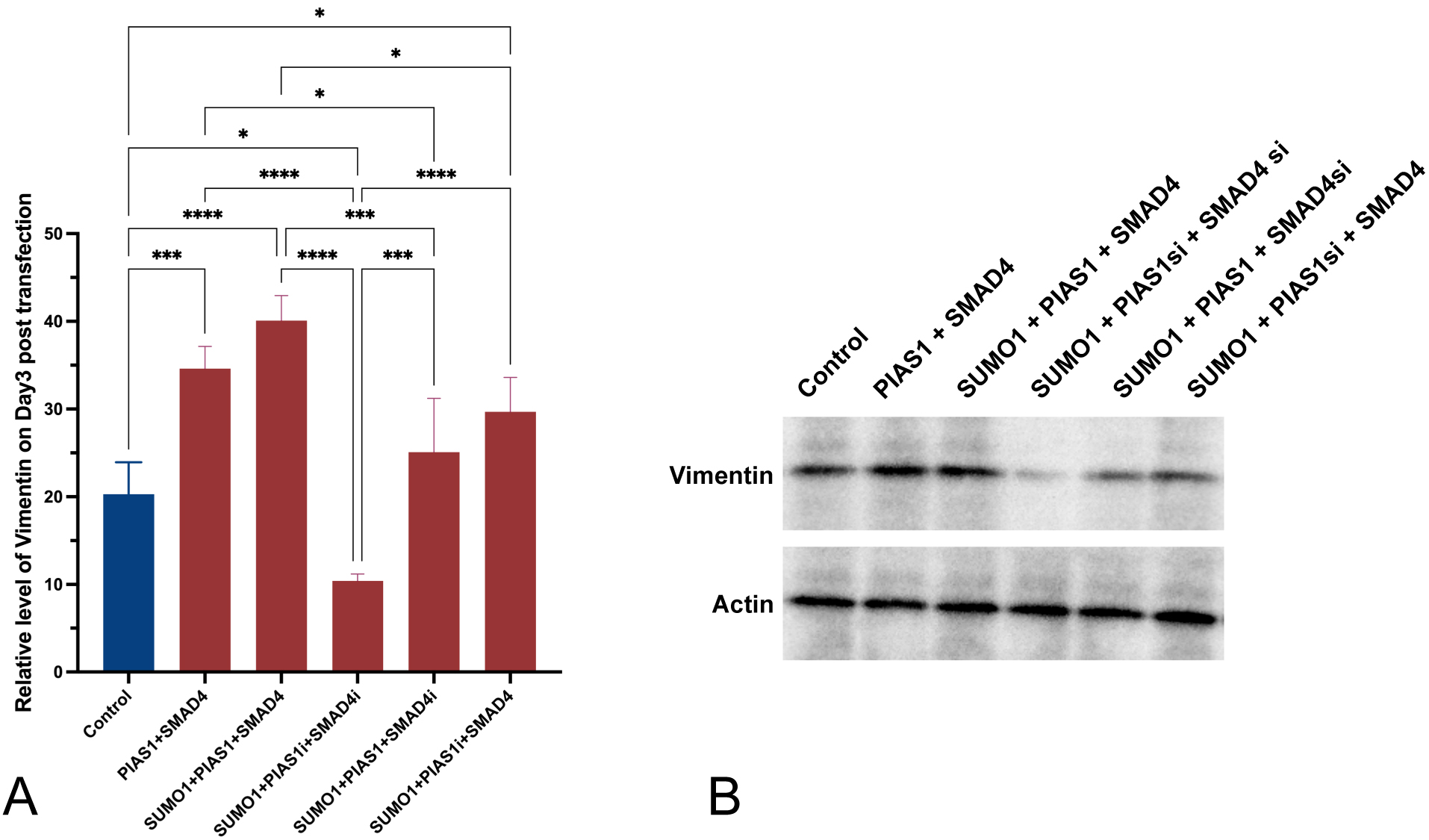
In a parallel experiment involving all groups of cell cultures generated above, we quantified both mRNA expression level and protein level of vimentin microfilament using RT-qPCR and WB, respectively.
