1. Introduction
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the fifth most common cancer and accounts for
a significant proportion of cancer-associated deaths around the world. Moreover,
the incidence and mortality of HCC have been
increasing in recent decades [1]. Treatments for HCC are diverse and include
immunotherapy, liver transplantation, surgical resection, molecular targeted
therapy, transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE), radiotherapy, and
chemotherapy [2]. The past few decades have witnessed advances from basic
research to clinical translation in HCC. Nevertheless, the prognosis remains poor
owing to low surgical resection rates, high rates of relapse, and rapid
progression [3]. In light of this, the identification of novel therapeutic
strategies for HCC is imperative.
Numerous studies have highlighted epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) as
the key mechanism responsible for progression of solid tumors such as colon,
breast, liver and lung cancers [4, 5, 6]. Indeed, accumulating evidence suggests that
EMT in liver carcinogenesis is a multistep process which is involved in cancer
invasion and migration. The EMT phenotype is feartured by downregulation of
epithelial cell-cell adhesion molecule E-cadherin, and upregulation of
mesenchymal-associated biomarkers like N-cadherin and Vimentin [6]. Moreover, the
formation of new blood vessels from pre-existing vasculature, serves major roles
in the growth, invasion, and metastasis of HCC, which is a highly vascularized
tumor type. Notably, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), tightly related
to HCC, acts as a crucial mediator during various HCC biological processes such
as invasion, metastasis, and angiogenesis [7, 8]. It is also worth noting that
hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) binds to the promoter of
VEGF, leading overexpression of VEGF and subsequent angiogenesis [9].
HIF-1 is produced by the response of hypoxia directly and is correlated
with HCC recurrence and metastasis after initial treatment [10]. Moreover,
HIF-1 can initiate hypoxia-induced EMT and metastasis by
transcriptionally regulating EMT-associated elements, such as E-cadherin, and
Vimentin [11]. Therefore, anti-angiogenesis via the blockade of the
HIF-1/VEGF pathway may represent an effective therapeutic strategy
against HCC and an alternative to conventional therapy.
Arsenic compounds are active ingredients in traditional Chinese medicine. They
have been applied extensively and are receiving increased attention due to
significant breakthroughs in the field of leukemia treatment. FDA has approved
arsenic trioxide (ATO) for its striking efficacy in treating acute promyelocytic
leukemia (APL) [12]. Recent studies have indicated that repurposing of ATO could
rescue structural p53 mutations and thus be widely applicable for personalized
cancer therapies [13]. Compared with ATO, arsenic sulfide (AsS) has
the advantages of being relatively safe, abundant, and orally administrated.
Recent investigations in solid tumors such as gastric cancer, colon cancer and
osteosarcoma also support the usage of AsS [14, 15, 16]. Previous studies
indicated that AsS reduced the migration
and invasion of several types of solid tumors [17]. Specifically, our group has
reported that AsS induces double strand DNA breaks (DSB) through
nuclear factor of activated T-cells (NFATc3) for cell death by the upregulated
expression of RAG1 [18]. However, the specific underlying mechanism has not been
completely understood.
For our current investigation, we identified the impact of AsS on
the viability of HepG2 and Hep3B HCC cells and normal hepatocyte cell L02. Our
results indicate that AsS supppresses the migration and invasion of
HCC. The antimetastatic effect in HCC of AsS was first described by
our experiments. Subsequently, we revealed that suppression effect of
AsS was mediated by the HIF-1/VEGF pathway. In a word,
these experimental results conclude that AsS exerts its anticancer
effect in HCC cells through the HIF-1/VEGF pathway.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1 Cell Culture and Reagents
Human hepatocellular carcinoma cells (HepG2 and Hep3B) and human umbilical vein
endothelial cells (HUVEC) were acquired from the National Collection of
Authenticated Cell Cultrures (Shanghai, China). Normal hepatocyte cell L02
(Pricella, Wuhan, Hubei, China) was also prepared for experiments. HepG2, Hep3B,
L02, and HUVEC cells were incubated in DMEM (Hyclone, Logan, UT, USA) containing
1% penicillin streptomycin (Hyclone, Logan, UT, USA) and 10% fetal bovine serum
(FBS) (Hyclone, Logan, UT, USA). The cells were incubated with 5% CO at 37
°C and were mycoplasma free (Mycoalert Mycoplasma Detection Kit, Lonza, Switzerland). The study was carried out in accordance with the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of Xin Hua Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University. Before purchasing, all cell lines were authenticated by each supplier. Highly purified AsS was obtained by the Shanghai
Jiaotong University (China). The purity of AsS was confirmed to be
98.0% by repeated X-ray powder diffraction analysis (Institute of Geology and
Mineral Resources, Xi’an, Shannxi, China). Highly purified realgar was dissolved
in DPBS (C14190500CP, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) and sterilized by filtration [19]. Antibodies for VEGF (sc-7269) and
N-cadherin (sc-8424) were acquired from Santa Cruz (Santa Cruz, CA, USA),
antibodies against E-cadherin (96743SF), Snail (3879S), Notch1 (3608S),
-tubulin (2128S), Hes1 (11988S) and c-Myc (18583S) were acquired from
Cell Signaling Technology (Danvers, MA, USA) and antibody against HIF-1
(A22041), and Vimentin (A19607) were acquired from Abclonal (Wuhan, Hubei,
China).
2.2 CCK-8 Assay
The proliferation of cells was detected utilizing the cell counting kit-8
(CCK-8) kit. In brief, HCC and HUVEC cells were suspended. Afterward, HCC cells
were incubated with various doses of AsS. HUVEC cells were treated
with conditioned medium from AsS treated HCC cells. CCK-8 reagent was
then added for 2 h in darkness, and absorbance was assessed at 450 nm with
microplate reader EL 800 (Bio-TEK, Wenusky, VT, USA). Cells incubated in DMEM
without any treatment were used as the control.
2.3 Wound Healing Assay
Cells were plated in 6-well plates and grown until 90–100% confluence was
reached. The monolayers were scraped using a 200 µL sterile pipette tip,
and detached cells were then removed by rinsing in PBS (WB6018, Biotechwell, Shanghai,
China). This experiment was conducted using serum-free DMEM for cell culture for
24 h at 37 °C. The cell migration distance was observed and photographed
under a microscope to assess the speed of wound closure. Each independent
experiment was replicated for three times.
2.4 Transwell Assay
After pretreatment of AsS for 24 h, HCC cells (1.5
10 cells per well) were harvested and seeded into the upper chamber. DMEM
medium with 10% FBS was placed in the lower chamber. Approximately 24 h later,
the chambers were first fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde (C01-06002, Bioss, Beijing, China)
for 0.5 h and then stained with 0.1% crystal violet (60505ES25, Yeasen, Shanghai, China)
for 20 min.
2.5 Tube Formation Assay
Matrigel (Biotechwell, Shanghai, China) was added to plates and cultured for 2 h
in 37 °C to solidify. Conditioned medium was collected from HCC cells
that had been treated with different concentration of AsS for 24 h.
HUVECs were seeded onto the Matrigel in culture medium and incubated for 6 h with
the conditioned medium at 37 °C. Tube formation was photographed by a
microscope.
2.6 ELISA
Cells were planted into 6-well plates (1.0 10 cells per well)
and stimulated with different concentrations of AsS for 24 h. The
culture medium supernatant was then collected after centrifugation and stored at
–80 °C. According to commonly used procedures, the VEGF content was
detected utilizing enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (CSB-E11718h,
Cusabio, Wuhan, Hubei, China).
2.7 Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
As instructions for use indicated, total ribonucleic acid (RNA) was extracted
from cells utilizing TRIzol reagent (15596018, Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA). The
RNA quantity was measured using a NanoDrop ND-1100 (NanoDrop Technologies). Only
samples with A260/A280 ratio ranging from 1.8 to 2.0 were considered as pure RNA.
RNA was reverse-transcribed into complementary DNA (cDNA) using the
PrimeScript kit (Takara, Shiga, Japan). GAPDH was utilized as the internal
control for messenger RNA (mRNA) quantification. All samples were run in
triplicate. The primer sequences was presented in Table 1.
Table 1.Primer sequences for qRT-PCR.
| Gene name |
Prime sequence (5′-3′) |
PCR condition |
| VEGF |
|
40 cycles |
| Forward |
5′-CTACCTCCACCATGCCAAGT-3′ |
Denaturation (15 sec, at 95 °C) |
| Reverse |
5′-AGCTGCGCTGATAGACATCC-3′ |
| FGF2 |
|
Annealing (15 sec, at 60 °C) |
| Forward |
5′-GGAGAAGAGCGACCCTCAC-3′ |
| Reverse |
5′-AGCCAGGTAACGGTTAGCAC-3′ |
| PDGFA |
|
| Forward |
5′-GGCACTTGACACTGCTCGT-3′ |
| Reverse |
5′-GCAAGACCAGGACGGTCATTT-3′ |
| GAPDH |
|
Extension (45 sec, at 72 °C) |
| Forward |
5′-GGAGGAGTGGGTGTCGCTGT-3′ |
| Reverse |
5′-GTGGACCTGACCTGCCGTC-3′ |
2.8 Western Blot Analysis
Protein was extracted from HCC cells by lysis with radioimmunoprecipitation
assay (RIPA) buffer from Yeasen (China) and measured using the bicinchoninic acid
assay. We used sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
(SDS-PAGE) (20315ES05, Yeasen, Shanghai, China) to separate the protein samples
and transferred the protein onto PVDF membranes (FFP24) from Millipore (Beyotime,
Shanghai, China). Membranes were first blocked in 5% skim milk powder in PBS (Phosphate Buffered Saline)
with 0.1% Tween-20 at 37 °C for 2 h. They were then incubated with
primary antibodies overnight at 4 °C. Secondary antibodies conjugated
with horseradish peroxidase (Beyotime, Shanghai, China) were incubated with
membranes at 37 °C for 1 h. Targeted proteins were visualized utilizing
enhanced chemiluminescence reagent (Millipore, Burlington, MA, USA) and
photographed utilizing Amersham ImageQuant 800 (Cytiva, Tokyo, Japan).
2.9 Immunofluorescence (IF)
HCC cells were seeded onto coverslips and treated with AsS. 4%
paraformaldehyde (PFA) was used to fix cells at 4 °C for 0.5 h. Next,
cells were permeabilized in 0.1% Triton X-100 (20107ES76, Yeasen, Shanghai,
China) for 0.5 h and treated with blocking buffer (PBST containing 3% goat
serum, Biotechwell, Shanghai, China) at 37 °C for 1 h. The appropriate
primary antibodies against VEGF (1:150) and HIF-1 (1:100) were then
incubated with coverslips at 4 °C overnight. This was followed by
incubation with fluorescent-conjugated secondary antibodies (1:1000) at 37
°C for 2 h. DAPI was utilized for nuclear staining. Finally, the cells
were photographed using a fluorescence microscope.