Introducing excessive SUMO1 only, with endogenous inhibition of both SMAD4 and PIAS1, was accompanied by decreased vimentin expression and translation in A549 cells, in comparison to control (p = 0.0202, Fig. 3A). If excessive SMAD4 was introduced, vimentin mRNA expression and translation were enhanced (p = 0.0303 with SUMO1 and endogenous inhibition of PIAS1). PIAS1 added up to the effect generated by SUMO1 plus SMAD4 (p = 0.0129), and the upregulating effect was achieved to the maximum when all SUMO1, PIAS1, and SMAD4 were excessively produced. Interestingly, with the presence of upregulation of SUMO1 and inhibition of endogenous SMAD4, the level of vimentin was significantly (p = 0.0004) overcome by the introduction of PIAS1 and comparable to the level observed in control.
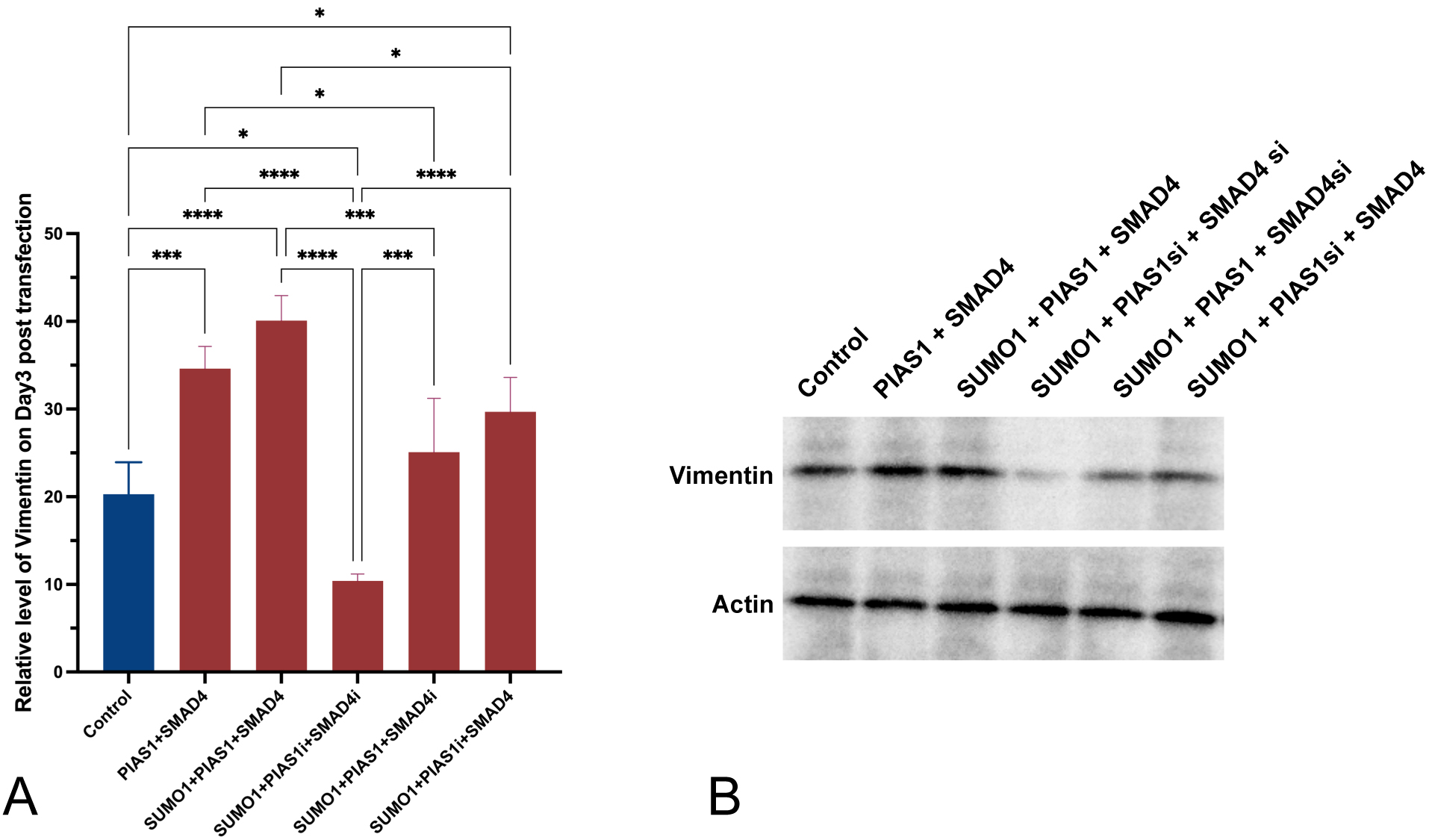 Fig. 3.