2.10 Statistical Analysis
All data are shown as means standard errors of means and were conducted
utilizing the Statistical Product and Service Solutions (SPSS) v22.0 (IBM
Corporation., Armonk, NY, USA). For all tests, p 0.05 was considered
statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1 AsS Inhibits the Proliferation of HCC Cells
Chemical structure of AsSis shown in Fig. 1A. Normal hepatocyte
cell L02 and HCC cells received various concentrations of AsS (0, 1,
3, 5, 10, 15, and 20 µM) to detect its anticancer influence. The results
showed that arsenic sulfide caused a progressive decrease in HCC cell
proliferation in a dose-& time-dependent pattern, but not on L02 cell (Fig. 1B,C). To further investigate the impact of AsS on proliferation, we
treated HepG2 and Hep3B with 5-FU (5-fluorouracil), sorafenib, and DDP
(cisplatin), which were widely used on HCC (Fig. 1D). The DPBS group was regarded
as a negative control.
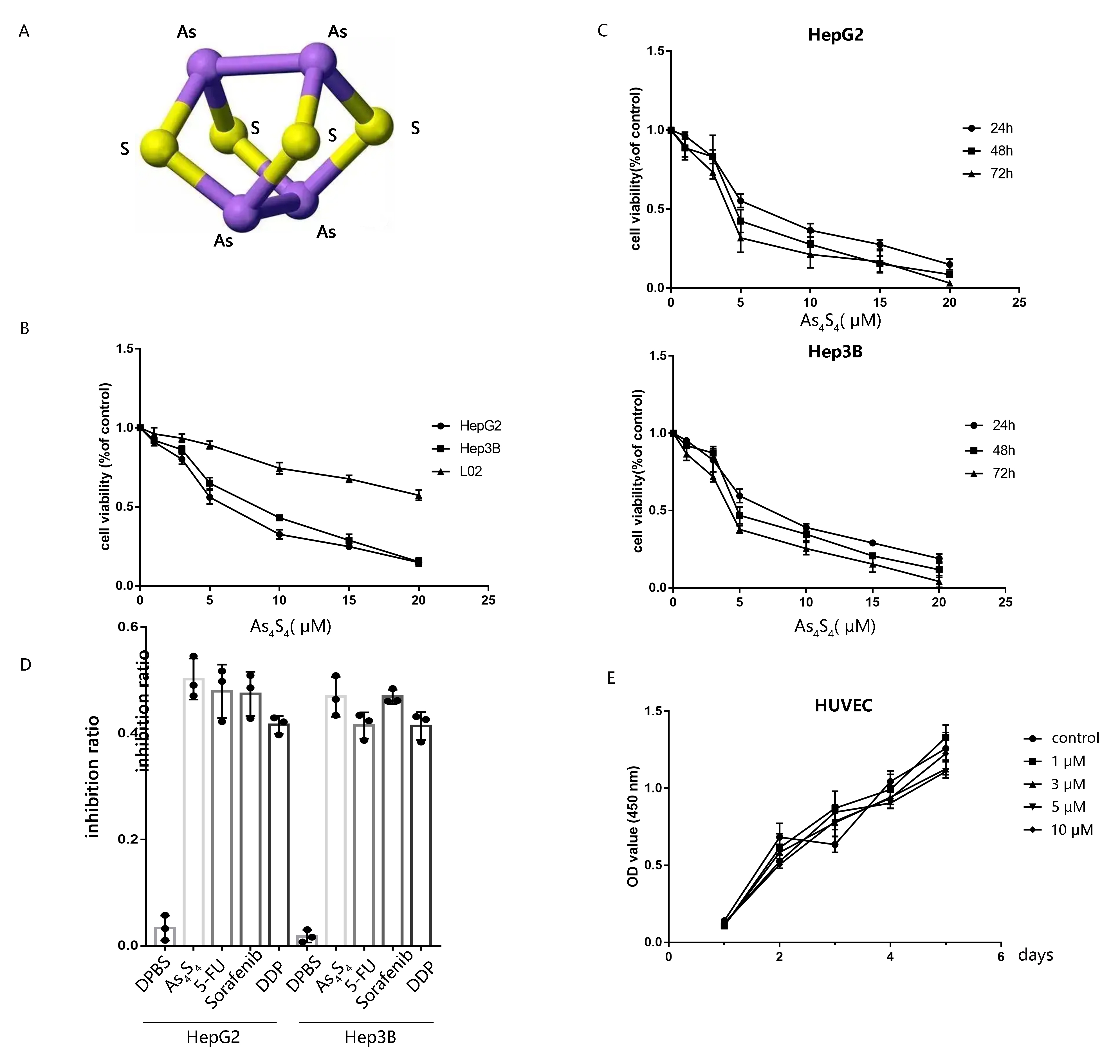 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.
AsS decreases the viability of HCC cells. (A) The
chemical structure of AsS. (B) The cytotoxicity of AsS
was evaluated against HepG2, Hep3B, and L02 for 24 h. (C) HepG2 and Hep3B cells
were treated with AsS for 24, 48, or 72 h at different concentrations
(0, 1, 3, 5, 10, 15, and 20 µM) and the cell viability detected by the
CCK-8 assay. (D) HepG2 and Hep3B cells were treated with DPBS, arsenic sulfide (5
µM), 5-FU (5-fluorouracil, 20 µg/mL), sorafenib (6 µM), and DDP
(cisplatin, 8 µg/mL) for 24 h. (E) The effect of conditioned medium from
AS-treated HCC cells on the proliferation of HUVECs was evaluated by
the CCK-8 assay.
We next used the CCK8 assay to determine whether AsS also inhibits
the proliferation of HUVECs. Conditioned medium from HCC cells exposed with
different concentration of AsS for 24 h was collected and incubated
with HUVECs in culture medium. However, the CCK-8 assay revealed that cell
proliferation didn’t show significant difference between AS-treated
and control cells (p 0.05) (Fig. 1E). Hence, the results showed
that AsS had no discernible impact on the proliferation of HUVECs
in vitro.
3.2 AsS Inhibits Migration and Invasion by HCC Cells
To determine whether AsS influences the migration and invasion of
HCC, we conducted wound-healing and transwell invasion assay. As shown in Fig. 2,
AsS conspicuously inhibited both the migration and invasion of HCC.
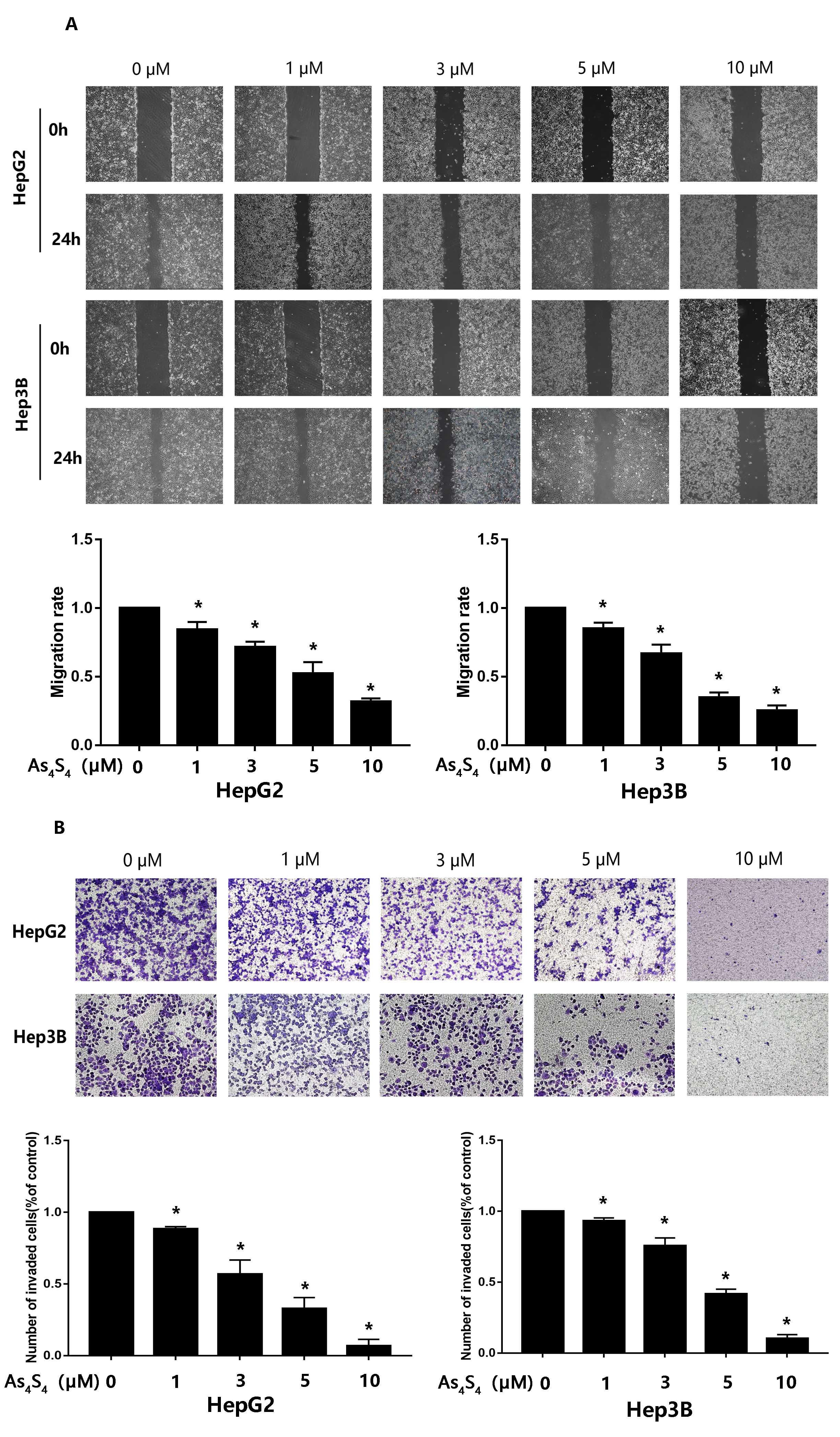 Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.
AsS represses the migration and invasion of HCC
cells. (A) HepG2 and Hep3B cells were treated with different concentration of
AsS (0, 1, 3, 5, and 10 µM) for 24 h. The wound healing assay
was conducted to test the effect of AsS on the migration of HCC
cells. , p 0.05 compared with the control group. (B) The
influence of AsS on the invasive ability of HCC cells was evaluated
by transwell. Cells were seeded into the inner chamber and treated with different
concentrations of AsS (0, 1, 3, 5, and 10 µM) for 24 h. The
histogram shows the average number of cells that had invaded per field.
*, p 0.05 compared with control group.