Fig. 3.Increased production of vimentin was observed to be accompanied
by the excessive PIAS1-SUMO1-SMAD4 complex. (A) Relative level of vimentin
measured using RT-qPCR three days post-transfection. (B) Western blot showing
vimentin protein amount across different conditions. Experiments were performed
with quadruplicates in each group, quantitative data analyses were conducted in
Prism 9.0, the error bar showed standard error (SD), ANOVA was applied,
two-tailed p values were indicated as *p
The high incidence and mortality of lung cancer, especially NSCLC as one major component, makes it an important area to explore. Despite the advances that we have been making in terms of the combinative treatment regimen, such as target therapy plus chemotherapy on the foundation of surgical evaluation and interventions, eradication of NSCLC seems to be extremely hard, as indicated by the low survival rate and frequent reoccurrence, which is especially true for metastasized cases. Most NSCLC cases, notably those with increased intra-tumoral heterogeneity, are associated with an increased likelihood of relapse and a greater chance of metastases; this directly leads to poorer prognosis since patients are mostly in late stages when a diagnosis is confirmed. Even though the genomic landscapes vary depending on the different histological subtypes and also whether or not some predisposing factors exist (cigarette exposure, for example), some interesting common genetic mutations have been identified, such as KRAS from both LUAD and LUSC [37], which is later linked to EMT [38, 39], a process thought to be playing a crucial role in the metastasis of many malignancies including NSCLC [13, 14].
One group explored the function of SMAD4 in colorectal cancer and observed that
direct silencing SMAD4 compromised the sensitivity of colorectal cancer cells to
Cetuximab (a monoclonal antibody against EGFR) as the EMT is promoted and cells
are losing epithelial characteristics [30]. Another group focused on prostate
carcinoma and also found the inhibitory effect of suppressed SMAD4 on EMT, with a
subsequential decrease in mesenchymal markers such as vimentin [31]. Lin
et al. [32] revealed that the TGF-
As described formerly, vimentin has been widely used as an indicator of EMT, and
its expression is linked with the ability of NSCLC to metastasize. However,
discrepancies exist when it comes to whether SUMOylation of SMAD4 necessarily
means upregulation of vimentin. Contrary to what Kang et al. [29] have
described, we observed higher production of vimentin protein accompanied by
increased SMAD4 and PIAS1. Still, endogenous SUMO1 was enough to mediate this
effect, as shown by the insignificant differences between cultures with excessive
SUMO1 or not (p = 0.7569, Fig. 3). The differences between the cell
lines tested might have contributed to the differences, and considering that it
could take days for this screening marker for EMT to change even with ideal
direct stimulation from TGF-
In conclusion, this study uncovers novel interactions between PIAS1 and SMAD4 in
NSCLC, revealing their role in regulating cell migration and potential metastasis
mechanisms. The findings contribute to understanding NSCLC’s molecular
mechanisms, potentially leading to innovative therapeutic strategies, prognostic
markers, and drug targets for improved patient treatment and management. But in
the same time, we acknowledge several limitations in our study. We did not
explicitly investigate whether cell migration activities originated from
TGF
To conclude, our study further confirmed the interactions between PIAS1 and SMAD4 on the post-translational level. With the presence of high PIAS1, SUMO1-SMAD4 proportion was greatly increased in vitro; this in accordance with highly expressed cytoskeletal element vimentin, increased the ability of A549 NSCLC cells to migrate.
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
CW and XZ conceptualised and conceived the main idea, designed the program and extracted the data, QD and ZC conducted the experimental study. SY provided help and advice on CW analysed of the data. CW and ZD wrote the manuscript. ZD curated the data. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript for publication. All authors contributed to editorial changes in the manuscript.
Not applicable.
We are grateful to the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences for their help with this research.
This work was supported by Key Reasearch Foundation of Hwa Mei Hospital, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, China (Grant No. 2020HMZD02, No. 2022HMZD09); supported by Ningbo Health Branding Subject Fund (Grant No. PPXK2018-05); supported by Basic Public Welfare Research Program of Zhejiang Province, China (No. LTGY23H010001); supported by Medical Scientific Research Foundation of Zhejiang Province, China (No. 2022KY1125, No. 2023KY280); supported by Ningbo Clinical Research Center for Respiratory System Disease of Zhejiang Province, China (No. 2022L004).
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Publisher’s Note: IMR Press stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.