3.3 AsS Reverses EMT in HCC Cells
EMT is a crucial stage in the growth of tumors as it confers migratory and
invasive properties to cancer cells, thus eventually leading to metastasis. To
evaluate the effect of AsS on EMT, we examined EMT-associated
biomarkers via Western blot. The expression of epithelial biomarkers such as
E-cadherin upregulated in a dose-dependent manner following exposure to
increasing concentrations of AsS for 24 h, compared to the control.
In contrast, the expression of mesenchymal-associated biomarkers such as
N-cadherin, Vimentin and Snail reduced (Fig. 3).
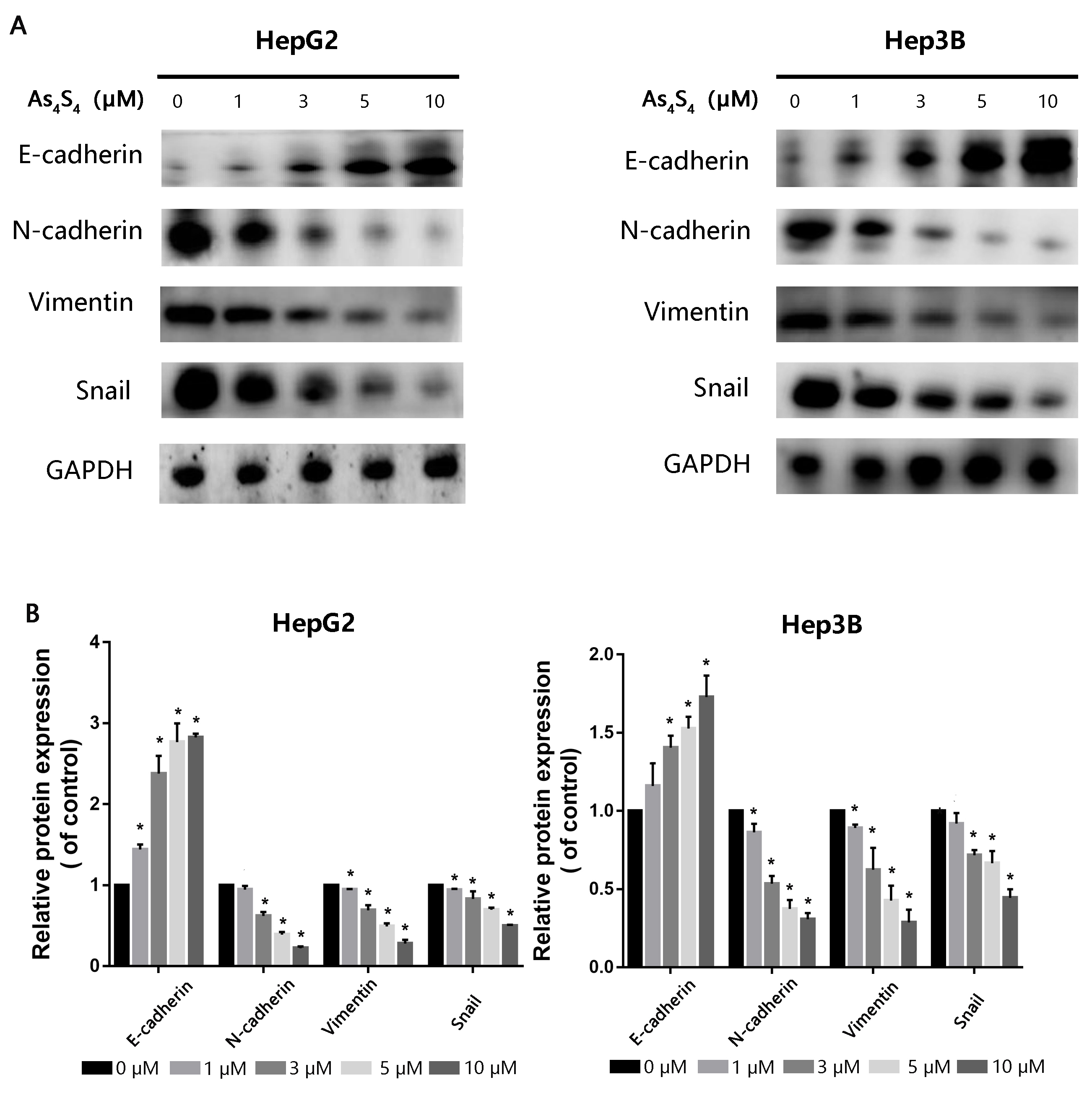 Fig. 3.
Fig. 3.
The impact of AsS on expression of EMT-related
markers. (A) HepG2 and Hep3B cells were pretreated with increasing concentrations
of AsS for 24 h. Western blot assay was then used to evaluate protein
expression levels for E-cadherin, N-cadherin, Snail and Vimentin. GAPDH was used
as the loading control. (B) Detailed quantitative results of Western blot were
gathered. *, p 0.05 compared with control group.
3.4 AsS Inhibits HCC-Induced Tube Formation by HUVECs
HCC is a hypervascular tumor and angiogenesis is critical for its growth,
metastasis, and neoplastic progression. To assess the anti-angiogenic potency of
AsS, HUVECs were incubated in culture medium from
AsS-treated HCC cells. Tube formation was visualized using microscope
photography. Conditioned medium derived from AS-treated HCC cells was
found to significantly reduce the angiogenic capacity of HUVECs (Fig. 4A). We
hypothesized that the anti-angiogenic effect of AsS on HCC cells
contributed to the above phenomenon. To explore possible molecular mechanism of
this anti-angiogenic activity, we detected the expression of angiogenesis-related
factors produced by AsS-treated HCC cells, including VEGF, PDGFA, and
FGF2. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction revealed that VEGF
expression was evidently decreased compared to that of the other factors (Fig. 4B). Since VEGF is a pivotal activator of angiogenesis-related pathways, we
utilized ELISA to measure VEGF levels in the conditioned medium of HCC.
AsS was found to significantly reduce the secretion of VEGF from HCC
in a concentration-dependent pattern (Fig. 4C).
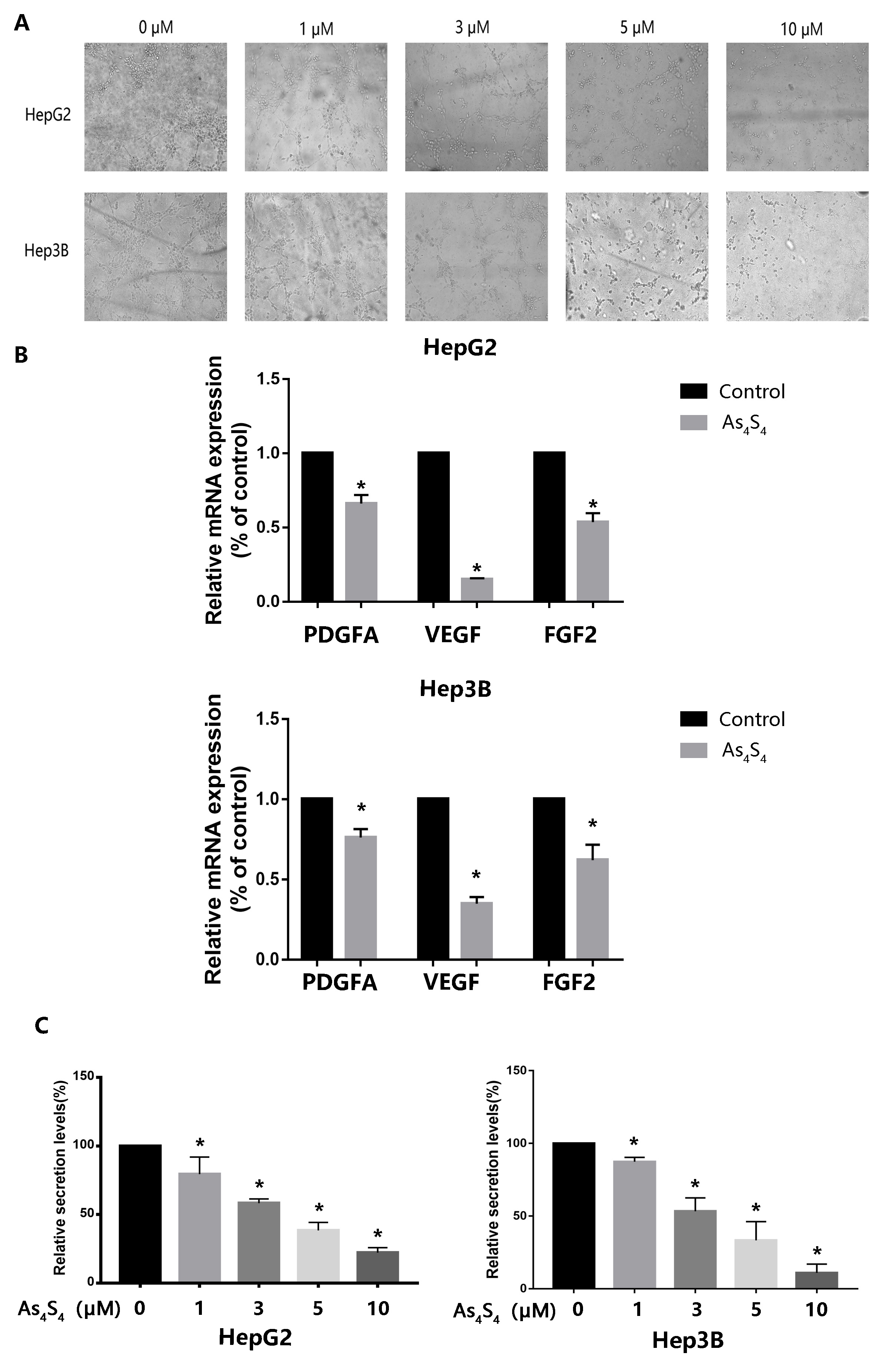 Fig. 4.
Fig. 4.
Effect of AsS on HCC-induced tube formation by
HUVECs. (A) The culture medium from HepG2 and Hep-3B cells treated with the
indicated concentrations (0, 1, 3, 5, and 10 µM) of AsS for 24
h was collected. It was then applied to HUVECs for analysis of angiogenesis with
the tube formation assay. (B) HCC cells were treated with 5 µM
AsS for 24 h. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction assay
was then used to measure the cellular mRNA expression of VEGF, PDGFA, and FGF2.
(C)VEGF protein secreted from HCC cells into the
culture medium was analyzed by ELISA. *, p 0.05 compared
with control group.
3.5 AsS Inhibits the HIF-1/VEGF Pathway in
HCC
The HIF-1/VEGF pathway is a crucial regulator of tumor angiogenesis
and metastasis. We therefore investigated the impact of AsS on VEGF
and HIF-1 expression in HCC cells using immunofluorescence staining. As
depicted in Fig. 5A, AsS reduced the expression of both
HIF-1 and VEGF. Western blot also represented clearly that reduced
expression of VEGF and HIF-1 proteins were consistent with the
immunofluorescence staining (Fig. 5B). Notch signaling is a highly conserved
intercellular signaling pathway that serves a pivotal role in the modulation of
HIF-1 [20]. To determine whether the
prohibition of VEGF expression by AsS was mediated by blockade of the
Notch pathway, we detected the protein levels of Notch-1, Hes-1 and c-Myc in HCC
cells by Western blot (Fig. 5B). These results showed that Notch-1, c-Myc and
Hes-1 expression were all downregulated following treatment with AsS.
 Fig. 5.
Fig. 5.
Effect of AsS on the expression of HIF-1,
VEGF, and the Notch pathway. (A) Immunofluorescence assays for the expression of
HIF-1 and VEGF proteins in HepG2 and Hep3B cells treated with or
without 5 µM AsS for 24 h. (B) Western blot was utilized to detect HIF-1, VEGF and Notch pathway
protein expression in HCC cells pretreated with various concentrations of
AsS.
A previous study showed that CoCl is a hypoxia mimetic that stabilizes
HIF-1 and the expression of hypoxia-associated responsive biomarkers
[21]. We examined the increase of HIF-1 in HCC cells after incubation
with a 200 µM dose of CoCl for 24 h. The results represented that
CoCl treatment clearly increased the levels of HIF-1, VEGF,
E-cadherin, Vimentin, c-Myc and Hes-1 (Fig. 6). However, as shown in Fig. 6,
these increases were suppressed by AsS. In order to confirm whether
the inhibition of metastasis by AsS owed to the
HIF-1/VEGF/Notch/EMT pathway, HepG2 and Hep3B cells were pretreated
with various doses of AsS or DAPT for 24 h. The cells were then
analyzed to determine the expression of HIF-1, VEGF, E-cadherin,
Vimentin, c-Myc and Hes-1 proteins by western blot. AsS, DAPT (a specific inhibitor of Notch receptor cleavage), and
the combination of AsS and DAPT were shown to inhibit
CoCl-mediated expression of HIF-1, VEGF and the representative
EMT markers of E-cadherin and Vimentin (Fig. 6). These results indicate that
AsS can suppress angiogenesis by blocking activation of the
HIF-1/VEGF/Notch/EMT pathway.
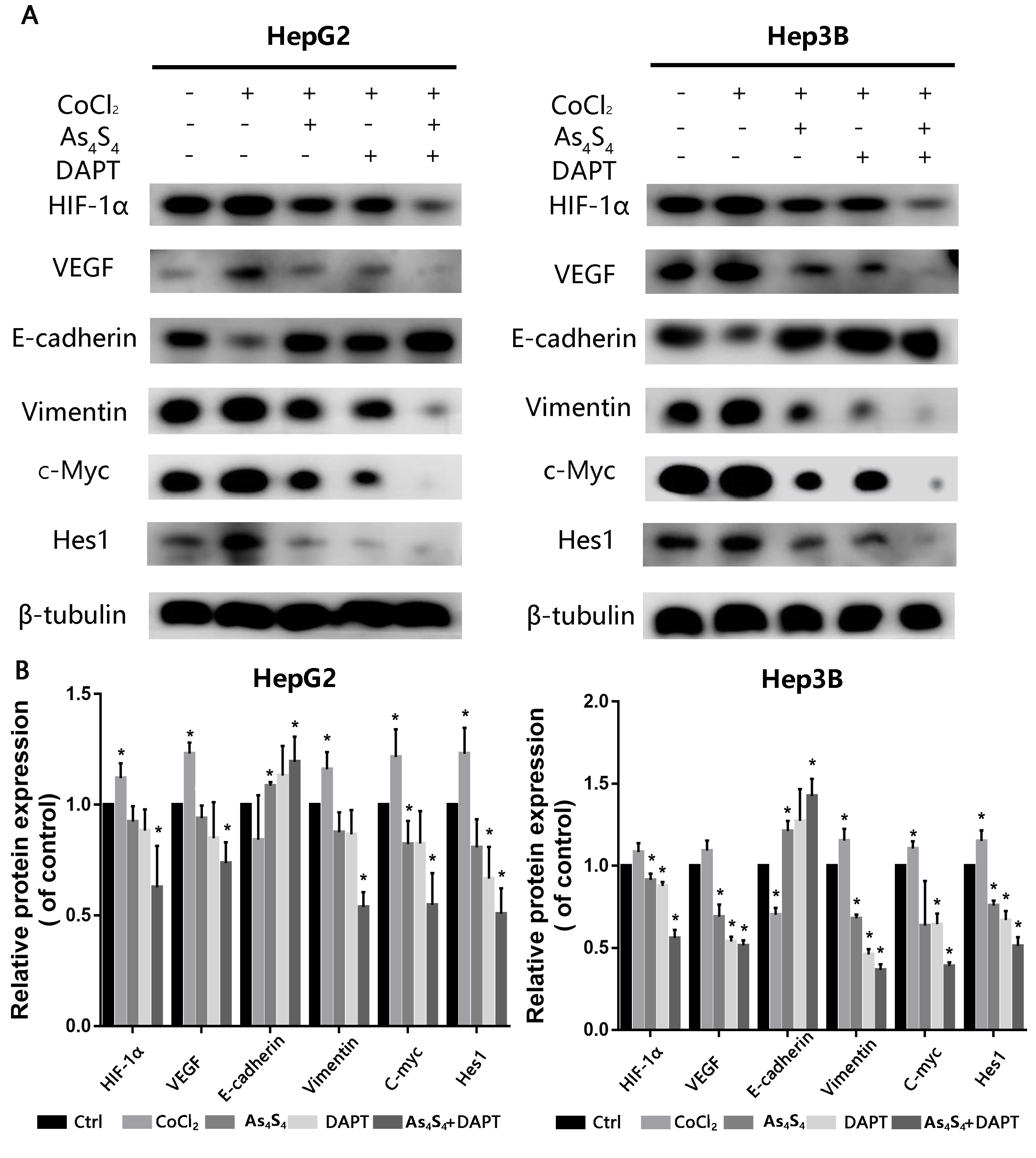 Fig. 6.
Fig. 6.
AsS and DAPT inhibit EMT via the
HIF-1/EMT/Notch pathway. (A) HepG2 and Hep3B cells were treated with 5
µM AsS for 24 h. The expression of HIF-1, VEGF,
E-cadherin, Vimentin, c-Myc and Hes-1 proteins were evaluated by western blot
assay. -tubulin was used as the loading control. (B) Detailed
quantitative results of Western blot were gathered. *, p
0.05 compared with control group.
4. Discussion
Characterized by its high rates of mortality, recurrence, and metastasis, HCC is
a major contributor of disability-adjusted life-years in cancer patients,
accounting for 28% of the overall burden worldwide [22]. Metastasis is a
multistep cellular process which involves adhesion, migration, invasion and
angiogenesis. There is currently an unmet medical need for effective treatments
that target EMT and angiogenesis in metastatic cancers [23]. Arsenic compounds
have shown impressive anti-neoplastic activity, both in vitro and
in vivo. A previous experiment suggested that AsS suppressed
cell invasion, metastasis and EMT in gastric cancer through the increased
expression of miR-4665-3p [24]. Importantly, AsS can enhance the
action of BET (Bromodomain and Extraterminal) inhibitors on EMT in gastric and colon cancer cells through
mitochondrial-mediated induction of apoptosis [16]. Nevertheless, few scholars
have explored the inhibitory impacts of AsS on HCC metastasis. The
present study show that AsS inhibits the migration and invasion of
HCC in a dose-dependent pattern, just like inhibiting HCC-induced angiogenesis.
Furthermore, we investigated the molecular mechanism that underlies the
anti-metastatic properties of AsS, which appears to involve
suppression of the HIF-1/VEGF pathway, angiogenesis, and EMT.
Other researches have implicated the pivotal role of EMT in the metastasis and
invasion of tumor cells [25]. Indeed, once detached from the primary sites to the
metastatic sites, the migration of tumor cells has been proposed as the first
step in metastasis [26]. E-cadherin plays a major role in epithelial cell
adhesion [27], with the reduce of E-cadherin rendering cells more motile and
invasive. Indeed, decreased E-cadherin expression is related to poor prognosis of
HCC patients [28]. In the present research, AsSincreased expression
of N-cadherin and vimentin and attenuated the expression of E-cadherin,
suggesting that it can significantly inhibit the EMT process in HCC.
Angiogenesis facilitates tumor progression and metastasis, while providing
adequate nutrition and oxygen for the tumor cells. As a common feature in solid
tumors, hypoxia leads to the induction of angiogenesis through the pivotal
mediator of HIF. HIF1 is a heterodimer consisting of two subunits: HIF1
and HIF1 [29]. Overexpression of HIF-1 in tumor tissue is
significantly correlated with metastasis, poor prognosis, and resistance to
treatment [30]. HIF-1 also promotes invasiveness and EMT in many cancer
types [31]. Previous studies have shown that HIF-1 was strongly
associated with Vimentin expression, but negatively correlated to E-cadherin
expression. VEGF is transcriptionally activated by HIF-1 and positively
regulates angiogenesis [32], while aberrant activation of Notch signaling is
associated with angiogenesis, metastasis and EMT [33]. Hypoxia activates Notch1
to promote EMT in the tumor microenvironment via transcriptional factors
such as HIF-1 [34]. Our present study indicates that AsS
plays a vital role in blocking HIF-1 and VEGF signaling pathways
directly in HCC cells, thereby attenuating hypoxia-induced angiogenesis. To the
best of our knowledge, this is the first report showing that AsS
inhibits not only the migration and invasion of HCC but also HCC-induced
angiogenesis, which showed no noticeable cytotoxicity at relatively low
concentrations.
5. Conclusions
Taken together, our study has identified a therapeutic approach for
hypervascular and highly metastatic liver cancer. AsS was proven to
suppress the metastasis of HCC by inhibiting tumor cell invasion, migration, and
angiogenesis through the HIF-1/VEGF pathway. Collectively, results
above suggest that AsS may be a safe and effective antitumor agent
against highly metastatic HCC and should be considered as a potential drug
candidate in further clinical trials.
Availability of Data and Materials
Data supporting the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Author Contributions
SC and SL designed the research study. SL and YC designed and performed most of the experiments, analyzed data, and prepared the manuscript as leading authors. TK, CZ and ZF conducted the statistical analysis of data and contributed to editing and commented on the article. SC disupervised the project.
All authors contributed to editorial changes in the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. All authors have participated sufficiently in the work and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Only human cancer cell lines were used in this study. No ethics approval and
consent to participate was therefore relevant.
Acknowledgment
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
(Grant no. 81874353 and 82074074) and Beijing Science and Technology Innovation
Medical Development Foundation (Grant no. KC2021-JX-0186-126).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1. Fig. 2.
Fig. 2. Fig. 3.
Fig. 3. Fig. 4.
Fig. 4. Fig. 5.
Fig. 5. Fig. 6.
Fig. 6.





